Network Pharmacology and Molecular Docking Analysis of Active Compounds in Tualang Honey against Atherosclerosis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
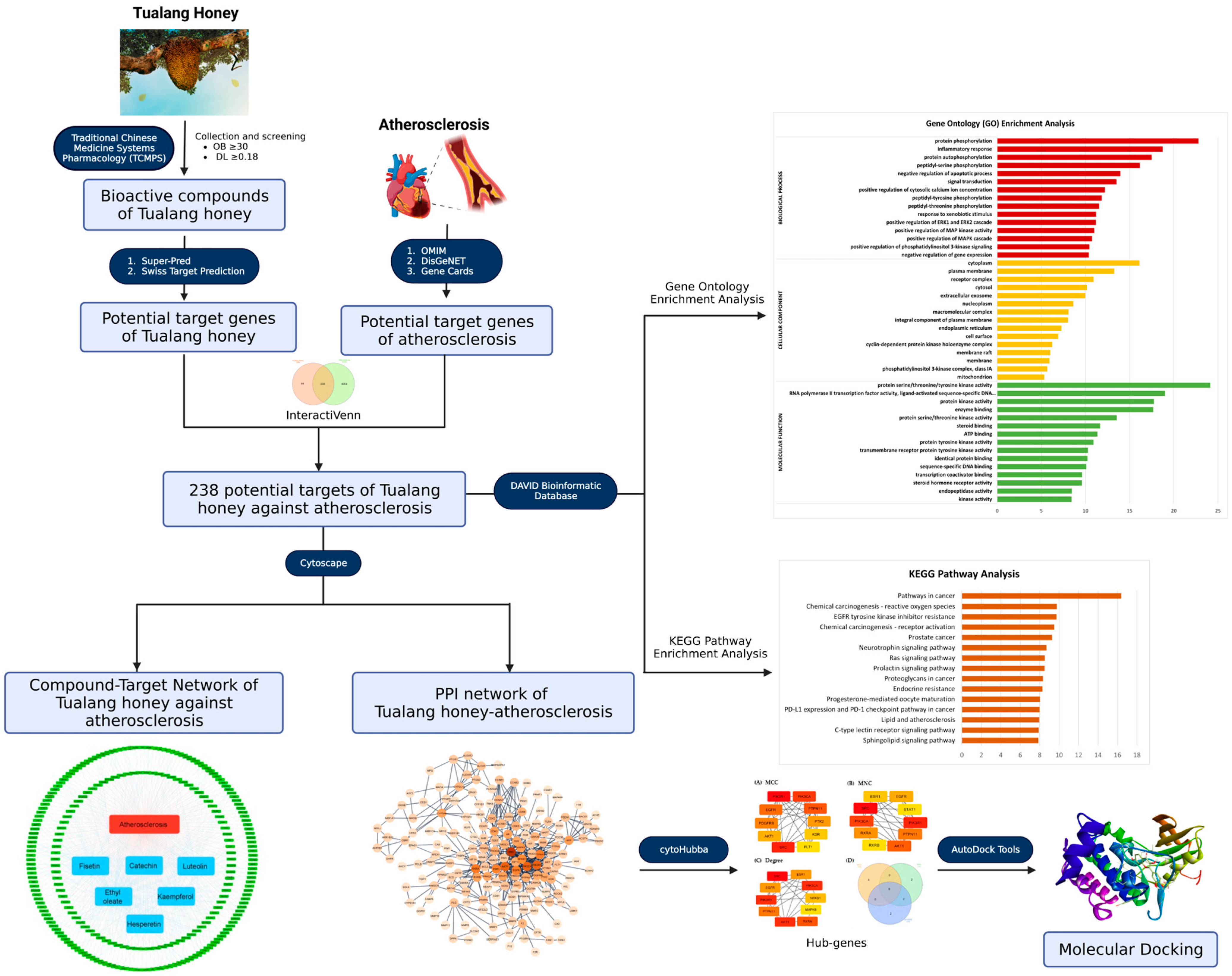
2.1. Bioactive Compounds of Tualang Honey
2.2. Screening of Bioactive Compounds in Tualang Honey
2.3. Prediction of Target Genes in Tualang Honey Bioactive Compounds
2.4. Prediction of Target Genes in Atherosclerosis
2.5. Construction of Venn Diagram
2.6. Compound-Target Network
2.7. Protein–Protein Interaction (PPI) Network Analysis
2.8. Gene Ontology and Pathway Enrichment Analysis
2.9. Molecular Docking
3. Results
3.1. Screening and Identification of Active Compounds in Tualang Honey
3.2. Target Gene Prediction of Tualang Honey and Atherosclerosis
3.3. Common Target of Tualang Honey and Atherosclerosis
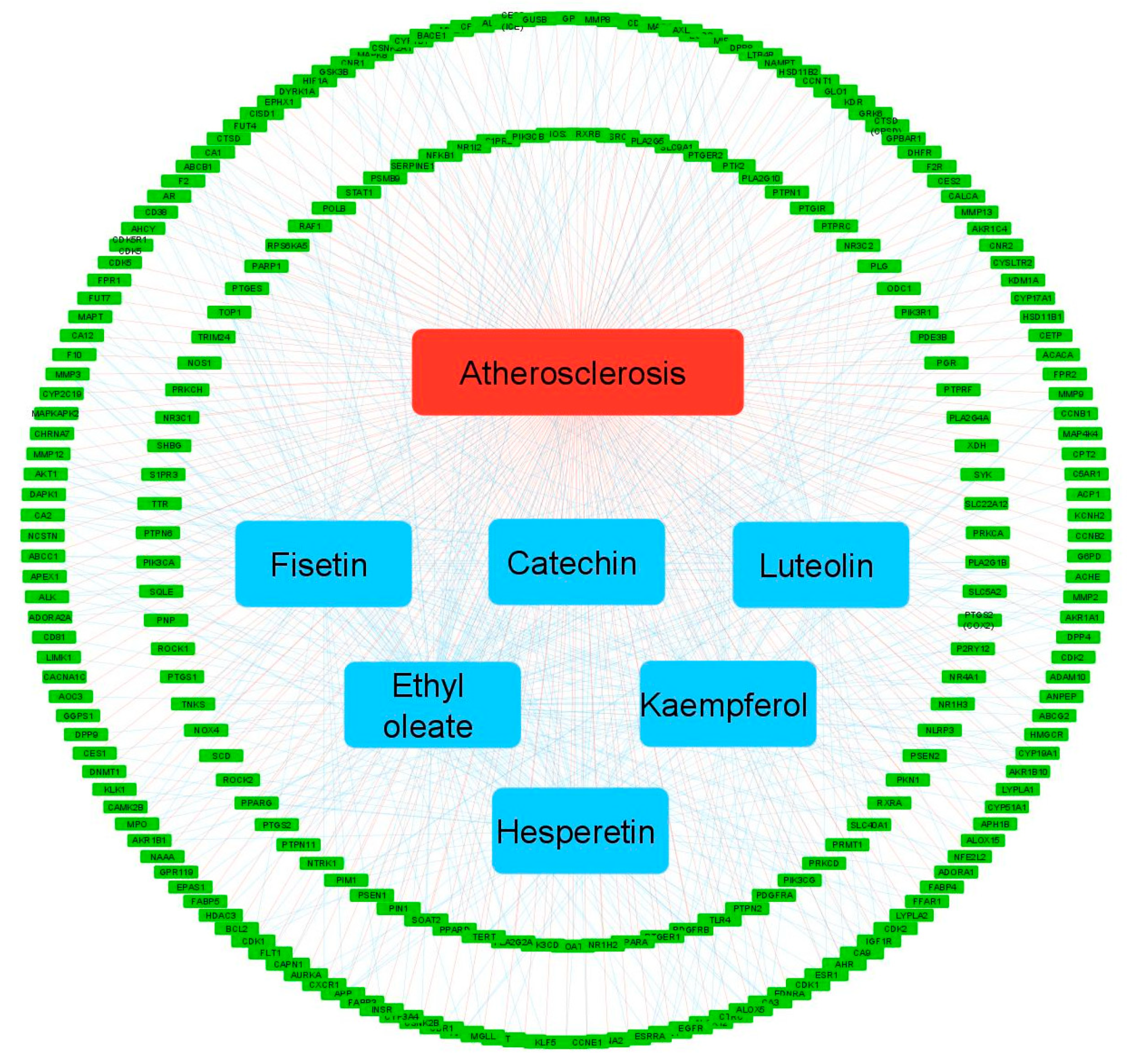
3.4. Compound-Target Network Constructions
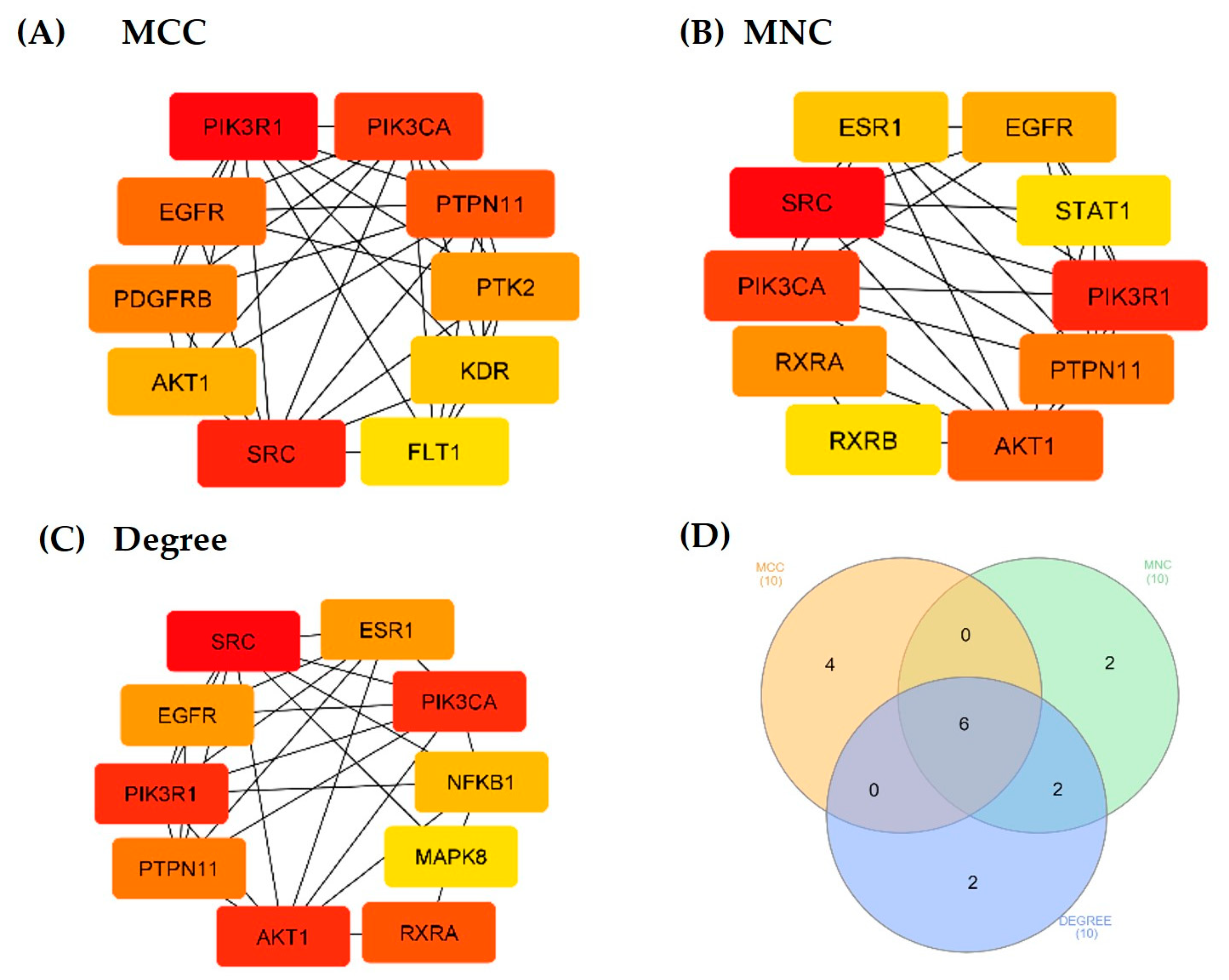
3.5. Protein–Protein Interaction (PPI) Network
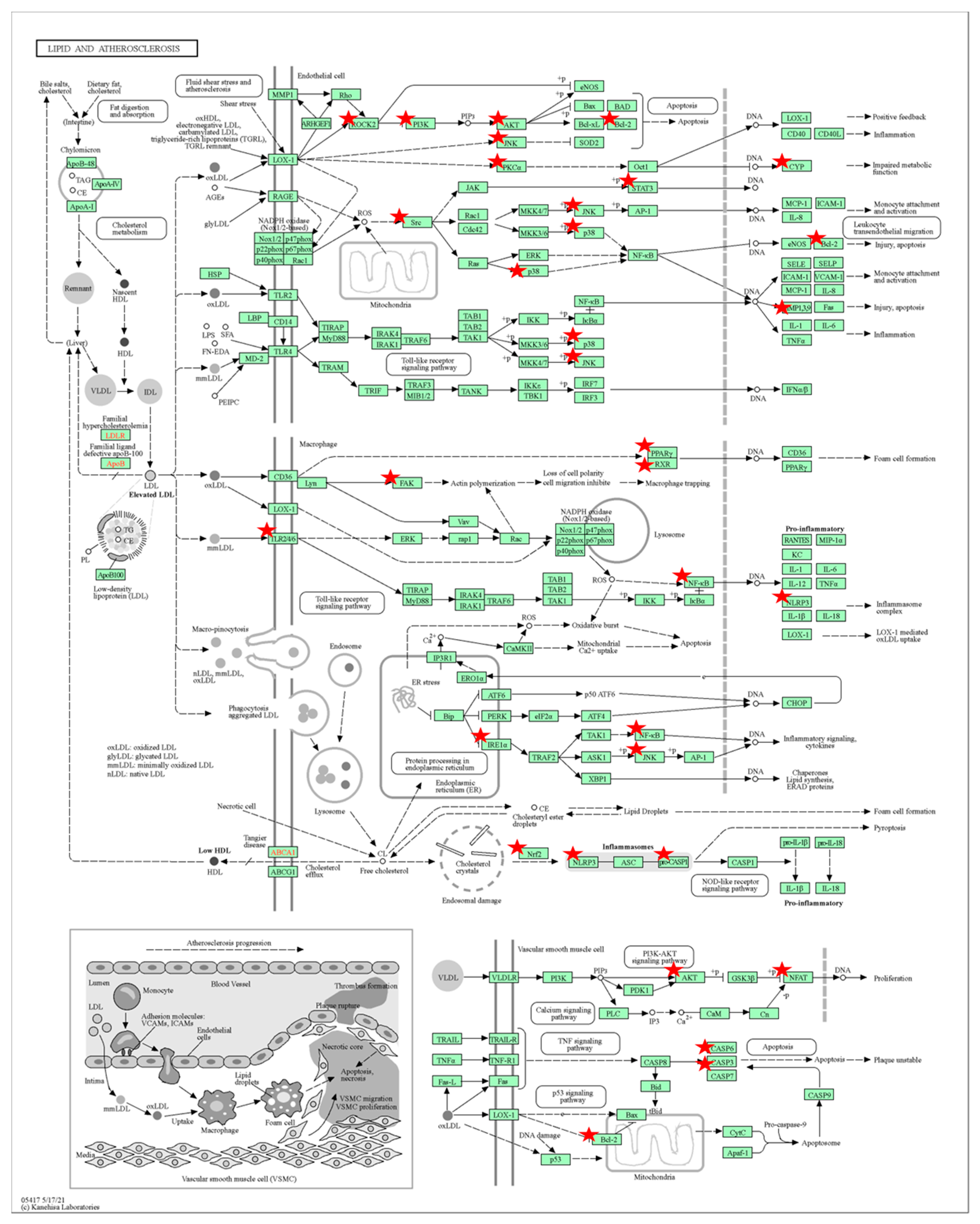
3.6. Gene Ontology and Pathway Enrichment Analysis
3.7. Molecular Docking
