Effects of Ultrasound-Assisted Soy Lecithin Addition on Rehydration Behavior and Physical Properties of Egg White Protein Powder
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Reagents
2.2. Preparation of Samples
2.3. Analysis of Powder Rehydration
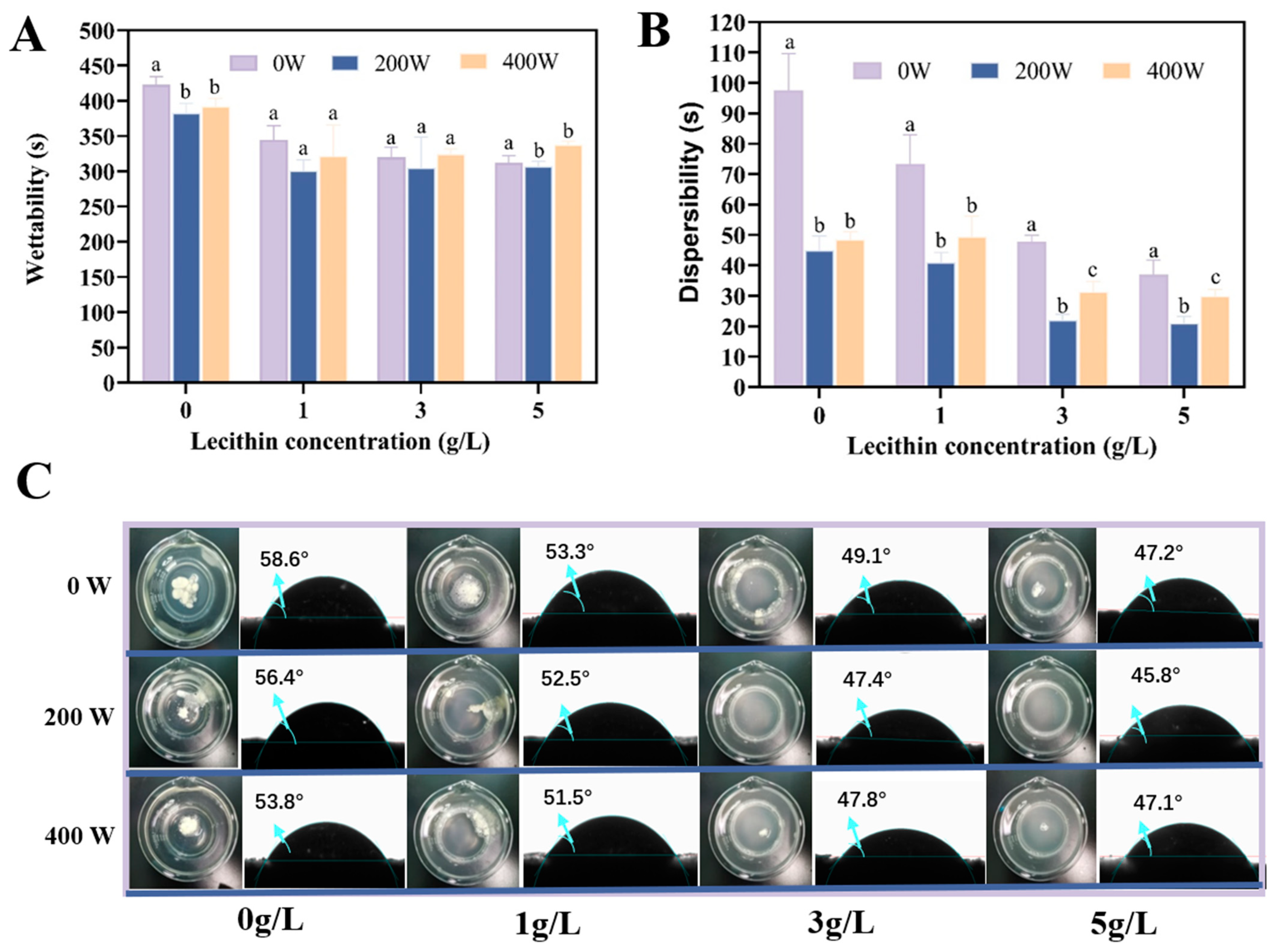
2.3.1. Wettability
2.3.2. Dispersibility
2.3.3. Contact Angle
2.4. Powder Characteristics
2.4.1. Color
2.4.2. Moisture Content
2.4.3. Bulk Density
2.5. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
2.6. Zeta Potential and Particle Size
2.7. Measurement of Free Sulfhydryl (-SH) Group
2.8. Surface Hydrophobicity (H0) Measurement
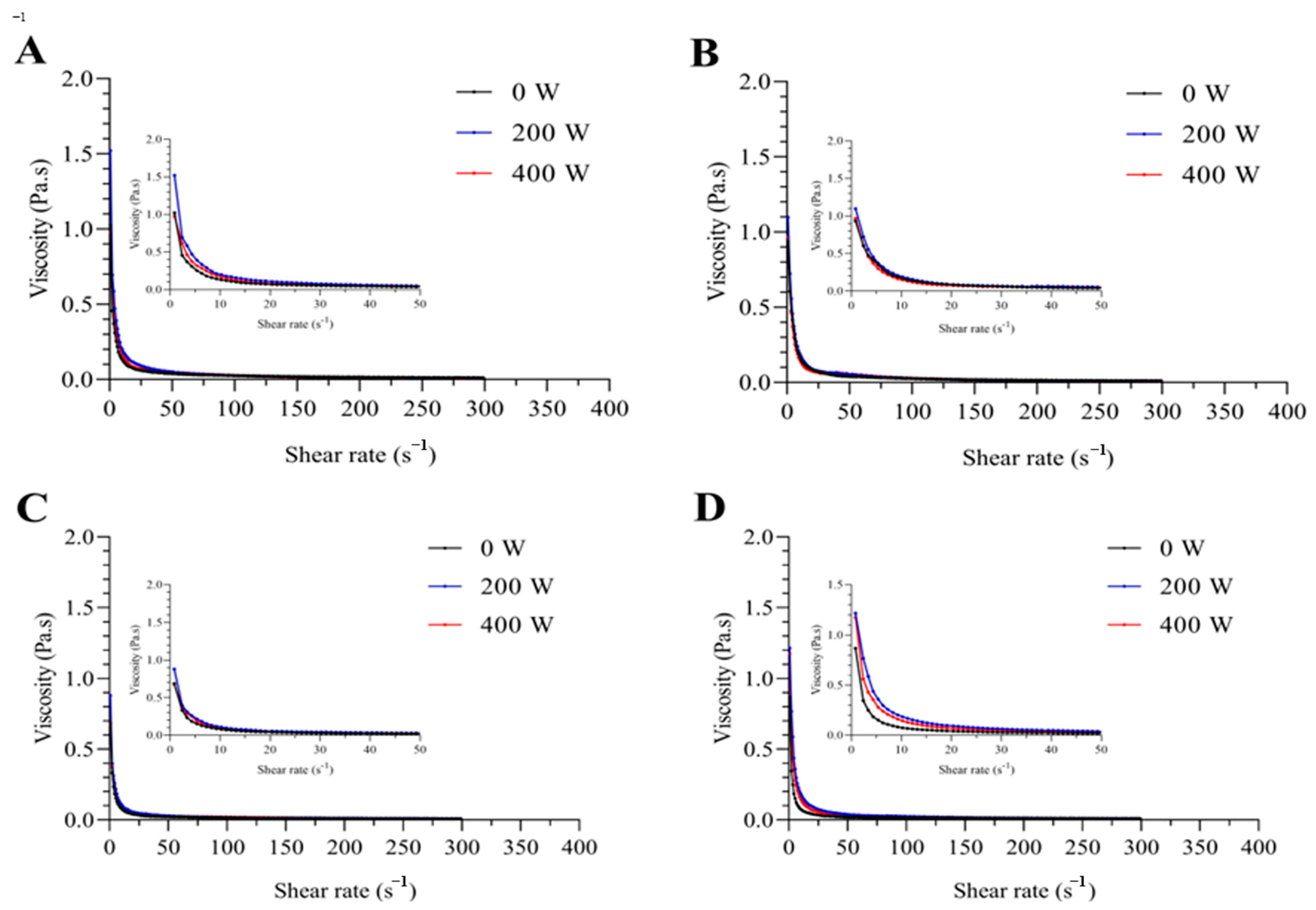
2.9. Apparent Viscosity
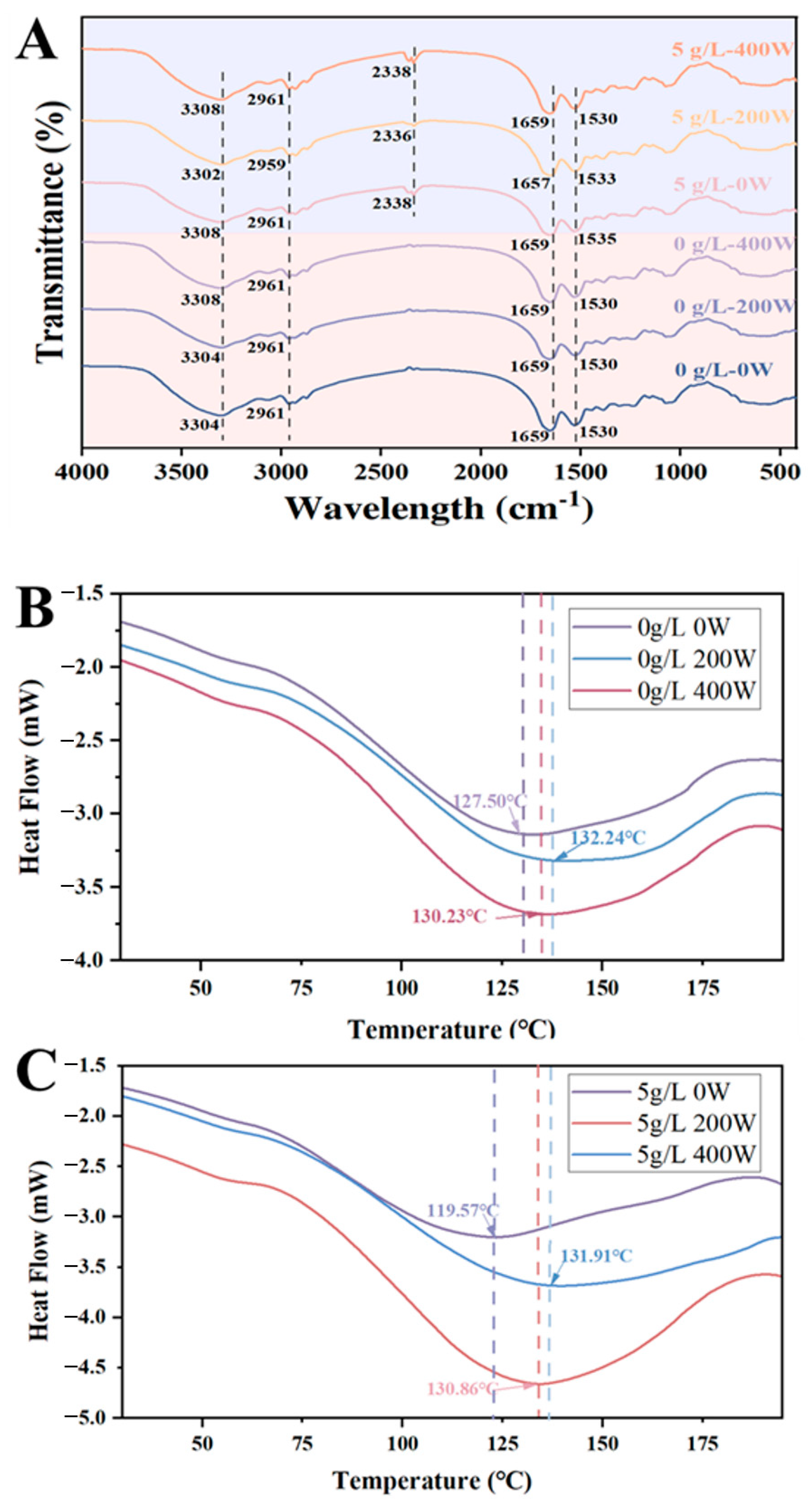
2.10. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FT-IR)
2.11. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Wettability and Dispersibility
3.2. Powder Property Analysis
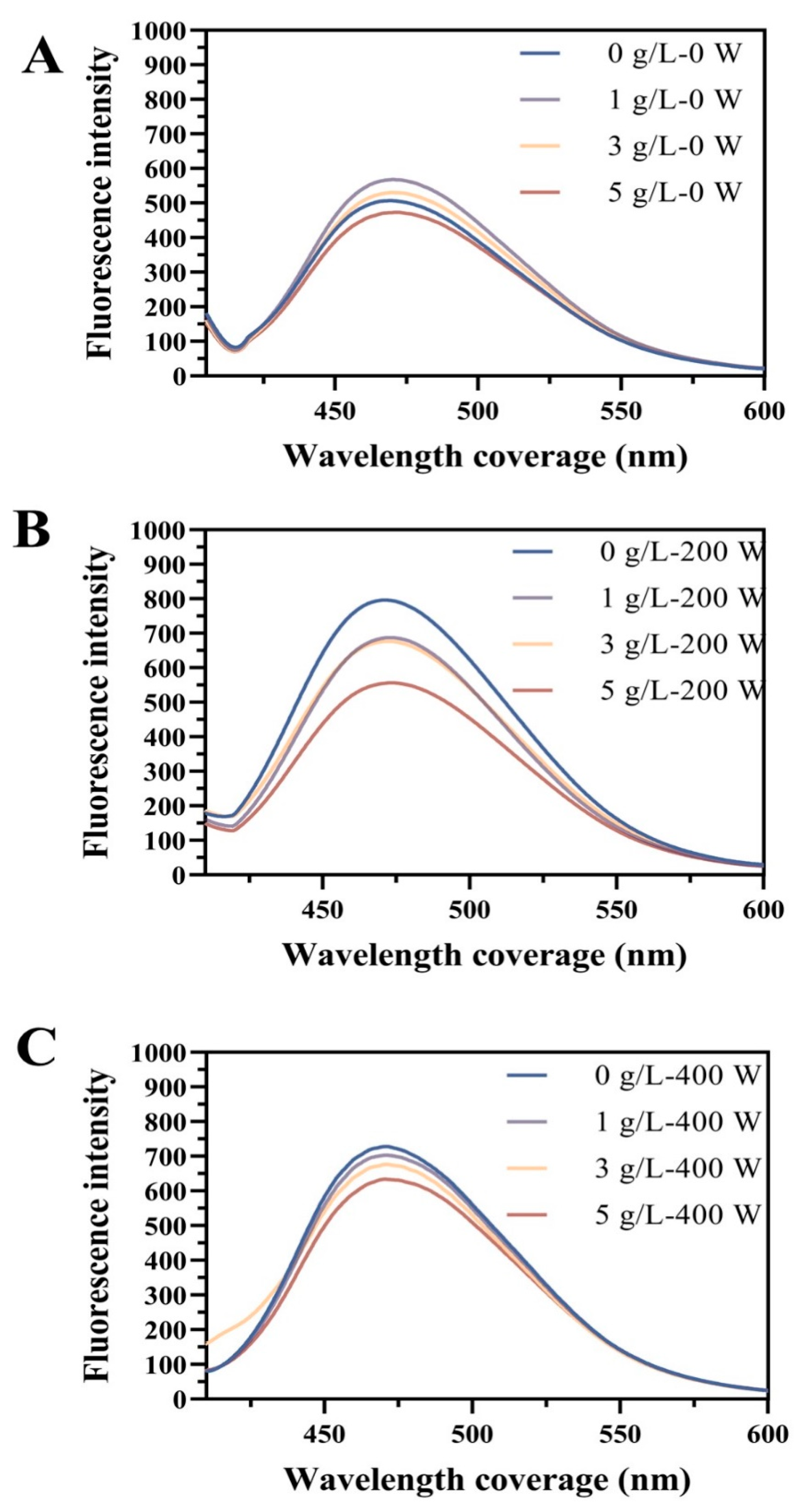
3.3. Particle Size, Zeta Potential and Free Sulfhydryl (-SH) Group Analysis
3.4. Surface Hydrophobicity (H0)
3.5. Apparent Viscosity
3.6. FT-IR and DSC Analysis
3.7. Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM)
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dong, X.; Zhang, Y.-Q. An insight on egg white: From most common functional food to biomaterial application. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B-Appl. Biomater. 2021, 109, 1045–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Jin, Y.; Sheng, L. Impact of microwave assisted phosphorylation on the physicochemistry and rehydration behaviour of egg white powder. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 100, 105380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Huang, C.; Wang, J.; Li, Z.; Xu, Q.; Chen, L.; Feng, X.; Ma, M. Improving rehydration of egg white powder through modifying its physicochemistry properties by ultrasound-assisted glutaminase deamidation. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 133, 107950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, L. Current Progress in the Utilization of Soy-Based Emulsifiers in Food Applications—A Review. Foods 2021, 10, 1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, J.; Cronin, K.; Fitzpatrick, J.; Miao, S. Enhanced wetting behaviours of whey protein isolate powder: The different effects of lecithin addition by fluidised bed agglomeration and coating processes. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 71, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lallbeeharry, P.; Tian, Y.; Fu, N.; Wu, W.; Woo, M.; Selomulya, C.; Chen, X. Effects of ionic and nonionic surfactants on milk shell wettability during co-spray-drying of whole milk particles. J. Dairy Sci. 2014, 97, 5303–5314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, J.; Cronin, K.; Fitzpatrick, J.; Fenelon, M.; Miao, S. Effects of fluid bed agglomeration on the structure modification and reconstitution behaviour of milk protein isolate powders. J. Food Eng. 2015, 167, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Yang, Q.; Yang, M.; Du, Z.; Wei, C.; Zhang, T.; Liu, B.; Liu, J. Ultrasound-assisted Maillard reaction of Ovalbumin/Xylose:the enhancement of functional properties and its mechanism. Ultrason. Sonochemistry 2021, 73, 105477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, W.; Zhang, X.; Chen, W.; Wang, Z.; He, R.; Ma, H. Effects of ultrasonic and graft treatments on grafting degree, structure, functionality, and digestibility of rapeseed protein isolate-dextran conjugates. Ultrason. Sonochemistry 2018, 42, 250–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Fu, N.; Wu, W.; Zhu, D.; Huang, J.; Yun, S.; Chen, X. Effects of Co-spray Drying of Surfactants with High Solids Milk on Milk Powder Wettability. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2014, 7, 3121–3135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Hua, Y.; Kong, X. Effects of limited enzymatic hydrolysis on dispersion properties of soy protein concentrate. Cereals Oils 2008, 6, 20–23. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, T.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Jiang, H.; Yan, Z.; Liu, J.; Liu, X. Effect of soy lecithin concentration on physiochemical properties and rehydration behavior of egg white protein powder: Role of dry and wet mixing. J. Food Eng. 2022, 328, 111062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masum, A.; Huppertz, T.; Chandrapala, J.; Adhikari, B.; Zisu, B. Physicochemical properties of spray-dried model infant milk formula powders: Influence of whey protein-to-casein ratio. Int. Dairy J. 2020, 100, 104565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdem, B.; Kaya, S. Production and application of freeze dried biocomposite coating powders from sunflower oil and soy protein or whey protein isolates. Food Chem. 2021, 339, 127976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapoor, R.; Feng, H. Characterization of physicochemical, packing and microstructural properties of beet, blueberry, carrot and cranberry powders: The effect of drying methods. Powder Technol. 2022, 395, 290–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Jiang, H.; Zhang, M.; Gong, P.; Yang, M.; Zhang, T.; Liu, X. Ions-regulated aggregation kinetics for egg white protein: A promising formulation with controlled gelation and rheological properties. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 200, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Zhang, M.; Gong, P.; Jiang, H.; Liu, J.; Liu, X. Ions-induced ovalbumin foaming properties enhancement: Structural, rheological, and molecular aggregation mechanism. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 124, 107221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimada, K.; Cheftel, J. Determination of sulfhydryl groups and disulfide bonds in heat-induced gels of soy protein isolate. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1988, 36, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, J.; Yan, Z.; Zhang, R.; Du, Z.; Shang, X.; Zhang, T.; Liu, X. Mechanism of ultrasound-induced soybean/egg white composite gelation: Gel properties, morphological structure and co-aggregation kinetics. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 266, 131267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.; Liu, J.; Ren, J.; Li, C.; Wang, Z.; Dai, L.; Cao, S.; Zhang, R.; Liu, X. Magnesium ions regulated ovalbumin-lysozyme heteroprotein complex: Aggregation kinetics, thermodynamics and morphologic structure. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 253, 126487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Li, S.; Yang, M.; Li, Y.; Ma, S.; Zhang, H.; Li, L.; Liu, X.; Liu, J.; Du, Z. The influence of unique interfacial networks based on egg white proteins for the stabilization of high internal phase Pickering emulsions: Physical stability and free fatty acid release kinetics. Food Chem. 2024, 442, 138448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, K.; Xia, Y.; Gao, H.; Chen, W.; Hou, J.; Jiang, Z. Influence of Ultrasonic Power and Ultrasonic Time on the Physicochemical and Functional Properties of Whey Protein Isolate. Int. J. Food Eng. 2019, 15, 20170370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.; Sun, S.; Sun, Z.; Wang, Q.; Jin, Y.; Sheng, L. Ultrasonic-assisted spray drying as a tool for improving the instant properties of egg white powder. Food Struct. 2022, 33, 100289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.; Zhang, M.; Fang, Z.; Liu, Y. Effects of ultrasound and microwave pretreatments on the ultrafiltration desalination of salted duck egg white protein. Food Bioprod. Process. 