Characterization of Lactic Acid Bacteria Isolated from Spontaneously Fermented Sausages: Bioprotective, Technological and Functional Properties
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Traditional Spontaneously Fermented Sausages Characterization
2.2. Isolation of LAB Strains and DNA Extraction
2.3. Fingerprinting-Based Clustering and 16S rRNA Identification of Biotypes
2.4. Determination of Antibiotic Susceptibility
2.5. Biogenic Amine Production
2.6. Antimicrobial Activity Assay
2.7. Kinetic Modelling of Microbial Growth and Acidification
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Spontaneous Fermented Sausages Characterization
3.2. Clustering of LAB Isolates and 16S rRNA Sequencing
3.3. Determination of Antibiotic Susceptibility (MIC)
3.4. Determination of Biogenic Amines
3.5. Antimicrobial Activity Assay
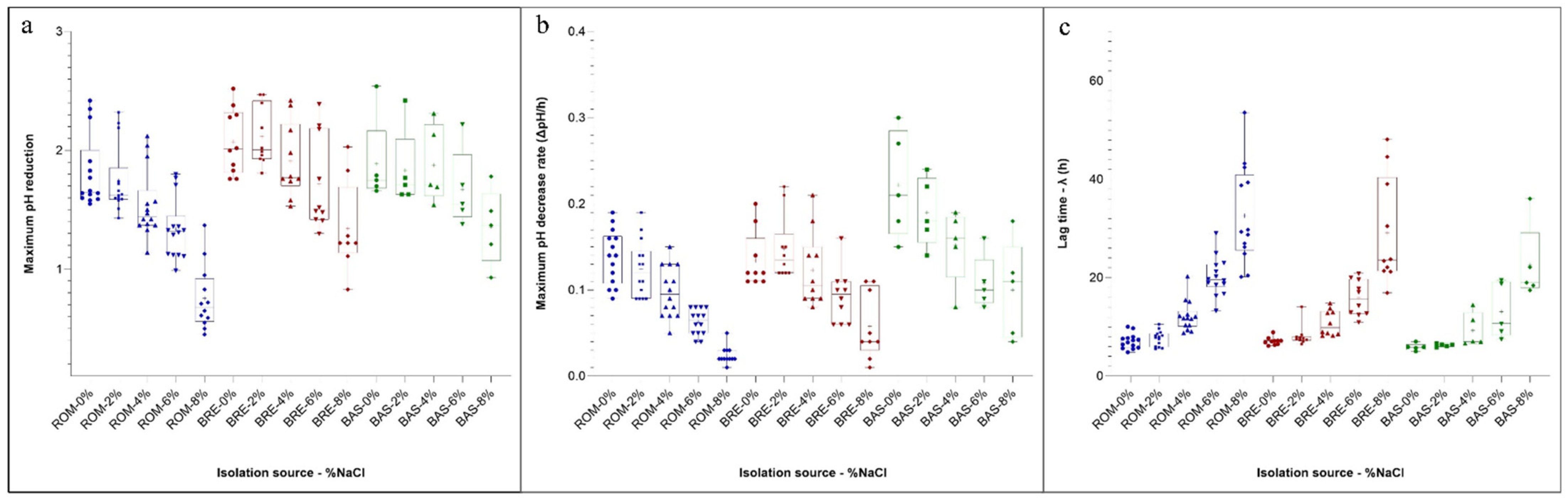
3.6. Growth and Acidification Kinetics
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Roccato, A.; Uyttendaele, M.; Barrucci, F.; Cibin, V.; Favretti, M.; Cereser, A.; Dal Cin, M.; Pezzuto, A.; Piovesana, A.; Longo, A.; et al. Artisanal Italian salami and soppresse: Identification of control strategies to manage microbiological hazards. Food Microbiol. 2017, 61, 5–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabanelli, G.; Coloretti, F.; Chiavari, C.; Grazia, L.; Lanciotti, R.; Gardini, F. Effects of starter cultures and fermentation climate on the properties of two types of typical Italian dry fermented sausages produced under industrial conditions. Food Control 2012, 26, 416–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franciosa, I.; Alessandria, V.; Dolci, P.; Rantsiou, K.; Cocolin, L. Sausage fermentation and starter cultures in the era of molecular biology methods. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2018, 279, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gänzle, M.G. Lactic metabolism revisited: Metabolism of lactic acid bacteria in food fermentations and food spoilage. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2015, 2, 106–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lücke, F.K. Utilization of microbes to process and preserve meat. Meat Sci. 2000, 56, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- IARC. IARC Monographs on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans. 2010. Available online: http://monographs.iarc.fr/ENG/Monographs/vol96/index.php (accessed on 1 February 2020).
