Rapid Food Authentication Using a Portable Laser-Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy System
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Types of Food Samples and Sample Preparation
2.1.1. Liquid Samples
Balsamic Vinegar
Vanilla Extracts
2.1.2. Solid Samples
Cheeses
Coffee Beans
2.1.3. Powdered Food Samples
Spices
2.2. Benchtop and Handheld LIBS Systems Setup
2.3. Classification Procedures
3. Results
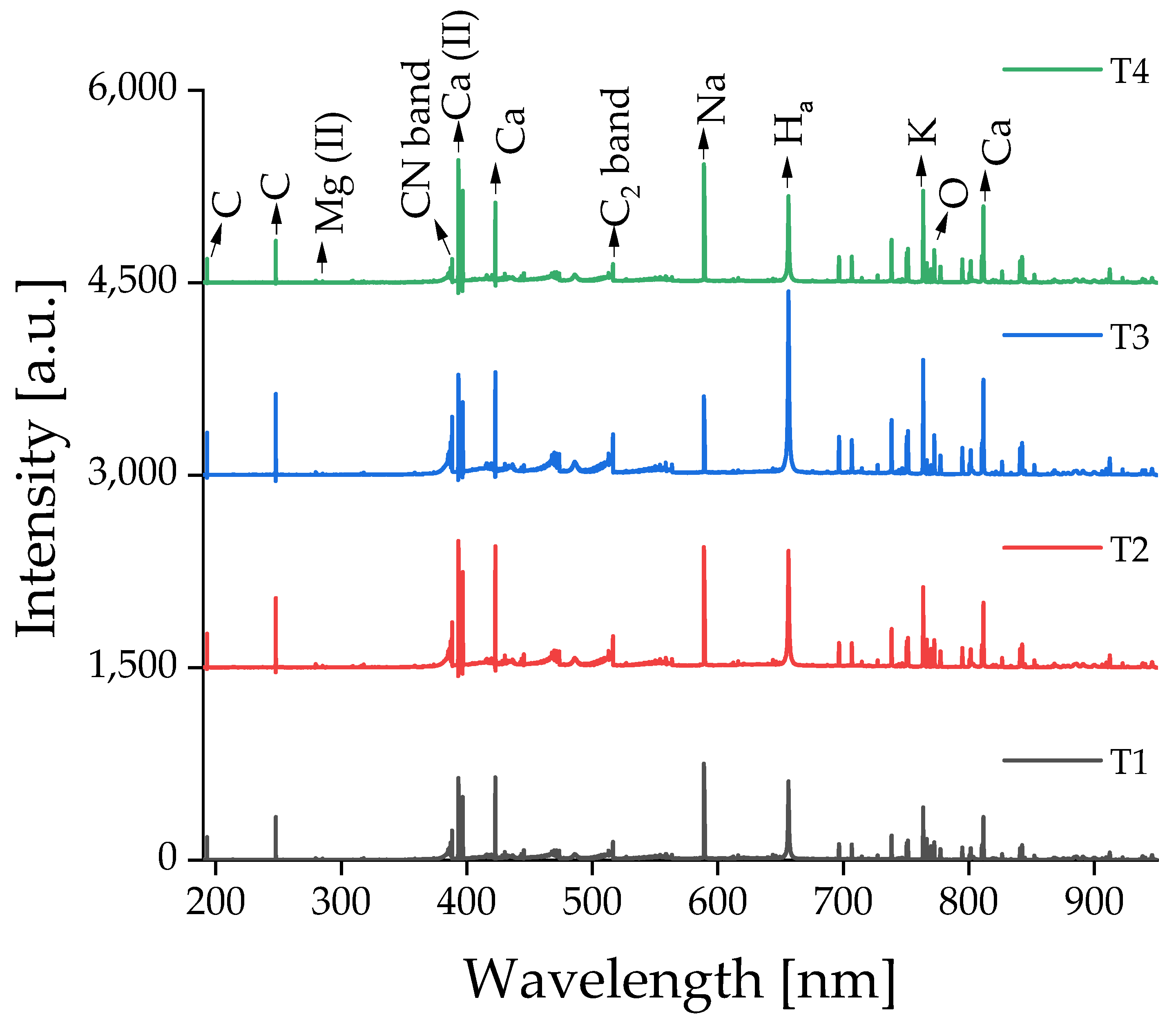
3.1. LIBS Measurements
3.2. Classification Using the Elastic Net Approach
3.3. Food Fraud Detection
4. Discussion
4.1. Sample Preparation
4.2. Water Activity
4.3. Spectral Classification
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Code | Balsamic Vinegar Samples |
|---|---|
| B1 | Balsamic Vinegar of Modena |
| B2 | Balsamic Vinegar of Modena (Colavita) |
| B3 | Barrel-aged Balsamic Vinegar (Napa Valley Harvest) |
| B4 | Gran Deposito Aceto Balsamico di Modena (Giuseppe Giusti) |
| B5 | Gold Quality Balsamic Vinegar of Modena (Trader Joe’s) |
| B6 | Prof. Andrea Cossarizza’s private collection balsamic vinegar |
| Code | Vanilla Samples |
|---|---|
| V1 | Pure vanilla extract (Kroger, Cincinnati, OH) |
| V2 | Imitation vanilla flavor (Kroger, Cincinnati, OH) |
| V3 | Pure vanilla extract (McCormick & Company, Baltimore, MD) |
| V4 | San Luis Rey pure vanilla (La Vencedora e Hijos SA de CV, San Luis Potosi, Mexico |
| V5 | Vanilla syrup (1883 Maison Routin, La Motte Servolex, France) |
| V6 | Simple Truth Madagascar vanilla extract (Kroger, Cincinnati, OH) |
| Code | Alpine-Style Cheese Samples |
|---|---|
| C1 | Abondance AOP |
| C2 | Appenzeller |
| C3 | Austrian Alps Gruyère |
| C4 | Berggenuss |
| C5 | Brenta |
| C6 | Charles Arnaud Comté AOP 6 Month Aged |
| C7 | Charles Arnaud Comté AOP Reserve 12 Months Aged |
| C8 | Comté AOP Grande Reserve 24 Months Aged |
| C9 | Comté AOP Reserve 10 Month Aged |
| C10 | Frantal Emmental |
| C11 | Gruyère AOP |
| C12 | Hoch Ybrig |
| C13 | Kaltbach Cave Aged Emmental AOP |
| C14 | Kaltbach Cave Aged Swiss Gruyère AOP |
| C15 | Parpan Alpkaese |
| C16 | Wisconsin Gruyère Alpine-Style Cheese |
| Code | Coffee Samples |
|---|---|
| F1 | Italian Dark Roast (OLDE Brooklyn Coffee, Brooklyn, NY) |
| F2 | Guatemalan Antigua Blend (Copper Moon Coffee, Lafayette, IN) |
| F3 | Lavazza Super Crema (Luigi Lavazza SpA, New York, NY) |
