Transglutaminase Crosslinked Milk Protein Concentrate and Micellar Casein Concentrate: Impact on the Functionality of Imitation Mozzarella Cheese Manufactured on a Small Scale Using a Rapid Visco Analyzer
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
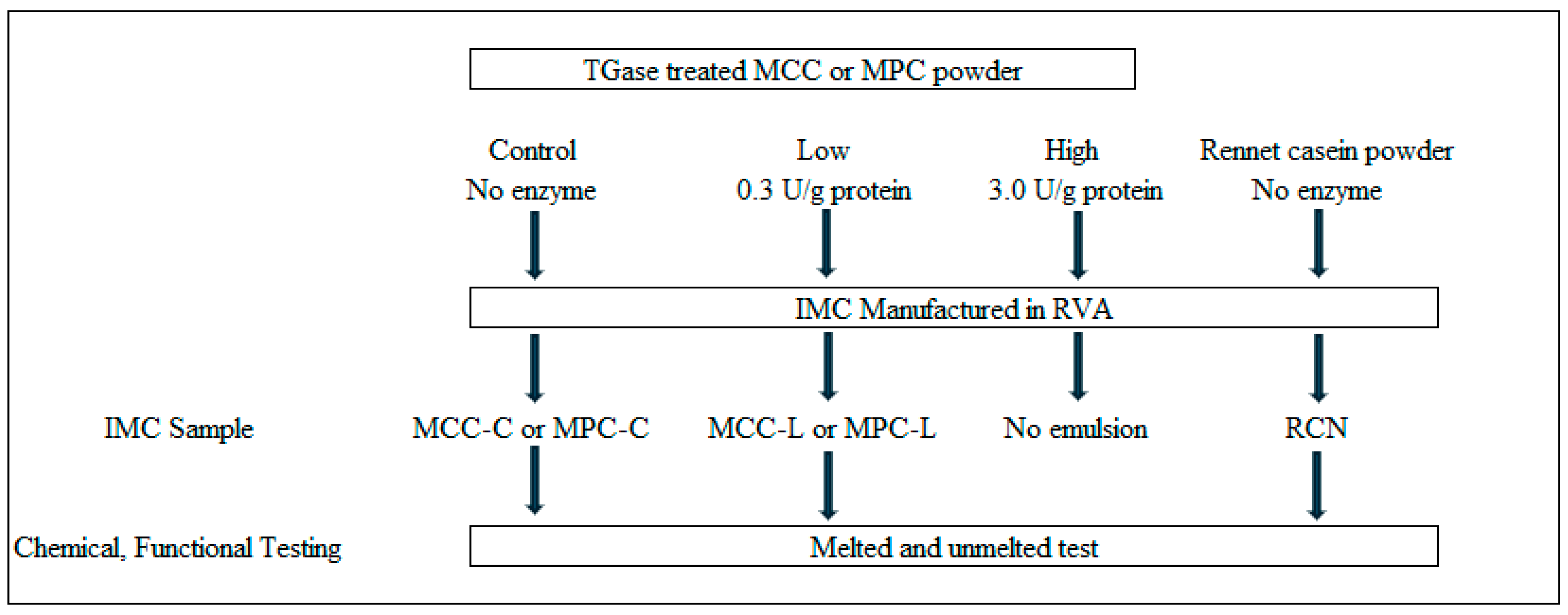
2.1. Experimental Design
2.2. Manufacture of Treatment Powders
2.3. Proximate Compositional Analysis
2.4. Imitation Mozzarella Cheese Formulation and Manufacture
2.4.1. IMC Formulation
2.4.2. IMC Manufacture
2.5. Functional Properties Analysis
2.5.1. Textural Properties—Unmelted
2.5.2. Textural Properties—Melted
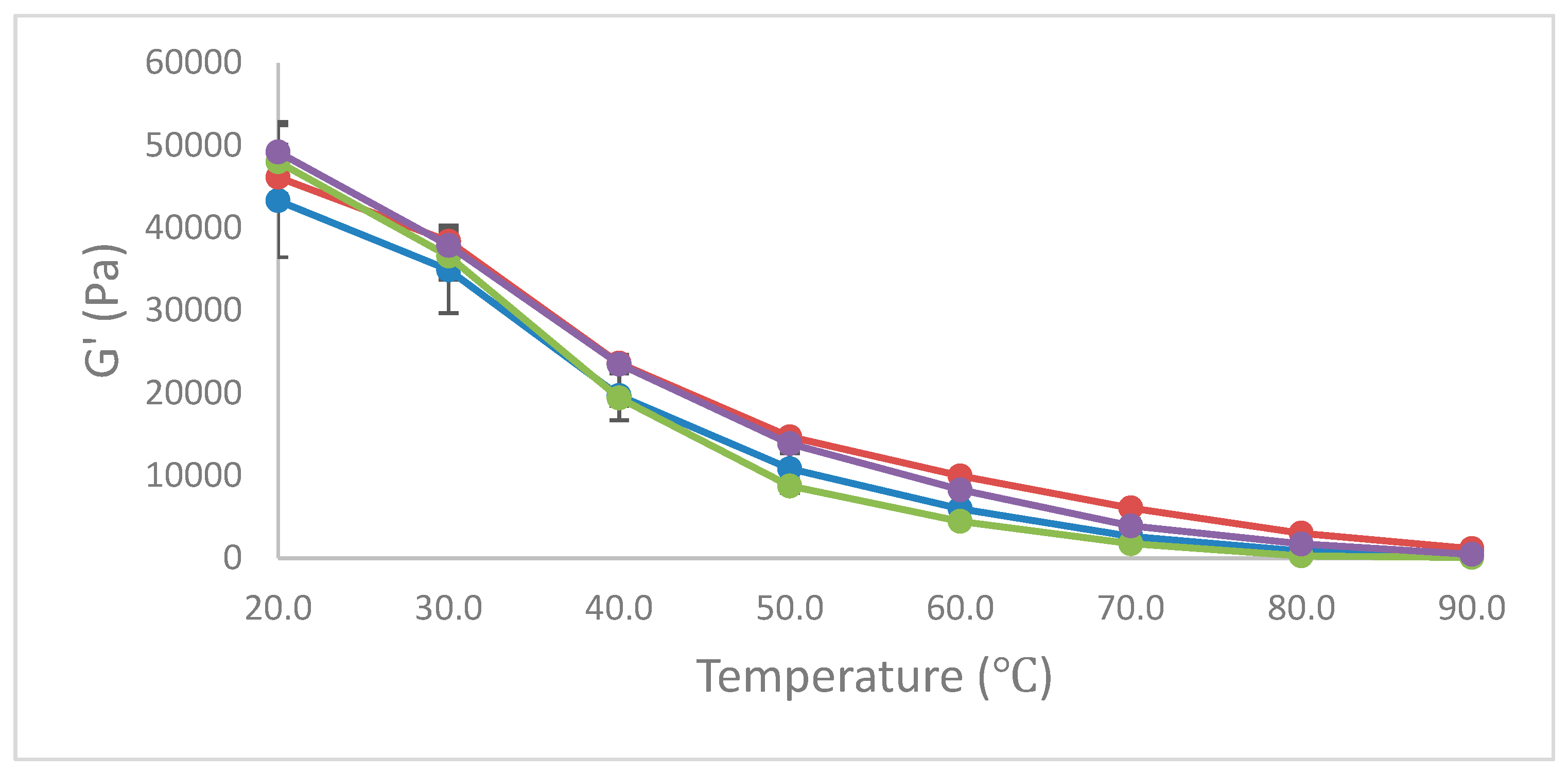
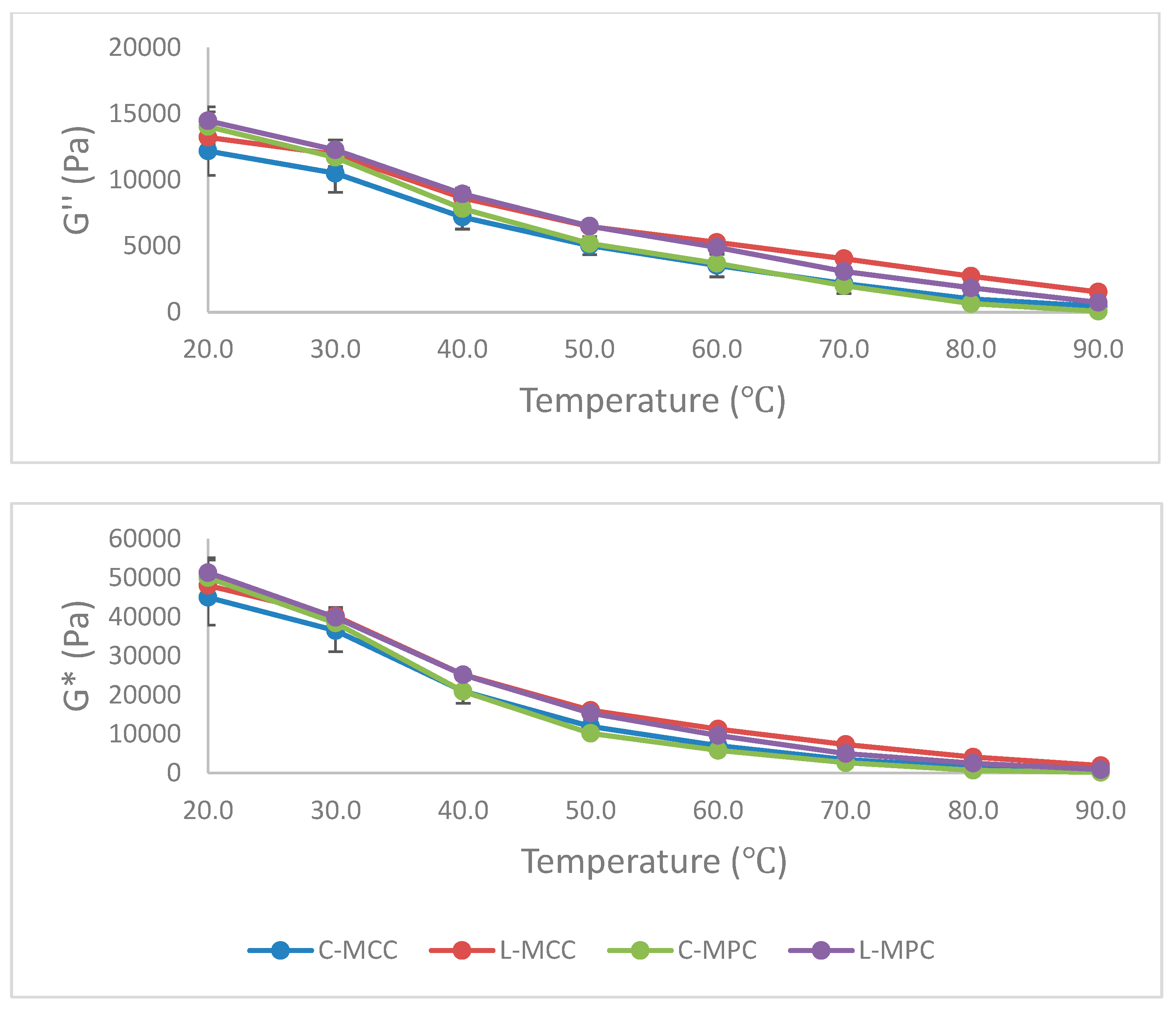
Dynamic Stress Rheology (DSR)
Modified Schreiber Melt Test
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Treatment Powder Composition and TGase Crosslinking
3.2. IMC Composition and Manufacture
3.2.1. IMC Composition
3.2.2. IMC Manufacture
3.3. IMC Functionality
3.3.1. Unmelted Textural Characteristics
3.3.2. Melted Characteristics
3.4. Comparison with RCN Samples
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Masotti, F.; Cattaneo, S.; Stuknytė, M.; De Non, I. Status and developments in analogue cheese formulations and functionalities. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 7, 158–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guniee, T.P. Pasteurized Processed and Imitation Cheese Products. In Cheese: Chemistry, Physics and Microbiology, 4th ed.; McSweeney, P.L.H., Fox, P.F., Cotter, P.D., Everett, D.W., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2017; Chapter 46; pp. 1133–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachmann, H.P. Cheese analogues: A review. Int. Dairy J. 2001, 11, 505–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Riordan, E.D.; Duggan, E.; O’Sullivan, M.; Noronha, N. Production of analogue cheeses. In Processed Cheese and Analogues; Tamime, A.Y., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd., Publication: Chichester, UK, 2011; pp. 219–244. [Google Scholar]
- Shukri, A.M.; Alias, A.K.; Murad, M.; Yen, K.-S.; Cheng, L.-H. A review of natural cheese and imitation cheese. J. Food Process Preserv. 2022, 46, e16112. [Google Scholar]
