Utilizing Nano-Adsorbents and Electrostatic Field Treatment for Sustainable Refinement of Crude Canola Oil
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Effects of Nanoparticles on Crude Canola Oil Acid Value, Pigment Content, Peroxide Value, and Fatty Acid Composition
2.2. Removal of Al2O3 Nano-Adsorbent from Canola Oil
2.3. Canola Oil Loss
2.4. Reusability of Al2O3 Nano-Adsorbent for Crude Canola Oil Neutralization
2.5. Characterization of Al2O3 Nano-Adsorbent Using Electron Microscopy
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
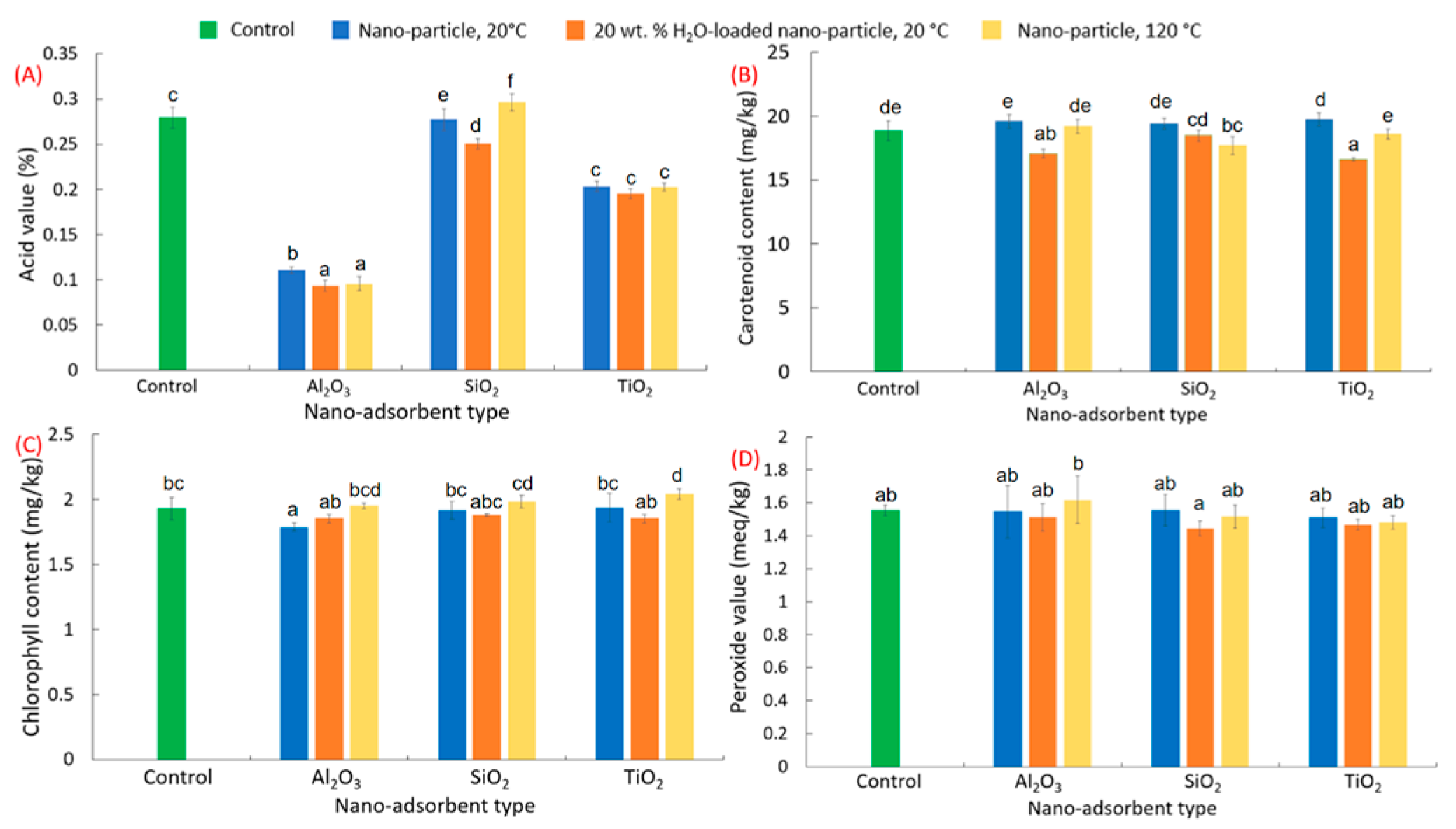
3.1. Nanoparticles in Crude Canola Oil Refining
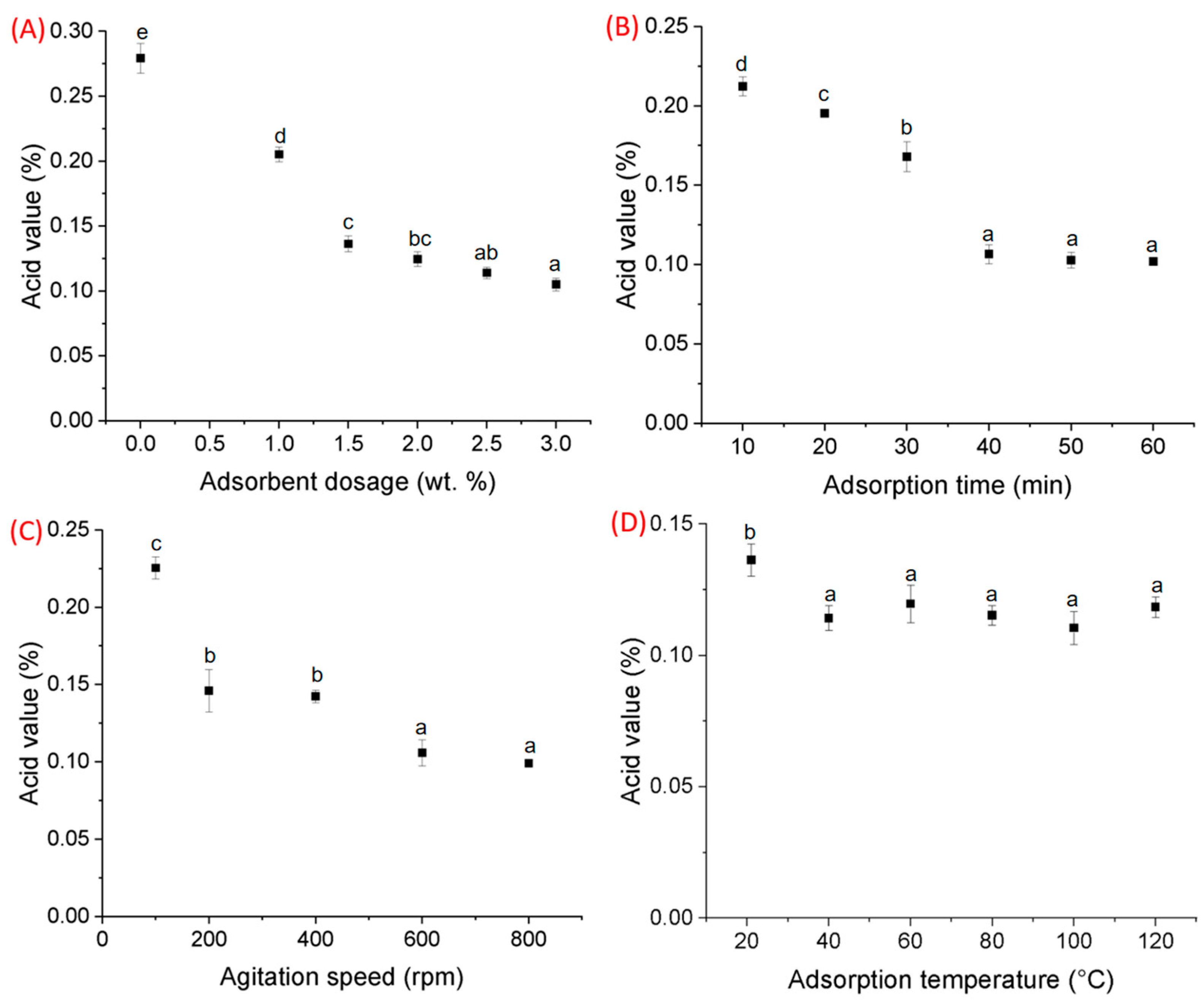
3.2. Adsorptive Parameters of Al2O3 Nano-Adsorbent on Crude Canola Oil Acid Value
3.3. Al2O3 Nano-Adsorbent Removal from Canola Oil
3.4. Neutral Oil Loss
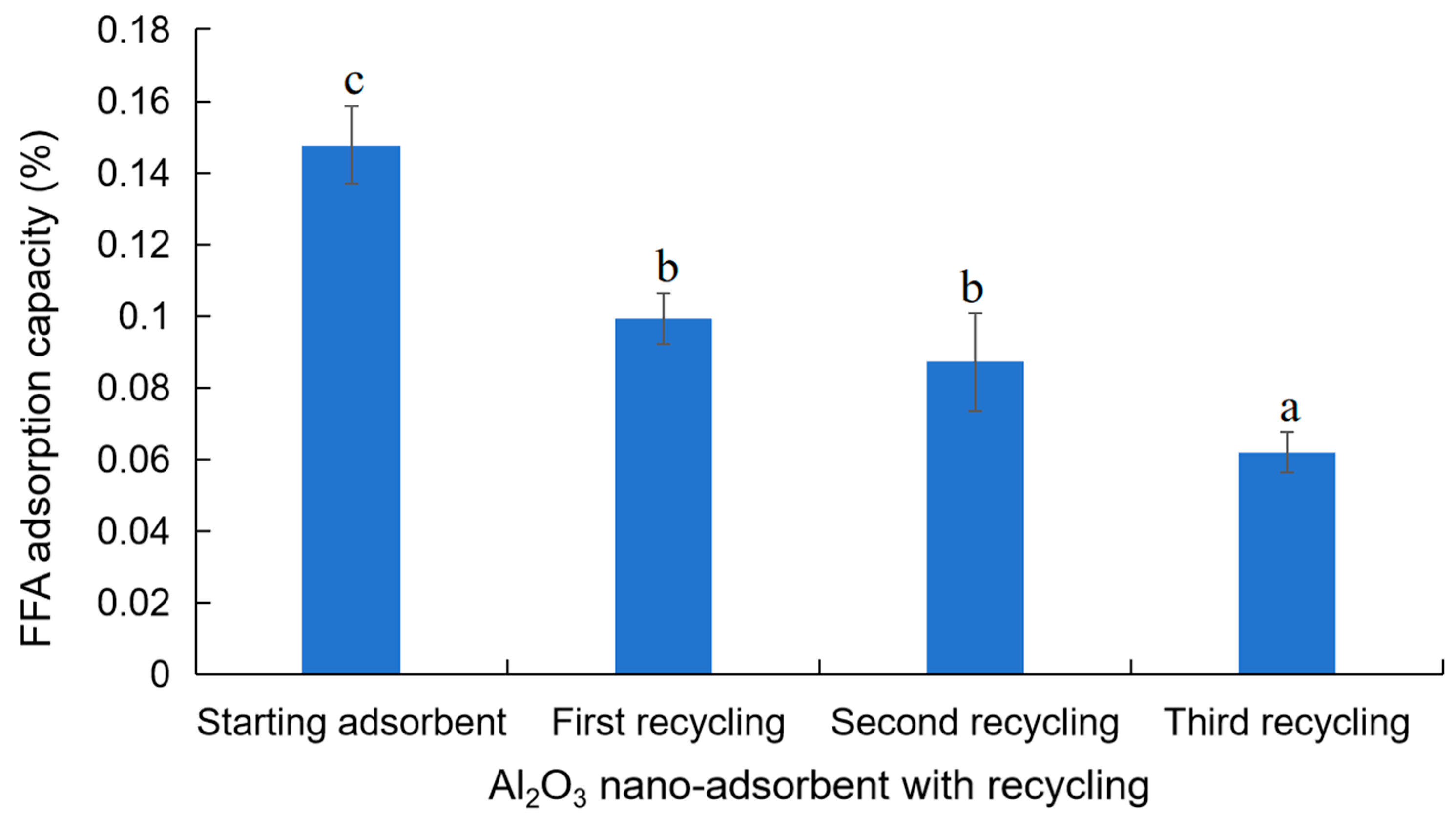
3.5. Reusability of Al2O3 Nano-Adsorbent on Crude Canola Oil Neutralization
3.6. Canola Oil Fatty Acid Profile with Al2O3 Nano-Adsorbent Treatment
3.7. Characterization of Al2O3 Nano-Adsorbent by Electron Microscopy
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Research and Markets. Canola Oil: Global Strategic Business Report. 2024. Available online: https://finance.yahoo.com/news/global-canola-oil-market-reach-230800784.html?guccounter=1 (accessed on 18 August 2024).
- Przybylski, P.; Eskin, M.N.A. Oil composition and properties. In Canola Chemistry, Production, Processing, and Utilization, 1st ed.; Daun, J.K., Eskin, M.N.A., Hickling, D., Eds.; AOCS Press: Champaign, IL, USA, 2011; pp. 189–227. [Google Scholar]
- Ghazani, S.M.; García-Llatas, G.; Marangoni, A.G. Micronutrient content of cold-pressed, hot-pressed, solvent extracted and RBD canola oil: Implications for nutrition and quality. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2014, 116, 380–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simopoulos, A.P. Essential fatty acids in health and chronic disease. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1999, 70, 560–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proctor, A.; Clark, P.K.; Parker, C.A. Rice hull ash adsorbent performance under commercial soy oil bleaching conditions. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 1995, 72, 459–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paradiso, V.M.; Gomes, T.; Nasti, R.; Caponio, F.; Summo, C. Effects of free fatty acids on the oxidative processes in purified olive oil. Food Res. Int. 2010, 43, 1389–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharby, S. Refining vegetable oils: Chemical and physical refining. Sci. World J. 2022, 2022, 6627013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; McClements, D.J.; Decker, E.A. Minor Components in Food Oils: A Critical Review of their Roles on Lipid Oxidation Chemistry in Bulk Oils and Emulsions. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2011, 51, 901–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Carvalho, G.C.; de Fátima Vitória de Moura, M.; de Castro, H.G.C.; da Silva Júnior, J.H.; da Silva, H.E.B.; dos Santos, K.M.; Rocha, Z.M.S. Influence of the atmosphere on the decomposition of vegetable oils: Study of the profiles of FTIR spectra and evolution of gaseous products. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2020, 140, 2247–2258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waraho, T.; McClements, D.J.; Decker, E.A. Impact of free fatty acid concentration and structure on lipid oxidation in oil-in-water emulsions. Food Chem. 2011, 129, 854–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aisan, S.; Chetpattananondh, P.; Chongkhong, S. Assessment of water degumming and acid degumming of mixed algal oil. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 5115–5123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaber, M.A.F.M.; Tujillo, F.T.; Mansour, M.P.; Juliano, P. Improving oil extraction from Canola seeds by conventional and advanced methods. Food Eng. Rev. 2018, 10, 198–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, P.H.; Chen, S.H. Effect of moisture content, system pressure, and temperature on the adsorption of carbon dioxide in carbon nanotube and graphite composite structures using molecular dynamics simulations. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2016, 16, 8654–8661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Icyer, N.C.; Durak, M.Z. Ultrasound-assisted bleaching of canola oil: Improve the bleaching process by central composite design. LWT 2018, 97, 640–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceriani, R.; Meirelles, A.J.A. Formation of trans PUFA during deodorization of canola oil: A study through computational simulation. Chem. Eng. Process. Process Intensif. 2007, 46, 375–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chew, S.C.; Nyam, K.L. Refining of edible oils. In Lipids and Edible Oils; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 213–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulaiman, M.A.; Oni, A.O.; Fadare, D.A. Energy and Exergy Analysis of a Vegetable Oil Refinery. Energy Power Eng. 2012, 4, 358–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, R.A.; Sanyal, P.B.; Chattopadhyay, N.; Kaul, S.N. Treatment and reuse of wastes of a vegetable oil refinery. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2003, 37, 101–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrauskaitè, V.; De Greyt, W.F.; Kellens, M.J. Physical refining of coconut oil: Effect of crude oil quality and deodorization conditions on neutral oil loss. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2000, 77, 581–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mfn, N. Reduction of Peroxide Value in Used Palm Cooking Oil Using Bagasse Adsorbent. Am. Int. J. Contemp. Res. 2012, 2, 185–191. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, Y.; Liu, C.; Xiong, W.; Liang, Q.; Xuan, P.; Zeng, X.; Zeng, S.; Zhou, Q.; Huang, F. Silicon dioxide as an efficient adsorbent in the degumming of rapeseed oil. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 268, 122344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Tse, T.J.; Chicilo, F.; Shen, J.; Purdy, S.K.; Meda, V.; Reaney, M.J.T. Electrostatic field and nano-adsorbents for refining fatty acid methyl esters for use as biodiesel. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 373, 133679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, X. Effect of attapulgite pore size distribution on soybean oil bleaching. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 84, 687–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, L.; Feng, J.; Li, W.; Luo, Z. High-Performance Separation of Phenolic Compounds from Coal-Based Liquid Oil by Deep Eutectic Solvents. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 7777–7783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husein, M.; Nassar, N. Nanoparticle preparation using the single microemulsions scheme. Curr. Nanosci. 2008, 4, 370–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Mahendra, S.; Alvarez, P.J.J. Nanomaterials in the Construction Industry: A Review of Their Applications and Environmental Health and Safety Considerations. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 3580–3590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Husein, D.Z.; Hassanien, R.; Al-Hakkani, M.F. Green-synthesized copper nano-adsorbent for the removal of pharmaceutical pollutants from real wastewater samples. Heliyon 2019, 5, e02339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Tse, T.J.; Shen, J.; Meda, V.; Reaney, M.J.T. Water modification of micro- and nano-adsorbents: A strategy for enhancing biodiesel refining efficiency. Energy Conserv. Manag. X 2024, 23, 100592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belhaj, A.F.; Elraies, K.A.; Mahmood, S.M.; Zulkifli, N.N.; Akbari, S.; Hussien, O.S.E. The effect of surfactant concentration, salinity, temperature, and pH on surfactant adsorption for chemical enhanced oil recovery: A review. J. Pet. Explor. Prod. Technol. 2020, 10, 125–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Liu, Y.; Ou, S.; Tan, Y.; Tang, S. Refining of biodiesel by ceramic membrane separation. Fuel Process. Technol. 2009, 90, 422–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eow, J.S.; Ghadiri, M. Electrostatic enhancement of coalescence of water droplets in oil: A review of the technology. Chem. Eng. J. 2002, 85, 357–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, B.Y.; Paradiso, A.; Kawabe, M.; Madou, M.J. A novel dielectrophoretic oil filter. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part D—J. Automob. Eng. 2006, 220, 481–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Shen, J.; Tse, T.J.; Purdy, S.K.; Meda, V.; Reaney, M.J.T. Electrostatic treatment as a novel and efficient method in crude canola oil refining. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 360, 131905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arutunian, S.G.; Aginian, M.A.; Margaryan, A.V.; Lazareva, E.G.; Chung, M. Electric field lines of an arbitrarily moving charged particle. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2109.10792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.C.; Chen, D.H. Adsorption kinetics and thermodynamics of acid dyes on a carboxymethylated chitosan-conjugated magnetic nano-adsorbent. Macromol. Biosci. 2005, 5, 254–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manyangadze, M.; Chikuruwo, N.H.M.; Chakra, C.S.; Narsaiah, T.B.; Radhakumari, M.; Danha, G. Enhancing adsorption capacity of nano-adsorbents via surface modification: A review. S. Afr. J. Chem. Eng. 2020, 31, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, B.H.; Yeh, C.C.; Chen, D.H. Surface modification of iron oxide nanoparticles with polyarginine as a highly positively charged magnetic nano-adsorbent for fast and effective recovery of acid proteins. Process Biochem. 2012, 47, 799–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haripriyan, U.; Gopinath, K.P.; Arun, J. Chitosan based nano adsorbents and its types for heavy metal removal: A mini review. Mater. Lett. 2022, 312, 131670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merle, N.; Tabassum, T.; Scott, S.L.; Motta, A.; Szeto, K.; Taoufik, M.; Gauvin, R.M.; Delevoye, L. High-Field NMR, Reactivity, and DFT Modeling Reveal the γ-Al2O3 Surface Hydroxyl Network. Angew. Chem. 2022, 134, e202207316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Shan, G.; Liu, H.; Xing, J. Surface modification of γ-Al2O3 nano-particles with gum arabic and its applications in adsorption and biodesulfurization. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2007, 201, 6917–6921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuleasan, S.; Tekin, A. Alkaline neutralization of crude soybean oil by various adsorbents. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2008, 110, 261–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghazani, S.M.; Marangoni, A.G. Minor components in canola oil and effects of refining on these constituents: A review. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2013, 90, 923–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Sathivel, S. Purifying salmon oil using adsorption, neutralization, and a combined neutralization and adsorption process. J. Food Eng. 2010, 96, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ergozhin, Y.; Dzhusipbekov, U.; Teltayev, B.; Nurgalieva, G.; Shakirova, A.; Khudaibergenova, K.; Izmailova, G.; Yelshibayev, N. Crude oil contaminated soil: Its neutralization and use. Sustainability 2020, 12, 3087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putranti, M.L.T.A.; Wirawan, S.K.; Bendiyasa, I.M. Adsorption of free fatty acid (FFA) in low-grade cooking oil used activated natural zeolite as adsorbent. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 299, 012085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.C.; Chen, D.H. Recovery of gold (III) ions by a chitosan coated magnetic nano-adsorbent. Gold Bulletin. 2006, 39, 98–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, N.A.; Ibrahim, F.; Yafouz, B. Dielectrophoresis for biomedical sciences applications: A review. Sensors 2017, 17, 449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.; Tse, T.J.; Chicilo, F.; Meda, V.; Reaney, M.J.T. Electrostatic field as an emergent technology in refining crude oils: A review. In Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition; Taylor & Francis: Abingdon, UK, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peles, J.; Cacace, B.; Carbrello, C.; Giglia, S.; Zydney, A.L. Global pore blockage-cake filtration model including pressure effects on protein fouling in virus filtration. J. Membr. Sci. 2022, 662, 120961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haryono, I.; Rochmanto, B.; Mohtar, M.; Setiapraja, H.; Yubaidah, S. The effects of particle contamination on high blend palm biodiesel against fuel filter blockage. In AIP Conference Proceedings; AIP Publishing: College Park, MD, USA, 2024; Volume 2891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minea, A.A. A review on electrical conductivity of nano-particle-en hanced fluids. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingram, J.C. Data on Edible Vegetable Oil Processes. Ph.D. Thesis, University Libraries, Rolla, MO, USA, 1924; p. 57. Available online: https://core.ac.uk/download/pdf/229061175.pdf (accessed on 5 November 2023).
