Effects of Stir-Frying and Heat–Moisture Treatment on the Physicochemical Quality of Glutinous Rice Flour for Making Taopian, a Traditional Chinese Pastry
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Cooked GRF and Taopian
2.2.1. Preparation of Cooked GRF
2.2.2. Preparation of Taopian
2.3. Characterization of the Cooked GRF and Taopian
2.3.1. Color Measurements and Photo Acquisition
2.3.2. Morphology and Particle Size of the Cooked GRF
2.3.3. Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
2.3.4. Structural Characterization of Starch in the Cooked GRF
2.3.5. Moisture Content and Water Activity Measurements of the Cooked GRF
2.3.6. WAI, WSI and OBC Measurements of the Cooked GRF
2.3.7. Pasting Characterization of the Cooked GRF
2.3.8. Low-Field Nuclear Magnetic Resonance of Taopian
2.3.9. Textural Analysis of Taopian
2.3.10. Sensory Evaluation of Taopian
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
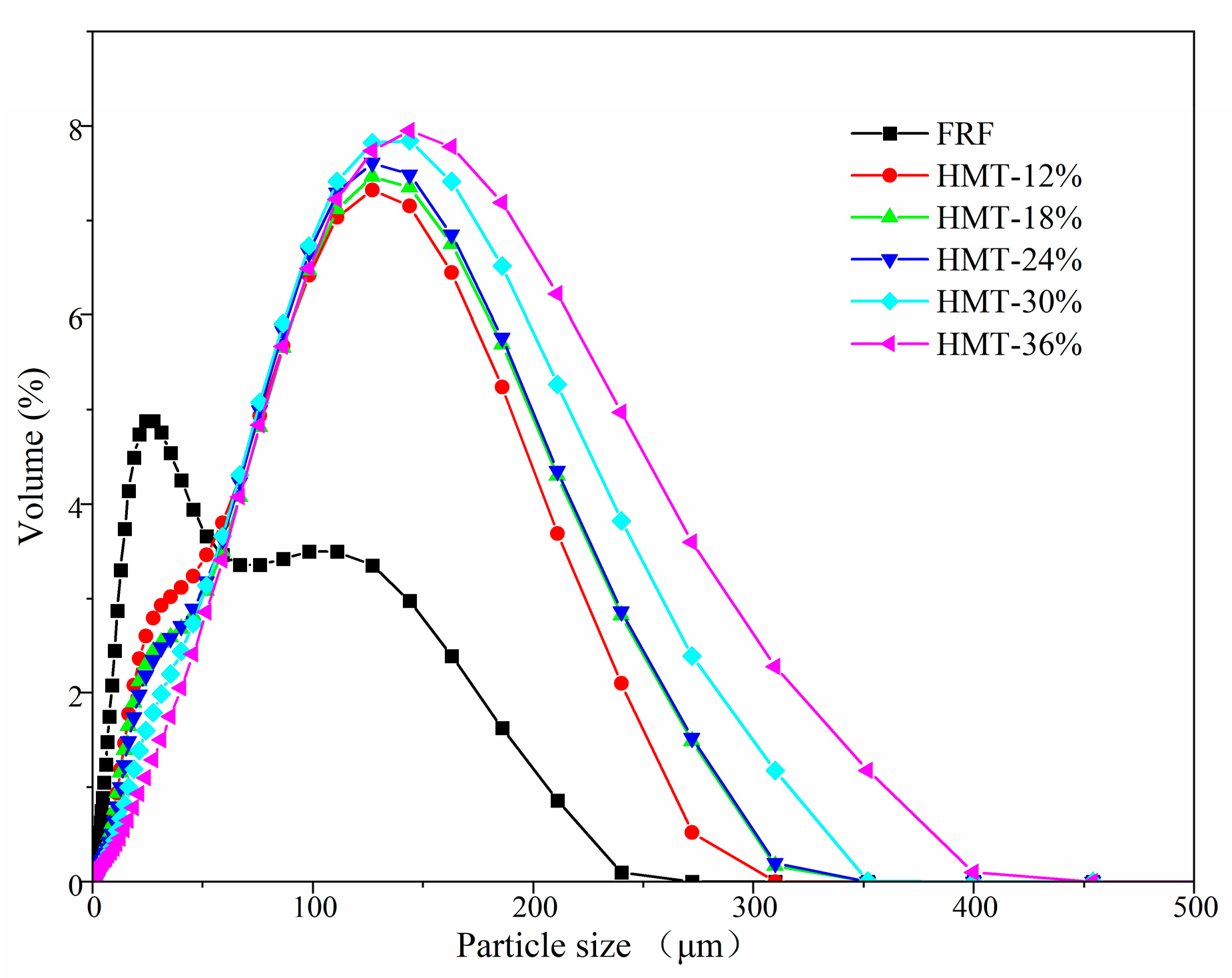
3.1. Color, Morphology and Particle Size of Cooked GRF
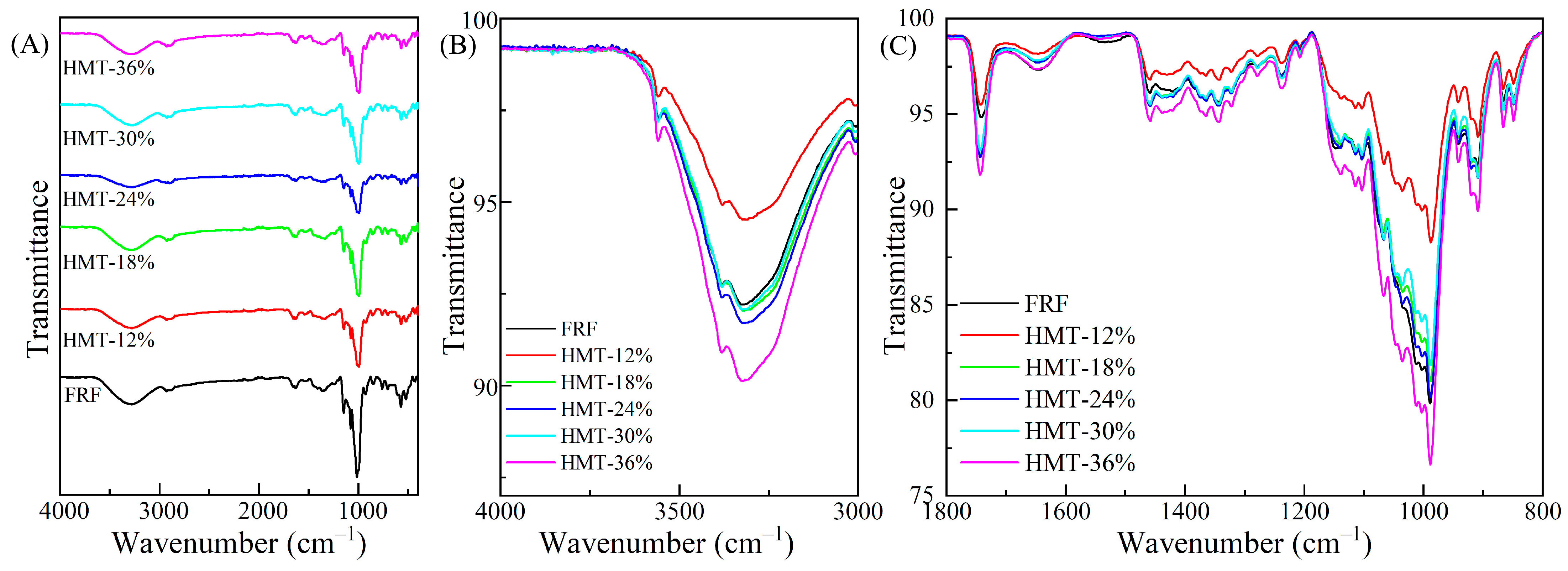
3.2. Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
3.3. Structural Characteristics of Starch in the Cooked GRF
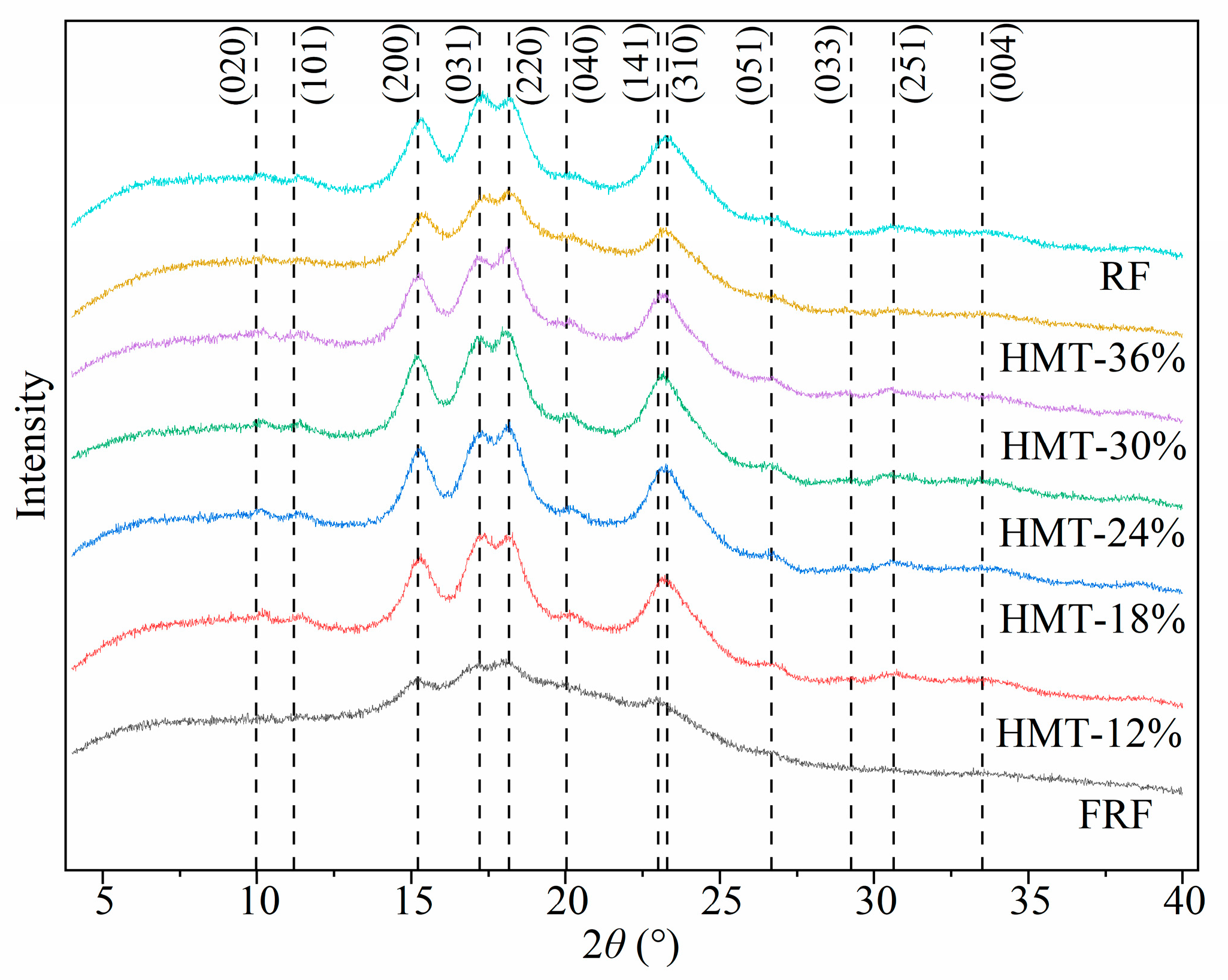
3.3.1. Crystalline Structure of Starch in the Cooked GRF
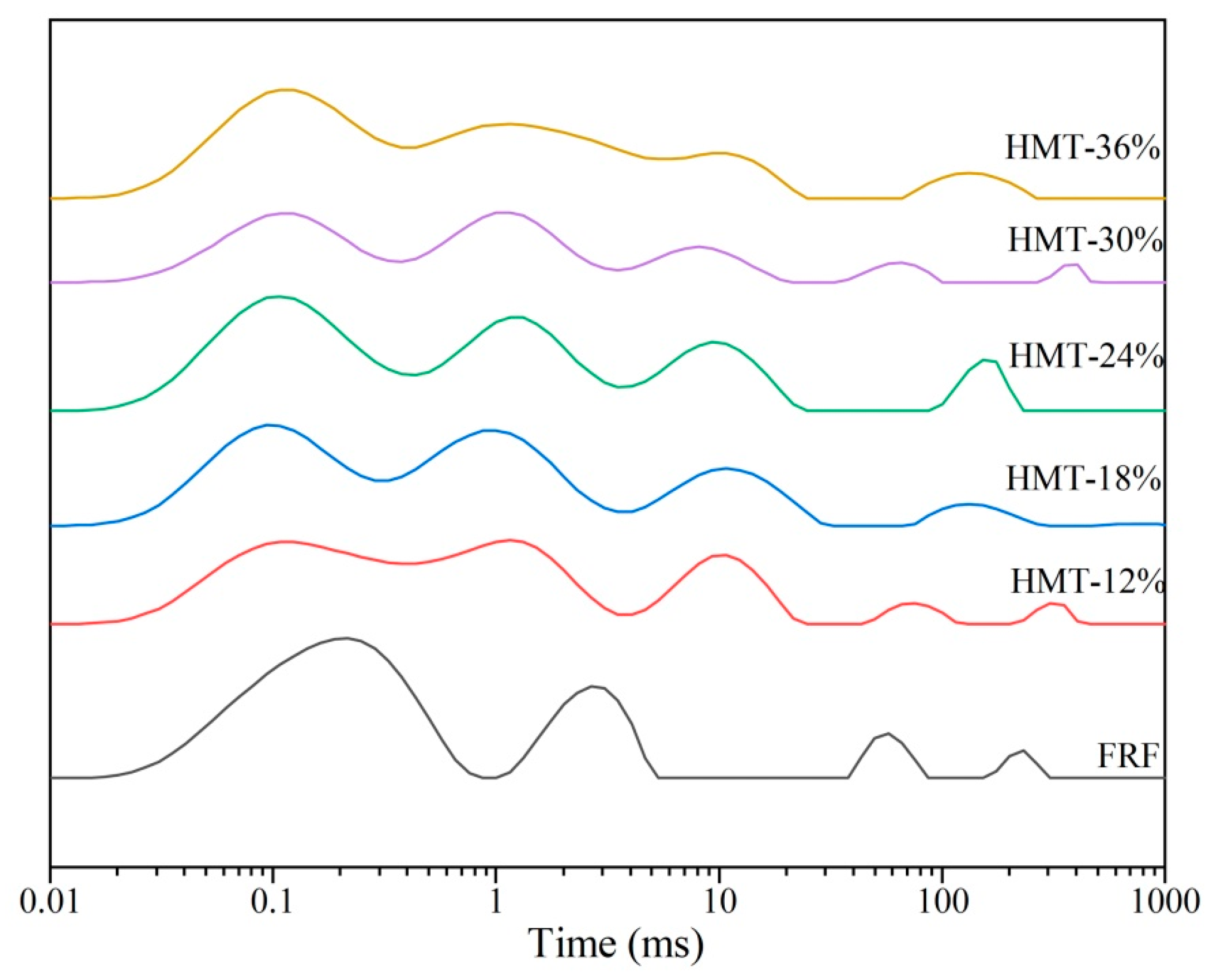
3.3.2. Lamellar Structures of Starch in the Cooked GRF
3.4. Physicochemical Properties of the Cooked GRF
3.4.1. Water Content, Water Activity and Hydration Properties
3.4.2. Oil Binding
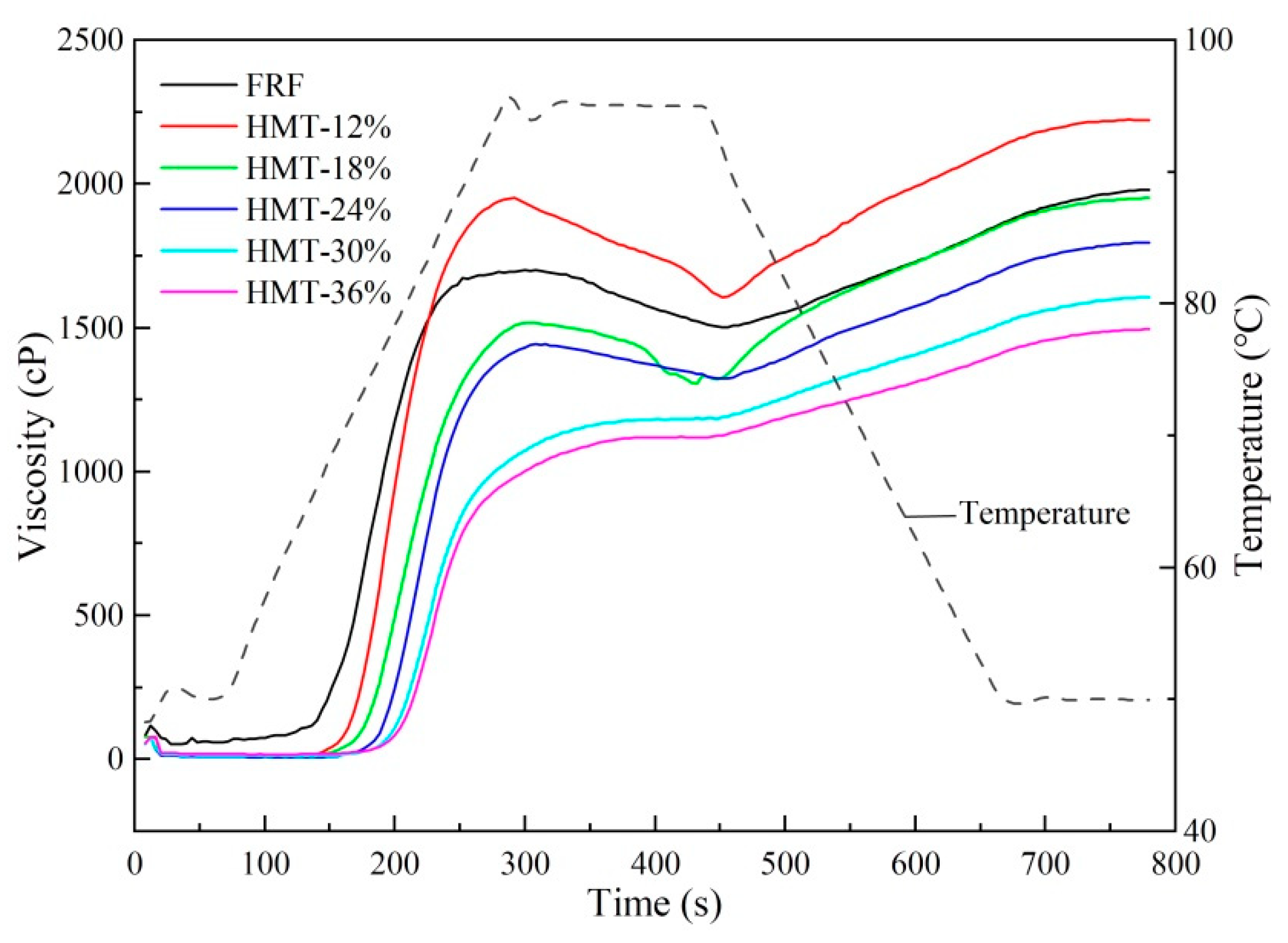
3.4.3. Pasting Properties
3.5. Physicochemical Properties of Taopian
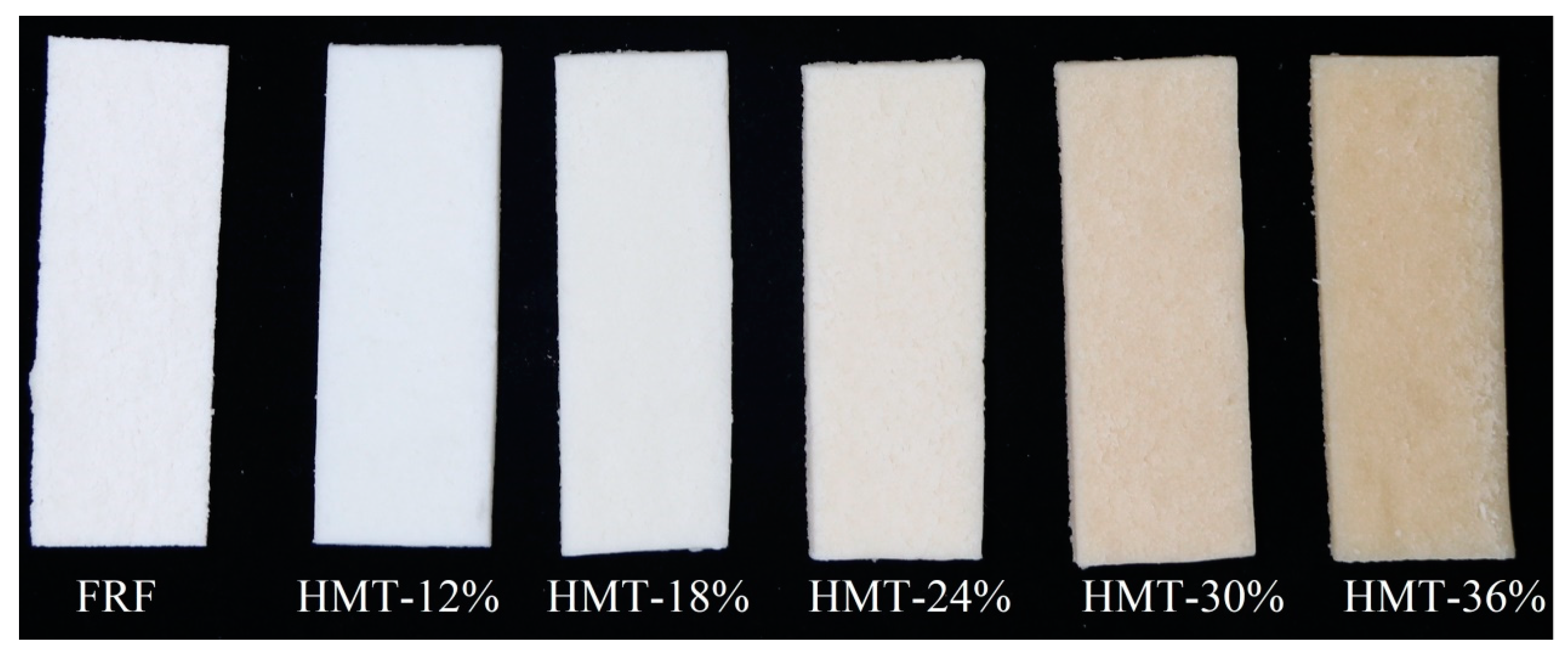
3.5.1. Appearance and Color of Taopian
3.5.2. Water Distribution of Taopian
3.5.3. Textural Properties of Taopian
3.6. Sensory Properties of Taopian
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Evaluation Index | Specific Feature Description |
|---|---|
| Appearance | Normal color, dense and uniform surface structure (7–9) |
| White or slightly yellow, slightly loose structure, no crack (4–6) | |
| Brown or ustulate, loose and rough structure with cracks (1–3) | |
