Development and Evaluation of Calcium-Fortified Multi-Millet Biscuits: A Nutritious Alternative to Refined Wheat Flour
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
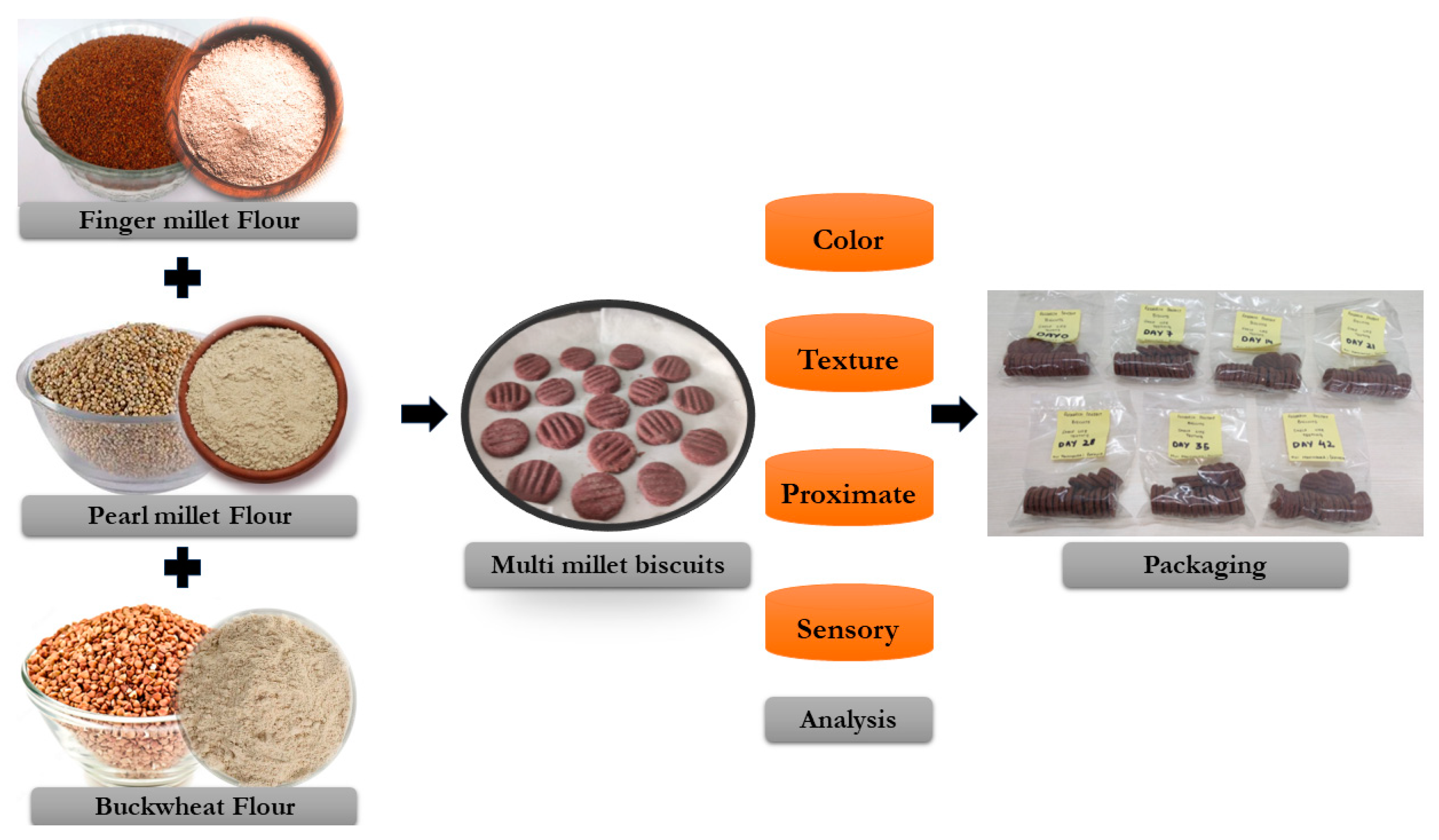
2.2. Preparation of Fortified Multi-Millet Biscuits
2.3. Experimental Design for Optimization of Multi-Millet Flour
2.4. Physico-Chemical Characteristics
2.4.1. Physical Properties
Dough and Biscuit Yield
Thickness, Diameter, and Spread Ratio
2.4.2. Functional Properties
2.4.3. Proximate Analysis
2.4.4. Mineral Analysis
2.5. Color Analysis
2.6. Texture Profile Analysis
2.7. Rheology
2.7.1. Farinograph
2.7.2. Viscosity
2.8. Packaging and Storage
2.9. Sensory Analysis
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Statistical Analysis for Optimization Using RSM
3.2. The Effect of Independent Variables on Selected Responses
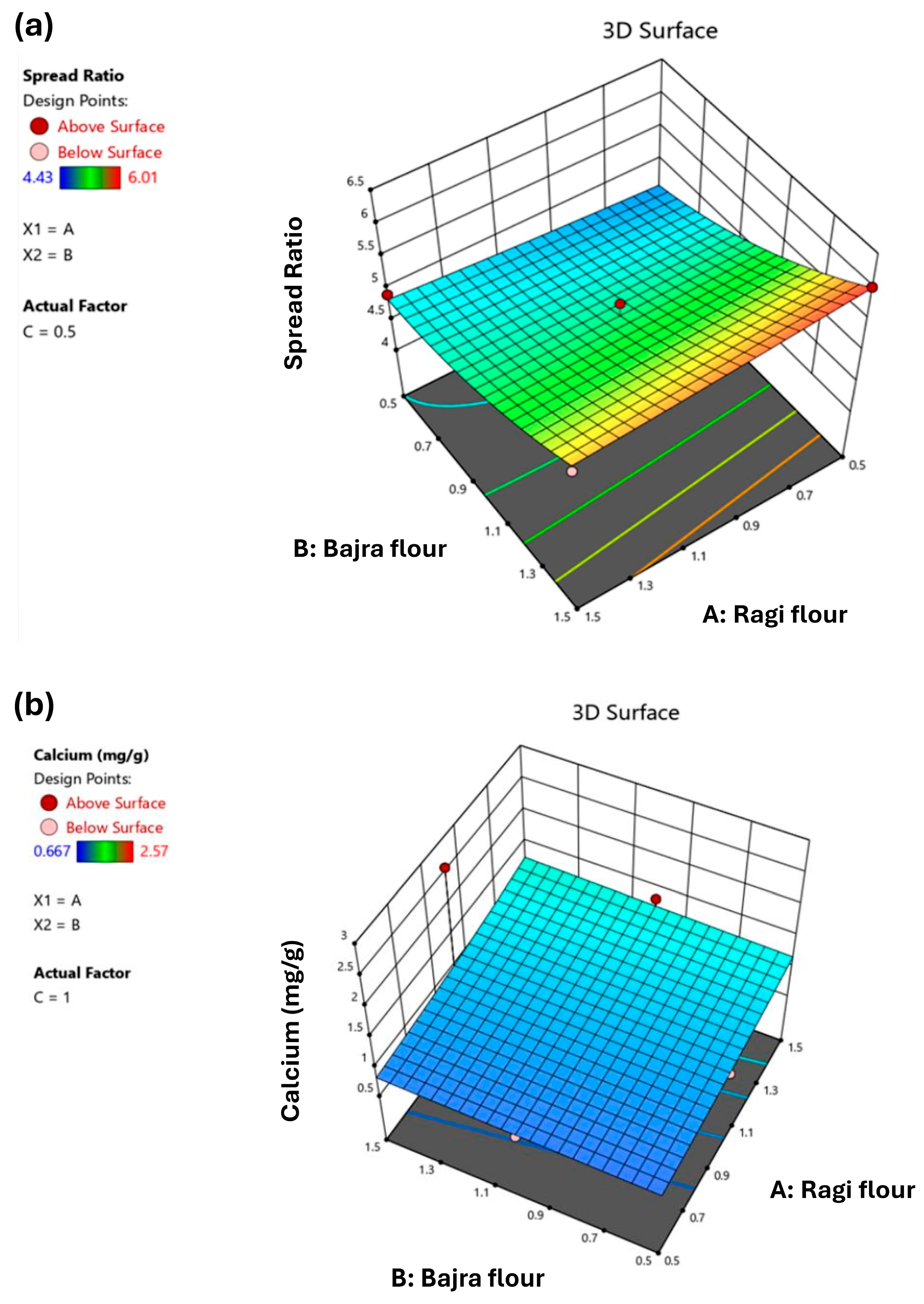
3.2.1. Spread Ratio
3.2.2. Overall Acceptability
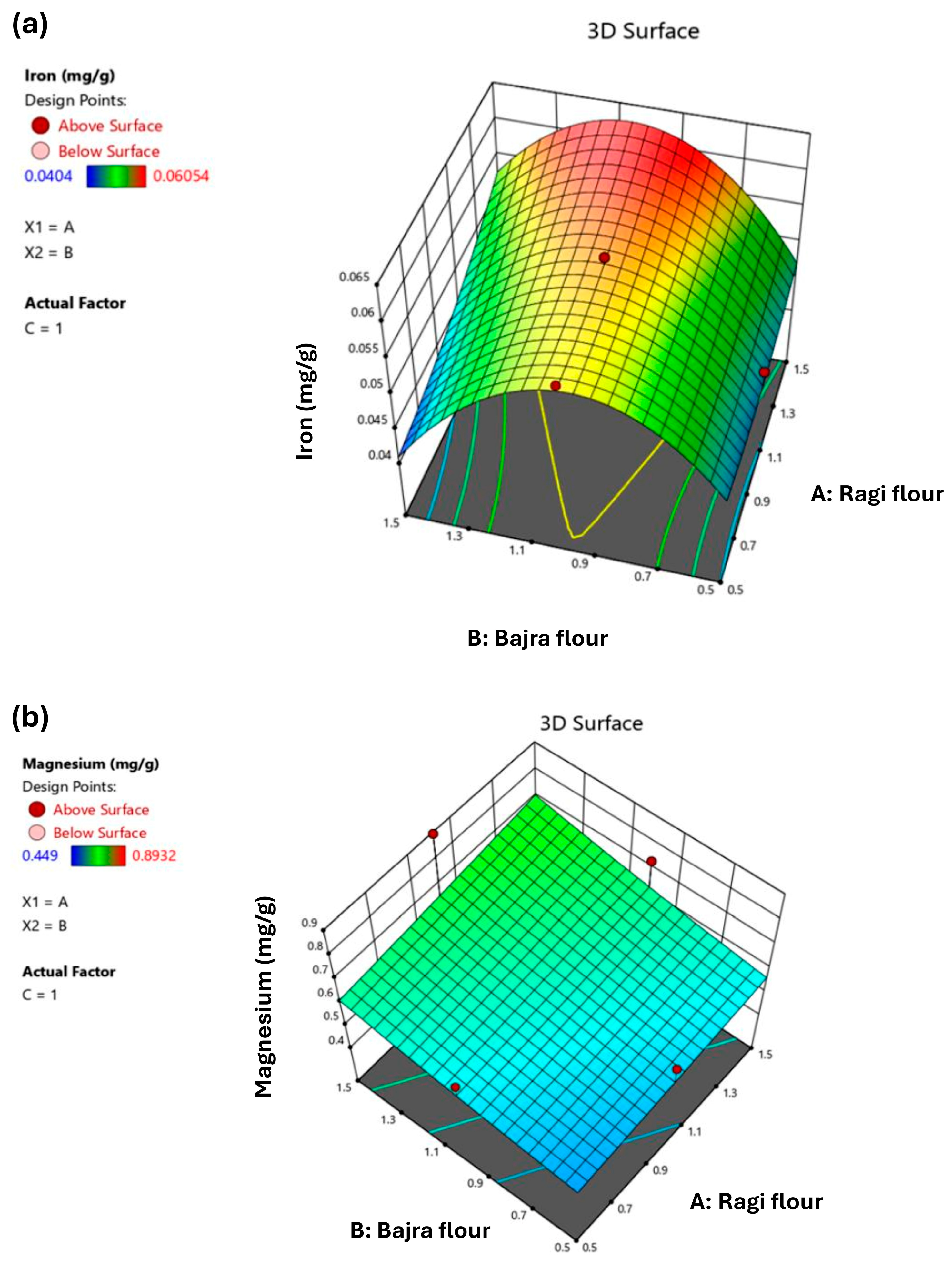
3.2.3. Minerals
3.3. Regression Equations and Model Fitting
3.4. Optimization of Multi-Millet Flour Ratio and Model Validation
3.5. Physico-Chemical Characteristics
3.5.1. Physical Properties
3.5.2. Functional Properties
3.5.3. Proximate Analysis
3.5.4. Mineral Analysis
3.6. Color analysis
3.7. Texture Profile Analysis
3.8. Rheology
3.8.1. Farinograph
3.8.2. Viscosity
3.9. Sensory Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lohan, A.; Kaushik, R.; Bansal, V.; Gandhi, K. Flex seeds and finger millet enriched functional rusk. Int. J. Food Stud. 2020, 9, 213–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, R.T.; Bisarya, D. General review of major, minor millets nutrient composition, production, and bioavailability. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 10404–10412. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, N.; Sahu, J.K.; Bansal, V.; Esua, O.J.; Rana, S.; Bhardwaj, A.; Bangar, S.P.; Adedeji, A.A. Trends in millet and pseudomillet proteins—Characterization, processing, and food applications. Food Res. Int. 2023, 164, 112310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sood, S.; Joshi, D.C.; Chandra, A.K.; Kumar, A. Phenomics and genomics of finger millet: Current status and future prospects. Planta 2019, 250, 731–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devi, P.B.; Vijayabharathi, R.; Sathyabama, S.; Malleshi, N.G.; Priyadarisini, V.B. Health benefits of finger millet (Eleusine coracana L.) polyphenols and dietary fiber: A Review. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 51, 1021–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekara, A.; Shahidi, F. Bioaccessibility and antioxidant potential of millet grain phenolics as affected by simulated in vitro digestion and microbial fermentation. J. Funct. Foods. 2012, 4, 226–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selladurai, M.; Pulivarthi, M.K.; Raj, A.S.; Iftikhar, M.; Prasad, P.V.; Siliveru, K. Considerations for gluten free foods-pearl and finger millet processing and market demand. Grain Oil Sci. Technol. 2023, 6, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.; Khatkar, B.S.; Kaushik, R. Effect of reducing agents on wheat gluten and quality characteristics of flour and cookies. Ann. Univ. Dunarea Jos Galati Food Technol. 2013, 37, 68–81. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, A.; Metwal, M.; Gupta, A.K.; Puranik, S.; Singh, M.; Gupta, S.; Babu, B.K.; Sood, S.; Yadav, R. Nutraceutical value of Finger Millet (Eleusine coracana (L.) Gaertn.), and their improvement using omics approaches. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, S.; Gupta, A.; Singh, S.R.K.; Bharti, N.; Singh, K.P.; Mahajan, V.; Gupta, H.S. Compositional and varietal influence of finger millet flour on rheological properties of dough and quality of biscuit. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2011, 44, 616–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Singh, S.; Kumar, G.; Krishnan, V.; Berwal, M.K.; Goswami, S.; Vinutha, T.; Mishra, G.P.; Satyavathi, C.T.; Singh, B.; et al. Iron and Zinc at a cross-road: A trade-off between micronutrients and anti-nutritional factors in pearl millet flour for enhancing the bioavailability. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2022, 111, 104591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias-Martins, A.M.; Pessanha, K.L.F.; Pacheco, S.; Rodrigues, J.A.S.; Carvalho, C.W.F. Potential Use of Pearl Millet (Pennisetum glaucum (L.) R. Br.) in Brazil: Food Security, Processing, Health Benefits, and Nutritional Products. Food Res. Int. 2018, 109, 175–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandrasekara, A.; Shahidi, F. Bioactivities and antiradical properties of millet grains and hulls. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 9563–9957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baljeet, S.; Ritika, B.; Roshan, L. Studies on functional properties and incorporation of buckwheat flour for biscuit making. Int. Food Res. J. 2010, 17, 1067–1076. [Google Scholar]
- Maurya, A.K.; Singh, A.; John, V.; Murmu, R. Occurrence of Alternaria alternata Causing Leaf Spot in Buckwheat (Fagopyrum Esculentum). Int. J. Environ. Agric. Res. 2021, 7, 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Zhang, Q.H. Advances in the development of functional foods from buckwheat. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2001, 41, 451–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saklani, A.; Kaushik, R.; Kumar, K. Response surface analysis and process optimization of non-cereals (elephant foot yam, taro and water chestnut) snacks. Int. J. Food Stud. 2021, 10, 296–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, W. Book review of response surface methodology: Process and product optimization using designed experiments 4th edition. J. Qual. Technol. 2017, 49, 186–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handa, C.; Goomer, S.; Siddhu, A. Physicochemical Properties and Sensory Evaluation of Fructoligosaccharide Enriched Cookies. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2012, 49, 192–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, N.; Khatkar, B.; Kaushik, R. Isolation and development of wheat-based gluten edible film and its physicochemical properties. Int. Food Res. J. 2017, 24, 94–101. [Google Scholar]
- Kaushik, R.; Chawla, P.; Kumar, N.; Janghu, S.; Lohan, A. Effect of pre-milling treatments on wheat gluten extraction and noodle quality. Food Sci. Technol. Int. 2018, 24, 627–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horowitz, W. Official Methods of Analysis of the Association of Analytical Chemists; Association of Official Analytical Chemists (AOAC): Washington, DC, USA, 1980; ISBN 0935584145. [Google Scholar]
