Bos indicus Carcasses Suspended by the Pelvic Bone Require a Shorter Aging Time to Meet Consumer Expectations Regarding Meat Quality
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals and Carcasses
2.2. Aging
2.3. Sensory Analysis
2.4. Laboratory Analysis
2.4.1. pH and Meat Color
2.4.2. Purge Loss, Shear Force and Cooking Loss
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Carcass Traits
3.2. Meat Quality Traits
3.3. Correlations
4. Discussion
4.1. Carcass and Meat Quality Traits
4.2. Meat Aging
4.3. Meat Quality Correlations
4.4. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Junior, C.C.; Goulart, R.S.; Albertini, T.Z.; Feigl, B.J.; Cerri, C.E.P.; Vasconcelos, J.T.; Bernoux, M.; Lanna, D.P.D.; Cerri, C.C. Brazilian beef cattle feedlot manure management: A country survey. J. Anim. Sci. 2013, 91, 1811–1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, T.S.; Albertini, T.Z.; Barioni, L.G.; de Medeiros, S.R.; Millen, D.D.; Dos Santos, A.C.R.; Goulart, R.S.; Lanna, D.P.D. Perception of consultants, feedlot owners, and packers regarding management and marketing decisions on feedlots: A national survey in Brazil (Part II). Can. J. Anim. Sci. 2020, 100, 759–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filho, N.B.S.; Oliveira, R.L.; Cruz, C.H.; Leão, A.G.; Ribeiro, O.L.; Borja, M.S.; Silva, T.M.; Abreu, C.L. Physicochemical and sensory characteristics of meat from young Nellore bulls fed different levels of palm kernel cake. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2016, 96, 3590–3595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, N.V.; Aboujaoude, C.; Vieira, G.S.; Paiva, V.V.; Neto, R.A.M.; Gondim, V.S.; Alves, L.R.; Torres, M.C.L.; Antunes, R.C. Carcass and meat quality traits in Nellore and F1 Nellore-Araguaia crosses. Genet. Mol. Res. 2015, 14, 5379–5389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santiago, B.; Baldassini, W.; Tomaz, L.; Rocha, L.; Santos, W.; Curi, R.; Chardulo, L.A.; Neto, O.M. Comparison of dental carcass maturity in non-castrated male F1 Angus-Nellore cattle finished in feedlot. Food Sci. Anim. Resour. 2021, 41, 554–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, L.F.; Balieiro, J.C.C.; Ferrinho, A.M.; Martins, T.; da Silva Corte, R.R.P.; de Amorim, T.R.; de Jesus Mangini Furlan, J.; Baldi, F.; Pereira, A.S.C. Gender status effect on carcass and meat quality traits of feedlot Angus × Nellore cattle. Anim. Sci. J. 2019, 90, 1078–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado, E.F.; Aguiar, A.P.; Ortega, E.M.M.; Spoto, M.H.F.; Castillo, C.J.C. Brazilian consumers’ perception of tenderness of beef steaks classified by shear force and taste. Sci. Agric. 2006, 63, 232–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blanco, M.; Ripoll, G.; Delavaud, C.; Casasús, I. Performance, carcass and meat quality of young bulls, steers and heifers slaughtered at a common body weight. Livest. Sci. 2020, 240, 104156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Severino, M.; Gagaoua, M.; Baldassini, W.; Ribeiro, R.; Torrecilhas, J.; Pereira, G.; Chardulo, L.A.; Padilha, P.; Neto, O.R.M. Proteomics Unveils Post-Mortem Changes in Beef Muscle Proteins and Provides Insight into Variations in Meat Quality Traits of Crossbred Young Steers and Heifers Raised in Feedlot. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 12259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrico, D.D.; Hutchings, S.C.; Ha, M.; Bittner, E.P.; Fuentes, S.; Warner, R.D.; Dunshea, F.R. Novel techniques to understand consumer responses towards food products: A review with a focus on meat. Meat Sci. 2018, 144, 30–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferguson, D.M.; Jiang, S.T.; Hearnshaw, H.; Rymill, S.R.; Thompson, J.M. Effect of electrical stimulation on protease activity and tenderness of M. longissimus from cattle with different proportions of Bos indicus content. Meat Sci. 2000, 55, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayraktaroglu, A.G.; Kahraman, T. Effect of muscle stretching on meat quality of biceps femoris from beef. Meat Sci. 2011, 88, 580–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamatara, K.; Mpairwe, D.; Christensen, M.; Eskildsen, C.E.; Mutetikka, D.; Muyonga, J.; Mushi, D.; Omagor, S.; Nantongo, Z.; Madsen, J. Influence of age and method of carcass suspension on meat quality attributes of pure bred Ankole bulls. Livest. Sci. 2014, 169, 175–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, R.; Polkinghorne, R.; Thompson, J.M. Development of the Meat Standards Australia (MSA) prediction model for beef palatability. Aust. J. Exp. Agric. 2008, 48, 1368–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nian, Y.; Allen, P.; Harrison, S.M.; Kerry, J.P. Effect of castration and carcass suspension method on the quality and fatty acid profile of beef from male dairy cattle. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2018, 98, 4339–4350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Mao, Y.; Liang, R.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, R.; Zhu, L.; Han, G.; Luo, X. Effect of suspension method on meat quality and ultra-structure of Chinese Yellow Cattle under 12–18 °C pre-rigor temperature controlled chilling. Meat Sci. 2016, 115, 45–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AUS-MEAT. Australian Beef Carcase Evaluation—Chiller Assessment, Version 8; AUS-MEAT Limited: Murarrie, QLD, Australia, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Watson, R.; Gee, A.; Polkinghorne, R.; Porter, M. Consumer assessment of eating quality—Development of protocols for Meat Standards Australia (MSA) testing. Aust. J. Exp. Agric. 2008, 48, 1360–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salueña, B.H.; Gamasa, C.S.; Rubial, J.M.D.; Odriozola, C.A. CIELAB color paths during meat shelf life. Meat Sci. 2019, 157, 107889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lopes, L.S.F.; Ferreira, M.S.; Baldassini, W.A.; Curi, R.A.; Pereira, G.L.; Neto, O.R.M.; Oliveira, H.N.; Silva, J.A.I.I.V.; Munari, D.P.; Chardulo, L.A.L. Application of the principal component analysis, cluster analysis, and partial least square regression on crossbreed Angus-Nellore bulls feedlot finished. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2020, 52, 3655–3664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AMSA. Research Guidelines for Cookery, Sensory Evaluation, and Instrumental Tenderness Measurements of Meat; American Meat Science Association: Kearney, MO, USA, 2015; ISBN 8005172672. [Google Scholar]
- Wheeler, T.L.; Koohmaraie, M.; Cundiff, L.V.; Dikeman, M.E. Effects of cooking and shearing methodology on variation in Warner-Bratzler shear force values in beef. J. Anim. Sci. 1994, 72, 2325–2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sanches, P.D.F.; Zocchi, S.S. Quadrados latinos balanceados para a vizinhança: Planejamento e análise de dados sensoriais. Rev. Bras. Biom. 2010, 28, 21–42. [Google Scholar]
- MLA. Meat Standards Australia Beef Information Kit. Available online: https://www.mla.com.au/globalassets/mla-corporate/marketing-beef-and-lamb/msa_tt_beefinfokit_jul13_lr.pdf (accessed on 1 December 2022).
