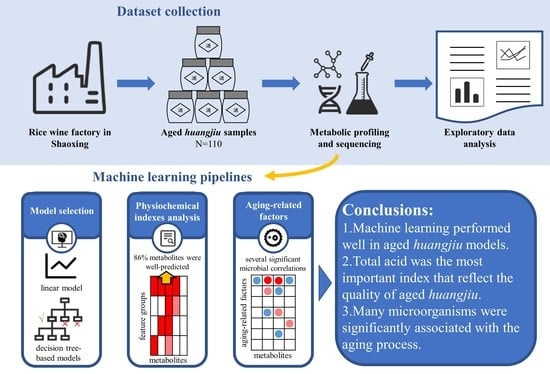
Impact of Aging Microbiome on Metabolic Profile of Natural Aging Huangjiu through Machine Learning
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collections
2.2. Measurement of Physiochemical Indexes
2.3. Metabolite Profiling and Preprocessing
2.4. Sequencing and Microbiome Preprocessing
2.5. Predictive Models of Aging Metabolites
2.6. Feature Attribution Analysis
2.7. Bioinformatics and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. An Aging Huangjiu Microbiome-Metabolomic Dataset Collection
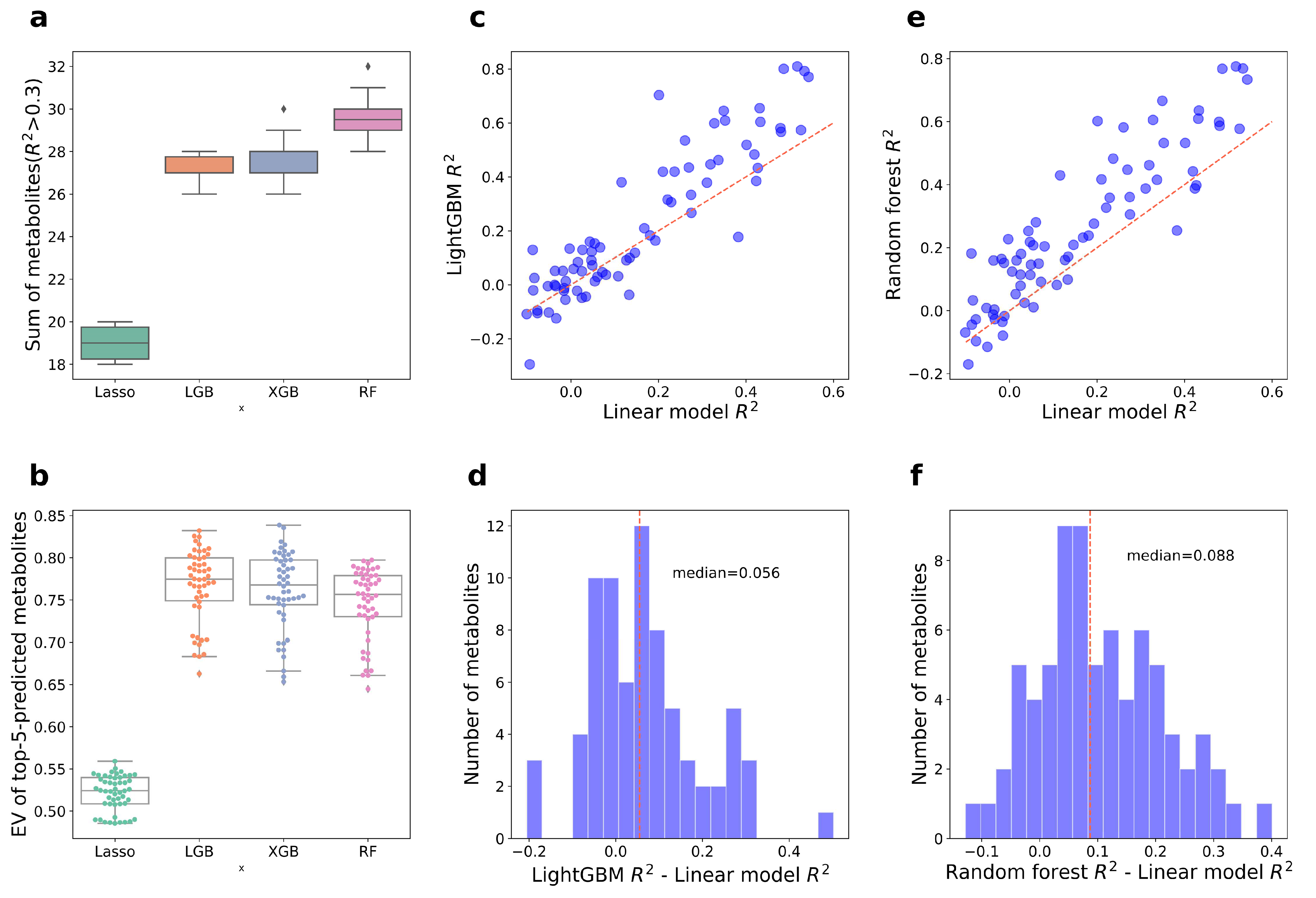
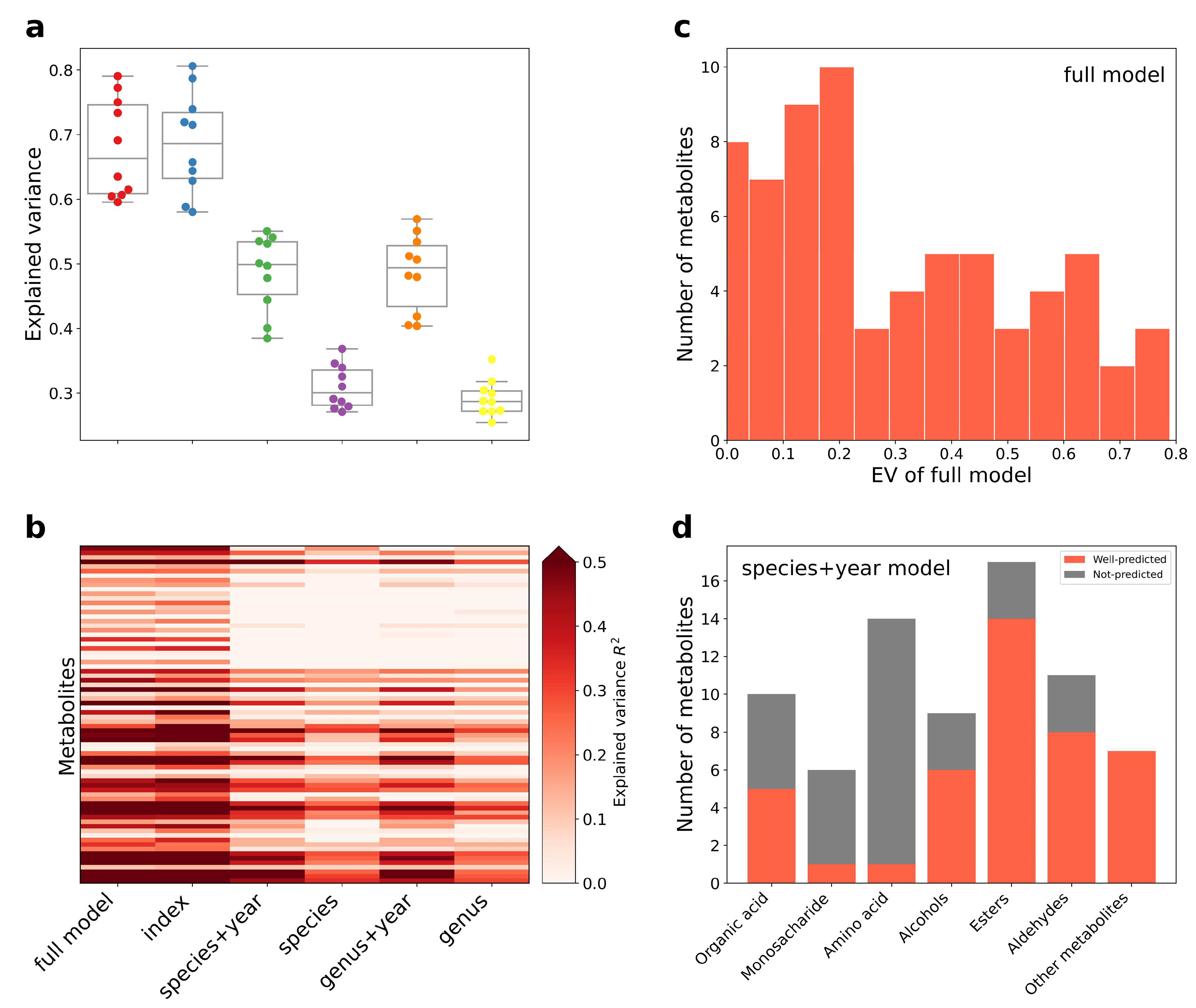
3.2. Construction of Aging Huangjiu Microbiome-Metabolome Models
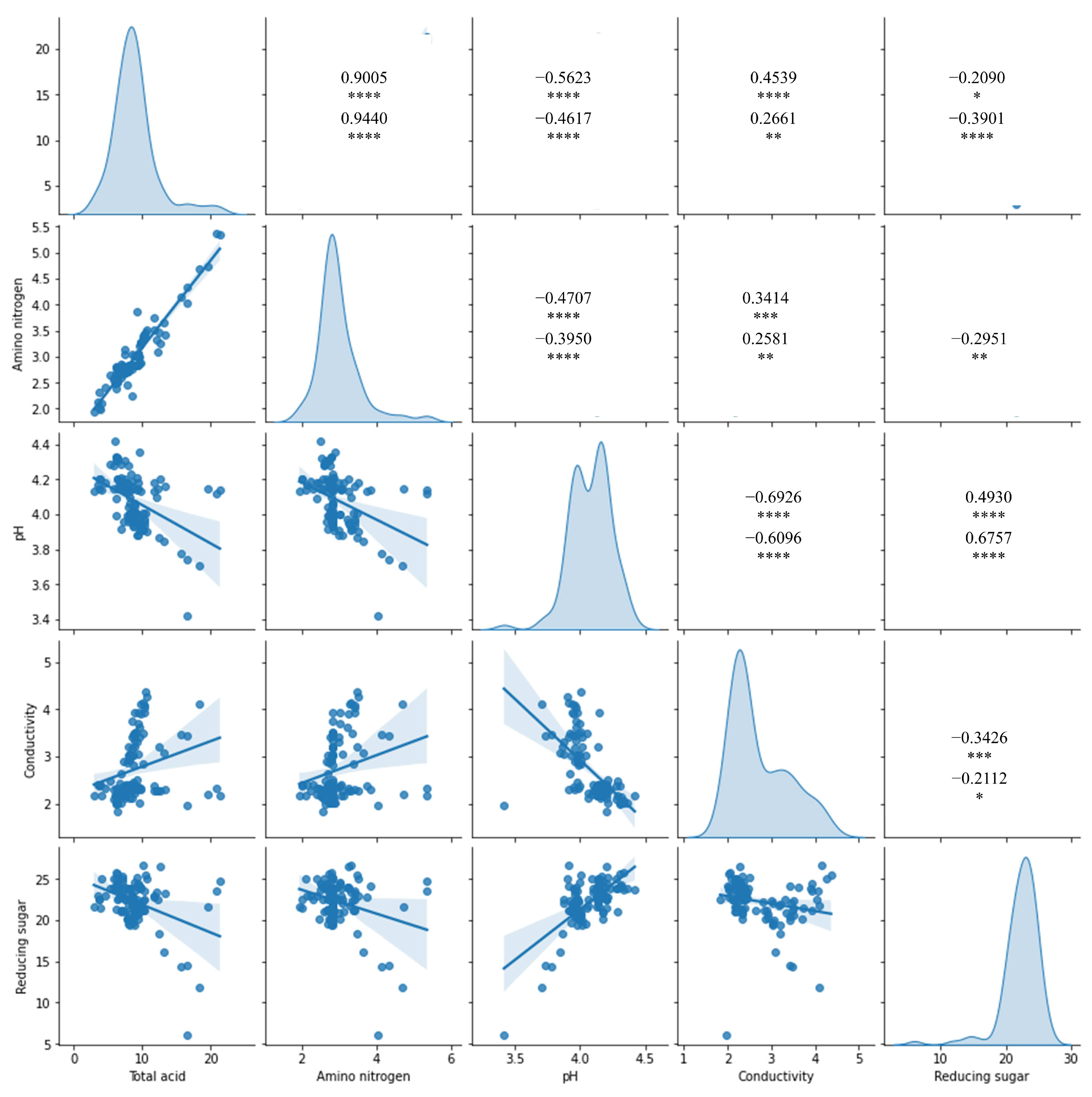
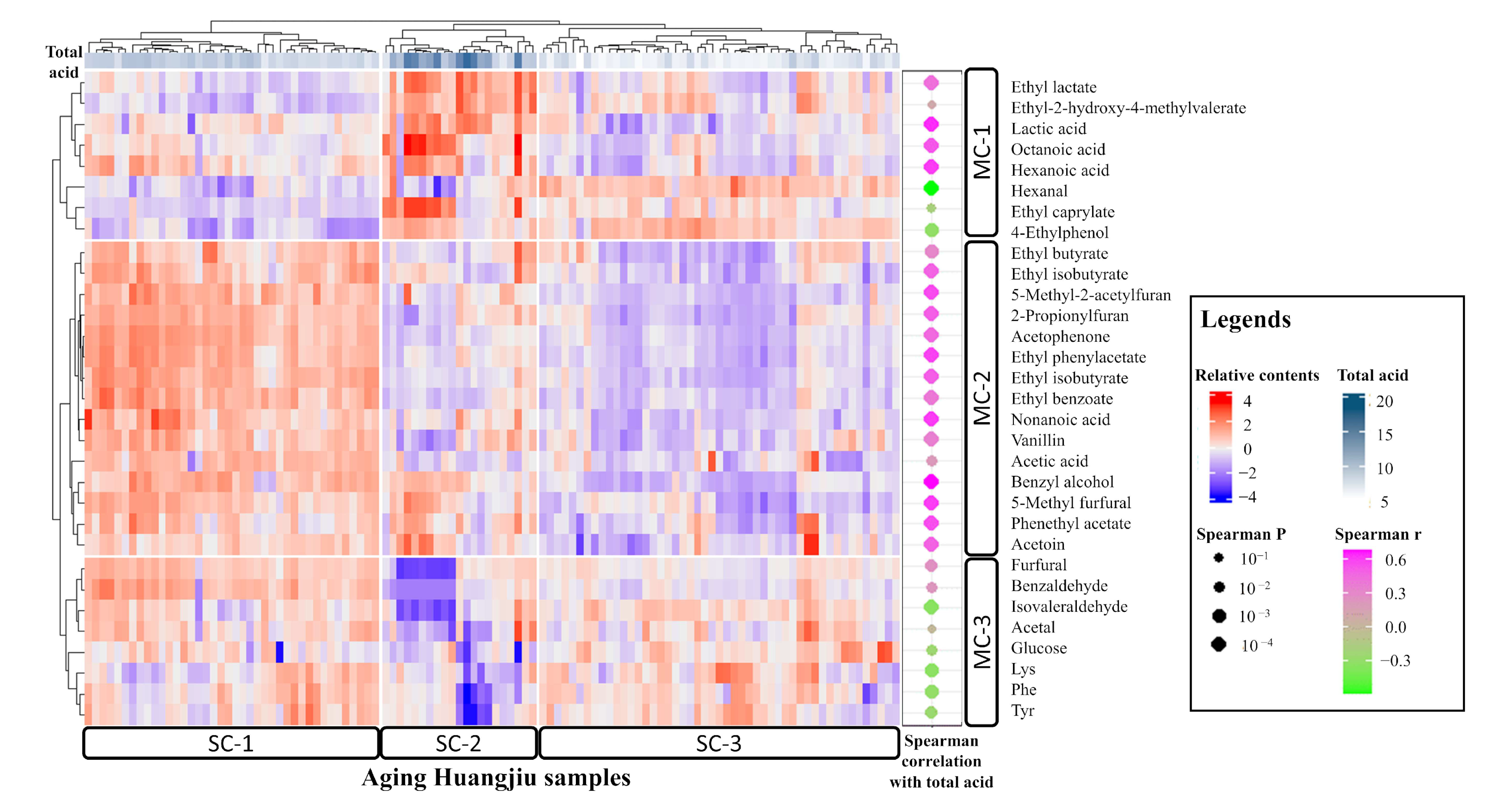
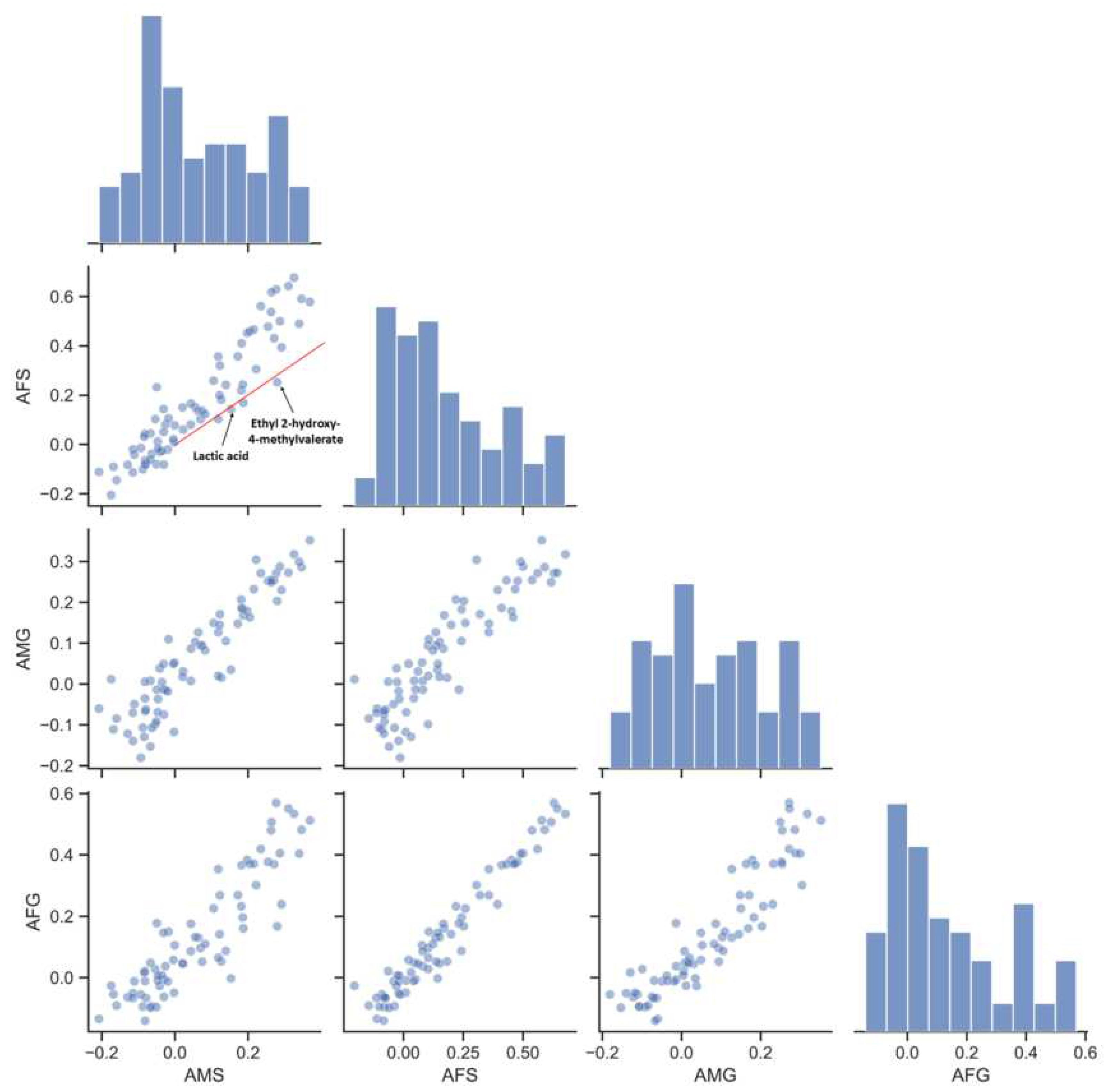
3.3. Index–Metabolome Association of Aging Huangjiu
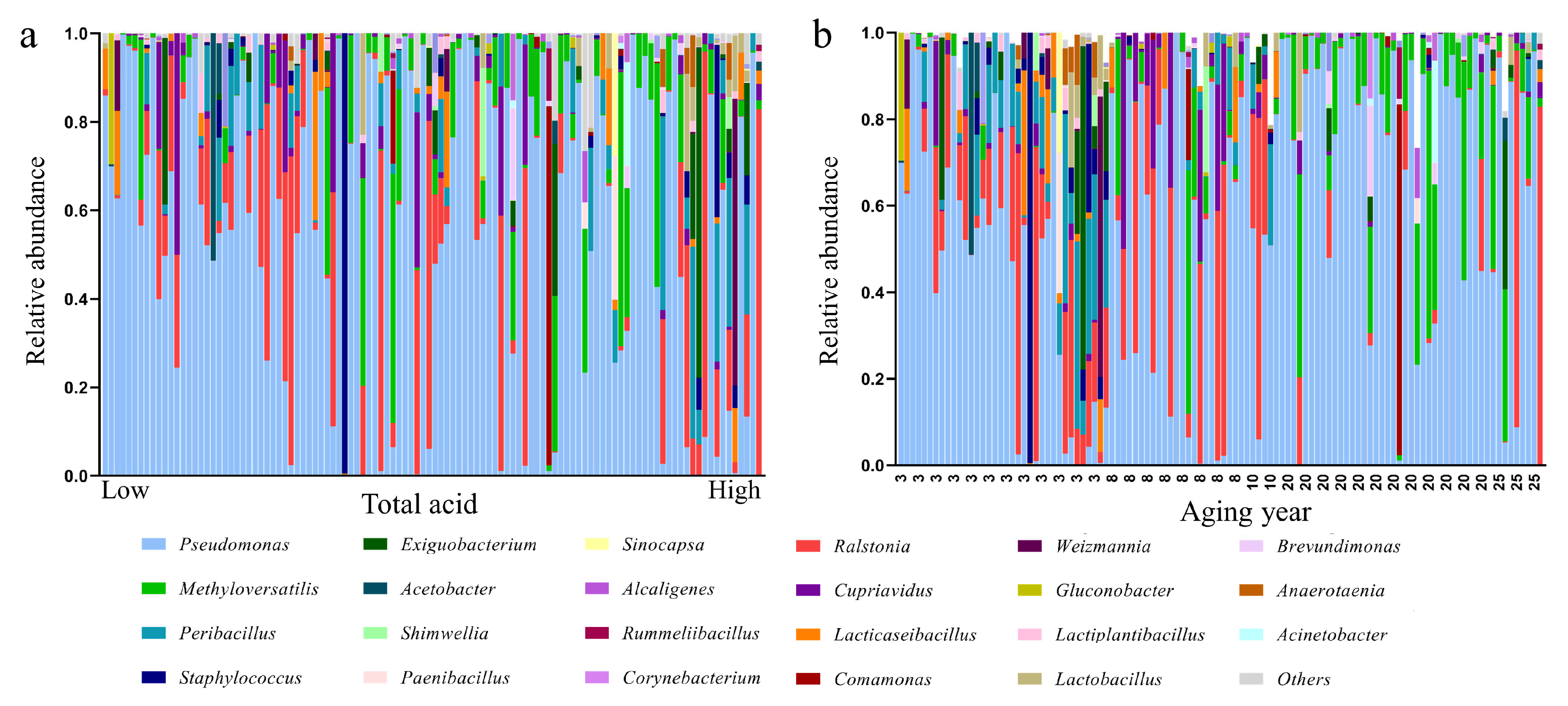
3.4. Influence of Aging-Related Factors on Metabolites
3.5. Contribution of Aging Microbiome
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, G.; Huang, Z.; Wu, L.; Wu, Q.; Guo, W.; Zhao, W.; Liu, B.; Zhang, W.; Rao, P.; Lv, X.; et al. Microbial diversity and flavor of Chinese rice wine (Huangjiu): An overview of current research and future prospects. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2021, 42, 37–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Hu, W.; Xia, Y.; Mu, Z.; Tao, L.; Song, X.; Zhang, H.; Ni, B.; Ai, L. Flavor Formation in Chinese Rice Wine (Huangjiu): Impacts of the Flavor-Active Microorganisms, Raw Materials, and Fermentation Technology. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Ai, L.; Mu, Z.; Liu, H.; Yan, X.; Ni, L.; Zhang, H.; Xia, Y. Flavor compounds with high odor activity values (OAV > 1) dominate the aroma of aged Chinese rice wine (Huangjiu) by molecular association. Food Chem. 2022, 383, 132370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, C.; Zhu, H.; Zhu, W.; Zhu, Y.; Peng, Q.; Elsheery, N.I.; Fu, J.; Xie, G.; Zheng, H.; Han, J.; et al. The sensory and flavor characteristics of Shaoxing Huangjiu (Chinese rice wine) were significantly influenced by micro-oxygen and electric field. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 9, 6006–6019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bossaert, S.; Winne, V.; Van Opstaele, F.; Buyse, J.; Verreth, C.; Herrera-Malaver, B.; Verstrepen, K.J.; De Rouck, G.; Crauwels, S.; Lievens, B. Impact of wood species on microbial community composition, beer chemistry and sensory characteristics during barrel-ageing of beer. Int. J. Food Sci. 2022, 57, 1122–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cibrario, A.; Perello, M.C.; Miot-Sertier, C.; Riquier, L.; de Revel, G.; Ballestra, P.; Dols-Lafargue, M. Carbohydrate composition of red wines during early aging and incidence on spoilage by Brettanomyces bruxellensis. Food Microbiol. 2020, 92, 103577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, Y.; Zhong, W.; He, Z.; Zhao, W.; Huang, M.; Bai, W. Research progress of lactic acid bacteria in Chinese rice wine. China Brew. 2015, 34, 5–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, G.; Zheng, H.; Qiu, Z.; Lin, Z.; Peng, Q.; Bealu, G.-D.; Elsheery, N.I.; Lu, Y.; Shen, C.; Fu, J.; et al. Study on relationship between bacterial diversity and quality of Huangjiu (Chinese Rice Wine) fermentation. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 9, 3885–3892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Chen, L.; Liu, Y.; He, J.; Liu, L.; Zhang, L.; Yang, H. Isolation and identification of contaminated microorganisms from jar installed Huangjiu (rice wine) during storage. China Brew. 2018, 37, 81–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Ke, F.; Liu, W.; Xu, Y.; Chen, S. Biological characteristics of spoilage microbes in the storage of Huangjiu. Food Ferment. Ind. 2021, 47, 106–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Xia, Y.; Hu, W.; Tao, L.; Liu, H.; Xie, C.; Bai, W.; Ai, L. Soaking induced discrepancies in oenological properties, flavor profiles, microbial community and sensory characteristic of Huangjiu (Chinese rice wine). LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 139, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Roos, J.; Verce, M.; Aerts, M.; Vandamme, P.; De Vuyst, L. Temporal and Spatial Distribution of the Acetic Acid Bacterium Communities throughout the Wooden Casks Used for the Fermentation and Maturation of Lambic Beer Underlines Their Functional Role. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2018, 84, e02846-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Z.; Wu, X.; Zhu, Y. Isolation, identification and growth optimization of Lactobacillus fructivorans causing rancidity of Chinese rice wine. Food Sci. China 2018, 39, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, T.; Hu, Z.; Chen, L.; Chen, D.; Wang, X.; Yao, L.; Sun, M.; Song, S.; Wang, H. Quantitative structure-activity relationships (QSAR) of aroma compounds in different aged Huangjiu. J. Food Sci. 2020, 85, 