- Raghuramulu, N.; Nair, M.; Kalyanasundaram, S. A Manual of Laboratory Techniques, 1st ed.; National Institute of Nutrition, Indian Council of Medical Research: Hyderabad, India, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Hammer, D.; Basic-Dvorzak, M.; Perring, L. Multielement ICP-OES analysis of mineral premixes used to fortify foods. At. Spectrosc. 2004, 25, 30–36. [Google Scholar]
- Angioloni, A.; Collar, C. Bread crumb quality assessment: A plural physical approach. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2009, 229, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saklani, A.; Kaushik, R.; Chawla, P.; Kumar, N.; Kumar, M. Effect of taro (Colocasia esculenta) enrichment on physicochemical and textural properties of cake. Int. J. Food Stud. 2021, 10, S114–S125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorat, S.; Ramachandran, P. Effect of finger millet flour on rheological properties of wheat dough for the preparation of bread. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2016, 5, 74–81. [Google Scholar]
- Grillo, O.; Rizzo, V.; Saccone, R.; Fallico, B.; Mazzaglia, A.; Venora, G.; Muratore, G. Use of image analysis to evaluate the shelf life of bakery products. Food Res. Int. 2014, 62, 514–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallagher, E.; O’brien, C.; Scannell, A.; Arendt, E. Use of response surface methodology to produce functional short dough biscuits. J. Food Eng. 2003, 56, 269–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madamba, P.S. The response surface methodology: An application to optimize dehydration operations of selected agricultural crops. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2002, 35, 584–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasir, G.; Chand, K.; Azaz Ahmad Azad, Z.R.; Nazir, S. Optimization of finger millet and carrot pomace-based fiber enriched biscuits using response surface methodology. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 57, 4613–4626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longvah, T.; Ananthan, I.; Bhaskarachary, K.; Venkaiah, K. Indian Food Composition Tables; National Institute of Nutrition, Indian Council of Medical Research: Hyderabad, India, 2017; ISBN 9789352676774. [Google Scholar]
- Kulthe, A.; Thorat, S.; Lande, S. Evaluation of physical and textural properties of cookies prepared from pearl millet flour. Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. Appl. Sci. 2017, 6, 692–701. [Google Scholar]
