A New Combination of Bifidobacterium bifidum and Lactococcus lactis Strains with Synergistic Effects Alleviates Colitis-Associated Colorectal Cancer
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cells and Bacterial Strains
2.2. Hoechst Staining Assay
2.3. Cell Viability Assay
2.4. Evaluation of HT-29 Cell Apoptosis by Flow Cytometry
2.5. Quantitative Real-Time PCR (qRT-PCR)
2.6. Animals and Experimental Design
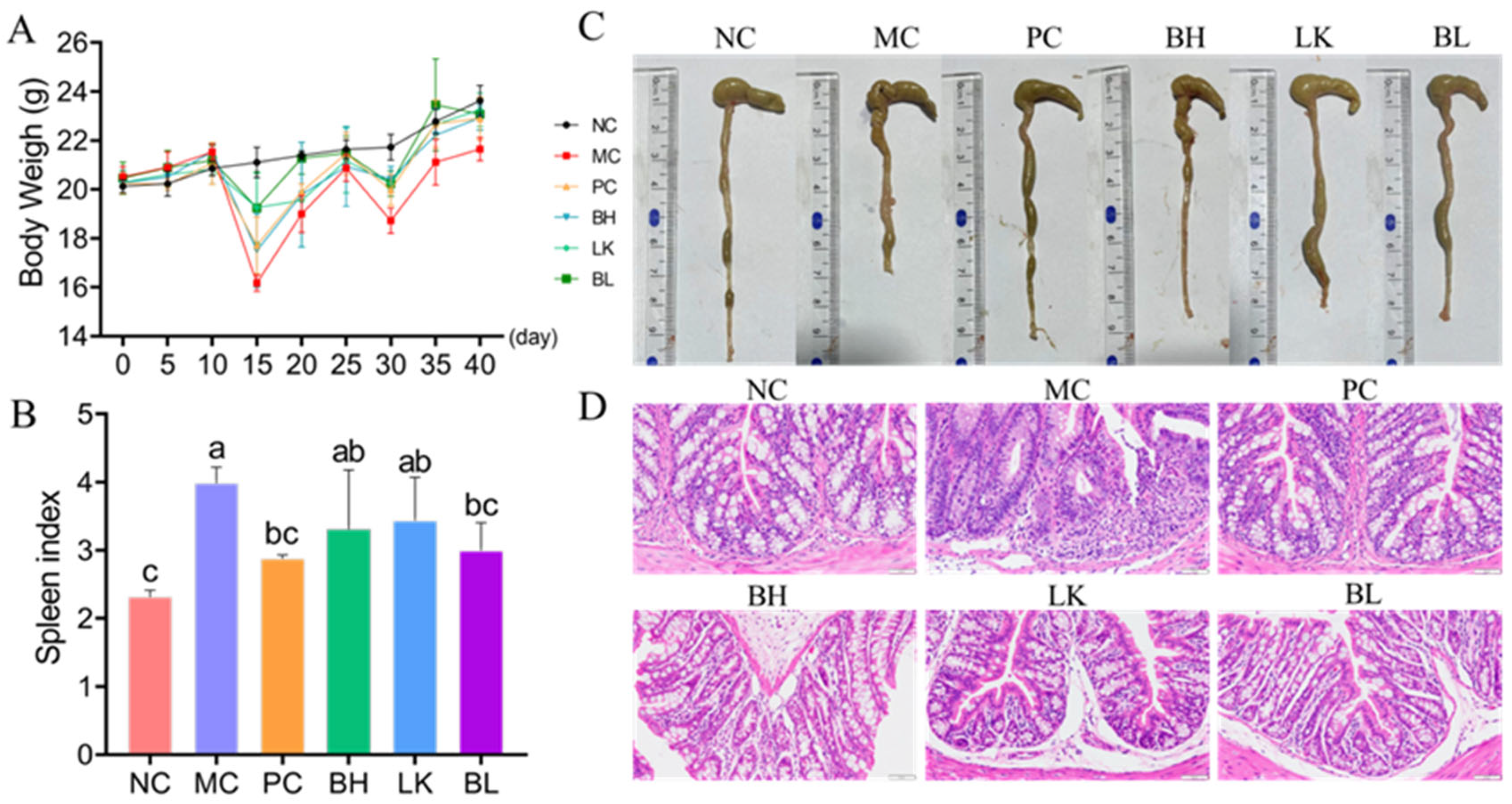
2.7. Organ Index
2.8. Histopathologic Analysis
2.9. Evaluation of Myeloperoxidase (MPO) Activity and Hypoxia-Inducible Factor 1-Alpha (HIF-1α) Level
2.10. Cytokine Levels Analysis
2.11. 16 S rRNA Sequencing
3. Results
3.1. Examination of Apoptosis Morphology in HT-29 Cell
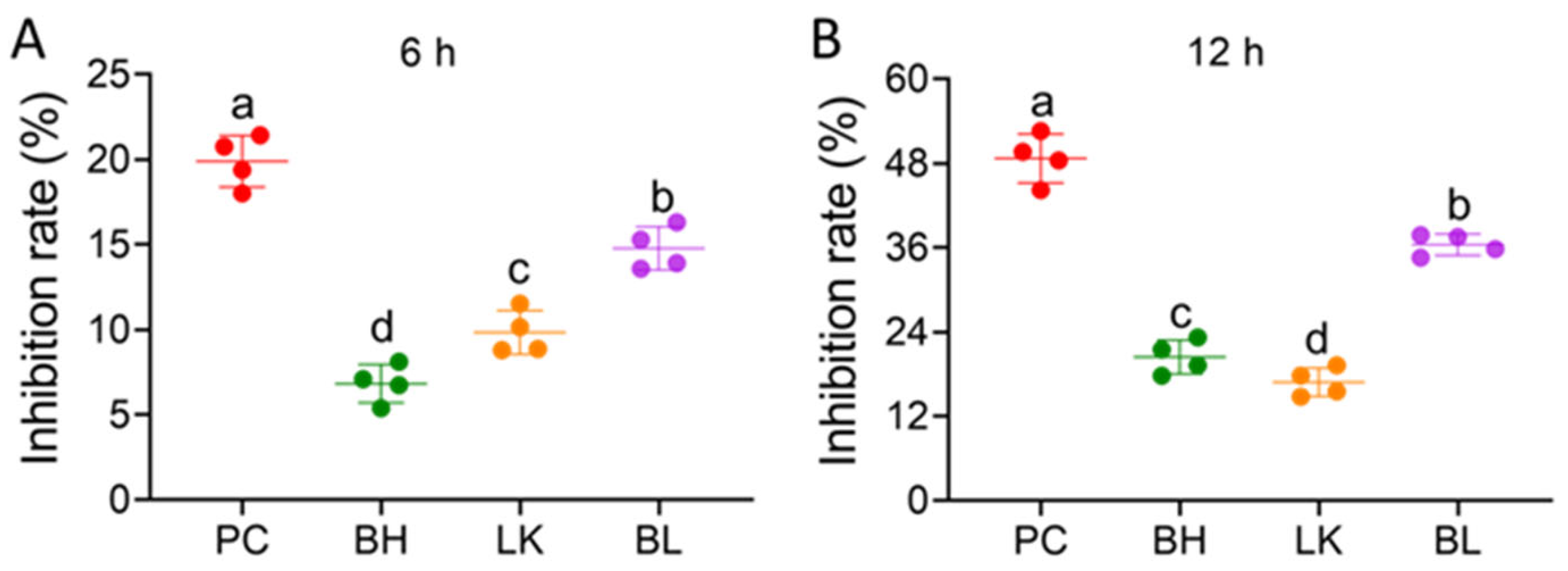
3.2. Cell Viability