3273–3281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Zheng, D.; Xie, T.; Xie, J.; Tian, H.; Ai, L.; Chen, C. Comprehensive two-dimensional gas chromatography mass spectrometry-based untargeted metabolomics to clarify the dynamic variations in the volatile composition of Huangjiu of different ages. J. Food Sci. 2022, 87, 1563–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Chen, C.; Lei, Z. Meta-omics insights in the microbial community profiling and functional characterization of fermented foods. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 65, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Lu, Z.; Chai, L.; Shi, J.; Xu, Z. Research strategies for microbial ecology of traditional Chinese fermented foods. Sci. Sin. Vitae 2019, 49, 575–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mannaa, M.; Han, G.; Seo, Y.-S.; Park, I. Evolution of Food Fermentation Processes and the Use of Multi-Omics in Deciphering the Roles of the Microbiota. Foods 2021, 10, 2861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namkung, J. Machine learning methods for microbiome studies. J. Microbiol. 2020, 58, 206–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adebo, O.A.; Oyeyinka, S.A.; Adebiyi, J.A.; Feng, X.; Wilkin, J.D.; Kewuyemi, Y.O.; Abrahams, A.M.; Tugizimana, F. Application of gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS)-based metabolomics for the study of fermented cereal and legume foods: A review. Int. J. Food Sci. 2021, 56, 1514–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.; Xue, Y.; Chen, X.; Han, B.