A Recombinant Alginate Lyase Algt1 with Potential in Preparing Alginate Oligosaccharides at High-Concentration Substrate
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Strains and Chemicals
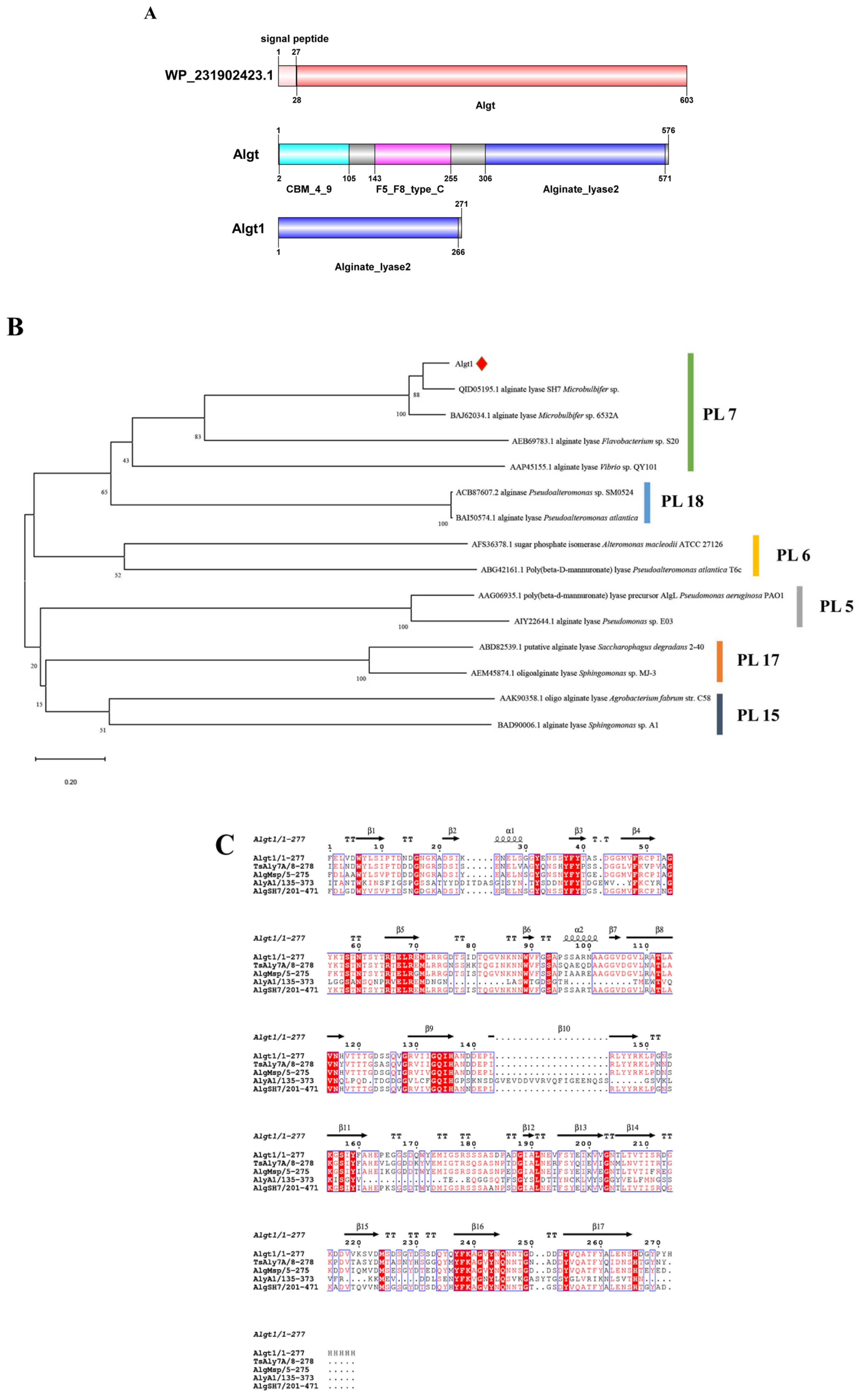
2.2. Sequence Analysis
2.3. Construction of Recombinant Alginate Lyases
2.4. Heterologous Expression of Alginate Lyases in P. pastoris and Purification
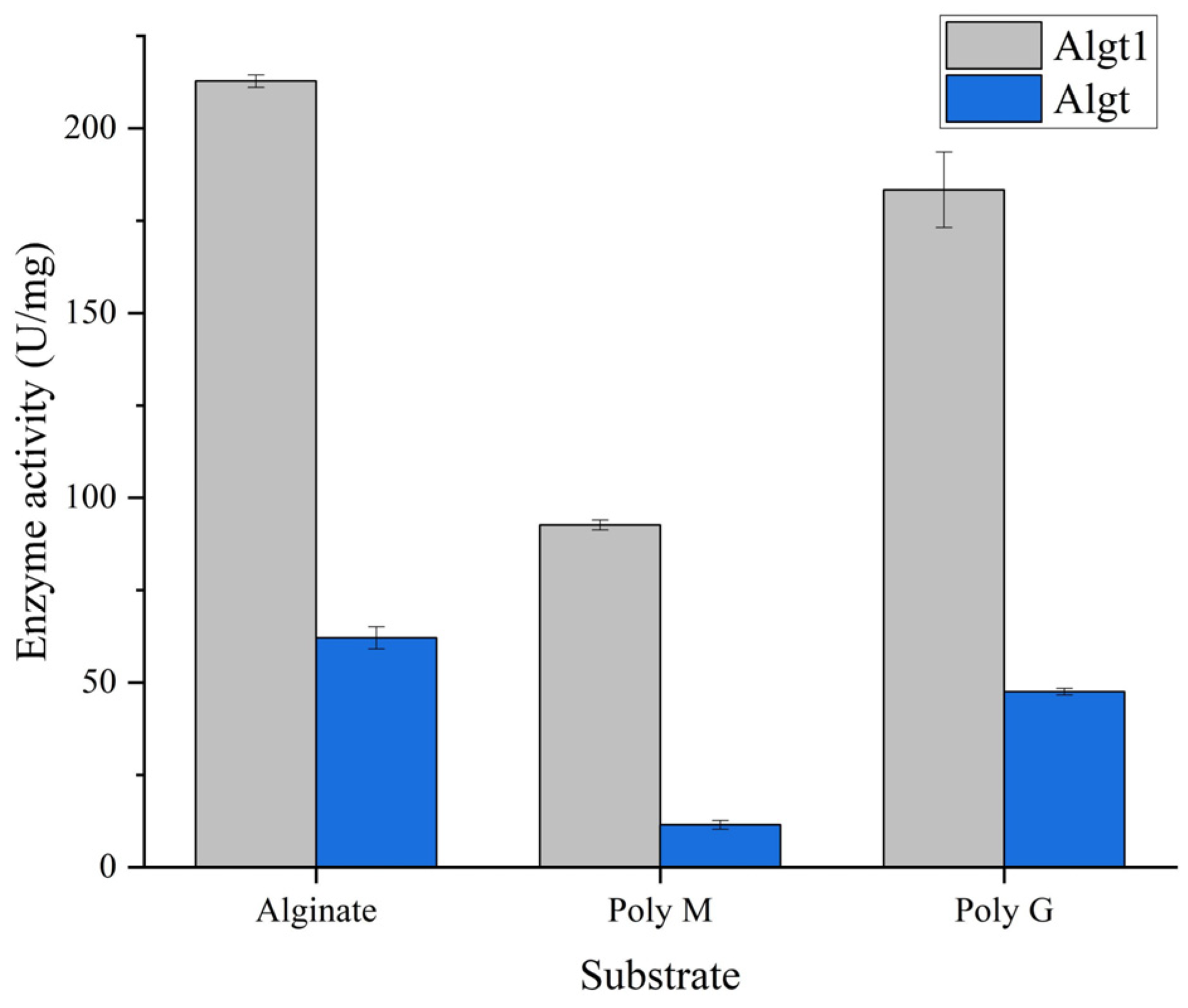
2.5. Enzymatic Activity Assay of Algt and Algt1
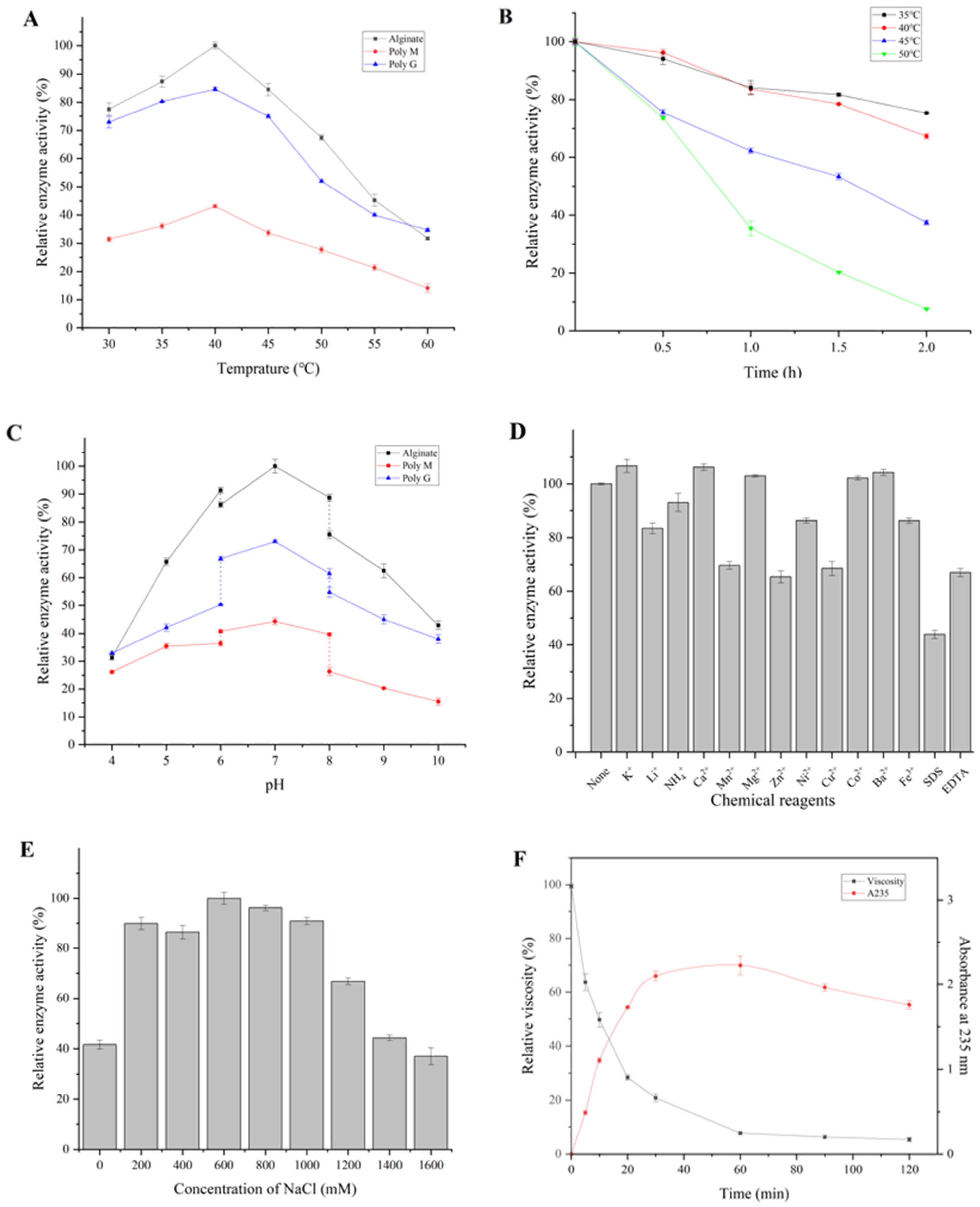
2.6. Biochemical Characterization of Algt1
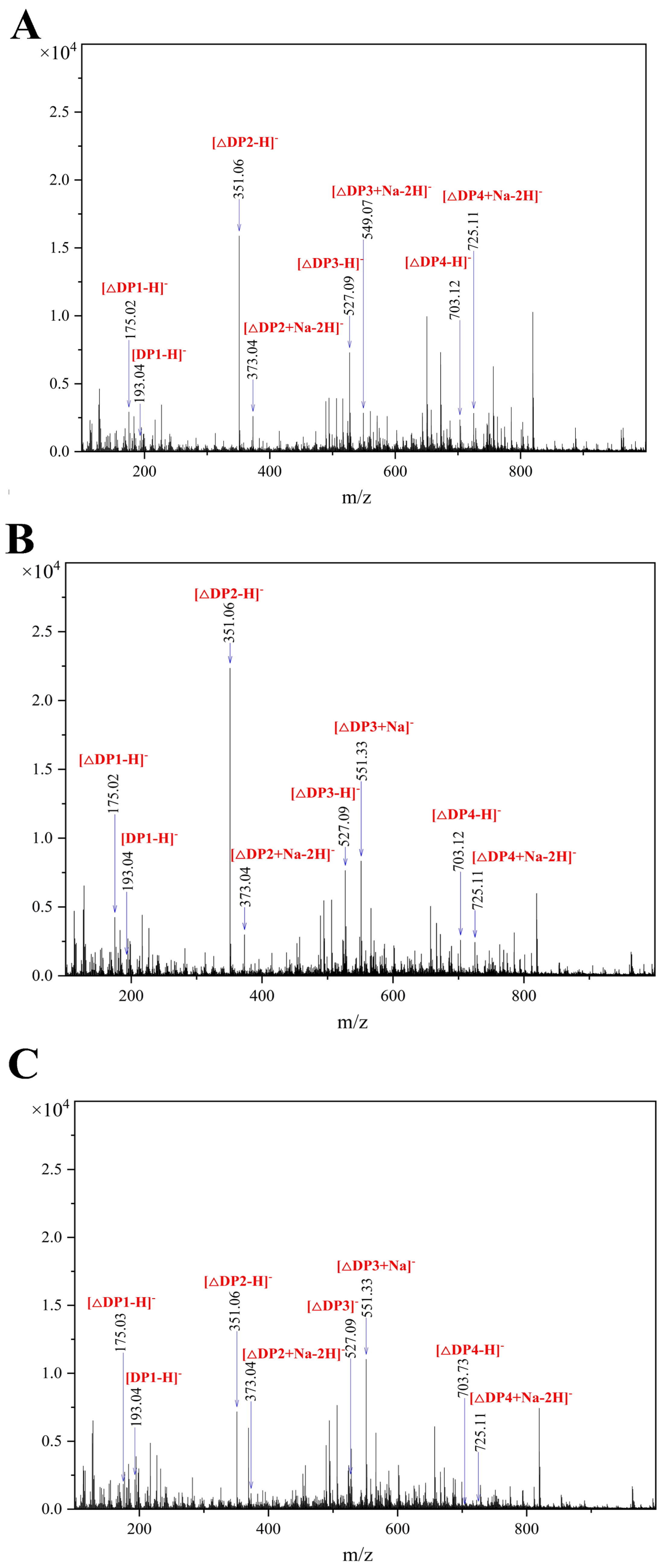
2.7. Analysis on Hydrolysis Products of Algt1
2.8. AOS Batch Preparation at High-Concentration Substrate
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Sequence Analysis of Algt and Algt1
3.2. Heterologous Expression of Algt and Algt1 in P. pastoris and Their Enzymatic Activity
3.3. Biochemical Properties of Algt1
3.4. Analysis of the Enzymatic Hydrolysates
3.5. Potential of Algt1 for AOS Batch Preparation at High-Concentration Substrate
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mabeau, S.; Kloareg, B. Isolation and Analysis of the Cell Walls of Brown Algae: Fucus spiralis, F. ceranoides, F. vesiculosus, F. serratus, Bifurcaria bifurcata and Laminaria digitata. J. Exp. Bot. 1986, 38, 1573–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hay, I.D.; Ur Rehman, Z.; Moradali, M.F.; Wang, Y.; Rehm, B.H.A. Microbial Alginate Production, Modification and Its Applications. Microb. Biotechnol. 2013, 6, 637–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vásquez-Ponce, F.; Higuera-Llantén, S.; Pavlov, M.S.; Ramírez-Orellana, R.; Marshall, S.H.; Olivares-Pacheco, J. Alginate Overproduction and Biofilm Formation by Psychrotolerant Pseudomonas mandelii Depend on Temperature in Antarctic Marine Sediments. Electron. J. Biotechnol. 