Sensory Attributes and Instrumental Chemical Parameters of Commercial Spanish Cured Ewes’ Milk Cheeses: Insights into Cheese Quality Figures
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cheese Samples
2.2. Sample Preparation
2.3. Optimization of HS-SPME Procedure
2.4. Analysis of Texture, Color, pH, Humidity, and Water Activity
2.5. Sensory Analysis
2.5.1. Descriptive Sensory Analysis
2.5.2. Affective Sensory Analysis
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Optimization of Volatiles Extracted from Hard-Cured Ewe Cheese Samples by HS-SPME
3.1.1. Fitting the Model
3.1.2. Effects of Independent Variables on Volatiles Extraction
3.1.3. Determination of Optimal HS-SPME Conditions
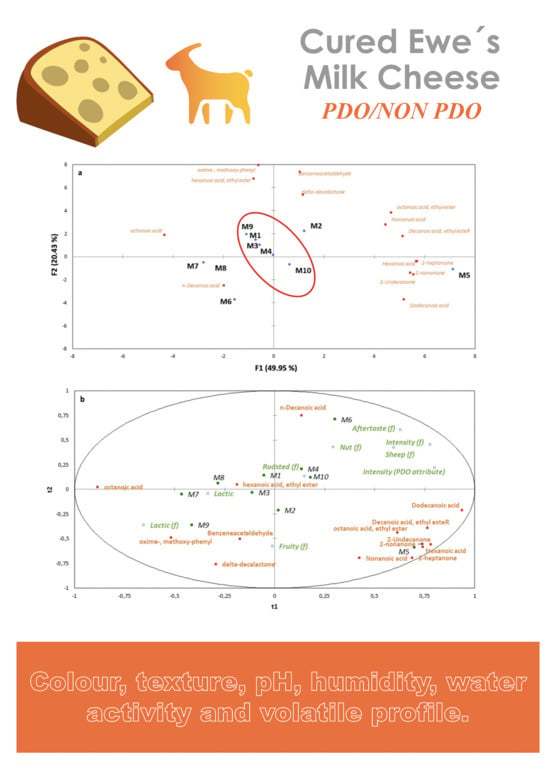
3.2. Characterization of the Main Volatile Compounds in Spanish Hard-Cured Ewe Cheeses Using HS-SPME–GC–MS
3.3. Color, Texture, Humidity, Water Activity and pH Analysis
3.4. Descriptive Sensory Analysis
3.5. Affective Sensory Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mohapatra, A.; Shinde, A.K.; Singh, R. Sheep Milk: A Pertinent Functional Food. Small Rumin. Res. 2019, 181, 6–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAOSTAT Statistics Database-Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. Available online: https://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#data (accessed on 3 January 2023).
- Ministry of Agriculture, Fishing and Food. The Sheep and Goat Milk Sector in Figures. 2022. Available online: https://www.mapa.gob.es/eu/ganaderia/estadisticas/mercados_agricolas_ganaderos.aspx (accessed on 3 January 2023).
- Ochoa-Flores, A.A.; Hernández-Becerra, J.A.; Velázquez-Martínez, J.R.; Piña-Gutiérrez, J.M.; Hernández-Castellano, L.E.; Toro-Mujica, P.; Chay-Canul, A.J.; Vargas-Bello-Pérez, E. Chemical and Fatty Acid Composition of Manchego Type and Panela Cheeses Manufactured from Either Hair Sheep Milk or Cow Milk. J. Dairy. Sci. 2021, 104, 7457–7465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawȩcka, A.; Sosin-Bzducha, E. Seasonal Changes of the Chemical Composition of Cheese Obtained from the Milk of Indigenous Polish Breeds of Sheep. J. Anim. Feed. Sci. 2014, 23, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MAPA Denominaciones de Origen e Indicaciones Geográficas Protegidas. Available online: https://www.mapa.gob.es/es/alimentacion/temas/calidad-diferenciada/dop-igp/ (accessed on 10 May 2021).
- Ministry Ley 6/2015, de 12 de Mayo, de Denominaciones de Origen e Indicaciones Geográficas Protegidas de Ámbito Territorial Supraautonómico. Boletín Oficial Del Estado, Spain. 2015; 41158–41187.
- Ministry Real Decreto 1113/2006, de 29 de Septiembre, Por El Que Se Aprueban Las Normas de Calidad Para Quesos y Quesos Fundidos. Boletín Oficial Del Estado, Spain. 2015; 1–7.
