Mathematical Modeling and Design of Parboiled Paddy-Impinging Stream Dryer Using the CFD-DEM Model
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Mathematical Equations
2.1.1. Gas Phase Motion
2.1.2. Particle Motion
2.1.3. Energy Equation
2.1.4. Moisture Transfer Equation
3. Model Assumptions and Simulation Cases
4. Boundary and Initial Conditions
5. Results and Discussion
5.1. Simulation of Drying Process in an ISD
5.1.1. Effect of Air Velocity
5.1.2. Effect of Impinging Distance
5.1.3. Feed Rate Effect
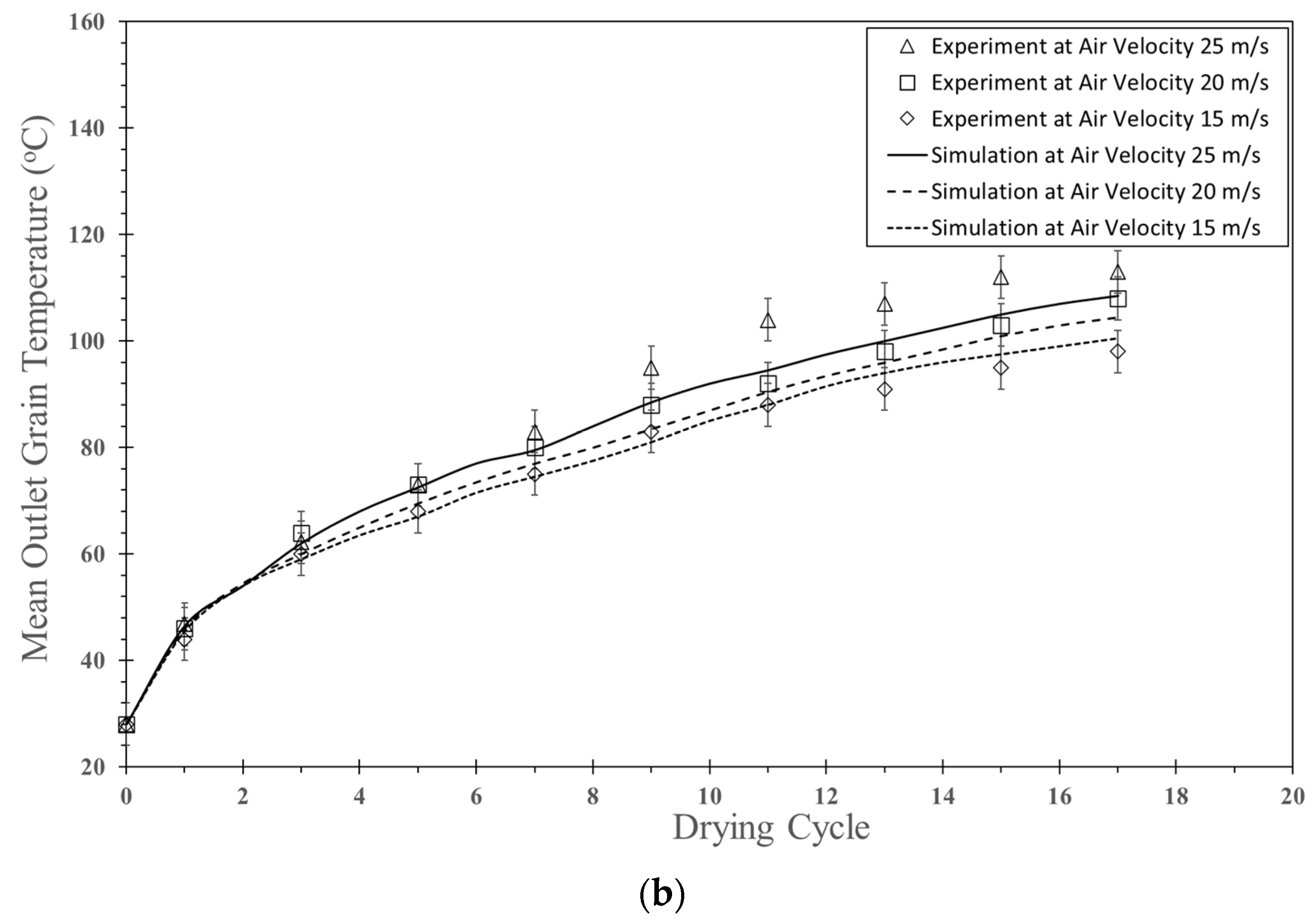
5.1.4. Particle Mean Residence Time
5.2. Design of an ISD
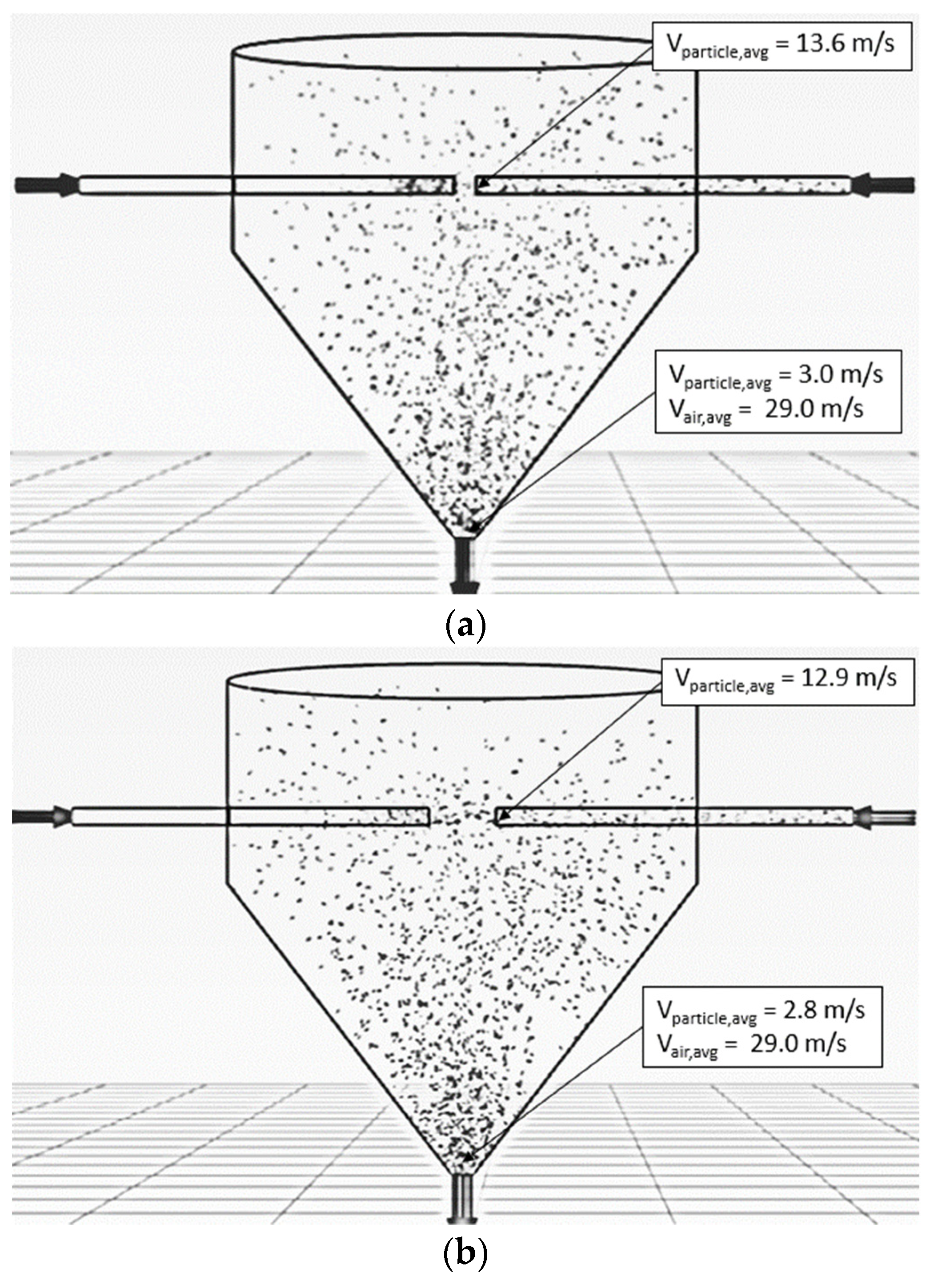
5.2.1. Increase of Inlet Pipe Diameter
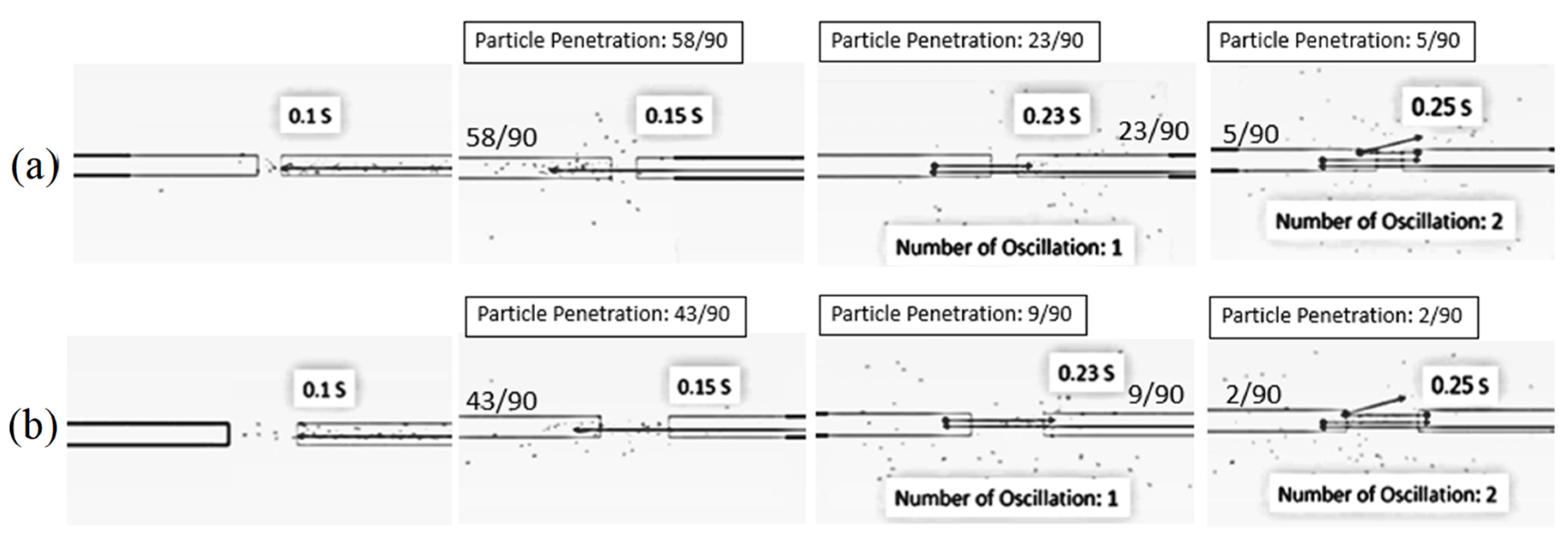
5.2.2. Two Stages of Impinging Stream
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Nomenclature: | |
| Surface area of parboiled paddy (m2) | |
| The order of particles in control volume (-) | |
| Gas phase specific heat (kJ/kg·K) | |
| Parboiled paddy-specific heat (kJ/kg·K) | |
| Equivalent spherical diameter for a particle (m) | |
| Arrhenius factor (m2/s) | |
| Effective diffusion coefficient (m2/s) | |
| Activation energy (J/mol) | |
| Contact force (N) | |
| Normal contact force (N) | |
| Tangential contact force (N) | |
| Drag force (N) | |
| Gravity force (N) | |
| Gravity acceleration (m/s2) | |
| Turbulence kinetic energy due to mean velocity gradients (kg/(m·s3)) | |
| Convective heat transfer coefficient (W/m2·K) | |
| Latent heat coefficient (J/kg) | |
| Mass transfer coefficient (m/s) | |
| Turbulence kinetic energy (m2/s2) | |
| Gas thermal conductivity (W/m·K) | |
| Total mass of a parboiled paddy (kg) | |
| The transferred mass from particle phase to gas phase (kg/s) | |
| Equivalent moisture content in parboiled paddy (d.b.) | |
| Dry moisture content in parboiled paddy (d.b.) | |
| Moisture content at parboiled paddy surface (d.b.) | |
| The number of particles in control volume (-) | |
| Gas phase pressure (N/m2) | |
| Parboiled paddy radius (m) | |