| F4 | Despierta tus Sentidos (Nespresso USA Inc., Long Island City, NY) |
| F5 | Café Cubano Roast (Mayorga Organics, Rockville, MD) |
| F6 | Artisan Blend (Koffee Kult, Hollywood, FL) |
| F7 | Shot Tower Espresso (Verena Street Coffee Co., Dubuque, IA) |
| Code | Spices Samples |
|---|---|
| S1 | East Indian ground nutmeg (McCormick & Company, Baltimore, MD) |
| S2 | Classic ground nutmeg (McCormick & Company, Baltimore, MD |
| S3 | Ground mustard (Kroger, Cincinnati, OH) |
| S4 | Smidge & Spoon crushed red pepper (Kroger, Cincinnati, OH) |
| S5 | Cayenne pepper (Spice Islands, Ankeny, IA) |
| S6 | Ground cumin (McCormick & Company, Baltimore, MD) |
| S7 | Private Selection ground cumin (Kroger, Cincinnati, OH) |
| S8 | Simple Truth organic ground turmeric (Kroger, Cincinnati, OH) |
| Experiment Run | Accuracy [%] | |
|---|---|---|
| Benchtop | Handheld | |
| 1 | 89.1 | 91.3 |
| 2 | 91.5 | 92.3 |
| 3 | 89.4 | 89.4 |
| 4 | 90.5 | 91.8 |
| 5 | 90.8 | 89.9 |
| 6 | 89.8 | 90.8 |
| 7 | 91.6 | 91.3 |
| 8 | 90.8 | 89.6 |
| 9 | 88.4 | 92.3 |
| 10 | 89.8 | 90.8 |
| 90.17 (1.04) | 90.95 (1.05) | |
| Experiment Run | Accuracy [%] | |
|---|---|---|
| Benchtop | Handheld | |
| 1 | 99.4 | 98.8 |
| 2 | 100 | 98.8 |
| 3 | 100 | 100 |
| 4 | 98.9 | 100 |
| 5 | 100 | 99.0 |
| 6 | 99.4 | 98.6 |
| 7 | 100 | 99.2 |
| 8 | 100 | 100 |
| 9 | 98.9 | 99.4 |
| 10 | 100 | 100 |
| 99.66 (0.47) | 99.38 (0.58) | |
References
- Moyer, D.C.; DeVries, J.W.; Spink, J. The economics of a food fraud incident—Case studies and examples including melamine in wheat gluten. Food Control 2017, 71, 358–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spink, J.; Moyer, D.C. Defining the public health threat of food fraud. J. Food Sci. 2011, 76, R157–R163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spink, J.; Bedard, B.; Keogh, J.; Moyer, D.C.; Scimeca, J.; Vasan, A. International survey of food fraud and related terminology: Preliminary results and discussion. J. Food Sci. 2019, 84, 2705–2718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Manning, L.; Soon, J.M. Food safety, food fraud, and food defense: A fast evolving literature. J. Food Sci. 2016, 81, R823–R834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Decernis. Food Fraud Database. Available online: https://decernis.com/products/food-fraud-database/ (accessed on 12 December 2022).