- Ennis, M.P.; Mulvihill, D.M. Compositional characteristics of rennet caseins and hydration characteristics of the caseins in a model system as indicators of performance in Mozzarella cheese analogue manufacture. Food Hydrocoll. 1999, 13, 325–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mounsey, J.S.; O’Riordan, E.D. Empirical and Dynamic Rheological Data Correlation to Characterize Melt Characteristics of Imitation Cheese. J. Food Sci. 1999, 64, 701–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salunke, P.; Marella, C.; Amamcharla, J.K.; Muthukumarappan, K.; Metzger, L.E. Use of Micellar Casein Concentrate and Milk Protein Concentrate Treated with Transglutaminase in Imitation cheese products—Unmelted texture. J. Dairy Sci. 2022, 105, 7891–7903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salunke, P.; Marella, C.; Amamcharla, J.K.; Muthukumarappan, K.; Metzger, L.E. Use of Micellar Casein Concentrate and Milk Protein Concentrate Treated with Transglutaminase in Imitation cheese products—Melt and Stretch properties. J. Dairy Sci. 2022, 105, 7904–7916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noronha, N.; O’Riordan, E.D.; O’Sullivan, M. Influence of processing parameters on the texture and microstructure of imitation cheese. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2008, 226, 385–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapoor, R.; Metzger, L.E. Process cheese: Scientific and technological aspects—A review. Comp. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2008, 7, 194–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salunke, P.; Metzger, L.E. Functional characteristics of process cheese product as affected by milk protein concentrate and micellar casein concentrate at different usage levels. Int. Dairy J. 2022, 128, 105317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, R.; Jana, A.H.; Aparnathi, K.D.; Prajapati, P.S. Process standardization for rennet casein-based Mozzarella cheese analogue. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2010, 47, 574–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dharaiya, C.; Jana, A.; Patel, A.; Patel, D. Comparison of natural Mozzarella cheese with acid casein-based Mozzarella cheese analogue. Indian J. Dairy Sci. 2021, 74, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammam, A.R.A.; Metzger, L.E. Characteristics of imitation Mozzarella cheese manufactured without emulsifying salts using a combination of culture-based acid curd and micellar casein concentrate. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 11, 4616–4624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Rathod, G.; Meletharayil, G.H.; Kapoor, R.; Sankarlal, V.M.; Amamcharla, J.K. Invited review: Shelf-stable dairy protein beverages—Scientific and technological aspects. J. Dairy Sci. 2022, 105, 9327–9346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salunke, P.; Marella, C.; Metzger, L.E. Microfiltration and Ultrafiltration process to produce Micellar Casein and Milk Protein Concentrates with 80% Crude Protein Content: Partitioning of various protein fractions and constituents. Dairy 2021, 2, 367–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salunke, P.; Metzger, L.E. Impact of transglutaminase treated micellar casein concentrate and milk protein concentrate on the functionality of process cheese product slice formulations. Food Mater. Res. 2023, 3, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salunke, P.; Biswas, A.C.; Metzger, L.E. Manufacture of loaf-type processed cheese products using transglutaminase crosslinked micellar casein concentrate and milk protein concentrate. Int. J. Dairy Technol. 2023, 76, 727–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapoor, R.; Metzger, L.E. Small-scale manufacture of process cheese using a rapid visco analyzer. J. Dairy Sci. 2005, 88, 3382–3391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapoor, R.; Lehtola, P.; Metzger, L.E. Comparison of pilot-scale and rapid visco analyzer process cheese manufacture. J. Dairy Sci. 2004, 87, 2813–2821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trivedi, D.; Bennett, R.J.; Hemar, Y.; Reid, D.C.W.; Lee, S.K.; Illingworth, D. Effect of different starches on rheological and microstructural properties of (II) commercial processed cheese. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2008, 43, 2197–2203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, W.; Watanabe, Y.; Satoh, H.; Inoue, K.; Moriguchi, N.; Fusa, K.; Yanagisawa, Y.; Mutoh, T.; Nakamura, T. Effects of emulsifying conditions on creaming effect, mechanical properties and microstructure of processed cheese using a rapid visco-analyzer. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2018, 82, 476–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, K.; Nakanou, K.; Mizuno, R.; Iwatsuki, K. Characterization by rapid visco analyzer of suitability of different types of cheese as ingredients for processed cheese. J. Jpn. Soc. Food Sci. Technol.