- Subdirección General de Producciones Ganaderas y Cinegéticas, Dirección General de Producciones y Mercados Agrarios. Indicadores Semestrales Situación Sector Ovino Leche España, Spain. 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Reinders, M.J.; Banovic, M.; Guerrero, L. Chapter 1—Introduction; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; ISBN 9780128148884. [Google Scholar]
- Sánchez, I.; Seseña, S.; Poveda, J.M.; Cabezas, L.; Palop, L. Genetic Diversity, Dynamics, and Activity of Lactobacillus Community Involved in Traditional Processing of Artisanal Manchego Cheese. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2006, 107, 265–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rovai, M.; Caja, G.; Quevedo, J.M.; Manuelian, C.L.; Saldo, J.; Salama, A.A.K.; Torre, P.; Arana, I.; Such, X.; Leitner, G. Effect of Subclinical Intramammary Infection on Milk Quality in Dairy Sheep: II. Matured-Pressed Cheese (Manchego) Produced from Milk of Uninfected and Infected Glands and from Their Blends. Small Rumin. Res. 2015, 126, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- JCCM Junta de Comunidades de Castilla-La Mancha. Pliego de Condiciones “D.O.P. Queso Manchego”. Available online: https://pagina.jccm.es/agricul/paginas/comercial-industrial/consejos_new/manchego.htm (accessed on 3 January 2023).
- Ballesteros, C.; Poveda, J.M.; González-Viñas, M.A.; Cabezas, L. Microbiological, Biochemical and Sensory Characteristics of Artisanal and Industrial Manchego Cheeses. Food Control 2006, 17, 249–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado, F.J.; González-Crespo, J.; Cava, R.; García-Parra, J.; Ramírez, R. Characterisation by SPME-GC-MS of the Volatile Profile of a Spanish Soft Cheese P.D.O. Torta Del Casar during Ripening. Food Chem. 2010, 118, 182–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plutowska, B.; Wardencki, W. Aromagrams—Aromatic Profiles in the Appreciation of Food Quality. Food Chem. 2007, 101, 845–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavia, M.; Guamis, B.; Trujillo, A.J.; Capellas, M.; Ferragut, V. Changes in Microstructural, Textural and Colour Characteristics during Ripening of Manchego-Type Cheese Salted by Brine Vacuum Impregnation. Int. Dairy. J. 1999, 9, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sendra, E.; Saldo, J. Servilleta Cheese. Proteolysis, Colour and Texture. Milchwissenschaft 2004, 59, 34–37. [Google Scholar]
- Fernández-García, E.; Carbonell, M.; Nuñez, M. Volatile Fraction and Sensory Characteristics of Manchego Cheese. 1. Comparison of Raw and Pasteurized Milk Cheese. J. Dairy Res. 2002, 69, 579–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villaseñor, M.J.; Valero, E.; Sanz, J.; Castro, I.M. Analysis of Volatile Components of Manchego Cheese by Dynamic Headspace Followed by Automatic Thermal Desorption-GC-MS. Milchwissenschaft 2000, 55, 378–382. [Google Scholar]
- Siano, F.; Fasulo, G.; Giaramita, L.; Sorrentino, A.; Boscaino, F.; Sprovieri, M.; Di Stasio, M.; Coccini, R.; Volpe, M.G. Chemical-Nutrition Composition, Microbiological Analysis and Volatile Compound Content of Fossa Cheese Ripenes in Diferents Pits. Ital. J. Food Sci. 2019, 31, 669–684. [Google Scholar]
- ISO Standard 8586-1; General Guidance for the Selection, Training and Monitoring of Assessors; Part 1: Selected Assessors; ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 1993.
- Vargas-Bello-Pérez, E.; Fehrmann-Cartes, K.; Íiguez-González, G.; Toro-Mujica, P.; Garnsworthy, P.C. Short Communication: Chemical Composition, Fatty Acid Composition, and Sensory Characteristics of Chanco Cheese from Dairy Cows Supplemented with Soybean and Hydrogenated Vegetable Oils. J. Dairy. Sci. 2015, 98, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miloradovic, Z.; Tomic, N.; Kljajevic, N.; Levic, S.; Pavlovic, V.; Blazic, M.; Miocinovic, J. High Heat Treatment of Goat Cheese Milk. The Effect on Sensory Profile, Consumer Acceptance and Microstructure of Cheese. Foods 2021, 10, 1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramírez-Rivera, E.J.; Ramón-Canul, L.G.; Díaz-Rivera, P.; Juárez-Barrientos, J.M.; Herman-Lara, E.; Prinyawiwatkul, W.; Herrera-Corredor, J.A. Sensory Profiles of Artisan Goat Cheeses as Influenced by the Cultural Context and the Type of Panel. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 52, 1789–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez-Rivera, E.D.J.; Díaz-Rivera, P.; Guadalupe Ramón-Canul, L.; Juárez-Barrientos, J.M.; Rodríguez-Miranda, J.; Herman-Lara, E.; Prinyawiwatkul, W.; Herrera-Corredor, J.A. Comparison of Performance and Quantitative Descriptive Analysis Sensory Profiling and Its Relationship to Consumer Liking between the Artisanal Cheese Producers Panel and the Descriptive Trained Panel. J. Dairy. Sci. 2018, 101, 5851–5864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cano-Lamadrid, M.; Martínez-Zamora, L.; Castillejo, N.; Cattaneo, C.; Pagliarini, E.; Artés-Hernández, F. How Does the Phytochemical Composition of Sprouts and Microgreens from Brassica Vegetables Affect the Sensory Profile and Consumer Acceptability? Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2023, 203, 112411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cano-Lamadrid, M.; Tkacz, K.; Turkiewicz, I.P.; Clemente-Villalba, J.; Sánchez-Rodríguez, L.; Lipan, L.; García-García, E.; Carbonell-Barrachina, Á.A.; Wojdyło, A. How a Spanish Group of Millennial Generation Perceives the Commercial Novel Smoothies? Foods 2020, 9, 1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cano-Lamadrid, M.; Vázquez-Araújo, L.; Sánchez-Rodríguez, L.; Wodyło, A.; Carbonell-Barrachina, Á.A. Consumers’ Opinion on Dried Pomegranate Arils to Determine the Best Processing Conditions. J. Food Sci. 2018, 83, 3085–3091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Rodríguez, L.; Cano-Lamadrid, M.; Carbonell-Barrachina, Á.A.; Sendra, E.; Hernández, F. Volatile Composition, Sensory Profile and Consumer Acceptability of HydroSOStainable Table Olives. Foods 2019, 8, 470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipan, L.; Cano-Lamadrid, M.; Corell, M.; Sendra, E.; Hernández, F.; Stan, L.; Vodnar, D.C.; Vázquez-Araújo, L.; Carbonell-Barrachina, Á.A. Sensory Profile and Acceptability of HydroSOStainable Almonds. Foods 2019, 8, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clemente-Villalba, J.; Cano-Lamadrid, M.; Issa-Issa, H.; Hurtado, P.; Hernández, F.; Carbonell-Barrachina, Á.A.; López-Lluch, D. Comparison on Sensory Profile, Volatile Composition and Consumer’s Acceptance for PDO or Non-PDO Tigernut (Cyperus esculentus L.) Milk. LWT 2021, 140, 110606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezerra, T.K.A.; Araújo, A.R.R.; Arcanjo, N.M.O.; da Silva, F.L.H.; Queiroga, R.C.R.E.; Madruga, M.S. Optimization of the HS-SPME-GC/MS Technique for the Analysis of Volatile Compounds in Caprine Coalho Cheese Using Response Surface Methodology. Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 36, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, A.V.; Pérez, S.E.M.; Butsko, M.; Moya, M.S.P.; Sanahuja, A.B. Authentication of “Adelita” Raspberry Cultivar Based on Physical Properties, Antioxidant Activity and Volatile Profile. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trujillo-Rodríguez, M.J.; Yu, H.; Cole, W.T.S.; Ho, T.D.; Pino, V.; Anderson, J.L.; Afonso, A.N. Polymeric Ionic Liquid Coatings versus Comercial Solid-Phase Microextraction Coatings for the Determination of Volatile Compounds in Cheeses. Talanta 2014, 121, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gómez-Ruiz, J.A.; Cabezas, L.; Martínez-Castro, I.; González-Viñas, M.A.; Poveda, J.M. InXuence of a DeWned-Strain Starter and Lactobacillus Plantarum as Adjunct Culture on Volatile Compounds and Sensory Characteristics of Manchego Cheese. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2008, 227, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, M.; Hospital, X.F.; Arias, K.; Hierro, E. Application of Pulsed Light to Sliced Cheese: Effect on Listeria Inactivation, Sensory Quality and Volatile Profile. Food Bioproc Technol. 2016, 9, 1335–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallia, S.; Fernández-García, E.; Olivier Bosset, J. Comparison of Purge and Trap and Solid Phase Microextraction Techniques for Studying the Volatile Aroma Compounds of Three European PDO Hard Cheeses. Int. Dairy. J. 2005, 15, 741–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McSweeney, P.L.H. Biochemistry of Cheese Ripening. Int. J. Dairy. Technol. 2004, 57, 127–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urgeghe, P.P.; Piga, C.; Addis, M.; Di Salvo, R.; Piredda, G.; Scintu, M.F.; Wolf, I.V.; Sanna, G. SPME/GC-MS Characterization of the Volatile Fraction of an Italian PDO Sheep Cheese to Prevalent Lypolitic Ripening: The Case of Fiore Sardo. Food Anal. Methods 2012, 5, 723–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- del Caja, M.M.; del Castillo, M.L.R.; Blanch, G.P. Solid-Phase Microextraction to the Study of the Stability of Selected Volatile Constituents in Irradiated Manchego Cheese. Food Anal. Methods 2011, 4, 608–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bovolenta, S.; Romanzin, A.; Corazzin, M.; Spanghero, M.; Aprea, E.; Gasperi, F.; Piasentier, E. Volatile Compounds and Sensory Properties of Montasio Cheese Made from the Milk of Simmental Cows Grazing on Alpine Pastures. J. Dairy. Sci. 2014, 97, 7373–7385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Good Scents Company Information System Providing Information for the Flavor, Fragrance, Food and Cosmetic Industries. Available online: http://www.thegoodscentscompany.com (accessed on 3 January 2023).