| Aroma | Pleasant scent, a distinct unique smell of cooked glutinous rice flour (7–9) |
| The smell of cooked glutinous rice flour is not obvious (4–6) | |
| Unpleasant odor or off odor (1–3) | |
| Hardness | Appropriate strength when chewing (7–9) |
| Slightly hard or chewy (4–6) | |
| Very soft or al dente (1–3) | |
| Graininess | Almost not grainy (7–9) |
| Slight grainy (4–6) | |
| Too grainy (1–3) | |
| Stickiness | Almost not sticky to teeth when chewing (7–9) |
| Slightly sticky to teeth when chewing (4–6) | |
| Too sticky to teeth when chewing (1–3) | |
| Taste | Pleasant taste (7–9) |
| Good or normal taste (4–6) | |
| Poor taste (1–3) | |
| Overall acceptability | Preferable (7–9) |
| Normal (4–6) | |
| Poor (1–3) |
| RF | FRF | HMT-12% | HMT-18% | ||||||||
| hkl | 2θ (°) | d (Å) | hkl | 2θ (°) | d (Å) | hkl | 2θ (°) | d (Å) | hkl | 2θ (°) | d (Å) |
| (020) | 9.981 | 8.855 | (200) | 15.106 | 5.8600 | (110) | 9.041 | 9.7736 | (020) | 9.981 | 8.855 |
| (101) | 11.194 | 7.8981 | (031) | 17.144 | 5.1677 | (020) | 9.981 | 8.8550 | (101) | 11.194 | 7.8981 |
| (200) | 15.106 | 5.8600 | (211) | 17.959 | 4.9350 | (101) | 11.194 | 7.8981 | (200) | 15.106 | 5.8600 |
| (031) | 17.144 | 5.1677 | (220) | 18.138 | 4.8868 | (200) | 15.106 | 5.8600 | (031) | 17.144 | 5.1677 |
| (220) | 18.138 | 4.8868 | (141) | 23.009 | 3.8621 | (031) | 17.144 | 5.1677 | (220) | 18.138 | 4.8868 |
| (310) | 23.297 | 3.8150 | (132) | 23.684 | 3.7535 | (220) | 18.138 | 4.8868 | (141) | 23.009 | 3.8621 |
| (132) | 23.684 | 3.7535 | (040) | 20.038 | 4.4275 | (312) | 28.726 | 3.1052 | |||
| (033) | 29.251 | 3.0507 | (310) | 23.297 | 3.8150 | (060) | 30.255 | 2.9517 | |||
| (251) | 30.630 | 2.9163 | (242) | 30.303 | 2.9471 | (400) | 30.484 | 2.9300 | |||
| (004) | 33.503 | 2.6725 | (251) | 30.630 | 2.9163 | (440) | 36.752 | 2.4434 | |||
| (271) | 39.676 | 2.2698 | (233) | 33.077 | 2.7059 | (262) | 38.029 | 2.3642 | |||
| (224) | 38.357 | 2.3448 | (510) | 38.718 | 2.3237 | ||||||
| HMT-24% | HMT-30% | HMT-36% | |||||||||
| hkl | 2θ (°) | d (Å) | hkl | 2θ (°) | d (Å) | hkl | 2θ (°) | d (Å) | |||
