Comparative Metabolic Profiling of Different Colored Rice Grains Reveals the Distribution of Major Active Compounds and Key Secondary Metabolites in Green Rice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials and Reagents
2.2. Metabolite Extraction and UHPLC–MS/MS Analysis
2.3. Identification and Quantification of Metabolites
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
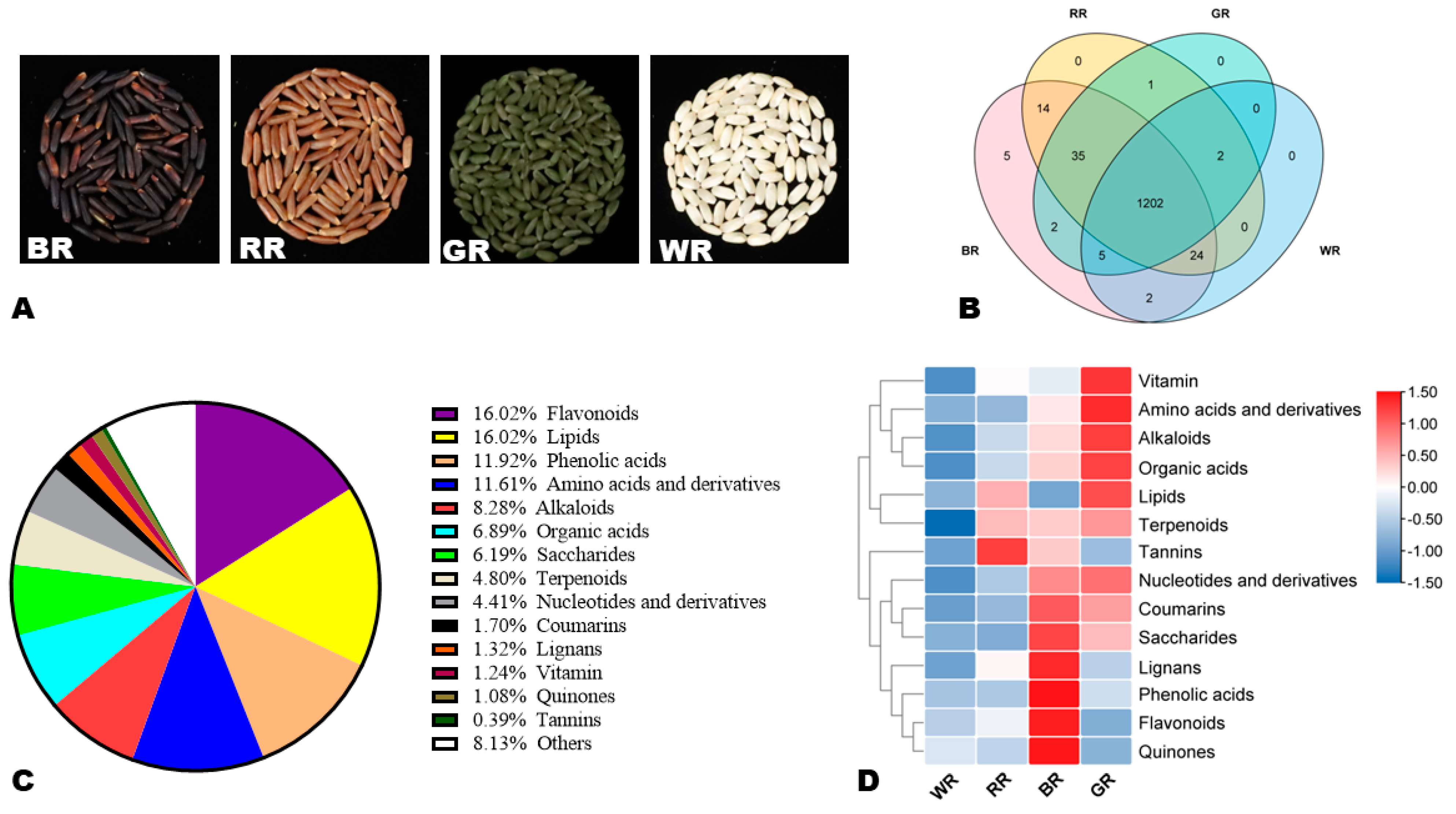
3.1. Metabolic Profiles of Black, Red, Green, and White Rice Grains
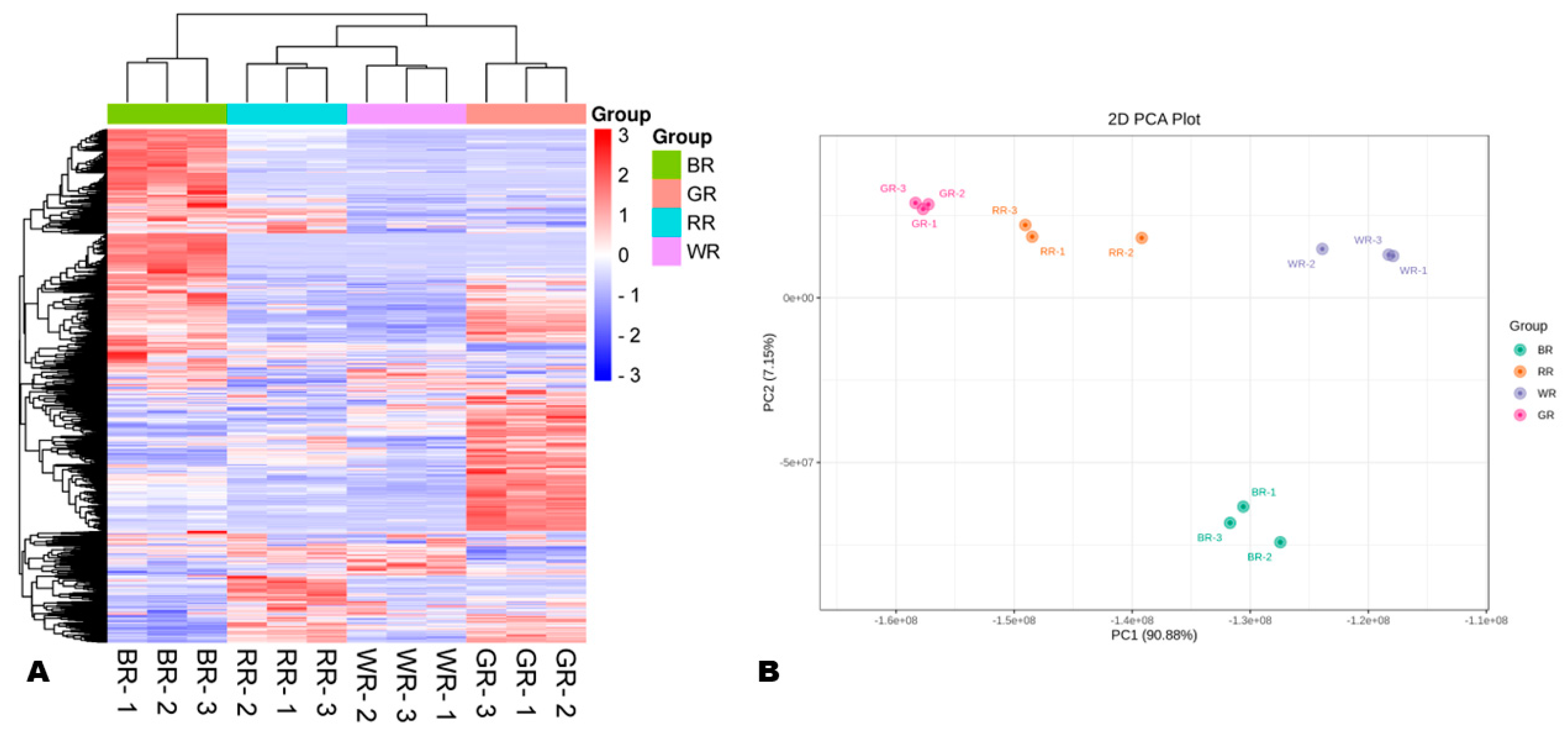
3.2. Variability of Metabolites in the Different Colored Rice Grains
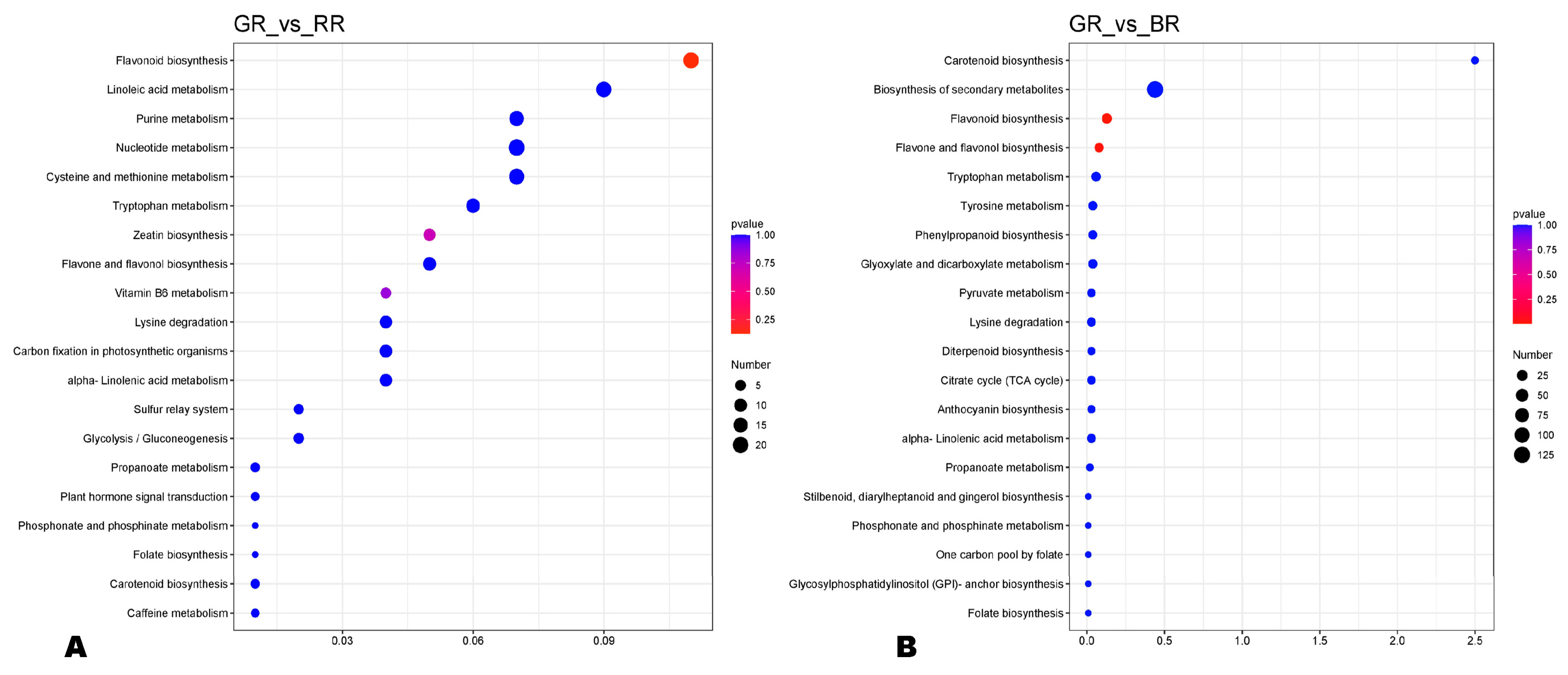
3.3. Differentially Accumulated Metabolites and KEGG Enrichment
3.4. Variation Characteristics of Major Bioactive Compounds in Black, Red, Green, and White Rice Grains
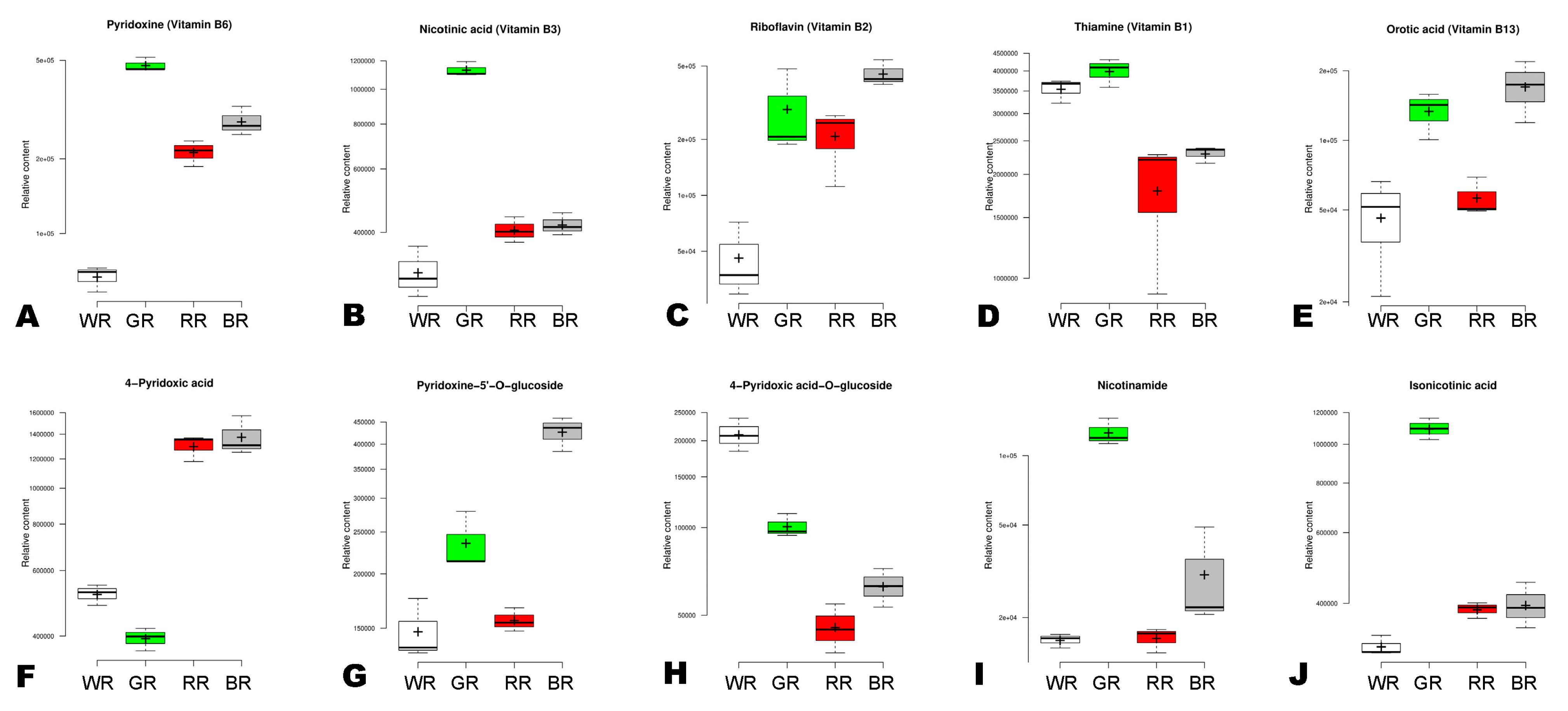
3.5. Distribution and Variation of Vitamins in the Different Colored Rice Grains
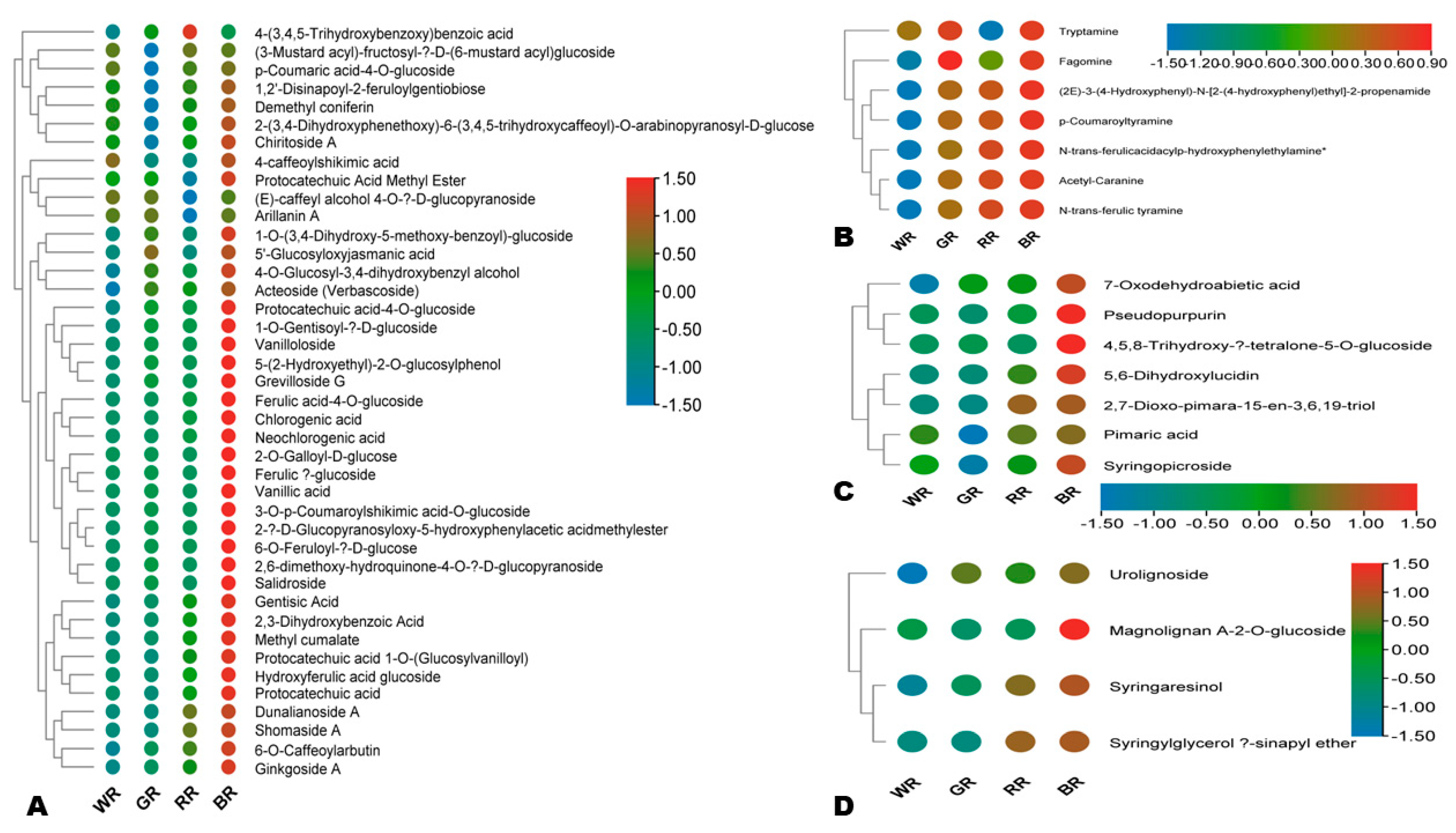
3.6. Key Secondary Metabolites in Green Rice
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Charalampopoulos, D.; Wang, R.; Pandiella, S.; Webb, C. Application of Cereals and Cereal Components in Functional Foods: A Review. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2002, 79, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nayak, S.N.; Aravind, B.; Malavalli, S.S.; Sukanth, B.S.; Poornima, R.; Bharati, P.; Hefferon, K.; Kole, C.; Puppala, N. Omics Technologies to Enhance Plant Based Functional Foods: An Overview. Front. Genet. 2021, 12, 742095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahidi, F.; Danielski, R.; Rhein, S.O.; Meisel, L.A.; Fuentes, J.; Speisky, H.; Schwember, A.R.; de Camargo, A.C. Wheat and Rice beyond Phenolic Acids: Genetics, Identification Database, Antioxidant Properties, and Potential Health Effects. Plants 2022, 11, 3283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sudan, J.; Urwat, U.; Farooq, A.; Pakhtoon, M.M.; Zaffar, A.; Naik, Z.A.; Batool, A.; Bashir, S.; Mansoor, M.; Sofi, P.A.; et