- Lê, S.; Josse, J.; Husson, F. FactoMineR: An R Package for Multivariate Analysis. J. Stat. Softw. 2008, 25, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kassambara, A.; Mundt, F. Package “Factoextra” for R: Extract and Visualize the Results of Multivariate Data Analyses, R Packag. Version; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Kaiser, H.F. Directional statistical decisions. Psychol. Rev. 1960, 67, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moran, L.; Barron, L.J.R.; Wilson, S.S.; O’Sullivan, M.G.; Kerry, J.P.; Prendiville, R.; Moloney, A.P. Effect of pelvic suspension and post-mortem ageing on the quality of three muscles from Holstein Friesian bulls and steers. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2021, 101, 1892–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pophiwa, P.; Webb, E.C.; Frylinck, L. A review of factors affecting goat meat quality and mitigating strategies. Small Rumin. Res. 2020, 183, 106035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basinger, K.L.; Shanks, B.C.; Apple, J.K.; Caldwell, J.D.; Yancey, J.W.S.; Backes, E.A.; Wilbers, L.S.; Johnson, T.M.; Bax, A.L. Application of tension to prerigor goat carcasses to improve cooked meat tenderness. Meat Sci. 2019, 147, R713–R715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinheiro, R.S.B.; de Souza, H.B.A. Métodos de suspensão da carcaça de ovelhas de descarte na qualidade da carne. Food Sci. Tecnol. 2011, 31, 221–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, Y.H.B.; Kerr, M.; Geesink, G.; Warner, R.D. Impacts of hanging method and high pre-rigor temperature and duration on quality attributes of ovine muscles. Anim. Prod. Sci. 2014, 54, 414–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Biffin, T.E.; Smith, M.A.; Bush, R.D.; Collins, D.; Hopkins, D.L. The effect of electrical stimulation and tenderstretching on colour and oxidation traits of alpaca (Vicunga pacos) meat. Meat Sci. 2019, 156, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchison, C.L.; Mulley, R.C.; Wiklund, E.; Flesch, J.S.; Sims, K. Effect of pelvic suspension on the instrumental meat quality characteristics of red deer (Cervus elaphus) and fallow deer (Dama dama) venison. Meat Sci. 2014, 98, 104–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polkinghorne, R.J.; Thompson, J.M. Meat standards and grading. A world view. Meat Sci. 2010, 86, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bekhit, A.E.D.A.; Carne, A.; Ha, M.; Franks, P. Physical interventions to manipulate texture and tenderness of fresh meat: A review. Int. J. Food Prop. 2014, 17, 433–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ferraz, J.B.S.; de Felício, P.E. Production systems—An example from Brazil. Meat Sci. 2010, 84, 238–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miguel, G.Z.; Faria, M.H.; Roça, R.O.; Santos, C.T.; Suman, S.P.; Faitarone, A.B.G.; Delbem, N.L.C.; Girao, L.V.C.; Homem, J.M.; Barbosa, E.K.; et al. Immunocastration improves carcass traits and beef color attributes in Nellore and Nellore×Aberdeen Angus crossbred animals finished in feedlot. Meat Sci. 2014, 96, 884–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearce, K.L.; Rosenvold, K.; Andersen, H.J.; Hopkins, D.L. Water distribution and mobility in meat during the conversion of muscle to meat and ageing and the impacts on fresh meat quality attributes—A review. Meat Sci. 2011, 89, 111–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaspal, M.H.; Ijaz, M.; Akhtar, M.J.; Nasir, J.; Ullah, S.; Badar, I.H.; Yar, M.K.; Ahmad, A. Effect of carcass electrical stimulation and suspension methods on meat quality characteristics of longissimus lumborum of young buffalo (Bubalus bubalis) Bulls. Food Sci. Anim. Resour. 2021, 41, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juárez, M.; Basarab, J.A.; Baron, V.S.; Valera, M.; Larsen, I.L.; Aalhus, J.L. Quantifying the relative contribution of ante- and post-mortem factors to the variability in beef texture. Animal 2012, 6, 1878–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chardulo, L.A.L.; Silveira, A.C.; Vianello, F. Analytical aspects for tropical meat quality assessment. In Food Quality, Safety and Technology; Lima, G.P.P., Vianello, F., Eds.; Springer: Vienna, Austria, 2013; pp. 53–62. ISBN 978-3-7091-1639-5. [Google Scholar]
- Bresolin, T.; Passafaro, T.L.; Braz, C.U.; Alves, A.A.C.; Carvalheiro, R.; Chardulo, L.A.L.; de Magalhães Rosa, G.J.; de Albuquerque, L.G. Investigating potential causal relationships among carcass and meat quality traits using structural equation model in Nellore cattle. Meat Sci. 2022, 187, 108771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Wezemael, L.; De Smet, S.; Ueland, Ø.; Verbeke, W. Relationships between sensory evaluations of beef tenderness, shear