Slight Temperature Deviation during a 56-Day Storage Period Does Not Affect the Microbiota of Fresh Vacuum-Packed Pork Loins
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
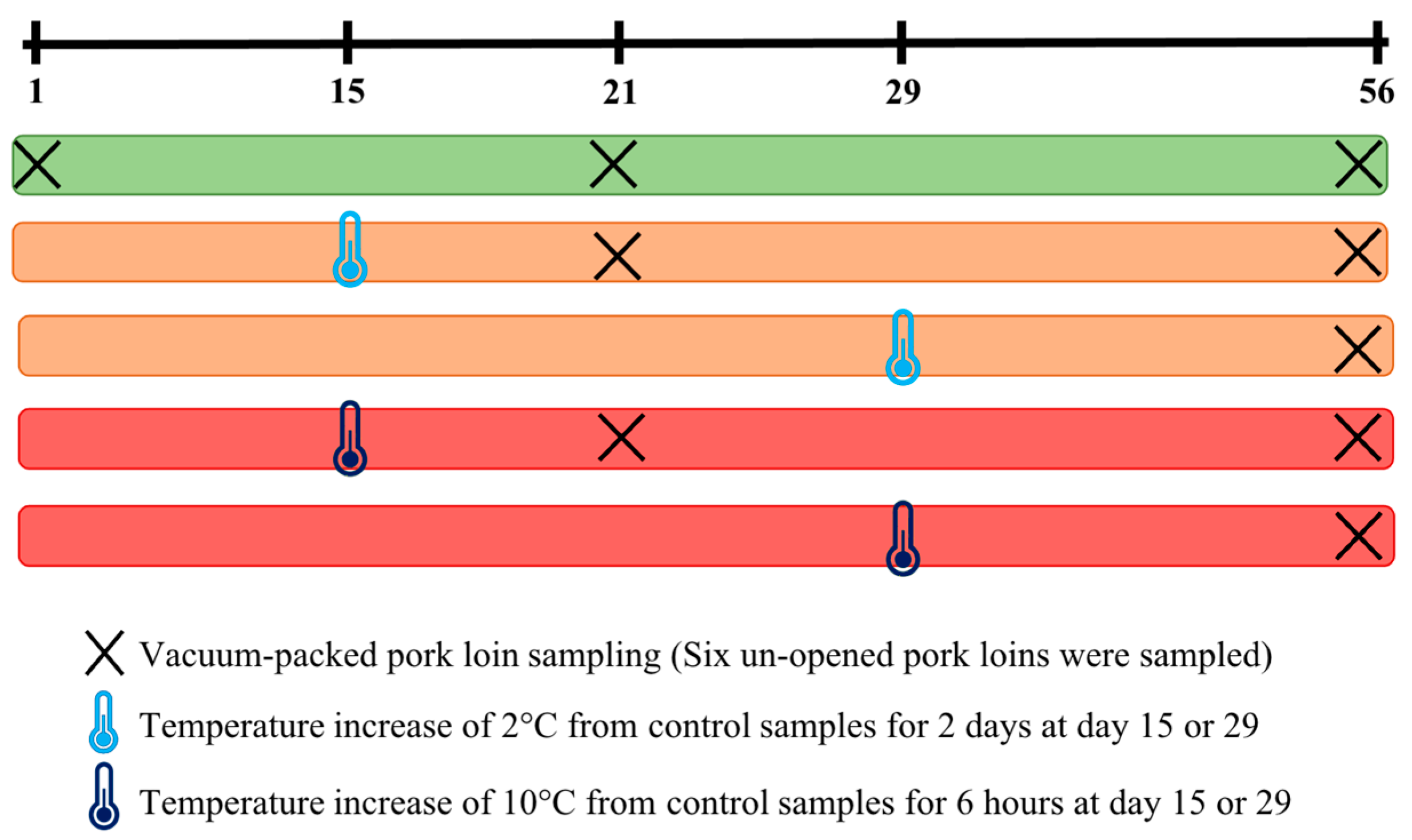
2.1. Sampling
2.2. Detection of Listeria monocytogenes and Salmonella spp.
2.2.1. Sample Preparation