| Volumetric mass source (kg/(s⸳m3) | |
| Volumetric gas–part interaction force (kg/(s2⸳m2) | |
| Volumetric heat source (W/m3) | |
| Gas phase time (s) | |
| Gas phase temperature (K) | |
| Particle Temperature (K) | |
| Gas phase velocity (m/s) | |
| Magnitude of gas phase velocity (m/s) | |
| Particle velocity (m/s) | |
| Magnitude of particle velocity (m/s) | |
| Volume for a particle (m3) | |
| Gas phase volume in control volume (m3) | |
| Control volume (m3) | |
| Gas phase distance (m) | |
| Greek Letters: | |
| Interphase momentum exchange coefficient (kg/m3·s) | |
| Gas phase void ration in control volume (-) | |
| Energy dissipation rate (m2/s3) | |
| Gas phase dynamic viscosity (kg/m·s) | |
| Turbulent viscosity (kg/m·s) | |
| Kinematic viscosity (m2/s) | |
| Density of moisture gas (kg/m3) | |
| Dry density of a parboiled paddy (kg/m3) | |
| Shear stress due to viscosity (N/m2) | |
| Dimensionless Numbers: | |
| Nusselt number | |
| Prandtl number | |
| Reynolds number | |
References
- Tamir, A. Impinging-Stream Reactors: Fundamentals and Applications; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Kudra, T.; Mujumdar, A.S. Impingement stream dryers for particles and pastes. Dry. Technol. 1989, 7, 219–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudra, T.; Mujumdar, A.S. Impinging stream dryers. In Handbook of Industrial Drying, 3rd ed.; Mujumdar, A.S., Ed.; CRC Press: New York, NY, USA, 2007; pp. 479–488. [Google Scholar]
- Nimmol, C.; Devahastin, S. Evaluation of performance and energy consumption of an impinging stream dryer for paddy. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2010, 30, 2204–2212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumklam, P.; Prachayawarakorn, S.; Devahastin, S.; Soponronnarit, S. Effects of Operating Parameters of Impinging Stream Dryer on Parboiled Rice Quality and Energy Consumption. Dry. Technol. 2020, 38, 634–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseinalipour, S.M.; Mujumdar, A.S. Flow, heat transfer and particle drying characteristics in confined opposing turbulent jets: A numerical study. Dry. Technol. 