- Manning, L.; Soon, J.M. Food fraud vulnerability assessment: Reliable data sources and effective assessment approaches. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 91, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montgomery, H.; Haughey, S.A.; Elliott, C.T. Recent food safety and fraud issues within the dairy supply chain (2015–2019). Glob. Food Secur. 2020, 26, 100447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popping, B.; De Dominicis, E.; Dante, M.; Nocetti, M. Identification of the geographic origin of Parmigiano Reggiano (P.D.O.) cheeses deploying non-targeted mass spectrometry and chemometrics. Foods 2017, 6, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gimonkar, S.; Van Fleet, E.; Boys, K.A. Chapter 13—Dairy product fraud. In Food Fraud; Hellberg, R.S., Everstine, K., Sklare, S.A., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2021; pp. 249–279. [Google Scholar]
- Cardin, M.; Cardazzo, B.; Mounier, J.; Novelli, E.; Coton, M.; Coton, E. Authenticity and Typicity of Traditional Cheeses: A Review on Geographical Origin Authentication Methods. Foods 2022, 11, 3379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amilien, V.; Moity-Maïzi, P. Controversy and sustainability for geographical indications and localized agro-food systems: Thinking about a dynamic link. Br. Food J. 2019, 121, 2981–2994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- European Commission. European Commission Food Quality Schemes Explained. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/info/food-farming-fisheries/food-safety-and-quality/certification/quality-labels/quality-schemes-explained_en (accessed on 12 December 2022).
- Ferreira, T.; Galluzzi, L.; de Paulis, T.; Farah, A. Three centuries on the science of coffee authenticity control. Food Res. Int. 2021, 149, 110690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galvin-King, P.; Haughey, S.A.; Elliott, C.T. Herb and spice fraud; the drivers, challenges and detection. Food Control 2018, 88, 85–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Silvis, I.C.J.; van Ruth, S.M.; van der Fels-Klerx, H.J.; Luning, P.A. Assessment of food fraud vulnerability in the spices chain: An explorative study. Food Control 2017, 81, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Shen, T.; Liu, F.; He, Y. Identification of coffee varieties using laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy and chemometrics. Sensors 2018, 18, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gussow, K.E.; Mariët, A. The scope of food fraud revisited. Crime Law Soc. Chang. 2022, 78, 621–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, D.I.; Muhamadali, H.; Haughey, S.A.; Elliott, C.T.; Goodacre, R. Point-and-shoot: Rapid quantitative detection methods for on-site food fraud analysis—Moving out of the laboratory and into the food supply chain. Anal. Methods 2015, 7, 9401–9414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Perestam, A.T.; Fujisaki, K.K.; Nava, O.; Hellberg, R.S. Comparison of real-time PCR and ELISA-based methods for the detection of beef and pork in processed meat products. Food Control 2017, 71, 346–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- López-Maestresalas, A.; Insausti, K.; Jarén, C.; Pérez-Roncal, C.; Urrutia, O.; Beriain, M.J.; Arazuri, S. Detection of minced lamb and beef fraud using NIR spectroscopy. Food Control 2019, 98, 465–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, K.M.; Andrade, M.V.O.; Almeida, M.R.; Fantini, C.; Sena, M.M. Raman spectroscopy and discriminant analysis applied to the detection of frauds in bovine meat by the addition of salts and carrageenan. Microchem. J. 2019, 147, 582–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassoun, A.; Måge, I.; Schmidt, W.F.; Temiz, H.T.; Li, L.; Kim, H.-Y.; Nilsen, H.; Biancolillo, A.; Aït-Kaddour, A.; Sikorski, M.; et al. Fraud in animal origin food products: Advances in emerging spectroscopic detection methods over the past five years. Foods 2020, 9, 1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hebling e Tavares, J.P.; da Silva Medeiros, M.L.; Barbin, D.F. Near-infrared techniques for fraud detection in dairy products: A review. J. Food Sci. 2022, 87, 1943–1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, G.; Kwak, J.; Choi, J.; Park, K. Detection of nutrient elements and contamination by pesticides in spinach and rice samples using laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 718–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Multari, R.A.; Cremers, D.A.; Dupre, J.A.M.; Gustafson, J.E. Detection of biological contaminants on foods and food surfaces using laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 8687–8694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Multari, R.A.; Cremers, D.A.; Scott, T.; Kendrick, P. Detection of pesticides and dioxins in tissue fats and rendering oils using laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 2348–2357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sezer, B.; Bilge, G.; Boyaci, I.H. Laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy based protein assay for cereal samples. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 9459–9463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markiewicz-Keszycka, M.; Cama-Moncunill, X.; Casado-Gavalda, M.P.; Dixit, Y.; Cama-Moncunill, R.; Cullen, P.J.; Sullivan, C. Laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS) for food analysis: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 65, 80–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sezer, B.; Durna, S.; Bilge, G.; Berkkan, A.; Yetisemiyen, A.; Boyaci, I.H. Identification of milk fraud using laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS). Int. Dairy J. 2018, 81, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velioglu, H.M.; Sezer, B.; Bilge, G.; Baytur, S.E.; Boyaci, I.H. Identification of offal adulteration in beef by laser induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS). Meat Sci. 2018, 138, 28–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velásquez-Ferrín, A.; Babos, D.V.; Marina-Montes, C.; Anzano, J. Rapidly growing trends in laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy for food analysis. Appl. Spectrosc. Rev. 2021, 56, 492–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miziolek, A.W.; Palleschi, V.; Schechter, I. Laser-Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy (LIBS): Fundamentals and Applications; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2006; p. 620. [Google Scholar]
- Cremers, D.A.; Radziemski, L.J. Handbook of Laser-Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy; Wiley: Chichester, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, J.; Xie, W.; Jiang, J.; Zhao, Z.; Zhou, F.; Liu, F. Fast quantification of honey adulteration with laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy and chemometric methods. Foods 2020, 9, 341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Muhammed Shameem, K.M.; Dhanada, V.S.; Harikrishnan, S.; George, S.D.; Kartha, V.B.; Santhosh, C.; Unnikrishnan, V.K. Echelle LIBS-Raman system: A versatile tool for mineralogical and archaeological applications. Talanta 2020, 208, 120482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, M.; Wei, L.; González, J.J.; Oropeza, D.; Chirinos, J.; Mao, X.; Lu, J.; Russo, R.E. Coal discrimination analysis using tandem laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy and laser ablation inductively coupled plasma time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 7003–7010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel-Salam, Z.; Al Sharnoubi, J.; Harith, M.A. Qualitative evaluation of maternal milk and commercial infant formulas via LIBS. Talanta 2013, 115, 422–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.; Li, Y.; Gu, X.; Bao, J.; Yang, H.; Sun, L. Laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy application in environmental monitoring of water quality: A review. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2014, 186, 8969–8980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bilge, G.; Boyacı, İ.H.; Eseller, K.E.; Tamer, U.; Çakır, S. Analysis of bakery products by laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy. Food Chem. 2015, 181, 186–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Huang, L.; Yao, M.; Hu, H.; Wang, C.; Liu, M. Quantitative analysis of chromium in potatoes by laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy coupled with linear multivariate calibration. Appl. Opt. 2015, 54, 7807–7812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nufiqurakhmah, N.; Nasution, A.; Suyanto, H. Laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS) for spectral characterization of regular coffee beans and Luwak coffee bean. In Proceedings of the Second International Seminar on Photonics, Optics, and Its Applications (ISPhOA 2016), Bali, Indonesia, 24–25 August 2016; p. 101500M. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Zheng, P.; Liu, H.; Fang, L. Classification of Chinese tea leaves using laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy combined with the discriminant analysis method. Anal. Methods 2016, 8, 3204–3209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mbesse Kongbonga, Y.G.; Ghalila, H.; Onana, M.B.; Ben Lakhdar, Z. Classification of vegetable oils based on their concentration of saturated fatty acids using laser induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS). Food Chem. 2014, 147, 327–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilge, G.; Sezer, B.; Eseller, K.E.; Berberoğlu, H.; Köksel, H.; Boyacı, İ.H. Determination of Ca addition to the wheat flour by using laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS). Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2016, 242, 1685–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilge, G.; Velioglu, H.M.; Sezer, B.; Eseller, K.E.; Boyaci, I.H. Identification of meat species by using laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy. Meat Sci. 2016, 119, 118–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temiz, H.T.; Sezer, B.; Berkkan, A.; Tamer, U.; Boyaci, I.H. Assessment of laser induced breakdown spectroscopy as a tool for analysis of butter adulteration. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2018, 67, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markiewicz-Keszycka, M.; Zhao, M.; Cama-Moncunill, X.; El Arnaout, T.; Becker, D.; O’Donnell, C.; Cullen, P.J.; Sullivan, C.; Casado-Gavalda, M.P. Rapid analysis of magnesium in infant formula powder using laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy. Int. Dairy J. 2019, 97, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nespeca, M.G.; Vieira, A.L.; Júnior, D.S.; Neto, J.A.G.; Ferreira, E.C. Detection and quantification of adulterants in honey by LIBS. Food Chem. 2020, 311, 125886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zar Pasha, A.; Anwer Bukhari, S.; Ali El Enshasy, H.; El Adawi, H.; Al Obaid, S. Compositional analysis and physicochemical evaluation of date palm (Phoenix dactylifera L.) mucilage for medicinal purposes. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2022, 29, 774–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moncayo, S.; Rosales, J.D.; Izquierdo-Hornillos, R.; Anzano, J.; Caceres, J.O. Classification of red wine based on its protected designation of origin (PDO) using Laser-induced Breakdown Spectroscopy (LIBS). Talanta 2016, 158, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.; Wang, W.; Shen, T.; Peng, J.; Kong, W. Rapid identification of kudzu powder of different origins using laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy. Sensors 2019, 19, 1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yan, J.; Yang, P.; Hao, Z.; Zhou, R.; Li, X.; Tang, S.; Tang, Y.; Zeng, X.; Lu, Y. Classification accuracy improvement of laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy based on histogram of oriented gradients features of spectral images. Opt. Express 2018, 26, 28996–29004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wadood, S.A.; Nie, J.; Li, C.; Rogers, K.M.; Khan, A.; Khan, W.A.; Qamar, A.; Zhang, Y.; Yuwei, Y. Rice authentication: An overview of different analytical techniques combined with multivariate analysis. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2022, 112, 104677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caceres, J.O.; Moncayo, S.; Rosales, J.D.; de Villena, F.J.M.; Alvira, F.C.; Bilmes, G.M. Application of laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS) and neural networks to olive oils analysis. Appl. Spectrosc. 2013, 67, 1064–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gazeli, O.; Bellou, E.; Stefas, D.; Couris, S. Laser-based classification of olive oils assisted by machine learning. Food Chem. 2020, 302, 125329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gyftokostas, N.; Stefas, D.; Couris, S. Olive oils classification via laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 3462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gondhalekar, C.; Rajwa, B.; Bae, E.; Patsekin, V.; Sturgis, J.; Kim, H.; Doh, I.-J.; Diwakar, P.; Robinson, J.P. Multiplexed detection of lanthanides using laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy: A survey of data analysis techniques. In Proceedings of the SPIE Defense + Commercial Sensing (Sensing for Agriculture and Food Quality and Safety XI), Baltimore, MD, USA, 16–17 April 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Gondhalekar, C.; Biela, E.; Rajwa, B.; Bae, E.; Patsekin, V.; Sturgis, J.; Reynolds, C.; Doh, I.-J.; Diwakar, P.; Stanker, L.; et al. Detection of E. coli labeled with metal-conjugated antibodies using lateral-flow assay and laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2020, 412, 1291–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Shen, S.; Huang, J.; Dong, M.; Lu, J.; Li, W. Feature selection of laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy data for steel aging estimation. Spectrochim. Acta Part B At. Spectrosc. 2018, 150, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, H.; Hastie, T. Regularization and variable selection via the elastic net. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B (Stat. Methodol.) 2005, 67, 301–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hastie, T.; Tibshirani, R.; Friedman, J. Linear Methods for Regression. In The Elements of Statistical Learning: Data Mining, Inference, and Prediction; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2009; pp. 43–99. [Google Scholar]
- Boucher, T.F.; Ozanne, M.V.; Carmosino, M.L.; Dyar, M.D.; Mahadevan, S.; Breves, E.A.; Lepore, K.H.; Clegg, S.M. A study of machine learning regression methods for major elemental analysis of rocks using laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy. Spectrochim. Acta Part B At. Spectrosc. 2015, 107, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.-L.; Wu, S.; Tang, H.-S.; Wang, K.; Duan, Y.-X.; Li, H. Progress of chemometrics in laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy analysis. Chin. J. Anal. Chem. 2015, 43, 939–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moncayo, S.; Manzoor, S.; Navarro-Villoslada, F.; Caceres, J.O. Evaluation of supervised chemometric methods for sample classification by laser induced breakdown spectroscopy. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2015, 146, 354–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.-N.; Liu, X.-F.; Yang, F.; Xu, W.-M.; Wang, J.-Y.; Shu, R. A review of artificial neural network based chemometrics applied in laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy analysis. Spectrochim. Acta Part B At. Spectrosc. 2021, 180, 106183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Afgan, M.S.; Gu, W.; Song, Y.; Wang, Y.; Hou, Z.; Song, W.; Li, Z. Recent advances in laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy quantification: From fundamental understanding to data processing. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2021, 143, 116385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Institute for Standards and Technology. NIST Atomic Spectra Database. Available online: https://www.nist.gov/pml/atomic-spectra-database (accessed on 12 December 2022).