- Curioni, P.M.G.; Bosset, J.O. Key Odorants in Various Cheese Types as Determined by Gas Chromatography-Olfactometry. Int. Dairy. J. 2002, 12, 959–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poveda, J.M.; Nieto-Arribas, P.; Seseña, S.; Chicón, R.; Castro, L.; Palop, L.; Cabezas, L. Volatile Composition and Improvement of the Aroma of Industrial Manchego Cheese by Using Lactobacillus paracasei subsp. Paracasei as Adjunct and Other Autochthonous Strains as Starters. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2014, 238, 485–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Castro, I.; Sanz, J.; Martín-Alvarez, P. Volatile Components of Manchego Cheese. J. Dairy. Res. 1991, 58, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sieber, R.; Bütikofer, U.; Bosset, J.O. Benzoic Acid as a Natural Compound in Cultured Dairy Products and Cheese. Int. Dairy. J. 1995, 5, 227–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, Y.F.; McSweeney, P.L.H.; Wilkinson, M.G. Lipolysis and Free Fatty Acid Catabolism in Cheese: A Review of Current Knowledge. Int. Dairy. J. 2003, 13, 841–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solano-Lopez, C.E.; Ji, T.; Alvarez, V.B. Volatile Compounds and Chemical Changes in Ultrapasteurized Milk Packaged in Polyethylene Terephthalate Containers. J. Food Sci. 2005, 70, c407–c412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Zhang, L.; Li, Y. Production of Volatile Compounds in Reconstituted Milk Reduced-Fat Cheese and the Physicochemical Properties as Affected by Exopolysaccharide-Producing Strain. Molecules 2012, 17, 14393–14408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taborda, G.; Gómez-Ruiz, J.A.; Martínez-Castro, I.; Amigo, L.; Ramos, M.; Molina, E. Taste and Flavor of Artisan and Industrial Manchego Cheese as Influenced by the Water-Soluble Extract Compounds. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2008, 227, 323–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McSweeney, P.L.H.; Fox, P.F.; Cotter, P.D.; Everett, D.W. Cheese: Chemistry, Physics and Microbiology, 4th ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; Volume 1, ISBN 9780122636530. [Google Scholar]
- Picon, A.; Serrano, C.; Gaya, P.; Medina, M.; Nuñez, M. The Effect of Liposome-Encapsulated Cyprosins on Manchego Cheese Ripening. J. Dairy. Sci. 1996, 79, 1699–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, C.A.; Gholamhosseinpour, A.; Ipsen, R.; Hougaard, A.B. The Effect of Age on Cheddar Cheese Melting, Rheology and Structure, and on the Stability of Feed for Cheese Powder Manufacture. Int. Dairy. J. 2016, 55, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calzada, J.; del Olmo, A.; Picon, A.; Gaya, P.; Nuñez, M. High-Pressure Processing for the Control of Lipolysis, Volatile Compounds and Off-Odours in Raw Milk Cheese. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2014, 7, 2207–2217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dufossé, L.; Galaup, P.; Carlet, E.; Flamin, C.; Valla, A. Spectrocolorimetry in the CIE L*a*b* Color Space as Useful Tool for Monitoring the Ripening Process and the Quality of PDO Red-Smear Soft Cheeses. Food Res. Int. 2005, 38, 919–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, T.; Sun, D.