-Nippon. Shokuhin Kagaku Kogaku Kaishi 2006, 53, 312–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janevski, O.; Hassan, A.N.; Metzger, L.E. Application of salt whey in process cheese food made from Cheddar cheese containing exopolysaccharides. J. Dairy Sci. 2012, 95, 3609–3616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammam, A.R.A.; Kapoor, R.; Metzger, L.E. Manufacture of process cheese products without emulsifying salts using acid curd and micellar casein concentrate. J. Dairy Sci. 2023, 106, 117–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Purna, S.K.G.; Pollard, A.; Metzger, L.E. Effect of formulation and manufacturing parameters on process cheese food functionality—I. Trisodium citrate. J. Dairy Sci. 2006, 89, 2386–2396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giri, A.; Kanawjia, S.; Khetra, Y. Textural and Melting Properties of Processed Cheese Spread as Affected by Incorporation of Different Inulin Levels. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2014, 7, 1533–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trivedi, D.; Bennett, R.J.; Hemar, Y.; Reid, D.C.W.; Lee, S.K.; Illingworth, D. Effect of different starches on rheological and microstructural properties of (I) model processed cheese. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2008, 43, 2191–2196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gampala, P.; Brennan, C.S. Potential Starch Utilisation in a Model Processed Cheese System. Starch-Starke 2008, 60, 685–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini-Parvar, S.H.; Matia-Merino, L.; Golding, M. Effect of basil seed gum (BSG) on textural, rheological and microstructural properties of model processed cheese. Food Hydrocoll. 2015, 43, 557–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, A.; Hewitt, S. Phase structures impact the rheological properties of rennet-casein-based imitation cheese containing starch. Food Hydrocoll. 2009, 23, 867–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giri, A.; Kanawjia, S.K.; Rajoria, A. Effect of phytosterols on textural and melting characteristics of cheese spread. Food Chem. 2014, 157, 240–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thionnet, O.; Havea, P.; Gillies, G.; Lad, M.; Golding, M. Influence of the Volume Fraction, Size and Surface Coating of Hard Spheres on the Microstructure and Rheological Properties of Model Mozzarella Cheese. Food Biophys. 