al. Explicating Genetic Architecture Governing Nutritional Quality in Pigmented Rice. PeerJ 2023, 11, e15901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rathna Priya, T.S.; Eliazer Nelson, A.R.L.; Ravichandran, K.; Antony, U. Nutritional and Functional Properties of Coloured Rice Varieties of South India: A Review. J. Ethn. Foods 2019, 6, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melini, V.; Panfili, G.; Fratianni, A.; Acquistucci, R. Bioactive Compounds in Rice on Italian Market: Pigmented Varieties as a Source of Carotenoids, Total Phenolic Compounds and Anthocyanins, before and after Cooking. Food Chem. 2019, 277, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, G.F.; Xu, X.R.; Zhang, Y.; Li, D.; Gan, R.Y.; Li, H. Bin Phenolic Compounds and Bioactivities of Pigmented Rice. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2013, 53, 296–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Guo, S.; Li, Y.; Yin, H.; Tian, L.; Cheng, G.; Li, Y. Red Rice Seed Coat Targeting SPHK2 Ameliorated Alcoholic Liver Disease via Restored Intestinal Barrier and Improved Gut Microbiota in Mice. Nutrients 2023, 15, 4176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kushwaha, U.K.S. Black Rice: Research, History and Development; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; ISBN 9783319301532. [Google Scholar]
- Ou, S.J.L.; Yang, D.; Pranata, H.P.; Tai, E.S.; Liu, M.H. Postprandial Glycemic and Lipidemic Effects of Black Rice Anthocyanin Extract Fortification in Foods of Varying Macronutrient Compositions and Matrices. Npj Sci. Food 2023, 7, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Shen, X.; Zhou, Y.; Zheng, X. Black Rice Anthocyanins Alleviate Hyperlipidemia, Liver Steatosis and Insulin Resistance by Regulating Lipid Metabolism and Gut Microbiota in Obese Mice. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 10160–10170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suwannasom, N.; Thepmalee, C.; Khoothiam, K.; Thephinlap, C. Evaluation of Anti-Hyperglycemia and Complications of Red and Black Thai Jasmine Rice Cultivars in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Rats. Molecules 2022, 27, 8043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Liu, D.; Ji, Y.; Liu, Y.; Xu, L.; Guo, Y. Dietary Supplementation of Black Rice Anthocyanin Extract Regulates Cholesterol Metabolism and Improves Gut Microbiota Dysbiosis in C57BL/6J Mice Fed a High-Fat and Cholesterol Diet. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2020, 64, 1900876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bordiga, M.; Gomez-Alonso, S.; Locatelli, M.; Travaglia, F.; Coïsson, J.D.; Hermosin-Gutierrez, I.; Arlorio, M. Phenolics Characterization and Antioxidant Activity of Six Different Pigmented Oryza sativa L. Cultivars Grown in Piedmont (Italy). Food Res. Int. 2014, 65, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.Q.; Nagao, N.; Itani, T.; Irifune, K. Anti-Oxidative Analysis, and Identification and Quantification of Anthocyanin Pigments in Different Coloured Rice. Food Chem. 2012, 135, 2783–2788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira-Caro, G.; Cros, G.; Yokota, T.; Crozier, A. Phytochemical Profiles of Black, Red, Brown, and White Rice from the Camargue Region of France. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 7976–7986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goufo, P.; Trindade, H. Rice Antioxidants: Phenolic Acids, Flavonoids, Anthocyanins, Proanthocyanidins, Tocopherols, Tocotrienols, c-Oryzanol, and Phytic Acid. Food Sci. Nutr. 2014, 2, 75–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Wu, H.; Zhao, M.; Yang, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Guo, Y.; Lin, Y.; Chen, H. OsMYB3 Is a R2R3-MYB Gene Responsible for Anthocyanin Biosynthesis in Black Rice. Mol. Breed. 