The Utilization by Bacteroides spp. of a Purified Polysaccharide from Fuzhuan Brick Tea
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Chemical Reagents
2.2. Preparation of FBTPS-3
2.3. Isolation of Bacteroides Species
2.4. Identification of Bacteroides Species
2.5. Determination of Growth Curve of Bacteroides Species
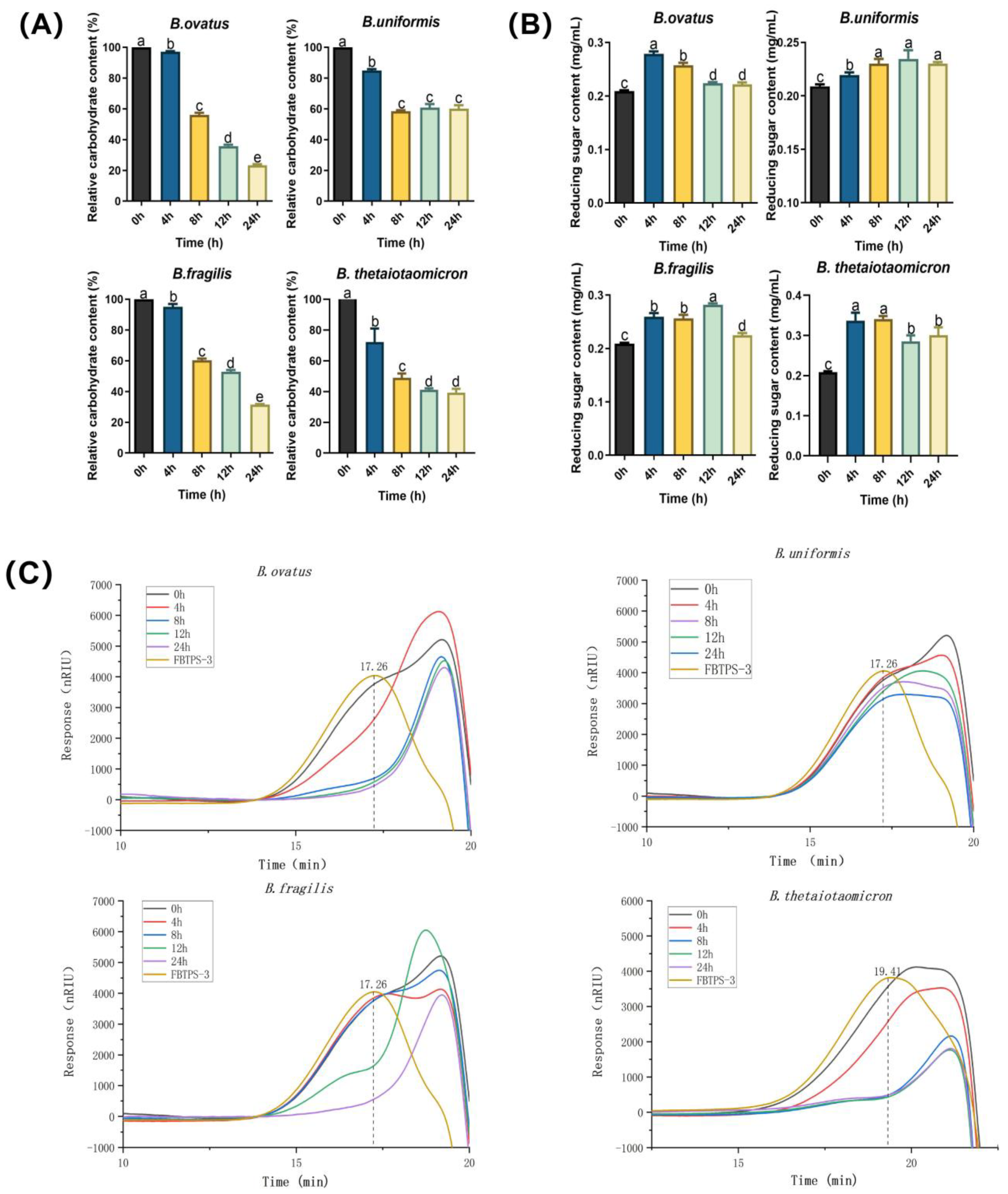
2.6. Analysis of FBTPS-3 Utilization by Bacteroides Members
2.7. Determinations of Contents of SCFAs
2.8. Transcriptome Analysis of BO
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Identification of Bacteroides Strains Isolated from the Human Feces
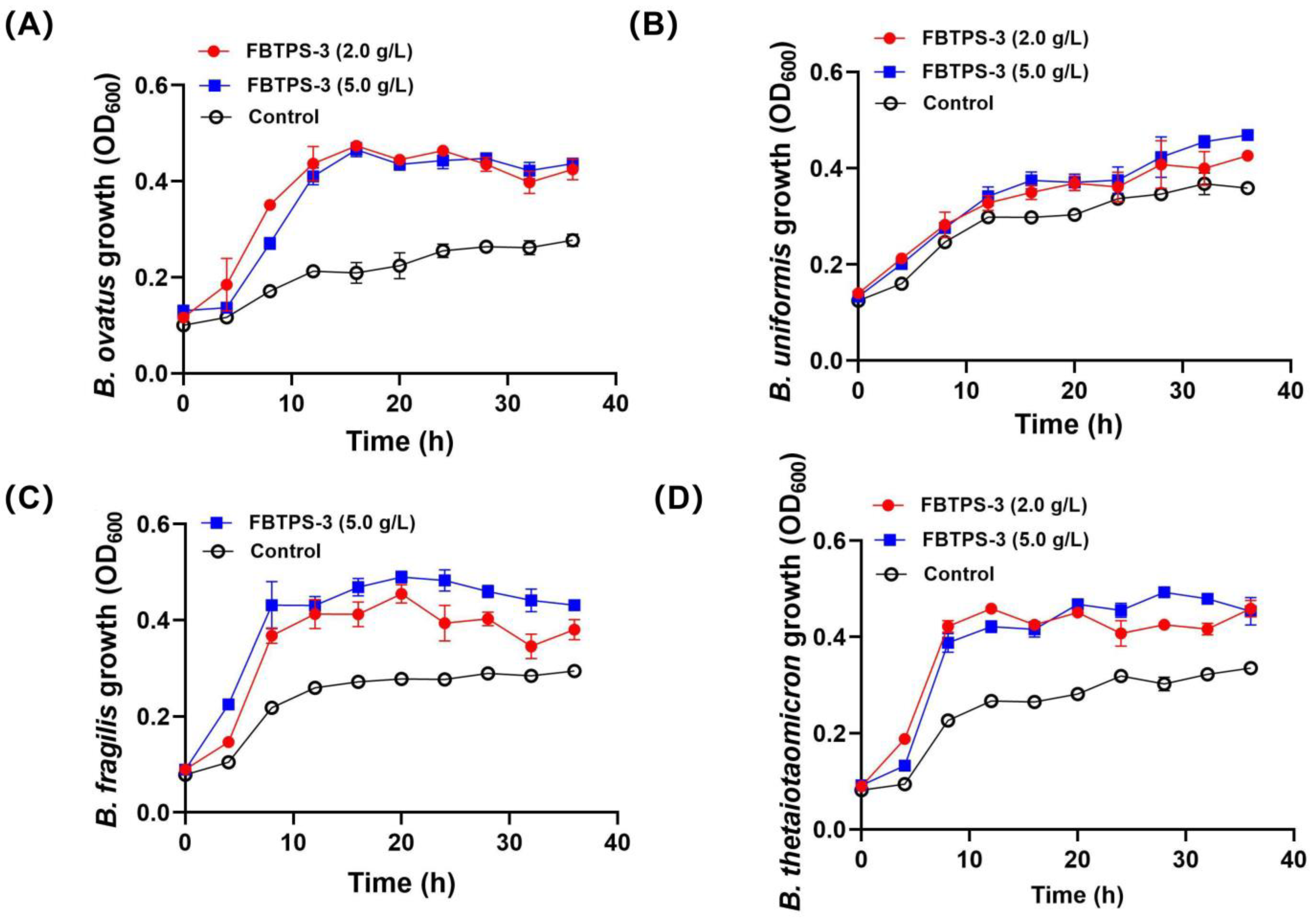
3.2. Utilization Capability of Four Bacteroides Species on FBTPS-3 in Single Culture
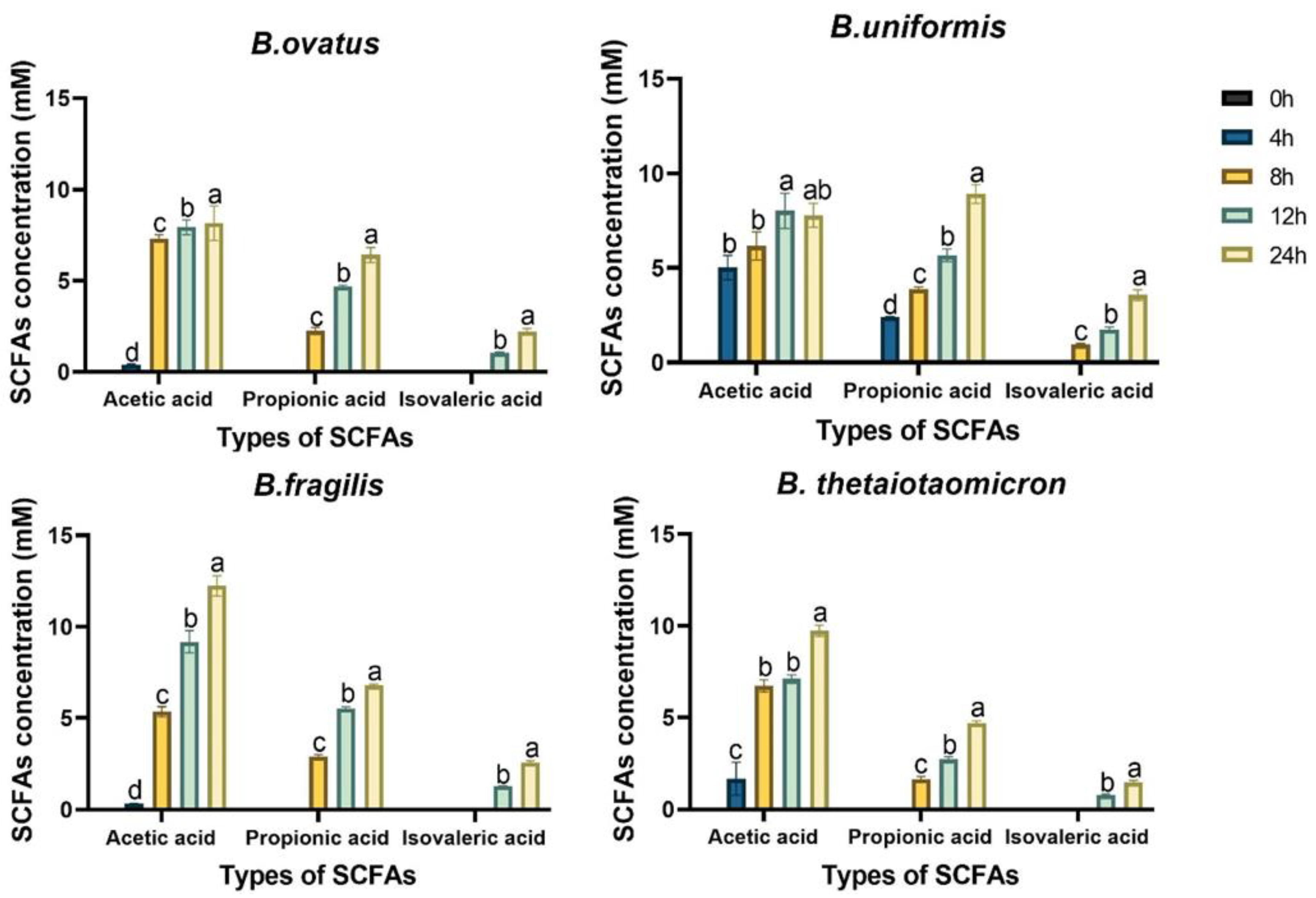
3.3. Production of SCFAs by four Bacteroides Species Grew on FBTPS-3
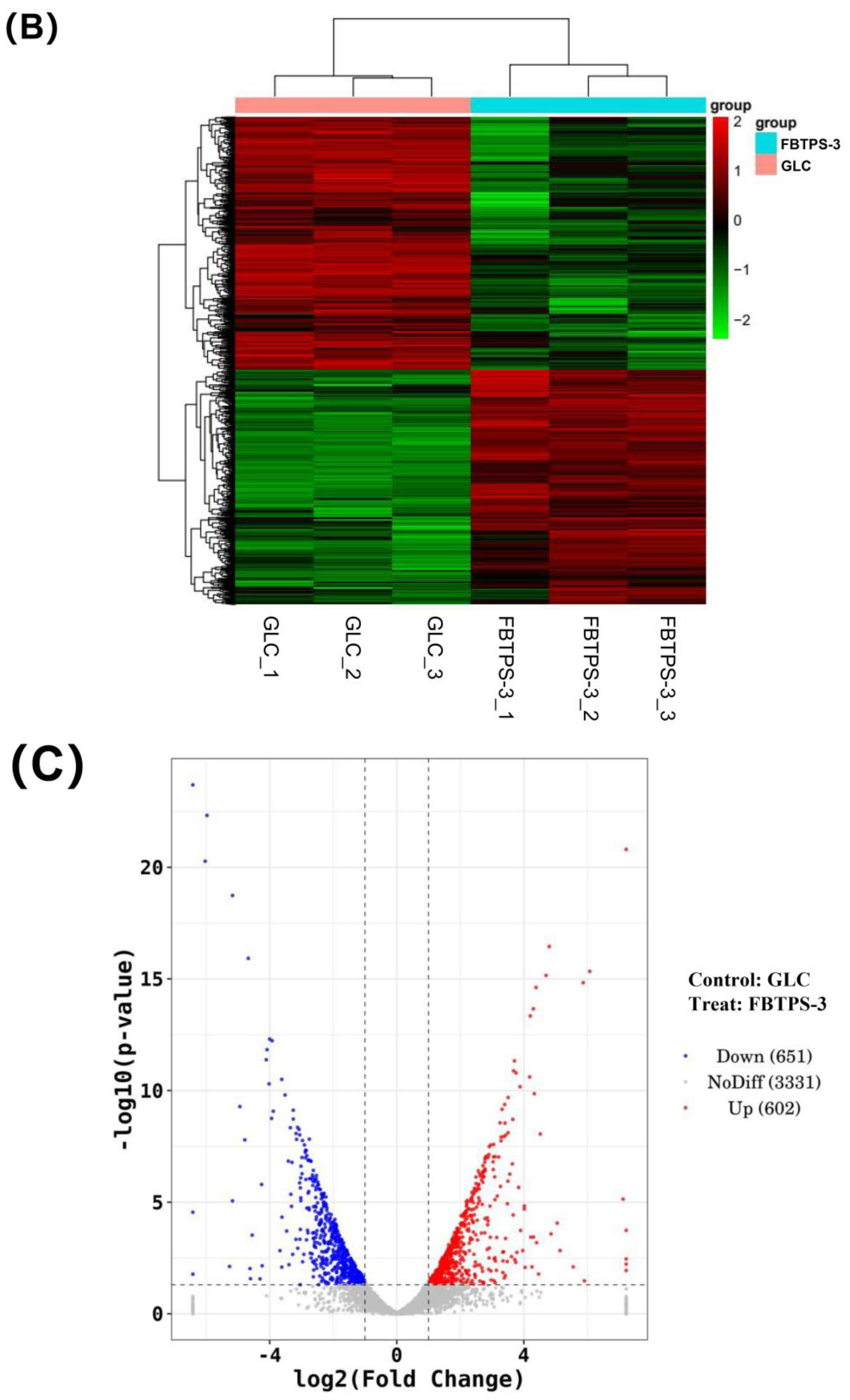
3.4. Up-Regulated PULs and CAZyme Clusters in the Transcriptome of BO
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- van Bueren, A.L.; Saraf, A.; Martens, E.C.; Dijkhuizen, L. Differential metabolism of exopolysaccharides from probiotic Lactobacilli by the human gut symbiont Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron. Appl. Environ. Microb. 2015, 81, 3973–3983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapebie, P.; Lombard, V.; Drula, E.; Terrapon, N.; Henrissat, B. Bacteroidetes use thousands of enzyme combinations to break down glycans. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 2043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McNulty, N.P.; Wu, M.; Erickson, A.R.; Pan, C.L.; Erickson, B.K.; Martens, E.C.; Pudlo, N.A.; Muegge, B.D.; Henrissat, B.; Hettich, R.L.; et al. Effects of diet on resource utilization by a model human gut microbiota containing Bacteroides cellulosilyticus WH2, a symbiont with an extensive glycobiome. PLoS Biol. 2013, 11, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larsbrink, J.; Zhu, Y.; Kharade, S.S.; Kwiatkowski, K.J.; Eijsink, V.G.H.; Koropatkin, N.M.; McBride, M.J.; Pope, P.B. A polysaccharide utilization locus from Flavobacterium johnsoniae enables conversion of recalcitrant chitin. Biotechnol. Biofuels Bioprod. 