In Vitro Infant Digestion of Whey Proteins Isolate–Lactose
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Whey Proteins Isolate–Lactose Conjugation
2.2.2. Preparation of Glycates Solution In Vitro Digestion
2.2.3. Simulated Gastric Fluid (SGF)
2.2.4. In Vitro Infant Gastric Digestion
2.2.5. Preparation of Phosphatidylcholine-Bile Salt (PC-BS)
2.2.6. Preparation of Bis-Tris HCL
2.2.7. In Vitro Infant Duodenal Digestion
2.2.8. Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate–Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis (SDS–PAGE)
3. Results
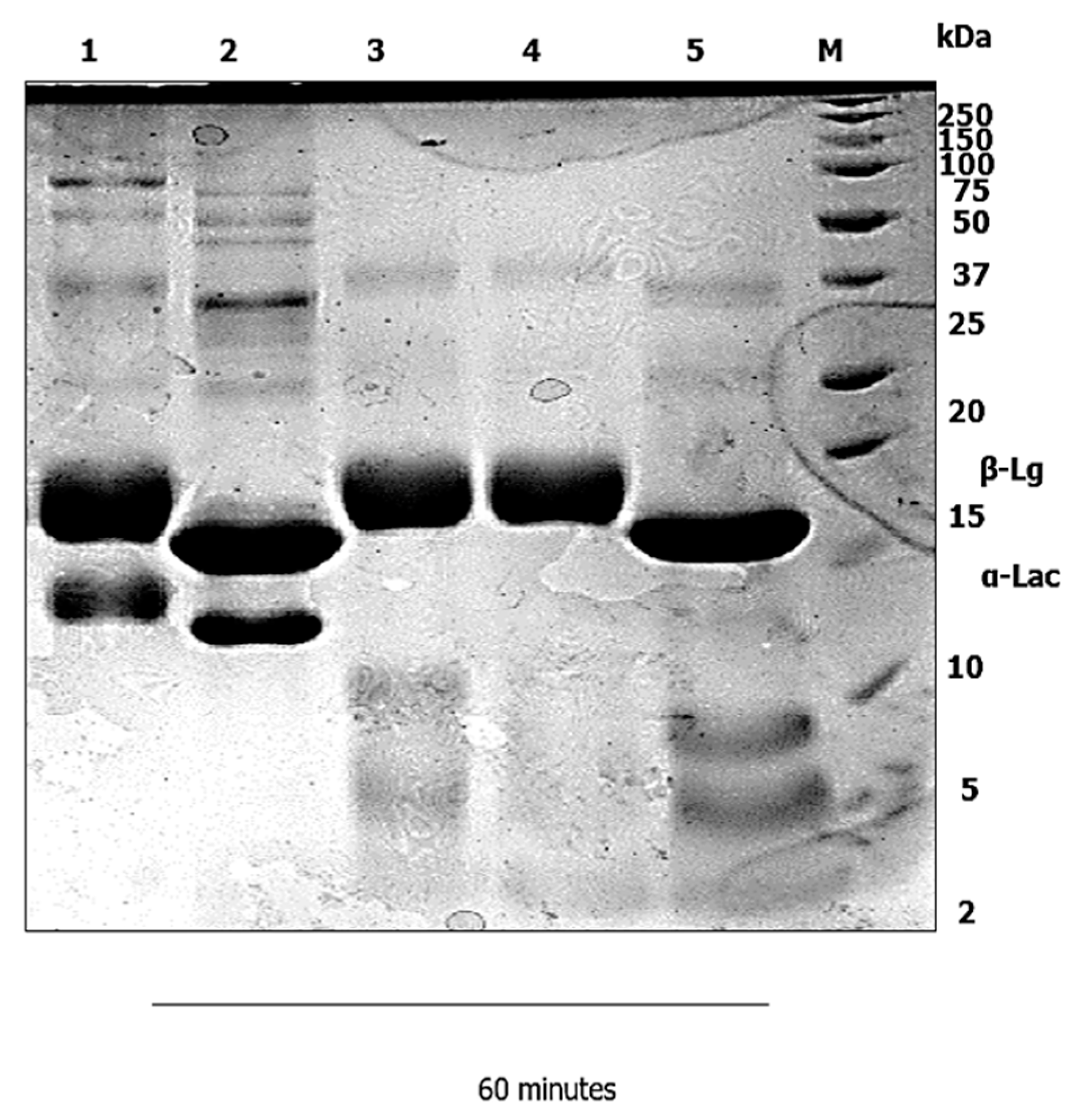
3.1. Gastric Digestion
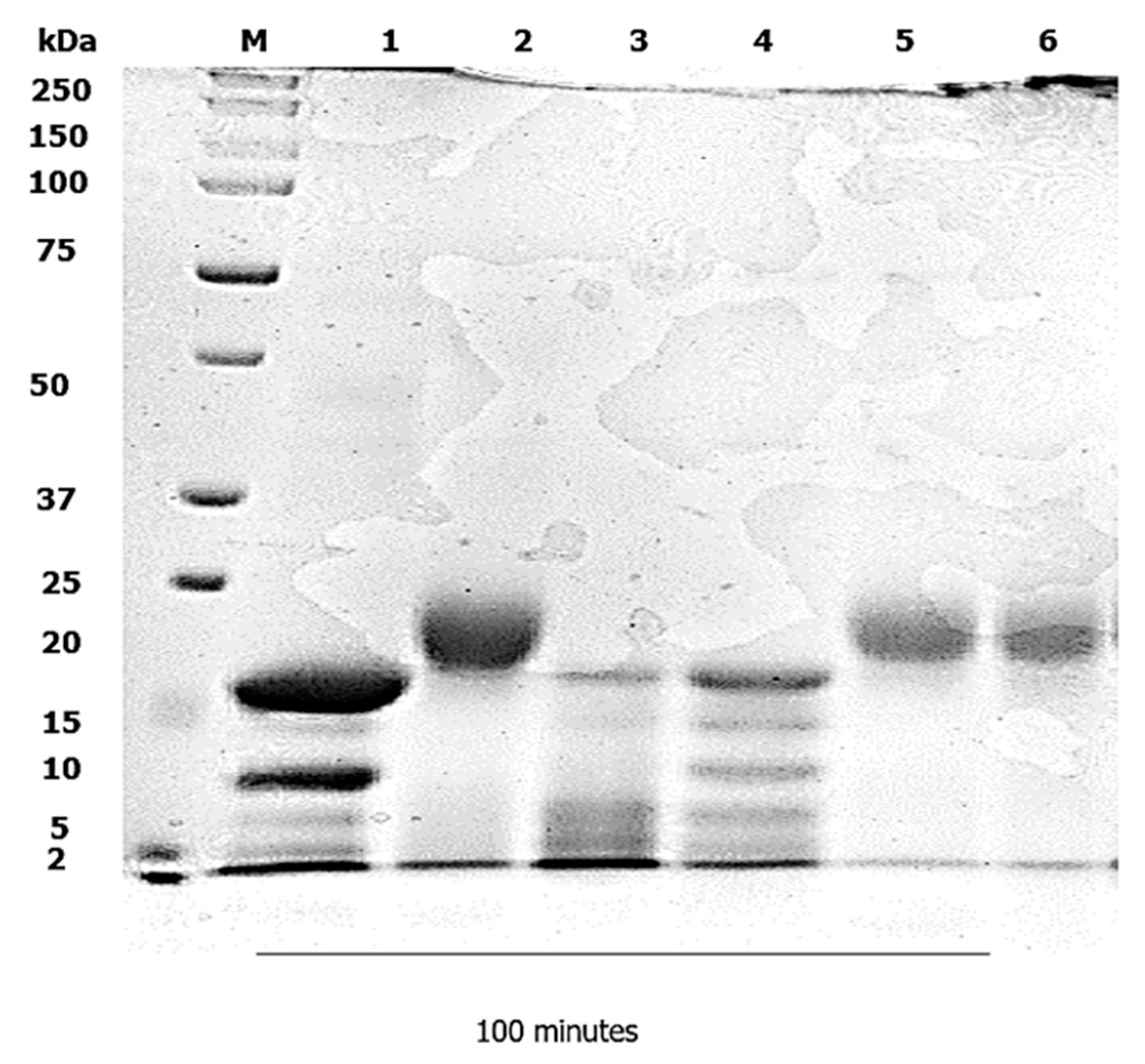
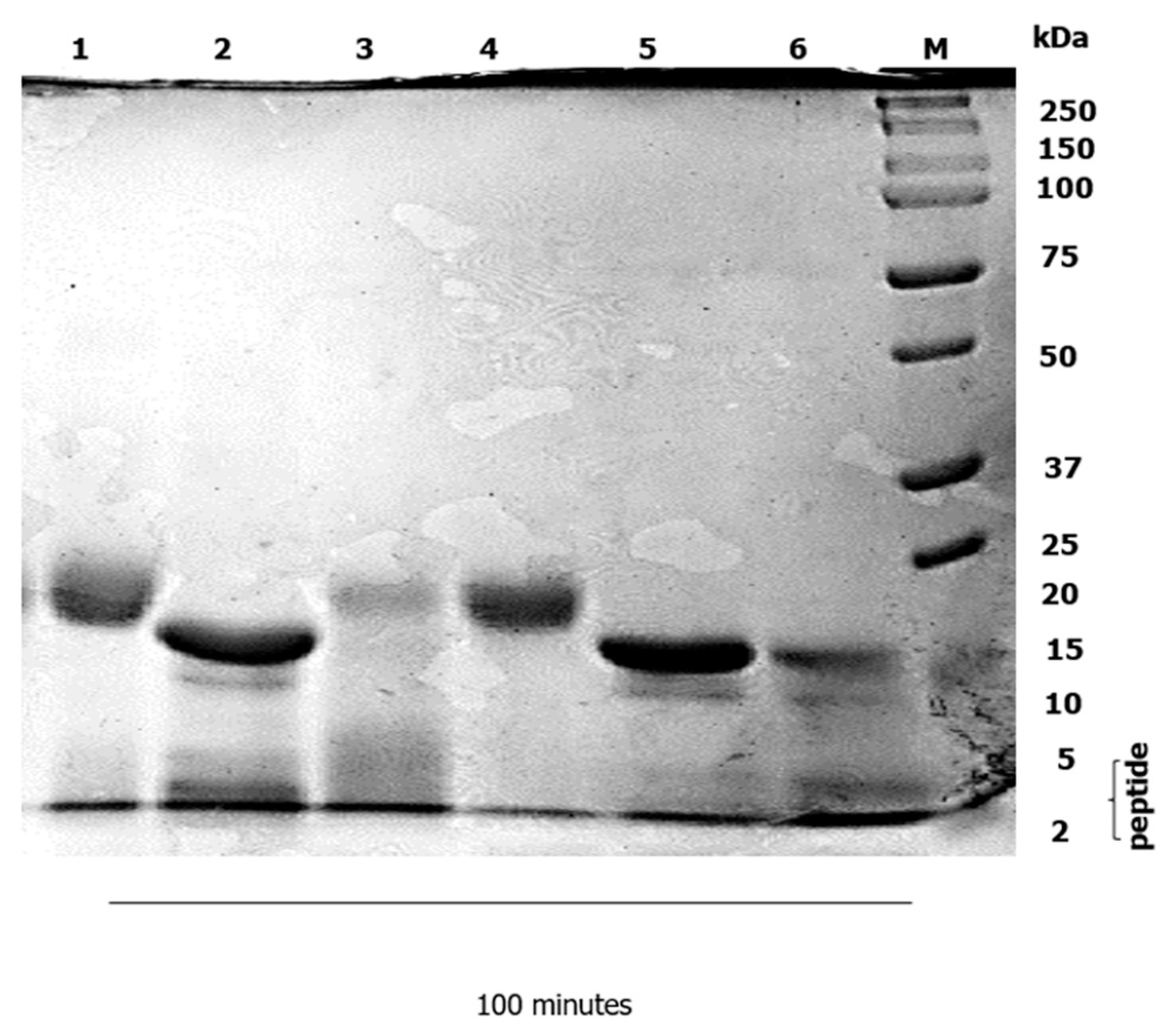
3.2. Duodenal Digestion
4. Discussion
4.1. Gastric Digestion
4.2. Duodenal Digestion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sarizan, S.; Julmohammad, N.; Matanjun, P.; Ab Wahab, N. Potential of Whey Protein Isolate-Lactose Conjugates in the In-Vitro Infant Digestion. Food Res. 2022, 6, 53–66. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.; Choi, Y.-S.; Jo, K.; Yong, H.I.; Jeong, H.G.; Jung, S. Improvement of Meat Protein Digestibility in Infants and the Elderly. Food Chem. 2021, 356, 129707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackie, A. Insights and Gaps on Protein Digestion. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2020, 31, 96–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Bongkosh, V. Effect of Initial Protein Concentration and PH on In Vitro Gastric Digestion of Heated Whey Proteins. Food Chem. 2014, 145, 473–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Li, L.; Lan, Q.; Li, M.; Wu, D.; Chen, H.; Liu, Y.; Lin, D.; Qin, W.; Zhang, Z.; et al. Protein Glycosylation: A Promising Way to Modify the Functional Properties and Extend the Application in Food System. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 59, 2506–2533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, S.I.; Jongen, W.M.; Van Boekel, M.A. A Review of Maillard Reaction in Food and Implications to Kinetic Modelling. Opera News 2008, 73, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gang, L.; Zhong, Q. Thermal Aggregation Properties of Whey Protein Glycated with Various Saccharides. Food Hydrocoll. 