2021, 41, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mackon, E.; Jeazet Dongho Epse Mackon, G.C.; Yao, Y.; Guo, Y.; Ma, Y.; Dai, X.; Jandan, T.H.; Liu, P. Integrative HPLC Profiling and Transcriptome Analysis Revealed Insights into Anthocyanin Accumulation and Key Genes at Three Developmental Stages of Black Rice (Oryza Sativa. L) Caryopsis. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1211326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mackon, E.; Jeazet Dongho Epse Mackon, G.C.; Ma, Y.; Kashif, M.H.; Ali, N.; Usman, B.; Liu, P. Recent Insights into Anthocyanin Pigmentation, Synthesis, Trafficking, and Regulatory Mechanisms in Rice (Oryza Sativa L.) Caryopsis. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.; Peng, S.; Nie, L. Active Compounds: A New Direction for Rice Value Addition. Food Chem. X 2023, 19, 100781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, T.; Sun, Y.; Lin, J.; Wang, J.; Zhang, X.; Yan, T.; Jia, Y. Chemical Constituents and Mechanisms from Hemerocallis Citrina Baroni with Anti-Neuroinflammatory Activity. J. Funct. Foods 2023, 102, 105427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Gu, C.; He, S.; Zhu, D.; Huang, Y.; Zhou, Q. Widely Targeted Metabolomics Analysis Reveals New Biomarkers and Mechanistic Insights on Chestnut (Castanea mollissima Bl.) Calcification Process. Food Res. Int. 2021, 141, 110128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Gong, L.; Guo, Z.; Wang, W.; Zhang, H.; Liu, X.; Yu, S.; Xiong, L.; Luoa, J. A Novel Integrated Method for Large-Scale Detection, Identification, and Quantification of Widely Targeted Metabolites: Application in the Study of Rice Metabolomics. Mol. Plant 2013, 6, 1769–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dossou, S.S.K.; Xu, F.; You, J.; Zhou, R.; Li, D.; Wang, L. Widely Targeted Metabolome Profiling of Different Colored Sesame (Sesamum indicum L.) Seeds Provides New Insight into Their Antioxidant Activities. Food Res. Int. 2022, 151, 110850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Cui, D.; Ma, X.; Han, B.; Han, L. Comparative