-W. Developments of Nondestructive Techniques for Evaluating Quality Attributes of Cheeses: A Review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 88, 527–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malegori, C.; Oliveri, P.; Mustorgi, E.; Boggiani, M.A.; Pastorini, G.; Casale, M. An In-Depth Study of Cheese Ripening by Means of NIR Hyperspectral Imaging: Spatial Mapping of Dehydration, Proteolysis and Lipolysis. Food Chem. 2021, 343, 128547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cipolat-Gotet, C.; Malacarne, M.; Summer, A.; Cecchinato, A.; Bittante, G. Modeling Weight Loss of Cheese during Ripening and the Influence of Dairy System, Parity, Stage of Lactation, and Composition of Processed Milk. J. Dairy. Sci. 2020, 103, 6843–6857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Sample Code | PDO | Minimum Maturation | Origin | Ingredients | Nutritional Information (100 g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M1 | Yes | - | - | Raw Manchega sheep milk, animal rennet, lactic ferments, egg lysozymes, non- edible crust | Energy value 437 kcal, fat 38 g (saturated 34 g), protein 24 g, salt 1.7 g |
| M3 | Yes | - | Ciudad Real | Raw sheep milk, animal rennet, lactic ferments, salt, egg lysozyme, natamycin preservative | Energy value 461 kcal, fat 39 g (saturated 26 g), protein 23 g, salt (g) 1.8 g |
| M4 | Yes | 4–5 months | Navarra | Raw sheep milk, rennet, Spanish dairy crops, salt, egg lysozyme, milk and derivatives, eggs | Energy value 478 kcal, fat 41.5 g (saturated 27.3 g), protein 26 g, salt 1.7 g |
| M9 | Yes | 4 months | Ciudad Real | Pasteurized La Mancha sheep’s milk, salt, lactic ferments, rennet, E-252, calcium chloride | Energy value 422 kcal, fat 36 g (saturated 23 g), protein 24 g, salt 1.7 g |
| M10 | Yes | 6–12 months | Cuenca | Raw sheep’s milk, lactic cultures, calcium chloride, salt, rennet, lysozyme preservative | Energy value 467 kcal, fat 33 g, (saturated 18.7 g), protein 23 g, salt 1.5 g |
| M2 | No | - | Palencia | Pasteurized sheep’s milk, salt, rennet, calcium chloride, E-1105, lactic ferments | Energy value 458 kcal, fat 36 g (saturated 25 g), protein 25 g, salt 1.7 g |
| M5 | No | 3–4 months | Cádiz | Pasteurized sheep’s milk, salt, rennet, lactic cultures, egg lysozyme | Energy value 425 kcal, fat 34.04 g (saturated 24.15 g), protein 25.61 g, salt 1.8 g |
| M6 | No | 10–14 months | Madrid | Milk, salt, rennet, E-509, egg lysozyme, lactic ferments, E202, natamycin, E172 | Energy value 485 kcal, fat 41 g (saturated 28 g), protein 28 g, salt 1.7 g |
| M7 | No | - | Madrid | Pasteurized sheep milk, lactic ferments, salt, rennet, E-252, E-202, E-235 | Energy value 441 kcal, fats 36.40 g (saturated 26 g), proteins 27 g, salt 1.6 g |
| M8 | No | - | - | Raw sheep’s milk, rennet, lactic ferments, salt; may contain egg | Energy value 434 kcal, fat 7 g (saturated 26 g), protein 25 g, salt 1.5 g |
| Run | Factor A | Factor B | Factor C | Sum of Areas |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 52.5 | 15 | 3 | 1.32 × 109 |
| 2 | 70 | 60 | 1.75 | 1.76 × 109 |
| 3 | 70 | 37.5 | 3 | 4.03 × 109 |
| 4 | 35 | 37.5 | 0.5 | 5.56 × 108 |
| 5 | 52.5 | 15 | 0.5 | 1.10 × 109 |