- Stiles, M.E. Biopreservation by lactic acid bacteria. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 1996, 70, 331–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zagorec, M.; Champomier-Vergès, M.C. Lactobacillus sakei: A starter for sausage fermentation, a protective culture for meat products. Microorganisms 2017, 5, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gálvez, A.; Abriouel, H.; Benomar, N.; Lucas, R. Microbial antagonists to food-borne pathogens and biocontrol. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2010, 21, 142–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chikindas, M.L.; Weeks, R.; Drider, D.; Chistyakov, V.A.; Dicks, L.M.T. Functions and emerging applications of bacteriocins. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2018, 49, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laulund, S.; Wind, A.; Derkx, P.M.F.; Zuliani, V. Regulatory and safety requirements for food cultures. Microorganisms 2017, 5, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herman, L.; Chemaly, M.; Cocconcelli, P.S.; Fernandez, P.; Klein, G.; Peixe, L.; Prieto, M.; Querol, A.; Suarez, J.E.; Sundh, I.; et al. The qualified presumption of safety assessment and its role in EFSA risk evaluations: 15 years past. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2019, 366, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaimee, G.; Halami, P.M. High level aminoglycoside resistance in Enterococcus, Pediococcus and Lactobacillus species from farm animals and commercial meat products. Ann. Microbiol. 2016, 66, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coton, M.; Lebreton, M.; Leyva Salas, M.; Garnier, L.; Navarri, M.; Pawtowski, A.; Le Blay, G.; Valence, F.; Coton, E.; Mounier, J. Biogenic amine and antibiotic resistance profiles determined for lactic acid bacteria and a Propionibacterium prior to use as antifungal bioprotective cultures. Int. Dairy J. 2018, 85, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardini, F.; Suzzi, S.; Lombardi, A.; Galgano, F.; Crudele, M.A.; Andrighetto, C.; Schirone, M.; Tofalo, R. A survey of yeasts in traditional sausages of southern Italy. FEMS Yeast Res. 2001, 1, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Gioia, D.; Mazzola, G.; Nikodinoska, I.; Aloisio, I.; Langerholc, T.; Rossi, M.; Raiomondi, S.; Melero, B.; Rovira, J. Lactic acid bacteria as protective cultures in fermented pork meat to prevent Clostridium spp. growth. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2016, 235, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaggìa, F.; Baffoni, L.; Galiano, M.; Nielsen, D.S.; Jakobsen, R.R.; Castro-Mejía, J.L.; Bosi, S.; Truzzi, F.; Musumeci, F.; Dinelli, G.; et al. Kombucha beverage from green, black and rooibos teas: A comparative study looking at microbiology, chemistry and antioxidant activity. Nutrients 2018, 11, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Food Safety Authority (EFSA)-FEEDAP. Guidance on the assessment of bacterial susceptibility to antimicrobials of human and veterinary importance. EFSA J. 2012, 10, 2740–2749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bover-Cid, S.; Holzapfel, W.H. Improved screening procedure for biogenic amine production by lactic acid bacteria. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 1999, 53, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabanelli, G.; Montanari, C.; Bargossi, E.; Lanciotti, R.; Gatto, V.; Felis, G.; Torriani, S.; Gardini, F. Control of tyramine and histamine accumulation by lactic acid bacteria using bacteriocin forming lactococci. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2014, 190, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwietering, M.H.; Jongenburger, I.; Rombouts, F.M.; Van’t Riet, K. Modeling of the bacterial growth curve. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1990, 56, 1875–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tremonte, P.; Sorrentino, E.; Pannella, G.; Tipaldia, L.; Sturchio, M.; Masucci, A.; Maiuro, L.; Coppola, R.; Succia, M. Detection of different microenvironments and Lactobacillus sakei biotypes in Ventricina, a traditional fermented sausage from central Italy. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2017, 242, 132–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guilbaud, M.; Zagorec, M.; Chaillou, S.; Champomier-Vergès, M.C. Intraspecies diversity of Lactobacillus sakei response to oxidative stress and variability of strain performance in mixed strains challenges. Food Microbiol. 2012, 29, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbieri, F.; Tabanelli, G.; Montanari, C.; Dall’Osso, N.; Šimat, V.; Smole Možina, S.; Baños, A.; Özogul, F.; Bassi, D.; Fontana, C.; et al. Mediterranean spontaneously fermented sausages: Spotlight on microbiological and quality features to exploit their bacterial biodiversity. Foods 2021, 10, 2691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janßen, D.; Eisenbach, L.; Ehrmann, M.A.; Vogel, R.F. Assertiveness of Lactobacillus sakei and Lactobacillus curvatus in a fermented sausage model. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2018, 285, 188–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaillou, S.; Champomier-Vergès, M.C.; Cornet, M. The complete genome sequence of the meat-borne lactic acid bacterium Lactobacillus sakei 23K. Nat. Biotechnol. 2005, 23, 1527–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fontana, C.; Bassi, D.; López, C.; Pisacane, V.; Otero, M.C.; Puglisi, E.; Rebecchi, A.; Cocconcelli, P.S.; Vignolo, G. Microbial ecology involved in the ripening of naturally fermented llama meat sausages. A focus on lactobacilli diversity. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2016, 236, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montanari, C.; Barbieri, F.; Magnani, M.; Grazia, L.; Gardini, F.; Tabanelli, G. Phenotypic diversity of Lactobacillus sakei strains. Front. Microbiol. 2003, 9, 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widenmann, A.W.; Schiffer, C.J.; Ehrmann, M.A.; Vogel, R.F. Impact of different sugars and glycosyltransferases on the assertiveness of Latilactobacillus sakei in raw sausage fermentations. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2022, 366, 109575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monger, X.C.; Gilbert, A.A.; Saucier, L.; Vincent, A.T. Antibiotic resistance: From pig to meat. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gevers, D.; Danielsen, M.; Huys, G.; Swings, J. Molecular characterization of tet (M) genes in Lactobacillus isolates from different types of fermented dry sausage. Appl. Environ. Microb. 2003, 69, 1270–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zonenschain, D.; Rebecchi, A.; Morelli, L. Erythromycin- and tetracycline-resistant lactobacilli in Italian fermented dry sausages. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2009, 107, 1559–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fontana, C.; Patrone, V.; Lopez, C.M.; Morelli, L.; Rebecchi, A. Incidence of tetracycline and erythromycin resistance in meat-associated bacteria: Impact of different livestock management strategies. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 2111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abriouel, H.; Muñoz, M.D.C.C.; Lerma, L.L.; Montoro, B.P.; Bockelmann, W.; Pichner, R.; Kabisch, J.; Cho, G.-S.; Franz, C.M.A.P.; Gálvez, A.; et al. New insights in antibiotic resistance of Lactobacillus species from fermented foods. Food Res. Int. 2015, 78, 465–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danielsen, M.; Wind, A. Susceptibility of Lactobacillus spp. to antimicrobial agents. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2003, 82, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aymerich, T.; Martin, B.; Garriga, M.; Vidal-Carou, M.C.; Bover-Cid, S.; Hugas, M. Safety properties and molecular strain typing of lactic acid bacteria from slightly fermented sausages. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2006, 100, 40–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Federici, S.; Ciarrocchi, F.; Campana, R.; Ciandrini, E.; Blasi, G.; Baffone, W. Identification and functional traits of lactic acid bacteria isolated from Ciauscolo salami produced in Central Italy. Meat Sci. 2014, 98, 575–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wunderlichova, L.; Bunkova, L.; Koutry, M.; Jancova, P.; Bunka, F. Formation, degradation, and detoxification of putrescine by foodborne bacteria: A review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2014, 13, 1012–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rimaux, T.; Rivière, A.; Illeghems, K.; Weckx, S.; De Vuyst, L.; Leroy, F. Expression of the arginine deiminase pathway genes in Lactobacillus sakei is strain dependent and is affected by the environmental pH. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 78, 4874–4883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omer, A.K.; Mohammed, R.R.; Ameen, P.S.M.; Abas, Z.A.; Ekici, K. Presence of biogenic amines in food and their public health implications: A review. J. Food Protect. 