Analysis of Rice Reveals Insights into the Mechanism of Colored Rice via Widely Targeted Metabolomics. Food Chem. 2022, 399, 133926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Thomas, H.R.; Frank, M.H.; He, Y.; Xia, R. TBtools: An Integrative Toolkit Developed for Interactive Analyses of Big Biological Data. Mol. Plant 2020, 13, 1194–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.W.; Zhang, R.F.; Zhang, F.X.; Liu, R.H. Phenolic Profiles and Antioxidant Activity of Black Rice Bran of Different Commercially Available Varieties. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 7580–7587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Shao, Y.; Bao, J.; Beta, T. Phenolic Compounds and Antioxidant Properties of Breeding Lines between the White and Black Rice. Food Chem. 2015, 172, 630–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirilertpanich, P.; Ekkaphan, P.; Andriyas, T.; Leksungnoen, N.; Ruengphayak, S.; Vanavichit, A.; De-Eknamkul, W.; Tansawat, R. Metabolomics Study on the Main Volatile Components of Thai Colored Rice Cultivars from Different Agricultural Locations. Food Chem. 2024, 434, 137424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, H.; Pu, X.; Zhu, X.; Yang, X.; Guo, H.; Diao, H.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Sun, X.; Zhang, H.; et al. Genome-Wide Association Study Reveals the Genetic Basis of Total Flavonoid Content in Brown Rice. Genes 2023, 14, 1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Tao, Y.; Ali, A.; Zhuang, Z.; Guo, D.; Guo, Q.; Riaz, A.; Zhang, H.; Xu, P.; Liao, Y.; et al. Transcriptome and Proteome Profiling of Different Colored Rice Reveals Physiological Dynamics Involved in the Flavonoid Pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Han, Q.; Qiao, C.; Song, J.; Cheng, C.L.; Xu, H. Chemical Markers for the Quality Control of Herbal Medicines: An Overview. Chin. Med. 2008, 3, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senadheera, S.P.A.S.; Ekanayake, S.; Wanigatunge, C. Anti-Diabetic