2017, 12, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prow, L.A.; Metzger, L.E. Melt analysis of process cheese spread or product using a rapid visco Analyzer. J. Dairy Sci. 2005, 88, 1277–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooi, R.; Barbano, D.M.; Bradley, R.L.; Budde, D.; Bulthaus, M.; Chettiar, M.; Lynch, J.; Reddy, R.E.; Arnold, A. Chemical and Physical Methods. Standard Methods for the Examination of Dairy Products, 17th ed.; Wehr, H.M., Frank, J.F., Eds.; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2004; Chapter 15; pp. 480–510. [Google Scholar]
- Breene, W.M. Application of texture profile analysis to instrumental food texture evaluation. J. Texture Stud. 1975, 6, 53–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salunke, P.; Metzger, L.E. Impact of transglutaminase treatment given to the skim milk before or after microfiltration on the functionality of micellar casein concentrate used in process cheese product and comparison with rennet casein. Int. Dairy J. 2022, 128, 105317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunasekaran, S.; Ak, M.M. Cheese Rheology and Texture; CRC Press LLC: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Lucey, J.A.; Johnson, M.E.; Horne, D.S. Invited review: Perspectives on the basis of the rheology and texture properties of cheese. J. Dairy Sci. 2003, 86, 2725–2743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutheerawattananonda, M.; Bastian, E.D. Monitoring process cheese meltability using dynamic stress rheometry. J. Texture Stud. 1998, 29, 169–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aboumahmoud, R.; Savello, P. Crosslinking of Whey Protein by Transglutaminase. J. Dairy Sci. 1990, 73, 256–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folk, J.E.; Finnlayson, J. The ɛ-(γ-glutamyl) lysine crosslink and the catalytic role of TGases. Adv. Protein Chem. 1977, 31, 1–133. [Google Scholar]
- Soares, L.H.B.; Albuquerque, P.M.; Assmann, F.; Ayub, M.A.Z. Physicochemical properties of three food proteins treated with transglutaminase. Ciência Rural 2004, 34, 1214–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smiddy, M.A.; Martin, J.-E.G.H.; Kelly, A.L.; de Kruif, C.G.; Huppertz, T. Stability of casein micelles cross-linked by transglutaminase. J. Dairy Sci. 2006, 89, 1906–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nonaka, M.; Sakamoto, H.; Toiguchi, S.; Kawajiri, H.; Soeda, T.; Motoki, M. Sodium caseinate and skim milk gels formed by incubation with microbial transglutaminase. J. Food Sci. 1992, 57, 1214–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Kruif, C.G.; Huppertz, T.; Urban, V.S.; Petukhov, A.V. Casein micelles and their internal structure. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2012, 171–172, 36–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, P.F.; Uniacke-Lowe, T.; McSweeney, P.L.H.; O’Mahony, J.A. Dairy Chemistry and Biochemistry; Blackie Academic & Professional (An imprint of Chapman & Hall): London, UK, 1998; p. 478. [Google Scholar]
- Mulvihill, D.M. Production, functional properties and utilization of milk protein products. In Advanced Dairy Chemistry-1: Proteins; Fox, P.F., Ed.; Elsevier Applied Science: London, UK, 1992; Volume 1, pp. 369–404. [Google Scholar]
- Augustin, M.A.; Oliver, C.M.; Hemar, Y. Casein, caseinates and milk protein concentrates. In Dairy Ingredients for Food Processing; Chandan, R.C., Kilara, A., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc., Publication: Mount Pleasant, IA, USA, 2011; Chapter 7; pp. 161–178. [Google Scholar]
- Nasr, W.I.A. Improving the properties of low fat mozzarella cheese made from buffalo milk using transglutaminase enzyme. Egypt. J. Dairy Sci. 2019, 47, 121–131. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Liu, Y.; Sun, Y.; Li, H.; Yu, J. Properties of polysaccharides and glutamine transaminase used in mozzarella cheese as texturizer and crosslinking agents. LWT 2019, 99, 411–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topcu, A.; Bulat, T.; Özer, B. Process design for processed Kashar cheese (a pasta-filata cheese) by means of microbial transglutaminase: Effect on physical properties, yield and proteolysis. LWT 2020, 125, 109226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savello, P.A.; Ernstrom, C.A.; Kalab, M. Microstructure and meltability of model process cheese made with rennet and acid casein. J. Dairy Sci. 1989, 72, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mleko, S.; Foegeding, E.A. Physical properties of rennet casein gels and processed cheese analogues containing whey proteins. Milchwissenschaft 2000, 55, 513–516. [Google Scholar]
- Mleko, S.; Foegeding, E.A. Incorporation of polymerized whey proteins into processed cheese. Milchwissenschaft 2001, 56, 612–615. [Google Scholar]
- Solowiej, B.; Mleko, S.; Gustaw, W.; Udeh, K.O. Effect of whey protein concentrates on texture, meltability and microstructure of acid casein processed cheese analogs. Milchwissenschaft 2010, 65, 169–173. [Google Scholar]