2016, 9, 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabisch, A.; Otto, A.; Koenig, S.; Becher, D.; Albrecht, D.; Schueler, M.; Teeling, H.; Amann, R.I.; Schweder, T. Functional characterization of polysaccharide utilization loci in the marine Bacteroidetes ‘Gramella forsetii’ KT0803. ISME J. 2014, 8, 1492–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, G.; Cao, J.W.; Mi, L.; Feng, D.; Deng, Q.; Sun, X.B.; Zhang, H.E.; Wang, Q.; Wang, J.K. BdPUL12 depolymerizes b-mannan-like glycans into mannooligosaccharides and mannose, which serve as carbon sources for Bacteroides dorei and gut probiotics. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 187, 664–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhang, B.; Hu, J.; Zhong, Y.; Sun, Y.; Nie, S. Utilization of four galactans by Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron A4 based on transcriptome. Food Front. 2021, 2, 218–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonnenburg, E.D.; Zheng, H.J.; Joglekar, P.; Higginbottom, S.K.; Firbank, S.J.; Bolam, D.N.; Sonnenburg, J.L. Specificity of polysaccharide use in intestinal Bacteroides species determines diet-induced microbiota alterations. Cell 2010, 141, 1241–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martens, E.C.; Lowe, E.C.; Chiang, H.; Pudlo, N.A.; Wu, M.; McNulty, N.P.; Abbott, D.W.; Henrissat, B.; Gilbert, H.J.; Bolam, D.N.; et al. Recognition and degradation of plant cell wall polysaccharides by two human gut symbionts. PLoS Biol. 2011, 9, e1001221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.J.; Wan, X.C.; Bao, G.H. Brick dark tea: A review of the manufacture, chemical constituents and bioconversion of the major chemical components during fermentation. Phytochem. Rev. 2015, 14, 499–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Peng, Y.; Xie, M.; Xu, W.; Chen, C.; Zeng, X.; Liu, Z. A critical review of Fuzhuan brick tea: Processing, chemical constituents, health benefits and potential risk. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. 2023, 63, 5447–5464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, F.J.; Wei, X.L.; Liu, H.Y.; Li, H.; Xia, Y.; Wu, D.T.; Zhang, P.Z.; Gandhi, G.R.; Li, H.B.; Gan, R.Y. State-of-the-art review of dark tea: From chemistry to health benefits. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 109, 126–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.J.; Xie, M.H.; Wan, P.; Chen, D.; Dai, Z.Q.; Ye, H.; Hu, B.; Zeng, X.X.; Liu, Z.H. Fuzhuan brick tea polysaccharides attenuate metabolic syndrome in high-fat diet induced mice in association with modulation in the gut microbiota. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 2783–2795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Z.Q.; Xie, Z.Y.; Chen, G.J.; Sun, Y.; Zeng, X.X.; Liu, Z.H. Anti-inflammatory and gut microbiota modulatory effects of polysaccharides from Fuzhuan brick tea on colitis in mice induced by dextran sulfate sodium. Food Funct. 2022, 13, 649–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durack, J.; Lynch, S.V. The gut microbiome: Relationships with disease and opportunities for therapy. J. Exp. Med. 2019, 216, 20–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manor, O.; Dai, C.Z.L.; Kornilov, S.A.; Smith, B.; Price, N.D.; Lovejoy, J.C.; Gibbons, S.M.; Magis, A.T. Health and disease markers correlate with gut microbiome composition across thousands of people. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Xie, M.; Wan, P.; Chen, D.; Ye, H.; Chen, L.; Zeng, X.; Liu, Z. Digestion under saliva, simulated gastric and small intestinal conditions and fermentation in vitro by human intestinal microbiota of polysaccharides from Fuzhuan brick tea. Food Chem. 2018, 244, 331–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.J.; Chen, G.J.; Chen, D.; Ye, H.; Sun, Y.; Zeng, X.X.; Liu, Z.H. Purified fraction of polysaccharides from Fuzhuan brick tea modulates the composition and metabolism of gut microbiota in anaerobic fermentation in vitro. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 140, 858–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, P.; Song, S.; Ai, C. Interaction of sulfated polysaccharides with intestinal Bacteroidales plays an important role in its biological activities. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 168, 496–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhao, R.; Zhou, H.L.; Wu, D.H. Deproteinization of polysaccharide from the stigma maydis by Sevag method. Adv. Mater. Res. 2011, 340, 416–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Wang, K.Q.; Sun, Y.; Ye, H.; Hu, B.; Zeng, X.X. Influences of structures of galactooligosaccharides and fructooligosaccharides on the fermentation in vitro by human intestinal microbiota. J. Funct. Food. 2015, 13, 158–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, G.V.; Abdel-Hamid, A.M.; Dutta, S.; D’Alessandro-Gabazza, C.N.; Wefers, D.; Farris, J.A.; Bajaj, S.; Wawrzak, Z.; Atomi, H.; Mackie, R.I.; et al. Degradation of complex arabinoxylans by human colonic Bacteroidetes. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satyavani, K.; Warrier, K.C.S.; Ramanathan, T.; Gurudeeban, S. Biochemical indicators for rooting in Casuarina equisetifolia clones. Asian J. Plant Sci. 2010, 9, 364–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Yan, Y.M.; Peng, Y.J.; Chen, D.; Mi, J.; Lu, L.; Luo, Q.; Li, X.Y.; Zeng, X.X.; Cao, Y.L. In vitro digestion under simulated saliva, gastric and small intestinal conditions and fermentation by human gut microbiota of polysaccharides from the fruits of Lycium barbarum. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 125, 751–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, Z.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; Dai, H.; Li, C.; Xue, Y.; Deng, Y.; Zhang, H.; Yu, Y.; Fang, H. Characterization of a novel carbendazim-degrading strain Rhodococcus sp. CX-1 revealed by genome and transcriptome analyses. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 754, 14137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grondin, J.M.; Tamura, K.; Dejean, G.; Abbott, D.W.; Brumer, H. Polysaccharide utilization Loci: Fueling microbial communities. J. Bacteriol. 2017, 199, e00860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKee, L.S.; La Rosa, S.L.; Westereng, B.; Eijsink, V.G.; Pope, P.B.; Larsbrink, J. Polysaccharide degradation by the Bacteroidetes: Mechanisms and nomenclature. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2021, 13, 559–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwalm, N.D., II; Groisman, E.A. Navigating the Gut Buffet: Control of polysaccharide utilization in Bacteroides spp. Trends Microbiol. 2017, 25, 1005–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Kan, X.; Chen, G.; Sun, Y.; Ran, L.; Yan, Y.; Mi, J.; Lu, L.; Zeng, X.; Cao, Y. The polysaccharides from the fruits of Lycium barbarum L. modify the gut community profile and alleviate dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis in mice. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 222, 2244–2257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Tu, T.; Zhang, D.; Ma, R.; You, S.; Wang, X.; Yao, B.; Luo, H.; Xu, B. Two acidic, thermophilic GH28 polygalacturonases from Talaromyces leycettanus JCM 12802 with application potentials for grape juice clarification. Food Chem. 2017, 237, 997–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Bai, Y.; Zeng, Z.; Peng, Y.; Zhou, W.; Shen, W.; Zeng, X.; Liu, Z. Structural characterization and immunostimulatory activity of heteropolysaccharides from Fuzhuan brick tea. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 1368–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Galvez, E.J.C.; Amend, L.; Almasi, E.; Iljazovic, A.; Lesker, T.R.; Bielecka, A.A.; Schorr, E.-M.; Strowig, T. A versatile genetic toolbox for Prevotella copri enables studying polysaccharide utilization systems. Embo J. 2021, 40, e108287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onumpai, C.; Kolida, S.; Bonnin, E.; Rastall, R.A. Microbial utilization and selectivity of pectin fractions with various structures. Appl. Environ. Microb. 2011, 77, 5747–5754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, R.P.; Rajarammohan, S.; Thakur, R.; Hassan, M. Linear and branched b-Glucans degrading enzymes from versatile Bacteroides uniformis JCM 13288T and their roles in cooperation with gut bacteria. Gut Microbes 2020, 12, e1826761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Centanni, M.; Carnachan, M.C.; Bell, T.J.; Daines, A.M.; Hinkley, S.F.R.; Tannock, G.W.; Sims, I.M. Utilization of complex pectic polysaccharides from New Zealand plants (Tetragonia tetragonioides and Corynocarpus laevigatus) by gut Bacteroides species. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 7755–7764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, J.; McKenzie, C.; Potamitis, M.; Thorburn, A.N.; Mackay, C.R.; Macia, L. The role of short-chain fatty acids in health and disease. Adv. Immunol. 2014, 121, 91–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tannock, G.W. Characteristics of Bacteroides isolates from the cecum of conventional mice. Appl. Environ. Microb. 1977, 33, 745–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eggerth, A.H.; Gagnon, B.H. The Bacteroides of human feces. J. Bacteriol. 1933, 25, 389–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macfarlane, S.; Macfarlane, G.T. Regulation of short-chain fatty acid production. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2003, 62, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, H.Z.; Zhao, J.X.; Zhang, H.; Zhai, Q.X.; Chen, W. Isolation of low-abundant Bacteroidales in the human intestine and the analysis of their differential utilization based on plant-derived polysaccharides. Fron. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, A.; De Vadder, F.; Kovatcheva-Datchary, P.; Backhed, F. From dietary fiber to host physiology: Short-chain fatty acids as key bacterial metabolites. Cell 2016, 165, 1332–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helbert, W.; Poulet, L.; Drouillard, S.; Mathieu, S.; Loiodice, M.; Couturier, M.; Lombard, V.; Terrapon, N.; Turchetto, J.; Vincentelli, R.; et al. Discovery of novel carbohydrate-active enzymes through the rational exploration of the protein sequences space. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 6063–6068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, L.; Xu, Y.; Li, Q.; Zhu, B. Pectinolytic lyases: A comprehensive review of sources, category, property, structure, and catalytic mechanism of pectate lyases and pectin lyases. Bioresour. Bioprocess. 2021, 8, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luis, A.S.; Briggs, J.; Zhang, X.Y.; Farnell, B.; Ndeh, D.; Labourel, A.; Baslé, A.; Cartmell, A.; Terrapon, N.; Stott, K.; et al. Dietary pectic glycans are degraded by coordinated enzyme pathways in human colonic Bacteroides. Nat. Microbiol. 2018, 3, 210–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caffall, K.H.; Mohnen, D. The structure, function, and biosynthesis of plant cell wall pectic polysaccharides. Carbohyd. Res. 2009, 344, 1879–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colquhoun, I.J.; Deruiter, G.A.; Schols, H.A.; Voragen, A.G.J. Identification by n.m.r. spectroscopy of oligosaccharides obtained by treatment of the hairy regions of apple pectin with rhamnogalacturonase. Carbohyd. Res. 1990, 206, 