| 6 | 52.5 | 37.5 | 1.75 | 2.18 × 109 |
| 7 | 52.5 | 37.5 | 1.75 | 2.27 × 109 |
| 8 | 70 | 15 | 1.75 | 2.70 × 109 |
| 9 | 52.5 | 37.5 | 1.75 | 2.36 × 109 |
| 10 | 70 | 37.5 | 0.5 | 2.44 × 109 |
| 11 | 52.5 | 60 | 3 | 3.05 × 109 |
| 12 | 52.5 | 60 | 0.5 | 1.88 × 109 |
| 13 | 52.5 | 37.5 | 1.75 | 2.19 × 109 |
| 14 | 35 | 15 | 1.75 | 4.80 × 108 |
| 15 | 52.5 | 37.5 | 1.75 | 4.24 × 109 |
| 16 | 35 | 60 | 1.75 | 1.01 × 109 |
| 17 | 35 | 37.5 | 3 | 8.76 × 108 |
| Sum of Squares | Freedom Degrees | Mean Square | F-Value | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 8.02 × 1018 | 1 | 8.02 × 1018 | 10.04 | 0.0339 * |
| B | 5.49 × 1017 | 1 | 5.49 × 1017 | 0.69 | 0.4537 |
| C | 1.38 × 1018 | 1 | 1.38 × 1018 | 1.72 | 0.2595 |
| AA | 1.10 × 1018 | 1 | 1.10 × 1018 | 1.38 | 0.3057 |
| AB | 5.47 × 1017 | 1 | 5.47 × 1017 | 0.69 | 0.4543 |
| AC | 4.06 × 1017 | 1 | 4.06 × 1017 | 0.51 | 0.5153 |
| BB | 1.77 × 1018 | 1 | 1.77 × 1018 | 2.22 | 0.2108 |
| BC | 2.26 × 1017 | 1 | 2.26 × 1017 | 0.28 | 0.6229 |
| CC | 1.09 × 1017 | 1 | 1.09 × 1017 | 0.14 | 0.7305 |
| Lack-of-fit | 1.64 × 1018 | 3 | 5.47 × 1017 | 0.68 | 0.6067 |
| Pure error | 3.20 × 1018 | 4 | 7.99 × 1017 | ||
| Total (corr.) | 1.92 × 1019 | 16 |
| Code b | Rt | O | F | M1 | M2 | M3 | M4 | M5 | M6 | M7 | M8 | M9 | M10 | ANOVA PDO/Non-PDO | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 15.7 | Sour, fatty | Cheesy, fruity | 0.03 ± 0.01 a | 0.19 ± 0.05 c | 0.04 ± 0.01 ad | 0.04 ± 0.01 ad | 0.60 ± 0.02 e | 0.01 ± 0.00 a | 0.02 ± 0.00 a | 0.04 ± 0.01 ad | 0.09 ± 0.01 bd | 0.12 ± 0.02 b | *** | 0.0004 |
| 2 | 18.3 | Ni | Ni | 5.38 ± 0.98 a | 3.36 ± 0.50 b | 3.86 ± 0.04 c | 2.52 ± 0.42 b | 2.52 ± 0.40 b | 2.31 ± 0.03 b | 2.85 ± 0.27 b | 3.31 ± 0.09 a | 4.71 ± 0.61 a | 2.11 ± 0.21 b | NS | 0.4053 |
| 3 | 18.9 | Fruity | Fruity | 0.23 ± 0.03 a | 0.18 ± 0.08 ab | 0.12 ± 0.01 b | 0.17 ± 0.03 ab | 0.02 ± 0.01 cd | 0.03 ± 0.01 cd | 0.05 ± 0.01 cd | 0.06 ± 0.00 d | 0.12 ± 0.01 bd | 0.13 ± 0.01 b | *** | 0.0003 |
| 4 | 20.3 | Sour, fatty | Sour, fruity | 17.00 ± 5.71 a | 15.73 ± 2.27 a | 14.84 ± 1.72 a | 18.61 ± 0.68 a | 54.90 ± 3.68 b | 7.22 ± 0.18 c | 3.77 ± 0.07 c | 7.23 ± 0.17 c | 7.53 ± 0.12 c | 12.34 ± 1.58 ac | NS | 0.1952 |
| 5 | 21.8 | Green | Honey | 0.14 ± 0.02 a | 0.36 ± 0.01 c | 0.26 ± 0.05 d | 0.09 ± 0.01 a | 0.12 ± 0.01 a | 0.03 ± 0.01 b | 0.10 ± 0.01 ab | 0.05 ± 0.00 b | 0.24 ± 0.01 d | 0.16 ± 0.01 a | *** | 0.0004 |
| 6 | 22.6 | Fruity | Cheesy | 0.31 ± 0.05 a | 0.79 ± 0.20 c | 0.10 ± 0.01 a | 0.10 ± 0.01 a | 4.03 ± 0.37 d | 0.06 ± 0.00 a | 0.04 ± 0.00 a | 0.06 ± 0.01 a | 0.30 ±0.03 a | 2.14 ± 0.16 b | * | 0.0468 |
| 7 | 25.6 | Waxy | Waxy | 0.34 ± 0.02 ac | 0.35 ± 0.07 ac | 0.25 ±0.02 ad | 0.26 ± 0.05 ad | 0.42 ± 0.07 c | 0.06 ± 0.01 b | 0.02 ± 0.00 b | 0.03 ± 0.01 b | 0.12 ± 0.01 bd | 0.21 ± 0.02 d | *** | 0.0005 |
| 8 | 26.3 | Fatty, cheesy | Soapy, brandy | 37.74 ± 1.67 a | 37.59 ± 0.92 a | 36.40 ± 1.37 a | 32.07 ± 3.22 ce | 10.57 ± 0.71 d | 28.45 ± 1.47 e | 82.16 ± 0.27 f | 46.42 ± 0.97 b | 50.94 ± 2.00 b | 34.26 ± 1.90 ac | ** | 0.0043 |
| 9 | 28.6 | Floral | Sweat, cheese | 0.17 ± 0.03 a | 0.22 ± 0.10 a | 0.06 ± 0.01 a | 0.04 ± 0.02 a | 1.69 ± 0.19 c | 0.01 ± 0.00 a | 0.04 ± 0.01 a | 0.05 ± 0.01 a | 0.07 ± 0.01 a | 0.56 ± 0.10 b | ** | 0.0014 |