- Dogan, I.S. Effect of Oven Types on the Characteristics of Biscuits Made from Refrigerated and Frozen Doughs. Food Technol. Biotechnol. 2006, 44, 117–122. [Google Scholar]
- Twinomuhwezi, H.; Awuchi, C.G.; Rachael, M. Comparative study of the proximate composition and functional properties of composite flours of amaranth, rice, millet, and soybean. Am. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 6, 6–19. [Google Scholar]
- López Córdoba, A.F.; Goyanes, S.N. Food Powder Properties; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 1–7. ISBN 9780081005965. [Google Scholar]
- Akubor, P.; Ukwuru, M. Functional properties and biscuit making potential of soybean and cassava flour blends. Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 2003, 58, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramashia, S.E.; Gwata, E.T.; Meddows-Taylor, S.; Anyasi, T.A.; Jideani, A.I.O. Some physical and functional properties of finger millet (Eleusine coracana) obtained in sub-Saharan Africa. Int. Food Res. J. 2018, 104, 110–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sade, F.O. Proximate, anti-nutritional factors and functional properties of processed pearl millet (Pennisetum glaucum). J. Food Technol. 2009, 7, 92–97. [Google Scholar]
- Nefale, F.E.; Mashau, M.E. Effect of germination period on the physicochemical, functional and sensory properties of finger millet flour and porridge. Asian J. Appl. Sci. 2018, 6, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awuchi, C.G. Proximate composition and functional properties of different grain flour composites for industrial applications. Int. J. Food Sci. 2019, 2, 43–64. [Google Scholar]
- Awuchi, C.G. The functional properties of foods and flours. Int. J. Adv. Acad. Res. 2019, 5, 139–160. [Google Scholar]
- Abioye, V.F.; Olodude, O.A.; Atiba, V.; Oyewo, I.O. Quality evaluation of chinchin produced from composite flours of wheat and germinated finger millet flour. Agri. Biol. J. USA 2020, 20, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tongpun, N. Formulation of Soy Protein-Enriched Instant Noodles. Master’s Thesis, Faculty of Graduate Studies, Mahidol University, Bangkok, Thailand, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Salunke, P.; Chavan, U.D.; Pm, K.; Lande, S. Studies on nutritional quality of barnyard millet cookies. Int. J. Chem. Stud. 2019, 7, 651–657. [Google Scholar]
