The Assessment of Iodine Concentrations in Colostrum and Breast Milk Using ICP-MS: The Impact of Delivery Type, Thyroid Function and Gestational Diabetes—A Pilot Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Study Group Design and Sample Collection
2.3. Samples Preparation
2.4. Instrumentation and Conditions
2.5. Validation Parameters
2.6. Statistical Approach
3. Results
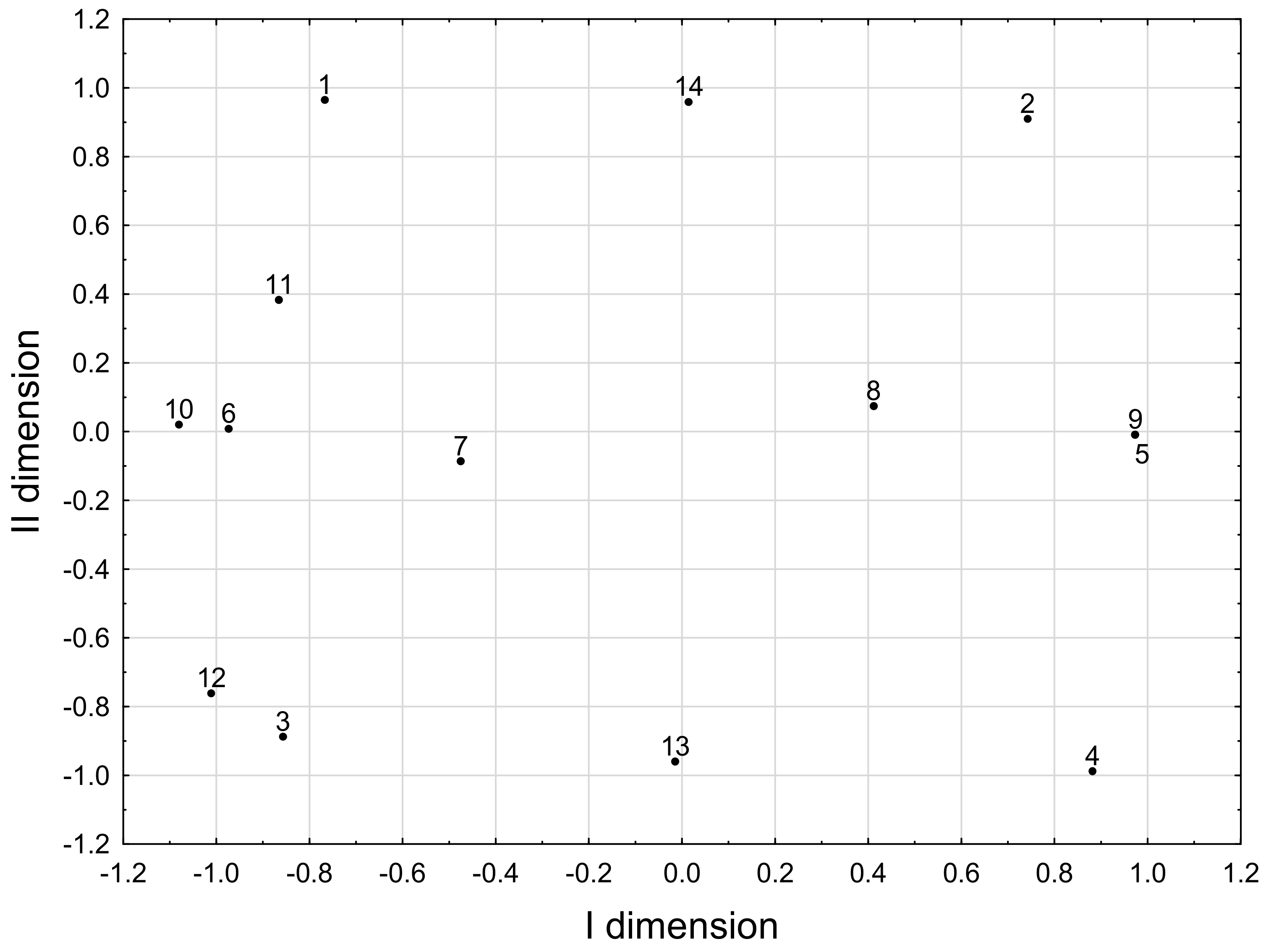
Correspondence Analysis Model
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Choudhry, H.; Nasrullah, M. Iodine Consumption and Cognitive Performance: Confirmation of Adequate Consumption. Food Sci. Nutr. 2018, 6, 1341–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velasco, I.; Bath, S.; Rayman, M. Iodine as Essential Nutrient during the First 1000 Days of Life. Nutrients 2018, 10, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LaFranchi, S.H. Thyroid Function in Preterm/Low Birth Weight Infants: Impact on Diagnosis and Management of Thyroid Dysfunction. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 666207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersson, M.; Braegger, C.P. The Role of Iodine for Thyroid Function in Lactating Women and Infants. Endocr. Rev. 2022, 43, 469–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jarosz, M.; Rychlik, E.; Stoś, K.; Charzewska, J. Normy Żywienia dla Populacji Polski i ich Zastosowanie; Narodowy Instytut Zdrowia Publicznego-Państwowy Zakład Higieny: Warszawa, Poland, 2020; ISBN 978-83-65870-28-5.