2021, 84, 1539–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA Panel on Biological Hazards (BIOHAZ). Scientific opinion on risk based control of biogenic amine formation in fermented foods. EFSA J. 2011, 9, 2393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcobal, A.; De Las Rivas, B.; Landete, J.M.; Tabera, L.; Muñoz, R. Tyramine and phenylethylamine biosynthesis by food bacteria. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. 2012, 52, 448–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janßen, D.; Dworschak, L.; Ludwig, C.; Ehrmann, M.A.; Vogel, R.F. Interspecies assertiveness of Lactobacillus curvatus and Lactobacillus sakei in sausage fermentations. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2020, 331, 108689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fontana, C.; Cocconcelli, P.S.; Vignolo, G.; Saavedra, L. Occurrence of antilisterial structural bacteriocins genes in meat borne lactic acid bacteria. Food Control 2015, 47, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swinnen, I.A.M.; Bernaerts, K.; Dens, E.J.J.; Geeraerd, A.H.; Impe, V.J.F. Predictive modelling of the microbial lag phase: A review. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2004, 94, 137–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ammor, S.; Dufour, E.; Zagorec, M.; Chaillou, S.; Chevallier, I. Characterization and selection of Lactobacillus sakei strains isolated from traditional dry sausage for their potential use as starter cultures. Food Microbiol. 2005, 22, 529–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaillou, S.; Lucquin, I.; Najjari, A.; Zagorec, M.; Champomier-Vergès, M.C. Population genetics of Lactobacillus sakei reveals three lineages with distinct evolutionary histories. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e73253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Salame Romagnolo (ROM) | Salame Bresciano (BRE) | Salame Basilicata (BAS) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Diameter (mm) | 55 | 80 | 35 |
| Final weight (g) | 800 | 500 | 250 |
| % NaCl (w/w in the batter) | 2.8 | 2.4 | 2.5 |
| Nitrate/nitrite addiction | Not added | KNO3 (0.015%) | Not added |
| Fat in the meat batter (%) | 20 (with lard cube) | 25 (minced with lean meat) | 25 (minced with lean meat) |
| Ripening time (days) | 60 | 75 | 30 |
| Weight loss (%) | 35 | 30 | 35 |
| Casing | Natural | Natural | Natural |
| Presence of moulds on casing | Yes | Yes | No |
| Indicator Strains Used in the Assays | Cultivation Conditions | Strains Used in the Well-Diffusion Assay (WDA) | Strains Used in the Spot Test |
|---|---|---|---|
| Clostridium sporogenes | RCM, 37 °C, 24–48 h, anaerobic | + | + |
| Listeria innocua DPC 3572 | BHI, 37 °C, 24 h | + | + |
| L. monocytogenes DPC 1768 | BHI, 37 °C, 24 h | + | + |
| Escherichia coli DPC 6054 | BHI, 37 °C, 24 h | + | + |
| Salmonella enterica ssp. Typhimurium DPC 6046 | BHI, 37 °C, 24 h | + | + |
| Latilactobacillus curvatus DSM 20019T | MRS, 30 °C, 24–48 h | + | − |
| Latilactobacillus sakei ssp. sakei LMG 13558 T | MRS, 30 °C, 24–48 h | + | − |
| Lactobacillus delbrueckii ssp. bulgaricus LMG 6901T | MRS, 37 °C, 24–48 h, anaerobic | + | − |
| Lactiplantibacillus plantarum DPC6124 | MRS, 37 °C, 24–48 h, | + | − |