| Imitation Mozzarella Cheese Treatment 3 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ingredient | C-MCC | L-MCC | C-MPC | L-MPC | RCN |
| % (w/w) | |||||
| Water | 42.66 | 42.56 | 42.50 | 42.45 | 40.83 |
| Lactic acid | 0.80 | 0.80 | 0.80 | 0.80 | 0.80 |
| Salt | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| Butter (unsalted) | 24.71 | 24.70 | 24.92 | 24.90 | 25.89 |
| Whey deproteinized | 1.93 | 2.05 | 0.72 | 0.81 | 4.66 |
| Citric Acid | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.50 |
| Kasal | 3.00 | 3.00 | 3.00 | 3.00 | 3.00 |
| Treatment powder | 25.39 | 25.39 | 26.55 | 26.54 | 23.33 |
| Total | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 |
| Parameters | Imitation Mozzarella Cheese Treatment 3 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C-MCC | L-MCC | C-MPC | L-MPC | RCN | |
| pH | 5.65 | 5.65 | 5.65 | 5.63 | 5.64 |
| Fat, % | 20.99 a | 20.94 b | 20.98 ab | 20.96 ab | 21.01 |
| Protein, % | 19.98 | 19.95 | 19.97 | 19.95 | 20.06 |
| Moisture, % | 47.95 | 47.84 | 48.01 | 47.97 | 48.03 |
| Factors | df | RVA-Viscosity | TT 3 | Change in Area | TPA-Hardness |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Replication | 2 | 58,606.64 (0.364) | 5.94 (0.737) | 1925.71 (0.818) | 2,733,702.88 (0.037) * |
| Product Type | 1 | 31,249.10 (0.454) | 200.63 (0.017) * | 158,224.26 (0.006) * | 994,241.96 (0.190) |
| Enzyme Level | 1 | 4,148,286.57 (<0.0001) * | 207.22 (0.015) * | 460,272.96 (0.0004) * | 2,768,266.69 (0.049) * |
| Product Type × Enzyme Level | 1 | 28,722.98 (0.472) | 9.13 (0.508) | 2319.63 (0.635) | 3,658,420.01 (0.030) * |
| Error | 6 | 48,708.38 | 18.46 | 9260.14 | 455,078.53 |
| Parameters | Imitation Mozzarella Cheese Treatment 3 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C-MCC | L-MCC | C-MPC | L-MPC | |
| RVA-viscosity, cP | 1650.0 c ± 267.2 | 2923.8 a ± 168.5 | 1849.9 b ± 272.8 | 2927.9 a ± 174.7 |
| TT 4, °C | 75.6 b ± 3.26 | 82.1 a ± 2.86 | 65.6 c ± 3.07 | 75.7 b ± 5.18 |
| Change Area, mm | 798.1 a ± 74.5 | 378.6 c ± 99.9 | 540.7 b ± 80.5 | 176.8 d ± 87.8 |
| Parameters | Imitation Mozzarella Cheese Treatment 3 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C-MCC | L-MCC | C-MPC | L-MPC | |
| Hardness, g | 5852.4 a ± 1551.9 | 5708.7 a ± 870.0 | 4172.4 b ± 895.1 | 6237.3 a ± 804.1 |
| Adhesiveness, g.s | −333.7 b ± 310.03 | −168.4 a ± 186.11 | −341.1 b ± 214.72 | −201.1 ab ± 81.66 |
| Springiness | 0.23 b ± 0.05 | 0.43 a ± 0.05 | 0.12 c ± 0.02 | 0.21 b ± 0.06 |