2017, 28, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhu, B.W.; Yao, Z.; Jiang, J.J. Directed Preparation, Structure–activity Relationship and Applications of Alginate Oligosaccharides with Specific Structures: A Systematic Review. Food Res. Int. 2023, 170, 112990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Wang, Y.; Qin, Y.M.; Shen, P.L.; Peng, Q. Structures, Properties and Application of Alginic Acid: A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 162, 618–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, N.; Wang, H.Y.; Yang, Z.Z.; Zhao, K.Y.; Li, S.Y.; He, N.N. The Role of Functional Oligosaccharides as Prebiotics in Ulcerative Colitis. Food Funct. 2022, 13, 6875–6893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saberi Riseh, R.; Gholizadeh Vazvani, M.; Ebrahimi-Zarandi, M.; Skorik, Y.A. Alginate-induced Disease Resistance in Plants. Polymers 2022, 14, 661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasudevan, U.M.; Lee, O.K.; Lee, E.Y. Alginate Derived Functional Oligosaccharides: Recent Developments, Barriers, and Future Outlooks. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 267, 118158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.Y.; He, N.N.; Wang, L.N. Efficiently Anti-obesity Effects of Unsaturated Alginate Oligosaccharides (UAOS) in High-fat Diet (HFD)-fed Mice. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.D.; Zhang, X.W.; Wu, L.Y.; Li, H.B.; Chen, Y.H.; Li, L.J.; Ni, H.; Li, Q.B.; Zhu, Y.B. Exolytic Products of Alginate by the Immobilized Alginate Lyase Confer Antioxidant and Antiapoptotic Bioactivities in Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 251, 116976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.T.; Li, L.L.; Ye, C.Q.; Yuan, J.Y.; Qin, S. Alginate Oligosaccharide Improves Lipid Metabolism and Inflammation by Modulating Gut Microbiota in High-fat Diet Fed Mice. Appl. Microbiol. Biot. 2020, 104, 3541–3554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, M.C.; Cao, Q.; Wang, Y.; Xiao, H.; Zhao, J.R.; Zhang, Q.; Ji, A.G.; Song, S.L. Advances in Research on the Bioactivity of Alginate Oligosaccharides. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.M.; Ning, C.; Yuan, M.X.; Yang, S.X.; Wei, X.Y.; Xiao, M.S.; Fu, X.D.; Zhu, C.L.; Mou, H.J. High-level Expression of a Thermophilic and Acidophilic β-Mannanase from Aspergillus kawachii IFO 4308 with Significant Potential in Mannooligosaccharide Preparation. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 295, 122257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Yang, S.Q.; Li, X.T.; Yan, Q.J.; Reaney, M.J.T.; Jiang, Z.Q. Alginate Oligosaccharides: Production, Biological Activities, and Potential Applications. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2019, 18, 1859–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dodero, A.; Vicini, S.; Alloisio, M.; Castellano, M. Sodium Alginate Solutions: Correlation between Rheological Properties and Spinnability. J. Mater. Sci. 2019, 54, 8034–8046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Offei, F.; Mensah, M.; Thygesen, A.; Kemausuor, F. Seaweed Bioethanol Production: A Process Selection Review on Hydrolysis and Fermentation. Fermentation 2018, 4, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.W.; Huang, L.S.; Tan, H.D.; Qin, Y.Q.; Du, Y.G.; Yin, H. Characterization of a New Endo-type PolyM-specific Alginate Lyase from Pseudomonas sp. Biotechnol. Lett. 2014, 37, 409–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Zhou, J.; Li, X.; Peng, Q.; Lu, H.; Du, Y. Characterization of a New Alginate Lyase from Newly Isolated Flavobacterium sp. S20. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2013, 40, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashimoto, W.; Miyake, O.; Ochiai, A.; Murata, K. Molecular Identification of Sphingomonas sp. A1 Alginate Lyase (A1-IV) as a Member of Novel Polysaccharide Lyase Family 15 and Implications in Alginate Lyase evolution. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2005, 99, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, S.; Wei, T.D.; Chen, X.L.; Li, C.Y.; Wang, P.; Xie, B.B.; Qin, Q.L.; Zhang, X.Y.; Pang, X.H.; Zhou, B.C. Molecular Insight into the Role of the N-terminal Extension in the Maturation, Substrate Recognition, and Catalysis of a Bacterial Alginate Lyase from Polysaccharide Lyase Family 18. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 29558–29569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.D.; Guo, Y.X.; Wang, X.X.; Li, H.B.; Ni, H.; Li, L.J.; Xiao, A.F.; Zhu, Y.B. Molecular Cloning and Characterization of AlgL17, a New Exo-oligoalginate Lyase from Microbulbifer sp. ALW1. Protein Expr. Purif. 2019, 161, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.Q.; Li, S.; Bao, S.X.; Mo, K.L.; Sun, D.M.; Hu, Y.H. Expression and Characterization of a Cold-adapted Alginate Lyase with Exo/endo-type Activity from a Novel Marine Bacterium Alteromonas portus HB161718(T). Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilgaard, B.; Vuillemin, M.; Holck, J.; Wilkens, C.; Meyer, A.S. Specificities and Synergistic Actions of Novel PL8 and PL7 Alginate Lyases from the Marine Fungus Paradendryphiella salina. J. Fungi 2021, 7, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, R.; Yi, Y.J.; Chen, Z.; Wang, B.X.; Li, X.H.; Zhou, Y.X. Characterization of a New Biofunctional, Exolytic Alginate Lyase from Tamlana sp. s12 with High Catalytic Activity and Cold-adapted Features. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.C.; Fu, Z.; Tang, L.Y.; Zhang, Z.L.; Han, F.; Yu, W.G. Biochemical Characterization of a Novel Exo-type PL7 Alginate Lyase VsAly7D from Marine Vibrio sp. QY108. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, S.Q.; Wang, B.; Lu, M.; Li, F.L. Defluviitalea phaphyphila sp. nov., a Novel Thermophilic Bacterium that Degrades Brown Algae. Appl. Environ. Microb. 2016, 82, 868–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobruchowska, J.M.; Bjornsdottir, B.; Fridjonsson, O.H.; Altenbuchner, J.; Watzlawick, H.; Gerwig, G.J.; Dijkhuizen, L.; Kamerling, J.P.; Hreggvidsson, G.O. Enzymatic Depolymerization of Alginate by Two Novel Thermostable Alginate Lyases from Rhodothermus marinus. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 981602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arntzen, M.