131–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ridley, B.L.; O’Neill, M.A.; Mohnen, D.A. Pectins: Structure, biosynthesis, and oligogalacturonide-related signaling. Phytochemistry 2001, 57, 929–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McNeil, M.; Darvill, A.G.; Albersheim, P. Structure of Plant Cell Walls: X. Rhamnogalacturonan I, a structurally complex pectic polysacchride in the walls of suspension-culyurde sycamore cells. Plant Physiol. 1980, 66, 1128–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voragen, A.G.J.; Coenen, G.-J.; Verhoef, R.P.; Schols, H.A. Pectin, a versatile polysaccharide present in plant cell walls. Struct. Chem. 2009, 20, 263–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
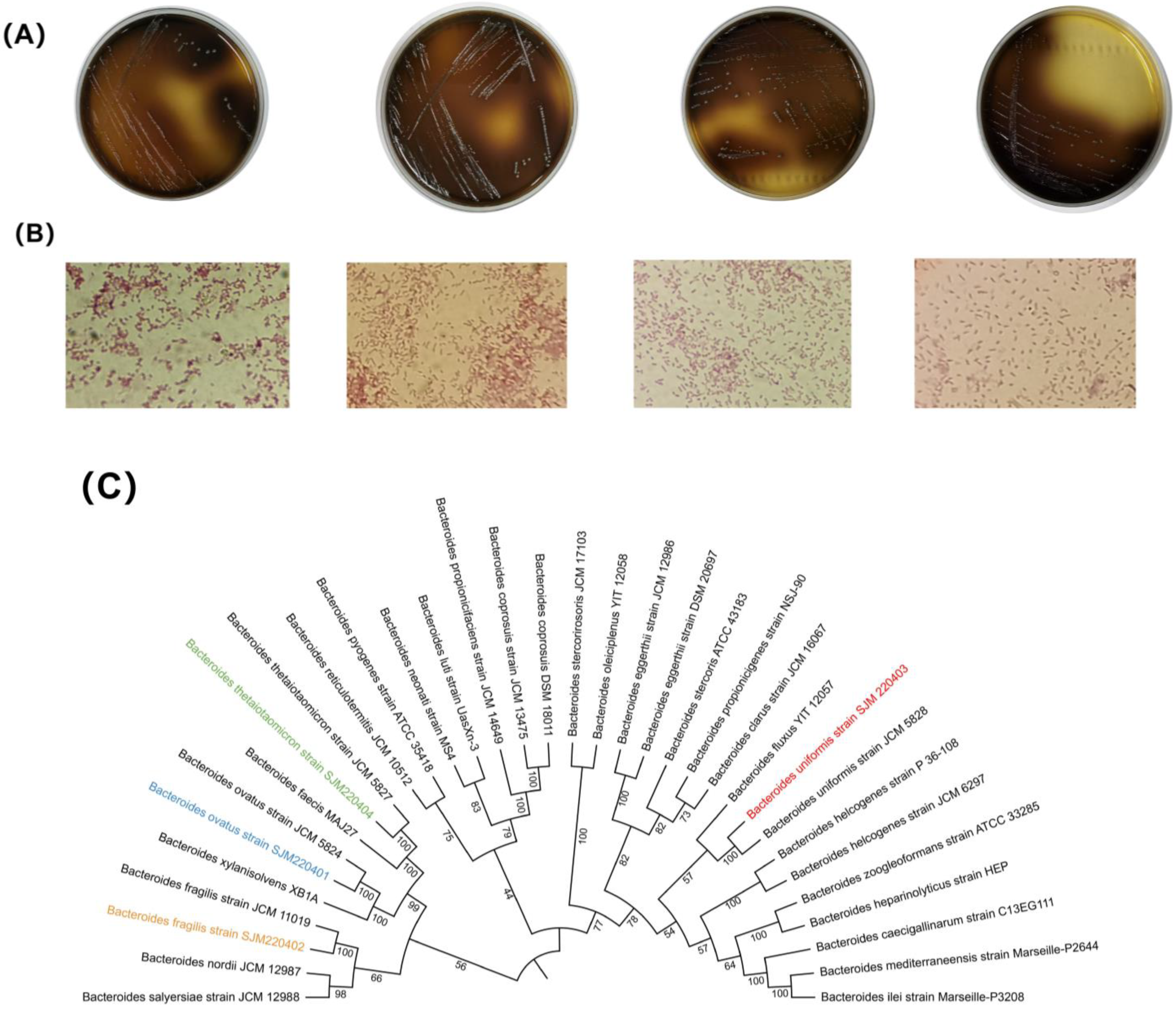



| Bacteroides Species | GenBank ID |
|---|---|
| B. ovatus | OQ781165.1 |
| B. uniformis | OR037385.1 |
| B. fragilis | OQ781170.1 |
| B. thetaiotaomicron | OR186207.1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shi, J.; Zhou, W.; Chen, G.; Yi, W.; Sun, Y.; Zeng, X. The Utilization by Bacteroides spp. of a Purified Polysaccharide from Fuzhuan Brick Tea. Foods 2024, 13, 1666. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13111666
Shi J, Zhou W, Chen G, Yi W, Sun Y, Zeng X. The Utilization by Bacteroides spp. of a Purified Polysaccharide from Fuzhuan Brick Tea. Foods. 2024; 13(11):1666. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13111666
Chicago/Turabian StyleShi, Jiameng, Wangting Zhou, Guijie Chen, Wei Yi, Yi Sun, and Xiaoxiong Zeng. 2024. "The Utilization by Bacteroides spp. of a Purified Polysaccharide from Fuzhuan Brick Tea" Foods 13, no. 11: 1666. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13111666
APA StyleShi, J., Zhou, W., Chen, G., Yi, W., Sun, Y., & Zeng, X. (2024). The Utilization by Bacteroides spp. of a Purified Polysaccharide from Fuzhuan Brick Tea. Foods, 13(11), 1666. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13111666








