Effect of Water Activity, pH, and Lactic Acid Bacteria to Inhibit Escherichia coli during Chihuahua Cheese Manufacture
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Strains
2.2. Preparation of E. coli and LAB Inocula
2.3. Effect of the Initial Concentration on the Growth of E. coli in Milk
2.4. Effect of the Presence of LAB and Cheddarization on the Survival of E. coli in Chihuahua Cheese
2.5. Effect of the pH and Water Activity on the Survival of E. coli in Curd
2.6. Determination of pH and Aw
2.7. Bacterial Quantification
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Development of E. coli in Milk from Four Different Initial Concentrations
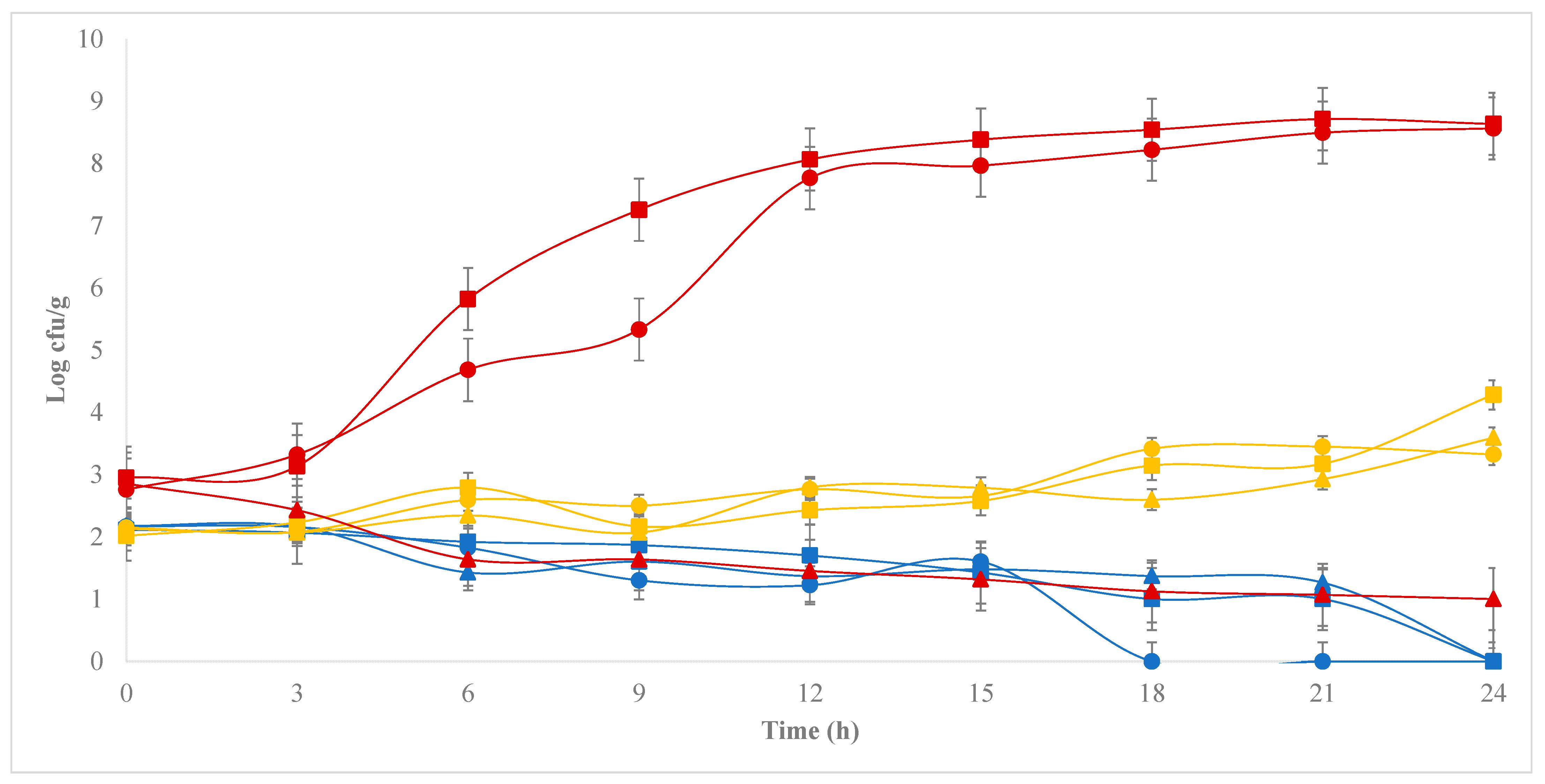
3.2. Development of E. coli during the Chihuahua Cheese-Making Process
3.3. Effect of pH and Water Activity on the Growth of E. coli in Simulated Curds
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cu, G.d.l.R.G.; Sánchez, B.M.; Vázquez, R.C. Calidad de La Leche Cruda. In Proceedings of the Primer Foro Sobre Ganadería Lechera de La Zona Alta de Veracruz, Veracruz, Mexico, 5 March 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Fuentes Fanegas, M.; Londoño Zapata, A.; Durango Zuleta, M.; Gutiérrez Buriticá, M.; Ochoa Agudelo, S.; Sepulveda Valencia, J. Antimicrobial Capacity of Native Lactic Acid Bacteria Isolated from Double Cream Cheese and Colombian Quesillo. Biotecnol. Sect. Agropecu. Agroind. 2017, 15, 45–55. [Google Scholar]
- Sánchez, L.; Tromps, J. Caracterización in vitro de bacterias ácido lácticas con potencial probiótico. Rev. Salud Anim. 2014, 36, 124–129. [Google Scholar]