1995, 13, 753–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseinalipour, S.M.; Mujumdar, A.S. A model for superheated steam drying of particles in an impinging stream dryer. In Mathematical Modeling and Numerical Techniques in Drying Technology; Turner, I., Mujumdar, A.S., Eds.; Marcel Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 1997; pp. 537–574. [Google Scholar]
- Choicharoen, K.; Devahastin, S.; Soponronnarit, S. Numerical simulation of multiphase transport phenomena during impinging stream drying of a particulate material. Dry. Technol. 2012, 30, 1227–2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Zhong, W.; Zhang, Y. LES-DPM simulation of turbulent gas-particle flow on opposed round jets. Powder Technol. 2015, 270, 302–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, M.; Zhao, C.; Zhou, B.; Guo, H.; Hao, Y. A modified DSMC method for simulating gas-particle two-phase impinging streams. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2011, 66, 4922–4931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, M.; Gong, J.; Chen, W.; Wang, Q. Mathematical model based on DSMC method for particulate drying in a coaxial impinging stream dryer. Dry. Technol. 2015, 33, 646–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crowe, C.; Sommerfeld, M.; Tsuji, Y. Multiphase Flow with Droplets and Particles; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Tsuji, Y.; Tanaka, T.; Yonemura, S. Cluster patterns in circulating fluidized beds predicted by numerical simulation (discrete particle model versus two fluid model). Powder Technol. 1998, 95, 254–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuji, Y.; Kawaguchi, T.; Tanaka, T. Discrete particle simulation of two-dimensional fluidized bed. Powder Technol. 