force measurements and consumer characteristics. Meat Sci. 2014, 97, 310–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldassini, W.A.; Chardulo, L.A.L.L.; Silva, J.A.V.V.; Malheiros, J.M.; Dias, V.A.D.D.; Espigolan, R.; Baldi, F.S.; Albuquerque, L.G.; Fernandes, T.T.; Padilha, P.M. Meat quality traits of Nellore bulls according to different degrees of backfat thickness: A multivariate approach. Anim. Prod. Sci. 2017, 57, 363–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Júnior, G.A.F.; Garcia, D.A.; Hortolani, B.; de Albuquerque, L.G. Phenotypic relationship of female sexual precocity with production and reproduction traits in beef cattle using multivariate statistical techniques. Ital. J. Anim. Sci. 2019, 18, 182–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sørheim, O.; Idland, J.; Halvorsen, E.C.; Frøystein, T.; Lea, P.; Hildrum, K.I. Influence of beef carcass stretching and chilling rate on tenderness of m. longissimus dorsi. Meat Sci. 2001, 57, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, J. Managing meat tenderness. Meat Sci. 2002, 62, 295–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
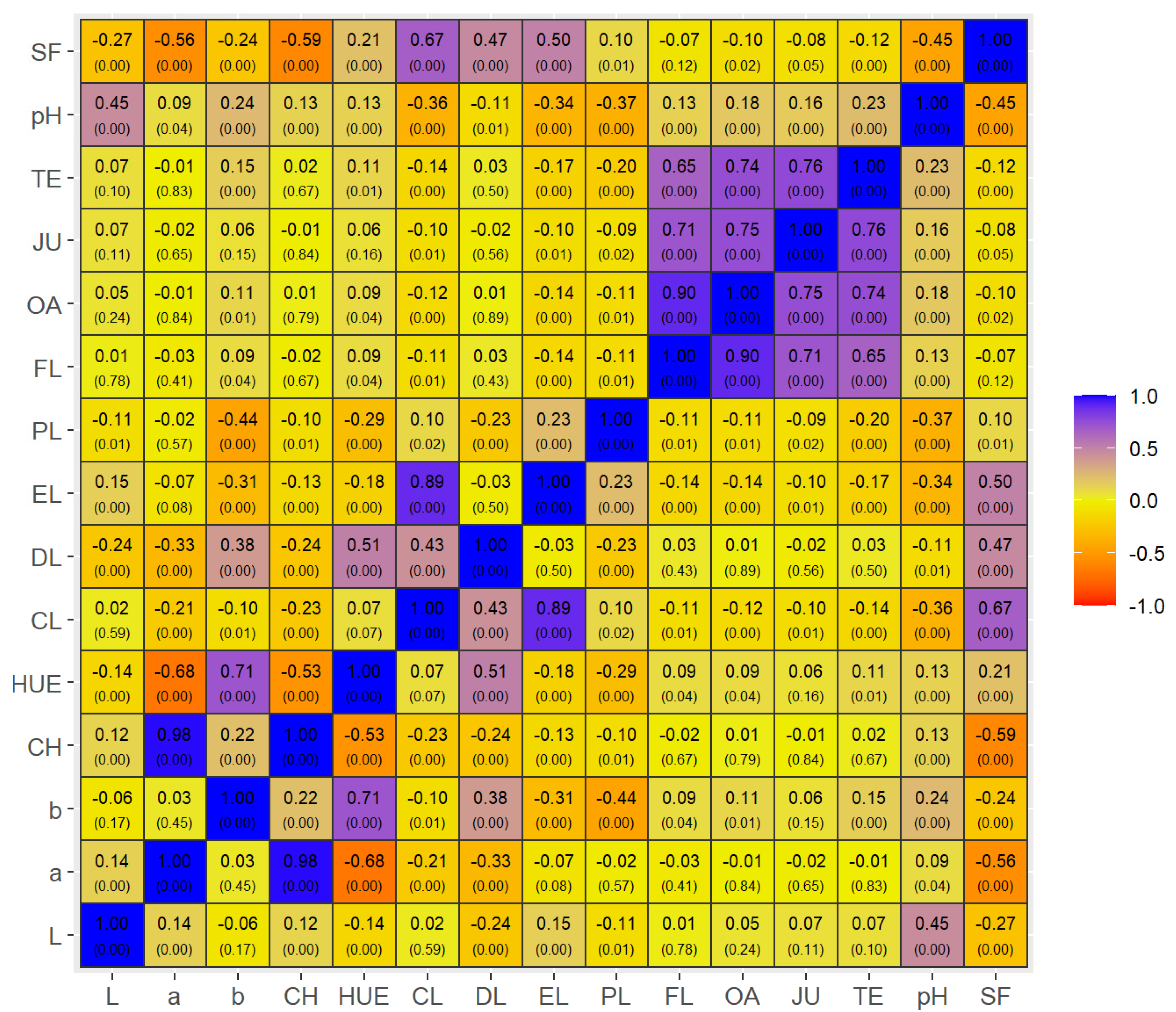
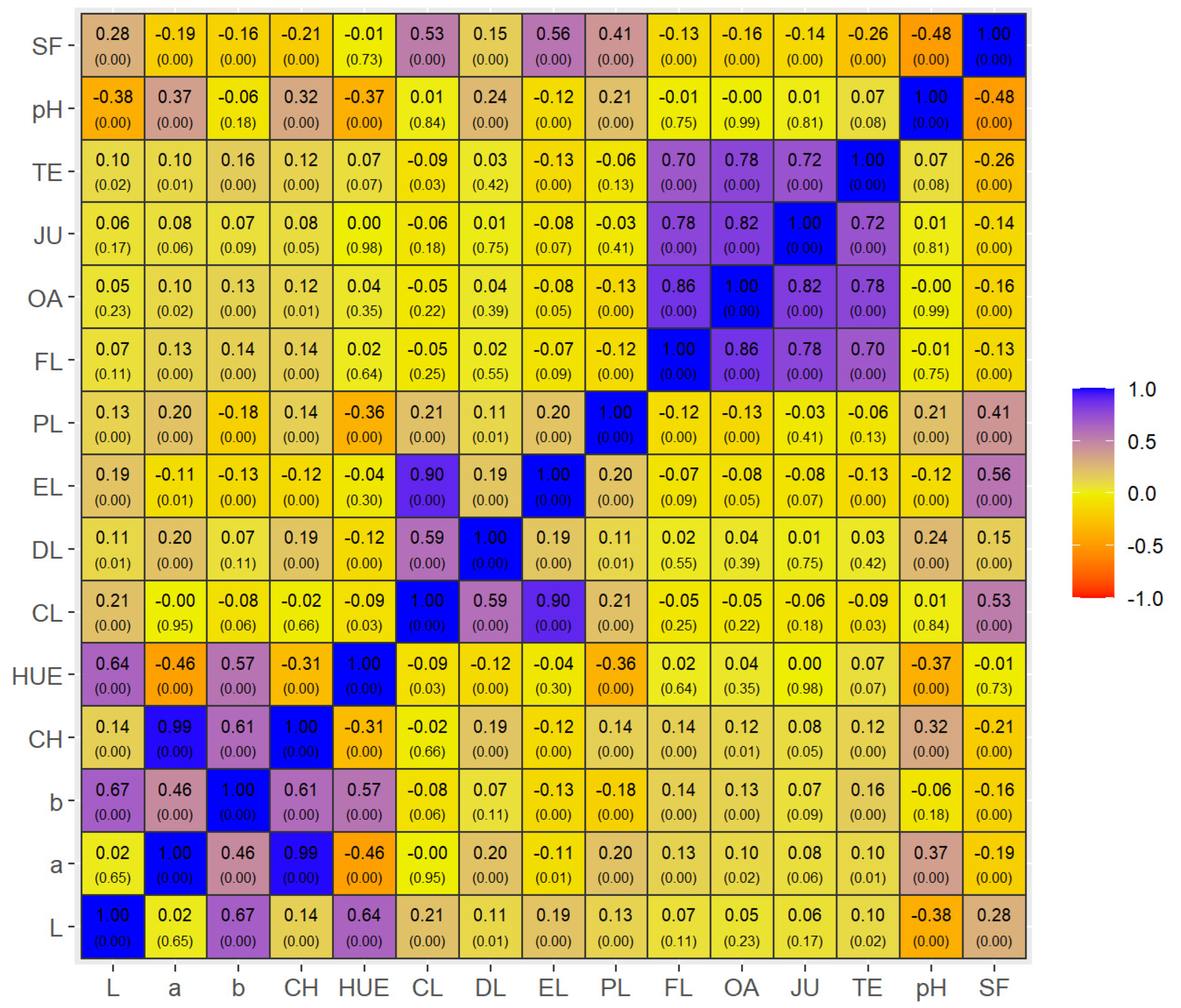


| Variables a | Nellore Bulls (Bos indicus) | Brangus Heifers (Bos taurus × Bos indicus) | p-Value e | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | SD | Mean | SD | ||
| Fatness score | 2.50 | 0.55 | 3.50 | 0.84 | 0.034 |
| Ribeye area, cm² | 87.67 | 7.92 | 72.67 | 6.44 | <0.01 |
| Conformation score | 3.17 | 0.75 | 3.17 | 0.41 | ns |
| Hump height, mm | 166.67 | 10.33 | 54.60 | 28.95 | <0.01 |
| Dental maturity b | 3.67 | 0.82 | 1.67 | 1.51 | 0.170 |
| Backfat thickness c, mm | 4.17 | 1.83 | 8.00 | 2.61 | 0.014 |
| Marbling score d | 108.33 | 20.41 | 301.67 | 53.07 | <0.01 |
| Ossification score | 196.67 | 25.03 | 180.00 | 31.62 | ns |
| Hot carcass weight, kg | 369.97 | 8.96 | 264.87 | 14.15 | <0.01 |
| Final pH (48 h) | 5.39 | 0.05 | 5.50 | 0.06 | ns |
| Carcass-Suspension Method | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Achilles Tendon | Pelvic Suspension | p-Value a | |||||||||
| Aging Period | |||||||||||
| Variables | 5 d | 15 d | 5 d | 15 d | |||||||
| Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | S | A | S × A | |
| Sensory | |||||||||||
| Tenderness | 61.02 a | 16.08 | 74.55 c | 13.96 | 69.85 b | 15.12 | 76.68 d | 14.08 | 0.003 | <0.001 | 0.099 |