2013, 32, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, F.; Nouzille, C.A.; Baechler, R.; Vuataz, G.; Raemy, A. Lactose Crystallisation and Early Maillard Reaction in Skim Milk Powder and Whey Protein Concentrates. J. Food Prot. 2005, 72, 2162–2169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, P.F.; Uniacke-Lowe, T.; McSweeney, P.L.H.; O’Mahony, J.A. Chemistry and biochemistry of cheese. In Dairy Chemistry and Biochemistry; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 499–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, L.; Zhao, M.; Cui, C.; Zhao, H.; Yang, B. Effect of Degree of Hydrolysis on the Antioxidant Activity of Loach (Misgurnus anguillicaudatus) Protein Hydrolysates. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2009, 10, 235–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, Z.C.; Zhang, L.; Wang, H.; Huang, X.Q.; Zhang, L.; Yang, K. Structure and Antioxidant Activity of Milk Model Systems after Microwave Heating. Food Sci. Technol. Res. 2014, 20, 345–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Damodaran, S. Amino Acids, Peptides and Proteins. In Fennema’s Food Chemistry, 4th ed.; Damodaran, S., Parkin, K.L., Fennema, O.R., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2007; pp. 219–323. [Google Scholar]
- Swaisgood, H.E. Characteristics of Milk. In Fennema’s Food Chemistry, 4th ed.; Damodaran, S., Parkin, K.L., Fennema, O.R., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2007; pp. 885–918. [Google Scholar]
- Böttger, F.H.; Etzel, M.R.; Lucey, J.A. In vitro infant digestion of whey protein–dextran glycates. Food Dig. 2013, 4, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Julmohammad, N. Synthesis of Lactose Phosphate and Its Conjugation with Whey Proteins; Research Space: Auckland, New Zealand, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Jiménez-Castaño, L.; Villamiel, M.; López-Fandiño, R. Glycosylation of Individual Whey Proteins by Maillard Reaction Using Dextran of Different Molecular Mass. Food Hydrocoll. 2007, 21, 433–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shani-Levi, C.; Alvito, P.; Andrés, A.; Assunção, R.; Barberá, R.; Blanquet-Diot, S.; Bourlieu, C.; Brodkorb, A.; Cilla, A.; Deglaire, A.; et al. Extending in vitro digestion models to specific human populations: Perspectives, practical tools and bio-relevant information. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 60, 52–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, J.L. Pediatric Swallowing and Feeding Assessment and Management (Second Edition). Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2002, 65, 263–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, J.; Bornhorst, G.M.; Henrick, B.M.; German, J.B. Protein digestion of baby foods: Study approaches and implications for infant health. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2018, 62, 1700231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Jo, K.; Jeong, H.G.; Choi, Y.S.; Yong, H.I.; Jung, S. Understanding protein digestion in infants and the elderly: Current in vitro digestion models. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wal, J.M. Bovine Milk Allergenicity. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2004, 93, S2–S11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minekus, M.; Alminger, M.; Alvito, P.; Ballance, S.; Bohn, T.; Bourlieu, C.; Carri’ere, F.; Boutrou, R.; Corredig, M.; Dupont, D.; et al. A Standardised Static In Vitro Digestion Method Suitable for Food—An International Consensus. Food and Function. 2014, 6, 1113–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The University of Manchester. Literature review: ‘In vitro digestibility tests for allergenicity assessment’. EFSA Support. Publ. 2013, 10, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phosanam, A.; Chandrapala, J.; Huppertz, T.; Adhikari, B.; Zisu, B. In vitro digestion of infant formula model systems: Influence of casein to whey protein ratio. Int. Dairy J. 2021, 117, 105008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.T.P.; Bhandari, B.; Cichero, J.; Prakash, S. Gastrointestinal digestion of dairy and soy proteins in infant formulas: An in vitro study. Food Res. Int. 2015, 76, 348–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakai, K.; Yoshino, K.; Satter, M.A.; Ota, F.; Nil, Y.; Fututa, K.; Ueda, N.; Shimizu, Y.; Yamamoto, S. Effects of pH variation and NaCl on in vitro digestibility of cow’s milk proteins in commercially available infant formulas. J. Nutr. Sci. Vitaminol. 2000, 46, 325–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatterton, D.E.; Nguyen, D.N.; Bering, S.B.; Sangild, P.T. Anti-Inflammatory Mechanisms of Bioactive Milk Proteins in the Intestine of Newborns. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2013, 45, 1730–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, R.; Portmann, R.; Dubois, S.; Recio, I.; Egger, L. Protein digestion of different protein sources using the INFOGEST static digestion model. Food Res. Int. 2020, 130, 108996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corrigan, B.; Brodkorb, A. The effect of pre-treatment of protein ingredients for infant formula on their in vitro gastro-intestinal behaviour. Int. Dairy J. 2020, 110, 104810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeece, M.; Huppertz, T.; Kelly, A. Effect of High-Pressure Treatment on In-Vitro Digestibility of β-Lactoglobulin. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2008, 9, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, F.J.; Mackie, A.R.; Mills, C. Phospholipid interactions protect the milk allergen α-lactalbumin from proteolysis during in vitro digestion. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 9810–9816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouzerzour, K.; Morgan, F.; Cuinet, I.; Bonhomme, C.; Jardin, J.; Le Huërou-Luron, I.; Dupont, D. In vivo digestion of infant formula in piglets: Protein digestion kinetics and release of bioactive peptides. Br. J. Nutr. 2012, 108, 2105–2114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Oliveira, F.C.; Coimbra, J.S.D.R.; de Oliveira, E.B.; Zuñiga, A.D.G.; Rojas, E.E.G. Food Protein-Polysaccharide Conjugates Obtained via the Maillard Reaction: A Review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2016, 56, 1108–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.; Damodaran, S.; Lucey, J.A. Formation of whey protein isolate (WPI)—Dextran conjugates in aqueous solutions. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 7113–7118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Li, H.; A’yun, Q.; Doost, A.S.; De Meulenaer, B.; Van der Meeren, P. Conjugation of Milk Proteins and Reducing Sugars and Its Potential Application in the Improvement of the Heat Stability of (Recombined) Evaporated Milk. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 108, 287–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chevalier, F.; Chobert, J.-M.; Popineau, Y.; Georgette Nicolas, M.; Haertlé, T. Improvement of functional properties of β-lactoglobulin glycated through the Maillard reaction is related to the nature of the sugar. Int. Dairy J. 2001, 11, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Lieshout, G.A.; Lambers, T.T.; Bragt, M.C.; Hettinga, K.A. How processing may affect milk protein digestion and overall physiological outcomes: A systematic review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 60, 2422–2445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Ye, A.; Lin, Q.; Han, J.; Singh, H. Gastric digestion of milk protein ingredients: Study using an in vitro dynamic model. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 6842–6852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez-Rivera, L.; Ménard, O.; Recio, I.; Dupont, D. Peptide mapping during dynamic gastric digestion of heated and unheated skimmed milk powder. Food Res. Int. 2015, 77, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Loughlin, I.B.; Murray, B.A.; Kelly, P.M.; Fitzgerald, R.J.; Brodkorb, A. Enzymatic hydrolysis of heat-induced aggregates of whey protein isolate. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 4895–4904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crittenden, R.G.; Bennett, L.E. Cow’s Milk Allergy: A Complex Disorder. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2005, 24, 582S–591S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, R.; Groetch, M.; Venter, C. When Should Infants with Cow’s Milk Protein Allergy Use an Amino Acid Formula? A Practical Guide. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2018, 6, 383–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Høst, A. Frequency of Cow’s Milk Allergy in Childhood. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2002, 89 (Suppl. S1), 33–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moimaz, S.A.S.; Amaral, M.A.; Garbin, C.A.S.; Saliba, T.A.; Saliba, O. Caries in Children with Lactose Intolerance and Cow’s Milk Protein Allergy. Braz. Oral Res. 2018, 32, e91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Restani, P.; Ballabio, C.; Di Lorenzo, C.; Tripodi, S.; Fiocchi, A. Molecular Aspects of Milk Allergens and Their Role in Clinical Events. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2009, 395, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, F.J. Gastrointestinal digestion of food allergens: Effect on their allergenicity. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2007, 61, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, Y.; Govers, C.; Tomassen, M.; Hettinga, K.; Wichers, H.J. Heat treatment of β-lactoglobulin affects its digestion and translocation in the upper digestive tract. Food Chem. 2020, 330, 127184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hochwallner, H.; Schulmeister, U.; Swoboda, I.; Spitzauer, S.; Valenta, R. Cow’s Milk Allergy: From Allergens to New Forms of Diagnosis, Therapy and Prevention. Methods 2014, 66, 