| (020) | 9.981 | 8.855 | (011) | 9.656 | 9.152 | (020) | 9.981 | 8.8550 | |||
| (101) | 11.194 | 7.8981 | (020) | 9.981 | 8.855 | (101) | 11.194 | 7.8981 | |||
| (200) | 15.106 | 5.8600 | (101) | 11.194 | 7.8981 | (031) | 17.144 | 5.1677 | |||
| (031) | 17.144 | 5.1677 | (200) | 15.106 | 5.8600 | (220) | 18.138 | 4.8868 | |||
| (220) | 18.138 | 4.8868 | (031) | 17.144 | 5.1677 | (040) | 20.038 | 4.4275 | |||
| (040) | 20.038 | 4.4275 | (220) | 18.138 | 4.8868 | (141) | 23.009 | 3.8621 | |||
| (141) | 23.009 | 3.8621 | (040) | 20.038 | 4.4275 | (132) | 23.684 | 3.7535 | |||
| (051) | 26.488 | 3.3622 | (141) | 23.009 | 3.8621 | (051) | 26.488 | 3.3622 | |||
| (242) | 30.303 | 2.9471 | (051) | 26.488 | 3.3622 | (033) | 29.251 | 3.0507 | |||
| (251) | 30.63 | 2.9163 | (033) | 29.251 | 3.0507 | (251) | 30.63 | 2.9163 | |||
| (161) | 32.353 | 2.7649 | (400) | 30.484 | 2.9300 | (152) | 31.214 | 2.8631 | |||
| (004) | 33.503 | 2.6725 | (411) | 32.048 | 2.7905 | (004) | 33.503 | 2.6725 | |||
| (303) | 34.025 | 2.6327 | (422) | 36.380 | 2.4675 | (253) | 38.977 | 2.3089 | |||
| (224) | 38.357 | 2.3448 | (352) | 38.175 | 2.3555 | ||||||
| (510) | 38.718 | 2.3237 | |||||||||
References
- Honda, Y.; Saito, Y.; Katsumi, N.; Nishikawa, M.; Takagi, H. Physicochemical properties of starch in rice flour with different hardening rates of glutinous rice cake (Mochi). J. Cereal Sci. 2023, 112, 103687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, H.C.; Cho, H.; Hong, J.J.; Ryu, R.K.; Hwang, K.T.; Regenstein, J.M. Physicochemical and organoleptic characteristics of seasoned beef patties with added glutinous rice flour. Meat Sci. 2012, 92, 464–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Zhang, W.; Zhou, G. Effects of glutinous rice flour on the physiochemical and sensory qualities of ground pork patties. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 58, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wu, F.; Xu, D.; Xu, X. Effects of milling methods on the properties of glutinous rice flour and sweet dumplings. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 58, 1848–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wu, F.; Xu, D.; Xu, X. Endogenous alpha-amylase explains the different pasting and rheological properties of wet and dry milled glutinous rice flour. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 113, 106425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Ding, G.; Yokoyama, W.; Zhong, F. Characteristics of annealed glutinous rice flour and its formation of fast-frozen dumplings. J. Cereal Sci. 2018, 79, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Qin, W.; Geng, D.; Liu, L.; Zhou, S.; Huang, J.; Tong, L. Quality control mechanism of glutinous rice flour during dynamic change of water in the process of semi-dry method. J. Chin. Inst. Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 21, 208–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, S.; Yang, X.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhang, H.; Wang, H. Effect of germination on nutritional properties and quality attributes of glutinous rice flour and dumplings. J. Food Compo. Anal. 2022, 108, 104440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Li, L.; Zheng, X. Recent advances in heat-moisture modified cereal starch: Structure, functionality and its applications in starchy food systems. Food Chem. 2021, 344, 128700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurinami, S.; Sugimoto, M. Effect of heat-moisture treatment of glutinous rice on promotion of hardness of mochi-kiji. J. Appl. Glycosci. 2007, 54, 23–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thuengtung, S.; Ketnawa, S.; Ding, Y.; Ogawa, Y. Effect of heat-moisture treatment to raw paddy rice (Oryza sativa L.) on cooked rice properties. J. Future Foods 2021, 1, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Gujral, H.S. Effect of sand roasting and microwave cooking on antioxidant activity of barley. Food Res. Int. 2011, 44, 235–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Audible|Hechuan Taopian|Ichongqing. Available online: https://www.ichongqing.info/culture/cultural-heritage/audible-hechuan-taopian/ (accessed on 4 June 2024).