| 10 | 28.8 | Waxy, cheesy | Cheesy, creamy | 0.73 ± 0.03 a | 1.81 ± 0.15 c | 0.82 ± 0.04 a | 1.48 ± 0.01 b | 2.18 ± 0.25 d | 0.75 ± 0.06 a | 0.92 ± 0.03 a | 0.49 ± 0.03 a | 1.58 ± 0.04 bc | 0.75 ± 0.10 a | * | 0.0217 |
| 11 | 30.9 | Sweet, apple | Waxy, fruity | 0.54 ± 0.09 a | 0.94 ± 0.17 b | 0.63 ± 0.04 a | 1.00 ± 0.36 ab | 1.28 ± 0.21 b | 0.32 ± 0.01 c | 0.03 ± 0.01 d | 0.06 ± 0.01 d | 0.33 ± 0.07 c | 0.63 ± 0.06 a | ** | 0.0025 |
| 12 | 31.6 | Fatty, citrus | Waxy, fruity | 35.39 ± 4.87 ac | 35.36 ± 2.81 a | 39.80 ± 1.51 ab | 41.50 ± 2.09 ab | 14.37 ± 1.26 c | 59.04 ± 1.47 d | 9.31 ± 0.51 e | 40.23 ± 0.80 b | 32.34 ± 2.76 a | 42.22 ± 0.67 ab | ** | 0.0013 |
| 13 | 35.9 | Coconut | Coconut | 0.27 ± 0.03 a | 0.49 ± 0.10 bc | 0.50 ± 0.03 b | 0.37 ± 0.02 c | 0.50 ± 0.03 b | 0.08 ± 0.01 d | 0.32 ± 0.01 a | 0.58 ± 0.08 b | 0.70 ± 0.04 e | 0.46 ± 0.04 b | ** | 0.0010 |
| 14 | 36.4 | Fatty, coconut | Fatty, waxy | 1.74 ± 0.20 a | 2.64 ± 0.33 b | 2.34 ± 0.07 b | 1.74 ± 0.07 a | 6.81 ± 0.63 c | 3.63 ± 0.08 d | 0.38 ± 0.04 e | 1.37 ± 0.15 a | 0.93 ± 0.14 a | 3.91 ± 0.25 d | NS | 0.7000 |
| Force at Fracture (N) | Deformation at Fracture (%) | Work for Fracture (N.mm) | Maximum Force for Compression (N) | L | a* | b* | Aw | Humidity | pH | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ANOVA | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** |
| M1 | 28.25 ± 5.94 b | 41.63 ± 2.80 g | 72.37 ± 12.80 b | 30.50 ± 6.53 b | 65.66 ± 4.05 de | −2.66 ± 0.49 bcd | 12.34 ± 1.73 f | 0.86 ± 0.00 c | 27.48 ± 1.30 de | 5.34 ± 0.08 d |
| M2 | 27.06 ± 6.69 bc | 53.21 ± 5.96 de | 103.38 ± 29.94 a | 28.23 ± 6.84 bc | 67.23 ± 6.50 cd | −2.20 ± 1.21 ab | 14.28 ± 2.20 cde | 0.87 ± 0.00 bc | 28.99 ± 2.44 cd | 5.53 ± 0.08 abc |
| M3 | 20.99 ± 4.01 e | 54.03 ± 4.53 d | 61.79 ± 14.25 bcd | 21.15 ± 3.95 f | 68.23 ± 4.57 bcd | −2.90 ± 0.94 cd | 14.22 ± 0.70 de | 0.86 ± 0.00 c | 25.70 ± 3.29 e | 5.43 ± 0.06 bcd |
| M4 | 38.87 ± 13.01 a | 51.38 ± 4.78 e | 99.39 ± 38.72 a | 40.22 ± 10.74 a | 63.40 ± 4.74 e | −3.14 ± 0.74 d | 13.80 ± 1.82 de | 0.85 ± 0.01 d | 28.48 ± 2.00 cde | 5.41 ± 0.13 cd |
| M5 | 21.77 ± 5.03 de | 47.72 ± 1.70 f | 49.18 ± 12.90 e | 21.98 ± 4.92 ef | 76.04 ± 4.55 a | −1.71 ± 0.80 a | 17.48 ± 2.04 a | 0.86 ± 0.01 bc | 26.82 ± 3.45 de | 5.14 ±0.10 e |
| M6 | 24.80 ± 5.63 bcd | 51.00 ± 3.41 e | 59.63 ± 17.36 cde | 25.21 ± 5.06 cde | 67.75 ± 5.81 cd | −2. 70 ± 1.12 bcd | 13.54 ± 1.36 e | 0.87 ± 0.01 bc | 31.04 ± 1.01 bc | 5.34 ± 0.12 d |
| M7 | 20.35 ± 4.24 e | 62.52 ± 2.12 b | 74.00 ± 18.04 b | 20.65 ± 4.16 f | 70.82 ± 5.25 b | −2.31 ± 0.86 b | 14.28 ± 1.32 cde | 0.87 ± 0.00 bc | 32.38 ± 0.89 b | 5.65 ± 0.10 a |
| M8 | 12.61 ± 2.73 f | 66.39 ± 2.69 a | 50.64 ± 12.14 de | 12.75 ± 2.66 g | 78.76 ± 2.27 a | −2.56 ± 0.26 bc | 15.28 ± 1.73 bc | 0.89 ± 0.01 a | 38.70 ± 0.59 a | 5.45 ± 0.18 bcd |
| M9 | 23.28 ± 3.08 cde | 56.53 ± 1.92 c | 68.21 ± 10.19 bc | 23.40 ± 3.02 def | 65.58 ± 3.58 de | −3.11 ± 1.00 d | 14.68 ± 1.23 cd | 0.87 ± 0.01 b | 28.50 ± 0.51 cde | 5.47 ± 0.44 bcd |
| M10 | 26.16 ± 7.22 bc | 57.10 ± 5.93 c | 53.24 ± 20.98 de | 26.50 ± 7.27 cd | 69.64 ± 3.44 bc | −2.91 ± 0.94 cd | 15.87 ± 2.06 b | 0.86 ± 0.00 cd | 28.89 ± 2.01 cd | 5.58 ± 0.10 ab |
