Development of a Novel Low-Calorie Lime Juice-Based Prebiotic Beverage Using a Combined Design Optimization Methodology
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of the Beverages
2.3. Determination of Physicochemical Properties
2.3.1. Extraction of Phytochemicals
2.3.2. Total Phenolic Content (TPC)
2.3.3. Total Flavonoid Content (TFC)
2.3.4. Antioxidant Capacity by the DPPH• Scavenging Assay
2.3.5. Ascorbic Acid Content (AA)
2.3.6. Total Soluble Solids (TSS), pH, and Titratable Acidity (TA)
2.4. Sensory Analysis of Beverage Samples
2.5. Experimental Design and Statistical Analysis
2.6. Overall Optimization of the Variables
2.7. Verification Experiments and Validation of the Model Equations
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Optimization of the Sensory Properties of the Beverages
3.1.1. Analysis of Regression Models
3.1.2. Analysis of the Response Surface
The Interaction Effects of Functional Ingredients on Taste
The Interaction Effects of Functional Ingredients on Flavor
The Interaction Effects of Functional Ingredients on Texture
The Interaction Effects of Functional Ingredients on Color
The Interaction Effects of Functional Ingredients on Overall Acceptance (OA)
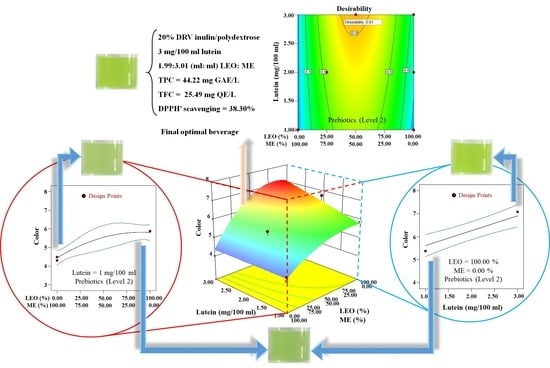
3.1.3. Overall Optimization of the Variables
3.1.4. Verification Experiments and Validation of the Model Equations
3.2. Determination of Physicochemical Properties
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Edwards, C.H.; Rossi, M.; Corpe, C.P.; Butterworth, P.J.; Ellis, P.R. The role of sugars and sweeteners in food, diet and health: Alternatives for the future. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 56, 158–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khawaja, A.H.; Qassim, S.; Hassan, N.A.; Arafa, E.-S.A. Added sugar: Nutritional knowledge and consumption pattern of a principal driver of obesity and diabetes among undergraduates in UAE. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Clin. Res. Rev. 2019, 13, 2579–2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.-T.; Li, B.; Xu, X.-J.; Ren, H.-B.; Yin, J.-Y.; Zhu, H.; Zhang, Y.-H. FTIR spectroscopy coupled with machine learning approaches as a rapid tool for identification and quantification of artificial sweeteners. Food Chem. 2020, 303, 125404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, W.; Wang, N.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, J.; Wu, S.; Zhu, Y. Simultaneous determination of sucralose and related compounds by high-performance liquid chromatography with evaporative light scattering detection. Food Chem. 2016, 204, 358–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.-W.; Chi, L.; Tu, P.; Xue, J.; Ru, H.; Lu, K. Quantitative proteomics reveals systematic dysregulations of liver protein metabolism in sucralose-treated mice. J. Proteom. 2019, 196, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agulló, V.; García-Viguera, C.; Domínguez-Perles, R. The use of alternative sweeteners (sucralose and stevia) in healthy soft-drink beverages, enhances the bioavailability of polyphenols relative to the classical caloric sucrose. Food Chem. 2022, 370, 131051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corbo, M.R.; Bevilacqua, A.; Petruzzi, L.; Casanova, F.P.; Sinigaglia, M. Functional beverages: The emerging side of functional foods: Commercial trends, research, and health implications. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2014, 13, 1192–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawaii, S.; Tomono, Y.; Katase, E.; Ogawa, K.; Yano, M. Quantitation of flavonoid constituents in citrus fruits. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1999, 47, 3565–3571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Li, S.; Ho, C.-T. Dietary bioactives and essential oils of lemon and lime fruits. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2022, 11, 753–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, J.B.; Batley, R.; Manson, D.; White, S.; Naiker, M. Volatile compounds, phenolic acid profiles and phytochemical content of five Australian finger lime (Citrus australasica) cultivars. LWT 2022, 154, 112640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohd-Hanif, H.; Shamsudin, R.; Adzahan, N.M. UVC dosage effects on the physico-chemical properties of lime (Citrus aurantifolia) juice. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2016, 25, 63–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dahl, W.J.; Stewart, M.L. Position of the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics: Health implications of dietary fiber. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2015, 115, 1861–1870. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kasapoğlu, K.N.; Daşkaya-Dikmen, C.; Yavuz-Düzgün, M.; Karaça, A.C.; Özçelik, B. Enrichment of Beverages With Health Beneficial Ingredients. In Value-Added Ingredients and Enrichments of Beverages; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019; pp. 63–99. [Google Scholar]
- Shahidi, F.; Ambigaipalan, P. Beverages fortified with omega-3 fatty acids, dietary fiber, minerals, and vitamins. In Handbook of Functional Beverages and Human Health; Routledge: Abingdon, UK, 2016; pp. 801–813. [Google Scholar]
- Cam, M.; Basyigit, B.; Alasalvar, H.; Yilmaztekin, M.; Ahhmed, A.; Sagdic, O.; Konca, Y.; Telci, I. Bioactive properties of powdered peppermint and spearmint extracts: Inhibition of key enzymes linked to hypertension and type 2 diabetes. Food Biosci. 2020, 35, 100577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asnaashari, S.; Delazar, A.; Habibi, B.; Vasfi, R.; Nahar, L.; Hamedeyazdan, S.; Sarker, S.D. Essential Oil from Citrus aurantifolia prevents ketotifen-induced weight-gain in mice. Phytother. Res. 2010, 24, 1893–1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dosoky, N.S.; Setzer, W.N. Biological activities and safety of Citrus spp. essential oils. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.; Yuan, Y.; Yang, S.; Wang, Y.; Lv, Z. Fabrication and characterization of zein/tea saponin composite nanoparticles as delivery vehicles of lutein. LWT 2020, 125, 109270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Zhu, Q.; Diao, C.; Wang, J.; Wu, Z.; Wang, H. Enhanced physicochemical stability of lutein-enriched emulsions by polyphenol-protein-polysaccharide conjugates and fat-soluble antioxidant. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 101, 105447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.J.; Ferruzzi, M.; Jones, O.G. Fate of lutein-containing zein nanoparticles following simulated gastric and intestinal digestion. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 87, 229–236. [Google Scholar]