- Li, Z.; Wu, Z.; Mo, G.; Xing, X.; Liu, P. A small-angle X-ray scattering station at Beijing Synchrotron Radiation Facility. Instrum. Sci. Technol. 2014, 42, 128–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, F.; Li, Z.; Li, Z.; Li, D.; Gao, Y.; Wang, B. Absolute intensity calibration and application at BSRF SAXS Station. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. A Accel. Spectrom. Detect. Assoc. Equip. 2018, 900, 64–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.-H. A program for SAXS data processing and analysis. Chin. Phys. C 2013, 37, 108002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB 5009.3-2016; National Food Safety Standard—Determination of Moisture in Food. National Health and Family Planning Commission of the PRC: Beijing, China, 2016. Available online: http://down.foodmate.net/standard/sort/3/49325.html (accessed on 4 June 2024).
- GB 5009.238-2016; National Food Safety Standard—Determination of Water Activity in Food. National Health and Family Planning Commission of the PRC: Beijing, China, 2016. Available online: http://down.foodmate.net/standard/sort/3/49405.html (accessed on 4 June 2024).
- Wang, G.; Yan, X.; Wang, B.; Hu, X.; Chen, X.; Ding, W. Effects of milling methods on the properties of rice flour and steamed rice cakes. LWT 2022, 167, 113848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, G.; Ni, P.; Lam, E.; Hrapovic, S.; Bing, D.; Yu, B.; Ai, Y. Exploring the functional attributes and in vitro starch and protein digestibility of pea flours having a wide range of amylose content. Food Chem. 2023, 405, 134938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Xie, L.; Shen, M.; Xiao, Y.; Yu, Q.; Chen, Y.; Xie, J. Dual modifications on the gelatinization, textural, and morphology properties of pea starch by sodium carbonate and Mesona chinensis polysaccharide. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 102, 105601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, Q.; Wang, X.; Dang, Y.; Zhu, L.; Chen, L.; Wang, X.; Ding, W. Evaluation method of texture of glutinous rice cakes (Niangao) and its key impact indicators. Foods 2024, 13, 621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wichchukit, S.; O’Mahony, M. The 9-point hedonic scale and hedonic ranking in food science: Some reappraisals and alternatives. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2015, 95, 2167–2178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Shi, D.; Chen, J.; Dong, H.; Chen, L. Effects of Chinese chestnut powder on starch digestion, texture properties, and staling characteristics of bread. Grain Oil Sci. Technol. 2023, 6, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokrzycki, W.; Tatol, M. Color difference delta E—A survey. Mach. Graph. Vis. 2012, 20, 383–411. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, H.; Shiraga, K.; Kondo, N.; Chen, S.; Yamashige, Y.; Ogawa, Y. Determining changes in crystallinity of rice starch after heat-moisture treatment using Terahertz Spectroscopy. Food Chem. 2023, 425, 136237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, M.; Bai, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, C. The impact of high hydrostatic pressure treatment time on the structure, gelatinization and thermal properties and in vitro digestibility of oat starch. Grain Oil Sci. Technol. 2022, 5, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Meng, Q.; Zhao, G.; Ye, F. Comparison of milling methods on the properties of common buckwheat flour and the quality of wantuan, a traditional Chinese buckwheat food. Food Chem. X 2023, 19, 100845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernal-Alvarez, L.R.; Martinez-Munoz, P.E.; Castillo-Paz, A.M.; Garcia-Vazquez, H.D.; Millán-Malo, B.M.; Rodriguez-Garcia, M.E. Infrared spectroscopy as a tool to study the vibrational, mechanical, and structural changes in commercial plastic bags: Physical principles. J. Mol. Struct. 