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tsao, C.W.; Aday, A.W.; Almarzooq, Z.I.; Alonso, A.; Beaton, A.Z.; Bittencourt, M.S.; Boehme, A.K.; Buxton, A.E.; Carson, A.P.; Commodore-Mensah, Y.; et al. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics-2022 Update: A Report from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2022, 145, E153–E639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathers, C.D.; Loncar, D. Projections of Global Mortality and Burden of Disease from 2002 to 2030. PLoS Med. 2006, 3, 2011–2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azman, W.; Ahmad, W. Annual report of the NCVD-ACS registry 2018–2019. Natl. Cardiovasc. Dis. Database 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Jebari-Benslaiman, S.; Galicia-García, U.; Larrea-Sebal, A.; Olaetxea, J.R.; Alloza, I.; Vandenbroeck, K.; Benito-Vicente, A.; Martín, C. Pathophysiology of Atherosclerosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrington, W.; Lacey, B.; Sherliker, P.; Armitage, J.; Lewington, S. Epidemiology of Atherosclerosis and the Potential to Reduce the Global Burden of Atherothrombotic Disease. Circ. Res. 2016, 118, 535–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mundi, S.; Massaro, M.; Scoditti, E.; Carluccio, M.A.; Van Hinsbergh, V.W.M.; Iruela-Arispe, M.L.; De Caterina, R. Endothelial