- Eneche, E.H. Biscuit-making potential of millet/pigeon pea flour blends. Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 1999, 54, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suma, P.F.; Asna Urooj, A.U.; Asha, M.R.; Jyotsna Rajiv, J.R. Sensory, physical and nutritional qualities of cookies prepared from Pearl Millet (Pennisetum Typhoideum). Int. J. Food Process. Technol. 2014, 5, 377. [Google Scholar]
- Omah, E.C.; Okafor, G.I. Selected Functional Properties, Proximate Composition of Flours and Sensory Characteristics of Cookies from Wheat and Millet-Pigeon Pea Flour Blends. Pak. J. Nutr. 2015, 14, 581–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, C.G. Buckwheat: Fagopyrum Esculentum Moench; Bioversity International: Rome, Italy, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Calvo, C.; Salvador, A.; Fiszman, S. Influence of colour intensity on the perception of color and sweetness in various fruit-flavored yogurts. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2001, 2, 99–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.D. Drying Technologies in Food Processing; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2009; p. 1. [Google Scholar]
- Patil, M.; Jain, S.; Sharma, G.P.; Jain, H.K. Textural studies of soy-jambul seed powder fortified biscuits. Food Sci. Res. J. 2011, 2, 26–30. [Google Scholar]
- Waldron, K.W.; Parker, M.L.; Smith, A.C. Plant cell walls and food quality. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2003, 2, 128–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mewis, J. Thixotropy—A general review. J. Newton. Fluid Mech. 1979, 6, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hozová, B.; Buchtová, V.; Dodok, L.; Zemanovič, J. Microbiological, nutritional and sensory aspects of stored amaranth biscuits and amaranth crackers. Nahrung 1997, 41, 155–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| F1 | F2 | F3 | R1 | R2 | R3 | R4 | R5 | R6 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Run | A | B | C | SR | OAA (0–9) | Ca (mg/g) | Fe (mg/g) | Mg (mg/g) | Se (mg/g) |
| 1 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 0.5 | 5.63 | 7.22 | 0.9505 | 0.05513 | 0.6388 | 0.02908 |
| 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 4.46 | 6.5 | 0.861 | 0.05812 | 0.5514 | 0.03066 |