-Z. Integrated multi-omics approaches to understand microbiome assembly in Jiuqu, a mixed-culture starter. Compr. Rev. Food. Sci. Food Saf. 2022, 21, 4076–4107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linardatos, P.; Papastefanopoulos, V.; Kotsiantis, S. Explainable AI: A Review of Machine Learning Interpretability Methods. Entropy 2021, 23, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samek, W.; Wiegand, T.; Müller, K.-R. Explainable Artificial Intelligence: Understanding, Visualizing and Interpreting Deep Learning Models. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1708.08296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stiglic, G.; Kocbek, P.; Fijacko, N.; Zitnik, M.; Verbert, K.; Cilar, L. Interpretability of machine learning-based prediction models in healthcare. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev-Data Mining Knowl. Discov. 2020, 10, e1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, H.; Lu, W.; Wu, T.; Yuan, W.; Zhu, J.; Lee, Y.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Chen, W. Human gut microbiome aging clocks based on taxonomic and functional signatures through multi-view learning. Gut Microbes 2022, 14, 2025016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bar, N.; Korem, T.; Weissbrod, O.; Zeevi, D.; Rothschild, D.; Leviatan, S.; Kosower, N.; Lotan-Pompan, M.; Weinberger, A.; Le Roy, C.I.; et al. A reference map of potential determinants for the human serum metabolome. Nature 2020, 588, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundberg, S.M.; Lee, S.-I. A Unified Approach to Interpreting Model Predictions. In Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017; pp. 4768–4777. [Google Scholar]