- Icyer, N.C.; Toker, O.S.; Karasu, S.; Tornuk, F.; Bozkurt, F.; Arici, M.; Sagdic, O. Combined design as a useful statistical approach to extract maximum amount of phenolic compounds from virgin olive oil waste. LWT 2016, 70, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salinas, D.; Garvin, A.; Ibarz, R.; Ibarz, A. Effect of apple fibre addition and temperature on the rheological properties of apple juice and compensation study. LWT 2019, 116, 108456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Nguyen, H.; Wismer, W.; Temelli, F. Development of an orange-flavoured functional beverage formulated with beta-glucan and coenzyme Q10-impregnated beta-glucan. J. Funct. Foods 2018, 47, 397–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arruda, H.S.; Silva, E.K.; Pereira, G.A.; Meireles, M.A.A.; Pastore, G.M. Inulin thermal stability in prebiotic carbohydrate-enriched araticum whey beverage. LWT 2020, 128, 109418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassani, L.; Tomadoni, B.; Moreira, M.R.; Agüero, M.V. Improving quality parameters of functional strawberry juices: Optimization of prebiotic fiber enrichment and geraniol treatment. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2018, 11, 2110–2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arya, S.; Shakya, N.K. High fiber, low glycaemic index (GI) prebiotic multigrain functional beverage from barnyard, foxtail and kodo millet. LWT 2021, 135, 109991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.-Y.; Chuang, C.-H.; Chen, H.-C.; Yang, K.-M. Lime (Citrus aurantifolia (Christm.) Swingle) essential oils: Volatile compounds, antioxidant capacity, and hypolipidemic effect. Foods 2019, 8, 398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wee, M.; Tan, V.; Forde, C. A comparison of psychophysical dose-response behaviour across 16 sweeteners. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FDA; CFR. A food labeling Guide, Guidance for Industry; U.S. Food and Drug Administration: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Cassani, L.; Tomadoni, B.; Viacava, G.; Ponce, A.; Moreira, M.d.R. Enhancing quality attributes of fiber-enriched strawberry juice by application of vanillin or geraniol. LWT—Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 72, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassani, L.; Gerbino, E.; del Rosario Moreira, M.; Gómez-Zavaglia, A. Influence of non-thermal processing and storage conditions on the release of health-related compounds after in vitro gastrointestinal digestion of fiber-enriched strawberry juices. J. Funct. Foods 2018, 40, 128–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghajanzadeh, S.; Kashaninejad, M.; Ziaiifar, A.M. Effect of infrared heating on degradation kinetics of key lime juice physicochemical properties. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2016, 38, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakhri, L.A.; Ghanbarzadeh, B.; Dehghannya, J.; Dadashi, S. Central composite design based statistical modeling for optimization of barrier and thermal properties of polystyrene based nanocomposite sheet for packaging application. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2021, 30, 100725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassani, L.; Tomadoni, B.; Moreira, M.d.R.; Ponce, A.; Agüero, M.V. Optimization of inulin: Oligofructose proportion and non-thermal processing to enhance microbiological and sensory properties of fiber-enriched strawberry juice. LWT 2017, 80, 446–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagarajappa, V.; Battula, S.N. Effect of fortification of milk with omega-3 fatty acids, phytosterols and soluble fibre on the sensory, physicochemical and microbiological properties of milk. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2017, 97, 4160–4168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domingos, L.; Xavier, A.; Mercadante, A.; Petenate, A.; Jorge, R.; Viotto, W. Oxidative stability of yogurt with added lutein dye. J. Dairy Sci. 2014, 97, 616–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imran, A.; Quispe, C.; Zeeshan, A.; Imran, M.; Nadeem, M.; Gilani, S.A.; Gondal, T.A.; Tufail, T.; Aslam, F.; Rodrigues, C.F. Development and antioxidant characterization of Ginger-Mint drink prepared through different extraction techniques. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2021, 15, 2576–2590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebouças, M.C.; Rodrigues, M.d.C.P.; Afonso, M.R.A. Optimization of the acceptance of prebiotic beverage made from cashew nut kernels and passion fruit juice. J. Food Sci. 2014, 79, S1393–S1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalyani Nair, K.; Kharb, S.; Thompkinson, D. Inulin dietary fiber with functional and health attributes—A review. Food Rev. Int. 2010, 26, 189–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beristain, C.; Cruz-Sosa, F.; Lobato-Calleros, C.; Pedroza-Islas, R.; Rodríguez-Huezo, M.; Verde-Calvo, J. Applications of soluble dietary fibers in beverages. Rev. Mex. Ing. Quim. 2006, 5, 81–95. [Google Scholar]
- Furlán, L.T.R.; Baracco, Y.; Lecot, J.; Zaritzky, N.; Campderrós, M.E. Influence of hydrogenated oil as cocoa butter replacers in the development of sugar-free compound chocolates: Use of inulin as stabilizing agent. Food Chem. 2017, 217, 637–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Mas, M.C.; Rambla, J.L.; López-Gresa, M.P.; Blázquez, M.A.; Granell, A. Volatile compounds in citrus essential oils: A comprehensive review. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahendran, G.; Rahman, L.U. Ethnomedicinal, phytochemical and pharmacological updates on Peppermint (Mentha× piperita L.)—A review. Phytother. Res. 2020, 34, 2088–2139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakhri, L.A.; Ghanbarzadeh, B.; Dehghannya, J.; Abbasi, F.; Ranjbar, H. Optimization of mechanical and color properties of polystyrene/nanoclay/nano ZnO based nanocomposite packaging sheet using response surface methodology. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2018, 17, 11–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, R.; Kamaruddin, N.S.B.C.; Min-Tze, L.; Karim, A. Sonication improves kasturi lime (Citrus microcarpa) juice quality. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2011, 18, 1295–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guimarães, R.; Barros, L.; Barreira, J.C.M.; Sousa, M.J.; Carvalho, A.M.; Ferreira, I.C.F.R. Targeting excessive free radicals with peels and juices of citrus fruits:Grapefruit, lemon, lime and orange. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2010, 48, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shang, H.-M.; Zhou, H.-Z.; Yang, J.-Y.; Li, R.; Song, H.; Wu, H.-X. In vitro and in vivo antioxidant activities of inulin. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0192273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ostadi, A.; Javanmard, A.; Amani Machiani, M.; Kakaei, K. Optimizing Antioxidant Activity and Phytochemical Properties of Peppermint (Mentha piperita L.) by Integrative Application of Biofertilizer and Stress-Modulating Nanoparticles under Drought Stress Conditions. Plants 2023, 12, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, J.; Jo, H.; Cho, A.R.; Kim, S.-J.; Han, J. Antioxidant and antimicrobial activities of various leafy herbal teas. Food Control 2013, 31, 403–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapp, K.; Hakala, E.; Orav, A.; Pohjala, L.; Vuorela, P.; Püssa, T.; Vuorela, H.; Raal, A. Commercial peppermint (Mentha× piperita L.) teas: Antichlamydial effect and polyphenolic composition. Food Res. Int. 2013, 53, 758–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riachi, L.G.; De Maria, C.A. Peppermint antioxidants revisited. Food Chem. 2015, 176, 72–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Middleton, E.; Kandaswami, C.; Theoharides, T.C. The effects of plant flavonoids on mammalian cells: Implications for inflammation, heart disease, and cancer. Pharmacol. Rev. 2000, 52, 673–751. [Google Scholar]
- Jangid, A.K.; Solanki, R.; Patel, S.; Pooja, D.; Kulhari, H. Genistein encapsulated inulin-stearic acid bioconjugate nanoparticles: Formulation development, characterization and anticancer activity. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 206, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corrêa-Ferreira, M.L.; Verdan, M.H.; dos Reis Lívero, F.A.; Galuppo, L.F.; Telles, J.E.Q.; Stefanello, M.É.A.; Acco, A.; de Oliveira Petkowicz, C.L. Inulin-type fructan and infusion of Artemisia vulgaris protect the liver against carbon tetrachloride-induced liver injury. Phytomedicine 2017, 24, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibarra, A.; Olli, K.; Pasman, W.; Hendriks, H.; Alhoniemi, E.; Raza, G.S.; Herzig, K.