Fish Freshness Indicator for Sensing Fish Quality during Storage
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Sample Preparation
2.3. Freshness Gas Indicator Development
2.4. Chromaticity Analysis
2.4.1. Polymer Matrix Solution Type and Concentration Differences
2.4.2. Freshness Indicator’s Different Substrate Response Sensitivities
2.5. pH Measurement
2.6. Total Volatile Basic Nitrogen (TVB-N) Content Measurement
2.7. Microbial Analysis
2.8. Ammonia Content Measurement
2.9. Monitoring the Freshness Indicator’s Fish Spoilage and Chromaticity Change
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Freshness Indicator Optimization from Chromaticity
3.2. Chemical and Microbiological Analysis of Stored Fish Samples
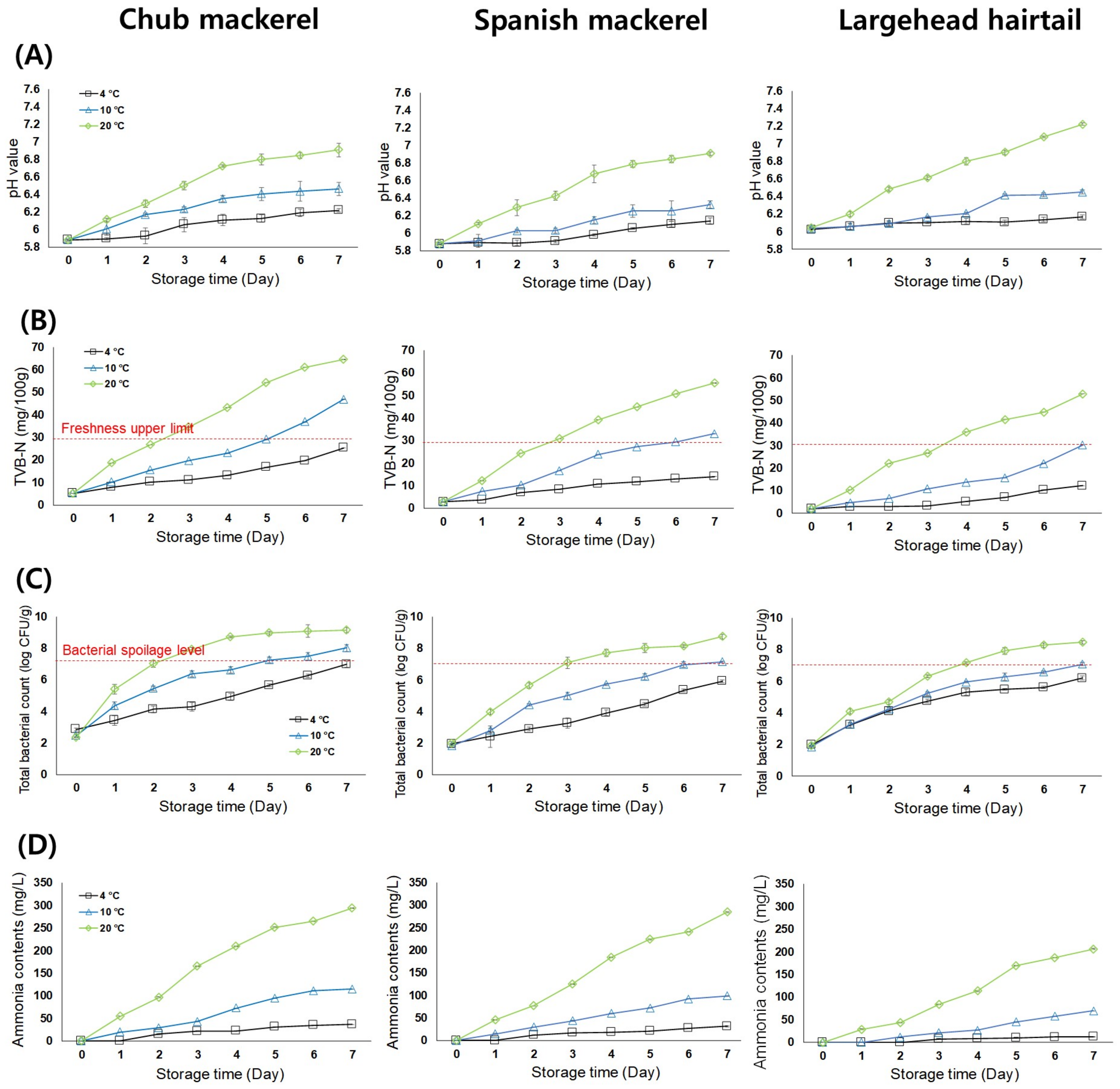
3.2.1. pH Measurement
3.2.2. Total Volatile Basic Nitrogen (TVB-N) Analysis
3.2.3. Microbial Analysis
3.2.4. Ammonia Content Analysis
3.3. Indicator Response during Storage
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pacquit, A.; Lau, K.T.; McLaughlin, H.; Frisby, J.; Quilty, B.; Diamond, D. Development of a volatile amine sensor for the monitoring of fish spoilage. Talanta 2006, 69, 515–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafa, F.; Andreescu, S. Chemical and Biological Sensors for Food-Quality Monitoring and Smart Packaging. Foods 2018, 7, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohail, M.; Sun, D.-W.; Zhu, Z. Recent developments in intelligent packaging for enhancing food quality and safety. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2018, 58, 2650–2662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaani, M.; Cozzolino, C.A.; Castelli, G.; Farris, S. An overview of the intelligent packaging technologies in the food sector. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 51, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao-wei, H.; Xiao-bo, Z.; Ji-yong, S.; Zhi-hua, L.; Jie-wen, Z. Colorimetric sensor arrays based on chemo-responsive dyes for food odor visualization. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 81, 90–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grzyb, A.; Wolna-Maruwka, A.; Niewiadomska, A. The Significance of Microbial Transformation of Nitrogen Compounds in the Light of Integrated Crop Management. Agronomy 2021, 11, 1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.-J.; Shin, H.-S. Development of a freshness indicator for monitoring the quality of beef during storage. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2019, 28, 1899–1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tonezzer, M. Detection of Mackerel Fish Spoilage with a Gas Sensor Based on One Single SnO2 Nanowire. Chemosensors 2021, 9, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, J.S.; Lall, S.P.; Anderson, D.M.; Mcniven, M.A. Evaluation of Protein-Quality in Fish Meals by Chemical and Biological Assays. Aquaculture 1993, 115, 305–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuswandi, B.; Wicaksono, Y.; Abdullah, A.; Heng, L.Y.; Ahmad, M. Smart packaging: Sensors for monitoring of food quality and safety. Sens. Instrum. Food Qual. Saf. 2011, 5, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chun, H.N.; Kim, B.; Shin, H.S. Evaluation of a freshness indicator for quality of fish products during storage. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2014, 23, 1719–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrne, L.; Lau, K.T.; Diamond, D. Monitoring of headspace total volatile basic nitrogen from selected fish species using reflectance spectroscopic measurements of pH sensitive films. Analyst 2002, 127, 1338–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, G.-Y.; Lee, S.; Shin, H.-S. Evaluation of gas freshness indicator for determination of skate (Raja kenojei) quality during storage. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2016, 25, 1497–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.-J.; Shin, H.-S. Effect of treatment with ozonated water on shelf life of refrigerated meat. Food Sci. Anim. Resour. 2011, 31, 617–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarnoski, P.J.; O’Keefe, S.F.; Jahncke, M.L.; Mallikarjunan, P.; Flick, G.J. Analysis of crab meat volatiles as possible spoilage indicators for blue crab (Callinectes sapidus) meat by gas chromatography—Mass spectrometry. Food Chem. 2010, 122, 930–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Béné, A.; Hayman, A.; Reynard, E.; Luisier, J.; Villettaz, J. A new method for the rapid determination of volatile substances: The SPME-direct method: Part II. Determination of the freshness of fish. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2001, 72, 204–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loughran, M.; Diamond, D. Monitoring of volatile bases in fish sample headspace using an acidochromic dye. Food Chem. 2000, 69, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.Y.; Zhang, Y.R.; Huang, L.; Wang, M.Y. A colorimetric gas-sensitive array sensor using filter paper for the analysis of fish freshness. Food Chem. 2022, 377, 132029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, S.T.; Yao, M.W.Y.; Wong, Y.C.; Wong, T.; Mok, C.S.; Sin, D.W.M. Evaluation of chemical indicators for monitoring freshness of food and determination of volatile amines in fish by headspace solid-phase microextraction and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2006, 224, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilahun, S.; An, H.S.; Hwang, I.G.; Choi, J.H.; Baek, M.W.; Choi, H.R.; Park, D.S.; Jeong, C.S. Prediction of α-solanine and α-chaconine in potato tubers from hunter color values and VIS/NIR spectra. J. Food Qual. 2020, 2020, 8884219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Xin, J.; Zhao, J. A novel technique for rapid evaluation of fish freshness using colorimetric sensor array. J. Food Eng. 2011, 105, 632–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.-W.; Kim, H.-J.; Seol, D.-E.; Ko, J.-Y.; Kim, S.-H.; Yang, J.-Y.; Lee, Y. Evaluation of Largehead Hairtail Trichiurus lepturus Freshness Using Sensory and Chemical Analyses. Korean J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2019, 52, 735–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, P.; Padrón, J.C.P.; Cansino, M.J.C.; Velázquez, E.S.; De Larriva, R.M. Total volatile base nitrogen and its use to assess freshness in European sea bass stored in ice. Food Control 2006, 17, 245–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gram, L.; Huss, H.H. Microbiological spoilage of fish and fish products. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 1996, 33, 121–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Florek, M.; Litwinczuk, A.; Skalecki, P.; Ryszkowska-Siwko, M. Changes of physicochemical properties of bullocks and heifers meat during 14 days of ageing under vacuum. Pol. J. Food Nutr. Sci. 2007, 57, 281–287. [Google Scholar]