Ø.; Pedersen, B.; Klau, L.J.; Stokke, R.; Oftebro, M.; Antonsen, S.G.; Fredriksen, L.; Sletta, H.; Aarstad, O.A.; Aachmann, F.L.; et al. Alginate Degradation: Insights Obtained through Characterization of a Thermophilic Exolytic Alginate Lyase. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2021, 87, e02399-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyazaki, M.; Nogi, Y.; Ohta, Y.; Hatada, Y.; Fujiwara, Y.; Ito, S.; Horikoshi, K. Microbulbifer agarilyticus sp. nov. and Microbulbifer thermotolerans sp. nov., Agar-degrading Bacteria Isolated from Deep-sea Sediment. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Micr. 2008, 58, 1128–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Wen, L.P.; Gao, X.J.; Jin, C.J.; Xue, Y.; Yao, X.B. DOG 1.0: Illustrator of Protein Domain Structures. Cell Res. 2009, 19, 271–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robert, X.; Gouet, P. Deciphering Key Features in Protein Structures with the New ENDscript Server. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, W320–W324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, M.; Li, N.N.; Yang, S.X.; Yu, Y.; Han, Z.L.; Li, L.; Mou, H.J. Study on Expression and Action Mode of Recombinant Alginate Lyases based on Conserved Domains Reconstruction. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 103, 807–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, G.L. Use of Dinitrosalicylic Acid Reagent for Determination of Reducing Sugar. Anal. Chem. 1959, 31, 426–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Q.; Zhou, L.C.; Hassanin, H.A.M.; Jiang, B.; Liu, Y.C.; Chen, J.J.; Zhang, T. A New Role of Family 32 Carbohydrate Binding Module in Alginate Lyase from Vibrio natriegens SK42.001 in Altering its Catalytic Activity, Thermostability and Product Distribution. Food Biosci. 2021, 42, 101112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, F.; Zhu, B.; Li, Q.; Yin, H.; Sun, Y.; Yao, Z.; Ming, D. Elucidation of a Unique Pattern and the Role of Carbohydrate Binding Module of an Alginate Lyase. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, F.; Li, Q.; Zhu, B.W.; Ni, F.; Sun, Y.; Yao, Z. Effects of Module Truncation on Biochemical Characteristics and Products Distribution of a New Alginate Lyase with two Catalytic Modules. Glycobiology 2019, 29, 876–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.Y.; Wen, S.H.; Liao, S.M.; Wang, Q.Z.; Pan, S.H.; Zhang, R.C.; Lei, F.; Liao, W.; Feng, J.; Huang, S.S. Characterization of a Bifunctional Alginate Lyase as a New Member of the Polysaccharide Lyase Family 17 from a Marine Strain BP-2. Biotechnol. Lett. 2019, 41, 1187–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Cui, D.D.; Ma, S.; Chen, W.K.; Chen, D.W.; Shen, H. Characterization of a Novel PL17 Family Alginate Lyase with Exolytic and Endolytic Cleavage Activity from Marine Bacterium Microbulbifer sp. SH-1. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 169, 551–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, H.R.; Yoo, J.S.; Choi, Y.L.; Jang, Y.S.; Lee, Y.S. Characterization of an Organic Solvent-tolerant Polysaccharide Lyase from Microbulbifer thermotolerans DAU221. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 169, 452–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.Y.; Wang, Y.; Gao, S.; Wu, H.; Wang, D.N.; Yu, W.G.; Han, F. Biochemical Characteristics and Molecular Mechanism of an Exo-type Alginate Lyase VxAly7D and its Use for the Preparation of Unsaturated Monosaccharides. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2020, 13, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swift, S.M.; Hudgens, J.W.; Heselpoth, R.D.; Bales, P.M.; Nelson, D.C. Characterization of AlgMsp, an Alginate Lyase from Microbulbifer sp. 6532A. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e112939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sha, L.; Huang, M.; Huang, X.; Huang, Y.; Shao, E.; Guan, X.; Huang, Z. Cloning and Characterization of a Novel Endo-Type Metal-Independent Alginate Lyase from the Marine Bacteria Vibrio sp. Ni1. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.L.; Dong, S.; Xu, F.; Dong, F.; Li, P.Y.; Zhang, X.Y.; Zhou, B.C.