2015, 96, 306–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thalía Flores-Jiménez, N.; Armando Ulloa, J.; Esmeralda Urías-Silvas, J.; Carmen Ramírez-Ramírez, J.; Ulises Bautista-Rosales, P.; Gutiérrez-Leyva, R. Influence of high-intensity ultrasound on physicochemical and functional properties of a guamuchil Pithecellobium dulce (Roxb.) seed protein isolate. Ultrason. Sonochemistry 2022, 84, 105976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, H.; Lee, Y.; Yoon, W. Effect of Moisture Content on the Grinding Process and Powder Properties in Food: A Review. Processes 2018, 6, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores-Jimenez, N.; Ulloa, J.; Silvas, J.; Ramirez, J.; Ulloa, P.; Rosales, P.; Carrillo, Y.; Leyva, R. Effect of high-intensity ultrasound on the compositional, physicochemical, biochemical, functional and structural properties of canola (Brassica napus L.) protein isolate. Food Res. Int. 2019, 121, 947–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuliana, M.; Truong, C.; Huynh, L.; Ho, Q.; Ju, Y. Isolation and characterization of protein isolated from defatted cashew nut shell: Influence of pH and NaCl on solubility and functional properties. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 55, 621–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jinapong, N.; Suphantharika, M.; Jamnong, P. Production of instant soymilk powders by ultrafiltration, spray drying and fluidized bed agglomeration. J. Food Eng. 2008, 84, 194–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teo, A.; Lam, Y.; Lee, S.; Goh, K. Spray drying of whey protein stabilized nanoemulsions containing different wall materials—Maltodextrin or trehalose. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 136, 110344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Jiang, W.; Chen, G.; Wang, Q.; McClements, D.; Liu, X.; Liu, F.; Ngai, T. Sonochemical effects on formation and emulsifying properties of zein-gum Arabic complexes. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 114, 106557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Wang, C.; Guo, M. Interactions between whey protein or polymerized whey protein and soybean lecithin in model system. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 9680–9692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otzen, D. Protein–surfactant interactions: A tale of many states. Biochim. et Biophys. Acta (BBA) Proteins Proteom. 2011, 1814, 562–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, H.; Zhao, N.; Li, S.; Sun, S.; Dong, X.; Yu, C. Physicochemical and emulsifying properties of mussel water-soluble proteins as affected by lecithin concentration. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 163, 180–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Surh, J.; Decker, E.; McClements, D. Influence of pH and pectin type on properties and stability of sodium-caseinate stabilized oil-in-water emulsions. Food Hydrocoll. 2005, 20, 607–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Jiang, Z.; Du, X.; Zhang, F.; Liu, Y.; Bai, X.; Sun, G. Impact of Surfactants on Nanoemulsions based on Fractionated Coconut Oil: Emulsification Stability and in vitro Digestion. J. Oleo Sci. 2020, 69, 227–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Zhang, W.; Yan, D.; Ma, L.; Ma, H. Solubility and aggregation of soy protein isolate induced by different ionic liquids with the assistance of ultrasound. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 164, 2277–2283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Li, Y.; Guo, S. Association of phosphatidylcholine with soybean 11S globulin. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2014, 23, 1785–1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Chang, C.; Shi, M.; Su, Y.; Gu, L.; Li, J.; Yang, Y. Interactions between lecithin and yolk granule and their influence on the emulsifying properties. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 101, 105510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, F.; He, L.; Ma, X.; Wang, D.; Ding, T.; Ye, X.; Liu, D. Ultrasound enhanced the binding ability of chitinase onto chitin: From an AFM insight. Ultrason. Sonochemistry 2020, 67, 105117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Wang, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, Z.; Liang, J.; Wang, R.; Chen, Y.; Ma, W.; Qi, B.; Zhang, M. Effects of ultrasound on the structure and physical properties of black bean protein isolates. Food Res. Int. 2014, 62, 595–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westphalen, A.; Briggs, J.; Lonergan, S. Influence of muscle type on rheological properties of porcine myofibrillar protein during heat-induced gelation. Meat Sci. 2006, 72, 697–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zisu, B.; Bhaskaracharya, R.; Kentish, S.; Ashokkumar, M. Ultrasonic processing of dairy systems in large scale reactors. Ultrason. Sonochemistry 2010, 17, 1075–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Zhou, R.; Xu, X.; Zhou, G.; Liu, D. Structural modification by high-pressure homogenization for improved functional properties of freeze-dried myofibrillar proteins powder. Food Res. Int. 2017, 100, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Zhang, X.; Tang, S.; Mi, S.; Lu, L.; Zeng, Q.; Xia, M.; Cai, Z. Improved effect of ultrasound-assisted enzymolysis on egg yolk powder: Structural properties, hydration properties and stability characteristics. Food Chem. 2022, 382, 132549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Powder | L* | a* | b* | Moisture Content (%) | ρbluk | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 W | 0 g/L | 105.00 ± 0.26 a | −0.33 ± 0.07 a | 17.61 ± 0.05 a | 2.39 ± 1.47 a | 0.48 ± 0.02 a |
| 1 g/L | 102.27 ± 0.06 b | −1.75 ± 0.09 b | 12.45 ± 0.02 b | 3.69 ± 2.50 b | 0.37 ± 0.02 b | |
| 3 g/L | 102.03 ± 0.12 c | −1.63 ± 0.06 b | 15.65 ± 0.01 c | 3.89 ± 1.03 b | 0.35 ± 0.01 b | |
| 5 g/L | 98.58 ± 0.22 c | −1.46 ± 0.07 c | 14.50 ± 0.01 d | 5.89 ± 2.57 c | 0.32 ± 0.01 c | |