- Rukchon, C.; Nopwinyuwong, A.; Trevanich, S.; Jinkarn, T.; Suppakul, P. Development of a food spoilage indicator for monitoring freshness of skinless chicken breast. Talanta 2014, 130, 547–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacquit, A.; Frisby, J.; Diamond, D.; Lau, K.T.; Farrell, A.; Quilty, B.; Diamond, D. Development of a smart packaging for the monitoring of fish spoilage. Food Chem. 2007, 102, 466–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morsy, M.K.; Zór, K.; Kostesha, N.; Alstrøm, T.S.; Heiskanen, A.; El-Tanahi, H.; Sharoba, A.; Papkovsky, D.; Larsen, J.; Khalaf, H. Development and validation of a colorimetric sensor array for fish spoilage monitoring. Food Control 2016, 60, 346–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Lee, S.; Lee, K.; Baek, S.; Seo, J. Development of a pH indicator composed of high moisture-absorbing materials for real-time monitoring of chicken breast freshness. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2017, 26, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, R.; Wang, L.; Su, Y.; He, S.; He, B.; Li, C.; Wang, C.; Liu, Y.; Chen, S. Preparation of pH-indicator films based on soy protein isolate/bromothymol blue and methyl red for monitoring fresh-cut apple freshness. J. Food Sci. 2021, 86, 4594–4610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Concentration of Ammonia (mg/L) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 15 | 30 | 50 | 100 | 200 | |
| ∆E | 0 a | 22.3 ± 1.9 b | 40.3 ± 3.4 c | 46.3 ± 1.5 c | 54.9 ± 1.7 d | 60.2 ± 1.2 e |
| L | 80.4 ± 1.9 f | 76.4 ± 1.1 e | 63.4 ± 2.7 d | 60.8 ± 1.6 c | 54.7 ± 1.7 b | 51.1 ± 1.0 a |
| a | 16.0 ± 3.1 d | 14.3 ± 1.4 c | −3.4 ± 4.1 a | −1.5 ± 0.9 b | 1.6 ± 0.6 b | 0.1 ± 0.9 b |
| b | 50.3 ± 2.4 f | 28.4 ± 2.2 e | 19.4 ± 3.0 d | 12.2 ± 2.1 c | 4.0 ± 2.2 b | 0.2 ± 1.2 a |
| Ammonia Concentration (mg/L) | ∆E Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| PTFE-D | PVDF-D | Breathron | |
| 0 | 0 aA | 0 aA | 0 aA |
| 15 | 10.1 ± 1.4 bA | 19.6 ± 1.7 bC | 15.0 ± 1.1 bB |
| 30 | 27.1 ± 2.1 bA | 26.1 ± 3.3 bA | 23.9 ± 2.4 bA |
| 50 | 42.3 ± 4.6 cB | 32.3 ± 2.1 cA | 29.2 ± 1.7 cA |
| 100 | 51.3 ± 1.0 dB | 43.4 ± 3.4 dA | 38.7 ± 2.5 dA |
| 200 | 54.9 ± 0.6 eB | 48.1 ± 2.0 eA | 44.9 ± 1.3 eA |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, D.-Y.; Park, S.-W.; Shin, H.-S. Fish Freshness Indicator for Sensing Fish Quality during Storage. Foods 2023, 12, 1801. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12091801
Kim D-Y, Park S-W, Shin H-S. Fish Freshness Indicator for Sensing Fish Quality during Storage. Foods. 2023; 12(9):1801. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12091801
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Do-Yeong, Sung-Woo Park, and Han-Seung Shin. 2023. "Fish Freshness Indicator for Sensing Fish Quality during Storage" Foods 12, no. 9: 1801. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12091801
APA StyleKim, D.-Y., Park, S.-W., & Shin, H.-S. (2023). Fish Freshness Indicator for Sensing Fish Quality during Storage. Foods, 12(9), 1801. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12091801






