Effect of Gluten Composition in Low-Allergy O-Free Wheat Flour on Cookie-Making Performance Compared with Flours with Different Gluten Strengths
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Analysis of Moisture and Protein Content of Flour Samples
2.3. Extraction of Glutein Components and SDS-PAGE Gel Electrophoresis of Flours
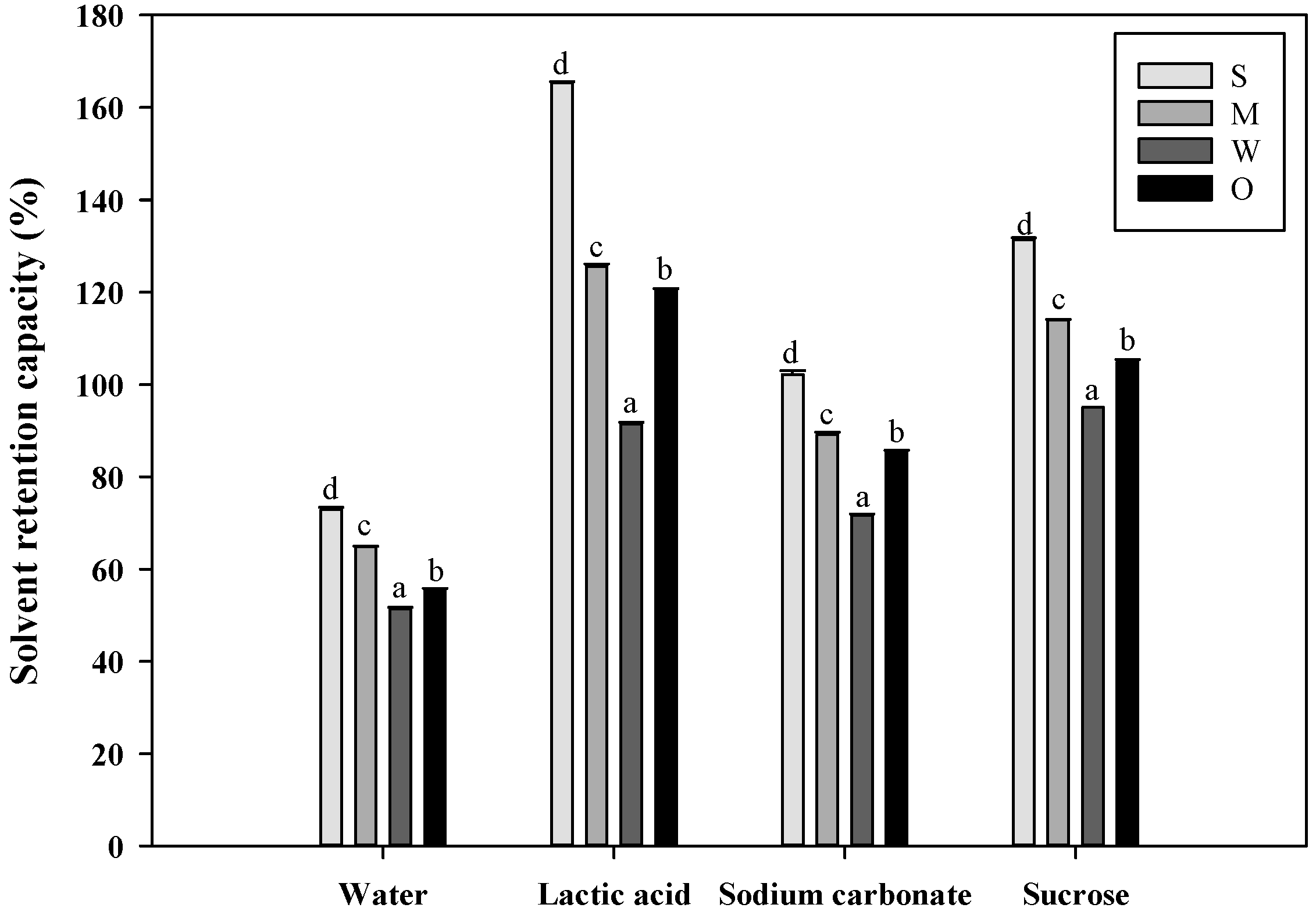
2.4. Analysis of Solvent Retention Capacity of Flours in Four Solutions
2.5. Analysis of Thermal Characteristics of Flour Using Differential Scanning Calorimetry
2.6. Determination of Flour Pasting Property Using Rapid Visco-Analyzer
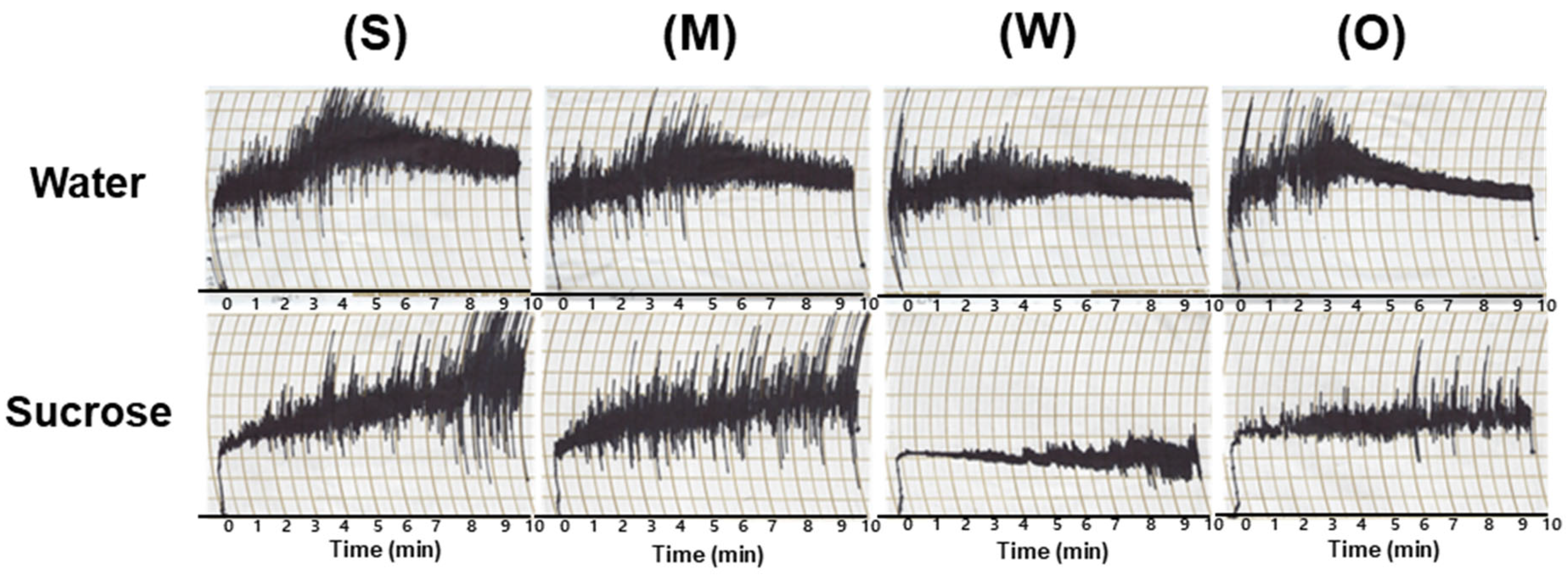
2.7. Analysis of Dough-Mixing Property of Flour using Mixograph
2.8. Preparation of Cookies
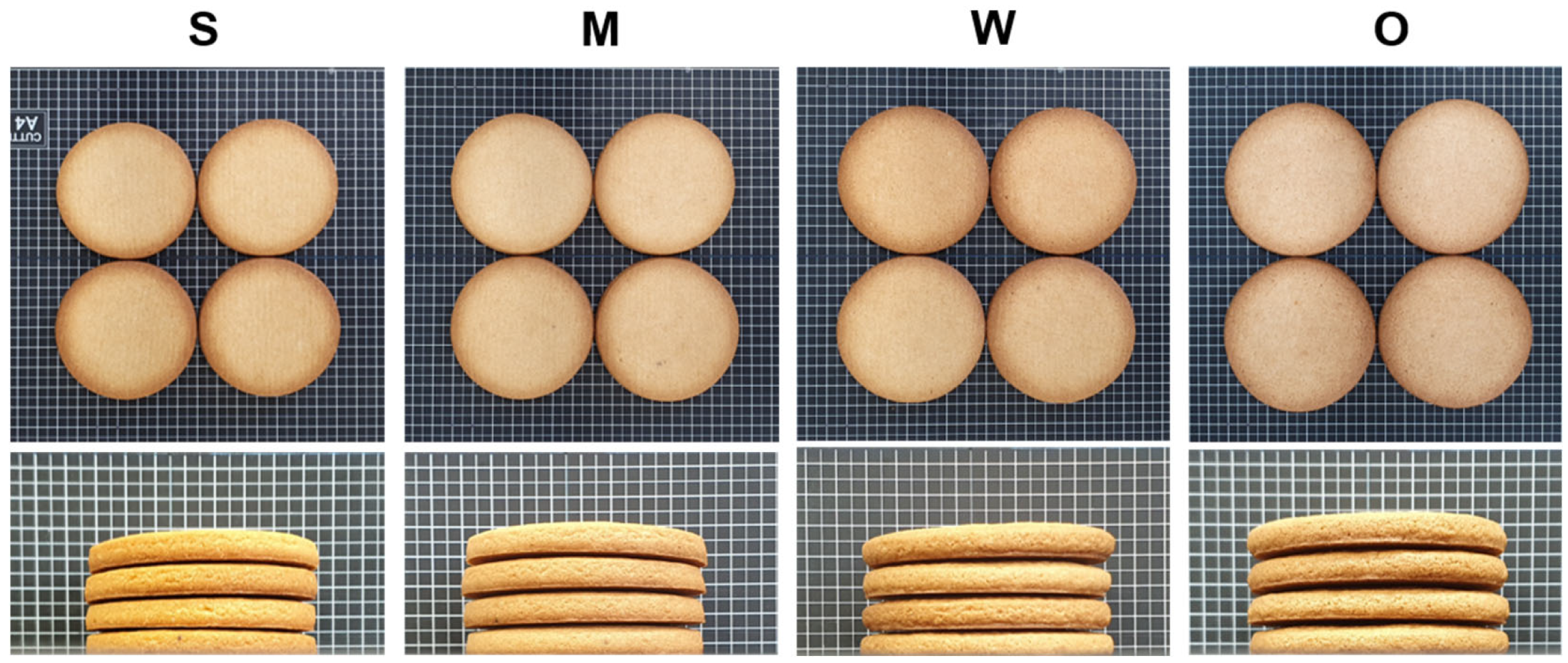
2.9. Assessment of Cookie Quality
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Physicochemical Properties of Flour and SDS-PAGE gel Electrophoresis of Gluten Protein
3.2. Solvent Retention Capacity of Flours
3.3. Gelatinization Properties of O-Free Flour in Water and Sucrose Solution Measured Using Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
3.4. Pasting Properties of O-Free Flour in Water and Sucrose Solution Measured Using Rapid Visco-Analyzer (RVA)
3.5. Dough-Mixing Properties of Flour Samples
3.6. Cookie-Making Performance of Flour Samples
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Satitsuksanoa, P.; Jansen, K.; Głobińska, A.; Van de Veen, W.; Akdis, M. Regulatory immune mechanisms in tolerance to food allergy. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, M.L.; Mullins, R.J. Food allergy: Is prevalence increasing? Intern. Med. J. 2017, 47, 256–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, C.S.; Yun, Y.M.; Choi, C.H.; Son, J.H.; Lee, J.Y.; Jeong, H.Y.; Kim, Y.J.; Cheong, Y.K.; Park, T.I. Gluten intolerance and reduced wheat-dependent exercise-induced anaphylaxis (WDEIA) wheat ‘O-free’. In Proceedings of the 2019 Annual Meeting of the Korean Society of Crop Science, Jinju, Republic of Korea, 18–19 April 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, Y.G.; Choi, S.C.; Kang, Y.; Kang, C.S.; Kim, C. Genomics approach to identify the cause of the missing omega-5 gliadin protein in O-free wheat. Plant Breed. Biotech. 2018, 6, 413–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, Y.J.; Cho, H.J.; Baek, N.Y.; Xia, T.Y.; Kweon, M. Quality of low allergy wheat ‘O-free’ flour and its bread- and noodle-making performance. Korean J. Food Cook. Sci. 2021, 37, 492–500. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, T.; Kim, K.; Kweon, M. Quality of low-allergy wheat (‘O-free’) flour and optimization of its bread- and noodle-making performance. Foods 2022, 11, 3399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, H.J.; Kim, H.; Moon, Y.; Kim, J.; Kweon, M. Effects of water amount and mixing time on fresh noodle-making performance of low-allergy wheat ‘O-free’ flour. Korean J. Food Cook. Sci. 2022, 38, 367–375. [Google Scholar]
- Slade, L.; Levine, H. Structure-function relationships of cookie and cracker ingredients. In The Science of Cookie and Cracker Production; Faridi, H., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1994; pp. 23–141. [Google Scholar]
- Pareyt, B.; Delcour, J.A. The role of wheat flour constituents, sugar, and fat in low moisture cereal-based products: A review on sugar-snap cookies. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2008, 48, 824–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kweon, M.; Slade, L.; Levine, H.; Martin, R.; Souza, E. Exploration of functionality of sugar functionality in sugar-snap and wire-cut cookie baking: Implications for potential sucrose replacement or reduction. Cereal Chem. 2009, 88, 537–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kweon, M.; Slade, L.; Levine, H.; Gannon, D. Cookie- versus cracker-baking-What’s the difference? Flour functionality requirements explored by SRC and Alveography. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2014, 54, 115–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pareyt, B.; Brijs, K.; Delcour, J.A. Sugar-snap cookie dough settting: The impact of sucrose on gluten functionality. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 7814–7818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pareyt, B.; Bruneel, C.; Biijs, K.; Goesaert, H.; Delcour, J.A. Flour sodium dodesyl sulfate (SDS)-extractable protein level as a cookie flour quality indicator. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 353–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moiraghi, M.; Vanzetti, L.; Bainotti, C.; Helguera, M.; León, A.; Pérez, G. Relationship between soft wheat flour physicochemical composition and cookie-making performance. Cereal Chem. 2011, 88, 130–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, B.; Wu, H.; Lu, C.; Lű, G.; Liu, D.; Li, M.; Jiang, W.; Song, G.; Gao, D. Effect of high-molecular-weight glutenin subunit deletion on soft wheat quality properties and sugar-snap cookie quality estimated through near-isogenic lines. J. Integr. Agric. 