| 3 | 0.5 | 1 | 1 | 5.02 | 6.97 | 0.7716 | 0.05611 | 0.5941 | 0.02934 |
| 4 | 1.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 4.92 | 6.86 | 1.205 | 0.05106 | 0.5128 | 0.03066 |
| 5 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 4.48 | 6.5 | 0.865 | 0.05814 | 0.5515 | 0.03067 |
| 6 | 1 | 0.5 | 1 | 4.78 | 7.33 | 0.922 | 0.04624 | 0.5925 | 0.03015 |
| 7 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 4.49 | 6.4 | 0.865 | 0.05814 | 0.5514 | 0.03066 |
| 8 | 0.5 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 4.69 | 7.4 | 0.667 | 0.04165 | 0.5634 | 0.03158 |
| 9 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 4.46 | 6.9 | 1.081 | 0.05818 | 0.6644 | 0.03163 |
| 10 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 4.48 | 6.5 | 0.865 | 0.05816 | 0.5514 | 0.03066 |
| 11 | 1 | 1 | 1.5 | 4.67 | 6.9 | 1.064 | 0.05597 | 0.6696 | 0.0294 |
| 12 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 1.5 | 4.82 | 7.21 | 0.697 | 0.0404 | 0.449 | 0.03102 |
| 13 | 1.5 | 1 | 1 | 4.58 | 7.34 | 1.332 | 0.05932 | 0.7299 | 0.03065 |
| 14 | 1 | 1 | 0.5 | 5.27 | 7.04 | 1.008 | 0.06054 | 0.6621 | 0.03144 |
| 15 | 0.5 | 1.5 | 0.5 | 6.01 | 7.15 | 0.819 | 0.04592 | 0.5225 | 0.03087 |
| 16 | 1 | 1.5 | 1 | 5.19 | 7.32 | 2.57 | 0.04058 | 0.8932 | 0.03104 |
| 17 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 4.43 | 6.2 | 0.93 | 0.0512 | 0.551 | 0.03061 |
| 18 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 4.57 | 6.5 | 0.865 | 0.05814 | 0.5513 | 0.03066 |
| 19 | 1.5 | 0.5 | 1.5 | 4.74 | 7.2 | 1.045 | 0.04764 | 0.5077 | 0.03102 |
| 20 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 4.47 | 6.5 | 0.864 | 0.05816 | 0.5514 | 0.03066 |
| Term | SR | OAA | Ca | Fe | Mg | Se |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F value | 8.13 | 1.61 | 3.56 | 17.49 | 3.29 | Nil |
| P > F | 0.0015 | 0.2332 | 0.0379 | <0.0001 | 0.0479 | Nil |
| Mean | 4.81 | 6.9 | 1.01 | 0.0529 | 0.593 | 0.0306 |
| SD | 0.4292 | 0.3785 | 0.3999 | 0.0068 | 0.0971 | 0.0007 |
| r2 | 0.8797 | 0.5922 | 0.4006 | 0.9403 | 0.3815 | Nil |
| Adequate Precision | 11.2618 | 4.4401 | 6.3215 | 13.371 | 6.5189 | Nil |
| (a) Physical properties | (b) Functional properties | ||
| Parameter | Result | Parameter | Result |
| Dough Weight (g) | 114.24 ± 1.98 | BD (g/mL) | 0.66 ± 0.063 |