2.2.2. Detection
2.3. 16S rRNA Gene Amplicon Sequencing
2.3.1. Sample Preparation
2.3.2. DNA Extraction, PCR Amplification, and Sequencing
2.3.3. Sequencing Data Processing
2.3.4. Sequencing and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Pathogen Detection
3.2. Sequencing Data
3.3. Evolution of the Microbiota of the Control Vacuum-Packed Loins
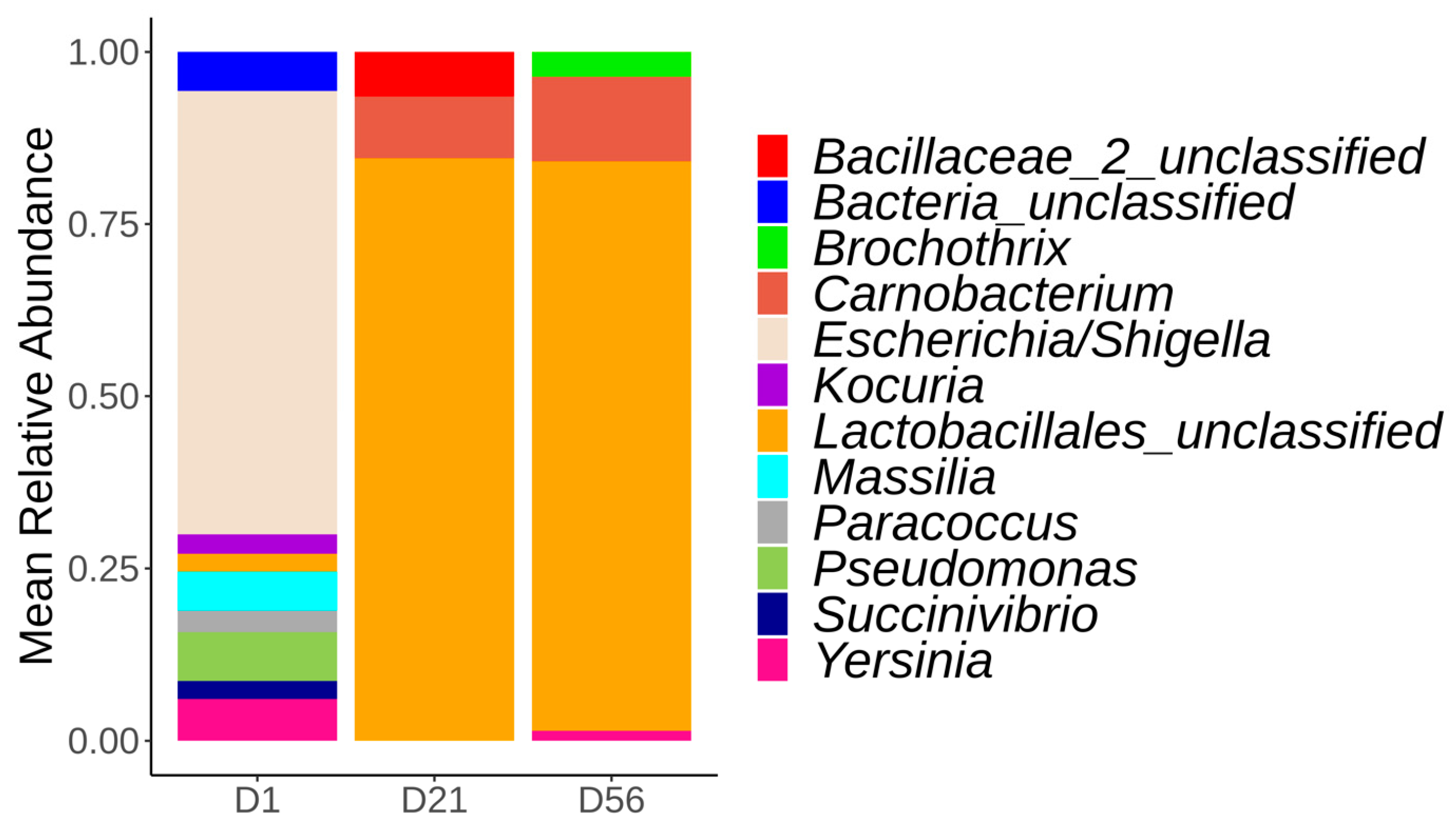
3.3.1. Bacterial Composition
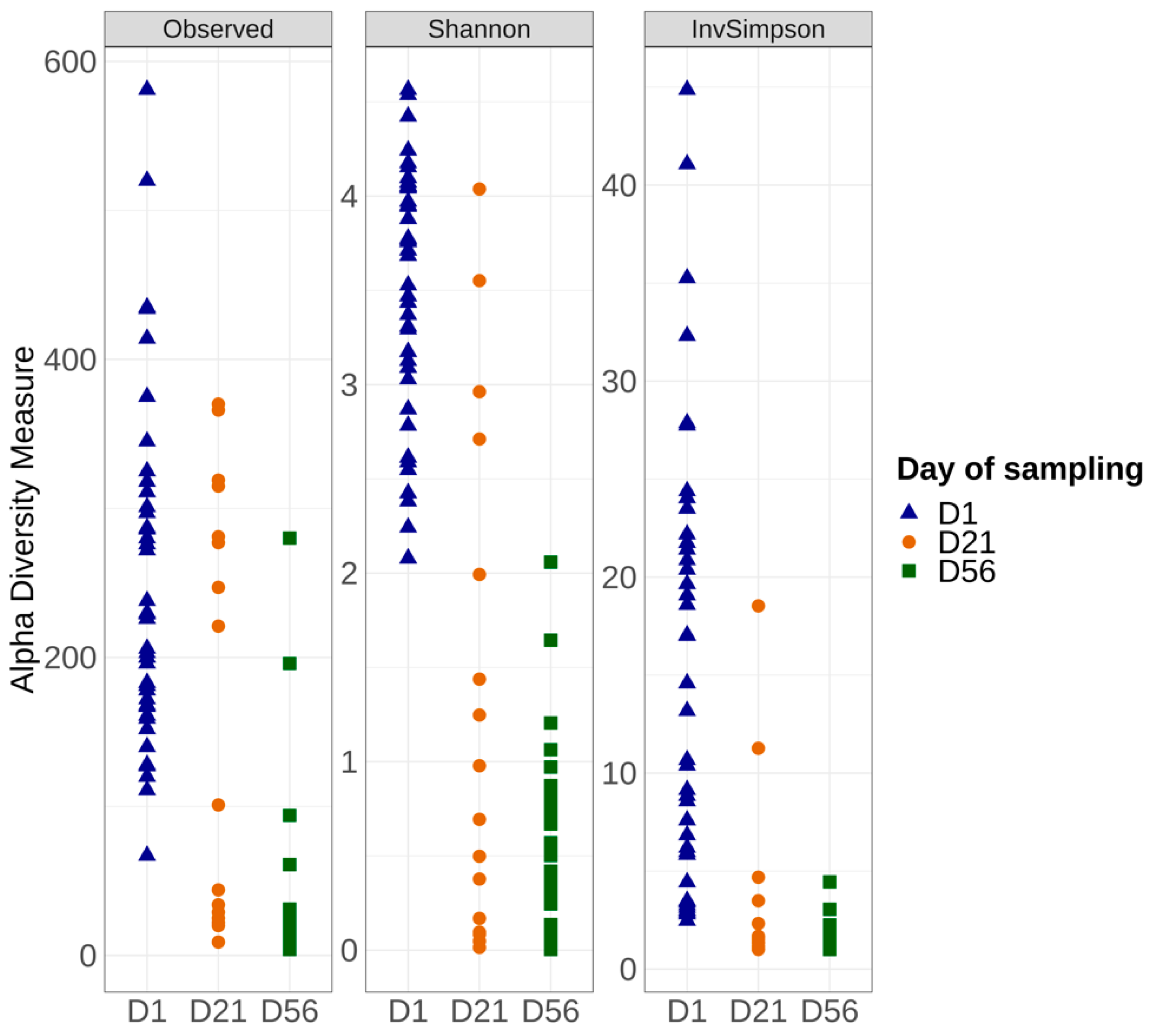
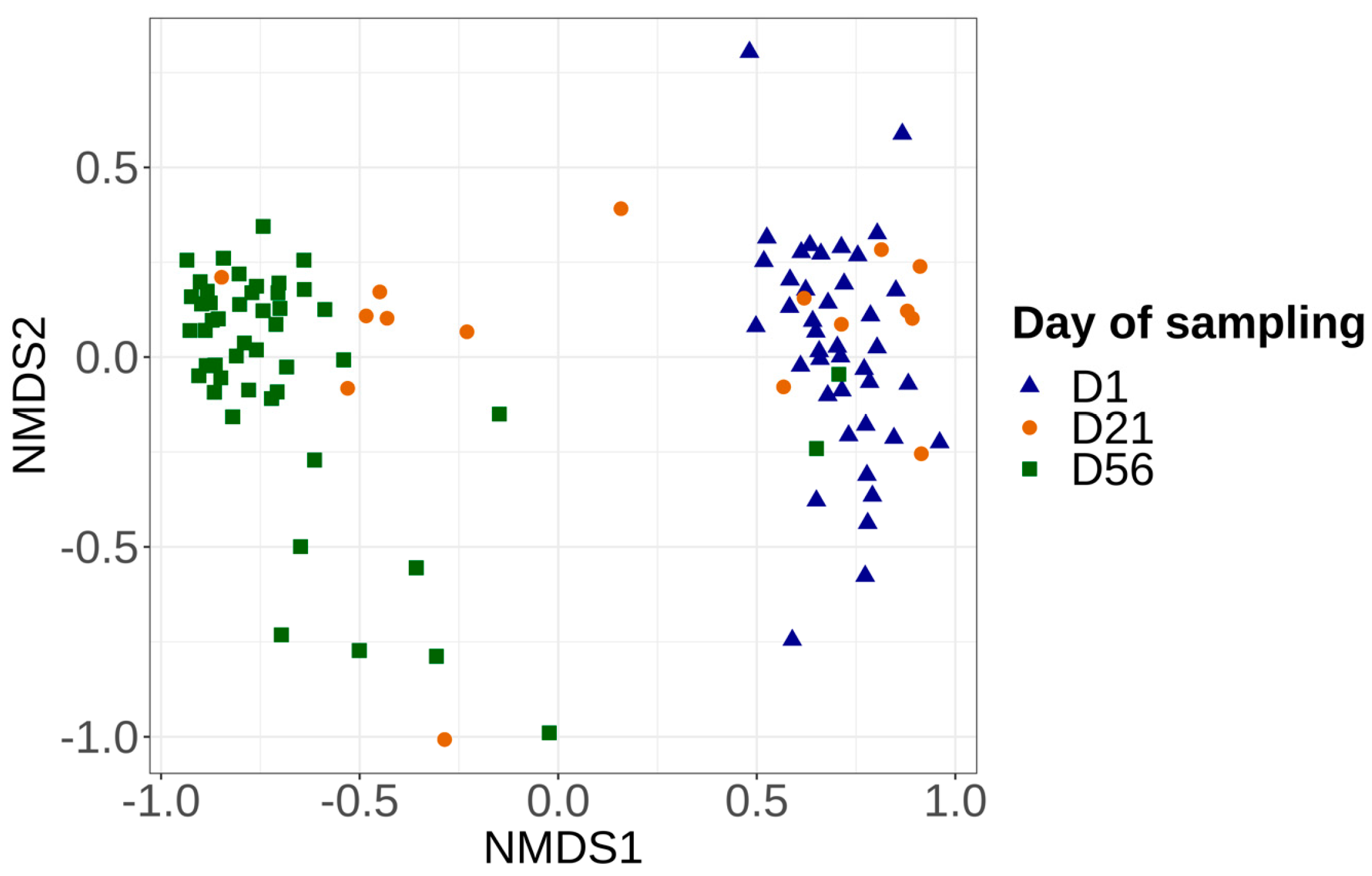
3.3.2. Alpha and Beta Diversities
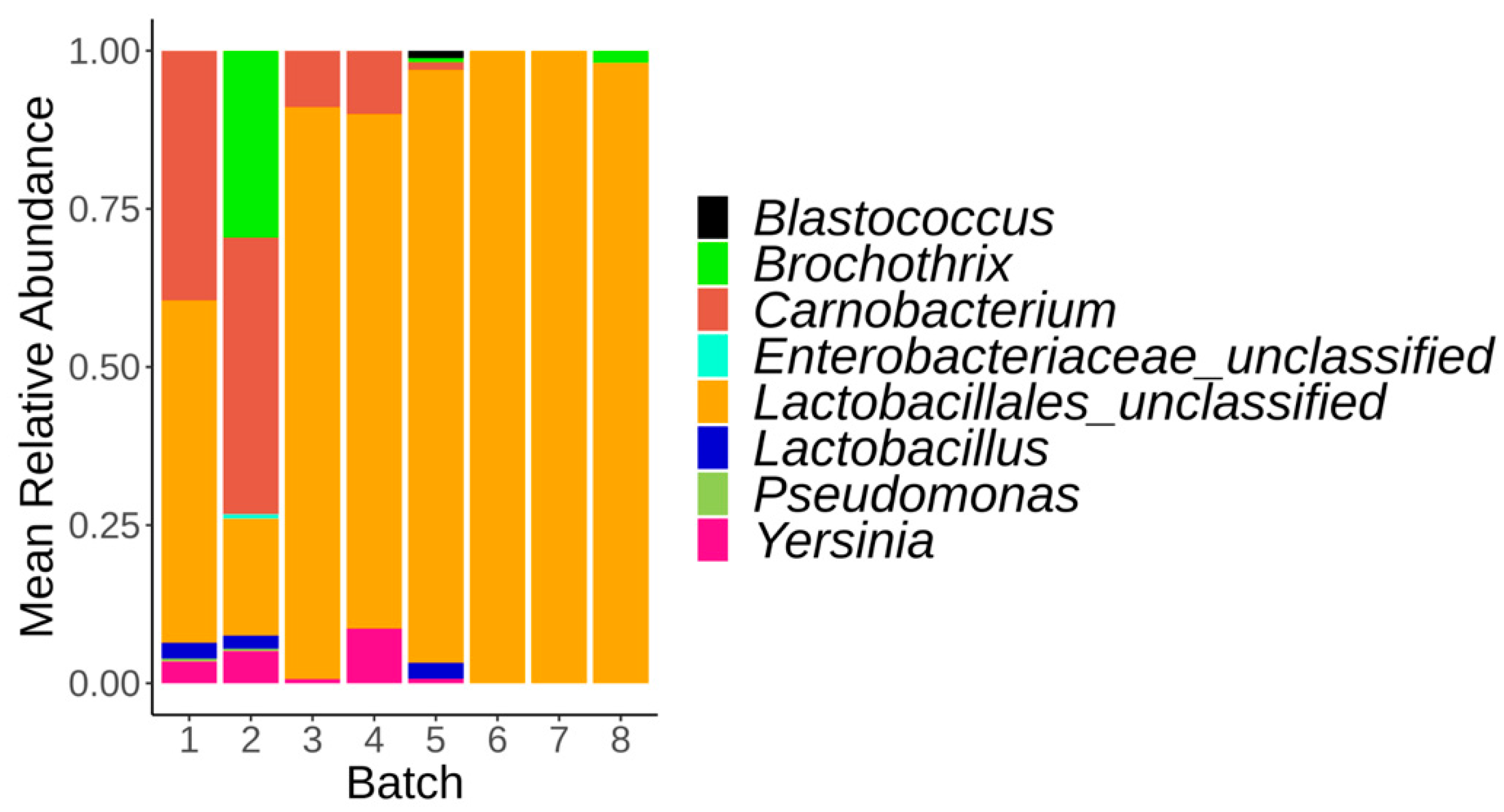
3.4. Impact of Production Batch on the Microbiota of Control Samples at Day 1 and Day 56