2018, 17, 1066–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, F.; Kim, J.; Baik, B.K. Influences of high-molecular-weight glutenin subunits and rye translocations on dough-mixing properties and sugar-snap cookie-baking quality of soft winter wheat. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2020, 100, 3850–3856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, C.S.; Jung, J.U.; Baik, B.K.; Park, C.S. Relationship between physicochemical characteristics of flour and sugar-snap cookie quality in Korean wheat cultivar. Int. Food Res. J. 2014, 21, 617–624. [Google Scholar]
- Veraverbeke, W.S.; Delcour, J.A. Wheat protein composition and properties of wheat glutenin in relation to breadmaking functionality. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2002, 42, 179–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wieser, H.; Koehler, P.; Scherf, K. Chemistry of wheat glutenin proteins: Qualitative composition. Cereal Chem. 2022, 100, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uthayakumaran, S.; Tomoskozi, S.; Tatham, A.S.; Savage, A.W.J.; Gianibelli, M.C.; Stoddard, F.L.; Bekes, F. Effects of gliadin fractions on functional properties of wheat dough depending on molecular size and hydrophobicity. Cereal Chem. 2001, 78, 138–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barak, S.; Mudgil, D.; Khatkar, B.S. Effect of composition of gluten proteins and dough rheological properties on the cookie-making quality. Br. Food J. 2013, 115, 564–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AACC. Approved Method of Analysis, 11th ed.; Method 10-53.01, 44-15.02, 46-30.01, 56-11.02; AACC International Inc.: St. Paul, MN, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Lookhart, G.; Bean, S. Separation and characterization of wheat protein fractions by high-performance capillary electrophoresis. Cereal Chem. 1995, 72, 527–532. [Google Scholar]
- Kweon, M.; Slade, L.; Levine, H. Potential sugar reduction in cookies formulated with sucrose alternatives. Cereal Chem. 2016, 93, 576–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Hung, P.; Maeda, T.; Morita, N. Waxy and high-amylose wheat starches and flours—Characteristics, functionality and application. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2006, 17, 448–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kweon, M.; Martin, R.; Souza, E. Effect of tempering conditions on milling performance and flour functionality. Cereal Chem. 2009, 86, 12–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, C.H.; Park, J.H.; Mo, Y.J.; Kim, K.M.; Kim, K.H.; Kang, C.S.; Park, T.I.; Cho, S.W.; Park, C.S. Effect of heterozygous genotypes at the Pinb-D1 loci on physicochemical properties of flour and end-use quality. Korean J. Breed. Sci. 2020, 52, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.H.; Yoon, Y.M.; Son, J.H.; Choi, C.H.; Kim, K.H.; Kim, K.M.; Cheong, Y.K.; Kang, C.S.; Yang, J. Enhancement of cookie quality by microwave treatment of allergy reaction-reduced “Ofree” wheat flour. Korean J. Crop Sci. 2019, 64, 366–372. [Google Scholar]
- Ozturk, S.; Kahraman, K.; Tiftik, B.; Koksel, H. Predicting the cookie quality of flours by using Mixolab®. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2008, 227, 1549–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dupont, F.M.; Samoil, V.; Chan, R. Extraction of up to 95% of wheat (Triticum aestivum) flour protein using warm sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) without reduction or sonication. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 7431–7438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dahesh, M.; Banc, A.; Duri, A.; Morel, A.H.; Ramos, L. Polymeric assembly of gluten proteins in an aqueous ethanol solvent. J. Phys. Chem. B 2014, 118, 11065–11076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waga, J.; Skoczowski, A. Development and characteristics of ω-gliadin-free wheat genotypes. Euphytica 2014, 195, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kweon, M.; Slade, L.; Levine, H. Solvent retention capacity (SRC) testing of wheat flour: Principles and value in predicting flour functionality in different wheat-based food processes in wheat breeding—A review. Cereal Chem. 2011, 88, 537–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, S.H.; Jeon, S.; Young, M.; Moon, Y.J.; Hong, Y.E.; Kweon, M. Quality of cookies formulated with Jeju magma seawater. Korean J. Food Cook. Sci. 2017, 33, 292–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaines, C.S. Collaborative study of methods for solvent retention capacity profiles (AACC Method 56-11). Cereal Foods World 2000, 45, 303–306. [Google Scholar]
- Faridi, H.; Gaines, C.; Finney, P. Soft wheat quality in production of cookies and crackers. In Wheat: Production, Properties and Quality; Bushuk, W., Rasper, V.F., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1994; pp. 154–168. [Google Scholar]