| Lacticaseibacillus paracasei ssp. paracasei DPC6130 | MRS, 30 °C, 24–48 h | + | − |
| Levilactobacillus brevis LMG 6906T | MRS, 37 °C, 24–48 h, anaerobic | + | − |
| Limosilactobacillus fermentum DPC 6193 | MRS, 37 °C, 24–48 h, anaerobic | + | − |
| Sample ROM | Sample BRE | Sample BAS | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lactic acid bacteria (log CFU/g) | 7.79 b | 9.09 a | 2.54 c |
| Staphylococci (log CFU/g) | 7.09 b | 6.75 a | 2.52 c |
| Enterococci (log CFU/g) | <1 b | 4.23 a | <1 b |
| pH | 6.01 b | 6.19 a | 5.86 b |
| aw | 0.853 b | 0.908 a | 0.831 c |
| Isolation Source | Strain | Closest Match | % Identification NCBI | Accession Number |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Salame Romagnolo (ROM) | C10G | Lat. sakei | 99.858 | MN173314 |
| C12G | Lat. sakei | 99.929 | MN173315 | |
| C16G | Lat. sakei | 99.721 | MN173316 | |
| C21G | Lat. sakei | 100.000 | MW548285 | |
| C22G | Lat. sakei | 99.857 | MN173317 | |
| C26G | Lat. curvatus | 99.785 | MN173318 | |
| C27G | Lat. sakei | 99.929 | MN173319 | |
| C45G | Lat. sakei | 99.786 | MN173320 | |
| C48G | Lat. sakei | 100.000 | MN173321 | |
| E1G | Lat. sakei | 99.786 | MN173322 | |
| E3G | Lat. sakei | 99.929 | MN173323 | |
| E8G | Lat. curvatus | 99.645 | MN173324 | |
| E13G | Lat. sakei | 99.857 | MN173325 | |
| E15G | Lat. sakei | 99.929 | MN173326 | |
| E17G | Lat. sakei | 99.786 | MN173327 | |
| E18G | Lat. curvatus | 99.856 | MN173328 | |
| E19G | Lat. sakei | 100.000 | MN173329 | |
| E22G | Lat. sakei | 99.588 | MW548286 | |
| E26G | Lat. sakei | 99.929 | MN173330 | |
| E28G | Lat. sakei | 99.929 | MN173331 | |
| Salame Bresciano (BRE) | C3B | Lat. sakei | 99.857 | MN120894 |
| C10B | Lat. sakei | 99.786 | MN173305 | |
| C14B | Lat. sakei | 99.929 | MN173306 | |
| C16B | Lat. sakei | 99.929 | MN173307 | |
| C17B | Lat. sakei | 99.857 | MN173308 | |
| C21B | Lat. sakei | 99.930 | MN173309 | |
| C22B | Lat. sakei | 99.859 | MN173310 | |
| E3B | Lat. sakei | 99.860 | MN173311 | |
| E7B | Lat. curvatus | 99.786 | MN173312 | |
| E15B | Lat. sakei | 99.930 | MN173313 | |
| E23B | Lat. sakei | 99.616 | MN215967 | |
| Salame Basilicata (BAS) | BC1 | Leuc. mesenteroides | 99.930 | MN173332 |
| BC6 | Lat. sakei | 99.930 | MN173333 | |
| BC20 | Lat. sakei | 99.930 | MN173334 | |
| BC33 | Lat. sakei | 99.930 | MN173335 | |
| BC35 | Lat. sakei | 100.000 | MN173336 | |
| BC50 | Lat. sakei | 99.929 | MN173337 | |
| BE2 | Lat. curvatus | 99.788 | MN173338 | |
| BE16 | Lat. sakei | 100.000 | MN173339 | |
| BE23 | Leuc. mesenteroides | 100.000 | MN173340 | |
| BE28 | Lat. curvatus | 99.861 | MN173341 |
| Antibiotic Minimal Inhibitory Concentration (µg/mL) | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Isolation Source | Species | Strains | Gen | Kan | Str | Tet | Ery | Cli | Chl | Amp |
| Salame Romagnolo (ROM) | Lat. sakei | C10G | 1 (S) a | 8 (S) | 16 (S) | 4 (S) | 0.12 (S) | 0.06 (S) | 4 (S) | 2 (S) |
| Lat. sakei | C12G | 1 (S) | 8 (S) | 16 (S) | 16 (R) b | 0.12 (S) | 0.25 (S) | 8 (R) | 2 (S) | |
| Lat. sakei | C16G | <0.5 (S) | <2 (S) | 8 (S) | 4 (S) | 0.06 (S) | 0.03 (S) | 4 (S) | 1 (S) | |
