Revolutionizing Phenolic Content Determination in Vegetable Oils: A Cutting-Edge Approach Using Smartphone-Based Image Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.1.1. Samples
2.1.2. Equipment Used for Total Phenolic Content Analysis
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Smartphone Image Acquisition
2.2.2. Image Analysis
2.2.3. Preparation of Calibration Curves for Total Phenolic Content Determination
2.2.4. Determination of Total Phenolic Content in Vegetable Oils
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Determining the Optimal Distance for Image Acquisition
3.2. Determination of Total Phenolic Content
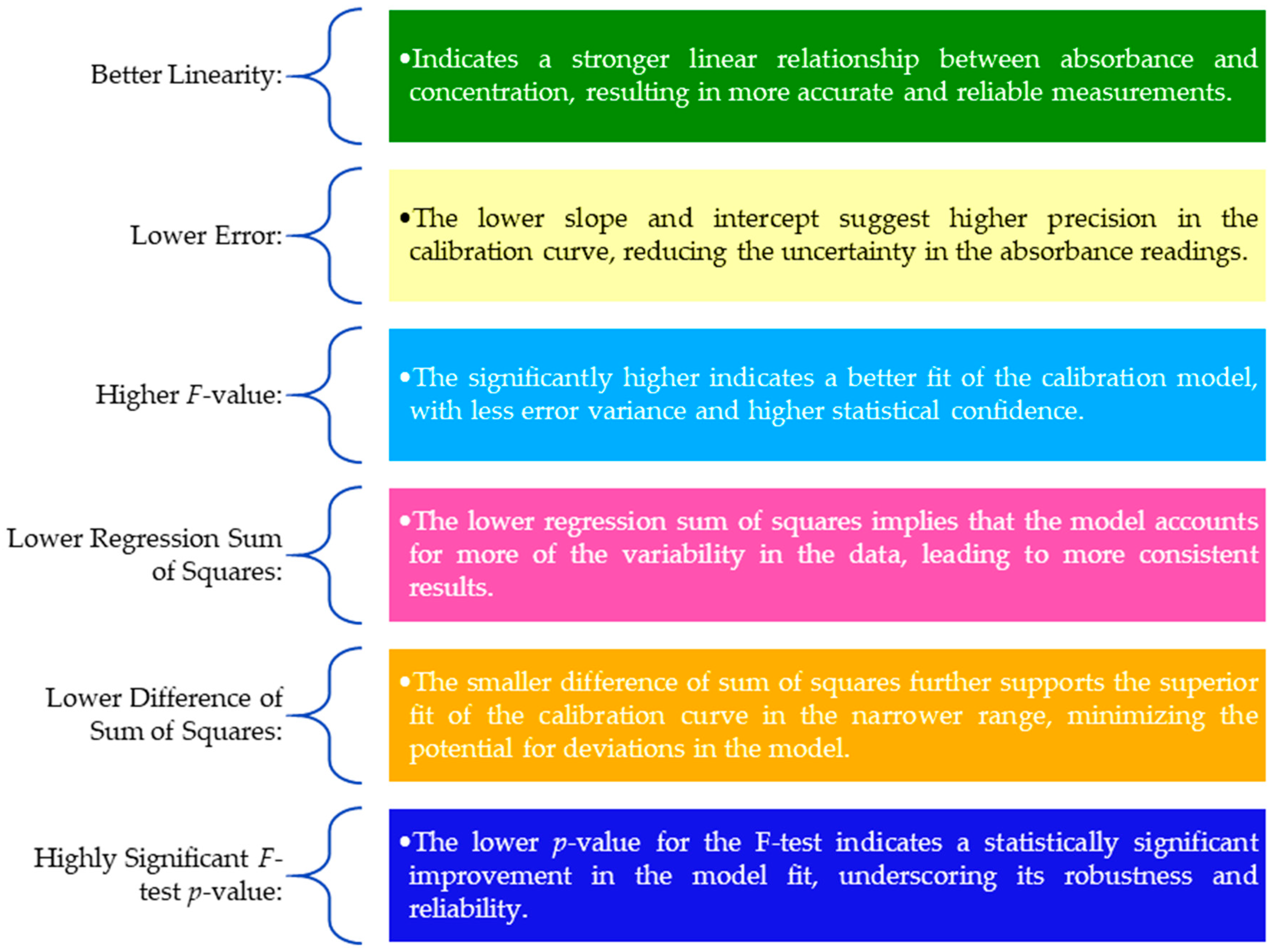
3.3. Validation of a Smartphone Analytical Method for Total Phenolic Content
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kumar, A.; Sharma, A.; Upadhyaya, K.C. Vegetable Oil: Nutritional and Industrial Perspective. Curr. Genomics 2016, 17, 230–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mikołajczak, N.; Tańska, M.; Ogrodowska, D. Phenolic Compounds in Plant Oils: A Review of Composition, Analytical Methods, and Effect on Oxidative Stability. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 113, 110–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkata, P.; Subramanyam, R. Evaluation of the Deleterious Health Effects of Consumption of Repeatedly Heated Vegetable Oil. Toxicol. Rep. 2016, 3, 636–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Servili, M.; Sordini, B.; Esposto, S.; Urbani, S.; Veneziani, G.; Di Maio, I.; Selvaggini, R.; Taticchi, A. Biological Activities of Phenolic Compounds of Extra Virgin Olive Oil. Antioxidants 2014, 3, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taghvaei, M.; Jafari, S.M. Application and Stability of Natural Antioxidants in Edible Oils in Order to Substitute Synthetic Additives. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 52, 1272–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedan, V.; Popp, M.; Rohn, S.; Nyfeler, M.; Bongartz, A. Characterization of Phenolic Compounds and Their Contribution to Sensory Properties of Olive Oil. Molecules 2019, 24, 2041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahidi, F.; Ambigaipalan, P. Phenolics and Polyphenolics in Foods, Beverages and Spices: Antioxidant Activity and Health Effects—A Review. J. Funct. Foods 2015, 18, 820–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fagionato Masiero, J.; Barbosa, E.J.; de Oliveira Macedo, L.; de Souza, A.; Nishitani Yukuyama, M.; Arantes, G.J.; Bou-Chacra, N.A. Vegetable Oils in Pharmaceutical and Cosmetic Lipid-Based Nanocarriers Preparations. Ind. Crops Prod. 2021, 170, 113838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tennant, D.; Gosling, J.P. Modelling Consumer Intakes of Vegetable Oils and Fats. Food Addit. Contam. Part A Chem. Anal. Control. Expo. Risk Assess. 