Permeability, LDL Deposition, and Cardiovascular Risk Factors-A Review. Cardiovasc. Res. 2018, 114, 35–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moss, J.W.E.; Ramji, D.P. Nutraceutical Therapies for Atherosclerosis. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2016, 13, 513–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, N.C.; Pang, J.; Ryan, J.D.M.; Watts, G.F. Nutraceuticals in the Management of Patients with Statin-Associated Muscle Symptoms, with a Note on Real-World Experience. Clin. Cardiol. 2018, 41, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkhalifah, M.K.; Alabduljabbar, K.A.; Alkhenizan, A.H. Effect of Natural Honey on Lowering Lipid Profile. Saudi Med. J. 2021, 42, 473–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegazi, A.G.; Abd El-Hady, F.K. Influence of Honey on the Suppression of Human Low Density Lipoprotein (LDL) Peroxidation (in Vitro). Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2009, 6, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.; Sulaiman, S.A.; Baig, A.A.; Ibrahim, M.; Liaqat, S.; Fatima, S.; Jabeen, S.; Shamim, N.; Othman, N.H. Honey as a Potential Natural Antioxidant Medicine: An Insight into Its Molecular Mechanisms of Action. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2018, 2018, 8367846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ranneh, Y.; Akim, A.M.; Hamid, H.A.; Khazaai, H.; Fadel, A.; Zakaria, Z.A.; Albujja, M.; Bakar, M.F.A. Honey and Its Nutritional and Anti-Inflammatory Value. BMC Complement. Med. Ther. 2021, 21, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalil, M.I.; Alam, N.; Moniruzzaman, M.; Sulaiman, S.A.; Gan, S.H. Phenolic Acid Composition and Antioxidant Properties of Malaysian Honeys. J. Food Sci. 2011, 76, 921–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Othman, Z.; Zakaria, R.; Hussain, N.; Hassan, A.; Shafin, N.; Al-Rahbi, B.; Ahmad, A. Potential Role of Honey in Learning and Memory. Med. Sci. 2015, 3, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devasvaran, K.; Tan, J.J.; Ng, C.T.; Fong, L.Y.; Yong, Y.K. Malaysian Tualang Honey Inhibits Hydrogen Peroxide-Induced Endothelial Hyperpermeability. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 2019, 1202676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalil, M.I.; Tanvir, E.M.; Afroz, R.; Sulaiman, S.A.; Gan, S.H. Cardioprotective Effects of Tualang Honey: Amelioration of Cholesterol and Cardiac Enzymes Levels. Biomed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 286051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syaheedah Wan Ghazali, W.; Mohamed, M.; Amrah Sulaiman, S.; Abdul Aziz, A.; Mohamed Yusoff, H. Toxicological & Environmental Chemistry Tualang Honey Supplementation Improves Oxidative Stress Status among Chronic Smokers. Toxicol. Environ. Chem. 2015, 97, 1017–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhang, B. Traditional Chinese Medicine Network Pharmacology: Theory, Methodology and Application. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 2013, 11, 110–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Liu, L.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; Meng, D.L. Virtual Screening of Active Compounds from Jasminum Lanceolarium and Potential Targets against Primary Dysmenorrhea Based on Network Pharmacology. Nat. Prod. Res. 2020, 35, 5853–5856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, J. PubMed 2.0. Med. Ref. Serv. Q. 2020, 39, 382–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Springer. Available online: https://link.springer.com/ (accessed on 26 January 2023).
- Science Direct. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com (accessed on 26 January 2023).