- Walstra, P.; Wouters, T.M.; Geurts, T.M. Dairy Science and Technology, 2nd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Tsegaye, M.; Ashenafi, M. Fate of Escherichia coli O157: H7 during the processing and storage of Ergo and Ayib, traditional Ethiopian dairy products. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2005, 103, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrantes, X.; Railey, D.; Arias, M.L.; Chaves, C. Evaluación del efecto de cultivos probióticos adicionados a yogurt comercial, sobre poblaciones conocidas de Listeria monocytogenes y Escherichia coli O157: H7. Arch. Latinoam. Nutr. 2004, 54, 293–297. [Google Scholar]
- de la Rosa-Hernández, M.C.; Cadena-Ramírez, A.; Téllez-Jurado, A.; Gómez-Aldapa, C.A.; Rangel-Vargas, E.; Chávez-Urbiola, E.A.; Castro-Rosas, J. Presence of Multidrug-Resistant Shiga Toxin–Producing Escherichia coli, Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli, and Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli on Fresh Cheeses from Local Retail Markets in Mexico. J. Food Prot. 2018, 81, 1748–1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Córdova, A.F.; Yescas, C.; Ortiz-Estrada, Á.M.; de los Ángeles De la Rosa-Alcaraz, M.; Hernández-Mendoza, A.; Vallejo-Cordoba, B. Invited review: Artisanal Mexican cheeses. J. Dairy Sci. 2016, 99, 3250–3262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NMX-F-738-COFOCALEC-2017; Sistema Producto Leche Alimento-Lácteo-Queso-Chihuahua-Denominación. Especificaciones y Métodos de Prueba. Diario Oficial de la Federación 18 (DCXCIII). Cofocalec: Guadalajara, Mexico, 2017.