2015, 32, 1397–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuentes, E.; Báez, M.E.; Bravo, M.; Cid, C.; Labra, F. Determination of Total Phenolic Content in Olive Oil Samples by UV-Visible Spectrometry and Multivariate Calibration. Food Anal. Methods 2012, 5, 1311–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrés-Cebrián, M.; Seró, R.; Saurina, J.; Núñez, O. HPLC-UV Polyphenolic Profiles in the Classification of Olive Oils and Other Vegetable Oils via Principal Component Analysis. Separations 2016, 3, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Türkucąr, S.A.; Karaçelik, A.A.; Karaköse, M. Phenolic Compounds, Essential Oil Composition, and Antioxidant Activity of Angelica Purpurascens (Avé-Lall.) Gill. Turkish J. Chem. 2021, 45, 956–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, H.; Huang, X.; Sun, Y.; Chen, Q.; Wei, Z.J.; Lv, R. Intelligent Evaluation of Total Polar Compounds (TPC) Content of Frying Oil Based on Fluorescence Spectroscopy and Low-Field NMR. Food Chem. 2021, 342, 128242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michiu, D.; Socaciu, M.I.; Fogarasi, M.; Jimborean, A.M.; Ranga, F.; Mureşan, V.; Semeniuc, C.A. Implementation of an Analytical Method for Spectrophotometric Evaluation of Total Phenolic Content in Essential Oils. Molecules 2022, 27, 1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Csepregi, K.; Kocsis, M.; Hideg, É. On the Spectrophotometric Determination of Total Phenolic and Flavonoid Contents. Acta Biol. Hung. 2013, 64, 500–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apostica, A.G.; Ichim, T.; Radu, V.M.; Bulgariu, L. Simple and Rapid Spectrophotometric Method for Phenol Determination in Aqueous Media. Bull. Polytech. Inst. Jassy 2018, 64, 9–18. [Google Scholar]
- Escarpa, A.; González, M.C. Approach to the Content of Total Extractable Phenolic Compounds from Different Food Samples by Comparison of Chromatographic and Spectrophotometric Methods. Anal. Chim. Acta 2001, 427, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anh-Dao, L.T.; Thanh-Nho, N.; Huu-Trung, B.; Tien-Giang, N.; Ut Dong, T.; Quoc-Duy, N.; Quang-Hieu, N.; Le-Vy, N.; Thanh-Dieu, N.T.; To, D.V.T.; et al. A Portable Colorimetric Tool Using a Smartphone Camera Applied for Determining Total Phenolic Contents in Coffee Products. Chinese J. Anal. Chem. 2023, 51, 100228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minh-Huy, D.; Anh-Dao, L.T.; Thanh-Nho, N.; Nhon-Duc, L.; Cong-Hau, N. Smartphone-Based Digital Images as a Low-Cost and Simple Colorimetric Approach for the Assessment of Total Phenolic Contents in Several Specific Vietnamese Dried Tea Products and Their Liquors. Food Chem. 2023, 401, 134147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, L.C.; de Souza Silva, A.F.; de Moraes, L.M.B.; Gonçalves, I.C.; de Godoy, B.B.R.; Rocha, F.R.P. A Greener and Faster Approach for Determination of Phenolic Compounds by Smartphone-Based Colorimetry. Proceedings 2021, 70, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezazadeh, M.; Seidi, S.; Lid, M.; Pedersen-Bjergaard, S.; Yamini, Y. The Modern Role of Smartphones in Analytical Chemistry. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 118, 548–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ledesma, C.M.; Krepsky, L.M.; Borges, E.M. Using a Flatbed Scanner and Automated Digital Image Analysis to Determine the Total Phenolic Content in Beer. J. Chem. Educ. 2019, 96, 2315–2321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apichai, S.; Thajee, K.; Pattananandecha, T.; Saenjum, C.; Grudpan, K. A Simple Minimized System Based on Moving Drops for Antioxidant Analysis Using a Smartphone. Molecules 2021, 26, 5744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morosanova, M.A.; Bashkatova, A.S.; Morosanova, E.I. Spectrophotometric and Smartphone-Assisted Determination of Phenolic Compounds Using Crude Eggplant Extract. Molecules 2019, 24, 4407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzatti, C.A.; Carboni, C.; Rodrigues, E.; Helfer, G.; Ben, A.; Utpott, M.; Tischer, B. Development of an Analytical Method Using Smartphones for the Assessment of Phenolic Compounds. Agri. Res. Tech. Open Access J. 2023, 27. [Google Scholar]
- Van Nguyen, H.; Jakmunee, J.; Youngvises, N.; Preechaburana, P. Determination of Both Total Phenolic Compound and Antioxidant Capacity of Herbal Teas Using Smartphone Digital Imaging. Chiang Mai J. Sci. 2022, 49, 420–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazani, E.J.O.; Barreto, M.S.; Demuner, A.J.; Dos Santos, M.H.; Cerceau, C.I.; Blank, D.E.; Firmino, M.J.M.; Souza, G.S.F.; Franco, M.O.K.; Suarez, W.T.; et al. Smartphone Application for Total Phenols Content and Antioxidant Determination in Tomato, Strawberry, and Coffee Employing Digital Imaging. Food Anal. Methods 2021, 14, 631–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, B.N.; Dalla Nora, F.M.; Boeira, C.P.; Verruck, S.; Da Rosa, C.S. Determination of Total Phenolic Compounds in Plant Extracts via Folin-Ciocalteu’s Method Adapted to the Usage of Digital Images. Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 42, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasitthirotjanayut, P.; Rodma, Y.; Boonloed, K.M.; Boonloed, A. Development of Colorimetric Methods for Determination of Total Phenolic Content in Tea. Pure Appl. Chem. Int. Conf. 2020, 10, 101–105. [Google Scholar]
- Pedroso, D.d.Q.; Knaul, L.E.; Kapp, M.N.; Gonçalves, C.d.C.S.; Boroski, M. Using Smartphone for Monitoring Colorimetric Reactions Aiming at Determining Antioxidant Activity. Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calabria, D.; Mirasoli, M.; Guardigli, M.; Simoni, P.; Zangheri, M.; Severi, P.; Caliceti, C.; Roda, A. Paper-Based Smartphone Chemosensor for Reflectometric on-Site Total Polyphenols Quantification in Olive Oil. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 305, 127522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeb, A. Spectroscopy of Phenolic Antioxidants. In Phenolic Antioxidants in Foods: Chemistry, Biochemistry and Analysis; Zeb, A., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 517–548. ISBN 978-3-030-74767-1. [Google Scholar]
- Kaggle Web Page. Available online: https://www.kaggle.com/ (accessed on 10 January 2024).
- GitHub Analysis of Smartphone Images for the Determination of Total Phenols. Available online: https://github.com/SanitaVucane/Analysis-of-Smartphone-images-in-RGB-colour-system (accessed on 3 February 2024).