- Chai, S.C.; Ju, T.; Dang, M.; Goldsmith, R.B.; Maroney, M.J.; Pochapsky, T.C. Characterization of metal binding in the active sites of acireductone dioxygenase isoforms from Klebsiella ATCC 8724. Biochemiestry 2008, 47, 2428–2438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, J.; Sheng, W.; Sun, L.; Xiang, J. Effect of calcination temperature on the activity and structure of MnOx/TiO2 adsorbent for Hg0 removal. Fuel Process. Technolol. 2015, 135, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, N.; Riead, M.M.H.; Bilal, M.; Yang, Y.; Khan, A.; Ali, F.; Karim, S.; Zhu, C.; Wenjie, Y.; Sher, F.; et al. Adsorptive remediation of environmental pollutants using magnetic hybrid materials as platform adsorbents. Chemosphere 2021, 284, 131279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Wang, W.; Zhao, Y.; Bai, H.; Wen, T.; Kang, S.; Song, G.; Song, S.; Komarneni, S. Removal of heavy metals and dyes by clay-based adsorbents: From natural clays to 1D and 2D nano-composites. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 420, 127574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gul, A.; Khaligh, N.G.; Julkapli, N.M. Surface modification of carbon-based nanoadsorbents for the advanced wastewater treatment. J. Mol. Struct. 2021, 1235, 130148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos Anjos, J.S.; De Araujo Gonzalez, W.; Lam, Y.L.; Frety, R. Catalytic decomposition of vegetable oil. Appl. Catal. 1983, 5, 299–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, S.; Sarkar, J. Selective adsorption of oil on self-organized surface patterns formed over soft thin PDMS films. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2019, 207, 970–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Fatty Acid Type | Untreated Canola Oil (%) | Al2O3 Nano-Adsorbent Treated Canola Oil (%) |
|---|---|---|
| C16:0 | 5.01 ± 0.03 | 5.00 ± 0.05 |
| C18:0 | 2.50 ± 0.02 | 2.50 ± 0.02 |
| C18:1 | 66.52 ± 0.07 | 66.57 ± 0.06 |
| C18:2 | 21.73 ± 0.04 | 21.70 ± 0.03 |
| C18:3 | 2.43 ± 0.02 | 2.43 ± 0.05 |
| C20:0 | 0.75 ± 0.01 | 0.75 ± 0.01 |
| C20:1 | 1.06 ± 0.01 | 1.05 ± 0.01 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, L.; Tse, T.J.; Chicilo, F.; Shen, J.; Meda, V.; Reaney, M.J.T. Utilizing Nano-Adsorbents and Electrostatic Field Treatment for Sustainable Refinement of Crude Canola Oil. Foods 2024, 13, 2707. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13172707
Zhou L, Tse TJ, Chicilo F, Shen J, Meda V, Reaney MJT. Utilizing Nano-Adsorbents and Electrostatic Field Treatment for Sustainable Refinement of Crude Canola Oil. Foods. 2024; 13(17):2707. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13172707
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Li, Timothy J. Tse, Farley Chicilo, Jianheng Shen, Venkatesh Meda, and Martin J. T. Reaney. 2024. "Utilizing Nano-Adsorbents and Electrostatic Field Treatment for Sustainable Refinement of Crude Canola Oil" Foods 13, no. 17: 2707. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13172707
APA StyleZhou, L., Tse, T. J., Chicilo, F., Shen, J., Meda, V., & Reaney, M. J. T. (2024). Utilizing Nano-Adsorbents and Electrostatic Field Treatment for Sustainable Refinement of Crude Canola Oil. Foods, 13(17), 2707. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13172707