1993, 77, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.H.; Yu, A.B. Numerical simulation of the gas-solid flow in a fluidized bed by combining discrete particle method with computational fluid dynamics. Chem. Eng. Sci. 1997, 52, 2785–2809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swasdisevi, T.; Tanthapanichakoon, W.; Charinpanitkul, T.; Kawaguchi, T.; Tanaka, T. Investigation of fluid and coarse-particle dynamics in a two-dimensional spouted bed. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2004, 27, 971–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sae-Heng, S.; Swasdisevi, T.; Amornkitbamrung, M. Investigation of temperature distribution and heat transfer in fluidized bed using a combined CFD-DEM model. Dry. Technol. 2011, 29, 697–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khomwachirakul, P.; Devahastin, S.; Swasdisevi, T.; Soponronnarit, S. Simulation of Flow and Drying Characteristics of High-Moisture Particles in an Impinging Stream Dryer via CFD-DEM. Dry. Technol. 2016, 34, 403–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Bu, C.; Chen, X. Development and test of CFD–DEM model for complex geometry: A coupling algorithm for Fluent and DEM. Comput. Chem. Eng. 2013, 58, 260–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, C.; Yu, Y. Mechanics of Fluidization. Chem. Eng. Prog. Symp. Ser. 1966, 62, 100–111. [Google Scholar]
- Haider, A.; Levenspiel, O. Drag Coefficient and Terminal Velocity of Spherical and Nonspherical Particles. Powder Technol. 1989, 58, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ANSYS Inc. ANSYS Fluent Theory Guide; ANSYS Inc.: Canonsburg, PA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Bird, R.B.; Stewart, W.E.; Lightfoot, E.N. Transport Phenomena, 2nd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Versteeg, H.; Malalasekera, W. An Introduction to Computational Fluid Dynamics. In The Finite Volume Method, 2nd ed.; Pearson Education Limited: Harlow, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Kaneko, K.; Shiojima, T.; Horio, M. DEM simulation of fluidized beds for gas-phase olefin polymerization. Chem. Eng. Sci. 1999, 54, 5809–5821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuji, Y.; Tanaka, T.; Ishida, T. Lagrangian numerical simulation of plug flow of cohesionless particles in a horizontal pipe. Powder Technol. 