- Calabria, D.; Guardigli, M.; Severi, P.; Trozzi, I.; Pace, A.; Cinti, S.; Zangheri, M.; Mirasoli, M. A Smartphone-Based Chemosensor to Evaluate Antioxidants in Agri-Food Matrices by in Situ AuNP Formation. Sensors 2021, 21, 5432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janu, C.; Kumar, D.R.S.; Reshma, M.V.; Jayamurthy, P.; Sundaresan, A.; Nisha, P. Comparative Study on the Total Phenolic Content and Radical Scavenging Activity of Common Edible Vegetable Oils. J. Food Biochem. 2014, 38, 38–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konuskan, D.B.; Kamiloglu, O.; Demirkeser, O. Fatty Acid Composition, Total Phenolic Content and Antioxidant Activity of Grape Seed Oils Obtained by Cold- Pressed and Solvent Extraction. Indian J. Pharm. Educ. Res. 2019, 53, 144–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rombaut, N.; Savoire, R.; Thomasset, B.; Bélliard, T.; Castello, J.; Van Hecke, É.; Lanoisellé, J.L. Grape Seed Oil Extraction: Interest of Supercritical Fluid Extraction and Gas-Assisted Mechanical Extraction for Enhancing Polyphenol Co-Extraction in Oil. Comptes Rendus Chim. 2014, 17, 284–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rombaut, N.; Savoire, R.; Thomasset, B.; Castello, J.; Van Hecke, E.; Lanoisellé, J.L. Optimization of Oil Yield and Oil Total Phenolic Content during Grape Seed Cold Screw Pressing. Ind. Crops Prod. 2015, 63, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Stefano, V.; Buzzanca, C.; Melilli, M.G.; Indelicato, S.; Mauro, M.; Vazzana, M.; Arizza, V.; Lucarini, M.; Durazzo, A.; Bongiorno, D. Polyphenol Characterization and Antioxidant Activity of Grape Seeds and Skins from Sicily: A Preliminary Study. Sustain. 