| Lat. sakei | C21G | <0.5 (S) | <2 (S) | 8 (S) | 4 (S) | 0.06 (S) | 0.03 (S) | 4 (S) | 1 (S) | |
| Lat. sakei | C22G | 1 (S) | 16 (S) | 32 (S) | >64 (R) | 0.12 (S) | 0.25 (S) | 4 (S) | >16 (R) | |
| Lat. curvatus | C26G | 2 (S) | 32 (S) | 16 (S) | 1 (S) | 0.06 (S) | 0.03 (S) | 8 (R) | 0.5 (S) | |
| Lat. sakei | C27G | <0.5 (S) | 4 (S) | 8 (S) | 4 (S) | 0.12 (S) | 0.03 (S) | 4 (S) | 2 (S) | |
| Lat. sakei | C45G | 2 (S) | 16 (S) | 32 (S) | 8 (S) | 0.12 (S) | 0.03 (S) | 4 (S) | 2 (S) | |
| Lat. sakei | C48G | 1 (S) | 8 (S) | 16 (S) | 8 (S) | 0.12 (S) | 0.06 (S) | 8 (R) | 4 (S) | |
| Lat. sakei | E1G | <0.5 (S) | 4 (S) | 16 (S) | 8 (S) | 0.12 (S) | 0.03 (S) | 4 (S) | 1 (S) | |
| Lat. sakei | E3G | 2 (S) | 16 (S) | 32 (S) | 16 (R) | 0.12 (S) | 0.5 (S) | 8 (R) | >16 (R) | |
| Lat. curvatus | E8G | 1 (S) | 8 (S) | 8 (S) | 2 (S) | 0.12 (S) | 0.12 (S) | 8 (R) | 1 (S) | |
| Lat. sakei | E13G | 1 (S) | 8 (S) | 64 (S) | 8 (S) | 0.12 (S) | 0.06 (S) | 4 (S) | 2 (S) | |
| Lat. sakei | E15G | <0.5 (S) | <2 (S) | 4 (S) | 2 (S) | 0.12 (S) | 0.03 (S) | 2 (S) | 2 (S) | |
| Lat. sakei | E17G | <0.5 (S) | 4 (S) | 8 (S) | 8 (S) | 0.12 (S) | 0.06 (S) | 4 (S) | 2 (S) | |
| Lat. curvatus | E18G | <0.5 (S) | <2 (S) | 4 (S) | 4 (S) | 0.06 (S) | 0.06 (S) | 2 (S) | 0.5 (S) | |
| Lat. sakei | E19G | 1 (S) | 8 (S) | 16 (S) | 4 (S) | 0.12 (S) | 0.06 (S) | 4 (S) | 1 (S) | |
| Lat. sakei | E22G | 1 (S) | 4 (S) | 16 (S) | 4 (S) | 0.25 (S) | 0.06 (S) | 4 (S) | 1 (S) | |
| Lat. sakei | E26G | <0.5 (S) | <2 (S) | 8 (S) | 4 (S) | 0.06 (S) | 0.03 (S) | 4 (S) | 1 (S) | |
| Lat. sakei | E28G | 0.5 (S) | <2 (S) | 4 (S) | 8 (S) | 0.12 (S) | 0.03 (S) | 4 (S) | 1 (S) | |
| Salame Bresciano (BRE) | Lat. sakei | C3B | 1 (S) | 4 (S) | 16 (S) | 4 (S) | 0.12 (S) | 0.12 (S) | 8 (R) | 2 (S) |
| Lat. sakei | C10B | 1 (S) | 8 (S) | 16 (S) | 2 (S) | 0.25 (S) | 0.03 (S) | 2 (S) | 2 (S) | |
| Lat. sakei | C14B | 1 (S) | 8 (S) | 16 (S) | 4 (S) | 0.12 (S) | 0.06 (S) | 1 (S) | 2 (S) | |
| Lat. sakei | C16B | <0.5 (S) | <2 (S) | 8 (S) | 4 (S) | 0.12 (S) | 0.06 (S) | 2 (S) | 0.5 (S) | |
| Lat. sakei | C17B | 1 (S) | 4 (S) | 16 (S) | 4 (S) | 0.5 (S) | 0.25 (S) | 4 (S) | 2 (S) | |
| Lat. sakei | C21B | <0.5 (S) | 4 (S) | 16 (S) | 4 (S) | 0.12 (S) | 0.12 (S) | 2 (S) | 4 (S) | |
| Lat. sakei | C22B | 2 (S) | 4 (S) | 1 (S) | 4 (S) | 0.25 (S) | 0.06 (S) | 4 (S) | 4 (S) | |
| Lat. sakei | E3B | <0.5 (S) | <2 (S) | 8 (S) | 4 (S) | 0.12 (S) | 0.06 (S) | 2 (S) | 0.5 (S) | |
| Lat. curvatus | E7B | <0.5 (S) | <2 (S) | 8 (S) | 2 (S) | 0.25 (S) | 0.06 (S) | 1 (S) | 2 (S) | |
| Lat. sakei | E15B | 1 (S) | 4 (S) | 16 (S) | 4 (S) | 0.12 (S) | 0.06 (S) | 2 (S) | 2 (S) | |
| Lat. sakei | E23B | 0.5 (S) | 2 (S) | 8 (S) | 8 (S) | 0.12 (S) | 0.06 (S) | 4 (S) | 2 (S) | |
| Salame Basilicata (BAS) | Leuc. mesenteroides | BC1 | 4 (S) | 64 (R) | 1 (S) | 2 (S) | 0.12 (S) | 0.12 (S) | 4 (S) | 2 (S) |
| Lat. sakei | BC6 | 8 (S) | 1 (S) | 32 (S) | >64 (R) | 0.12 (S) | 0.5 (S) | 2 (S) | 2 (S) | |
| Lat. sakei | BC20 | 4 (S) | 1 (S) | 32 (S) | 2 (S) | 0.12 (S) | 0.25 (S) | 2 (S) | 2 (S) | |