- Van Hekken, D.L.; Tunick, M.H.; Tomasula, P.M.; Corral, F.J.M.; Gardea, A.A. Mexican Queso Chihuahua: Rheology of fresh cheese. Int. J. Dairy Technol. 2007, 60, 5–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olson, D.W.; Van Hekken, D.L.; Tunick, M.H.; Tomasula, P.M.; Molina-Corral, F.J.; Gardea, A.A. Mexican Queso Chihuahua: Functional properties of aging cheese. J. Dairy Sci. 2011, 94, 4292–4299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayaloglu, A. Cheese: Microbiology of Cheese. In Reference Module in Food Science; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, A.M.; Roberts, T. The effect of pH, water activity, sodium nitrite and storage temperature on the growth of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli and salmonellae in a laboratory medium. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 1986, 3, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kornacki, J.L.; Marth, E.H. Fate of nonpathogenic and enteropathogenic Escherichia coli during the manufacture of Colby-like cheese. J. Food Prot. 1982, 45, 310–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rash, K.; Kosikowski, F. Influence of lactic acid starter bacteria on enteropathogenic Escherichia coli in ultrafiltration prepared Camembert cheese. J. Dairy Sci. 1982, 65, 537–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govaris, A.; Papageorgiou, D.K.; Papatheodorou, K. Behavior of Escherichia coli O157: H7 during the manufacture and ripening of feta and telemes cheeses. J. Food Prot. 2002, 65, 609–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leuschner, R.G.; Boughtflower, M.P. Laboratory-scale preparation of soft cheese artificially contaminated with low levels of Escherichia coli O157, Listeria monocytogenes, and Salmonella enterica serovars Typhimurium, Enteritidis, and Dublin. J. Food Prot. 2002, 65, 508–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lekkas, C.; Kakouri, A.; Paleologos, E.; Voutsinas, L.P.; Kontominas, M.G.; Samelis, J. Survival of Escherichia coli O157: H7 in Galotyri cheese stored at 4 and 12 C. Food Microbiol. 