2022, 14, 2–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemzadeh, A.; Karbalaii, M.T.; Jaafar, H.Z.E.; Rahmat, A. Phytochemical Constituents, Antioxidant Activity, and Antiproliferative Properties of Black, Red, and Brown Rice Bran. Chem. Cent. J. 2018, 12, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.H.; Lu, C.Z. Phenolic Composition and Antioxidant Properties of 2 Taxa of Macadamia Flowers. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2022, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frazzini, S.; Torresani, M.C.; Roda, G.; Dell’Anno, M.; Ruffo, G.; Rossi, L. Chemical and Functional Characterization of the Main Bioactive Molecules Contained in Hulled Cannabis Sativa L. Seeds for Use as Functional Ingredients. J. Agric. Food Res. 2024, 16, 101084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, M.; Kim, J.H.; Han, J.H.; Ryu, B.R.; Lim, Y.S.; Lim, J.D.; Park, S.H.; Kim, C.H.; Lee, S.U.; Kwon, T.H. In Vitro and In Vivo Anti-Inflammatory Potential of Cannabichromene Isolated from Hemp. Plants 2023, 12, 3966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddy, G.; Bar-Hai, A.; Hoffman, A.; Feldmann, M.; Domb, A. Novel Phenolate Salts of Bioactive Agents: Cannabidiol Phenolate Salts. Bioorg. Chem. 2023, 141, 106914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shuai, X.; Dai, T.; Chen, M.; Liang, R.; Du, L.; Chen, J.; Liu, C. Comparative Study of Chemical Compositions and Antioxidant. Foods 2021, 10, 1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jakubíková, M.; Sádecká, J.; Hroboňová, K. Determination