- Jung, E.J.; Moon, Y.; Kweon, M. Processing suitability of healthful carbohydrates for potential sucrose replacement to produce muffins with staling retardation. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 131, 109565. [Google Scholar]
- Allan, C.; Rajwa, B.; Mauer, L.J. Effects of sugars and sugar alcohols on the gelatinization temperature of wheat starch. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 84, 593–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renzetti, S.; van den Hoek, I.A.; van der Sman, R.G. Mechanisms controlling wheat starch gelatinization and pasting behaviour in presence of sugars and sugar replacers: Role of hydrogen bonding and plasticizer molar volume. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 119, 106880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, M.; Jeon, S.; Kweon, M. Study on applicability of allulose as a sucrose replacer in cookie making. J. East Asian Soc. Diet. Life 2016, 26, 450–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suhendro, E.L.; Kunetz, C.F.; McDonough, C.M.; Rooney, L.W.; Waniska, R.D. Cooking characteristics and quality of noodles from food sorghum. Cereal Chem. 2000, 77, 96–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batey, I.L. Interpretation of RVA curves. In The RVA Handbook; Crosbie, G.B., Ross, A.S., Eds.; AACC International Inc.: St. Paul, MN, USA, 2007; pp. 19–30. [Google Scholar]
- Isaak, C.; Sapirstein, H.; Wu, Y.; Graf, R. Effects of water absorption and salt on discrimination of wheat gluten strength assessed by dough mixing and protein composition. J. Cereal Sci. 2019, 89, 102752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovacs, M.I.P.; Fu, B.X.; Woods, S.M.; Khan, K. Thermal stability of wheat gluten protein: Its effect on dough properties and noodle texture. J. Cereal Sci. 2004, 39, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finnie, S.; Atwell, W.A. Composition of commercial flour. In Wheat Flour; Finnie, S., Atwell, W.A., Eds.; AACC International Inc.: St. Paul, MN, USA, 2016; pp. 31–42. [Google Scholar]