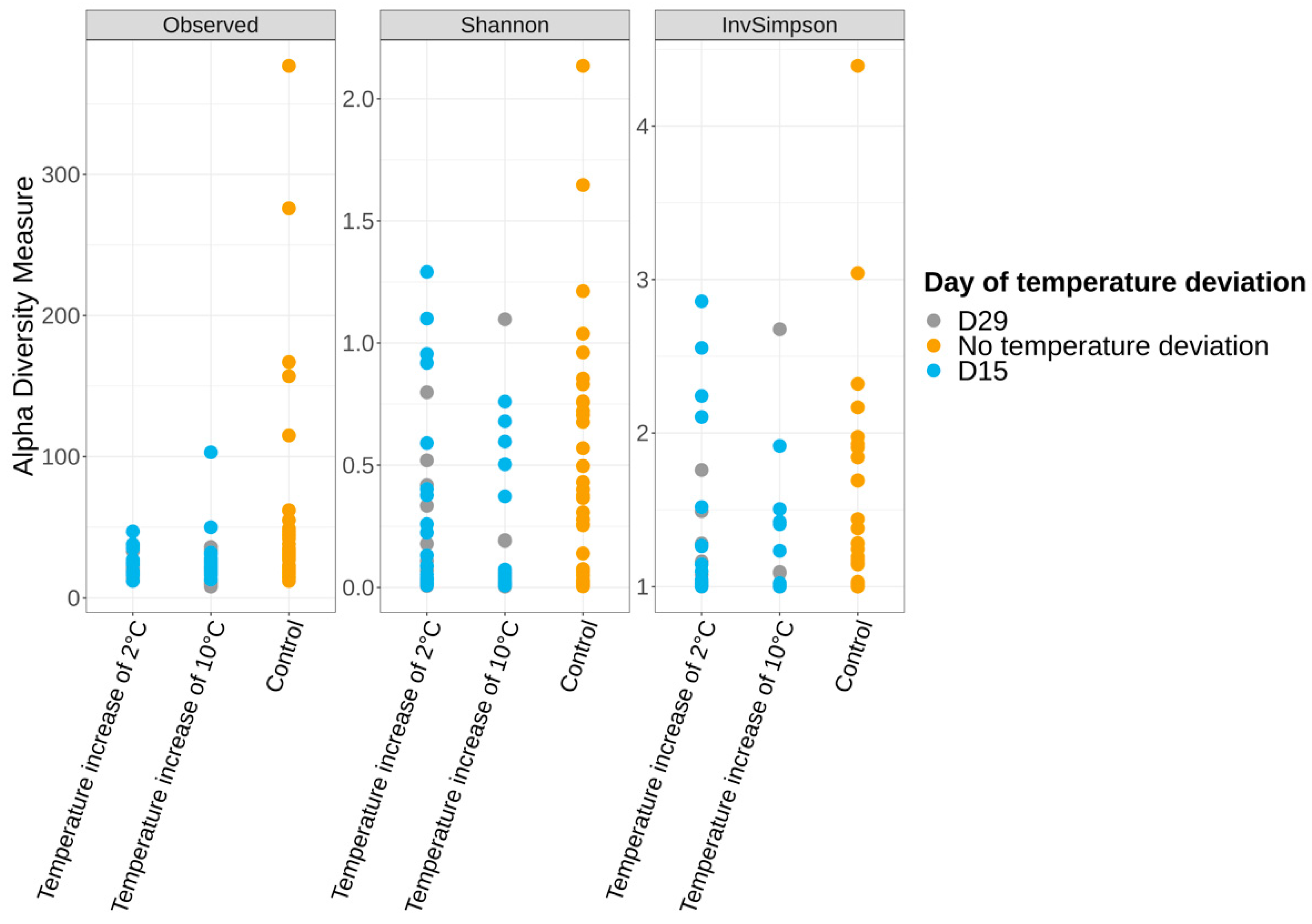
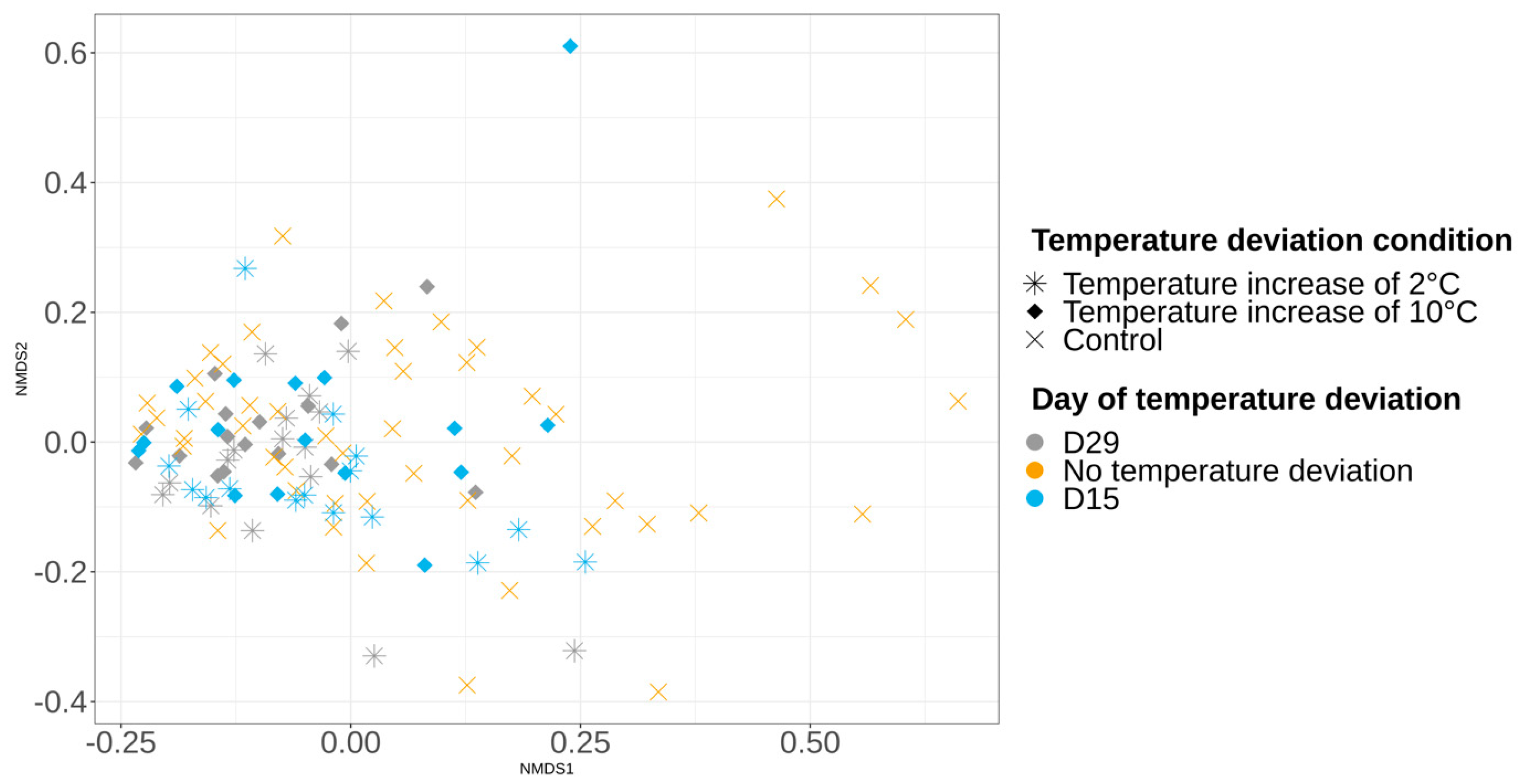
3.5. Impact of Temperature Deviations on the Vacuum-Packed Pork Loin Surface Microbiota at Day 56
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- OECD; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. OECD-FAO Agricultural Outlook 2022–2031; OECD-FAO Agricultural Outlook; OECD: Paris, France, 2022; ISBN 978-92-64-58870-7. [Google Scholar]
- Canadian Pork Council. Exportations de Porc En Chine. Available online: https://www.cpc-ccp.com/francais/canadian-pork-exports-in-china (accessed on 31 July 2018).