-H.; Tiihonen, K. Effects of polydextrose with breakfast or with a midmorning preload on food intake and other appetite-related parameters in healthy normal-weight and overweight females: An acute, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, and crossover study. Appetite 2017, 110, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Ren, P.; Mang, L.; Shen, N.; Chen, J.; Zhang, Y. In vitro fermentation of novel microwave-synthesized non-digestible oligosaccharides and their impact on the composition and metabolites of human gut microbiota. J. Funct. Foods 2019, 55, 156–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AOAC. AOAC Official Method 942.15: Acidity (Titratable) of Fruit Products; Official Methods of Analysis of AOAC International: Rockville, MD, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Tyl, C.; Sadler, G.D. pH and Titratable acidity. In Food Analysis; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; pp. 389–406. [Google Scholar]





| Design Point. | Components | Factors | Responses g | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mixture Components | Numeric Factor | Categoric Factor | Taste | Flavor | Texture | Color | Overall Acceptance | |||||||
| X1: LEO Solution (0.1 v/v) % a (mL) c | X2: ME % b (mL) c | X3: Lu (mg/100 mL) | X4: I/P Mixture d | Exp. V. e | Pre. V. f | Exp. V. | Pre. V. | Exp. V. | Pre. V. | Exp. V. | Pre. V. | Exp. V. | Pre. V. | |
| 1 | 50.00 (2.50) | 50.00 (2.50) | 3.00 | Level 1 | 7.3 ± 1.5 | 7.2 | 7.9 ± 1.4 | 7.9 | 7.2 ± 1.4 | 7.2 | 7.1 ± 1.7 | 7.0 | 8.3 ± 1.2 | 7.9 |
| 2 | 50.00 (2.50) | 50.00 (2.50) | 3.00 | Level 2 | 7.6 ± 1.2 | 7.8 | 7.7 ± 1.6 | 7.9 | 7.2 ± 0.7 | 6.7 | 6.6 ± 1.4 | 6.8 | 8.3 ± 1.2 | 8.2 |
| 3 | 0.00 (0.00) | 100.00 (5.00) | 3.00 | Level 1 | 5.3 ± 1.6 | 5.3 | 6.4 ± 0.9 | 6.3 | 6.5 ± 2.1 | 6.4 | 4.3 ± 1.2 | 4.3 | 6.3 ± 1.7 | 6.3 |
| 4 | 100.00 (5.00) | 0.00 (0.00) | 3.00 | Level 1 | 6.0 ± 1.5 | 6.0 | 6.9 ± 1.0 | 6.8 | 8.1 ± 1.7 | 8.0 | 7.1 ± 1.7 | 6.9 | 6.6 ± 1.1 | 6.6 |
| 5 | 75.00 (3.75) | 25.00 (1.25) | 2.00 | Level 1 | 6.5 ± 0.9 | 6.8 | 7.6 ± 1.2 | 7.7 | 7.7 ± 1.2 | 7.5 | 6.8 ± 1.4 | 6.6 | 7.0 ± 0.9 | 7.4 |
| 6 | 100.00 (5.00) | 0.00 (0.00) | 1.00 | Level 2 | 6.0 ± 0.7 | 6.0 | 6.8 ± 1.3 | 6.8 | 6.0 ± 1.6 | 5.9 | 5.9 ± 1.1 | 5.8 | 5.9 ± 0.9 | 6.0 |
| 7 | 0.00 (0.00) | 100.00 (5.00) | 1.00 | Level 1 | 5.3 ± 0.8 | 5.2 | 6.5 ± 1.7 | 6.3 | 6.2 ± 1.3 | 6.2 | 4.5 ± 1.6 | 4.4 | 5.3 ± 1.2 | 5.3 |
| 8 | 50.00 (2.50) | 50.00 (2.50) | 3.00 | Level 1 | 7.2 ± 1.1 | 7.2 | 7.8 ± 1.8 | 7.9 | 7.0 ± 1.0 | 7.2 | 6.9 ± 2.0 | 7.0 | 7.7 ± 1.3 | 7.9 |
| 9 | 50.00 (2.50) | 50.00 (2.50) | 1.00 | Level 1 | 7.0 ± 1.3 | 6.9 | 7.9 ± 1.5 | 7.9 | 7.1 ± 1.3 | 7.1 | 5.8 ± 0.8 | 5.7 | 7.6 ± 1.2 | 7.6 |
| 10 | 50.00 (2.50) | 50.00 (2.50) | 1.00 | Level 1 | 6.9 ± 1.9 | 6.9 | 7.8 ± 1.4 | 7.9 | 6.9 ± 2.3 | 7.1 | 5.6 ± 1.2 | 5.7 | 7.7 ± 1.7 | 7.6 |
| 11 | 100.00 (5.00) | 0.00 (0.00) | 3.00 | Level 2 | 6.3 ± 1.1 | 6.3 | 6.6 ± 2.1 | 6.8 | 5.9 ± 1.8 | 6.0 | 6.8 ± 1.4 | 7.1 | 6.5 ± 1.6 | 6.5 |
| 12 | 0.00 (0.00) | 100.00 (5.00) | 1.00 | Level 2 | 5.6 ± 1.5 | 5.5 | 6.1 ±1.8 | 6.3 | 7.5 ± 1.9 | 7.3 | 4.5 ± 1.7 | 4.4 | 6.3 ± 1.8 | 6.1 |
| 13 | 100.00 (5.00) | 0.00 (0.00) | 1.00 | Level 1 | 5.8 ± 1.2 | 5.7 | 7.0 ± 1.5 | 6.8 | 8.0 ± 1.7 | 7.9 | 5.4 ± 1.2 | 5.6 | 6.2 ± 1.0 | 6.1 |
| 14 | 25.00 (1.25) | 75.00 (3.75) | 2.00 | Level 2 | 7.2 ± 1.6 | 7.0 | 7.9 ± 1.4 | 7.4 | 6.4 ± 0.7 | 7.0 | 5.7 ± 1.5 | 5.5 | 7.7 ± 1.3 | 7.7 |