- Sezer, B.; Apaydin, H.; Bilge, G.; Boyaci, I.H. Coffee arabica adulteration: Detection of wheat, corn and chickpea. Food Chem. 2018, 264, 142–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamela, R.R.; Costa, V.C.; Sperança, M.A.; Pereira-Filho, E.R. Laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS) and wavelength dispersive X-ray fluorescence (WDXRF) data fusion to predict the concentration of K, Mg and P in bean seed samples. Food Res. Int. 2020, 132, 109037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, J.; Asghar, H.; Shah, S.K.H.; Naeem, M.; Abbasi, S.A.; Ali, R. Elemental analysis of sage (herb) using calibration-free laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy. Appl. Opt. 2020, 59, 4927–4932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- St-Onge, L.; Kwong, E.; Sabsabi, M.; Vadas, E.B. Rapid analysis of liquid formulations containing sodium chloride using laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2004, 36, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Díaz Pace, D.M.; D’Angelo, C.A.; Bertuccelli, D.; Bertuccelli, G. Analysis of heavy metals in liquids using Laser Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy by liquid-to-solid matrix conversion. Spectrochim. Acta Part B At. Spectrosc. 2006, 61, 929–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.; Wu, L.; Wang, B.; Chen, J.; Lu, J.; Ni, X. Determination of Ca and Mg in aqueous solution by laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy using absorbent paper substrates. Appl. Opt. 2011, 50, 5695–5699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alamelu, D.; Sarkar, A.; Aggarwal, S.K. Laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy for simultaneous determination of Sm, Eu and Gd in aqueous solution. Talanta 2008, 77, 256–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarkar, A.; Alamelu, D.; Aggarwal, S.K. Determination of thorium and uranium in solution by laser-induced breakdown spectrometry. Appl. Opt. 2008, 47, G58–G64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yaroshchyk, P.; Morrison, R.J.S.; Body, D.; Chadwick, B.L. Quantitative determination of wear metals in engine oils using LIBS: The use of paper substrates and a comparison between single- and double-pulse LIBS. Spectrochim. Acta Part B At. Spectrosc. 2005, 60, 1482–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keerthi, K.; George, S.D.; Kulkarni, S.D.; Chidangil, S.; Unnikrishnan, V.K. Elemental analysis of liquid samples by laser induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS): Challenges and potential experimental strategies. Opt. Laser Technol. 2022, 147, 107622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Gigant, L.; Baudelet, M.; Richardson, M. Correlation between laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy signal and moisture content. Spectrochim. Acta Part B At. Spectrosc. 