| Lat. sakei | BC33 | 2 (S) | 8 (S) | 1 (S) | 2 (S) | 0.12 (S) | 0.03 (S) | 4 (S) | 4 (S) | |
| Lat. sakei | BC35 | 4 (S) | 1 (S) | 32 (S) | 64 (R) | 0.12 (S) | 0.5 (S) | 2 (S) | 2 (S) | |
| Lat. sakei | BC50 | 2 (S) | 8 (S) | 32 (S) | 2 (S) | 0.12 (S) | 0.03 (S) | 4 (S) | 2 (S) | |
| Lat. curvatus | BE2 | 2 (S) | 1 (S) | 1 (S) | 4 (S) | 0.12 (S) | 0.03 (S) | 4 (S) | 4 (S) | |
| Lat. sakei | BE16 | 4 (S) | 32 (S) | 64 (S) | 4 (S) | 0.12 (S) | 0.03 (S) | 4 (S) | 8 (R) | |
| Leuc. mesenteroides | BE23 | 2 (S) | 8 (S) | 1 (S) | 32 (R) | 0.12 (S) | 0.06 (S) | 2 (S) | 2 (S) | |
| Lat. curvatus | BE28 | 1 (S) | 8 (S) | 1 (S) | 1 (S) | 0.12 (S) | 0.03 (S) | 2 (S) | 1 (S) | |
| Isolation Source | Species | Strains | C. sporogenes | L. monocytogenes | Salmonella spp. | E. coli |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Salame Romagnolo (ROM) | Lat. sakei | C10G | ||||
| Lat. sakei | C16G | |||||
| Lat. sakei | C21G | |||||
| Lat. sakei | C27G | |||||
| Lat. sakei | C45G | |||||
| Lat. sakei | E1G | |||||
| Lat. sakei | E13G | |||||
| Lat. sakei | E15G | |||||
| Lat. sakei | E17G | |||||
| Lat. sakei | E18G | |||||
| Lat. sakei | E19G | |||||
| Lat. sakei | E22G | |||||
| Lat. sakei | E26G | |||||
| Lat. sakei | E28G | |||||
| Salame Bresciano (BRE) | Lat. sakei | C10B | ||||
| Lat. sakei | C14B | |||||
| Lat. sakei | C16B | |||||
| Lat. sakei | C17B | |||||
| Lat. sakei | C21B | |||||
| Lat. sakei | C22B | |||||
| Lat. sakei | E3B | |||||
| Lat. curvatus | E7B | |||||
| Lat. sakei | E15B | |||||
| Lat. sakei | E23B | |||||
| Salame Basilicata (BAS) | Lat. sakei | BC20 | ||||
| Lat. sakei | BC33 | |||||
| Lat. sakei | BC50 | |||||
| Lat. curvatus | BE2 | |||||
| Lat. curvatus | BE28 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nikodinoska, I.; Tabanelli, G.; Baffoni, L.; Gardini, F.; Gaggìa, F.; Barbieri, F.; Di Gioia, D. Characterization of Lactic Acid Bacteria Isolated from Spontaneously Fermented Sausages: Bioprotective, Technological and Functional Properties. Foods 2023, 12, 727. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12040727
Nikodinoska I, Tabanelli G, Baffoni L, Gardini F, Gaggìa F, Barbieri F, Di Gioia D. Characterization of Lactic Acid Bacteria Isolated from Spontaneously Fermented Sausages: Bioprotective, Technological and Functional Properties. Foods. 2023; 12(4):727. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12040727
Chicago/Turabian StyleNikodinoska, Ivana, Giulia Tabanelli, Loredana Baffoni, Fausto Gardini, Francesca Gaggìa, Federica Barbieri, and Diana Di Gioia. 2023. "Characterization of Lactic Acid Bacteria Isolated from Spontaneously Fermented Sausages: Bioprotective, Technological and Functional Properties" Foods 12, no. 4: 727. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12040727
APA StyleNikodinoska, I., Tabanelli, G., Baffoni, L., Gardini, F., Gaggìa, F., Barbieri, F., & Di Gioia, D. (2023). Characterization of Lactic Acid Bacteria Isolated from Spontaneously Fermented Sausages: Bioprotective, Technological and Functional Properties. Foods, 12(4), 727. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12040727








