Combined Effects of Acrylamide and Ochratoxin A on the Intestinal Barrier in Caco-2 Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Cell Culture
2.3. Cell Viability
2.4. LDH Assay
2.5. Transepithelial Electrical Resistance (TEER) Assay
2.6. Paracellular Flux Assay
2.7. Detection of Production Level of ROS
2.8. ELISA Assay
2.9. Western Blot Analysis
2.10. Interaction and Correlation Analysis
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
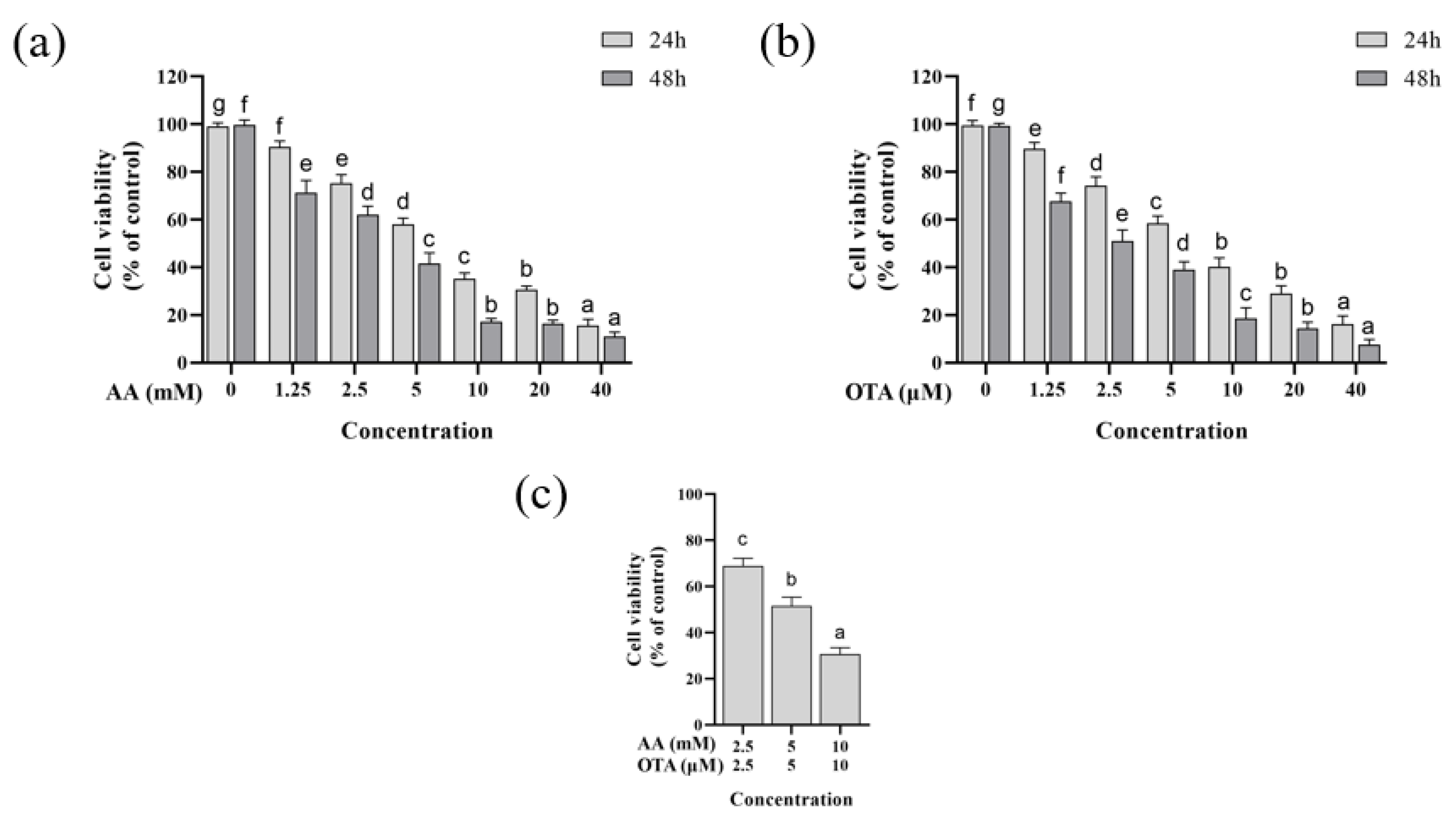
3.1. Cytotoxicity
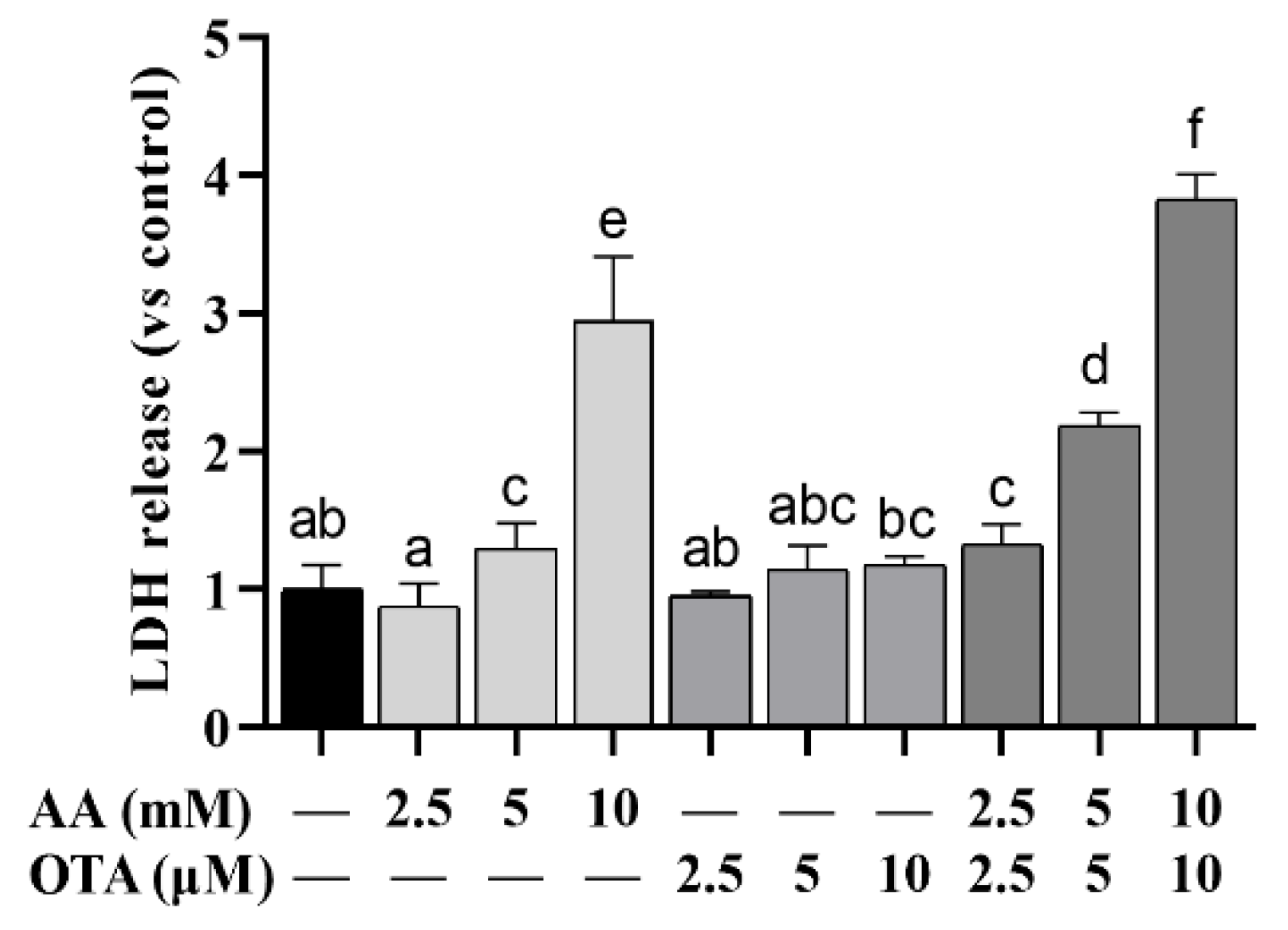
3.2. The LDH Leakage of Caco-2 Cells
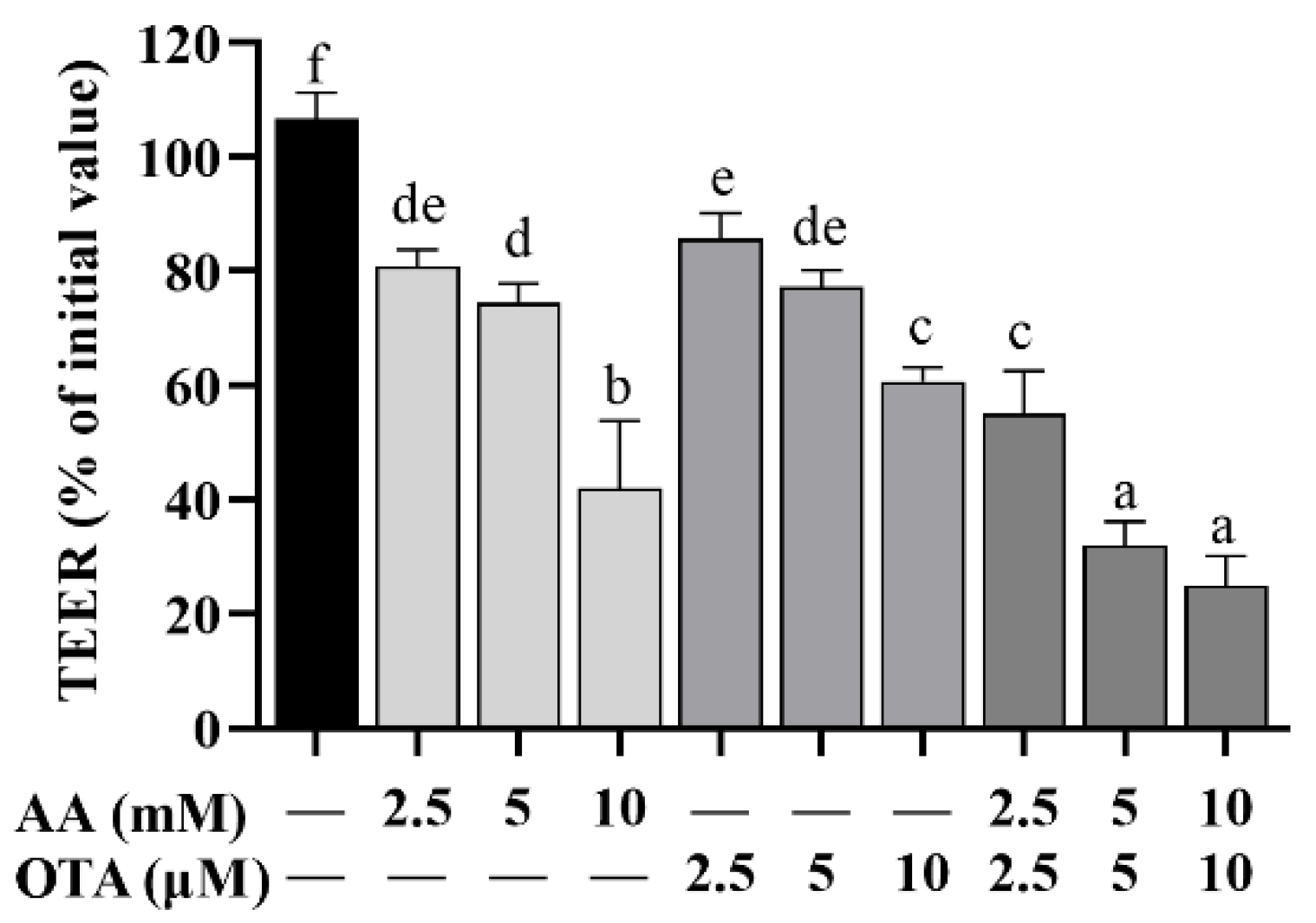
3.3. The TEER Values of Caco-2 Cells
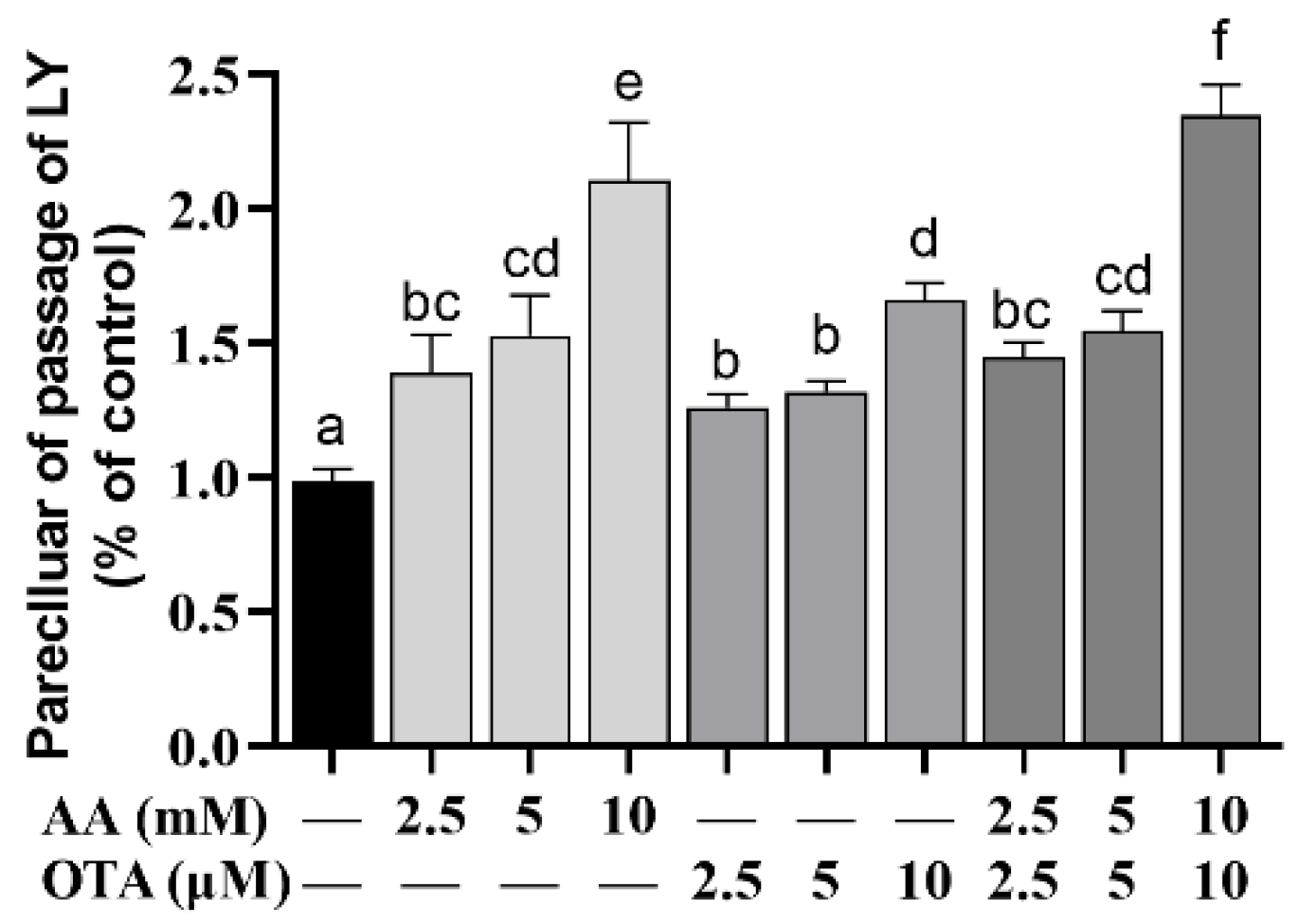
3.4. The Permeability of Caco-2 Cells
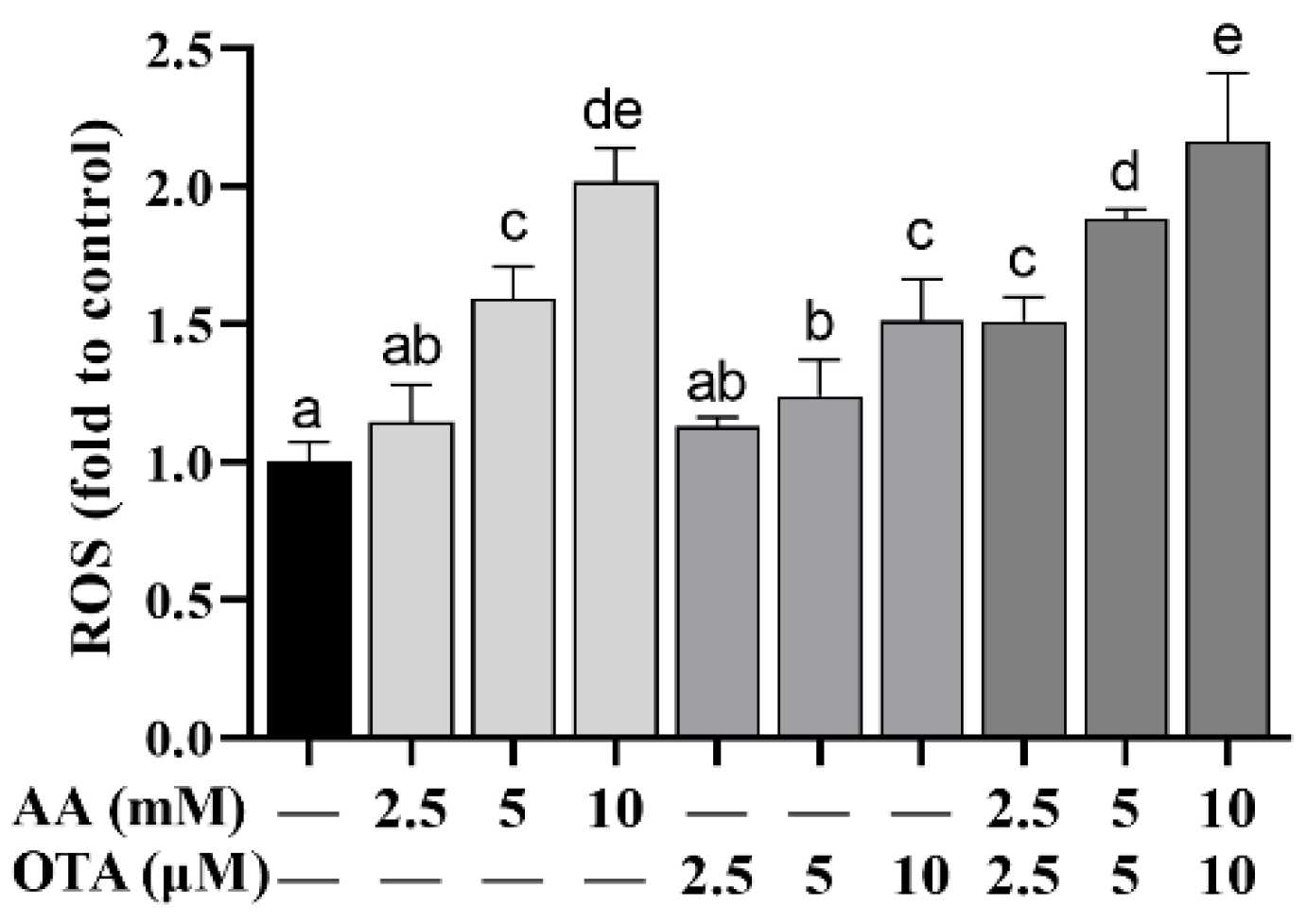
3.5. The ROS Level of Caco-2 Cells
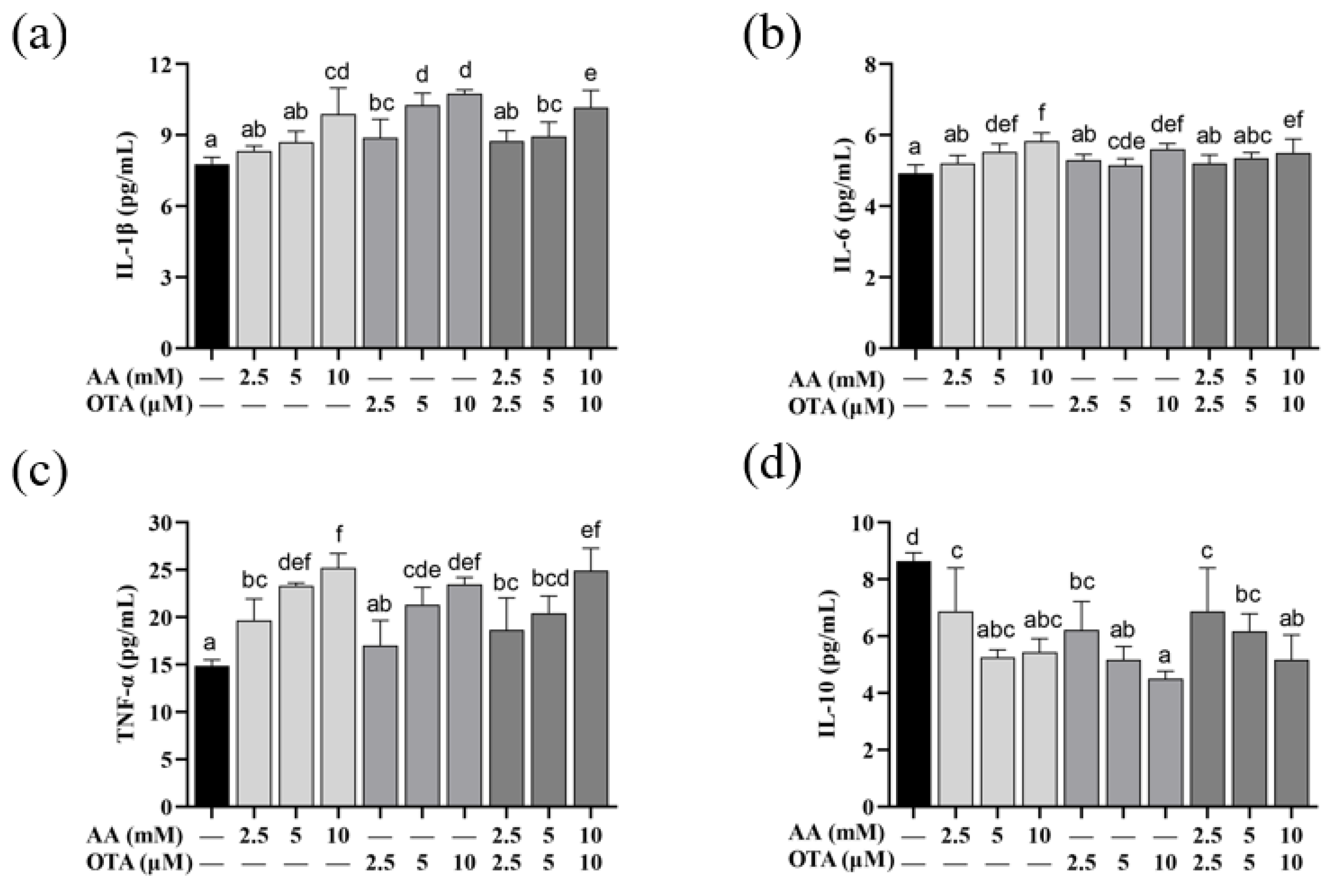
3.6. The Secretion of Inflammatory Cytokines of Caco-2 Cells
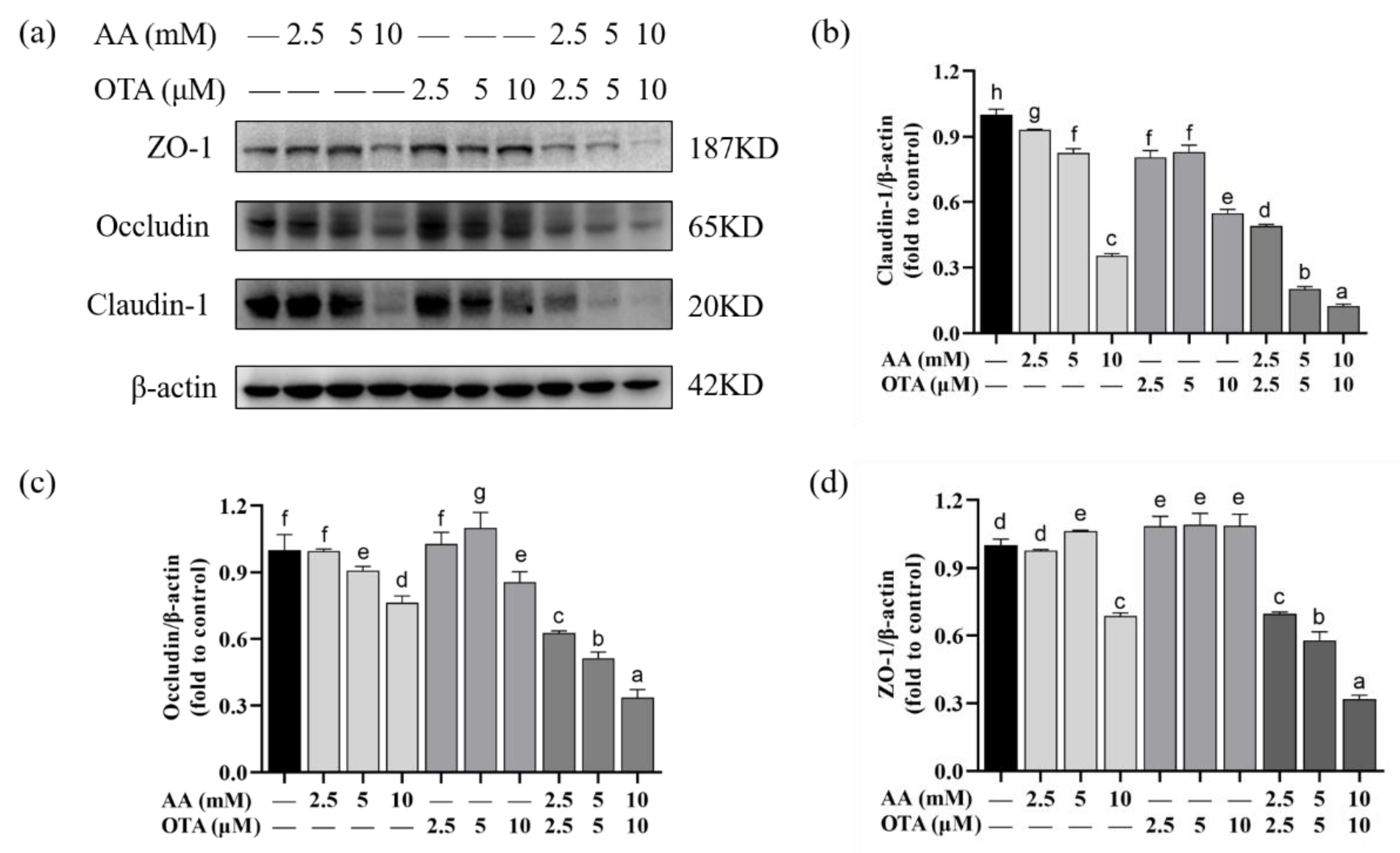
3.7. The TJ Protein Expression of Caco-2 Cells
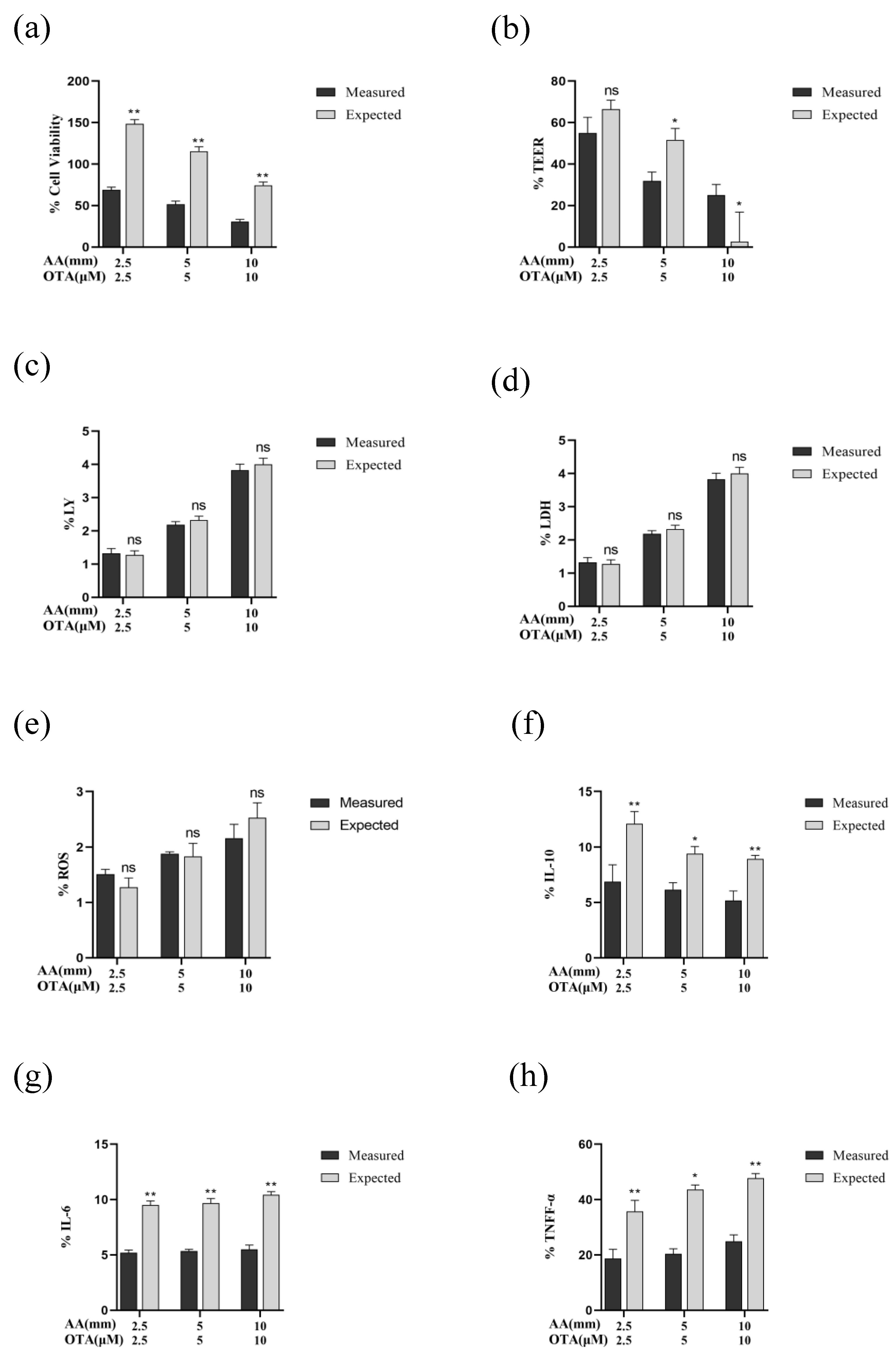
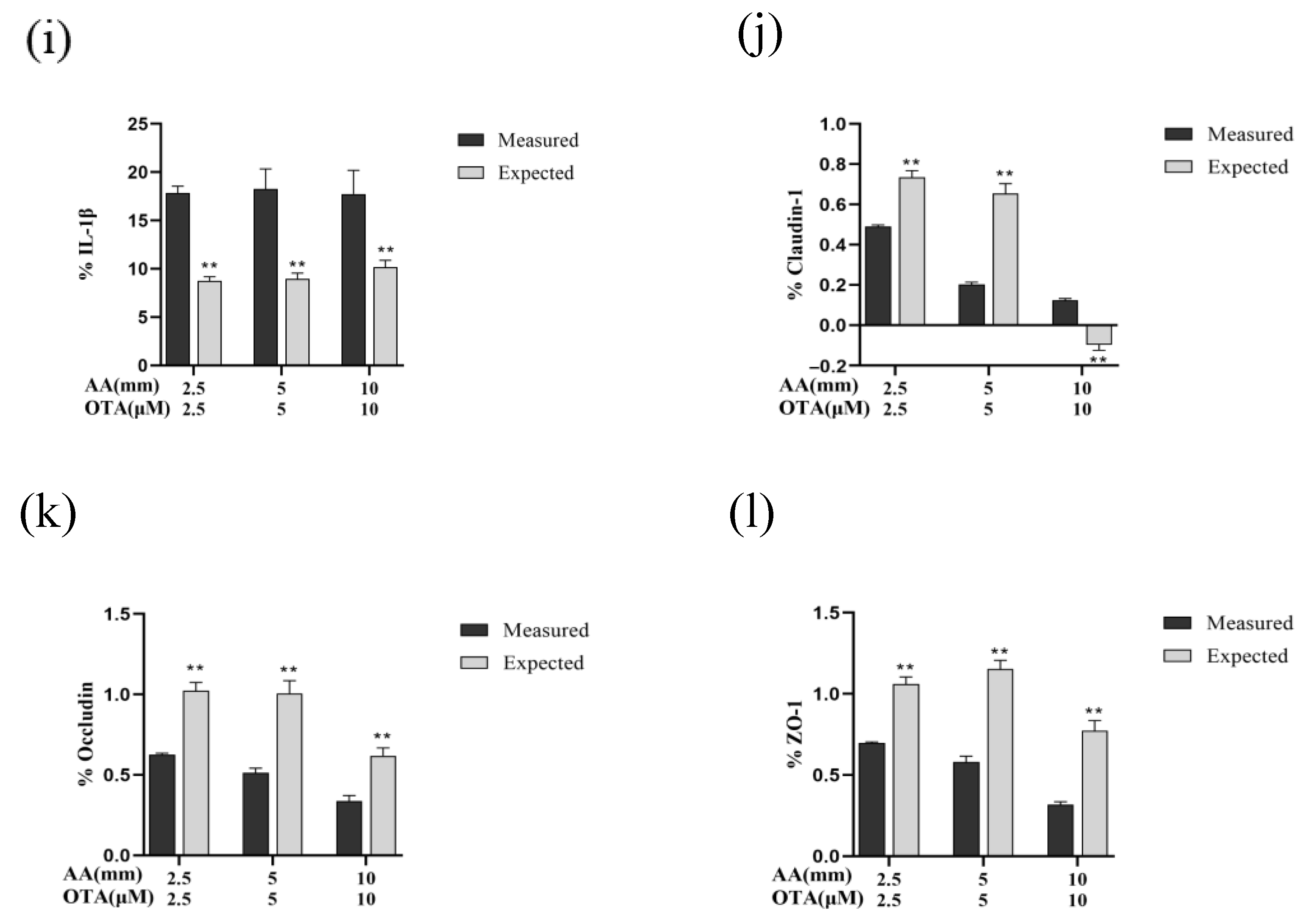
3.8. The Interactive Effects of the Combined Treatment of AA and OTA
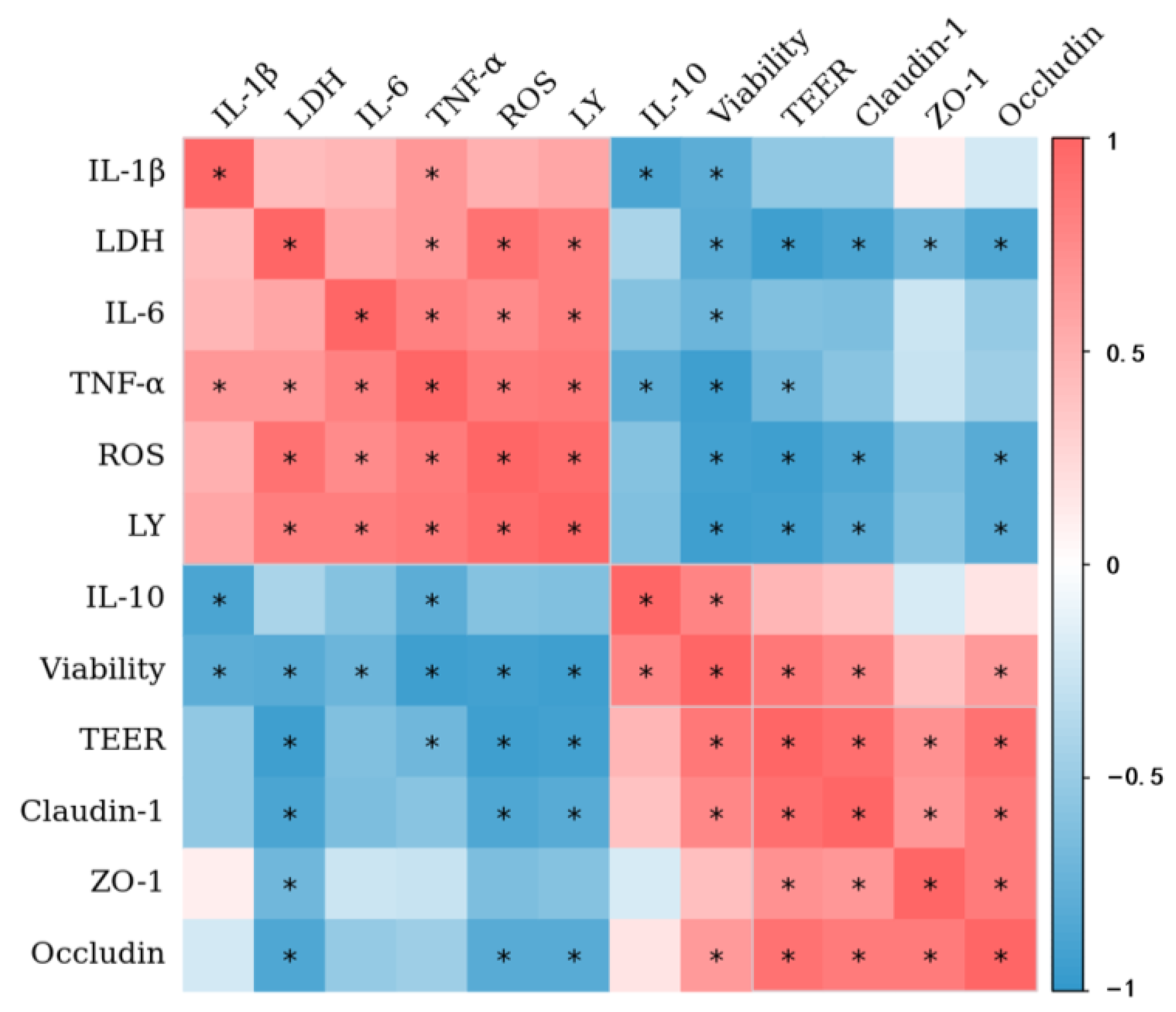
3.9. Correlation Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Molognoni, L.; Daguer, H.; Motta, G.E.; Merlo, T.C.; Lindner, J.D. Interactions of preservatives in meat processing: Formation of carcinogenic compounds, analytical methods, and inhibitory agents. Food Res. Int. 2019, 125, 108608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano-Niño, J.C.; Cavazos-Garduño, A.; González-Córdova, A.F.; Vallejo-Cordoba, B.; Hernández-Mendoza, A.; García, H.S. In vitro study of the potential protective role of lactobacillus strains by acrylamide binding. J. Food Saf. 2014, 34, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faria, M.; Ziv, T.; Gomez-Canela, C.; Ben-Lulu, S.; Prats, E.; Novoa-Luna, K.A.; Admon, A.; Pina, B.; Tauler, R.; Gomez-Olivan, L.M.; et al. Acrylamide acute neurotoxicity in adult zebrafish. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 7918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Li, M.; Zou, F.; Bai, S.; Jiang, X.; Tian, L.; Ou, S.; Jiao, R.; Bai, W. Protection of cyanidin-3-O-glucoside against acrylamide- and glycidamide-induced reproductive toxicity in leydig cells. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2018, 119, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liu, J.; Wang, Y.; Wei, S. Cancer risk and disease burden of dietary acrylamide exposure in China, 2016. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 238, 113551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu-xiang, N.; Fei, X.; Jian, S.; Rui-xue, Y.; Hong, Z. Factors influencing acrylamide formation during frying of food and their reduction. Jiangsu J. Agr. Sci. 2011, 27, 1405–1410. [Google Scholar]
- Cancer, I. Some Naturally Occurring Substances: Food Items and Constituents, Heterocyclic Aromatic Amines and Mycotoxins; International Agency for Research on Cancer: Lyon, France, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Alshannaq, A.; Yu, J.H. Occurrence, Toxicity, and Analysis of Major Mycotoxins in Food. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnoli, C.E.; Astoreca, A.L.; Chiacchiera, S.M.; Dalcero, A.M. Occurrence of ochratoxin A and ochratoxigenic mycoflora in corn and corn based foods and feeds in some South American countries. Mycopathologia 2007, 163, 249–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boudra, H.; Le Bars, P.; Le Bars, J. Thermostability of ochratoxin A in wheat under two moisture conditions. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1995, 61, 1156–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, H.S.; Brasel, J.M. Toxicity, metabolism, and impact of mycotoxins on humans and animals. Toxicology 2001, 167, 101–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, S.Z.; Nisar, S.; Asi, M.R.; Jinap, S. Natural incidence of aflatoxins, ochratoxin A and zearalenone in chicken meat and eggs. Food Control. 