- EFSA Panel on Dietetic Products, Nutrition and Allergies (NDA). Scientific Opinion on Dietary Reference Values for Iodine. EFS2 2014, 12, 3660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO Secretariat; Andersson, M.; De Benoist, B.; Delange, F.; Zupan, J. Prevention and Control of Iodine Deficiency in Pregnant and Lactating Women and in Children Less than 2-Years-Old: Conclusions and Recommendations of the Technical Consultation. Public Health Nutr. 2007, 10, 1606–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muro-Valdez, J.C.; Meza-Rios, A.; Aguilar-Uscanga, B.R.; Lopez-Roa, R.I.; Medina-Díaz, E.; Franco-Torres, E.M.; Zepeda-Morales, A.S.M. Breastfeeding-Related Health Benefits in Children and Mothers: Vital Organs Perspective. Medicina 2023, 59, 1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Modak, A.; Ronghe, V.; Gomase, K.P. The Psychological Benefits of Breastfeeding: Fostering Maternal Well-Being and Child Development. Cureus 2023, 15, 46730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Guideline: Protecting, Promoting and Supporting Breastfeeding in Facilities Providing Maternity and Newborn Services; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017; ISBN 978-92-4-155008-6. [Google Scholar]
- Ittermann, T.; Albrecht, D.; Arohonka, P.; Bilek, R.; De Castro, J.J.; Dahl, L.; Filipsson Nystrom, H.; Gaberscek, S.; Garcia-Fuentes, E.; Gheorghiu, M.L.; et al. Standardized Map of Iodine Status in Europe. Thyroid 2020, 30, 1346–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trofimiuk-Müldner, M.; Konopka, J.; Sokołowski, G.; Dubiel, A.; Kieć-Klimczak, M.; Kluczyński, Ł.; Motyka, M.; Rzepka, E.; Walczyk, J.; Sokołowska, M.; et al. Current Iodine Nutrition Status in Poland (2017): Is the Polish Model of Obligatory Iodine Prophylaxis Able to Eliminate Iodine Deficiency in the Population? Public Health Nutr. 2020, 23, 2467–2477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearce, E.N.; Caldwell, K.L. Urinary Iodine, Thyroid Function, and Thyroglobulin as Biomarkers of Iodine Status. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 104 (Suppl. 3), 898S–901S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neville, M.C. Lactation in the Human. Anim. Front. 2023, 13, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.Y.; Yi, D.Y. Components of Human Breast Milk: From Macronutrient to Microbiome and microRNA. Clin. Exp. Pediatr. 2020, 63, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bednarek, A.; Bodys-Cupak, I.; Serwin, A.; Cipora, E. Mothers’ Attitudes Towards Breastfeeding in Terms of Health Safety and Professional Lactation Education: A National Survey of Women. JMDH 2023, 16, 3273–3286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dold, S.; Baumgartner, J.; Zeder, C.; Krzystek, A.; Osei, J.; Haldimann, M.; Zimmermann, M.B.; Andersson, M. Optimization of a New Mass Spectrometry Method for Measurement of Breast Milk Iodine Concentrations and an Assessment of the Effect of Analytic Method and Timing of Within-Feed Sample Collection on Breast Milk Iodine Concentrations. Thyroid 2016, 26, 287–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dror, D.K.; Allen, L.H. Iodine in Human Milk: A Systematic Review. Adv. Nutr. 2018, 9, 347S–357S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ICH Harmonised Guideline. Validation of Analytical Procedures Q2(R2); International Council for Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Pharmaceuticals for Human Use: Geneva, Switzerland, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Nazeri, P.; Dalili, H.; Mehrabi, Y.; Hedayati, M.; Mirmiran, P.; Azizi, F. Breast Milk Iodine Concentration Rather than Maternal Urinary Iodine Is a Reliable Indicator for Monitoring Iodine Status of Breastfed Neonates. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2018, 185, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dold, S.; Zimmermann, M.B.; Aboussad, A.; Cherkaoui, M.; Jia, Q.; Jukic, T.; Kusic, Z.; Quirino, A.; Sang, Z.; San Luis, T.O.; et al. Breast Milk Iodine Concentration Is a More Accurate Biomarker of Iodine Status Than Urinary Iodine Concentration in Exclusively Breastfeeding Women. J. Nutr. 2017, 147, 528–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Sharp, A.; Villanueva, E.; Ma, Z.F. Breast Milk Iodine Concentration (BMIC) as a Biomarker of Iodine Status in Lactating Women and Children <2 Years of Age: A Systematic Review. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ureta-Velasco, N.; Keller, K.; Escuder-Vieco, D.; Serrano, J.C.E.; García-Lara, N.R.; Pallás-Alonso, C.R. Assessment of Iodine Concentration in Human Milk from Donors: Implications for Preterm Infants. Nutrients 2022, 14, 4304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, S.L.; Møller, M.; Laurberg, P. Iodine Concentrations in Milk and in Urine During Breastfeeding Are Differently Affected by Maternal Fluid Intake. Thyroid 2014, 24, 764–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Martínez, S.; Riestra-Fernández, M.; Martínez-Morillo, E.; Avello-Llano, N.; Delgado-Álvarez, E.; Menéndez-Torre, E.L. Nutritional Iodine Status in Pregnant Women from Health Area IV in Asturias (Spain): Iodised Salt Is Enough. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knøsgaard, L.; Andersen, S.; Hansen, A.B.; Sørensen, A.; Vestergaard, P.; Andersen, S.L. Iodine Status in Danish Pregnant Women after an Increase in Iodine Fortification. Clin. Endocrinol. 2023, 98, 407–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimmer, M.; Sieroszewski, P.; Oszukowski, P.; Huras, H.; Fuchs, T.; Pawłosek, A. Polish Society of Gynecologists and Obstetricians Recommendations on Supplementation in Pregnancy. Ginekol. Pol. 2020, 91, 644–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nazeri, P.; Kabir, A.; Dalili, H.; Mirmiran, P.; Azizi, F. Breast-Milk Iodine Concentrations and Iodine Levels of Infants According to the Iodine Status of the Country of Residence: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Thyroid 2018, 28, 124–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delange, F. Iodine Requirements during Pregnancy, Lactation and the Neonatal Period and Indicators of Optimal Iodine Nutrition. Public Health Nutr. 2007, 10, 1571–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galanty, A.; Grudzińska, M.; Paździora, W.; Służały, P.; Paśko, P. Do Brassica Vegetables Affect Thyroid Function?—A Comprehensive Systematic Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 3988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gosset, M.; Bentayeb, H.; Poulet, C.; Lecuyer, E.; Boutemy, M.; Chiah, A.; Douadi, Y.; Dayen, C. An unusual complication of thoracostomy. Rev. Mal. Respir. 2008, 25, 344–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuse, Y.; Ogawa, H.; Tsukahara, Y.; Fuse, Y.; Ito, Y.; Shishiba, Y.; Irie, M. Iodine Metabolism and Thyroid Function During the Perinatal Period: Maternal-Neonatal Correlation and Effects of Topical Povidone-Iodine Skin Disinfectants. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2023, 201, 2685–2700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smerdely, P.; Lim, A.; Boyages, S.C.; Waite, K.; Wu, D.; Roberts, V.; Leslie, G.; Arnold, J.; John, E.; Eastman, C.J. Topical Iodine-Containing Antiseptics and Neonatal Hypothyroidism in Very-Low-Birthweight Infants. Lancet 1989, 2, 661–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Findik, R.B.; Yilmaz, G.; Celik, H.T.; Yilmaz, F.M.; Hamurcu, U.; Karakaya, J. Effect of Povidone Iodine on Thyroid Functions and Urine Iodine Levels in Caesarean Operations. J. Matern.-Fetal Neonatal Med. 2014, 27, 1020–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kester, M.H.A.; Martinez De Mena, R.; Obregon, M.J.; Marinkovic, D.; Howatson, A.; Visser, T.J.; Hume, R.; Morreale De Escobar, G. Iodothyronine Levels in the Human Developing Brain: Major Regulatory Roles of Iodothyronine Deiodinases in Different Areas. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2004, 89, 3117–3128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moog, N.K.; Entringer, S.; Heim, C.; Wadhwa, P.D.; Kathmann, N.; Buss, C. Influence of Maternal Thyroid Hormones during Gestation on Fetal Brain Development. Neuroscience 2017, 342, 68–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garmendia Madariaga, A.; Santos Palacios, S.; Guillén-Grima, F.; Galofré, J.C. The Incidence and Prevalence of Thyroid Dysfunction in Europe: A Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 99, 923–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Wang, J.; Jiang, P.; Ren, F.; Lei, X.; Guo, H. Alteration of the Colostrum Whey Proteome in Mothers with Gestational Hypothyroidism. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0205987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siro, S.S.; Baumgartner, J.; Schoonen, M.; Ngounda, J.; Malan, L.; Symington, E.A.; Smuts, C.M.; Zandberg, L. Characterization of Genetic Variants in the SLC5A5 Gene and Associations With Breast Milk Iodine Concentration in Lactating Women of African Descent: The NUPED Study. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 692504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Parameter | Analytical Value/Feature |
|---|---|
| Nebuliser gas flow [L/min.] | 0.90 |
| RF power [W] | 1100 |
| Plasma gas flow [L/min.] | 15.0 |
| Cooling gas flow rate [L/min.] | 17 |
| Reaction gas | argon |
| Studied Group (Number of Participants) | Mean ± SD 1 (95%CI) | Median (min.–max.) | LQ-UQ 2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Entire group (n = 28) | 595 * (314; 1130) | 583 (195–2334) | 350–956 |
| Natural childbirth group (n = 14) | 400 ± 139 a (102; 698) | 398 (195–606) | 289–526 |
| Caesarean section group (n = 14) | 942 *a (565; 1571) | 956 (295–2334) | 731–1377 |
| Hypothyroidism group (n = 14) | 503 * (253; 998) | 589 (195–2334) | 295–798 |
| No hypothyroidism group/No use of L-thyroxine (n = 14) | 705 * (400; 1242) | 582 (289–1649) | 435–1230 |
| L-thyroxine in a dose of less than 50 µg/day (n = 5) | 410 (249; 676) | 302 (267–810) | 295–604 |
| L-thyroxine at a dose of 50 to 100 µg/day (n = 6) | 490 * (193; 1240) | 454 (195–2334) | 227–731 |
| L-thyroxine at a dose of more than 150 µg/day (n = 3) | 758 ± 169 (220; 1296) | 798 (573–904) | 573–904 |
| Gestational diabetes mellitus (n = 15) | 618 * (323; 1183) | 593 (227–1649) | 302–1230 |