of Total Phenolic Content and Selected Phenolic Compounds in Sweet Wines by Fluorescence Spectroscopy and Multivariate Calibration. Microchem. J. 2022, 181, 107834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zugazua-Ganado, M.; Bordagaray, A.; Ezenarro, J.; Garcia-Arrona, R.; Ostra, M.; Vidal, M. Adaptation of the Folin-Ciocalteu and Fast Blue BB Spectrophotometric Methods to Digital Image Analysis for the Determination of Total Phenolic Content: Reduction of Reaction Time, Interferences and Sample Analysis. LWT 2024, 193, 115756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanti, N.A.; Jahiding, M.; Edihar, M.; June, M.; June, M. Validation of UV-Vis Spectrophotometric Method for Determination of Bio Oil Total Phenolic Content from Pyrolisis of Cashew Nut Shell. Res. J. Pharm. Biol. Chem. Sci. 2017, 8, 1745–1752. [Google Scholar]
- Kalinowska, K.; Wojnowski, W.; Tobiszewski, M. Smartphones as Tools for Equitable Food Quality Assessment. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 111, 271–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upadhyay, S.; Kumar, A.; Srivastava, M.; Srivastava, A.; Dwivedi, A.; Singh, R.K.; Srivastava, S.K. Recent Advancements of Smartphone-Based Sensing Technology for Diagnosis, Food Safety Analysis, and Environmental Monitoring. Talanta 2024, 275, 126080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pongnumkul, S.; Chaovalit, P.; Surasvadi, N. Applications of Smartphone-Based Sensors in Agriculture: A Systematic Review of Research. J. Sensors 2015, 2015, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