- Shapley, L.S. A value for n-persons games. Ann. Math Stud. 1953, 28, 307–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundberg, S.M.; Erion, G.; Chen, H.; DeGrave, A.; Prutkin, J.M.; Nair, B.; Katz, R.; Himmelfarb, J.; Bansal, N.; Lee, S.-I. From local explanations to global understanding with explainable AI for trees. Nat. Mach. Intell. 2020, 2, 56–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolyen, E.; Rideout, J.R.; Dillon, M.R.; Bokulich, N.A.; Abnet, C.C.; Al-Ghalith, G.A.; Alexander, H.; Alm, E.J.; Arumugam, M.; Asnicar, F.; et al. Reproducible, interactive, scalable and extensible microbiome data science using QIIME 2. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 852–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedregosa, F.; Varoquaux, G.; Gramfort, A.; Michel, V.; Thirion, B.; Grisel, O.; Blondel, M.; Prettenhofer, P.; Weiss, R.; Dubourg, V.; et al. Scikit-learn: Machine Learning in Python. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2011, 12, 2825–2830. [Google Scholar]
- Ke, G.; Meng, Q.; Finely, T.; Wang, T.; Chen, W.; Ma, W.; Ye, Q.; Liu, T.-Y. LightGBM: A Highly Efficient Gradient Boosting Decision Tree. In Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017; pp. 3149–3157. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, N.; Hu, P.; Chen, C. A primary study on the possible original microorganisms leading to the rancidity of yellow rice wine. Food Ferment. Ind. 2014, 40, 24–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smalley, N.E.; Taipale, S.; De Marco, P.; Doronina, N.V.; Kyrpides, N.; Shapiro, N.; Woyke, T.; Kalyuzhnaya, M.G. Functional and genomic diversity of methylotrophic Rhodocyclaceae: Description of Methyloversatilis discipulorum sp. nov. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2015, 65, 2227–2233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Xie, G.; Sun, J.; Zou, H.; Wang, R.; Qian, B.; Zang, W.; Zhou, J.; Shou, H.; Bai, F. Research progress on the microorganisms of Chinese rice wine. Sci. Technol. Food Ind. 2016, 8, 374–380. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, X.; Xiang, F.; Tang, F.; Cai, W.; Guo, Z.; Hou, Q.; Yang, X.; Song, W.; Shan, C. Bacterial Communities and Prediction of Microbial Metabolic Pathway in Rice Wine Koji from Different Regions in China. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 748779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Zeng, Y.; Liu, W.; Wang, S.; Shen, C.; Shi, B. Effects of metals released in strong-flavor baijiu on the evolution of aroma compounds during storage. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 8, 1904–1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, W.; Huang, F.; He, Z.; Lin, X.; Liang, Z.; Lin, X. Dissolved oxygen level and aging effects of monascus rice wine storage with clay jar. Sci. Technol. Food Ind. 2016, 37, 166–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Yang, H.; Jing, X.; Xu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Yan, Z.; Qi, Y. Influence of different storage containers on the aroma composition of Fengxiang-type baijiu analyzed by gas chromatography-ion mobility spectroscopy and electronic nose. Food Sci. 2022, 43, 257–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, D.; Duan, J.; Li, Y.; He, F.; Li, H.; Sun, B. A review of changes of flavor compounds during Baijiu aging and recent progress in artificial aging techniques. Food Sci. 2021, 42, 260–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Cai, F.; Zhang, R.; Xu, J. Research advances in artificial aging