- Edwards, N.M.; Gianibelli, M.C.; McCaig, T.N.; Clarke, J.M.; Ames, N.P.; Larroque, O.R.; Dexter, J.E. Relationships between dough strength, polymeric protein quantity and composition for diverse durum wheat genotypes. J. Cereal Sci. 2007, 45, 140–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatkar, B.S.; Bell, A.E.; Schofield, J.D. A comparative study of the inter-relationships between mixograph parameters and bread-making qualities of wheat flours and glutens. J. Sci. Food Agric. 1996, 72, 71–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatkar, B.S.; Fido, R.J.; Tatham, A.S.; Schofield, J.D. Functional properties of wheat gliadins. I Effects on mixing characteristics and bread making quality. J. Cereal Sci. 1996, 35, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Day, L.; Augustin, M.A.; Batey, I.L.; Wrigley, C.W. Wheat-gluten uses and industry needs. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2006, 17, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Sun, W.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, Z.; Hu, H.; Zhao, M.; Li, W. Development of a novel model dough based on mechanically activated cassava starch and gluten protein: Application in bread. Food Chem. 2019, 300, 125196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Ingredient | Standard Weight (g) |
|---|---|
| Flour | 225.0 1 |
| Shortening | 90.0 |
| Sucrose | 94.5 |
| Corn syrup | 3.4 |
| Sodium bicarbonate | 2.3 |
| Non-fat dry milk | 2.3 |
| Salt | 2.8 |
| Ammonium bicarbonate | 1.1 |
| Water | 49.5 |
| Flour (1) | Moisture (%) | Ash (%) | Protein (3) (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| S | 13.72 ± 0.03 c(2) | 0.42 ± 0.00 b | 13.98 ± 0.02 d |
| M | 13.50 ± 0.04 b | 0.43 ± 0.01 b | 10.56 ± 0.02 b |
| W | 14.01 ± 0.01 d | 0.37 ± 0.00 a | 8.50 ± 0.02 a |
| O | 13.10 ± 0.00 a | 0.43 ± 0.00 b | 11.49 ± 0.01 c |
| Solvent (1) | Flour (2) | Tonset (°C) | Tpeak (°C) | Tend (°C) | Heat of Transition (ΔQ, J/g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Water | S | 60.8 ± 0.2 ab(3) | 70.8 ± 0.1 a | 90.6 ± 0.1 a | 3.0 ± 0.1 a |
| M | 58.9 ± 0.2 a | 69.2 ± 0.5 a | 91.0 ± 0.6 a | 3.5 ± 0.1 ab | |
| W | 61.5 ± 0.1 b | 68.2 ± 0.0 a | 86.0 ± 0.3 a | 3.7 ± 0.0 bc | |
| O | 64.1 ± 0.3 c | 69.8 ± 0.3 a | 87.9 ± 1.3 a | 3.5 ± 0.1 ab | |
| Sucrose | S | 88.5 ± 0.2 de | 101.6 ± 0.7 c | 120.4 ± 1.5 b | 3.4 ± 0.1 ab |
| M | 86.3 ± 0.8 d | 98.3 ± 1.1 bc | 119.1 ± 1.5 b | 3.9 ± 0.1 bc | |
| W | 87.5 ± 0.2 d | 96.9 ± 0.3 b | 118.9 ± 0.2 b | 4.2 ± 0.0 c | |
| O | 89.8 ± 0.6 e | 98.2 ± 1.2 bc | 117.0 ± 3.2 b | 3.9 ± 0.2 bc |
| Solvent (1) | Flour (2) | Peak Viscosity (cP) | Breakdown Viscosity (cP) | Final Viscosity (cP) | Setback Viscosity (cP) | Peak Time (min) | Pasting Temp (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Water | S | 3059 ± 18 g(3) | 1221 ± 19 g | 3482 ± 1 g | 1644 ± 3 f | 6.2 ± 0.0 a | 67.4 ± 0.2 a |