| Attribute | ANOVA | M1 | M2 | M3 | M4 | M5 | M6 | M7 | M8 | M9 | M10 | ANOVA PDO/Non-PDO | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Overall liking | *** | 6.3 ± 2.1 ab | 6.3 ± 1.7 ab | 6.6 ± 1.5 a | 6.5 ± 1.8 a | 6.4 ± 1.8 ab | 6.1 ± 2.1 ab | 4.9 ± 0.5 b | 6.4 ± 1.7 ab | 5.9 ± 2.0 ab | 6.4 ± 2.1 ab | *** | 0.0003 |
| Color | *** | 6.6 ± 1.8 b | 6.7 ± 1.7 b | 7.1 ± 1.4 a | 6.4 ± 1.9 bc | 6.2 ± 1.8 c | 6.6 ± 1.4 ab | 6.8 ± 1.5 b | 6.6 ± 1.8 b | 6.0 ± 1.9 c | 6.5 ± 1.7 bc | *** | 0.0000 |
| Odor | NS | 5.9 ± 1.9 | 6.1 ± 2.0 | 6.3 ± 1.7 | 6.1 ± 2.0 | 5.8 ± 2.2 | 6.0 ± 1.9 | 5.9 ± 1.8 | 5.8 ± 1.6 | 5.6 ± 1.7 | 6.1 ± 1.9 | *** | 0.0003 |
| Firmness | ** | 6.2 ± 1.7 ab | 5.4 ± 2.1 c | 6.4 ± 1.6 a | 6.1 ± 1.9 b | 6.3 ± 1.9 ab | 6.5 ± 1.6 a | 5.8 ± 2.1 b | 5.5 ± 2.0 bc | 6.2 ± 1.9 ab | 6.4 ± 1.6 a | *** | 0.0002 |
| Crumbliness | ** | 6.0 ± 1.9 ab | 5.6 ± 2.0 b | 6.0 ± 2.1 ab | 5.8 ± 1.9 b | 6.3 ± 1.9 a | 6.1 ± 1.8 ab | 5.8 ± 1.8 b | 5.6 ± 1.9 b | 5.7 ± 1.8 b | 6.2 ± 1.8 a | *** | 0.0004 |
| Sourness | NS | 6.0 ± 1.9 | 5.8 ± 1.9 | 6.2 ± 1.6 | 6.0 ± 1.7 | 6.1 ± 1.9 | 5.3 ± 1.9 | 6.3 ± 1.9 | 5.7 ± 1.8 | 5.9 ± 1.8 | 5.6 ± 1.8 | *** | 0.0004 |
| Saltiness | NS | 6.3 ± 1.8 | 6.3 ± 2.0 | 6.4 ± 1.6 | 6.6 ± 1.5 | 6.4 ± 1.8 | 5.9 ± 1.7 | 6.2 ± 1.7 | 6 ± 1.5 | 6.2 ± 1.6 | 6.0 ± 1.7 | *** | 0.0001 |
| Piquant | NS | 5.8 ± 1.7 | 5.4 ± 2.0 | 5.7 ± 1.6 | 5.9 ± 1.5 | 6.0 ± 1.8 | 5.4 ± 1.8 | 5.6 ± 1.8 | 5.6 ± 1.7 | 5.8 ± 1.7 | 5.7 ± 1.8 | *** | 0.0007 |
| Ewe flavor | NS | 6.2 ± 1.9 | 6 ± 1.8 | 6.2 ± 1.5 | 6.2 ± 1.7 | 6.4 ± 2.0 | 5.9 ± 2.1 | 5.7 ± 1.8 | 6.1 ± 1.6 | 5.9 ± 2.0 | 6.2 ± 2.0 | *** | 0.0002 |
| Aftertaste | *** | 6.2 ± 2.1 a | 5.9 ± 2.2 ab | 6.1 ± 2.0 ab | 6.4 ± 1.9 a | 5.8 ± 2.2 c | 5.1 ± 2.3 c | 6.3 ± 2.0 a | 6.2 ± 1.7 a | 6.1 ± 2.0 ab | 6 ± 2.3 ab | *** | 0.0003 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Beltrán Sanahuja, A.; Pesci de Almeida, R.; Igler Marí, K.-A.; Lamadrid, M.C.; Valdés García, A.; Nadal, E.S. Sensory Attributes and Instrumental Chemical Parameters of Commercial Spanish Cured Ewes’ Milk Cheeses: Insights into Cheese Quality Figures. Foods 2024, 13, 127. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13010127
Beltrán Sanahuja A, Pesci de Almeida R, Igler Marí K-A, Lamadrid MC, Valdés García A, Nadal ES. Sensory Attributes and Instrumental Chemical Parameters of Commercial Spanish Cured Ewes’ Milk Cheeses: Insights into Cheese Quality Figures. Foods. 2024; 13(1):127. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13010127
Chicago/Turabian StyleBeltrán Sanahuja, Ana, Rafaela Pesci de Almeida, Kilian-Anja Igler Marí, Marina Cano Lamadrid, Arantzazu Valdés García, and Esther Sendra Nadal. 2024. "Sensory Attributes and Instrumental Chemical Parameters of Commercial Spanish Cured Ewes’ Milk Cheeses: Insights into Cheese Quality Figures" Foods 13, no. 1: 127. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13010127
APA StyleBeltrán Sanahuja, A., Pesci de Almeida, R., Igler Marí, K.-A., Lamadrid, M. C., Valdés García, A., & Nadal, E. S. (2024). Sensory Attributes and Instrumental Chemical Parameters of Commercial Spanish Cured Ewes’ Milk Cheeses: Insights into Cheese Quality Figures. Foods, 13(1), 127. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13010127