2006, 23, 268–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlesser, J.; Gerdes, R.; Ravishankar, S.; Madsen, K.; Mowbray, J.; Teo, A.-L. Survival of a five-strain cocktail of Escherichia coli O157: H7 during the 60-day aging period of cheddar cheese made from unpasteurized milk. J. Food Prot. 2006, 69, 990–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wahi, S.; Bansal, S.; Ghosh, M.; Ganguli, A. Growth and survival of Escherichia coli O157: H7 during manufacture and storage of Indian cheese (paneer). Foodbourne Pathog. Dis. 2006, 3, 184–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raeisi, M.; Tajik, H.; Razavi, R.S.; Maham, M.; Moradi, M.; Hajimohammadi, B.; Naghili, H.; Hashemi, M.; Mehdizadeh, T. Essential oil of tarragon (Artemisia dracunculus) antibacterial activity on Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli in culture media and Iranian white cheese. Iran. J. Microbiol. 2012, 4, 30. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, S.; Hoffmann, W.; Bockelmann, W.; Hummerjohann, J.; Stephan, R.; Hammer, P. Fate of Shiga toxin-producing and generic Escherichia coli during production and ripening of semihard raw milk cheese. J. Dairy Sci. 2013, 96, 815–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhikari, A.; Yemmireddy, V.K.; Costello, M.J.; Gray, P.M.; Salvadalena, R.; Rasco, B.; Killinger, K. Effect of storage time and temperature on the viability of E. coli O157: H7, Salmonella spp., Listeria innocua, Staphylococcus aureus, and Clostridium sporogenes vegetative cells and spores in vacuum-packed canned pasteurized milk cheese. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2018, 286, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Shivaprasad, D.; Chauhan, K.; Taneja, N.K. Control of E. coli growth and survival in Indian soft cheese (paneer) using multiple hurdles: Phytochemicals, temperature and vacuum. LWT 2019, 114, 108350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, N.; Taniwaki, M.H.; Junqueira, V.C.A.; de Arruda Silveira, N.F.; Okazaki, M.M.; Gomes, R.A.R. Microbiological Examination Methods of Food and Water: A Laboratory Manual; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Bagel, A.; Sergentet, D. Shiga Toxin-Producing Escherichia coli and Milk Fat Globules. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dambrosio, A.; Capuozzo, F.; De Palo, P.; Mottola, A.; Storelli, M.M.; De Rosa, M.; Matrella, R.; Quaglia, N.C. Behaviour of Escherichia coli O157:H7 in raw and mild pasteurised donkey milk treated with high pressure. Int. Dairy J. 2023, 136, 105486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, K.C.; Goepfert, J. Growth of Salmonella at low pH. J. Food Sci. 1970, 35, 326–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, J.-H.; Vinay-Lara, E.; McMinn, R., Jr.; Glass, K.A.; Johnson, M.E.; Steele, J.L. Evaluation of NaCl, pH, and lactic acid on the growth of Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli in a liquid Cheddar cheese extract. J. Dairy Sci. 2014, 97, 6671–6679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’amico, D.J.; Druart, M.J.; Donnelly, C.W. Behavior of Escherichia coli O157: H7 during the manufacture and aging of Gouda and stirred-curd Cheddar cheeses manufactured from raw milk. J. Food Prot. 2010, 73, 2217–2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bluma, A.; Ciprovica, I. Diversity of lactic acid bacteria in raw milk. Res. Rural Dev. 2015, 1, 157–161. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, E.; Fan, L.; Jiang, Y.; Doucette, C.; Fillmore, S. Antimicrobial activity of bacteriocin-producing lactic acid bacteria isolated from cheeses and yogurts. AMB Express 2012, 2, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mufandaedza, J.; Viljoen, B.; Feresu, S.; Gadaga, T. Antimicrobial properties of lactic acid bacteria and yeast-LAB cultures isolated from traditional fermented milk against pathogenic Escherichia coli and Salmonella enteritidis strains. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2006, 108, 147–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otero, V.; Santos, J.A.; Rodríguez-Calleja, J.M.; García-López, M.-L. Behavior of Shiga-toxin-producing Escherichia coli in ewe milk stored at different temperatures and during the manufacture and ripening of a raw milk sheep cheese (Zamorano style). J. Dairy Sci. 2022, 105, 6527–6535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosikowski, E.V.; Mistry, V.V. Cheese and Fermented Milk Foods, 3rd ed.; University of Wisconsin-Madison: Madison, WI, USA, 1997; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Juneja, V.K.; Mukhopadhyay, S.; Ukuku, D.; Hwang, C.-A.; Wu, V.C.; Thippareddi, H. Interactive Effects of Temperature, pH, and Water Activity on the Growth Kinetics of Shiga Toxin–Producing Escherichia coli O104: H4. J. Food Prot. 2014, 77, 706–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chon, J.-W.; Kim, J.-W.; Song, K.-Y.; Lim, J.-S.; Bae, D.; Kim, H.; Seo, K.-H. Fate and survival of Listeria monocytogenes and Escherichia coli O157: H7 during ripening of cheddar cheeses manufactured from unpasteurized raw milk. LWT 2020, 133, 109944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
 ), 102 (
), 102 ( ), 104 (
), 104 ( ), 106 (●) cfu/g.
), 106 (●) cfu/g.
 ), 102 (
), 102 ( ), 104 (
), 104 ( ), 106 (●) cfu/g.
), 106 (●) cfu/g.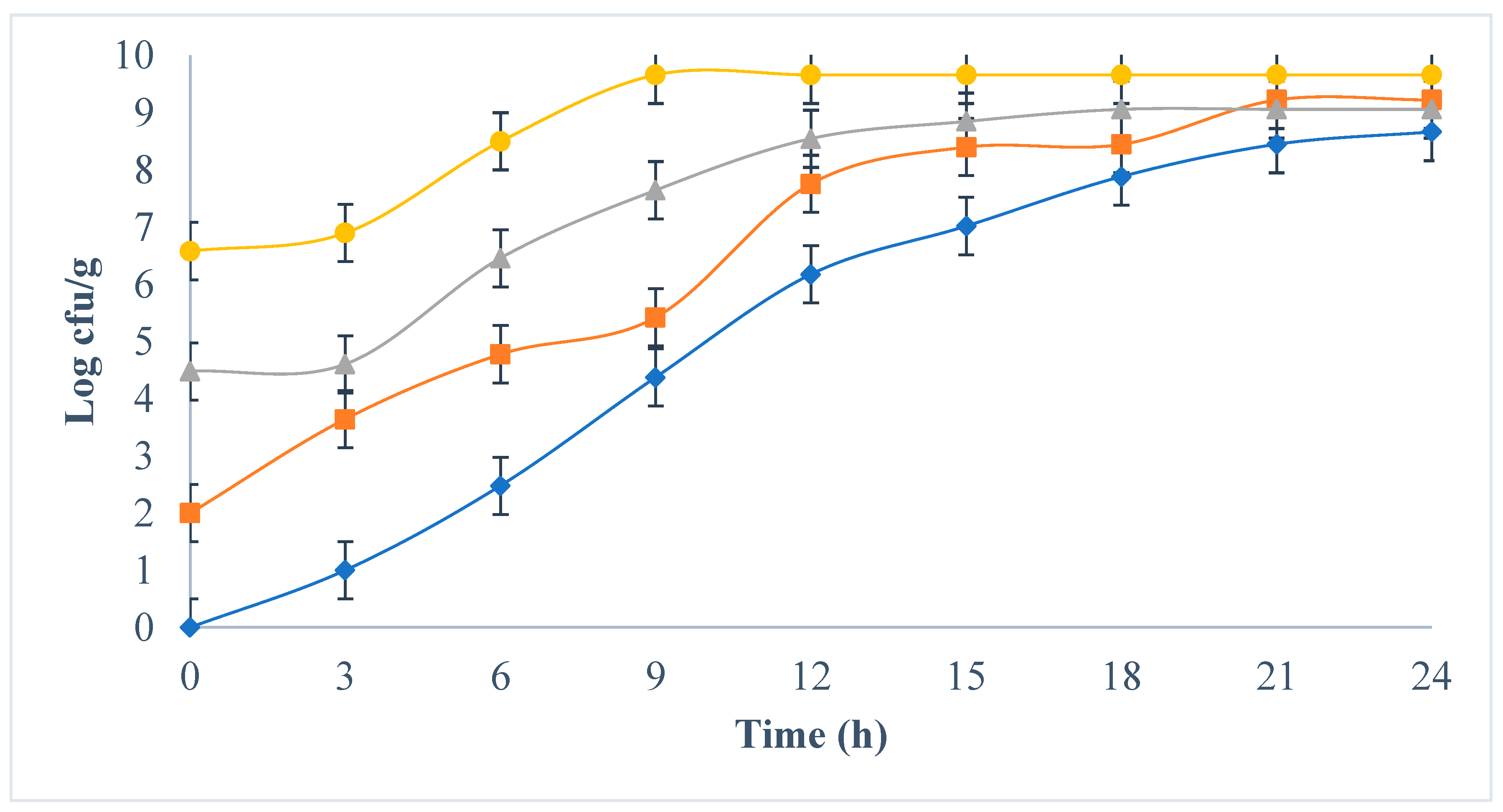
 ), 102 (
), 102 ( ), 104 (
), 104 ( ), 106 (●) cfu/g.
), 106 (●) cfu/g.
 ), 102 (
), 102 ( ), 104 (
), 104 ( ), 106 (●) cfu/g.
), 106 (●) cfu/g.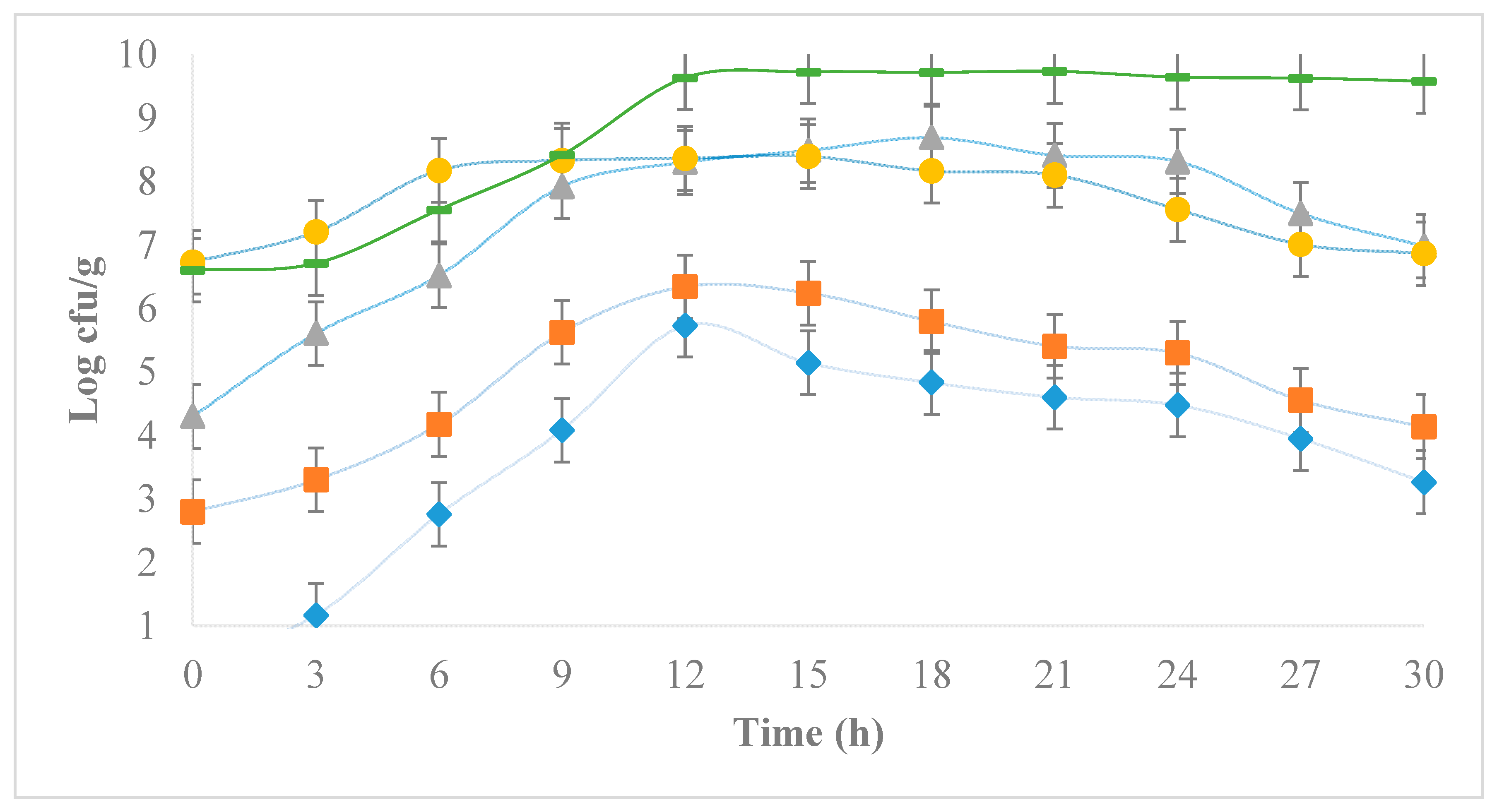
 ), 102 (
), 102 ( ), 104 (
), 104 ( ), 106 (●) cfu/g.
), 106 (●) cfu/g.
 ), 102 (