2024, 1303, 137580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Gu, Z.; Cheng, L.; Li, Z.; Li, C.; Ban, X.; Hong, Y. Effect of endogenous proteins and heat treatment on the in vitro digestibility and physicochemical properties of corn flour. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 135, 108220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, G.; Li, J.; Lin, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Ding, Y.; Guo, X.; Pan, Q.; Liu, Q.; Fu, X.; Yang, Y.; et al. The effect of heat-moisture treatment changed the binding of starch, protein and lipid in rice flour to affect its hierarchical structure and physicochemical properties. Food Chem. X 2023, 19, 100785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, B.; Liu, W.; Tan, H.; Yu, D.; Song, Z.; Lucia, L.A. Understanding shape and morphology of unusual tubular starch nanocrystals. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 151, 666–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Garcia, M.E.; Hernandez-Landaverde, M.A.; Delgado, J.M.; Ramirez-Gutierrez, C.F.; Ramirez-Cardona, M.; Millan-Malo, B.M.; Londoño-Restrepo, S.M. Crystalline structures of the main components of starch. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2021, 37, 107–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas-Molina, I.; Nieves-Hernandez, M.G.; Gutierrez-Cortez, E.; Barrón-García, O.Y.; Gaytán-Martínez, M.; Rodriguez-Garcia, M.E. Physicochemical changes in starch during the conversion of corn to tortilla in the traditional nixtamalization process associated with RS2. Food Chem. 2024, 439, 138088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, F.; Ma, F.; Kong, F.; Gao, Q.; Yu, S. Physicochemical properties and digestibility of hydrothermally treated waxy rice starch. Food Chem. 2015, 172, 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Y.; Ma, S.; Yan, J.; Sun, B.; Wang, X. Effect of heat-moisture treatment on the physicochemical properties, structure, morphology, and starch digestibility of highland barley (Hordeum vulgare L. Var. nudum Hook. f) flour. Foods 2022, 11, 3511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Liu, Y.; Chen, L.; Li, X.; Wang, J.; Xie, F. Insights into the multi-scale structure and digestibility of heat-moisture treated rice starch. Food Chem. 2018, 242, 323–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Xu, Z.; Liu, X.; Ma, M.; Khalid, S.; Bordiga, M.; Sui, Z.; Corke, H. Removing starch granule-associated surface lipids affects structure of heat-moisture treated hull-less barley starch. Carbohydr. Polym. 2023, 303, 120477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, Y.; Imaizumi, T.; Nishizu, T.; Anandalakshmi, R.; Katsuno, N. Effect of the addition of pregelatinized rice starch paste on the retrogradation of rice starch gel. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 145, 109159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Han, Z.; Wang, L.; Xiong, L. Physicochemical differences between sorghum starch and sorghum flour modified by heat-moisture treatment. Food Chem. 2014, 145, 756–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.R.; Tangsrianugul, N.; Sriprablom, J.; Wongsagonsup, R.; Wansuksri, R.; Suphantharika, M. Effect of heat-moisture treatment on the physicochemical properties and digestibility of proso millet flour and starch. Carbohydr. Polym. 2023, 307, 120630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, W.; Song, J.; Zhang, B.; Zhao, L.; Hu, Z.; Wang, K. The impacts of particle size on starch structural characteristics and oil-binding ability of rice flour subjected to dry heating treatment. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 223, 115053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, P.; Wang, M.; Du, X.; Chen, Z.; Liu, C.; Zhao, H. Morphological and physicochemical properties of rice starch dry heated with whey protein isolate. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 109, 106091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, W.; Lin, Z.; Wang, A.; Chen, Z.; He, Y.; Wang, L.; Liu, L.; Wang, F.; Tong, L.