| No gestational diabetes mellitus (n = 13) | 571 * (297; 1097) | 573 (195–2334) | 397–798 |
| Colostrum collected in the first day (n = 4) | 795 * (301; 2099) | 1140 (195–1649) | 550–1513 |
| Colostrum collected in the second day (n = 8) | 565 ± 183 (143; 987) | 572 (267–810) | 455–695 |
| Colostrum collected in the third day (n = 11) | 534 * (249; 1145) | 397 (227–2334) | 295–1008 |
| Colostrum collected in the fourth day (n = 4) | 618 * (422; 905) | 565 (435–1055) | 480–830 |
| Colostrum (n = 14) | 533 * (270; 1051) | 559 (195–1648) | 289–1008 |
| Milk after 1 month (n = 14) | 559 ± 180 (173; 945) | 568 (170–842) | 485–658 |
| Milk after 2 months (n = 8) | 495 ± 148 (154; 836) | 521 (174–650) | 461–586 |
| Milk after 3 months (n = 8) | 562 ± 139 (241; 883) | 560 (273–751) | 533–645 |
| Younger participants (20–30 years, n = 11) | 383 ± 133 b (90; 676) | 302 (227–606) | 289–526 |
| Older participants (31–42 years, n = 17) | 819 *b (454; 1476) | 810 (195–2334) | 593–1230 |
| Pairs of Correlated Parameters | Correlation Coefficients | |
|---|---|---|
| no hypothyroidism | no L-T4 1 use | 1 |
| hypothyroidism | L-T4 1 at a dose <50 µg/day | 0.999 |
| iodine concentration-Q 2 3 | L-T4 1 at a dose >150 µg/day | 0.988 |
| hypothyroidism | L-T4 1 at a dose 50–100 µg/day | 0.918 |
| hypothyroidism | L-T4 1 at a dose >150 µg/day | 0.794 |
| iodine concentration-Q 2 2 | vaginal delivery | 0.784 |
| iodine concentration-Q 2 1 | vaginal delivery | 0.773 |
| iodine concentration-Q 2 4 | delivery by caesarean section | 0.736 |
| iodine concentration-Q 2 3 | delivery by caesarean section | 0.730 |
| iodine concentration-Q 2 4 | L-T4 1 at a dose 50–100 µg/day | −0.911 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kryczyk-Kozioł, J.; Moniak, P.; Zagrodzki, P.; Lauterbach, R.; Huras, H.; Staśkiewicz, M.; Krośniak, M.; Paśko, P.; Podsiadły, R.; Dobrowolska-Iwanek, J. The Assessment of Iodine Concentrations in Colostrum and Breast Milk Using ICP-MS: The Impact of Delivery Type, Thyroid Function and Gestational Diabetes—A Pilot Study. Foods 2024, 13, 2241. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13142241
Kryczyk-Kozioł J, Moniak P, Zagrodzki P, Lauterbach R, Huras H, Staśkiewicz M, Krośniak M, Paśko P, Podsiadły R, Dobrowolska-Iwanek J. The Assessment of Iodine Concentrations in Colostrum and Breast Milk Using ICP-MS: The Impact of Delivery Type, Thyroid Function and Gestational Diabetes—A Pilot Study. Foods. 2024; 13(14):2241. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13142241
Chicago/Turabian StyleKryczyk-Kozioł, Jadwiga, Paulina Moniak, Paweł Zagrodzki, Ryszard Lauterbach, Hubert Huras, Magdalena Staśkiewicz, Mirosław Krośniak, Paweł Paśko, Robert Podsiadły, and Justyna Dobrowolska-Iwanek. 2024. "The Assessment of Iodine Concentrations in Colostrum and Breast Milk Using ICP-MS: The Impact of Delivery Type, Thyroid Function and Gestational Diabetes—A Pilot Study" Foods 13, no. 14: 2241. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13142241
APA StyleKryczyk-Kozioł, J., Moniak, P., Zagrodzki, P., Lauterbach, R., Huras, H., Staśkiewicz, M., Krośniak, M., Paśko, P., Podsiadły, R., & Dobrowolska-Iwanek, J. (2024). The Assessment of Iodine Concentrations in Colostrum and Breast Milk Using ICP-MS: The Impact of Delivery Type, Thyroid Function and Gestational Diabetes—A Pilot Study. Foods, 13(14), 2241. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13142241