- Ru, J.; Li, P.; Wang, J.; Zhou, W.; Li, B.; Huang, C.; Li, P.; Guo, Z.; Tao, W.; Yang, Y.; et al. TCMSP: A Database of Systems Pharmacology for Drug Discovery from Herbal Medicines. J. Cheminform. 2014, 6, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Wang, J.; Zhou, W.; Wang, Y.; Yang, L. Systems Approaches and Polypharmacology for Drug Discovery from Herbal Medicines: An Example Using Licorice. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2013, 146, 773–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daina, A.; Michielin, O.; Zoete, V. SwissTargetPrediction: Updated Data and New Features for Efficient Prediction of Protein Targets of Small Molecules. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, W357–W3664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nickel, J.; Gohlke, B.O.; Erehman, J.; Banerjee, P.; Rong, W.W.; Goede, A.; Dunkel, M.; Preissner, R. SuperPred: Update on Drug Classification and Target Prediction. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, W26–W31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amberger, J.S.; Bocchini, C.A.; Schiettecatte, F.; Scott, A.F.; Hamosh, A. OMIM.Org: Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM®), an Online Catalog of Human Genes and Genetic Disorders. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, D789–D798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piñero, J.; Queralt-Rosinach, N.; Bravo, À.; Deu-Pons, J.; Bauer-Mehren, A.; Baron, M.; Sanz, F.; Furlong, L.I. DisGeNET: A Discovery Platform for the Dynamical Exploration of Human Diseases and Their Genes. Database 2015, 2015, bav028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safran, M.; Dalah, I.; Alexander, J.; Rosen, N.; Iny Stein, T.; Shmoish, M.; Nativ, N.; Bahir, I.; Doniger, T.; Krug, H.; et al. GeneCards Version 3: The Human Gene Integrator. Database 2010, 2010, baq020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heberle, H.; Meirelles, G.V.; da Silva, F.R.; Telles, G.P.; Minghim, R. Interactivenn: A Web-Based Tool for the Analysis of Sets through Venn Diagrams. BMC Bioinform. 2015, 16, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, P.; Markiel, A.; Ozier, O.; Baliga, N.S.; Wang, J.T.; Ramage, D.; Amin, N.; Schwikowski, B.; Ideker, T. Cytoscape: A Software Environment for Integrated Models of Biomolecular Interaction Networks. Genome Res. 2003, 13, 2498–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szklarczyk, D.; Gable, A.L.; Lyon, D.; Junge, A.; Wyder, S.; Huerta-Cepas, J.; Simonovic, M.; Doncheva, N.T.; Morris, J.H.; Bork, P.; et al. STRING V11: Protein-Protein Association Networks with Increased Coverage, Supporting Functional Discovery in Genome-Wide Experimental Datasets. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D607–D613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, C.H.; Chen, S.H.; Wu, H.H.; Ho, C.W.; Ko, M.T.; Lin, C.Y. CytoHubba: Identifying Hub Objects and Sub-Networks from Complex Interactome. BMC Syst. Biol. 2014, 8, S11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dennis, G.; Sherman, B.T.; Hosack, D.A.; Yang, J.; Gao, W.; Lane, H.C.; Lempicki, R.A. DAVID: Database for Annotation, Visualization, and Integrated Discovery. Genome Biol. 2003, 4, R60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanehisa, M.; Furumichi, M.; Sato, Y.; Kawashima, M.; Ishiguro-Watanabe, M. KEGG for taxonomy-based analysis of pathways and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, D587–D592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherman, B.T.; Hao, M.; Qiu, J.; Jiao, X.; Baseler, M.W.; Lane, H.C.; Imamichi, T.; Chang, W. DAVID: A web server for functional enrichment analysis and functional annotation of gene lists (2021 update). Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, W216–W221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.W.; Sherman, B.T.; Lempicki, R.A. Systematic and integrative analysis of large gene lists using DAVID bioinformatics resources. Nat. Protoc. 2009, 4, 44–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berman, H.M.; Westbrook, J.; Feng, Z.; Gilliland, G.; Bhat, T.N.; Weissig, H.; Shindyalov, I.N.; Bourne, P.E. The Protein Data Bank. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; Chen, J.; Cheng, T.; Gindulyte, A.; He, J.; He, S.; Li, Q.; Shoemaker, B.A.; Thiessen, P.A.; Yu, B.; et al. PubChem in 2021: New Data Content and Improved Web Interfaces. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, D1388–D1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dassault Systèmes. Biovia Discovery Studio 2021. San Diego 2020. Available online: https://www.3ds.com/support/ (accessed on 20 February 2023).