2012, 73, 71–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayvaz, H.; Sezer, B.; Dogan, M.A.; Bilge, G.; Atan, M.; Boyaci, I.H. Multiparametric analysis of cheese using single spectrum of laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy. Int. Dairy J. 2019, 90, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clegg, S.M.; Sklute, E.; Dyar, M.D.; Barefield, J.E.; Wiens, R.C. Multivariate analysis of remote laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy spectra using partial least squares, principal component analysis, and related techniques. Spectrochim. Acta Part B At. Spectrosc. 2009, 64, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geladi, P. Chemometrics in spectroscopy. Part 1. Classical chemometrics. Spectrochim. Acta Part B At. Spectrosc. 2003, 58, 767–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foegeding, E.A. Food authentication in the 21st century: The power of analytical methods combined with big data analysis. J. Food Sci. 2018, 83, 1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Danezis, G.P.; Tsagkaris, A.S.; Camin, F.; Brusic, V.; Georgiou, C.A. Food authentication: Techniques, trends & emerging approaches. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2016, 85, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Granato, D.; Putnik, P.; Kovačević, D.B.; Santos, J.S.; Calado, V.; Rocha, R.S.; Cruz, A.G.D.; Jarvis, B.; Rodionova, O.Y.; Pomerantsev, A. Trends in chemometrics: Food authentication, microbiology, and effects of processing. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2018, 17, 663–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Barron, L.J.R.; Fernández de Labastida, E.; Perea, S.; Chávarri, F.; de Vega, C.; Soledad Vicente, M.a.; Isabel Torres, M.a.; Isabel Nájera, A.; Virto, M.; Santisteban, A.; et al. Seasonal changes in the composition of bulk raw ewe’s milk used for Idiazabal cheese manufacture. Int. Dairy J. 2001, 11, 771–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montel, M.-C.; Buchin, S.; Mallet, A.; Delbes-Paus, C.; Vuitton, D.A.; Desmasures, N.; Berthier, F. Traditional cheeses: Rich and diverse microbiota with associated benefits. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2014, 177, 136–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quigley, L.; O’Sullivan, O.; Stanton, C.; Beresford, T.P.; Ross, R.P.; Fitzgerald, G.F.; Cotter, P.D. The complex microbiota of raw milk. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2013, 37, 664–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sánchez-Gamboa, C.; Hicks-Pérez, L.; Gutiérrez-Méndez, N.; Heredia, N.; García, S.; Nevárez-Moorillón, G.V. Seasonal influence on the microbial profile of Chihuahua cheese manufactured from raw milk. Int. J. Dairy Technol. 2018, 71, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Hekken, D.L.; Drake, M.A.; Tunick, M.H.; Guerrero, V.M.; Molina-Corral, F.J.; Gardea, A.A. Effect of pasteurization and season on the sensorial and rheological traits of Mexican Chihuahua cheese. Dairy Sci. Technol. 2008, 88, 525–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dundar, M.; Hirleman, E.D.; Bhunia, A.K.; Robinson, J.P.; Rajwa, B. Learning with a non-exhaustive training dataset: A case study: Detection of bacteria cultures using optical-scattering technology. In Proceedings of the 15th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, Paris, France, 28 June–1 July 2009; pp. 279–288. [Google Scholar]