3.3. Assaying of Apoptosis
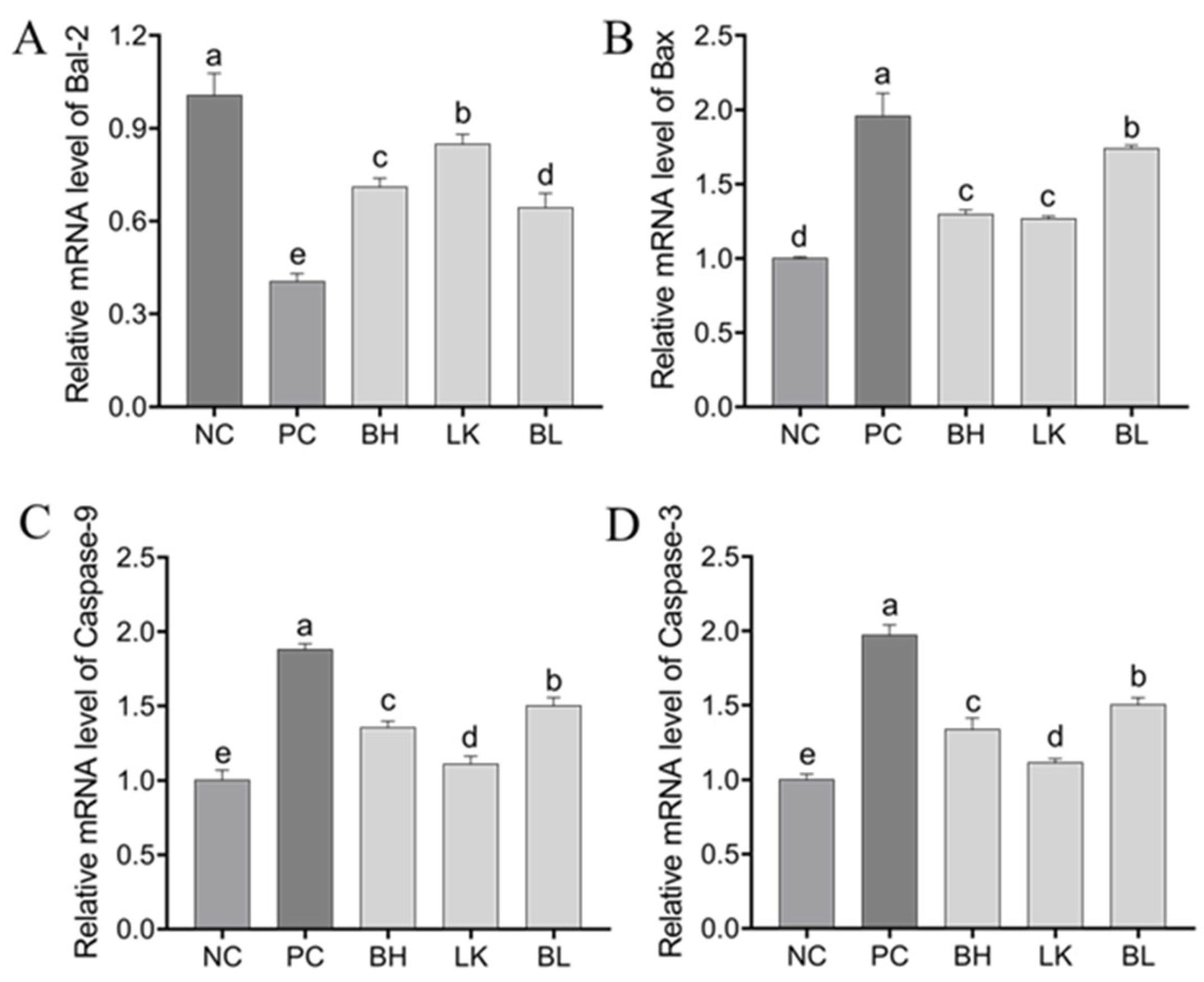
3.4. Expression of Genes and Proteins Related to Apoptosis in HT-29 Cells
3.5. Pathogenesis
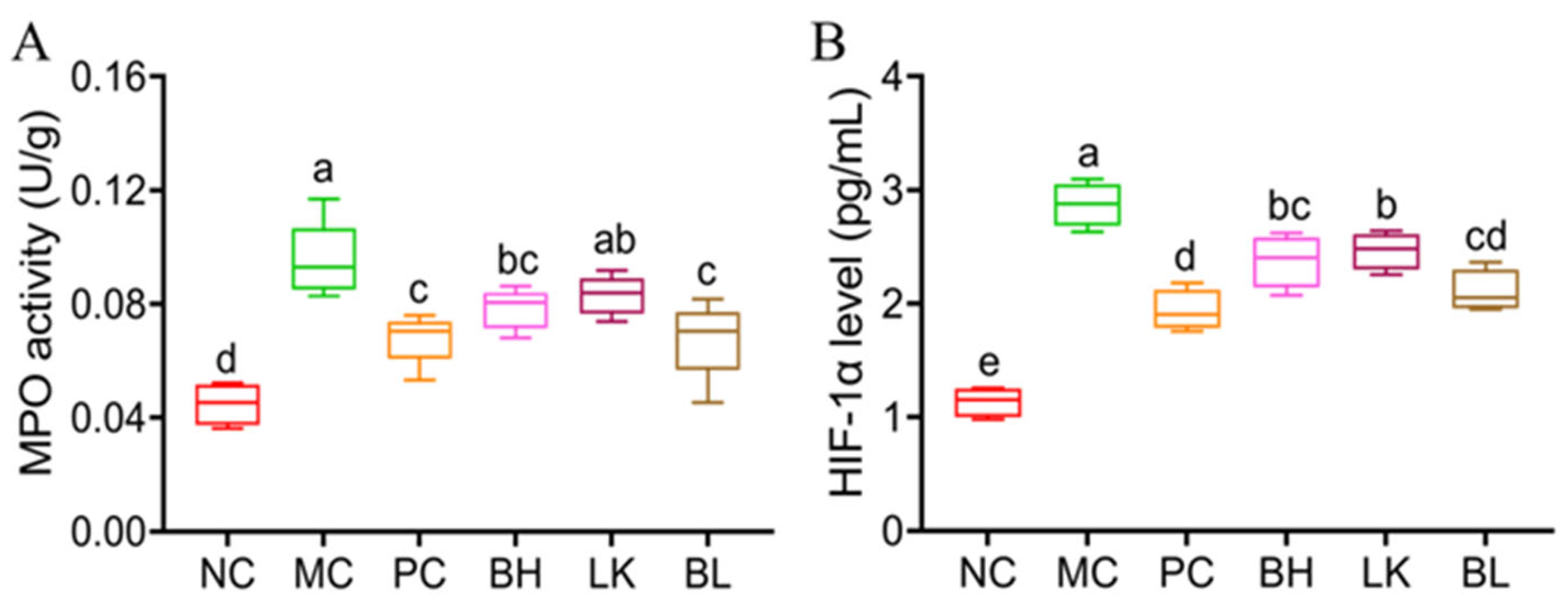
3.6. MPO Activity and HIF-1α Levels
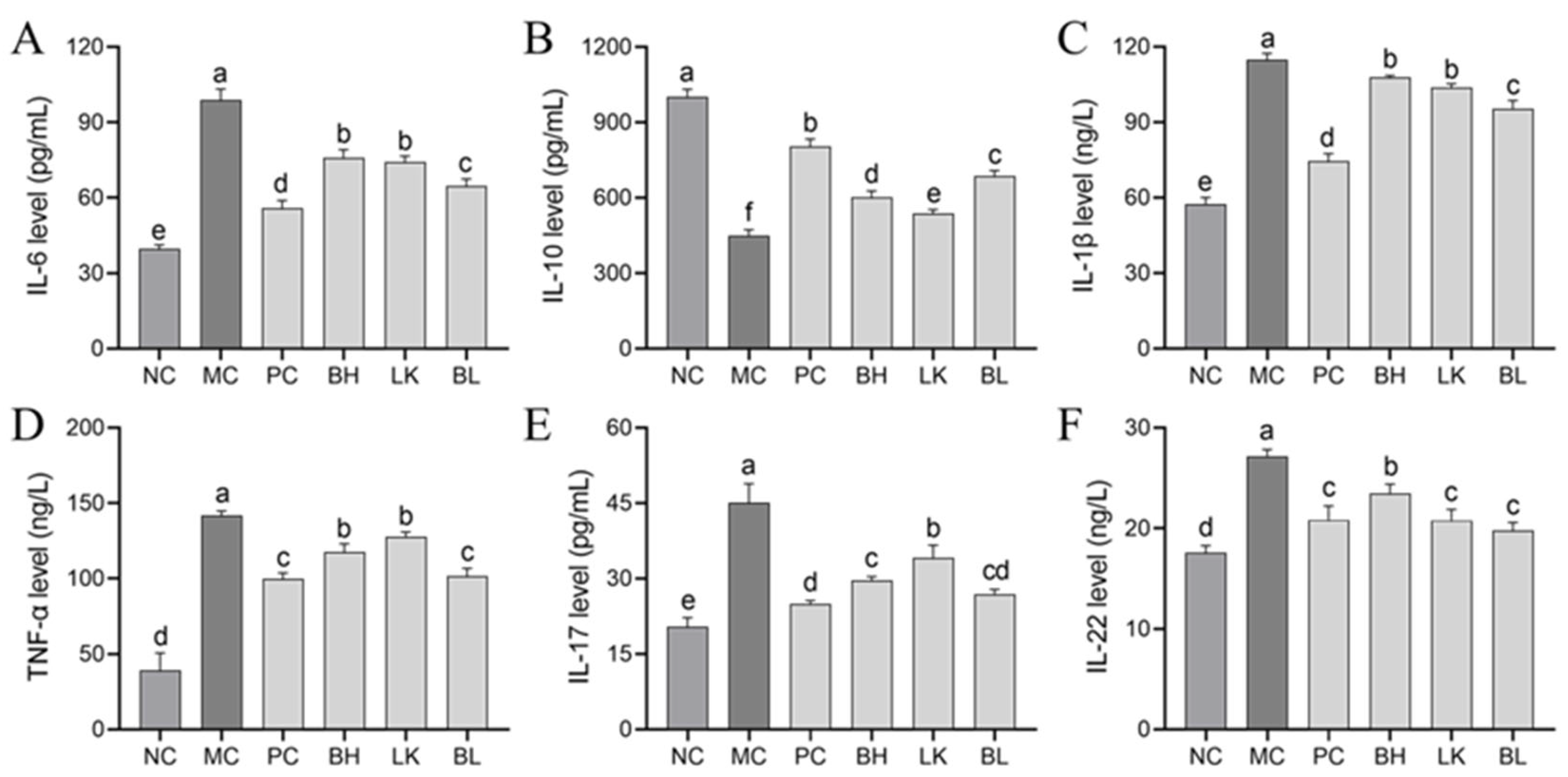
3.7. Cytokine Levels
3.8. Tight Junction Protein Expression
3.9. NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation
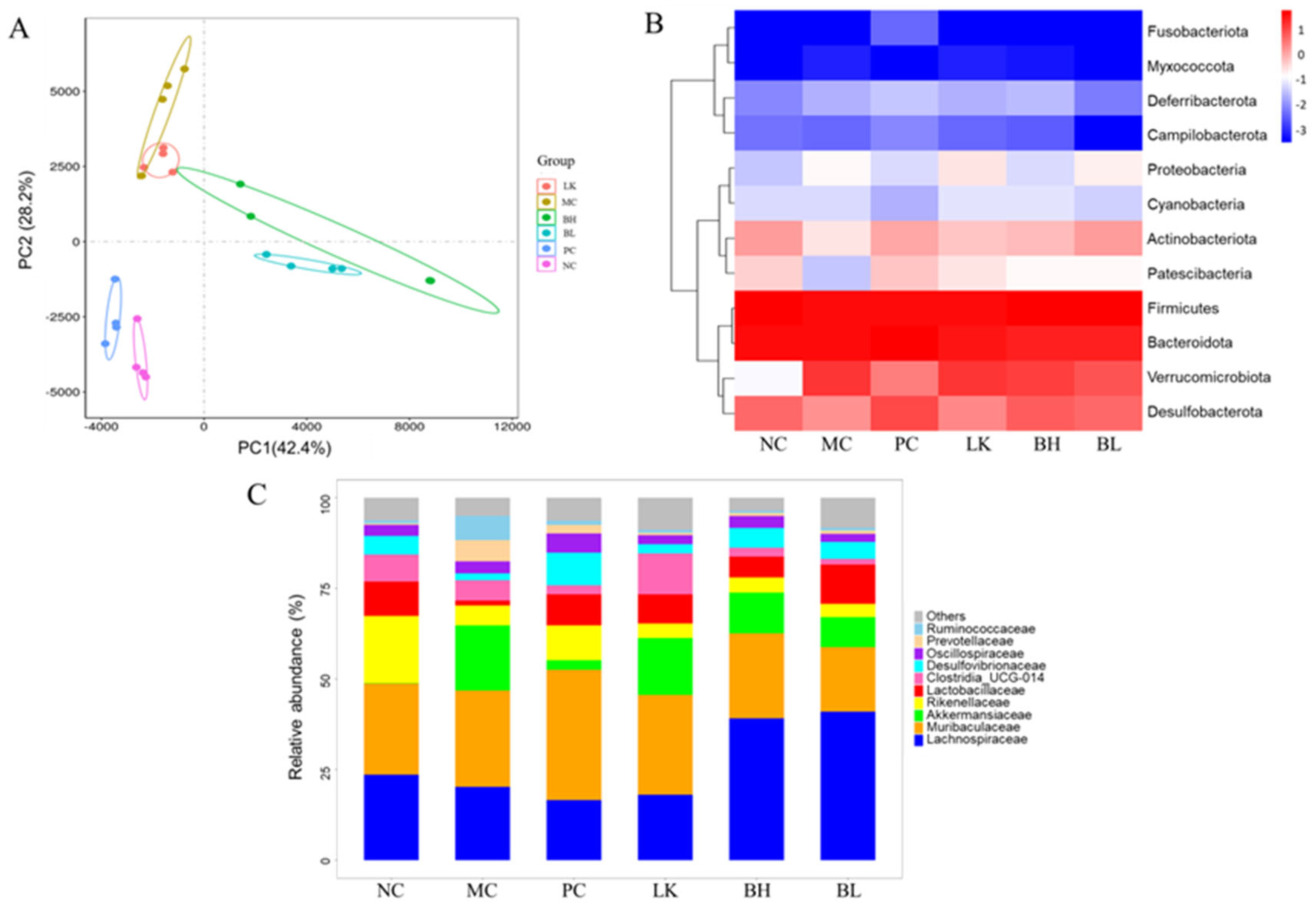
3.10. Composition of Gut Microbiota
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gonda, T.A.; Tu, S.; Wang, T.C. Chronic inflammation, the tumor microenvironment and carcinogenesis. Cell Cycle 2009, 8, 2005–2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nardone, O.M.; Zammarchi, I.; Santacroce, G.; Ghosh, S.; Iacucci, M. Inflammation-driven colorectal cancer