1992, 71, 239–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawaguchi, T.; Sakamoto, M.; Tanaka, T.; Tsuji, Y. Quasi-three-dimensional numerical simulation of spouted beds in cylinder. Powder Technol. 2000, 109, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Zhang, M.; Yuan, Z. Three-dimensional numerical simulation method for gas-solid injector. Powder Technol. 2005, 160, 180–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wongbubpa, N.; Yabsungnoen, T.; Treeamnuk, K.; Treeamnuk, T.; Prakotmak, P. Computer Simulation Study of Paddy Motion in Hot Air-Drying Chamber. In Proceedings of the 22nd Thai Society of Agricultural Engineering National Conference, Khon Kaen, Thailand, 12–13 May 2021; pp. 148–155. [Google Scholar]
- Gan, T.; Ping, S.; Yanqi, Z.; Lingfeng, Y.; Hong, Z. Experimental Research on Friction Coefficient between Grain Bulk and Bamboo Clappers. In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Frontiers of Materials Synthesis and Processing, Changsha, China, 28–29 October 2017; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Zhuang, Y.-Q.; Chen, X.-M.; Luo, Z.-H.; Xiao, J. CFD–DEM modeling of gas–solid flow and catalytic MTO reaction in a fluidized bed reactor. Comput. Chem. Eng. 2014, 60, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Cheng, Y.; Ding, Y.; Jin, Y. CFD-DEM simulation of gas-solid reacting flows in fluid catalytic cracking (FCC) process. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2010, 65, 542–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manal, H.; Shaimaa, M. Heat and Mass Transfer During Air Drying of Fruits. Iraqi J. Mech. Mater. Eng. 2008, 8, 110–126. [Google Scholar]