| 200 W | 0 g/L | 101.90 ± 0.10 a | −2.11 ± 0.02 a | 16.82 ± 0.03 a | 2.35 ± 1.20 a | 0.31 ± 0.01 a |
| 1 g/L | 101.67 ± 0.31 a | −1.81 ± 0.08 b | 15.03 ± 0.04 b | 3.15 ± 2.12 a | 0.29 ± 0.01 b | |
| 3 g/L | 100.37 ± 0.15 b | −1.85 ± 0.02 b | 17.24 ± 0.01 c | 4.27 ± 1.84 b | 0.27 ± 0.01 c | |
| 5 g/L | 99.90 ± 0.04 c | −0.94 ± 0.03 c | 13.44 ± 0.03 d | 4.31 ± 0.52 b | 0.27 ± 0.01 c | |
| 400 W | 0 g/L | 101.20 ± 0.10 a | −2.06 ± 0.12 a | 15.16 ± 0.06 a | 2.07 ± 2.21 a | 0.39 ± 0.01 a |
| 1 g/L | 101.20 ± 0.10 a | −1.92 ± 0.03 ab | 14.27 ± 0.02 b | 1.60 ± 1.74 a | 0.37 ± 0.01 b | |
| 3 g/L | 101.47 ± 0.06 b | −1.78 ± 0.09 b | 12.15 ± 0.02 c | 3.35 ± 0.19 a | 0.37 ± 0.01 b | |
| 5 g/L | 99.14 ± 0.12 c | −1.31 ± 0.05 c | 14.32 ± 0.05 b | 2.60 ± 1.75 a | 0.36 ± 0.01 b | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cao, S.; Liu, X.; Zheng, Z.; Yan, Z.; Zhang, T.; Liu, J.; Yu, T. Effects of Ultrasound-Assisted Soy Lecithin Addition on Rehydration Behavior and Physical Properties of Egg White Protein Powder. Foods 2024, 13, 2252. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13142252
Cao S, Liu X, Zheng Z, Yan Z, Zhang T, Liu J, Yu T. Effects of Ultrasound-Assisted Soy Lecithin Addition on Rehydration Behavior and Physical Properties of Egg White Protein Powder. Foods. 2024; 13(14):2252. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13142252
Chicago/Turabian StyleCao, Sijia, Xuanting Liu, Zhiyuan Zheng, Zhaohui Yan, Ting Zhang, Jingbo Liu, and Ting Yu. 2024. "Effects of Ultrasound-Assisted Soy Lecithin Addition on Rehydration Behavior and Physical Properties of Egg White Protein Powder" Foods 13, no. 14: 2252. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13142252
APA StyleCao, S., Liu, X., Zheng, Z., Yan, Z., Zhang, T., Liu, J., & Yu, T. (2024). Effects of Ultrasound-Assisted Soy Lecithin Addition on Rehydration Behavior and Physical Properties of Egg White Protein Powder. Foods, 13(14), 2252. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13142252