), 102 ( ), 104 (
), 104 ( ), 106 (●) cfu/g.
), 106 (●) cfu/g.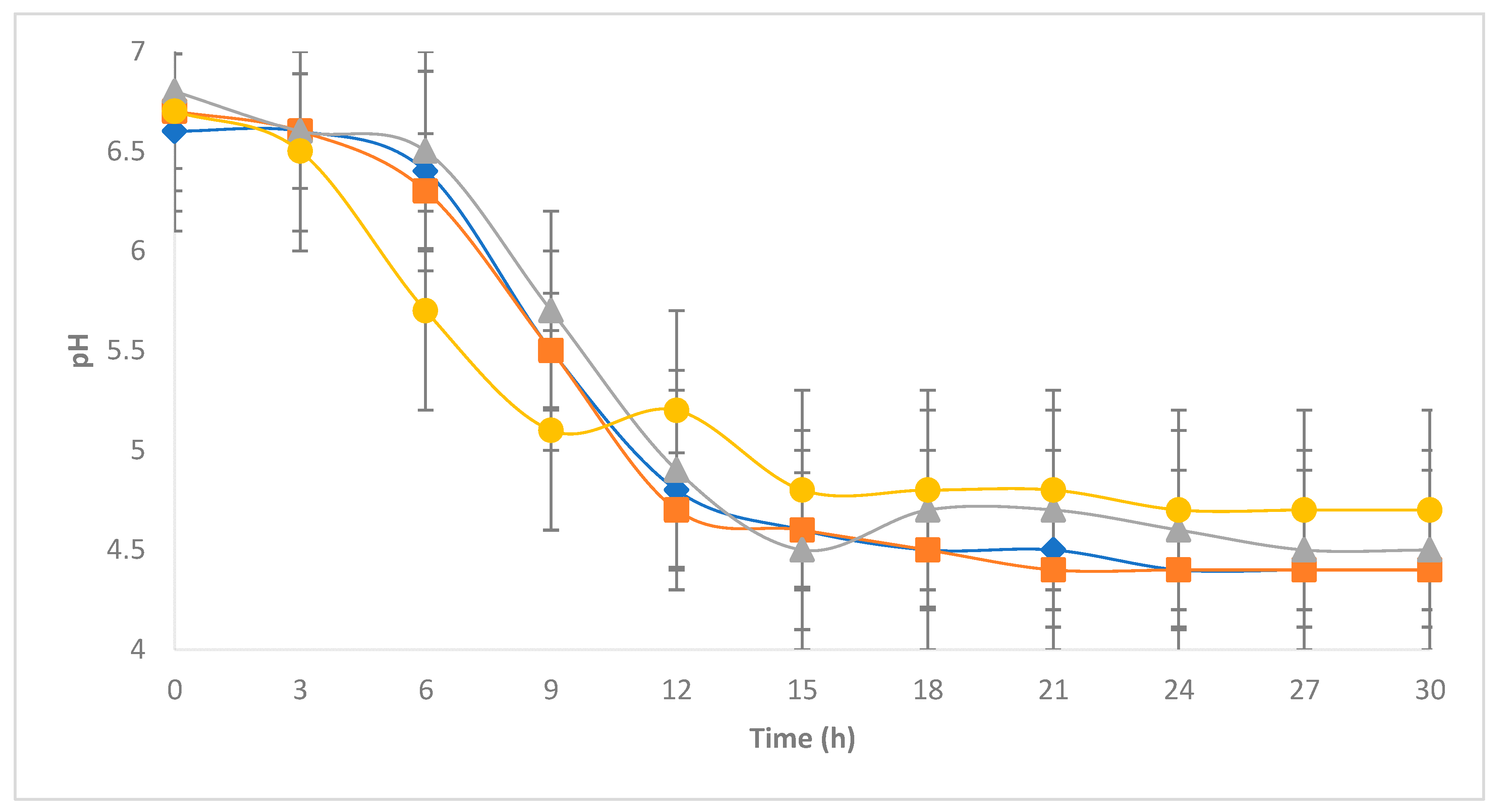

| Aw | pH | Day 1 | Day 63 | Day 126 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.8 | 7.0 | ND | ND | ND |
| 0.8 | 6.0 | ND | ND | ND |
| 0.8 | 5.0 | ND | ND | ND |
| 0.9 | 7.0 | 2.10 × 103 | 6.60 × 102 | ND |
| 0.9 | 6.0 | 1.91 × 103 | 1.50 × 102 | ND |
| 0.9 | 5.0 | 3.98 × 103 | 1.80 × 102 | ND |
| 1.0 | 7.0 | 3.60 × 108 | 9.00 × 105 | 5.30 × 104 |
| 1.0 | 6.0 | 4.30 × 108 | 2.90 × 105 | 1.00 × 104 |
| 1.0 | 5.0 | 1.00 × 10 | ND | ND |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chacón-Flores, N.A.; Olivas-Orozco, G.I.; Acosta-Muñiz, C.H.; Gutiérrez-Méndez, N.; Sepúlveda-Ahumada, D.R. Effect of Water Activity, pH, and Lactic Acid Bacteria to Inhibit Escherichia coli during Chihuahua Cheese Manufacture. Foods 2023, 12, 3751. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12203751
Chacón-Flores NA, Olivas-Orozco GI, Acosta-Muñiz CH, Gutiérrez-Méndez N, Sepúlveda-Ahumada DR. Effect of Water Activity, pH, and Lactic Acid Bacteria to Inhibit Escherichia coli during Chihuahua Cheese Manufacture. Foods. 2023; 12(20):3751. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12203751
Chicago/Turabian StyleChacón-Flores, Nidia Aracely, Guadalupe Isela Olivas-Orozco, Carlos Horacio Acosta-Muñiz, Néstor Gutiérrez-Méndez, and David Roberto Sepúlveda-Ahumada. 2023. "Effect of Water Activity, pH, and Lactic Acid Bacteria to Inhibit Escherichia coli during Chihuahua Cheese Manufacture" Foods 12, no. 20: 3751. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12203751
APA StyleChacón-Flores, N. A., Olivas-Orozco, G. I., Acosta-Muñiz, C. H., Gutiérrez-Méndez, N., & Sepúlveda-Ahumada, D. R. (2023). Effect of Water Activity, pH, and Lactic Acid Bacteria to Inhibit Escherichia coli during Chihuahua Cheese Manufacture. Foods, 12(20), 3751. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12203751