- Frydman, A.; Vasseur, J.; Moureh, J.; Sionneau, M.; Tharrault, P. Comparison of superheated steam and air operated spray dryers using computational fluid dynamics. Dry. Technol. 1998, 16, 1305–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, B.S.; Chakraverty, A. Physical Properties of Raw and Parboiled Paddy. Biosyst. Eng. 2004, 88, 461–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iguaz, A.; San, M.; Arroqui, T.; Fernandez, T. Thermophysical properties of medium grain rough rice (LIDO cultivar) at medium and low Temperatures. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2003, 217, 224–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lague, C.; Jenkins, B.M. Modeling Pre-Harvest Stress-Cracking of Rice Kernels. Trans. Am. Soc. Agric. Eng. 1991, 34, 1812–1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madhiyanon, T.; Techaprasan, A.; Soponronnarit, S. Mathematical Models Based on Heat Transfer and Coupled Heat and Mass Transfer for Rapid High Temperature Treatment in Fluidized Bed: Application for Grain Heat Disinfestations. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2006, 49, 2277–2290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bootkote, P.; Soponronnarit, S.; Prachayawarakorn, S. Process of Producing Parboiled Rice with Different Colors by Fluidized Bed Drying Technique Including Tempering. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2016, 9, 1574–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laughton, M.A.; Warne, D.J. Electrical Engineer’s Reference Book; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Kumklam, P. Parboiled Paddy Drying Using Impinging Stream Dryer: Scaling up from Laboratory Scale to Prototype. Ph.D. Thesis, Energy Technology, School of Energy, Environment and Materials, King Mongkut’s University of Technology Thonburi, Bangkok, Thailand, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- David, M. Pneumatic Conveying Design Guide; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2004. [Google Scholar]
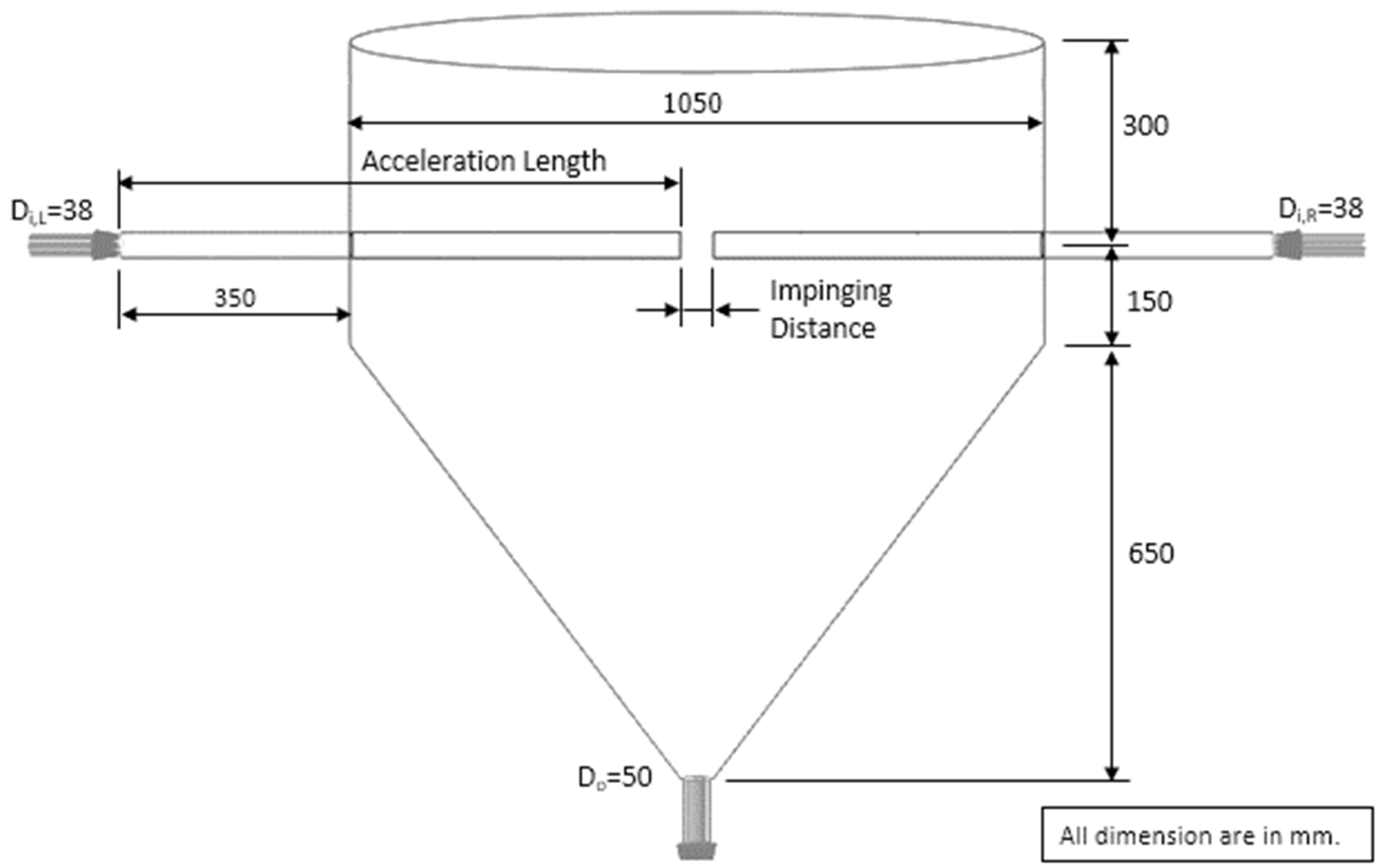
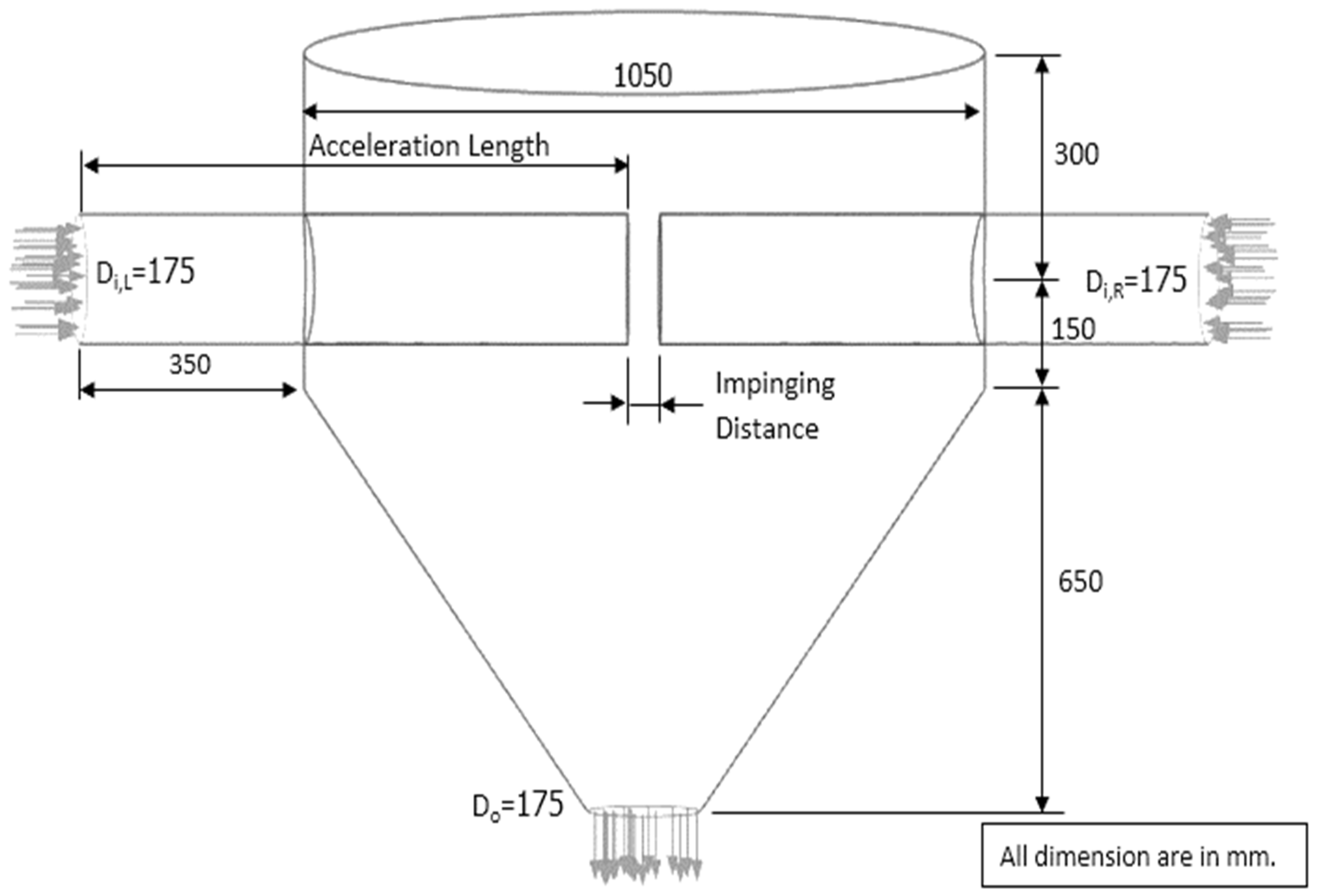
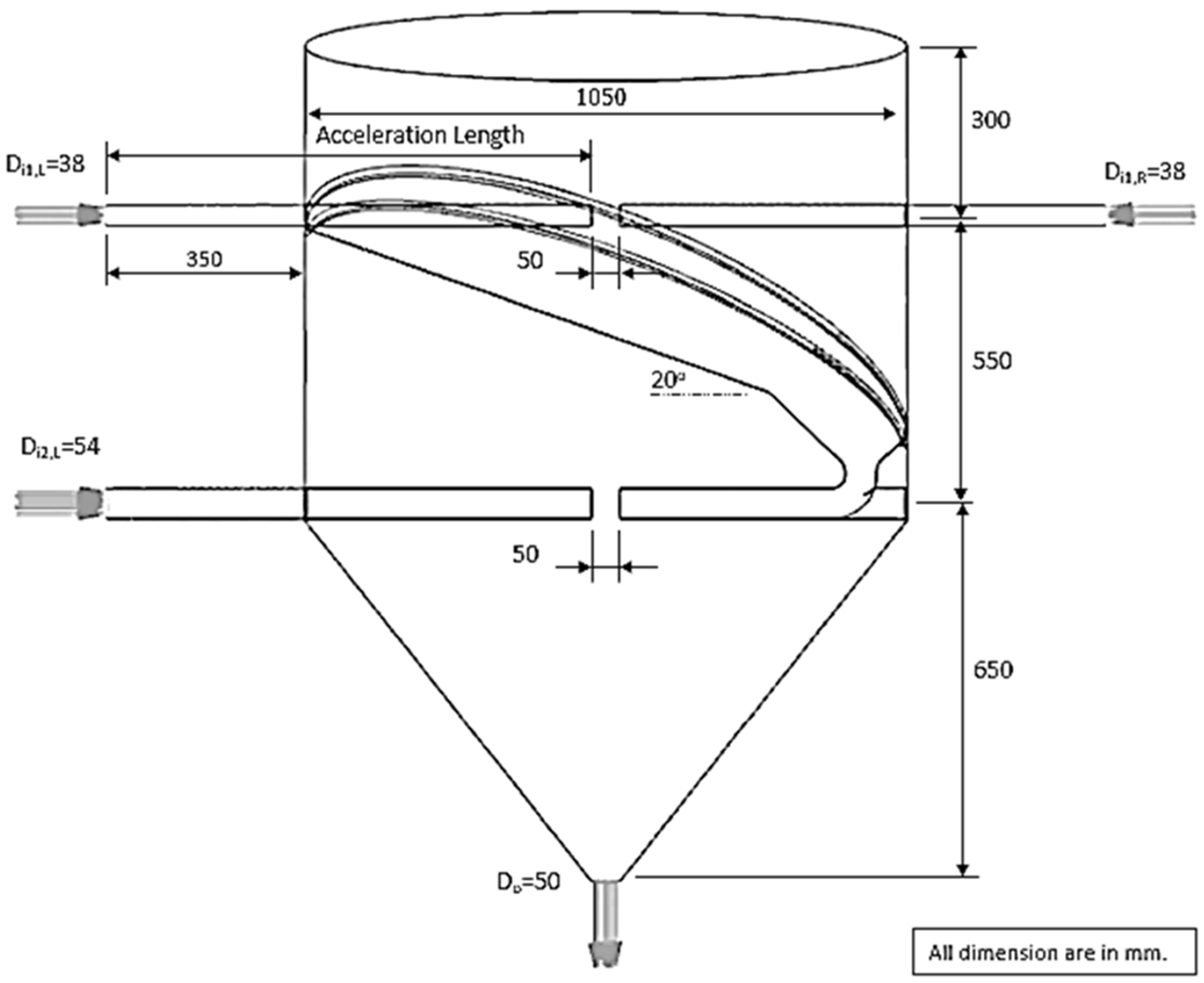
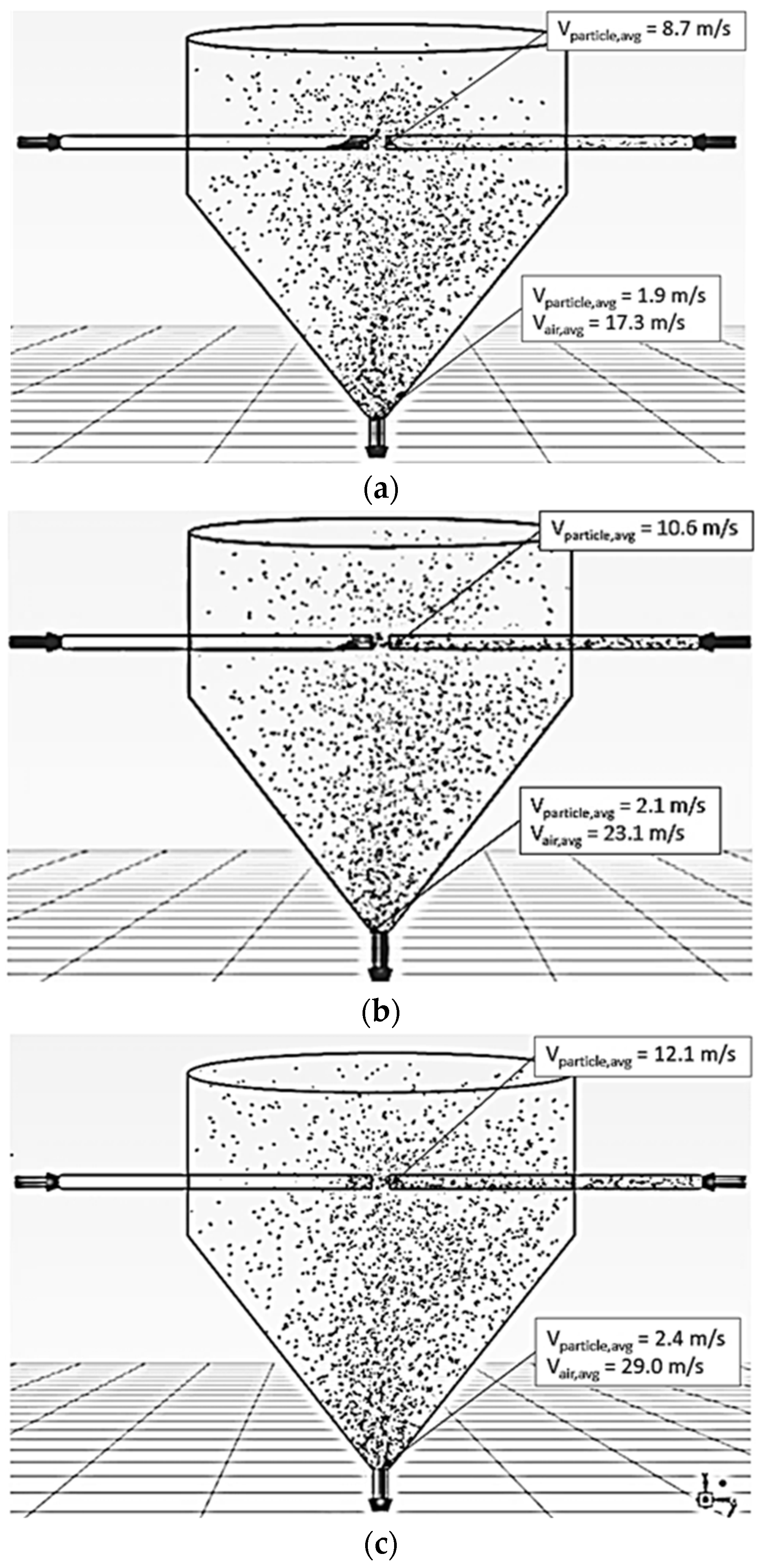
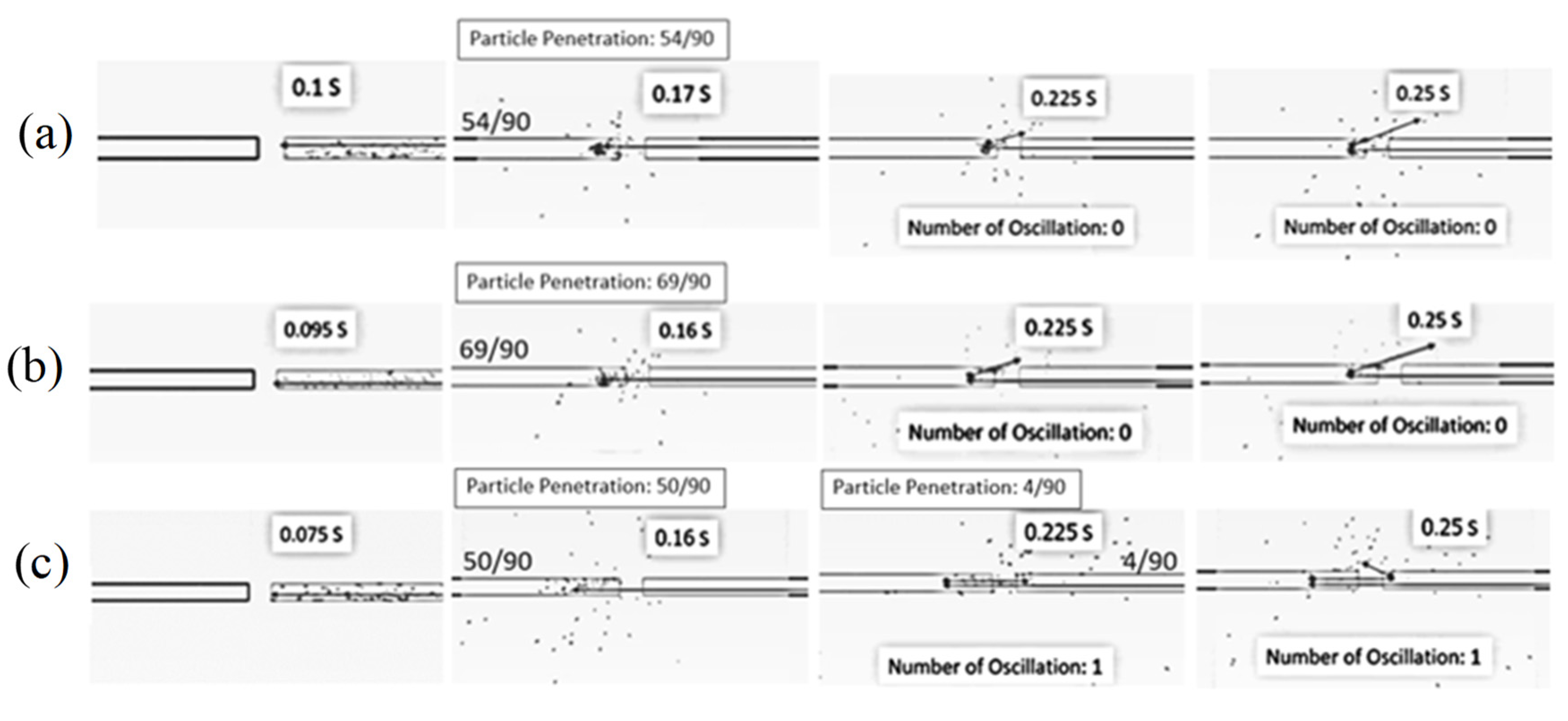



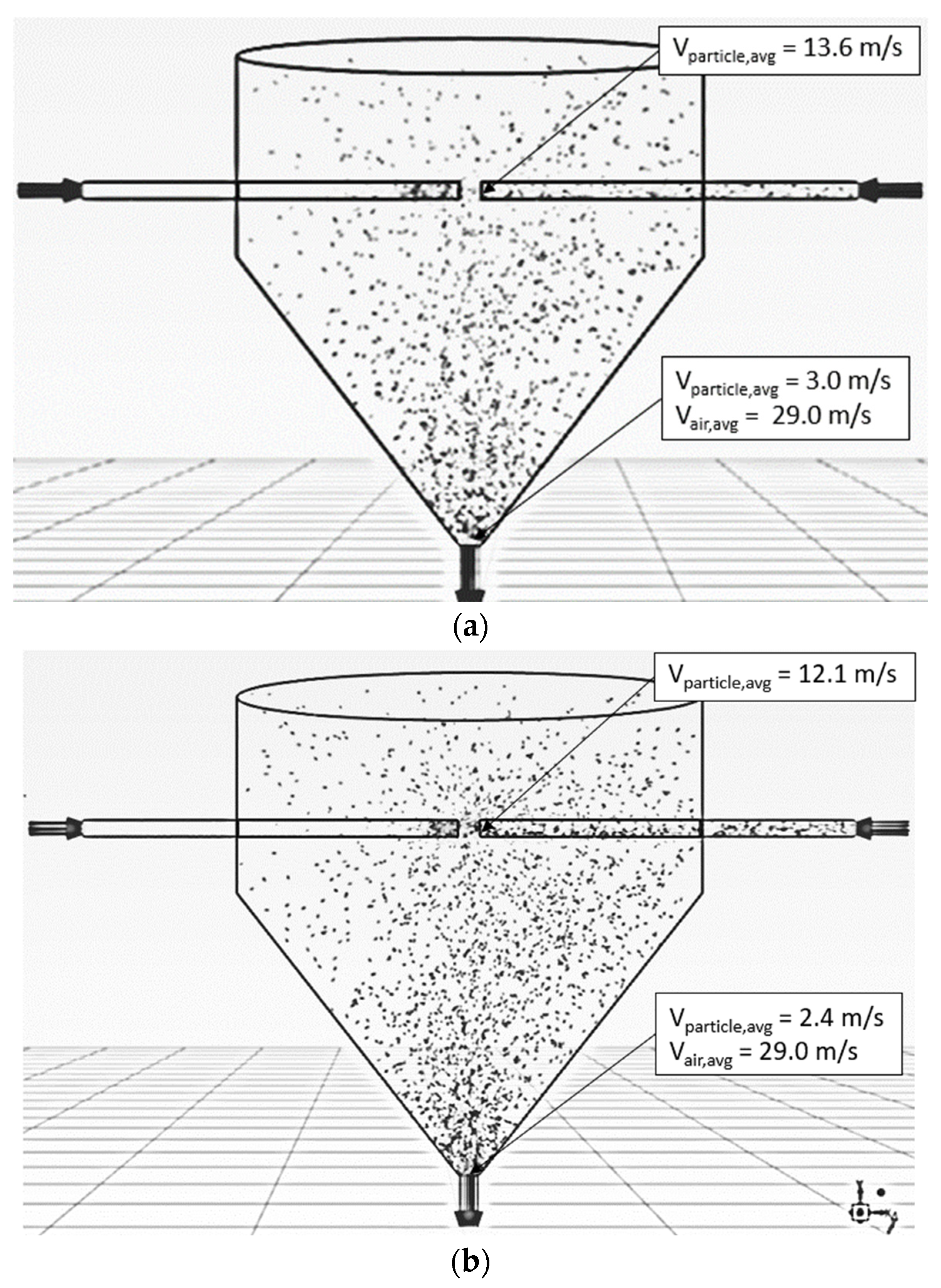


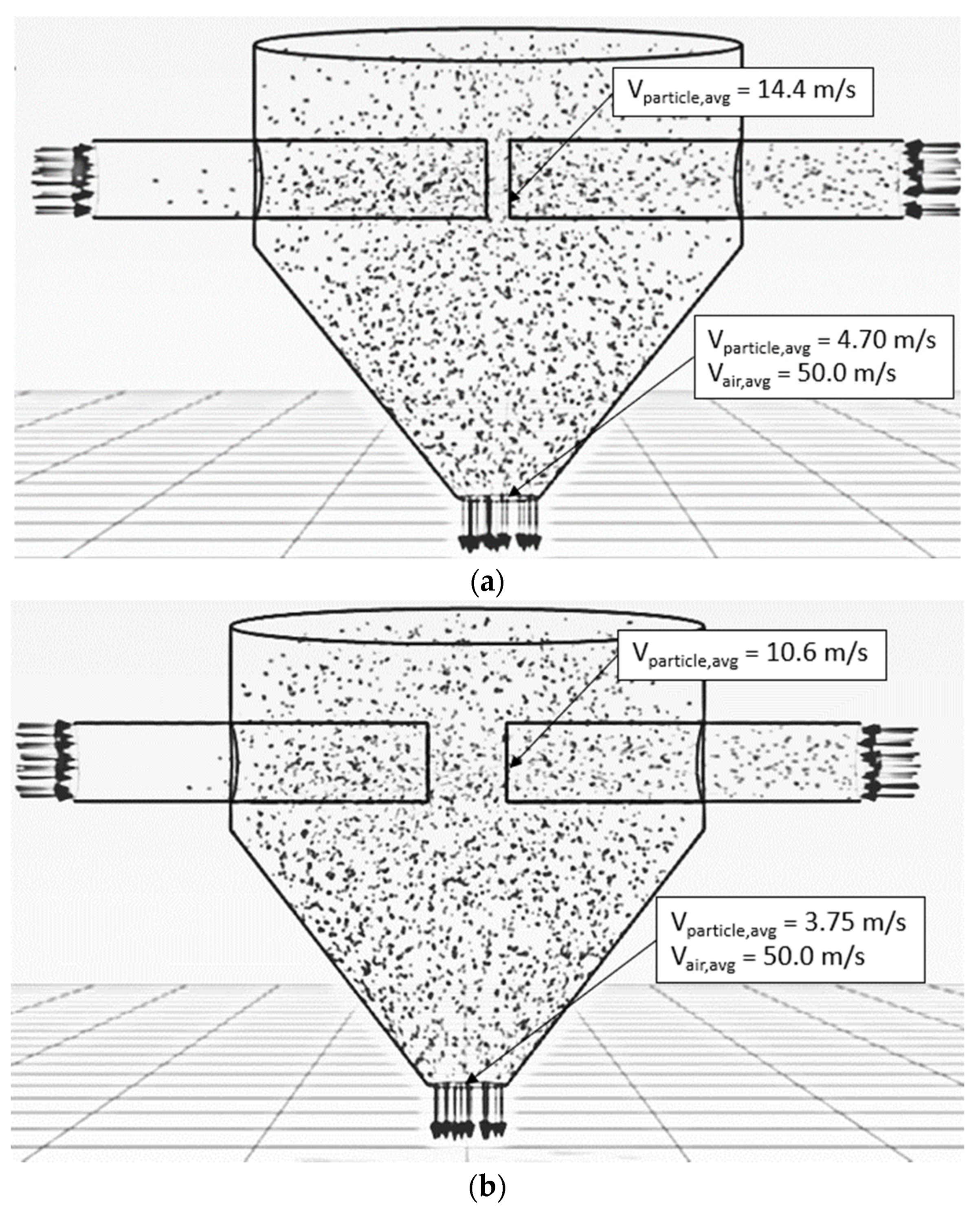