- Rajwa, B.; Dundar, M.M.; Akova, F.; Bettasso, A.; Patsekin, V.; Dan Hirleman, E.; Bhunia, A.K.; Robinson, J.P. Discovering the unknown: Detection of emerging pathogens using a label-free light-scattering system. Cytom. Part A 2010, 77A, 1103–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
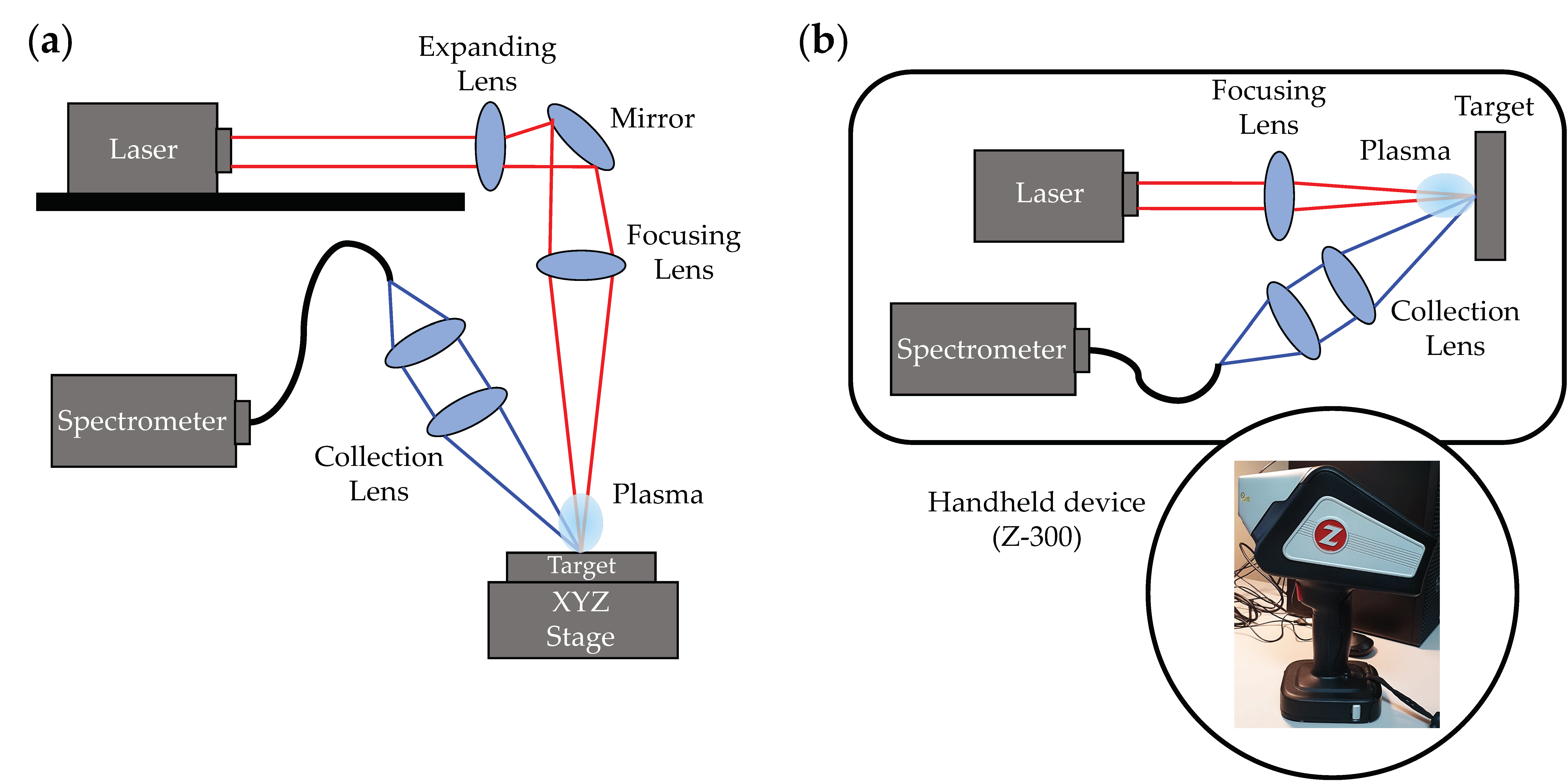





| Food Forms | Liquid | Solid | Powder | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Products | Balsamic vinegar | Vanilla extract | Coffee beans | Cheeses | Spices |
| Varieties or brands | 6 | 6 | 7 | 16 | 8 |
| Testing methods | NC membrane | NC membrane | Surface shots | Surface shots | Surface shots |
| Time Point | Benchtop LIBS | Handheld LIBS |
|---|---|---|
| T1 | 0.0060 (17.4%) | 0.0071 (11.3%) |
| T2 | 0.0062 (10.6%) | 0.0063 (15.3%) |
| T3 | 0.0056 (10.0%) | 0.0067 (16.3%) |
| T4 | 0.0054 (18.6%) | 0.0074 (18.3%) |
| Food Products | Classifier Accuracy | |
|---|---|---|
| Benchtop LIBS | Handheld LIBS | |
| 16 cheeses | ||
| T1 | 85.80 ± 1.57% | 81.20 ± 1.51% |
| T2 | 82.20 ± 1.53% | 83.00 ± 1.34% |
| T3 | 87.60 ± 1.99% | 84.70 ± 1.79% |
| T4 | 84.10 ± 1.93% | 84.20 ± 1.71% |
| 6 coffee varieties | 85.00 ± 1.94% | 92.70 ± 2.30% |
| 6 vanilla extracts | 94.50 ± 1.51% | 98.30 ± 0.69% |
| 6 balsamic vinegars | 88.20 ± 2.10% | 90.80 ± 1.88% |
| 8 powdered spices | 99.30 ± 0.70% | 84.50 ± 1.94% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, X.; Shin, S.; Gondhalekar, C.; Patsekin, V.; Bae, E.; Robinson, J.P.; Rajwa, B. Rapid Food Authentication Using a Portable Laser-Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy System. Foods 2023, 12, 402. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12020402
Wu X, Shin S, Gondhalekar C, Patsekin V, Bae E, Robinson JP, Rajwa B. Rapid Food Authentication Using a Portable Laser-Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy System. Foods. 2023; 12(2):402. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12020402
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Xi, Sungho Shin, Carmen Gondhalekar, Valery Patsekin, Euiwon Bae, J. Paul Robinson, and Bartek Rajwa. 2023. "Rapid Food Authentication Using a Portable Laser-Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy System" Foods 12, no. 2: 402. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12020402
APA StyleWu, X., Shin, S., Gondhalekar, C., Patsekin, V., Bae, E., Robinson, J. P., & Rajwa, B. (2023). Rapid Food Authentication Using a Portable Laser-Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy System. Foods, 12(2), 402. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12020402