| Biscuit Weight (g) | 5.27 ± 0.34 | WAC (%) | 150.56 ± 6.13 |
| Thickness (mm) | 7.966 ± 0.10 | OAC (%) | 175 ± 7.07 |
| Diameter (mm) | 36.36 ± 0.24 | SI (g/g) | 0.09 ± 0.007 |
| Spread Ratio | 4.56 ± 0.032 | SC (mL) | 10 ± 1.4 |
| % Baking Loss | 12.44 ± 1.52 | FC (%) | 0.7 ± 0.14 |
| (c) Proximate analysis | (d) Mineral analysis | ||
| Parameter | Result | Parameter | Result |
| Moisture (%) | 3.1 ± 0.14 | Ca (fortified) | 1.462 ± 0.051 |
| Protein (%) | 5.472 ± 0.31 | Ca | 1.256 ± 0.015 |
| Fat (g/100 g) | 29.5 ± 0.85 | Fe | 0.16 ± 0.007 |
| Ash (g/100 g) | 2.8 ± 0.57 | Mg | 0.682 ± 0.005 |
| Crude Fiber (g/100 g) | 0.741 ± 0.008 | Zn | 0.15 ± 0.002 |
| Carbohydrate (g/100 g) | 58.387 ± 0.17 | Na | 1.49 ± 0.03 |
| Energy (kcal/g) | 5.8015 ± 0.004 | ||
| Day | Appearance | Color | Taste | Flavor | Texture | OAA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Day 0 | 8.053 ± 0.85 | 7.842 ± 1.07 | 8.053 ± 0.91 | 8 ± 1.05 | 8 ± 0.82 | 8.263 ± 0.65 |
| Day 7 | 8.053 ± 0.91 | 7.842 ± 1.07 | 8 ± 0.82 | 7.842 ± 1.01 | 8 ± 0.82 | 8.158 ± 0.69 |
| Day 14 | 8 ± 0.94 | 7.684 ± 0.95 | 7.895 ± 1.05 | 7.631 ± 1.12 | 8 ± 0.94 | 8.053 ± 0.85 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Manchanda, M.; Rawat, D.; Chandra, A.; Saini, R.K. Development and Evaluation of Calcium-Fortified Multi-Millet Biscuits: A Nutritious Alternative to Refined Wheat Flour. Foods 2024, 13, 1696. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13111696
Manchanda M, Rawat D, Chandra A, Saini RK. Development and Evaluation of Calcium-Fortified Multi-Millet Biscuits: A Nutritious Alternative to Refined Wheat Flour. Foods. 2024; 13(11):1696. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13111696
Chicago/Turabian StyleManchanda, Mili, Divya Rawat, Abhishek Chandra, and Ramesh Kumar Saini. 2024. "Development and Evaluation of Calcium-Fortified Multi-Millet Biscuits: A Nutritious Alternative to Refined Wheat Flour" Foods 13, no. 11: 1696. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13111696
APA StyleManchanda, M., Rawat, D., Chandra, A., & Saini, R. K. (2024). Development and Evaluation of Calcium-Fortified Multi-Millet Biscuits: A Nutritious Alternative to Refined Wheat Flour. Foods, 13(11), 1696. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13111696