- Steffen, C.; Thomas, K.; Huniar, U.; Hellweg, A.; Rubner, O.; Schroer, A. AutoDock4 and AutoDockTools4: Automated Docking with Selective Receptor Flexibility. J. Comput. Chem. 2010, 31, 2967–2970. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, J.J.; Azmi, S.M.; Yong, Y.K.; Cheah, H.L.; Lim, V.; Sandai, D.; Shaharuddin, B. Tualang Honey Improves Human Corneal Epithelial Progenitor Cell Migration and Cellular Resistance to Oxidative Stress in Vitro. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e105233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chew, C.Y.; Chua, L.S.; Soontorngun, N.; Lee, C.T. Discovering Potential Bioactive Compounds from Tualang Honey. Agric. Nat. Resour. 2018, 52, 361–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.; Othman, N.H. Review of the Medicinal Effects of Tualang Honey and a Comparison with Manuka Honey. Malays. J. Med. Sci. 2013, 20, 6. [Google Scholar]
- Nurul Syazana, M.S.; Gan, S.H.; Halim, A.S.; Shah, N.S.M.; Sukari, H.A. Analysis of Volatile Compounds of Malaysian Tualang (Koompassia Excelsa) Honey Using Gas Chromatography Mass Spectrometry. Afr. J. Tradit. Complement. Altern. Med. AJTCAM 2012, 10, 180–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranneh, Y.; Ali, F.; Zarei, M.; Akim, A.M.; Hamid, H.A.; Khazaai, H. Malaysian Stingless Bee and Tualang Honeys: A Comparative Characterization of Total Antioxidant Capacity and Phenolic Profile Using Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry. LWT 2018, 89, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurul Syazana, M.S.; Halim, A.S.; Gan, S.H.; Shamsuddin, S. Antiproliferative Effect of Methanolic Extraction of Tualang Honey on Human Keloid Fibroblasts. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2011, 11, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lusis, A.J. Atherosclerosis. Nature 2000, 407, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erejuwa, O.O.; Sulaiman, S.A.; Ab Wahab, M.S.; Sirajudeen, K.N.S.; Salleh, S.; Gurtu, S. Honey Supplementation in Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats Elicits Antihypertensive Effect via Amelioration of Renal Oxidative Stress. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2012, 2012, 7–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caporali, A.; Emanueli, C. Cardiovascular Actions of Neurotrophins. Physiol. Rev. 2009, 89, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, G.M.; França-Falcão, M.S.; Calzerra, N.T.M.; Luz, M.S.; Gadelha, D.D.A.; Balarini, C.M.; Queiroz, T.M. Role of Renin-Angiotensin System Components in Atherosclerosis: Focus on Ang-II, ACE2, and Ang-1–7. Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Huang, Z.; Huang, W.; Chen, X.; Shan, P.; Zhong, P.; Khan, Z.; Wang, J.; Fang, Q.; Liang, G.; et al. Inhibition of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Attenuates Atherosclerosis via Decreasing Inflammation and Oxidative Stress. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 45917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glezer, A.; Santana, M.R.; Bronstein, M.D.; Donato, J.; Jallad, R.S. The Interplay between Prolactin and Cardiovascular Disease. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 13, 3553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borodzicz-Jażdżyk, S.; Jażdżyk, P.; Łysik, W.; Cudnoch-Jȩdrzejewska, A.; Czarzasta, K. Sphingolipid Metabolism and Signaling in Cardiovascular Diseases. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 9, 2363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siasos, G.; Tousoulis, D.; Tsigkou, V.; Kokkou, E.; Oikonomou, E.; Vavuranakis, M.; Basdra, E.K.; Papavassiliou, A.G.; Stefanadis, C. Flavonoids in Atherosclerosis: An Overview of Their Mechanisms of Action. Curr. Med. Chem. 2013, 20, 2641–2660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auclair, S.; Milenkovic, D.; Besson, C.; Chauvet, S.; Gueux, E.; Morand, C.; Mazur, A.; Scalbert, A. Catechin Reduces Atherosclerotic Lesion Development in Apo E-Deficient Mice: A Transcriptomic Study. Atherosclerosis 2009, 204, e21–e27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangels, D.R.; Mohler, E.R. Catechins as Potential Mediators of Cardiovascular Health. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2017, 37, 757–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, L.; Jia, Q.; Cao, H.; Chen, C.; Xing, S.; Huang, Y.; Shen, D. Fisetin Ameliorates Atherosclerosis by Regulating PCSK9 and LOX-1 in ApoE-/- Mice. Exp. Ther. Med. 2021, 21, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Zou, D.; Chen, X.; Wu, H.; Xu, D. Hesperetin Inhibits Foam Cell Formation and Promotes Cholesterol Efflux in THP-1-Derived Macrophages by Activating LXRα Signal in an AMPK-Dependent Manner. J. Physiol. Biochem. 2021, 77, 405–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, L.; Luo, C.; Li, X.; Zhou, Y.; He, H. The Anti-Inflammatory Effect of Kaempferol on Early Atherosclerosis in High Cholesterol Fed Rabbits. Lipids Health Dis. 2013, 12, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, D.; Li, D.; Wu, W. Inhibitory Effects and Mechanisms of Luteolin on Proliferation and Migration of Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells. Nutrients 2013, 5, 1648–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaillard, T. Evaluation of AutoDock and AutoDock Vina on the CASF-2013 Benchmark. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2018, 58, 1697–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Qian, Y.; Sun, Z.; Shen, X.; Cai, Y.; Li, L.; Wang, Z. Role of PI3K in the Progression and Regression of Atherosclerosis. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.D.; Sukhova, G.K.; Libby, P.; Schvartz, E.; Lichtenstein, A.H.; Field, S.J.; Kennedy, C.; Madhavarapu, S.; Luo, J.; Wu, D.; et al. Deletion of the Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase P110gamma Gene Attenuates Murine Atherosclerosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 8077–8082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Compound | Oral Bioavailability OB (≥30%) | Drug-Likeness DL (≥0.18) |
|---|---|---|
| Catechin | 54.83 | 0.24 |
| Ethyl oleate | 32.4 | 0.19 |
| Fisetin | 52.6 | 0.24 |
| Hesperetin | 70.31 | 0.27 |
| Kaempferol | 41.88 | 0.24 |
| Luteolin | 36.16 | 0.25 |
| Compound | Binding Energy (kcal/mol) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SRC | PIK3R1 | PIK3CA | EGFR | PTPN11 | AKT1 | |
| Catechin | −6.30 | −6.16 | −10.28 | −8.68 | −6.78 | −6.43 |
| Ethyl oleate | −3.57 | −3.45 | −7.59 | −6.63 | −4.59 | −4.58 |
| Fisetin | −5.88 | −5.71 | −10.50 | −9.19 | −6.95 | −7.11 |
| Hesperetin | −5.84 | −5.85 | −10.33 | −7.97 | −6.55 | −6.41 |
| Kaempferol | −6.05 | −5.94 | −10.08 | −9.25 | −6.93 | −6.70 |
| Luteolin | −6.08 | −5.99 | −10.67 | −8.01 | −6.59 | −6.98 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shamsol Azman, A.N.S.; Tan, J.J.; Abdullah, M.N.H.; Bahari, H.; Lim, V.; Yong, Y.K. Network Pharmacology and Molecular Docking Analysis of Active Compounds in Tualang Honey against Atherosclerosis. Foods 2023, 12, 1779. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12091779
Shamsol Azman ANS, Tan JJ, Abdullah MNH, Bahari H, Lim V, Yong YK. Network Pharmacology and Molecular Docking Analysis of Active Compounds in Tualang Honey against Atherosclerosis. Foods. 2023; 12(9):1779. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12091779
Chicago/Turabian StyleShamsol Azman, Ain Nabila Syahira, Jun Jie Tan, Muhammad Nazrul Hakim Abdullah, Hasnah Bahari, Vuanghao Lim, and Yoke Keong Yong. 2023. "Network Pharmacology and Molecular Docking Analysis of Active Compounds in Tualang Honey against Atherosclerosis" Foods 12, no. 9: 1779. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12091779
APA StyleShamsol Azman, A. N. S., Tan, J. J., Abdullah, M. N. H., Bahari, H., Lim, V., & Yong, Y. K. (2023). Network Pharmacology and Molecular Docking Analysis of Active Compounds in Tualang Honey against Atherosclerosis. Foods, 12(9), 1779. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12091779