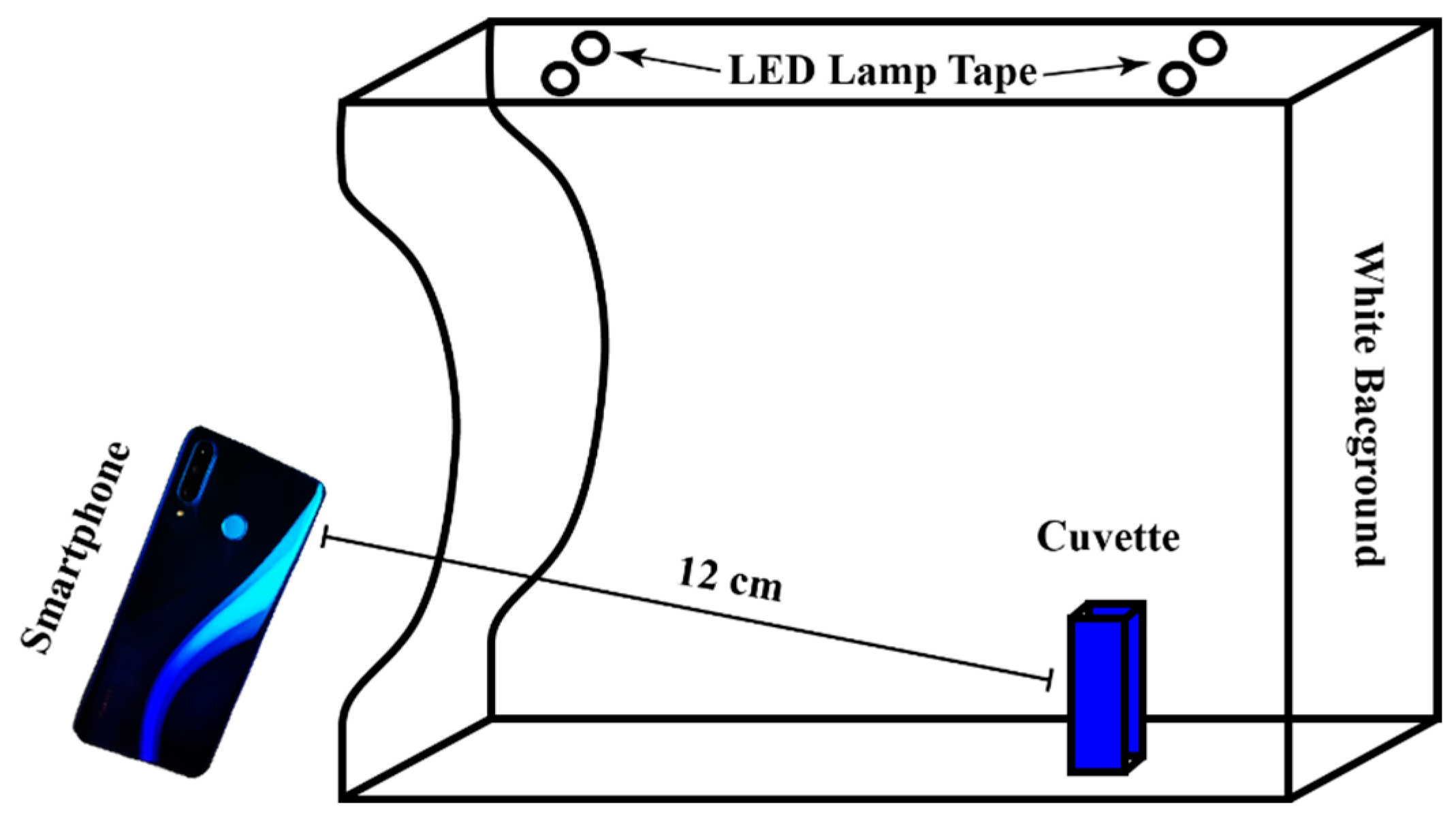
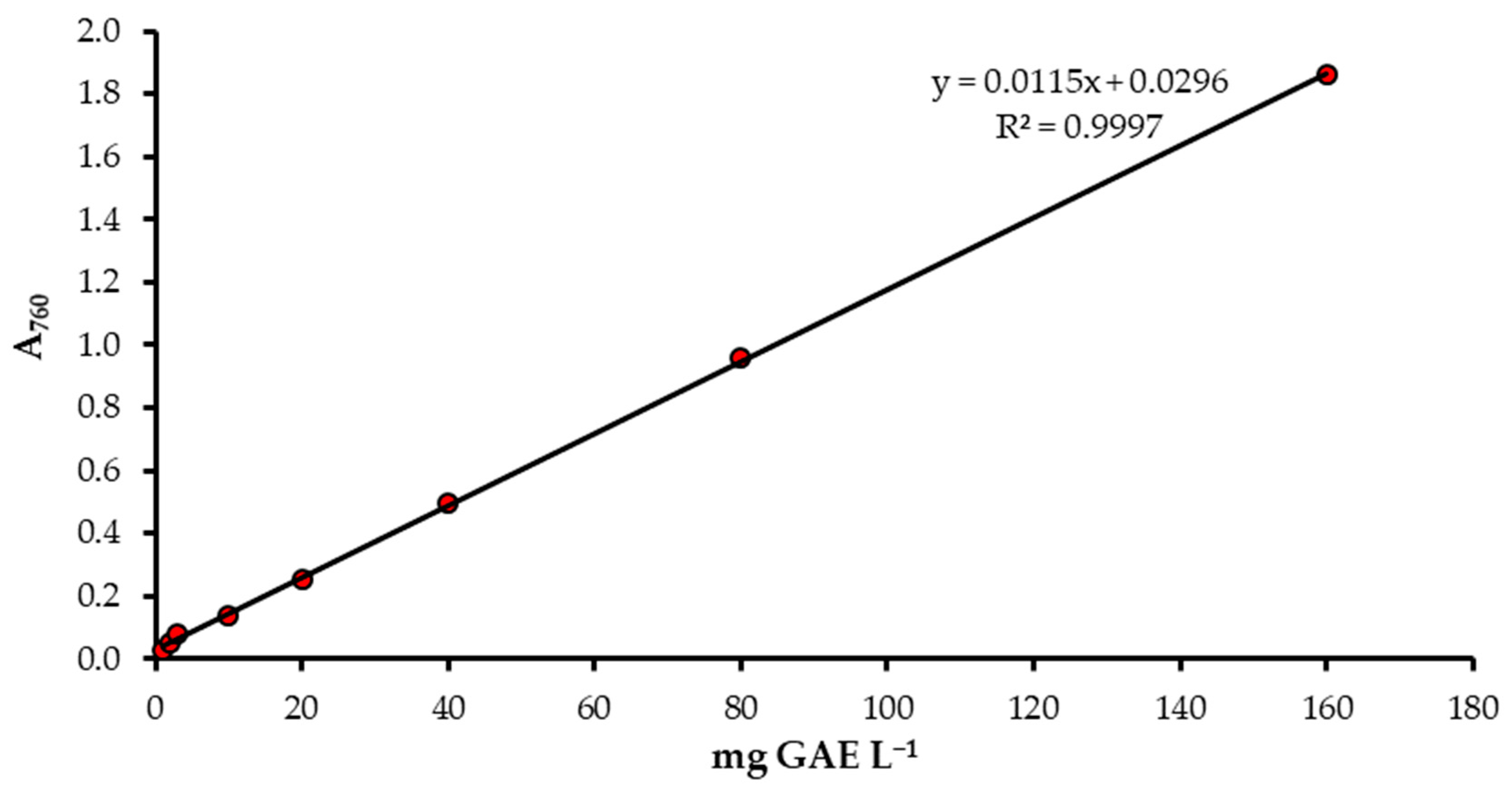



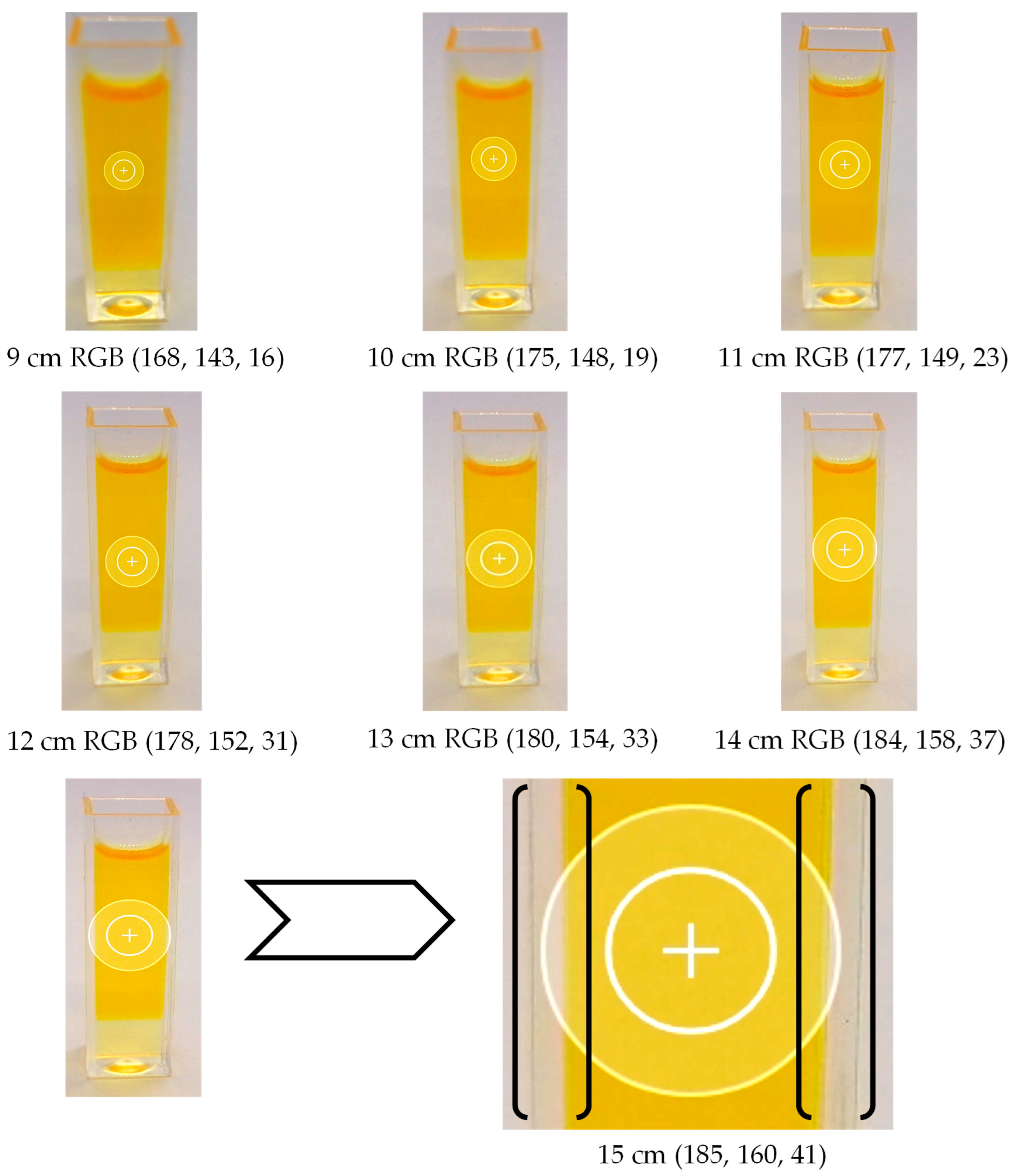
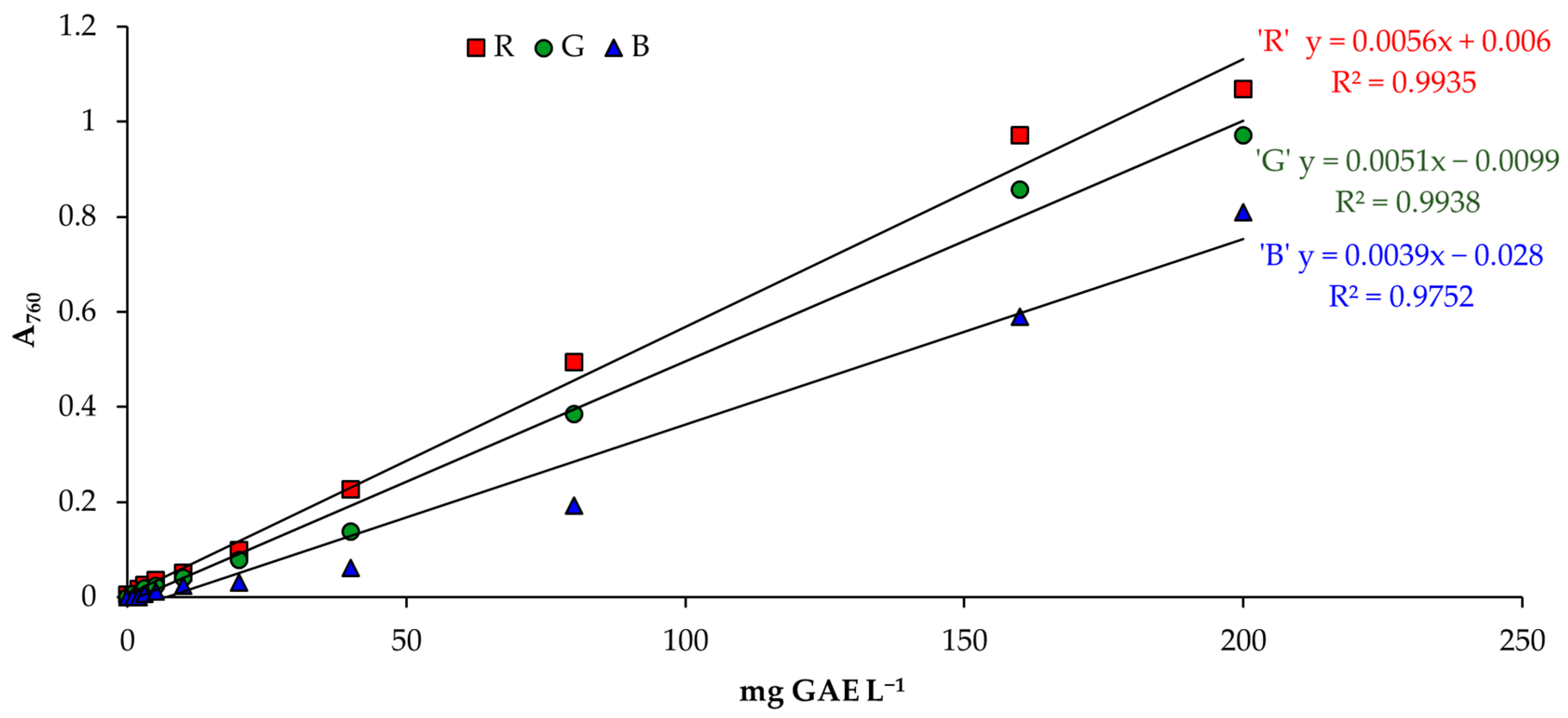

| Specification | |
|---|---|
| Display |
|
| Processor |
|
| Operating system |
|
| Main camera |
|
| Distance, cm | Color | R | G | B |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 9 | White | 187 ± 1 | 185 ± 1 | 188 ± 1 |
| Black | 20 ± 1 | 19 ± 1 | 20 ± 1 | |
| 10 | White | 188 ± 1 | 186 ± 1 | 188 ± 1 |
| Black | 19 ± 1 | 19 ± 1 | 20 ± 1 | |
| 11 | White | 188 ± 1 | 187 ± 1 | 189 ± 1 |
| Black | 18 ± 1 | 20 ± 1 | 19 ± 1 | |
| 12 | White | 189 ± 1 | 189 ± 1 | 190 ± 1 |
| Black | 17 ± 1 | 19 ± 1 | 18 ± 1 | |
| 13 | White | 188 ± 1 | 189 ± 1 | 188 ± 1 |
| Black | 18 ± 1 | 20 ± 1 | 19 ± 1 | |
| 14 | White | 187 ± 1 | 188 ± 1 | 187 ± 1 |
| Black | 18 ± 1 | 20 ± 1 | 19 ± 1 | |
| 15 | White | 180 ± 1 | 180 ± 1 | 182 ± 1 |
| Black | 19 ± 1 | 18 ± 1 | 19 ± 1 |
| Indices | Gallic Acid Concentration (1–200 mg L−1) | Indices | |
|---|---|---|---|
| a | 0.00563 | 0.006 | b |
| a error | 0.00015 | 0.012 | b error |
| r2 | 0.993 | 0.033750898 | y error |
| F | 1375.24616 | 9 | df |
| Regression sum of squares | 1.56657465 | 0.010252108 | Difference of sum of squares |
| F-test | 3.7374 × 10−11 | ||
| Gallic Acid Concentration (1–160 mg L−1) | |||
| a | 0.00608 | −0.002 | b |
| a error | 0.00007 | 0.004 | b error |
| r2 | 0.999 | 0.01139195 | y error |
| F | 6778.851302 | 8 | df |
| Regression sum of squares | 0.879735097 | 0.00103821 | Difference of sum of squares |
| F-test | 5.28141 × 10−13 | ||