| M | 2454 ± 3 e | 859 ± 1 e | 2752 ± 1 e | 1157 ± 1 d | 6.1 ± 0.1 a | 67.3 ± 0.4 a | |
| W | 2732 ± 21 f | 761 ± 8 d | 3519 ± 21 g | 1548 ± 8 e | 6.1 ± 0.0 a | 81.9 ± 0.4 b | |
| O | 2804 ± 13 f | 1022 ± 40 f | 3354 ± 21 f | 1572 ± 31 e | 6.2 ± 0.1 a | 87.5 ± 0.5 c | |
| Sucrose | S | 1299 ± 23 c | 103 ± 4 ab | 1399 ± 23 b | 203 ± 4 a | 7.0 ± 0.0 b | 91.5 ± 0.5 d |
| M | 1742 ± 7 d | 214 ± 4 c | 1987 ± 15 d | 459 ± 4 b | 7.0 ± 0.1 b | 90.7 ± 0.7 d | |
| W | 1177 ± 13 b | 187 ± 6 bc | 1533 ± 9 c | 543 ± 2 c | 7.0 ± 0.0 b | 92.0 ± 0.1 d | |
| O | 547 ± 0 a | 64 ± 2 a | 673 ± 4 a | 189 ± 6 a | 6.9 ± 0.1 b | 92.8 ± 0.0 d |
| Flour (1) | Cookie Geometry (cm) | Top Surface Color | Cookie Firmness (N) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Width | Length | Height | L* | a* | b* | ||
| S | 7.0 ± 0.1 a(2) | 7.0 ± 0.6 a | 0.94 ± 0.01 a | 65.1 ± 0.1 b | 12.5 ± 0.3 ab | 32.8 ± 0.2 b | 12.9 ± 0.1 a |
| M | 7.1 ± 0.8 a | 7.2 ± 0.3 a | 1.06 ± 0.01 b | 65.8 ± 0.2 b | 12.4 ± 0.3 a | 32.6 ± 0.3 b | 14.3 ± 0.2 b |
| W | 7.4 ± 0.6 b | 7.5 ± 0.4 b | 1.06 ± 0.01 b | 62.2 ± 0.4 a | 13.4 ± 0.2 b | 32.4 ± 0.5 b | 17.7 ± 2.0 d |
| O | 7.5 ± 0.6 b | 7.5 ± 1.0 b | 1.16 ± 0.01 c | 62.4 ± 0.1 a | 13.1 ± 0.1 ab | 31.0 ± 0.1 a | 16.5 ± 1.3 c |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Baek, N.; Moon, Y.; Kim, J.; Kweon, M. Effect of Gluten Composition in Low-Allergy O-Free Wheat Flour on Cookie-Making Performance Compared with Flours with Different Gluten Strengths. Foods 2023, 12, 3843. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12203843
Baek N, Moon Y, Kim J, Kweon M. Effect of Gluten Composition in Low-Allergy O-Free Wheat Flour on Cookie-Making Performance Compared with Flours with Different Gluten Strengths. Foods. 2023; 12(20):3843. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12203843
Chicago/Turabian StyleBaek, Nayeon, Yujin Moon, Jeongeon Kim, and Meera Kweon. 2023. "Effect of Gluten Composition in Low-Allergy O-Free Wheat Flour on Cookie-Making Performance Compared with Flours with Different Gluten Strengths" Foods 12, no. 20: 3843. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12203843
APA StyleBaek, N., Moon, Y., Kim, J., & Kweon, M. (2023). Effect of Gluten Composition in Low-Allergy O-Free Wheat Flour on Cookie-Making Performance Compared with Flours with Different Gluten Strengths. Foods, 12(20), 3843. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12203843