Properties of Rice-Based Herbal Porridges in Diabetic Wistar Rats. Phytother. Res. 2014, 28, 1567–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, H.H.; Hwang, I.G.; Lee, Y.M. Effects of Anthocyanin Supplementation on Blood Lipid Levels: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Nutr. 2023, 10, 1207751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, T.; Akshit, F.N.U.; Mohan, M.S. Effects of Anthocyanin Supplementation in Diet on Glycemic and Related Cardiovascular Biomarkers in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Front. Nutr. 2023, 10, 1159–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Limtrakul, P.; Semmarath, W.; Mapoung, S. Anthocyanins and Proanthocyanidins in Natural Pigmented Rice and Their Bioactivities. In Phytochemicals in Human Health; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Ateba, S.B.; Mvondo, M.A.; Ngeu, S.T.; Tchoumtchoua, J.; Awounfack, C.F.; Njamen, D.; Krenn, L. Natural Terpenoids Against Female Breast Cancer: A 5-Year Recent Research. Curr. Med. Chem. 2018, 25, 3162–3213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manayi, A.; Nabavi, S.M.; Daglia, M.; Jafari, S. Natural Terpenoids as a Promising Source for Modulation of GABAergic System and Treatment of Neurological Diseases. Pharmacol. Rep. 2016, 68, 671–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussain, G.; Rasul, A.; Anwar, H.; Aziz, N.; Razzaq, A.; Wei, W.; Ali, M.; Li, J.; Li, X. Role of Plant Derived Alkaloids and Their Mechanism in Neurodegenerative Disorders. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2018, 14, 341–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Liu, J.; Wang, J.; Duan, X.; Hui, S. Key Secondary Metabolite Markers for Wuchang Daohuaxiang Rice Discrimination in China. Food Res. Int. 2023, 169, 112943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Compounds | Class | KEGG ID | Log2FC | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GR_vs_BR | GR_vs_RR | GR_vs_WR | RR_vs_BR | WR_vs_BR | WR_vs_RR | |||