| Indices | Absorption |
|---|---|
| Gallic acid, mg L−1 | |
| LOD | 1.254 |
| LOQ | 3.801 |
| Measuring range, mg L−1 | |
| from | 3.801 |
| to | 160 |
| Sample (n = 10) | %RSD | Repeatability mg GAE 100 g−1 | Accuracy mg GAE 100 g−1 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average | Max | Average | Max | ||
| Vegetable oils | 0.67 | 0.0344 | 0.1414 | 0.0689 | 0.2828 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vucane, S.; Cinkmanis, I.; Juhnevica-Radenkova, K.; Sabovics, M. Revolutionizing Phenolic Content Determination in Vegetable Oils: A Cutting-Edge Approach Using Smartphone-Based Image Analysis. Foods 2024, 13, 1700. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13111700
Vucane S, Cinkmanis I, Juhnevica-Radenkova K, Sabovics M. Revolutionizing Phenolic Content Determination in Vegetable Oils: A Cutting-Edge Approach Using Smartphone-Based Image Analysis. Foods. 2024; 13(11):1700. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13111700
Chicago/Turabian StyleVucane, Sanita, Ingmars Cinkmanis, Karina Juhnevica-Radenkova, and Martins Sabovics. 2024. "Revolutionizing Phenolic Content Determination in Vegetable Oils: A Cutting-Edge Approach Using Smartphone-Based Image Analysis" Foods 13, no. 11: 1700. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13111700
APA StyleVucane, S., Cinkmanis, I., Juhnevica-Radenkova, K., & Sabovics, M. (2024). Revolutionizing Phenolic Content Determination in Vegetable Oils: A Cutting-Edge Approach Using Smartphone-Based Image Analysis. Foods, 13(11), 1700. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13111700