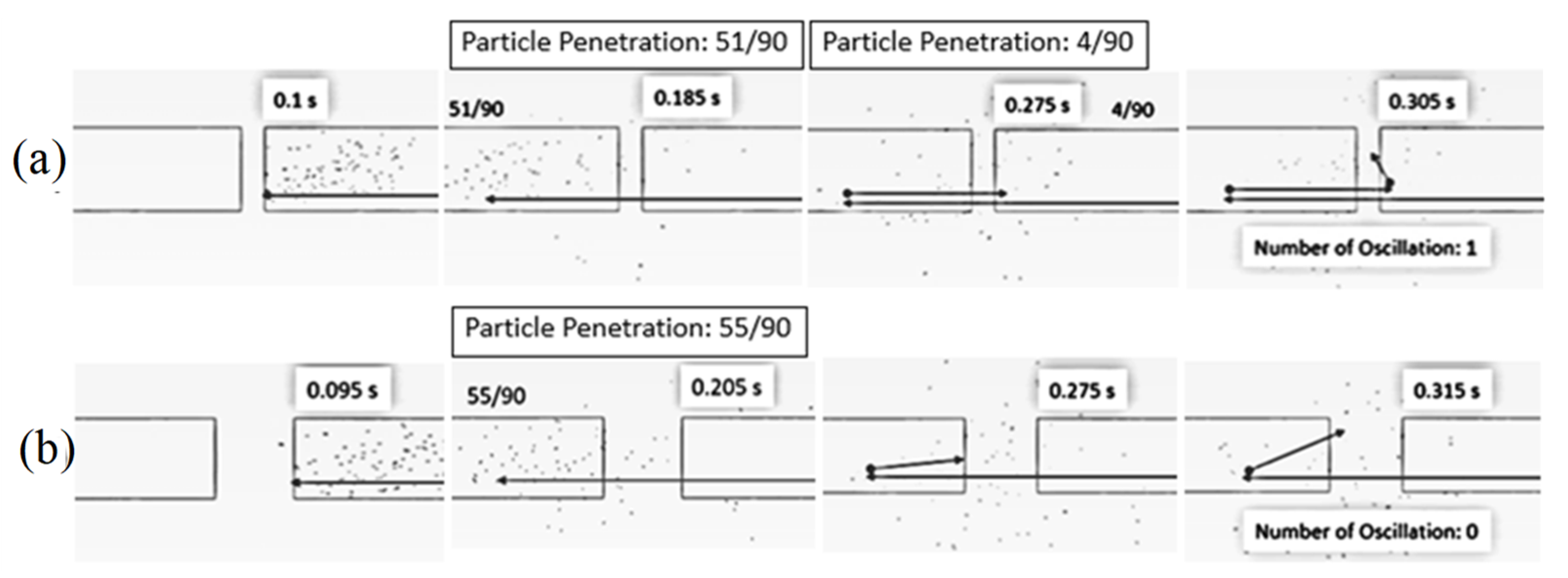

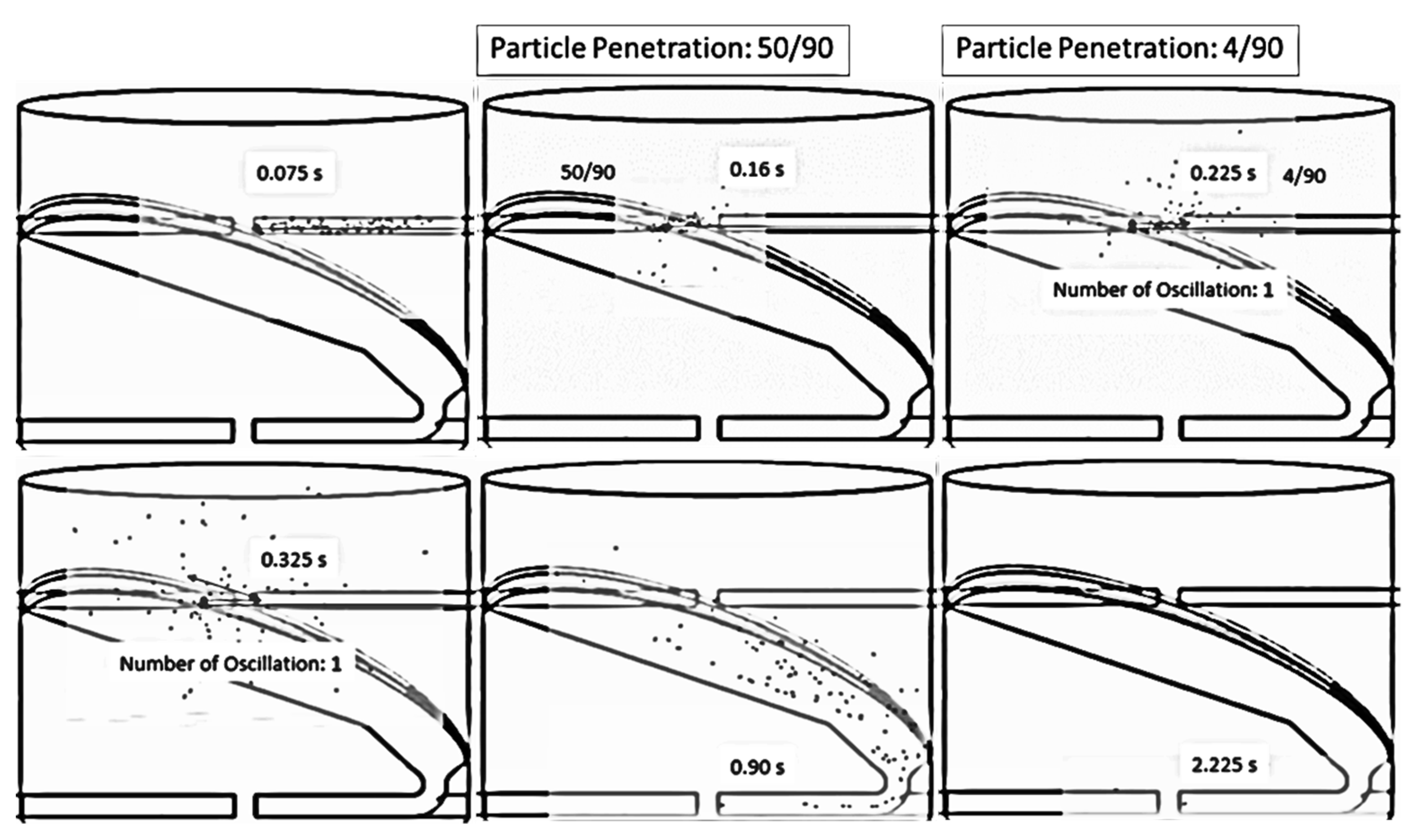
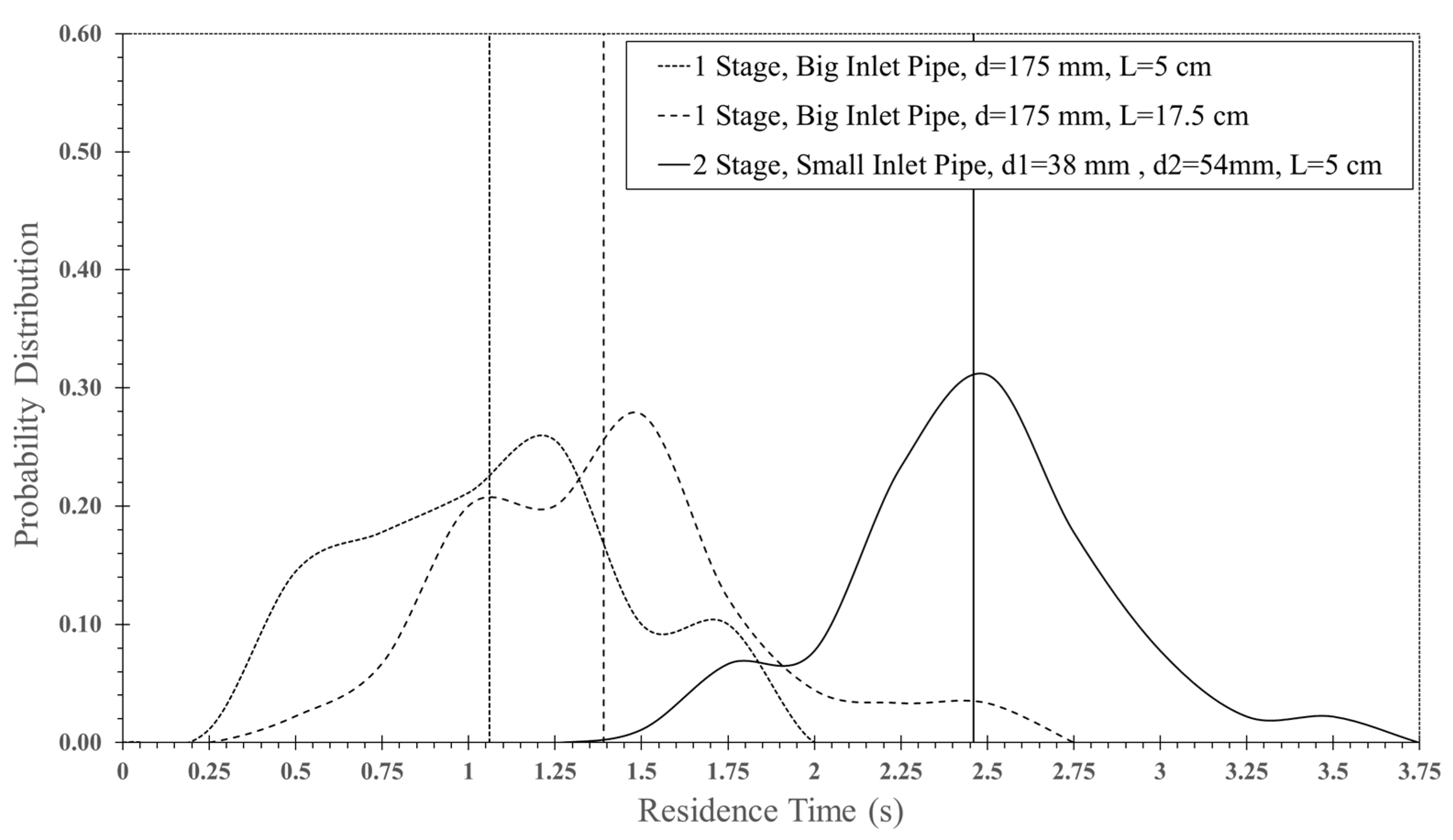
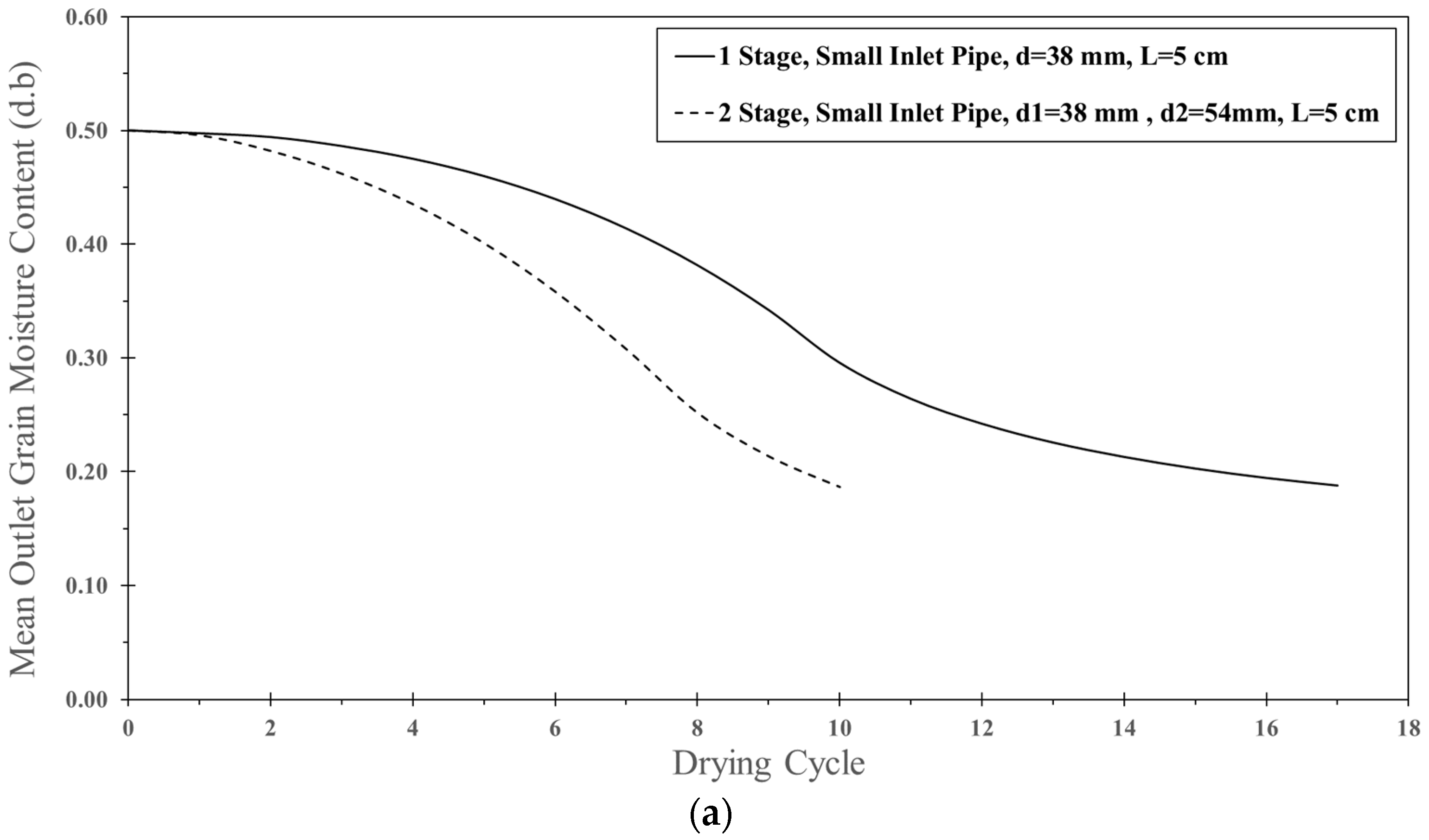
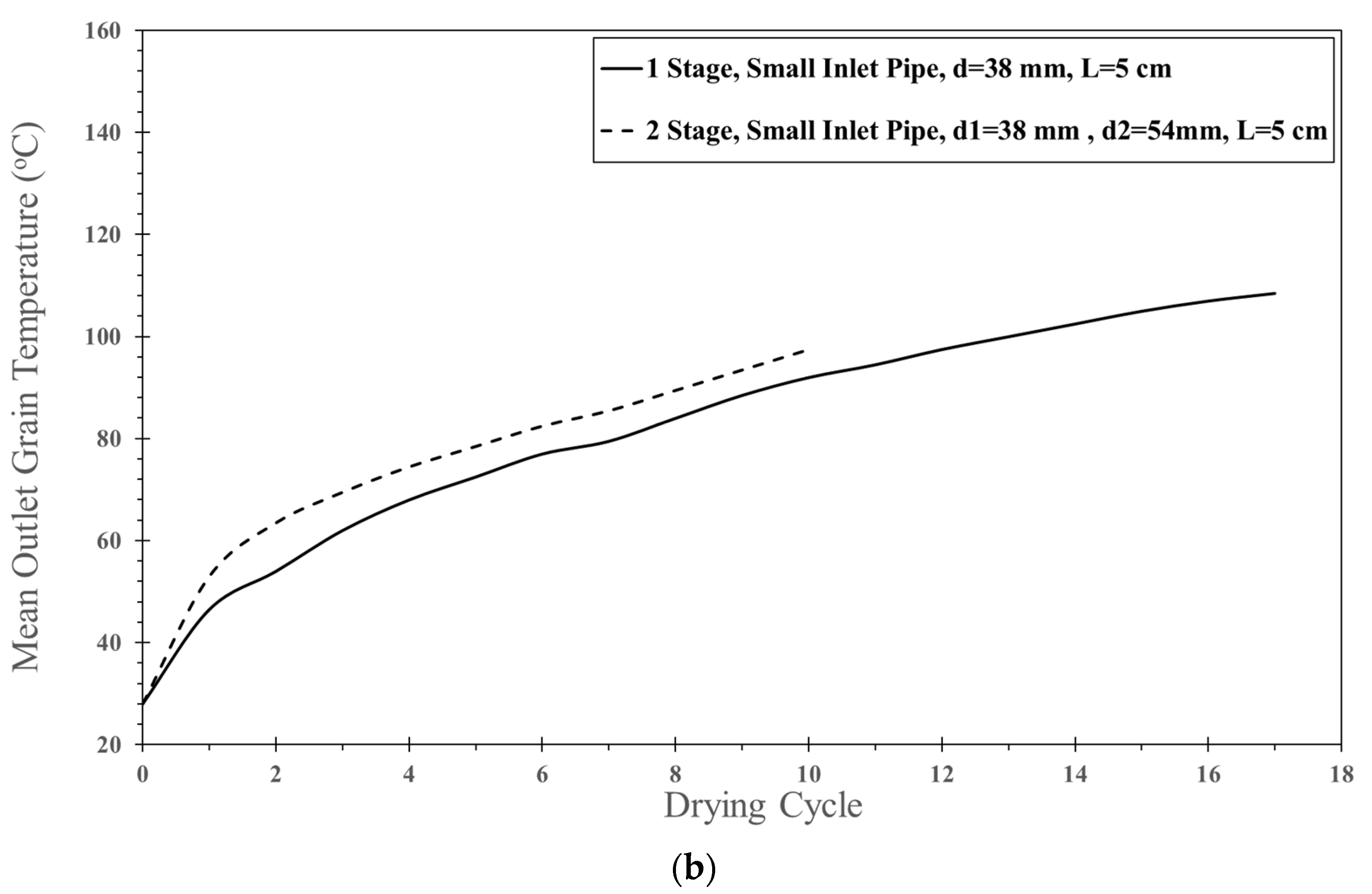
| Feed Rate (kg dry/h) | Air Temperature (°C) | Air Velocity (m/s) | Inlet Pipe Diameter (mm) | Impinging Distance (cm) | Stable Time (s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 320 | 190 | 15 | 38 | 5 | 1.68 |
| 190 | 20 | 38 | 5 | 1.70 | |
| 190 | 25 | 38 | 5 | 1.83 | |
| 160 | 190 | 25 | 38 | 5 | 2.17 |
| 190 | 25 | 38 | 15 | 1.90 | |
| 320 | 190 | 25 | 175 | 5 | 1.90 |
| 190 | 25 | 175 | 17.5 | 2.17 | |
| 190 | 25 | First Stage: 38, Second Stage: 54 | 5 | 3.10 |
| Properties | Correlation Used in Simulation |
|---|---|
| Diameter (m) [5] | 0.0039 |
| Density (kg/m3) [35] | (1835 Mdb) + 487.03 |
| Heat capacity (kJ/kgK) [36] | 1.1188 + (5.8362 × 10−3 Tp) + (3.4695 × 10−2 Mdb) − (1.3432 × 10−4 Tp Mdb) − (2.4808 × 10−4 Mdb2) |
| Thermal conductivity (W/mK) [37] | (0.0637 + 0.0958 (Mdb/(Mdb + 1)))/ (0.656 − 0.475 (Mdb/(Mdb + 1))) |
| Heat of vaporization (kJ/kg) [36,38] | (2502 − (2.386 Tp,c)) × (1 + (2.496 (e−21.733·Mdb))) |
| Spring constant (N/m) [17,26,27,28] | 1000 |
| Restitution coefficient [29] | |
| Particle–particle | 0.6 |
| Particle–wall | 0.6 |
| Initial moisture content (d.b.) [5] | 0.5 |
| Arrhenius factor (m2/s) [39] | 2.55 × 10−7 |
| Activation energy (J/mol) [39] | 20,580 |
| Properties | Correlation Used in Simulation |
|---|---|
| Thermal conductivity (W/mK) | (1.3 × 10−3) + ((9.11 × 10−5)Ta) − ((2.52 × 10−8)Ta2) |
| Heat capacity (kJ/kgK) | 990 − ((1.77 × 10−2)Ta) + ((1.91 × 10−4)Ta2) |
| Viscosity (Pas) | (3.53 × 10−6) + ((5.54 × 10−8)Ta) + ((1.70 × 10−11)Ta2) |
| Feed Rate (kg dry/h) | Air Temperature (°C) | Air Velocity (m/s) | Inlet Pipe Diameter (mm) | Impinging Distance (cm) | Mean Residence Time (s) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Simulation | Experiment [5,41] | Percent Relative Error | |||||
| 320 | 190 | 15 | 38 | 5 | 1.26 | 1.4 0.18 | 10.0% |