| p-Coumaroyltyramine | Alkaloids | - | 3.06 | 1.10 | −11.95 | 1.96 | 15.01 | 13.05 |
| N-Feruloylserotonin | Alkaloids | - | 1.16 | −1.89 | −3.66 | 3.05 | 4.82 | 1.77 |
| Fagomine | Alkaloids | C10144 | −1.18 | −7.21 | −15.92 | 6.03 | 14.74 | 8.71 |
| (2E)-3-(4-Hydroxyphenyl)-N-[2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)ethyl]-2-propenamide | Alkaloids | - | 3.01 | 1.07 | −11.43 | 1.94 | 14.44 | 12.50 |
| 6,7-dihydroxy-1,3-dimethoxyxanthen-9-one | Flavonoids | - | 9.73 | 3.26 | −1.50 | 6.47 | 11.23 | 4.76 |
| 1,8-dihydroxy-4,5-dimethoxy-3-{[(2s,3r,4s,5s,6r)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxan-2-yl]oxy}xanthen-9-one | Flavonoids | - | 14.62 | 11.16 | 7.78 | 3.46 | 6.84 | 3.38 |
| Tamarixin | Flavonoids | - | 16.06 | 8.73 | 10.03 | 7.33 | 6.04 | −1.30 |
| Eriodictyol | Flavonoids | C05631 | 9.43 | 2.85 | −7.35 | 6.58 | 16.78 | 10.20 |
| 2′,3′,4′,5,7-Pentahydroxyflavone | Flavonoids | - | 11.84 | 3.99 | 1.24 | 7.85 | 10.60 | 2.75 |
| Hesperetin | Flavonoids | C01709 | 9.28 | 2.32 | −7.13 | 6.96 | 16.41 | 9.45 |
| Tricin-7-O-rutinoside | Flavonoids | - | 7.23 | 5.59 | 3.74 | 1.63 | 3.48 | 1.85 |
| Isorhamnetin | Flavonoids | C10084 | 9.91 | 1.75 | −1.68 | 8.16 | 11.59 | 3.43 |
| Homoeriodictyol | Flavonoids | C09756 | 9.40 | 1.98 | −7.66 | 7.42 | 17.06 | 9.64 |
| 2-Hydroxyxanthone | Flavonoids | - | 4.98 | 2.07 | −8.66 | 2.91 | 13.64 | 10.73 |
| Homeriodictyol | Flavonoids | - | 9.40 | 2.02 | −8.08 | 7.37 | 17.48 | 10.11 |
| Tamarixetin-3-O-rutinoside | Flavonoids | - | −11.02 | 1.64 | −2.37 | −12.66 | −8.66 | 4.01 |
| Tricin-7-O-neohesperidoside | Flavonoids | - | 7.23 | 5.59 | 3.74 | 1.63 | 3.48 | 1.85 |
| Pinobanksin | Flavonoids | C09826 | 4.20 | 2.55 | −1.83 | 1.64 | 6.02 | 4.38 |
| Jaceosidin | Flavonoids | - | 8.74 | 3.89 | 1.47 | 4.85 | 7.27 | 2.42 |
| Naringenin | Flavonoids | C00509 | 4.91 | 3.01 | −1.33 | 1.91 | 6.24 | 4.34 |