| Cohesiveness | 0.17 b ± 0.02 | 0.19 a ± 0.03 | 0.13 c ± 0.01 | 0.15 b ± 0.02 |
| Gumminess | 972.6 a ± 346.9 | 1071.1 a ± 242.3 | 542.5 b ± 125.1 | 964.6 a ± 213.6 |
| Chewiness | 235.0 b ± 123.2 | 456.6 a ± 130.0 | 64.8 c ± 20.9 | 214.5 b ± 99.2 |
| Resilience | 0.031 b ± 0.00 | 0.041 a ± 0.01 | 0.025 c ± 0.01 | 0.031 b ± 0.00 |
| Parameters | Imitation Mozzarella Cheese Treatment 3 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RCN | C-MCC | L-MCC | C-MPC | L-MPC | |
| Unmelted characteristics | |||||
| Hardness, g | 6386.3 ± 728.87 | NS | NS | NS | NS |
| Adhesiveness, g.s | −202.1 ± 86.20 | NS | NS | NS | NS |
| Springiness | 0.40 ± 0.09 | * | NS | * | * |
| Cohesiveness | 0.21 ± 0.02 | NS | NS | * | * |
| Gumminess | 1331.3 ± 270.49 | NS | NS | * | NS |
| Chewiness | 546.5 ± 208.07 | * | NS | * | * |
| Resilience | 0.04 ± 0.01 | NS | NS | NS | NS |
| Melted characteristics | |||||
| RVA-Viscosity, cP | 3488.0 ± 498.53 | * | NS | * | NS |
| TT 4, °C | 57.5 ± 0.42 | * | * | NS | * |
| Change Area, mm | 1142.7 ± 25.69 | * | * | * | * |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Salunke, P.; Metzger, L.E. Transglutaminase Crosslinked Milk Protein Concentrate and Micellar Casein Concentrate: Impact on the Functionality of Imitation Mozzarella Cheese Manufactured on a Small Scale Using a Rapid Visco Analyzer. Foods 2024, 13, 2720. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13172720
Salunke P, Metzger LE. Transglutaminase Crosslinked Milk Protein Concentrate and Micellar Casein Concentrate: Impact on the Functionality of Imitation Mozzarella Cheese Manufactured on a Small Scale Using a Rapid Visco Analyzer. Foods. 2024; 13(17):2720. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13172720
Chicago/Turabian StyleSalunke, Prafulla, and Lloyd E. Metzger. 2024. "Transglutaminase Crosslinked Milk Protein Concentrate and Micellar Casein Concentrate: Impact on the Functionality of Imitation Mozzarella Cheese Manufactured on a Small Scale Using a Rapid Visco Analyzer" Foods 13, no. 17: 2720. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13172720
APA StyleSalunke, P., & Metzger, L. E. (2024). Transglutaminase Crosslinked Milk Protein Concentrate and Micellar Casein Concentrate: Impact on the Functionality of Imitation Mozzarella Cheese Manufactured on a Small Scale Using a Rapid Visco Analyzer. Foods, 13(17), 2720. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13172720