22–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macierzanka, A.; Böttger, F.; Lansonneur, L.; Groizard, R.; Jean, A.S.; Rigby, N.M.; Cross, K.; Wellner, N.; Mackie, A. The effect of gel structure on the kinetics of simulated gastrointestinal digestion of bovine β-lactoglobulin. Food Chem. 2012, 134, 2156–2163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenelon, M.A.; Hickey, R.M.; Buggy, A.; McCarthy, N.; Murphy, E.G. Whey Proteins in Infant Formula. Whey Proteins: From Milk to Medicine; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ménard, O.; Bourlieu, C.; De Oliveira, S.C.; Dellarosa, N.; Laghi, L.; Carrière, F.; Capozzi, F.; Dupont, D.; Deglaire, A. A first step towards a consensus static in vitro model for simulating full-term infant digestion. Food Chem. 2018, 240, 338–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bourlieu, C.; Ménard, O.; Bouzerzour, K.; Mandalari, G.; Macierzanka, A.; Mackie, A.R.; Dupont, D. Specificity of Infant Digestive Conditions: Some Clues for Developing Relevant In Vitro Models Specificity of Infant Digestive Conditions: Some Clues for Developing Relevant In Vitro Models. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2014, 54, 1427–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebenthal, E.; Lee, P.C.; Heitlinger, L.A. Impact of development of the gastrointestinal tract on infant feeding. J. Pediatr. 1983, 102, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damodaran, S.; Li, Y. A Two-Step Enzymatic Modification Method to Reduce Immuno-Reactivity of Milk Proteins. Food Chemistry. 2017, 237, 724–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dupont, D.; Mandalari, G.; Molle, D.; Jardin, J.; Léonil, J.; Faulks, R.M.; Wickham, M.S.; Clare Mills, E.N.; Mackie, A.R. Comparative Resistance of Food Proteins to Adult and Infant In Vitro Digestion Models. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2010, 54, 767–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halabi, A.; Croguennec, T.; Bouhallab, S.; Dupont, D.; Deglaire, A. Modification of Protein Structures by Altering the Whey Protein Profile and Heat Treatment Affects: In Vitro Static Digestion of Model Infant Milk Formulas. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 6933–6945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, M.S.; Léonil, J.; Henry, G.; Cauty, C.; Carvalho, A.F.; Bouhallab, S. Heating and glycation of β-lactoglobulin and β-casein: Aggregation and in vitro digestion. Food Res. Int. 2014, 55, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teodorowicz, M.; Van Neerven, J.; Savelkoul, H. Food Processing: The Influence of the Maillard Reaction on Immunogenicity and Allergenicity of Food Proteins. Nutrients 2017, 9, 835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moscovici, A.M.; Joubran, Y.; Briard-Bion, V.; Mackie, A.; Dupont, D.; Lesmes, U. The Impact of the Maillard Reaction on the In Vitro Proteolytic Breakdown of Bovine Lactoferrin in Adults and Infants. Food Funct. 2014, 5, 1898–1908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Bai, Y.; Everaert, N.; Li, X.; Tian, G.; Hou, C.; Zhang, D. Effects of Protein Phosphorylation on Glycolysis through the Regulation of Enzyme Activity in Ovine Muscle. Food Chem. 2019, 293, 537–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Govers, C.; Bastiaan-Net, S.; Van Der Hulst, N.; Hettinga, K.; Wichers, H.J. Hydrophobicity and aggregation, but not glycation, are key determinants for uptake of thermally processed β-lactoglobulin by THP-1 macrophages. Food Res. Int. 2019, 120, 102–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Gong, Y.; Gern, J.E.; Ikeda, S.; Lucey, J.A. Glycation of whey protein with dextrans of different molar mass: Effect on immunoglobulin E–binding capacity with blood sera obtained from patients with cow milk protein allergy. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 6823–6834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sabari, S.; Julmohammad, N.; Jahurul, H.A.M.; Matanjun, P.; Ab. Wahab, N. In Vitro Infant Digestion of Whey Proteins Isolate–Lactose. Foods 2023, 12, 667. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12030667
Sabari S, Julmohammad N, Jahurul HAM, Matanjun P, Ab. Wahab N. In Vitro Infant Digestion of Whey Proteins Isolate–Lactose. Foods. 2023; 12(3):667. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12030667
Chicago/Turabian StyleSabari, Sarizan, Norliza Julmohammad, Haque Akanda Md Jahurul, Patricia Matanjun, and Noorakmar Ab. Wahab. 2023. "In Vitro Infant Digestion of Whey Proteins Isolate–Lactose" Foods 12, no. 3: 667. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12030667
APA StyleSabari, S., Julmohammad, N., Jahurul, H. A. M., Matanjun, P., & Ab. Wahab, N. (2023). In Vitro Infant Digestion of Whey Proteins Isolate–Lactose. Foods, 12(3), 667. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12030667