| Liking of flavor | 63.55 a | 14.23 | 75.08 b | 11.26 | 70.61 a | 14.96 | 72.00 b | 11.86 | 0.230 | <0.001 | 0.005 |
| Juiciness | 62.80 a | 13.76 | 71.79 b | 12.72 | 70.02 a | 14.75 | 71.01 b | 14.22 | 0.085 | 0.002 | 0.017 |
| Overall acceptance | 64.45 a | 13.61 | 76.00 c | 12.02 | 71.79 b | 13.31 | 75.28 d | 11.71 | 0.058 | <0.001 | 0.017 |
| Objective | |||||||||||
| Redness (a *) | 13.42 | 0.60 | 12.52 | 1.15 | 13.92 | 0.75 | 13.05 | 0.65 | ns | ns | ns |
| Yellowness (b *) | 5.54 | 0.42 | 5.58 | 0.33 | 5.54 | 0.42 | 5.61 | 0.43 | ns | ns | ns |
| Lightness (L *) | 30.34 | 1.75 | 31.03 | 1.76 | 30.82 | 1.81 | 31.16 | 2.53 | ns | ns | ns |
| Hue | 21.33 | 1.26 | 24.16 | 2.77 | 21.70 | 0.78 | 23.30 | 2.06 | ns | ns | ns |
| Chroma | 14.41 | 0.65 | 13.72 | 0.10 | 14.98 | 0.83 | 14.21 | 0.59 | ns | ns | ns |
| Meat pH | 5.46 | 0.05 | 5.53 | 0.03 | 5.49 | 0.01 | 5.53 | 0.04 | ns | ns | ns |
| Drip loss, % | 6.01 | 0.01 | 6.70 | 0.01 | 5.10 | 1.5 | 5.8 | 1.5 | ns | ns | ns |
| Evaporation loss, % | 25.90 | 2.01 | 24.20 | 2.10 | 24.90 | 2.91 | 21.90 | 3.10 | ns | ns | ns |
| Cooking loss, % | 32.01 a | 3.01 | 30.90 b | 1.61 | 30.10 b | 3.01 | 27.70 c | 3.60 | 0.042 | 0.167 | 0.578 |
| Purge loss, % | 3.40 | 1.60 | 2.80 | 1.10 | 3.40 | 1.60 | 2.60 | 1.10 | ns | ns | ns |
| Shear force, N | 50.40 a | 8.04 | 48.34 b | 7.35 | 44.62 c | 6.96 | 42.95 c | 5.00 | 0.061 | 0.521 | 0.952 |
| Carcass-Suspension Method | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Achilles Tendon | Pelvic Suspension | p-Value a | |||||||||
| Aging Period | |||||||||||
| Variables | 5 d | 15 d | 5 d | 15 d | |||||||
| Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | S | A | S × A | |
| Sensory | |||||||||||
| Tenderness | 68.15 a | 20.43 | 70.30 a | 15.11 | 76.75 b | 16.91 | 75.56 b | 11.13 | <0.001 | 0.936 | 0.372 |
| Liking of flavor | 71.95 a | 16.06 | 67.80 c | 10.95 | 76.48 b | 15.62 | 69.83 c | 12.61 | 0.057 | 0.003 | 0.416 |
| Juiciness | 69.55 | 14.98 | 68.02 | 12.58 | 72.81 | 16.20 | 69.02 | 12.64 | ns | ns | ns |
| Overall acceptance | 73.38 a | 15.70 | 71.31 a | 11.96 | 77.96 b | 14.98 | 73.03 b | 11.93 | 0.063 | 0.083 | 0.445 |
| Objective | |||||||||||
| Redness (a *) | 13.48 | 1.29 | 12.13 | 0.70 | 14.28 | 1.13 | 12.77 | 1.87 | ns | ns | ns |
| Yellowness (b *) | 5.53 | 0.83 | 5.50 | 0.46 | 5.98 | 0.86 | 5.91 | 0.60 | ns | ns | ns |