-T. Influence of particle size on the properties of rice flour and quality of gluten-free rice bread. LWT 2021, 151, 112236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Jia, J.; Gao, M.; Liu, Y.; Dou, B.; Zhang, N. Effect of different heat-moisture treatment times on the structure, physicochemical properties and in vitro digestibility of Japonica starch. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 259, 129173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, M.O.; Geirinhas, H.; Duarte, S.; Graça, C.; de Sousa, I. Impact of red flour beetle infestations in wheat flour and their effects on dough and bread physical, chemical, and color properties. J. Stored Prod. Res. 2023, 102, 102095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smarzyński, K.; Sarbak, P.; Kowalczewski, P.Ł.; Różańska, M.B.; Rybicka, I.; Polanowska, K.; Fedko, M.; Kmiecik, D.; Masewicz, Ł.; Nowicki, M.; et al. Low-field NMR study of shortcake biscuits with cricket powder, and their nutritional and physical characteristics. Molecules 2021, 26, 5417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Obadi, M.; Shi, J.; Sun, J.; Chen, Z.; Xu, B. Determination of moisture, total lipid, and bound lipid contents in oats using Low-Field Nuclear Magnetic Resonance. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2020, 87, 103401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Zhang, M.; Chen, H. LF-NMR intelligent evaluation of rheology and printability for 3D printing of cookie dough pretreated by microwave. LWT 2020, 132, 109752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Tu, C.; Rui, X.; Gao, Y.; Li, W.; Wang, K.; Xiao, Y.; Dong, M. Study of water dynamics in the soaking, steaming, and solid-state fermentation of glutinous rice by LF-NMR: A novel monitoring approach. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 3261–3270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.; Wen, Y.; Qiu, C.; Zhan, Q.; Sui, Z.; Corke, H. Milling affects rheological and gel textural properties of rice flour. Cereal Chem. 2020, 97, 205–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
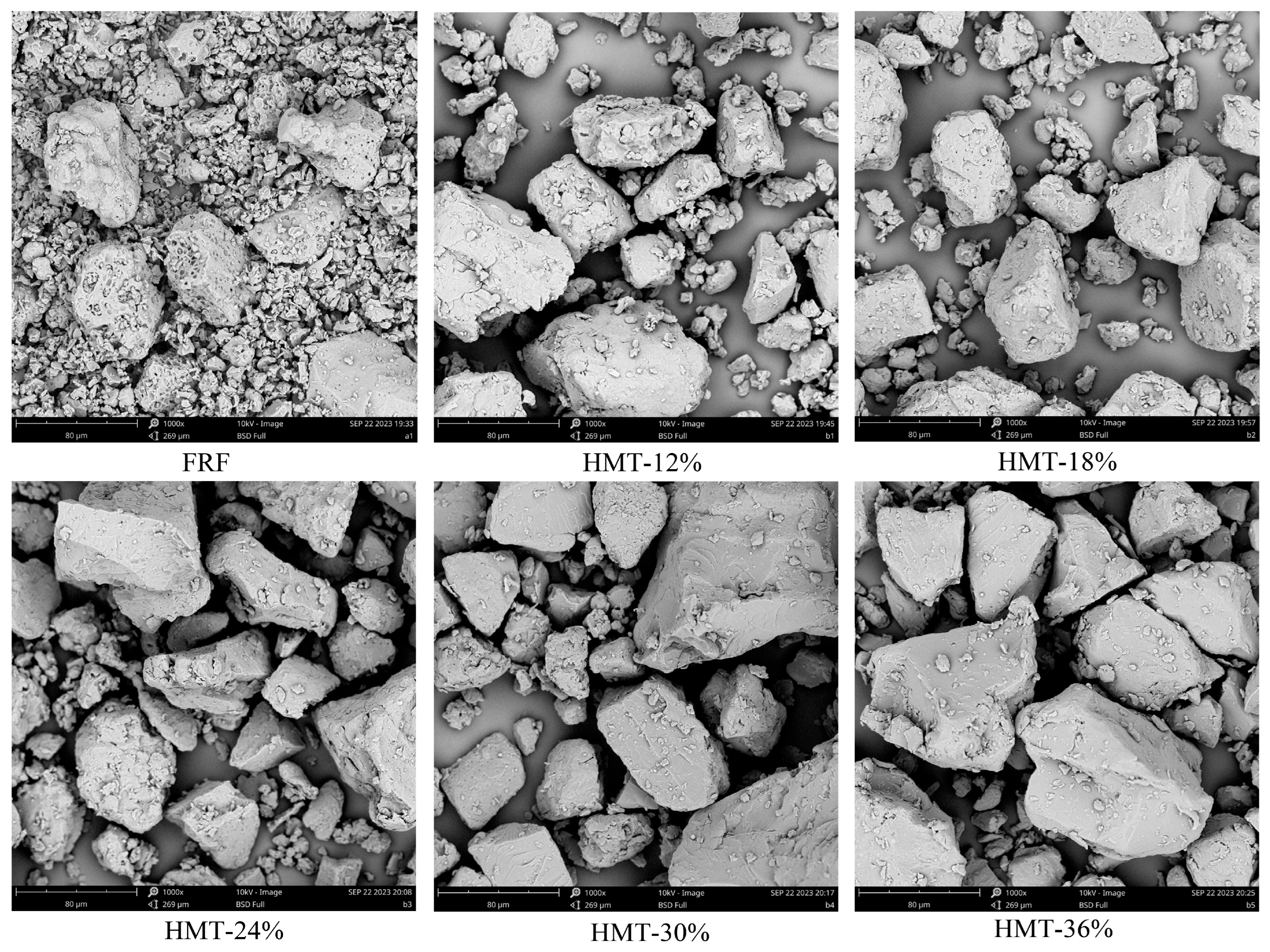
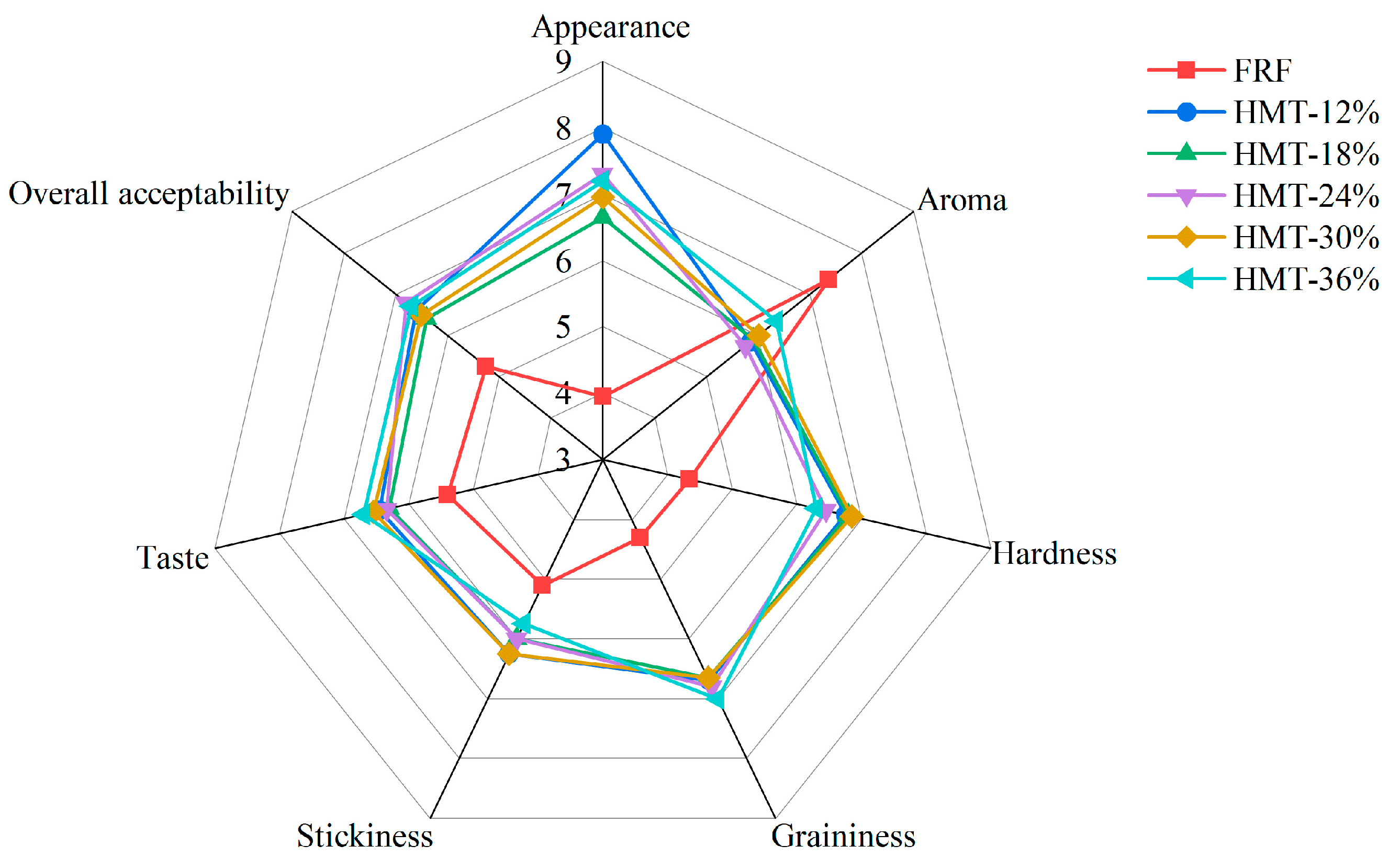
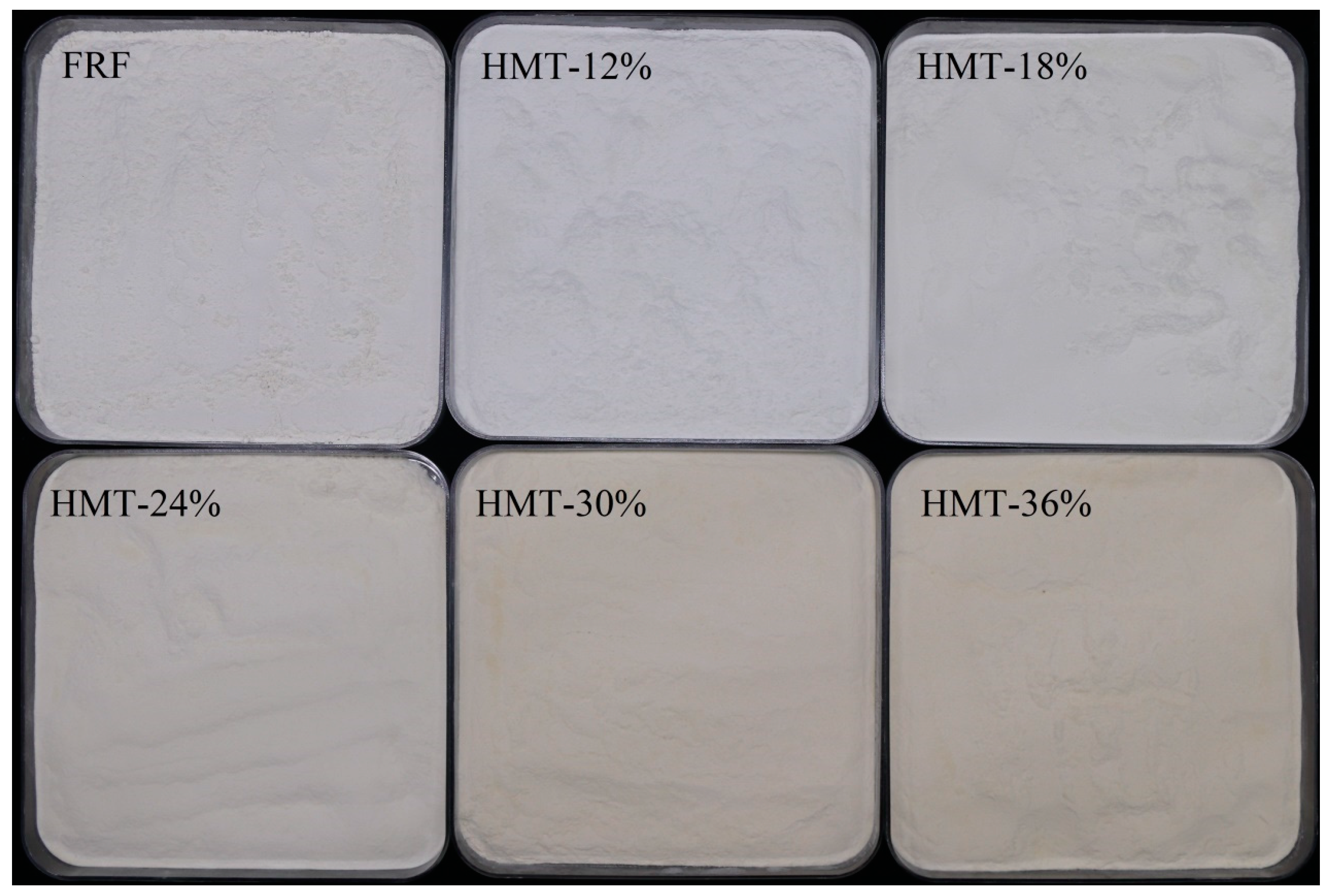



| FRF | HMT-12% | HMT-18% | HMT-24% | HMT-30% | HMT-36% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Color | ||||||
| L* | 96.34 ± 0.14 a | 96.26 ± 0.13 a | 95.52 ± 0.31 b | 95.25 ± 0.08 c | 91.91 ± 0.11 d | 90.99 ± 0.08 e |
| a* | −0.05 ± 0.01 f | 0.33 ± 0.02 e | 0.62 ± 0.02 c | 0.42 ± 0.01 d | 2.16 ± 0.07 b | 2.62 ± 0.04 a |
| b* | 5.37 ± 0.03 e | 7.76 ± 0.19 d | 8.55 ± 0.08 c | 8.35 ± 0.26 c | 12.86 ± 0.23 b | 14.43 ± 0.14 a |
| WI | 93.50 ± 0.10 a | 91.38 ± 0.22 b | 90.32 ± 0.08 c | 90.38 ± 0.26 c | 84.65 ± 0.25 d | 82.79 ± 0.14 e |
| ΔE | — | 2.43 ± 0.21 d | 3.37 ± 0.08 c | 3.21 ± 0.19 c | 8.98 ± 0.34 b | 10.85 ± 0.13 a |
| Particle size | ||||||
| D(10) | 9.02 | 18.9 | 18.8 | 20.8 | 26.7 | 34.7 |
| D(50) | 33.7 | 89.5 | 97.3 | 99.3 | 111 | 124 |
| D(90) | 133 | 193 | 205 | 206 | 225 | 253 |
| Span | 3.68 | 1.95 | 1.91 | 1.87 | 1.79 | 1.76 |
| D[3,4] | 53.7 | 97.8 | 105 | 107 | 119 | 136 |
| D[2,3] | 20.2 | 37.2 | 37.9 | 40.4 | 49.6 | 60.7 |
| FRF | HMT-12% | HMT-18% | HMT-24% | HMT-30% | HMT-36% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RC (%) | 19.92 ± 2.30 d | 42.61 ± 2.94 a | 42.92 ± 3.13 a | 41.22 ± 2.05 a | 36.67 ± 2.92 b | 23.08 ± 2.79 d |
| Rg (nm) | 2.11 ± 0.02 b | 1.86 ± 0.00 e | 1.92 ± 0.02 d | 1.93 ± 0.01 d | 2.00 ± 0.01 c | 2.14 ± 0.00 a |
| Dm | 2.28 ± 0.00 a | 1.86 ± 0.01 c | 1.80 ± 0.01 d | 1.77 ± 0.04 d | 1.84 ± 0.01 c | 2.04 ± 0.00 b |
| dBragg (nm) | 7.17 ± 0.00 c | 7.22 ± 0.00 c | 7.35 ± 0.03 b | 7.33 ± 0.11 b | 7.33 ± 0.06 b | 7.75 ± 0.06 a |
| dc (nm) | 2.54 ± 0.01 b | 2.45 ± 0.00 e | 2.49 ± 0.01 c | 2.48 ± 0.00 d | 2.49 ± 0.00 cd | 2.63 ± 0.00 a |
| da (nm) | 3.01 ± 0.00 f | 3.23 ± 0.00 e | 3.36 ± 0.00 b | 3.29 ± 0.00 d | 3.30 ± 0.00 c | 3.43 ± 0.00 a |