| 15 | 100.00 (5.00) | 0.00 (0.00) | 2.00 | Level 2 | 6.3 ± 1.2 | 6.2 | 6.8 ± 1.9 | 6.8 | 5.9 ± 1.7 | 5.9 | 6.7 ± 1.3 | 6.4 | 6.3 ± 0.9 | 6.2 |
| 16 | 0.00 (0.00) | 100.00 (5.00) | 2.00 | Level 1 | 5.3 ± 1.6 | 5.3 | 6.5 ± 0.8 | 6.3 | 6.3 ± 0.7 | 6.3 | 4.4 ± 1.3 | 4.4 | 5.8 ± 1.2 | 5.8 |
| 17 | 0.00 (0.00) | 100.00 (5.00) | 1.00 | Level 2 | 5.4 ± 1.3 | 5.5 | 5.9 ± 0.5 | 6.3 | 7.3 ± 0.7 | 7.3 | 4.3 ± 1.3 | 4.4 | 6.0 ± 1.1 | 6.1 |
| Source | Suggested Models | Sequential p-Value | Partial Sum of Squares | Lack of Fit (LOF) | Model Summary Statistics (MSS) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mix Order | Process Order | Mix | Process | Sum of Squares | Mean Square | R2 | Adj-R2 | Pred-R2 | ||
| Taste | Quadratic | Linear | <0.001 ** | 0.011 * | 10.04 | 1.26 | 0.27 | 0.98 | 0.96 | 0.92 |
| Flavor | Quadratic | Mean | <0.001 ** | - | 7.03 | 3.52 | 0.11 | 0.91 | 0.90 | 0.87 |
| Texture | Linear | Linear | <0.001 ** | <0.001 ** | 7.07 | 1.41 | 0.13 | 0.90 | 0.86 | 0.80 |
| Color | Quadratic | Linear | 0.001 ** | 0.003 ** | 17.71 | 2.21 | 0.12 | 0.97 | 0.95 | 0.84 |
| Overall acceptance | Quadratic | Linear | <0.001 ** | 0.033 * | 12.90 | 1.61 | 0.64 | 0.97 | 0.94 | 0.90 |
| Source | Taste | Flavor | Texture | Color | Overall Acceptance | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reg. Co. a | F-Value | p-Value | Reg. Co. | F-Value | p-Value | Reg. Co. | F-Value | p-Value | Reg. Co. | F-Value | p-Value | Reg. Co. | F-Value | p-Value | |
| X1 | 5.99 | - | - | 6.80 | - | - | 6.95 | - | - | 6.35 | - | - | 6.27 | - | - |
| X2 | 5.42 | - | - | 6.29 | - | - | 6.83 | - | - | 4.39 | - | - | 6.21 | - | - |
| X1 × 2 | 6.46 | 235.68 | <0.001 ** | 5.28 | 125.28 | <0.001 ** | - | - | - | 3.59 | 31.63 | 0.001 ** | 6.58 | 120.76 | <0.001 ** |
| X1 × 3 | 0.14 | 2.92 | 0.126 | - | - | - | 0.05 | 0.19 | 0.672 | 0.65 | 27.87 | 0.001 ** | 0.25 | 4.96 | 0.057 |
| X1 × 4 | 0.17 | 5.44 | 0.048 * | - | - | - | −1.01 | 93.16 | <0.001 ** | 0.09 | 0.66 | 0.440 | −0.04 | 0.15 | 0.712 |
| X2 × 3 | 0.05 | 0.21 | 0.660 | - | - | - | 0.10 | 0.53 | 0.482 | −0.04 | 0.05 | 0.835 | 0.49 | 9.57 | 0.015 * |
| X2 × 4 | 0.15 | 2.66 | 0.142 | - | - | - | 0.53 | 20.78 | 0.001 ** | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.941 | 0.40 | 9.56 | 0.015 * |
| X1 × 2 × 3 | 0.18 | 0.20 | 0.670 | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1.30 | 4.47 | 0.067 | −0.79 | 1.87 | 0.209 |
| X1 × 2 × 4 | 0.57 | 1.82 | 0.214 | - | - | - | - | - | - | −0.61 | 0.91 | 0.369 | −0.10 | 0.50 | 0.500 |
| Model | - | 48.42 | <0.001 ** | - | 69.42 | <0.001 ** | - | 20.13 | <0.001 ** | - | 37.08 | 0.001 ** | - | 30.77 | <0.001 ** |
| Linear mixture | - | 36.22 | 0.001 ** | - | 13.55 | 0.003 ** | - | 0.46 | 0.513 | - | 172.68 | <0.001 ** | - | 3.98 | 0.081 |
| LOF b | - | 2.21 | 0.273 | - | 4.88 | 0.109 | - | 4.26 | 0.130 | - | 4.63 | 0.119 | - | 0.75 | 0.636 |
| R2 | 0.98 | - | - | 0.91 | - | - | 0.90 | - | - | 0.97 | - | - | 0.97 | - | - |
| R2adj c | 0.96 | - | - | 0.90 | - | - | 0.86 | - | - | 0.95 | - | - | 0.94 | - | - |
| R2pred d | 0.92 | - | - | 0.87 | - | - | 0.80 | - | - | 0.84 | - | - | 0.90 | - | - |