- Koutsoumanis, K.; Taoukis, P.S. Meat Safety, Refrigerated Storage and Transport: Modeling and Management. In Improving the Safety of Fresh Meat; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2005; pp. 503–561. ISBN 978-1-85573-955-0. [Google Scholar]
- Nychas, G.-J.E.; Skandamis, P.N.; Tassou, C.C.; Koutsoumanis, K.P. Meat Spoilage during Distribution. Meat Sci. 2008, 78, 77–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doulgeraki, A.I.; Ercolini, D.; Villani, F.; Nychas, G.-J.E. Spoilage Microbiota Associated to the Storage of Raw Meat in Different Conditions. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2012, 157, 130–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- James, S.J.; James, C. Chilling and Freezing of Foods. In Food Processing; Clark, S., Jung, S., Lamsal, B., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2014; pp. 79–105. ISBN 978-1-118-84631-5. [Google Scholar]
- Bellés, M.; Alonso, V.; Roncalés, P.; Beltrán, J.A. The Combined Effects of Superchilling and Packaging on the Shelf Life of Lamb. Meat Sci. 2017, 133, 126–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, S.; Li, X.; Wang, H.; Sun, Z.; Zhang, C.; Guan, W.; Blecker, C. Effect of Sub-Freezing Storage (−6, −9 and −12 °C) on Quality and Shelf Life of Beef. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 53, 2129–2140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez, M.; Lorenzo, J.M. Effect of Packaging Conditions on Shelf-Life of Fresh Foal Meat. Meat Sci. 2012, 91, 513–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cayuela, J.; Gil, M.; Bañón, S.; Garrido, M. Effect of Vacuum and Modified Atmosphere Packaging on the Quality of Pork Loin. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2004, 219, 316–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casaburi, A.; Piombino, P.; Nychas, G.-J.; Villani, F.; Ercolini, D. Bacterial Populations and the Volatilome Associated to Meat Spoilage. Food Microbiol. 2015, 45, 83–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Wei, Z.; Zhou, G.; Kristiansen, K.; Wang, C. Effects of Different Storage Temperatures on Bacterial Communities and Functional Potential in Pork Meat. Foods 2022, 11, 2307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, Q.; Gu, Q.; Chen, M.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, X.; Zhang, J. High-Throughput Sequencing Analysis of Bacterial Community Composition and Quality Characteristics in Refrigerated Pork during Storage. Food Microbiol. 2019, 83, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gram, L.; Ravn, L.; Rasch, M.; Bruhn, J.B.; Christensen, A.B.; Givskov, M. Food Spoilage—Interactions between Food Spoilage Bacteria. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2002, 78, 79–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Zhou, G.; Ye, K.; Wang, S.; Xu, X.; Li, C. Microbial Changes in Vacuum-Packed Chilled Pork during Storage. Meat Sci. 2015, 100, 145–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chenoll, E.; Macián, M.C.; Elizaquível, P.; Aznar, R. Lactic Acid Bacteria Associated with Vacuum-Packed Cooked Meat Product Spoilage: Population Analysis by RDNA-Based Methods. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2007, 102, 498–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holley, R.A.; Peirson, M.D.; Lam, J.; Tan, K.B. Microbial Profiles of Commercial, Vacuum-Packaged, Fresh Pork of Normal or Short Storage Life. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2004, 97, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pennacchia, C.; Ercolini, D.; Villani, F. Spoilage-Related Microbiota Associated with Chilled Beef Stored in Air or Vacuum Pack. Food Microbiol. 2011, 28, 84–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Youssef, M.K.; Gill, C.O.; Yang, X. Storage Life at 2 °C or −1.5 °C of Vacuum-Packaged Boneless and Bone-in Cuts from Decontaminated Beef Carcasses: Storage Life of Vacuum-Packaged Beef Primals from Decontaminated Carcasses. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2014, 94, 3118–3124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youssef, M.K.; Gill, C.O.; Tran, F.; Yang, X. Unusual Compositions of Microflora of Vacuum-Packaged Beef Primal Cuts of Very Long Storage Life. J. Food Prot. 2014, 77, 2161–2167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Self, J.L.; Luna-Gierke, R.E.; Fothergill, A.; Holt, K.G.; Vieira, A.R. Outbreaks Attributed to Pork in the United States, 1998–2015. Epidemiol. Infect. 2017, 145, 2980–2990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baer, A.A.; Miller, M.J.; Dilger, A.C. Pathogens of Interest to the Pork Industry: A Review of Research on Interventions to Assure Food Safety: Pathogens of Pork Industry: A review of research on interventions to assure food safety. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2013, 12, 183–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonardi, S.; Bassi, L.; Brindani, F.; D’Incau, M.; Barco, L.; Carra, E.; Pongolini, S. Prevalence, Characterization and Antimicrobial Susceptibility of Salmonella Enterica and Yersinia Enterocolitica in Pigs at Slaughter in Italy. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2013, 163, 248–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA Panel on Biological Hazards (BIOHAZ); Ricci, A.; Allende, A.; Bolton, D.; Chemaly, M.; Davies, R.; Fernández Escámez, P.S.; Girones, R.; Herman, L.; Koutsoumanis, K.; et al. Listeria Monocytogenes Contamination of Ready-to-eat Foods and the Risk for Human Health in the EU. EFSA J. 2018, 16, e05134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nastasijevic, I.; Milanov, D.; Velebit, B.; Djordjevic, V.; Swift, C.; Painset, A.; Lakicevic, B. Tracking of Listeria Monocytogenes in Meat Establishment Using Whole Genome Sequencing as a Food Safety Management Tool: A Proof of Concept. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2017, 257, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Djordjević, J.; Bošković, M.; Starčević, M.; Ivanović, J.; Karabasil, N.; Dimitrijević, M.; Lazić, I.B.; Baltić, M.Ž. Survival of Salmonella Spp. in Minced Meat Packaged under Vacuum and Modified Atmosphere. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2018, 49, 607–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bērziņš, A.; Terentjeva, M.; Korkeala, H. Prevalence and Genetic Diversity of Listeria Monocytogenes in Vacuum-Packaged Ready-to-Eat Meat Products at Retail Markets in Latvia. J. Food Prot. 2009, 72, 1283–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kramarenko, T.; Roasto, M.; Keto-Timonen, R.; Mäesaar, M.; Meremäe, K.; Kuningas, M.; Hörman, A.; Korkeala, H. Listeria Monocytogenes in Ready-to-Eat Vacuum and Modified Atmosphere Packaged Meat and Fish Products of Estonian Origin at Retail Level. Food Control 2016, 67, 48–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knox, B.L.; van Laack, R.L.J.M.; Davidson, P.M. Relationships between Ultimate PH and Microbial, Chemical, and Physical Characteristics of Vacuum-Packaged Pork Loins. J. Food Sci. 2008, 73, M104–M110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, L.; Djenane, D.; Cilla, I.; Beltrán, J.A.; Roncalés, P. Effect of Varying Oxygen Concentrations on the Shelf-Life of Fresh Pork Sausages Packaged in Modified Atmosphere. Food Chem. 2006, 94, 219–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Gao, F.; Xu, X.L.; Su, Y.; Ye, K.P.; Zhou, G.H. Changes in the Bacterial Communities of Vacuum-Packaged Pork during Chilled Storage Analyzed by PCR–DGGE. Meat Sci. 2010, 86, 889–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagadeesan, B.; Gerner-Smidt, P.; Allard, M.W.; Leuillet, S.; Winkler, A.; Xiao, Y.; Chaffron, S.; Van Der Vossen, J.; Tang, S.; Katase, M.; et al. The Use of next Generation Sequencing for Improving Food Safety: Translation into Practice. Food Microbiol. 2019, 79, 96–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.Y.; Zhou, G.H.; Xu, X.L.; Li, C.B.; Zhu, W.Y. Changes of Bacterial Diversity and Main Flora in Chilled Pork during Storage Using PCR-DGGE. Food Microbiol. 2006, 23, 607–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stellato, G.; La Storia, A.; De Filippis, F.; Borriello, G.; Villani, F.; Ercolini, D. Overlap of Spoilage-Associated Microbiota between Meat and the Meat Processing Environment in Small-Scale and Large-Scale Retail Distributions. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 82, 4045–4054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassey, A.P.; Chen, Y.; Boateng, E.F.; Zhang, Y.; Diao, X.; Nasiru, M.M.; Tang, C.; Ye, K.; Li, C.; Zhou, G. Evaluation of Physicochemical, Microbiological, and Sensory Profiles of Vacuum-Packed Cooked Low-Salt Pork Belly under Refrigeration and Room-Temperature Storage. LWT 2022, 167, 113847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shedleur-Bourguignon, F.; Thériault, W.P.; Longpré, J.; Thibodeau, A.; Fravalo, P. Use of an Ecosystem-Based Approach to Shed Light on the Heterogeneity of the Contamination Pattern of Listeria Monocytogenes on Conveyor Belt Surfaces in a Swine Slaughterhouse in the Province of Quebec, Canada. Pathogens 2021, 10, 1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kérouanton, A.; Marault, M.; Petit, L.; Grout, J.; Dao, T.T.; Brisabois, A. Evaluation of a Multiplex PCR Assay as an Alternative Method for Listeria Monocytogenes Serotyping. J. Microbiol. Methods 2010, 80, 134–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larivière-Gauthier, G.; Thibodeau, A.; Letellier, A.; Yergeau, É.; Fravalo, P. Salmonella Shedding Status of the Sow Affects the Microbiota of Their Piglets at Weaning. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2019, 126, 411–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braley, C.; Fravalo, P.; Gaucher, M.-L.; Larivière-Gauthier, G.; Shedleur-Bourguignon, F.; Longpré, J.; Thibodeau, A. Similar Carcass Surface Microbiota Observed Following Primary Processing of Different Pig Batches. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 849883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schloss, P.D.; Wescott, S.L.; Ryabin, T. Introducing Mothur: Open-Source, Platform-Independent, Community-Supported Software for Describing and Comparing Microbial Communities. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 7537–7541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rognes, T.; Flouri, T.; Nichols, B.; Quince, C.; Mahé, F. VSEARCH: A Versatile Open Source Tool for Metagenomics. PeerJ 2016, 4, e2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMurdie, P.J.; Holmes, S. Phyloseq: An R Package for Reproducible Interactive Analysis and Graphics of Microbiome Census Data. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e61217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oksanen, J.; Blanchet, F.; Friendly, M.; Kindt, R.; Legendre, P.; Minchin, P.R.; O’Hara, R.B.; Simpson, G.L.; Solymos, P.; Stevens, M.H.H.; et al. Vegan: Community Ecology Package. R Package. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/346579465_vegan_community_ecology_package_version_25-7_November_2020 (accessed on 10 August 2022).