associated with colitis: From pathogenesis to changing therapy. Cancers 2023, 15, 2389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feagins, L.A.; Souza, R.F.; Spechler, S.J. Carcinogenesis in IBD: Potential targets for the prevention of colorectal cancer. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2009, 6, 297–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamichhane, P.; Maiolini, M.; Alnafoosi, O.; Hussein, S.; Alnafoosi, H.; Umbela, S.; Richardson, T.; Alla, N.; Lamichhane, N.; Subhadra, B. Colorectal cancer and probiotics: Are bugs really drugs? Cancers 2020, 12, 1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.H.; Lim, Y.J. The role of microbiome in colorectal carcinogenesis and its clinical potential as a target for cancer treatment. Intest. Res. 2022, 20, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fusco, A.; Savio, V.; Cimini, D.; D’Ambrosio, S.; Chiaromonte, A.; Schiraldi, C.; Donnarumma, G. In vitro evaluation of the most active probiotic strains able to improve the intestinal barrier functions and to prevent inflammatory diseases of the gastrointestinal system. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darbandi, A.; Mirshekar, M.; Shariati, A.; Moghadam, M.T.; Lohrasbi, V.; Asadolahi, P.; Talebi, M. The effects of probiotics on reducing the colorectal cancer surgery complications: A periodic review during 2007–2017. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 39, 2358–2367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, W.; Wang, S.; Guan, J.; Shi, J.; Evivie, S.E.; Yan, F.; Li, N.; Chen, J.; Li, B.; Huo, G. Milk fermented with Lactococcus lactis KLDS4. 