technology of Baijiu. Sci. Technol. Food Ind. 2021, 42, 389–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Su, Y.; Zhang, Y.L.; Zhu, P.Y.; Mei, Z.L.; Zhou, X.N.; Yu, H. Potential use of ultrasound to promote fermentation, maturation, and properties of fermented foods: A review. Food Chem. 2021, 357, 129805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iosip, E.; Bahrim, G.E.; Stanciuc, N.; Constantin, O.E.; Croitoru, C.; Rapeanu, G. Improvement of the red wines quality by using yeast derivatives as an alternative to lees aging. Ann. Univ. Dunarea Jos Galati Fascicle Vi-Food Technol. 2022, 46, 40–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, H.; Liu, S.; Zhou, Z.; Zhao, H.; Xu, Y.; Mao, J. Impact of Aging Microbiome on Metabolic Profile of Natural Aging Huangjiu through Machine Learning. Foods 2023, 12, 906. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12040906
Yu H, Liu S, Zhou Z, Zhao H, Xu Y, Mao J. Impact of Aging Microbiome on Metabolic Profile of Natural Aging Huangjiu through Machine Learning. Foods. 2023; 12(4):906. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12040906
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Huakun, Shuangping Liu, Zhilei Zhou, Hongyuan Zhao, Yuezheng Xu, and Jian Mao. 2023. "Impact of Aging Microbiome on Metabolic Profile of Natural Aging Huangjiu through Machine Learning" Foods 12, no. 4: 906. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12040906
APA StyleYu, H., Liu, S., Zhou, Z., Zhao, H., Xu, Y., & Mao, J. (2023). Impact of Aging Microbiome on Metabolic Profile of Natural Aging Huangjiu through Machine Learning. Foods, 12(4), 906. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12040906