2014, 43, 98–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostry, V.; Malir, F.; Toman, J.; Grosse, Y. Mycotoxins as human carcinogens-the IARC Monographs classification. Mycotoxin Res. 2017, 33, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantle, P. Risk assessment and the importance of ochratoxins. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2002, 50, 143–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maaroufi, K.; Achour, A.; Betbeder, A.; Hammami, M.; Ellouz, F.; Creppy, E.; Bacha, H. Foodstuffs and human blood contamination by the mycotoxin ochratoxin A: Correlation with chronic interstitial nephropathy in Tunisia. Arch. Toxicol. 1995, 69, 552–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svensson, K.; Abramsson, L.; Becker, W.; Glynn, A.; Hellenäs, K.-E.; Lind, Y.; Rosen, J. Dietary intake of acrylamide in Sweden. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2003, 41, 1581–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogdanova, E.; Rozentale, I.; Pugajeva, I.; Emecheta, E.E.; Bartkevics, V. Occurrence and risk assessment of mycotoxins, acrylamide, and furan in Latvian beer. Food Addit. Contam. Part B 2018, 11, 126–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobrowolski, P.; Huet, P.; Karlsson, P.; Eriksson, S.; Tomaszewska, E.; Gawron, A.; Pierzynowski, S.G. Potato fiber protects the small intestinal wall against the toxic influence of acrylamide. Nutrition 2012, 28, 428–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhai, S.; Zhu, Y.; Feng, P.; Li, M.; Wang, W.; Yang, L.; Yang, Y. Ochratoxin A: Its impact on poultry gut health and microbiota, an overview. Poult. Sci. 2021, 100, 101037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pernice, R.; Hauder, J.; Koehler, P.; Vitaglione, P.; Fogliano, V.; Somoza, V. Effect of sulforaphane on glutathione-adduct formation and on glutathione_S_transferase-dependent detoxification of acrylamide in Caco-2 cells. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2009, 53, 1540–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romero, A.; Ares, I.; Ramos, E.; Castellano, V.; Martinez, M.; Martinez-Larranaga, M.R.; Anadon, A.; Martinez, M.A. Mycotoxins modify the barrier function of Caco-2 cells through differential gene expression of specific claudin isoforms: Protective effect of illite mineral clay. Toxicology 2016, 353–354, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ficheux, A.S.; Sibiril, Y.; Parent-Massin, D. Co-exposure of Fusarium mycotoxins: In vitro myelotoxicity assessment on human hematopoietic progenitors. Toxicon 2012, 60, 1171–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bensassi, F.; Gallerne, C.; Sharaf el Dein, O.; Hajlaoui, M.R.; Lemaire, C.; Bacha, H. In vitro investigation of toxicological interactions between the fusariotoxins deoxynivalenol and zearalenone. Toxicon 2014, 84, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.J.; Ryu, D. Significance of Ochratoxin A in Breakfast Cereals from the United States. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 9404–9409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.J.; Gu, B.-J.; Ganjyal, G.; Ryu, D. Reduction of ochratoxin A in direct steam injected oat-based infant cereals with baking soda. Food Control. 2019, 96, 441–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkhalifah, D.H.; EL-Sideek, L.E.; Deabes, M.M.; Elgammal, M.H.; Farag Zaied, S.A. Comparing effect of Egyptian, Saudi Arabian coffee cup preparations on Ochratoxin A and Acrylamide content. Int. J. Acad. Res. 2013, 5, 168–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seal, C.J.; de Mul, A.; Eisenbrand, G.; Haverkort, A.; Franke, K.; Lalljie, S.; Mykkänen, H.; Reimerdes, E.; Scholz, G.; Somoza, V. Risk-benefit considerations of mitigation measures on acrylamide content of foods—A case study on potatoes, cereals and coffee. Br. J. Nutr. 2008, 99, S1–S46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chulze, S.N. Strategies to reduce mycotoxin levels in maize during storage: A review. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2010, 27, 651–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zilic, S.; Nikolic, V.; Mogol, B.A.; Hamzalioglu, A.; Tas, N.G.; Kocadagli, T.; Simic, M.; Gokmen, V. Acrylamide in Corn-Based Thermally Processed Foods: A Review. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 4165–4181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fotakis, G.; Timbrell, J.A. In vitro cytotoxicity assays: Comparison of LDH, neutral red, MTT and protein assay in hepatoma cell lines following exposure to cadmium chloride. Toxicol. Lett. 2006, 160, 171–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Li, S.; Wang, J.; Luo, C.; Zhao, S.; Zheng, N. Modulation of Intestinal Epithelial Permeability in Differentiated Caco-2 Cells Exposed to Aflatoxin M1 and Ochratoxin A Individually or Collectively. Toxins 2017, 10, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, G.; Zhang, L.; Wang, H.; Chen, Q.; Wu, X.; Yan, X.; Chen, Y.; Xie, M. Protective effects of a Ganoderma atrum polysaccharide against acrylamide induced oxidative damage via a mitochondria mediated intrinsic apoptotic pathway in IEC-6 cells. Food Funct. 2018, 9, 1133–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heussner, A.H.; Dietrich, D.R.; O’Brien, E. In vitro investigation of individual and combined cytotoxic effects of ochratoxin A and other selected mycotoxins on renal cells. Toxicol. Vitr. 2006, 20, 332–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clarke, R.; Connolly, L.; Frizzell, C.; Elliott, C.T. Cytotoxic assessment of the regulated, co-existing mycotoxins aflatoxin B1, fumonisin B1 and ochratoxin, in single, binary and tertiary mixtures. Toxicon 2014, 90, 70–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pyo, M.C.; Shin, H.S.; Jeon, G.Y.; Lee, K.W. Synergistic Interaction of Ochratoxin A and Acrylamide Toxins in Human Kidney and Liver Cells. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2020, 43, 1346–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iftikhar, M.; Iftikhar, A.; Zhang, H.; Gong, L.; Wang, J. Transport, metabolism and remedial potential of functional food extracts (FFEs) in Caco-2 cells monolayer: A review. Food Res. Int. 2020, 136, 109240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaut, A.; De Saeger, S.; Sergent, T.; Schneider, Y.J.; Larondelle, Y.; Pussemier, L.; Van Peteghem, C. Study of the gastrointestinal biotransformation of zearalenone in a Caco-2 cell culture system with liquid chromatographic methods. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2008, 28, 966–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamiloglu, S.; Capanoglu, E.; Grootaert, C.; Van Camp, J. Anthocyanin absorption and metabolism by human intestinal Caco-2 cells—A review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 21555–21574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assunção, R.; Ferreira, M.; Martins, C.; Diaz, I.; Padilla, B.; Dupont, D.; Bragança, M.; Alvito, P. Applicability of in vitro methods to study patulin bioaccessibility and its effects on intestinal membrane integrity. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health Part A 2014, 77, 983–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, M.C.; Gheux, A.; Coton, M.; Madec, S.; Hymery, N.; Coton, E. In vitro co-culture models to evaluate acute cytotoxicity of individual and combined mycotoxin exposures on Caco-2, THP-1 and HepaRG human cell lines. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2018, 281, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okumura, R.; Takeda, K. Maintenance of intestinal homeostasis by mucosal barriers. Inflamm. Regen. 2018, 38, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Gao, Y.; Li, S.; Wu, C.; Wang, J.; Zheng, N. Modulation of Mucin (MUC2, MUC5AC and MUC5B) mRNA Expression and Protein Production and Secretion in Caco-2/HT29-MTX Co-Cultures Following Exposure to Individual and Combined Aflatoxin M1 and Ochratoxin A. Toxins 2019, 11, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camilleri, M. Leaky gut: Mechanisms, measurement and clinical implications in humans. Gut 2019, 68, 1516–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Zhang, L.; Wu, T.; Li, Y.; Zhou, X.; Ruan, Z. Indole-3-propionic Acid Improved the Intestinal Barrier by Enhancing Epithelial Barrier and Mucus Barrier. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 1487–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, T. Regulation of intestinal epithelial permeability by tight junctions. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2013, 70, 631–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, F.; Chen, W.; Zhao, L.; Lu, Q.; Wang, C.; Liu, R. Procyanidin A 1 and its digestive products prevent acrylamide-induced intestinal barrier dysfunction via the MAPK-mediated MLCK pathway. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 11956–11965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alizadeh, A.; Akbari, P.; Varasteh, S.; Braber, S.; Malekinejad, H.; Fink-Gremmels, J. Ochratoxin A challenges the intestinal epithelial cell integrity: Results obtained in model experiments with Caco-2 cells. World Mycotoxin J. 2019, 12, 399–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLaughlin, J.; Padfield, P.J.; Burt, J.P.; O’Neill, C.A. Ochratoxin A increases permeability through tight junctions by removal of specific claudin isoforms. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2004, 287, C1412–C1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speijers, G.J.A.; Speijers, M.H.M. Combined toxic effects of mycotoxins. Toxicol. Lett. 2004, 153, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak, A.; Zaklos-Szyda, M.; Zyzelewicz, D.; Koszucka, A.; Motyl, I. Acrylamide Decreases Cell Viability, and Provides Oxidative Stress, DNA Damage, and Apoptosis in Human Colon Adenocarcinoma Cell Line Caco-2. Molecules 2020, 25, 368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yma, B.; Hk, A.; Yf, C.; My, A.; Sk, D.; Sk, C.; Mm, A.; So, A. Mechanism of reactive oxygen species generation and oxidative DNA damage induced by acrylohydroxamic acid, a putative metabolite of acrylamide. Mutat. Res./Genet. Toxicol. Environ. Mutagen. 2021, 873, 503420. [Google Scholar]