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Xie, B.B. Characterization of a New Cold-adapted and Salt-activated Polysaccharide Lyase Family 7 Alginate Lyase from Pseudoalteromonas sp. SM0524. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Cui, D.D.; Chen, D.W.; Chen, W.K.; Ma, S.; Shen, H. Purification and Characterization of a Novel Endolytic Alginate Lyase from Microbulbifer sp. SH-1 and its Agricultural Application. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preiss, J.; Ashwell, G. Alginic Acid Metabolism in Bacteria. I. Enzymatic Formation of Unsaturated Oligosaccharides and 4-deoxy-L-erythro-5-hexoseulose Uronic Acid. J. Biol. Chem. 1962, 237, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Zheng, L.; Guo, Z.L.; Tang, T.C.; Zhu, B.W. Alginate Degrading Enzymes: An Updated Comprehensive Review of the Structure, Catalytic Mechanism, Modification Method and Applications of Alginate Lyases. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2021, 41, 953–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.K.; Chen, Q.C.; Zhou, B.; Wang, X.J.; Liu, S.Q. Mannooligosaccharide Preparation by the Hydrolysis of Konjac Flour with a Thermostable Endomannanase from Talaromyces cellulolyticus. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2019, 127, 520–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Alginate Lyase | Source | Family | Expression System | Specific Activity (U/mg) | Optimal Temperature/pH | Thermostability (Remained Enzymatic Activity) | Substrate Concentration | Hydrolytic Products | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Algt1 | M. thermotolerans DSM 19189 | PL7 | P. pastoris | 212.86 | 40 °C/7.0 | 80.9% (40 °C, 90 min) | 20% | DP1–4 | This study |
| AlgL17 | Microbulbifer sp. ALW1 | PL17 | E. coli | 28.99 | 35 °C/8.0 | 20% (35 °C, 10 min) | 0.5% | DP1–4 | [21] |
| Alg2951 | A. portus HB161718T | PL7 | E. coli | / | 25 °C/8.0 | 66.5% (40 °C, 30 min) | 1% | DP1, DP3 | [22] |
| AlgSH17 | Microbulbifer sp. SH-1 | PL17 | E. coli | 55.62 | 30 °C/7.0 | 20% (40 °C, 60 min) | 1% | DP1–6 | [38] |