- Saraiva, C.; Fontes, M.C.; Patarata, L.; Martins, C.; Cadavez, V.; Gonzales-Barron, U. Modelling the Kinetics of Listeria Monocytogenes in Refrigerated Fresh Beef under Different Packaging Atmospheres. LWT—Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 66, 664–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueroa-López, A.M.; Maldonado-Mendoza, I.E.; López-Cervantes, J.; Verdugo-Fuentes, A.A.; Ruiz-Vega, D.A.; Cantú-Soto, E.U. Prevalence and Characterization of Listeria Monocytogenes Isolated from Pork Meat and on Inert Surfaces. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2019, 50, 817–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez, R.; Ponce-Alquicira, E.; Braña Varela, D.; Perez-Chabela, M. de L.; Universidad Autonoma Metropolitana, México Prevalence of Pathogenic Microorganisms in Pork Meat Offered for Retail Sale in Supermarkets of Mexico City. Nacameh 2020, 14, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, J.L.; Cadavez, V.A.P.; Machado, M.A.M.; Dias, B.d.C.L.; da Cunha-Neto, A.; Gonzales-Barron, U.; Figueiredo, E.E.d.S. Behavior of Spoilage Bacteria and Salmonella Enterica Subspecies Enterica O:4,5 in Vacuum-Packaged Beef during Refrigeration. Ciênc. Rural 2020, 50, e20200090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laukkanen, R.; Martínez, P.O.; Siekkinen, K.-M.; Ranta, J.; Maijala, R.; Korkeala, H. Contamination of Carcasses with Human Pathogenic Yersinia Enterocolitica 4/O:3 Originates from Pigs Infected on Farms. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2009, 6, 681–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanantwerpen, G.; Van Damme, I.; De Zutter, L.; Houf, K. Seroprevalence of Enteropathogenic Yersinia Spp. in Pig Batches at Slaughter. Prev. Vet. Med. 2014, 116, 193–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fredriksson-Ahomaa, M.; Stolle, A.; Stephan, R. Prevalence of Pathogenic Yersinia Enterocolitica in Pigs Slaughtered at a Swiss Abattoir. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2007, 119, 207–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonardi, S.; Bruini, I.; D’Incau, M.; Van Damme, I.; Carniel, E.; Brémont, S.; Cavallini, P.; Tagliabue, S.; Brindani, F. Detection, Seroprevalence and Antimicrobial Resistance of Yersinia Enterocolitica and Yersinia Pseudotuberculosis in Pig Tonsils in Northern Italy. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2016, 235, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Damme, I.; Berkvens, D.; Vanantwerpen, G.; Baré, J.; Houf, K.; Wauters, G.; De Zutter, L. Contamination of Freshly Slaughtered Pig Carcasses with Enteropathogenic Yersinia Spp.: Distribution, Quantification and Identification of Risk Factors. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2015, 204, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashidani, H.; Iwata, T.; Yamaguchi, S.; Hara-Kudo, Y.; Okatani, T.A.; Watanabe, M.; Lee, K.-I.; Kumagai, S. Survival of Pathogenic Yersinia Enterocolitica in Vacuum-Packed or Non-Vacuum-Packed Pork at Low Temperature. Biocontrol Sci. 2008, 13, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, M.; Williams, M.; Bissett, A.; Ross, T.; Bowman, J.P. Effect of Abattoir, Livestock Species and Storage Temperature on Bacterial Community Dynamics and Sensory Properties of Vacuum Packaged Red Meat. Food Microbiol. 2021, 94, 103648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valero, A.; Rodríguez, M.-Y.; Posada-Izquierdo, G.D.; Pérez-Rodríguez, F.; Carrasco, E.; García-Gimeno, R.M. Risk Factors Influencing Microbial Contamination in Food Service Centers. In Significance, Prevention and Control of Food Related Diseases; Makun, H.A., Ed.; InTech: London, UK, 2016; ISBN 978-953-51-2277-7. [Google Scholar]
- Kaur, M.; Shang, H.; Tamplin, M.; Ross, T.; Bowman, J.P. Culture-Dependent and Culture-Independent Assessment of Spoilage Community Growth on VP Lamb Meat from Packaging to Past End of Shelf-Life. Food Microbiol. 2017, 68, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ercolini, D.; Russo, F.; Torrieri, E.; Masi, P.; Villani, F. Changes in the Spoilage-Related Microbiota of Beef during Refrigerated Storage under Different Packaging Conditions. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 4663–4671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luong, N.-D.M.; Coroller, L.; Zagorec, M.; Membré, J.-M.; Guillou, S. Spoilage of Chilled Fresh Meat Products during Storage: A Quantitative Analysis of Literature Data. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faucitano, L.; Ielo, M.C.; Ster, C.; Lo Fiego, D.P.; Methot, S.; Saucier, L. Shelf Life of Pork from Five Different Quality Classes. Meat Sci. 2010, 84, 466–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Wang, H.; Hrycauk, S.; Klassen, M.D. Effects of Peroxyacetic Acid Spray and Storage Temperature on the Microbiota and Sensory Properties of Vacuum-Packed Subprimal Cuts of Meat. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2021, 87, e03143-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Braley, C.; Gaucher, M.-L.; Fravalo, P.; Shedleur-Bourguignon, F.; Longpré, J.; Thibodeau, A. Slight Temperature Deviation during a 56-Day Storage Period Does Not Affect the Microbiota of Fresh Vacuum-Packed Pork Loins. Foods 2023, 12, 1695. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12081695
Braley C, Gaucher M-L, Fravalo P, Shedleur-Bourguignon F, Longpré J, Thibodeau A. Slight Temperature Deviation during a 56-Day Storage Period Does Not Affect the Microbiota of Fresh Vacuum-Packed Pork Loins. Foods. 2023; 12(8):1695. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12081695
Chicago/Turabian StyleBraley, Charlotte, Marie-Lou Gaucher, Philippe Fravalo, Fanie Shedleur-Bourguignon, Jessie Longpré, and Alexandre Thibodeau. 2023. "Slight Temperature Deviation during a 56-Day Storage Period Does Not Affect the Microbiota of Fresh Vacuum-Packed Pork Loins" Foods 12, no. 8: 1695. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12081695
APA StyleBraley, C., Gaucher, M.-L., Fravalo, P., Shedleur-Bourguignon, F., Longpré, J., & Thibodeau, A. (2023). Slight Temperature Deviation during a 56-Day Storage Period Does Not Affect the Microbiota of Fresh Vacuum-Packed Pork Loins. Foods, 12(8), 1695. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12081695