| 190 | 20 | 38 | 5 | 1.38 | 1.8 0.20 | 23.3% | |
| 190 | 25 | 38 | 5 | 1.40 | 2.2 0.20 | 36.4% | |
| 160 | 190 | 25 | 38 | 5 | 1.53 | 2.6 0.12 | 41.2% |
| 190 | 25 | 38 | 15 | 1.32 | 2.4 0.15 | 45.0% | |
| 320 | 190 | 25 | 175 | 5 | 1.06 | N/A | N/A |
| 190 | 25 | 175 | 17.5 | 1.39 | N/A | N/A | |
| 190 | 25 | First Stage: 38, Second Stage: 54 | 5 | 2.46 | N/A | N/A | |
| Feed Rate (kg dry/h) | Air Temperature (°C) | Impinging Distance (cm) | Air Velocity (m/s) | No. of Stage | D (m) | D/d | d (m) | 1st Drying Cycle (Min = 0.5 d.b.) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean Residence Time (s) | Mean Outlet Moisture (d.b.) | ∆M (d.b) | ||||||||
| 320 | 190 | 5 | 25 | 1 | 1.05 | 27.6 | 0.038 | 1.40 | 0.4995 | 0.0005 |
| 320 | 190 | 5 | 25 | 1 | 1.05 | 6 | 0.175 | 1.06 | 0.4982 | 0.0018 |
| 320 | 190 | 17.5 | 25 | 1 | 1.05 | 6 | 0.175 | 1.39 | 0.4979 | 0.0021 |
| 320 | 190 | 5 | 25 | 2 | 1.05 | 27.6 1* | 0.038 1* | 2.46 | 0.4955 | 0.0045 |
| 19.5 2* | 0.054 2* | |||||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Swasdisevi, T.; Thianngoen, W.; Prachayawarakorn, S. Mathematical Modeling and Design of Parboiled Paddy-Impinging Stream Dryer Using the CFD-DEM Model. Foods 2024, 13, 1559. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13101559
Swasdisevi T, Thianngoen W, Prachayawarakorn S. Mathematical Modeling and Design of Parboiled Paddy-Impinging Stream Dryer Using the CFD-DEM Model. Foods. 2024; 13(10):1559. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13101559
Chicago/Turabian StyleSwasdisevi, Thanit, Wut Thianngoen, and Somkiat Prachayawarakorn. 2024. "Mathematical Modeling and Design of Parboiled Paddy-Impinging Stream Dryer Using the CFD-DEM Model" Foods 13, no. 10: 1559. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13101559
APA StyleSwasdisevi, T., Thianngoen, W., & Prachayawarakorn, S. (2024). Mathematical Modeling and Design of Parboiled Paddy-Impinging Stream Dryer Using the CFD-DEM Model. Foods, 13(10), 1559. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13101559