| L (nm) | 5.55 ± 0.01 f | 5.68 ± 0.00 e | 5.85 ± 0.01 b | 5.77 ± 0.00 d | 5.79 ± 0.01 c | 6.06 ± 0.01 a |
| FRF | HMT-12% | HMT-18% | HMT-24% | HMT-30% | HMT-36% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Physical properties | ||||||
| MC | 10.97 ± 0.02 f | 12.79 ± 0.01 a | 12.35 ± 0.02 b | 12.25 ± 0.01 c | 12.00 ± 0.02 d | 11.49 ± 0.04 e |
| Aw | 0.631 ± 0.013 a | 0.627 ± 0.018 a | 0.602 ± 0.006 bc | 0.623 ± 0.017 ab | 0.617 ± 0.002 ab | 0.589 ± 0.004 c |
| WAI (%) | 301.7 ± 28.2 a | 150.2 ± 1.7 c | 148.5 ± 1.0 c | 144.6 ± 2.1 c | 163.1 ± 1.0 c | 185.9 ± 2.2 b |
| WSI (%) | 6.1 ± 0.6 a | 3.6 ± 0.2 b | 3.5 ± 0.1 b | 3.5 ± 0.2 b | 3.5 ± 0.1 b | 1.2 ± 0.5 c |
| OBC (%) | 105.8 ± 2.7 a | 102.2 ± 1.8 ab | 100.2 ± 4.7 ab | 100.4 ± 5.9 ab | 96.9 ± 1.9 b | 88.6 ± 1.1 c |
| Pasting properties | ||||||
| PT (°C) | 60.67 ± 8.77 c | 69.35 ± 0.05 b | 72.03 ± 0.41 ab | 74.78 ± 0.51 ab | 76.95 ± 0.48 a | 77.68 ± 0.45 a |
| PV (cP) | 1706.67 ± 34.36 b | 1953.33 ± 10.60 a | 1519.67 ± 21.96 c | 1444.33 ± 12.34 d | 1186.00 ± 35.76 e | 1126.33 ± 18.82 f |
| TV (cP) | 1502.33 ± 27.43 b | 1607.00 ± 21.93 a | 1297.33 ± 64.04 c | 1322.67 ± 21.01 c | 1168.33 ± 28.57 d | 1101 ± 3.61 e |
| FV (cP) | 1980.67 ± 10.21 b | 2222.33 ± 10.12 a | 1952.00 ± 12.12 b | 1797.00 ± 8.72 c | 1606.33 ± 45.24 d | 1495.33 ± 7.09 e |
| BD (cP) | 204.33 ± 31.56 b | 346.33 ± 16.62 a | 222.33 ± 65.99 b | 121.67 ± 9.29 c | 17.67 ± 7.37 d | 25.33 ± 16.20 d |
| SB (cP) | 478.33 ± 22.37 b | 615.33 ± 29.09 a | 654.67 ± 71.86 a | 474.33 ± 23.86 b | 438.00 ± 16.70 bc | 394.33 ± 10.69 c |
| FRF | HMT-12% | HMT-18% | HMT-24% | HMT-30% | HMT-36% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Color | ||||||
| L* | 88.15 ± 0.56 a | 87.74 ± 0.41 a | 86.68 ± 0.37 b | 84.08 ± 0.34 c | 77.84 ± 0.60 d | 71.89 ± 0.93 e |
| a* | 0.13 ± 0.16 c | −1.13 ± 0.15 e | −0.44 ± 0.16 d | 1.96 ± 0.60 b | 4.35 ± 0.49 a | 4.58 ± 0.48 a |
| b* | 10.68 ± 0.53 e | 9.67 ± 0.67 f | 12.81 ± 0.97 d | 17.44 ± 0.82 c | 21.97 ± 0.51 b | 24.42 ± 0.23 a |
| WI | 84.04 ± 0.70 a | 84.33 ± 0.23 a | 81.50 ± 0.76 b | 76.29 ± 0.58 c | 68.49 ± 0.66 d | 62.48 ± 0.67 e |
| ΔE | — | 1.89 ± 0.50 d | 2.81 ± 1.15 d | 8.14 ± 1.23 c | 15.87 ± 1.05 b | 21.76 ± 1.08 a |
| Textural characteristics | ||||||
| Hardness (g) | 13,139 ± 2557 c | 10,343 ± 1999 d | 15,955 ± 3071 ab | 14,054 ± 2364 bc | 18,133 ± 2893 a | 17,398 ± 1998 a |
| Adhesiveness (g·s) | 24.77 ± 18.32 d | 29.40 ± 9.89 d | 46.71 ± 12.11 bc | 37.38 ± 9.78 cd | 57.14 ± 14.78 b | 86.50 ± 14.37 a |
| Cohesiveness | 0.74 ± 0.05 a | 0.57 ± 0.06 c | 0.67 ± 0.06 b | 0.67 ± 0.05 b | 0.73 ± 0.05 a | 0.71 ± 0.03 ab |
| Chewiness | 6607.8 ± 2224.6 b | 3613.2 ± 1216.0 c | 6832.1 ± 2138.6 ab | 5615.2 ± 1581.1 b | 8444.5 ± 1716.9 a | 8361.6 ± 1466.6 a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xie, Q.; Wu, S.; Lai, S.; Ye, F. Effects of Stir-Frying and Heat–Moisture Treatment on the Physicochemical Quality of Glutinous Rice Flour for Making Taopian, a Traditional Chinese Pastry. Foods 2024, 13, 2069. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13132069
Xie Q, Wu S, Lai S, Ye F. Effects of Stir-Frying and Heat–Moisture Treatment on the Physicochemical Quality of Glutinous Rice Flour for Making Taopian, a Traditional Chinese Pastry. Foods. 2024; 13(13):2069. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13132069
Chicago/Turabian StyleXie, Qiuping, Shanshan Wu, Shiyu Lai, and Fayin Ye. 2024. "Effects of Stir-Frying and Heat–Moisture Treatment on the Physicochemical Quality of Glutinous Rice Flour for Making Taopian, a Traditional Chinese Pastry" Foods 13, no. 13: 2069. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13132069
APA StyleXie, Q., Wu, S., Lai, S., & Ye, F. (2024). Effects of Stir-Frying and Heat–Moisture Treatment on the Physicochemical Quality of Glutinous Rice Flour for Making Taopian, a Traditional Chinese Pastry. Foods, 13(13), 2069. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13132069