- Faucet-Marquis, V.; Pont, F.; Stormer, F.C.; Rizk, T.; Castegnaro, M.; Pfohl-Leszkowicz, A. Evidence of a new dechlorinated ochratoxin A derivative formed in opossum kidney cell cultures after pretreatment by modulators of glutathione pathways: Correlation with DNA-adduct formation. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2006, 50, 530–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tozlovanu, M.; Canadas, D.; Pfohl-Leszkowicz, A.; Frenette, C.; Paugh, R.J.; Manderville, R.A. Glutathione conjugates of ochratoxin A as biomarkers of exposure. Arch. Ind. Hyg. Toxicol. 2012, 63, 417–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.-S.; Long, T.-Y.; Chiang, S.-Y.; Wu, K.-Y. Characterization of primary glutathione conjugates with acrylamide and glycidamide: Toxicokinetic studies in Sprague Dawley rats treated with acrylamide. Chem.-Biol. Interact. 2021, 350, 109701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tedjiotsop Feudjio, F.; Dornetshuber, R.; Lemmens, M.; Hoffmann, O.; Lemmens-Gruber, R.; Berger, W. Beauvericin and enniatin: Emerging toxins and/or remedies? World Mycotoxin J. 2010, 3, 415–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Su, D.; Lu, J.; Nie, C.; Guo, Z.; Li, C.; Yu, Q.; Xie, J.; Chen, Y. Combined Effects of Acrylamide and Ochratoxin A on the Intestinal Barrier in Caco-2 Cells. Foods 2023, 12, 1318. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12061318
Su D, Lu J, Nie C, Guo Z, Li C, Yu Q, Xie J, Chen Y. Combined Effects of Acrylamide and Ochratoxin A on the Intestinal Barrier in Caco-2 Cells. Foods. 2023; 12(6):1318. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12061318
Chicago/Turabian StyleSu, Dan, Jiawen Lu, Chunchao Nie, Ziyan Guo, Chang Li, Qiang Yu, Jianhua Xie, and Yi Chen. 2023. "Combined Effects of Acrylamide and Ochratoxin A on the Intestinal Barrier in Caco-2 Cells" Foods 12, no. 6: 1318. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12061318
APA StyleSu, D., Lu, J., Nie, C., Guo, Z., Li, C., Yu, Q., Xie, J., & Chen, Y. (2023). Combined Effects of Acrylamide and Ochratoxin A on the Intestinal Barrier in Caco-2 Cells. Foods, 12(6), 1318. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12061318