| Lightness (L *) | 32.13 | 4.67 | 33.68 | 4.25 | 33.80 | 4.19 | 33.52 | 3.93 | ns | ns | ns |
| Hue | 22.26 | 1.94 | 24.42 | 2.05 | 22.65 | 2.27 | 25.05 | 3.25 | ns | ns | ns |
| Chroma | 14.58 | 1.45 | 13.32 | 0.69 | 15.49 | 1.27 | 14.09 | 1.79 | ns | ns | ns |
| Meat pH | 5.47 | 0.03 | 5.51 | 0.06 | 5.52 | 0.04 | 5.50 | 0.05 | ns | ns | ns |
| Drip loss, % | 6.60 | 1.90 | 5.80 | 1.40 | 6.40 | 0.70 | 6.01 | 1.80 | ns | ns | ns |
| Evaporation loss, % | 21.40 | 4.01 | 19.40 | 2.60 | 20.70 | 2.40 | 21.20 | 1.60 | ns | ns | ns |
| Cooking loss, % | 28.00 | 4.70 | 25.10 | 3.10 | 27.00 | 2.80 | 27.20 | 2.20 | ns | ns | ns |
| Purge loss, % | 1.20 | 0.60 | 1.90 | 1.50 | 2.10 | 1.70 | 2.10 | 2.80 | ns | ns | ns |
| Shear force, N | 35.89 | 9.22 | 31.87 | 5.58 | 35.99 | 7.55 | 32.95 | 6.18 | ns | ns | ns |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Baldassini, W.; Coutinho, M.; Rovadoscki, G.; Menezes, B.; Tagiariolli, M.; Torrecilhas, J.; Leonel, J.; Pereira, G.; Curi, R.; Machado Neto, O.; et al. Bos indicus Carcasses Suspended by the Pelvic Bone Require a Shorter Aging Time to Meet Consumer Expectations Regarding Meat Quality. Foods 2023, 12, 930. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12050930
Baldassini W, Coutinho M, Rovadoscki G, Menezes B, Tagiariolli M, Torrecilhas J, Leonel J, Pereira G, Curi R, Machado Neto O, et al. Bos indicus Carcasses Suspended by the Pelvic Bone Require a Shorter Aging Time to Meet Consumer Expectations Regarding Meat Quality. Foods. 2023; 12(5):930. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12050930
Chicago/Turabian StyleBaldassini, Welder, Marcelo Coutinho, Gregori Rovadoscki, Bruna Menezes, Murilo Tagiariolli, Juliana Torrecilhas, Júlia Leonel, Guilherme Pereira, Rogério Curi, Otávio Machado Neto, and et al. 2023. "Bos indicus Carcasses Suspended by the Pelvic Bone Require a Shorter Aging Time to Meet Consumer Expectations Regarding Meat Quality" Foods 12, no. 5: 930. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12050930
APA StyleBaldassini, W., Coutinho, M., Rovadoscki, G., Menezes, B., Tagiariolli, M., Torrecilhas, J., Leonel, J., Pereira, G., Curi, R., Machado Neto, O., & Chardulo, L. A. (2023). Bos indicus Carcasses Suspended by the Pelvic Bone Require a Shorter Aging Time to Meet Consumer Expectations Regarding Meat Quality. Foods, 12(5), 930. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12050930