| Alg17B | Strain BP-2 | PL17 | Native | 145 | 40–45 °C/7.5–8.0 | 10% (45 °C, 60 min) | 2% | DP1–6 | [37] |
| PsMan8A | P. salina | PL8 | P. pastoris | 245 | 25 °C/5.0 | ND | 0.15% | DP1–2 | [23] |
| Alys1 | Tamlana sp. s12 | PL7 | E. coli | 1350 | 35 °C/7.0–8.0 | 70% (50 °C, 60 min) | 1% | DP1 | [24] |
| VsAly7D | Vibrio sp. QY108 | PL7 | E. coli | 663 | 35 °C/8.0 | 20% (40 °C, 60 min) | 0.3% | DP1–2 | [25] |
| Parameters | Alginate | Poly M | Poly G |
|---|---|---|---|
| Specific activity (U/mg) | 212.86 | 93.87 | 186.19 |
| Km (mM) | 0.71 | 1.38 | 0.85 |
| Vmax (nmol/s) | 8.56 | 5.83 | 8.09 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liang, Q.; Huang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Xiao, M.; Ren, X.; Liu, T.; Li, H.; Yu, D.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, C. A Recombinant Alginate Lyase Algt1 with Potential in Preparing Alginate Oligosaccharides at High-Concentration Substrate. Foods 2023, 12, 4039. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12214039
Liang Q, Huang Y, Liu Z, Xiao M, Ren X, Liu T, Li H, Yu D, Wang Y, Zhu C. A Recombinant Alginate Lyase Algt1 with Potential in Preparing Alginate Oligosaccharides at High-Concentration Substrate. Foods. 2023; 12(21):4039. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12214039
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiang, Qingping, Youtao Huang, Zhemin Liu, Mengshi Xiao, Xinmiao Ren, Tianhong Liu, Hongyan Li, Dongxing Yu, Ying Wang, and Changliang Zhu. 2023. "A Recombinant Alginate Lyase Algt1 with Potential in Preparing Alginate Oligosaccharides at High-Concentration Substrate" Foods 12, no. 21: 4039. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12214039
APA StyleLiang, Q., Huang, Y., Liu, Z., Xiao, M., Ren, X., Liu, T., Li, H., Yu, D., Wang, Y., & Zhu, C. (2023). A Recombinant Alginate Lyase Algt1 with Potential in Preparing Alginate Oligosaccharides at High-Concentration Substrate. Foods, 12(21), 4039. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12214039





