Fabrication and Stability Improvement of Monoglyceride Oleogel/Polyglycerol Polyricinoleate-Stabilized W/O High Internal Phase Pickering Emulsions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Oleogels and HIPPEs
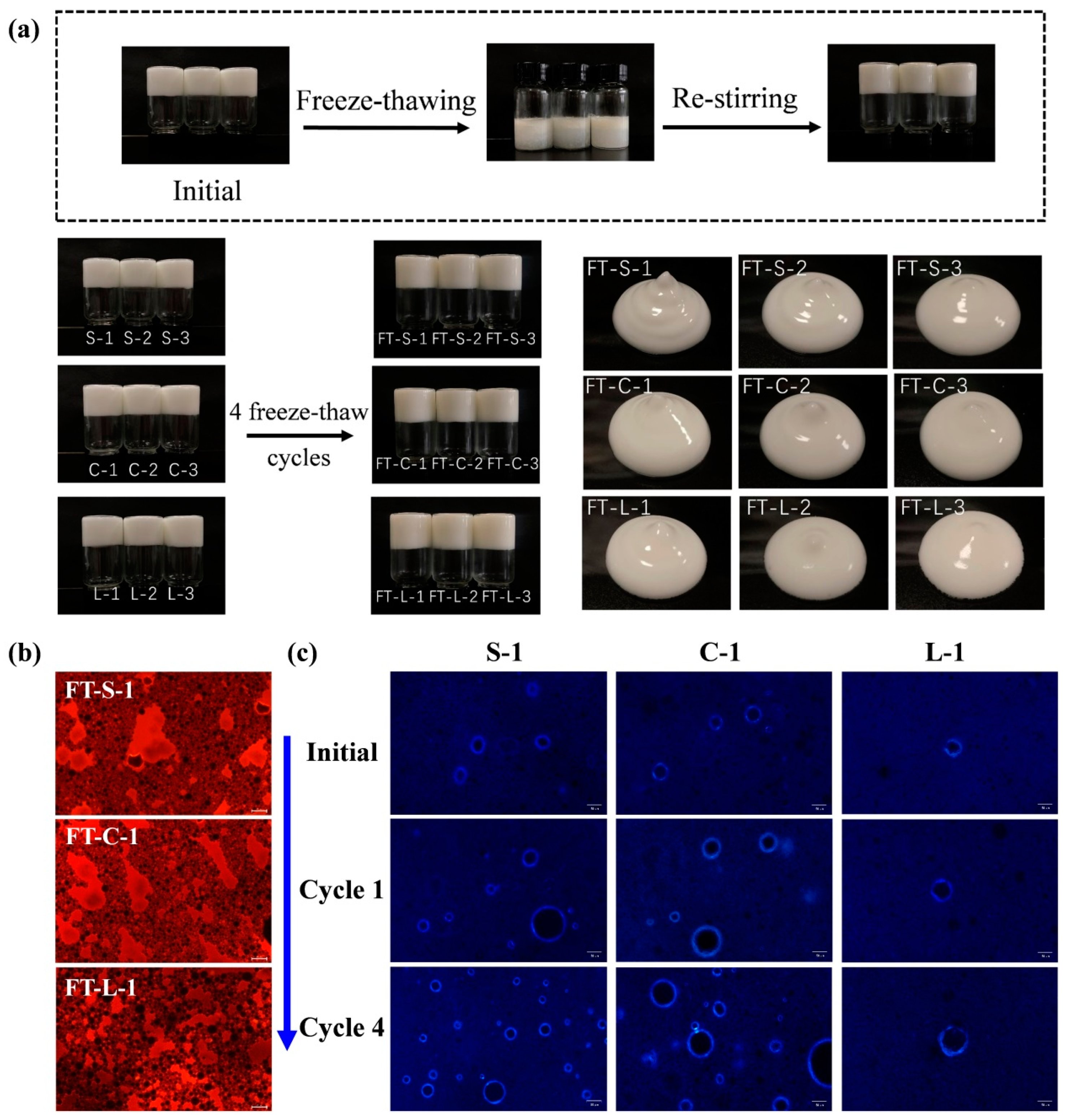
2.3. Freeze–Thaw Treatment
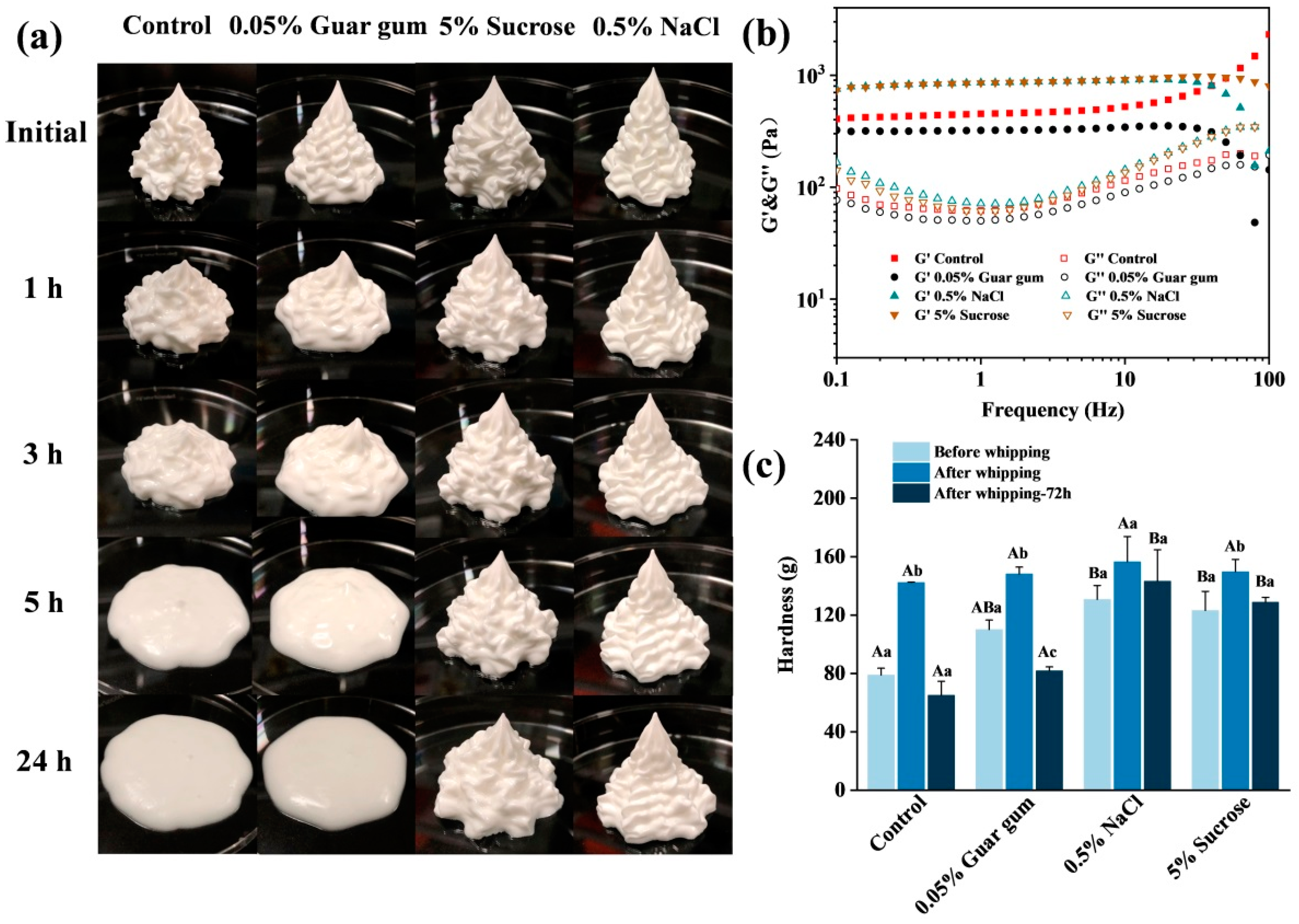
2.4. Whipping Treatment
2.5. Microstructure Observation
2.6. Particle Size Measurement
2.7. Rheological Characterization
2.8. Transverse Relaxation Analysis
2.9. Storage Stability
2.10. Shape Retention Ability of Whipped Samples
2.11. Interfacial Tension
2.12. Water Holding Capacity
2.13. Hardness
2.14. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Effect of MAG-Oleogels and PGPR on the Formation of W/O HIPPEs
3.2. Effect of MAGs and Water Phase Content on the Properties of HIPPEs
3.3. Effect of Freeze–Thaw Treatment on the Structure and Properties of HIPPEs
3.4. Influence of Internal Phase Composition on the Storage Stability and Properties of HIPPEs
3.5. Influence of Whipping Treatment on Texture and Properties of HIPPEs
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cheng, C.; Wu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Chen, J.; Zhong, Y.; Liang, R.; Peng, S.; McClements, D.J.; Liu, W. Tunable high internal phase emulsions (HIPEs) formulated using lactoferrin-gum Arabic complexes. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 113, 106445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, H.; Sun, G.; Lin, W.; Mu, C.; Ngai, T. Gelatin Particle-Stabilized High Internal Phase Emulsions as Nutraceutical Containers. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 13977–13984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tavernier, I.; Wijaya, W.; Van der Meeren, P.; Dewettinck, K.; Patel, A.R. Food-grade particles for emulsion stabilization. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 159–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kargar, M.; Fayazmanesh, K.; Alavi, M.; Spyropoulos, F.; Norton, I.T. Investigation into the potential ability of Pickering emulsions (food-grade particles) to enhance the oxidative stability of oil-in-water emulsions. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2012, 366, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, J.; Li, Y.; Huang, Q. Recent advances on food-grade particles stabilized Pickering emulsions: Fabrication, characterization and research trends. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 55, 48–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, M.; Warren, N.J.; Fielding, L.A.; Armes, S.P.; Verstraete, P.; Smets, J. Preparation of Double Emulsions using Hybrid Polymer/Silica Particles: New Pickering Emulsifiers with Adjustable Surface Wettability. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 20919–20927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, G.; Ge, J.; Jiang, P.; Ding, L. pH- and thermo-responsive Pickering emulsion stabilized by silica nanoparticles and conventional nonionic copolymer surfactants. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 616, 129–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wu, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, B.; Pei, Y.; Liu, S. Effects of the interaction between bacterial cellulose and soy protein isolate on the oil-water interface on the digestion of the Pickering emulsions. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 126, 107480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; McClements, D.J.; Zhou, W.; Peng, S.; Zhou, L.; Zou, L.; Liu, W. Influence of ionic strength and thermal pretreatment on the freeze-thaw stability of Pickering emulsion gels. Food Chem. 2020, 303, 125401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Rousseau, D. Fat crystals and water-in-oil emulsion stability. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 16, 421–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tambe, D.E.; Sharma, M.M. Factors Controlling the Stability of Colloid-Stabilized Emulsions: II. A Model for the Rheological Properties of Colloid-Laden Interfaces. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1994, 162, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.-Y.; Wang, Z.-M.; Yu, D.; Yu, S.-J.; Meng, H.-C.; Zhang, T.; Cheng, H.-L.; Yang, Z.-W.; Yang, Q.-Y.; Li, L. Fabrication of ultrastable water-in-oil high internal phase emulsion as versatile delivery vehicle through synergetic stabilization. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 126, 107455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Qiu, C.; Li, G.; Lee, W.J.; Tan, C.P.; Lai, O.M.; Wang, Y. Effect of diacylglycerol interfacial crystallization on the physical stability of water-in-oil emulsions. Food Chem. 2020, 327, 127014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Lee, W.J.; Tan, C.P.; Lai, O.M.; Wang, Y.; Qiu, C. W/O high internal phase emulsion featuring by interfacial crystallization of diacylglycerol and different internal compositions. Food Chem. 2022, 372, 131305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.C.; Tan, C.; Ravanfar, R.; Abbaspourrad, A. Ultrastable Water-in-Oil High Internal Phase Emulsions Featuring Interfacial and Biphasic Network Stabilization. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 26433–26441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Xu, J.; Tang, C.; Li, Y. Crystallization Behavior and Physical Properties of Monoglycerides-Based Oleogels as Function of Oleogelator Concentration. Foods 2023, 12, 345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Lei, Y.; Wu, Y.; Liang, H.; Li, J.; Pei, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, B.; Luo, X.; Liu, S. Beeswax: A potential self-emulsifying agent for the construction of thermal-sensitive food W/O emulsion. Food Chem. 2021, 349, 129203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Cao, Z.; Zhao, M.; Zhang, H.; Wang, J.; Sun, B. Synergistic influence of protein particles and low-molecular-weight emulsifiers on the stability of a milk fat-based whippable oil-in-water emulsion. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 127, 107520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Zhou, S.; Lu, K.; Zheng, Y.; Qi, B.; Li, Y. Effects of inducer type and concentration on the formation mechanism of W/O/W double emulsion gels. Food Chem. 2022, 379, 132166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chevalier, R.C.; Gomes, A.; Cunha, R.L. Tailoring W/O emulsions for application as inner phase of W/O/W emulsions: Modulation of the aqueous phase composition. J. Food Eng. 2021, 297, 110482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raviadaran, R.; Ng, M.H.; Manickam, S.; Chandran, D. Ultrasound-assisted water-in-palm oil nano-emulsion: Influence of polyglycerol polyricinoleate and NaCl on its stability. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2019, 52, 353–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamane, T. Monoacylglycerols. In Encyclopedia of Bioprocess Technology; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Ojeda-Serna, I.E.; Rocha-Guzmán, N.E.; Gallegos-Infante, J.A.; Cháirez-Ramírez, M.H.; Rosas-Flores, W.; Pérez-Martínez, J.D.; Moreno-Jiménez, M.R.; González-Laredo, R.F. Water-in-oil organogel based emulsions as a tool for increasing bioaccessibility and cell permeability of poorly water-soluble nutraceuticals. Food Res. Int. 2019, 120, 415–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santana, R.C.; Perrechil, F.A.; Cunha, R.L. High- and Low-Energy Emulsifications for Food Applications: A Focus on Process Parameters. Food Eng. Rev. 2013, 5, 107–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Huang, Q. Improving the Oral Bioavailability of Curcumin Using Novel Organogel-Based Nanoemulsions. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 5373–5379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.; Wang, Y.; Li, D.; Wang, L.-J. Freeze-thaw stability and rheological properties of soy protein isolate emulsion gels induced by NaCl. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 123, 107113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Thielen, I.; Berton-Carabin, C.C.; van der Linden, E.; Sagis, L.M.C. Nonlinear interfacial rheology and atomic force microscopy of air-water interfaces stabilized by whey protein beads and their constituents. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 101, 105466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, F.; Koehler, K.; Schuchmann, H.P. Stabilization of Water Droplets in Oil with PGPR for Use in Oral and Dermal Applications. J. Food Process Eng. 2013, 36, 276–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Márquez, A.L.; Medrano, A.; Panizzolo, L.A.; Wagner, J.R. Effect of calcium salts and surfactant concentration on the stability of water-in-oil (W/O) emulsions prepared with polyglycerol polyricinoleate. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2010, 341, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blijdenstein, T.B.J.; Zoet, F.D.; van Vliet, T.; van der Linden, E.; van Aken, G.A. Dextran-induced depletion flocculation in oil-in-water emulsions in the presence of sucrose. Food Hydrocoll. 2004, 18, 857–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatry, M.-C.; Qiu, Y.; Lapeyre, V.; Garrigue, P.; Schmitt, V.; Ravaine, V. Sugar-responsive Pickering emulsions mediated by switching hydrophobicity in microgels. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 561, 481–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickinson, E.; Matia Merino, L. Effect of sugars on the rheological properties of acid caseinate-stabilized emulsion gels. Food Hydrocoll. 2002, 16, 321–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maskan, M.; Göğüş, F. Effect of sugar on the rheological properties of sunflower oil–water emulsions. J. Food Eng. 2000, 43, 173–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, L.-H.; Wu, C.-L.; Luo, S.-Z.; Luo, J.-P.; Zheng, Z.; Jiang, S.-T.; Zhao, Y.-Y.; Zhong, X.-Y. Preparation and characteristics of sucrose-resistant emulsions and their application in soft candies with low sugar and high lutein contents and strong antioxidant activity. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 129, 107619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, S.; Almeida, R.; Batista, L.; Lima, J.; Sarinho, A.; Nascimento, A.; Lisboa, H. Investigation of Guar Gum and Xanthan Gum Influence on Essential Thyme Oil Emulsion Properties and Encapsulation Release Using Modeling Tools. Foods 2024, 13, 816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Formulation Optimization of HIPPEs | Texture Improvement of GMS-Oleogel-Based HIPPEs with 85% Water | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Type of MAG (Oleogelator) | Water Content | Internal Phase Composition | Content |
| GMS | 75%, 80%, 85% | Guar gum | 0.01%, 0.05%, 0.1% |
| GMC | 75%, 80%, 85% | NaCl | 0.5%, 1.0%, 1.5% |
| GML | 75%, 80%, 85% | Sucrose | 5%, 10%, 15% |
| Variants of experimental design | Variants of experimental design | ||
| Microstructure observation, droplet size, rheological characterization, freeze–thaw treatment | Microstructure observation, droplet size, rheological characterization, freeze–thaw treatment | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.; Xu, J.; Gong, J.; Li, Y. Fabrication and Stability Improvement of Monoglyceride Oleogel/Polyglycerol Polyricinoleate-Stabilized W/O High Internal Phase Pickering Emulsions. Foods 2024, 13, 1944. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13121944
Zhang Y, Xu J, Gong J, Li Y. Fabrication and Stability Improvement of Monoglyceride Oleogel/Polyglycerol Polyricinoleate-Stabilized W/O High Internal Phase Pickering Emulsions. Foods. 2024; 13(12):1944. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13121944
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Yingzhu, Jinqi Xu, Jinhua Gong, and Yan Li. 2024. "Fabrication and Stability Improvement of Monoglyceride Oleogel/Polyglycerol Polyricinoleate-Stabilized W/O High Internal Phase Pickering Emulsions" Foods 13, no. 12: 1944. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13121944
APA StyleZhang, Y., Xu, J., Gong, J., & Li, Y. (2024). Fabrication and Stability Improvement of Monoglyceride Oleogel/Polyglycerol Polyricinoleate-Stabilized W/O High Internal Phase Pickering Emulsions. Foods, 13(12), 1944. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13121944