| 2-Isopropylmalic acid | Organic acids | C02504 | 4.01 | 1.85 | −7.47 | 2.16 | 11.48 | 9.32 |
| Capillarisin | Others | C08999 | 10.15 | 2.06 | −7.44 | 8.09 | 17.60 | 9.51 |
| 4-O-Glucosyl-3,4-dihydroxybenzyl alcohol | Phenolic acids | - | 1.92 | −1.55 | −3.37 | 3.48 | 5.29 | 1.81 |
| Syringopicroside | Terpenoids | - | 16.61 | 10.26 | 8.88 | 6.35 | 7.73 | 1.38 |
| Pimaric acid | Terpenoids | C09159 | 16.55 | 14.96 | 13.89 | 1.58 | 2.66 | 1.07 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, M.; Zhai, L.; Tang, Q.; Ren, J.; Zhou, S.; Wang, H.; Yun, Y.; Yang, Q.; Yan, X.; Xing, F.; et al. Comparative Metabolic Profiling of Different Colored Rice Grains Reveals the Distribution of Major Active Compounds and Key Secondary Metabolites in Green Rice. Foods 2024, 13, 1899. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13121899
Zhao M, Zhai L, Tang Q, Ren J, Zhou S, Wang H, Yun Y, Yang Q, Yan X, Xing F, et al. Comparative Metabolic Profiling of Different Colored Rice Grains Reveals the Distribution of Major Active Compounds and Key Secondary Metabolites in Green Rice. Foods. 2024; 13(12):1899. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13121899
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Mingchao, Linan Zhai, Qingjie Tang, Junfang Ren, Shizhen Zhou, Huijian Wang, Yong Yun, Qingwen Yang, Xiaowei Yan, Funeng Xing, and et al. 2024. "Comparative Metabolic Profiling of Different Colored Rice Grains Reveals the Distribution of Major Active Compounds and Key Secondary Metabolites in Green Rice" Foods 13, no. 12: 1899. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13121899
APA StyleZhao, M., Zhai, L., Tang, Q., Ren, J., Zhou, S., Wang, H., Yun, Y., Yang, Q., Yan, X., Xing, F., & Qiao, W. (2024). Comparative Metabolic Profiling of Different Colored Rice Grains Reveals the Distribution of Major Active Compounds and Key Secondary Metabolites in Green Rice. Foods, 13(12), 1899. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13121899