| Adeq. Precision e | 21.66 | - | - | 16.67 | - | - | 13.52 | - | - | 15.44 | - | - | 17.36 | - | - |
| C.V. f % | 2.57 | - | - | 3.19 | - | - | 3.85 | - | - | 4.23 | - | - | 3.38 | - | - |
| Std. Dev. g | 0.16 | - | - | 0.23 | - | - | 0.26 | - | - | 0.24 | - | - | 0.23 | - | - |
| PRESS | 0.85 | - | - | 1.02 | - | - | 1.53 | - | - | 2.91 | - | - | 1.29 | - | - |
| Optimized Sample | Optimum Formula | Desirability | Responses at Optimum Point | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mixture Components | Numeric Factor | Categoric Factor | |||||||||
| LEO Solution (0.1 v/v) (%) | ME (%) | Lutein (mg/100 mL) | I/P Mixture | Taste | Odor | Texture | Color | Overall Acceptance | |||
| TV a | 7.17 | 7.87 | 7.36 | 7.20 | 7.88 | ||||||
| Opt 1 | 59.71 | 40.29 | 3.00 | Level 1 | 0.87 | AV b | 6.7 ± 1.4 | 6.9 ± 1.3 | 6.9 ± 1.1 | 7.4 ± 1.5 | 7.1 ± 1.6 |
| PE c (%) | −7.3 | −14.6 | −6.7 | 3.2 | −10.4 | ||||||
| TV | 7.18 | 7.87 | 7.34 | 7.17 | 7.89 | ||||||
| Opt 2 | 58.01 | 41.99 | 3.00 | Level 1 | 0.87 | AV | 6.5 ± 1.7 | 7.0 ± 1.4 | 7.6 ± 1.2 | 6.9 ± 1.1 | 6.9 ± 1.7 |
| PE (%) | −10.4 | −12.8 | 2.8 | −4.4 | −13.8 | ||||||
| TV | 7.75 | 7.86 | 6.75 | 6.75 | 8.22 | ||||||
| Opt 3 | 48.24 | 51.76 | 3.00 | Level 2 | 0.82 | AV | 6.5 ± 1.2 | 6.8 ± 1.6 | 7.1 ± 1.1 | 6.0 ± 1.5 | 6.6 ± 1.2 |
| PE (%) | −18.6 | −15.3 | 4.3 | −12.4 | −24.0 | ||||||
| TV | 7.76 | 7.87 | 6.72 | 6.79 | 8.21 | ||||||
| Opt 4 | 50.00 | 50.00 | 3.00 | Level 2 | 0.82 | AV | 6.9 ± 1.0 | 7.4 ± 1.4 | 6.3 ± 1.2 | 5.8 ± 1.6 | 7.2 ± 1.2 |
| PE (%) | −13.3 | −6.8 | −6.1 | −17.8 | −14.1 | ||||||
| TV | 7.72 | 7.84 | 6.78 | 6.68 | 8.23 | ||||||
| Opt 5 | 45.89 | 54.11 | 3.00 | Level 2 | 0.82 | AV | 7.9 ± 0.7 | 7.5 ± 1.2 | 7.5 ± 1.3 | 7.0 ± 1.2 | 8.2 ± 0.6 |
| PE (%) | 2.0 | −4.7 | 9.6 | 4.9 | −0.2 | ||||||
| Opt 6 | 39.78 | 60.22 | 3.00 | Level 2 | 0.81 | TV | 7.62 | 7.76 | 6.87 | 6.47 | 8.22 |
| AV | 6.5 ± 1.4 | 7.1 ± 1.3 | 7.5 ± 1.1 | 6.7 ± 1.5 | 6.9 ± 1.5 | ||||||
| PE (%) | −16.9 | −10.1 | 8.4 | 3.2 | −19.1 | ||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fakhri, L.A.; Ghanbarzadeh, B.; Falcone, P.M. Development of a Novel Low-Calorie Lime Juice-Based Prebiotic Beverage Using a Combined Design Optimization Methodology. Foods 2023, 12, 680. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12030680
Fakhri LA, Ghanbarzadeh B, Falcone PM. Development of a Novel Low-Calorie Lime Juice-Based Prebiotic Beverage Using a Combined Design Optimization Methodology. Foods. 2023; 12(3):680. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12030680
Chicago/Turabian StyleFakhri, Leila Abolghasemi, Babak Ghanbarzadeh, and Pasquale M. Falcone. 2023. "Development of a Novel Low-Calorie Lime Juice-Based Prebiotic Beverage Using a Combined Design Optimization Methodology" Foods 12, no. 3: 680. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12030680
APA StyleFakhri, L. A., Ghanbarzadeh, B., & Falcone, P. M. (2023). Development of a Novel Low-Calorie Lime Juice-Based Prebiotic Beverage Using a Combined Design Optimization Methodology. Foods, 12(3), 680. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12030680