0325 alleviates folate status in deficient mice. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 4571–4581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, J.; Wan, F.; Zhao, L.; Meng, X.; Li, B. Potential immunomodulatory activity of a selected strain Bifidobacterium bifidum H3-R2 as evidenced in vitro and in immunosuppressed mice. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, Y.; Wang, S.; Shi, J.; Xie, Q.; Li, N.; Guan, J.; Evivie, S.E.; Liu, F.; Li, B.; Huo, G. Effects of Lactobacillus acidophilus KLDS1. 0901 on proliferation and apoptosis of colon cancer cells. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 788040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Zhang, T.; Gao, J.; Jiang, X.; Tao, M.; Zeng, X.; Wu, Z.; Pan, D. Lactobacillus acidophilus CICC 6074 inhibits growth and induces apoptosis in colorectal cancer cells in vitro and in HT-29 cells induced-mouse model. J. Funct. Foods 2020, 75, 104290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Ding, Y.; Xu, C.; Hao, M.; Li, H.; Ding, L. Cldn-7 deficiency promotes experimental colitis and associated carcinogenesis by regulating intestinal epithelial integrity. Oncoimmunology 2021, 10, 1923910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, C.; Guo, D.; Fang, L.; Sang, T.; Wu, J.; Guo, C.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Chen, C.; Chen, J. Ganoderma lucidum polysaccharide modulates gut microbiota and immune cell function to inhibit inflammation and tumorigenesis in colon. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 267, 118231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levi-Galibov, O.; Lavon, H.; Wassermann-Dozorets, R.; Pevsner-Fischer, M.; Mayer, S.; Wershof, E.; Stein, Y.; Brown, L.E.; Zhang, W.; Friedman, G. Heat Shock Factor 1-dependent extracellular matrix remodeling mediates the transition from chronic intestinal inflammation to colon cancer. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 6245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, H.; Cai, Y.; Wang, L.; Jia, B.; Li, J.; Zhao, S.; Chu, X.; Lin, J.; Zhang, X.; Bian, Y. Berberine regulates Treg/Th17 balance to treat ulcerative colitis through modulating the gut microbiota in the colon. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.X.; Tao, Z.H.; Qian, Y.; Yu, C.Y.; Li, J.; Kang, Z.R.; Lu, S.; Xie, Y.; Hong, J.; Chen, H. ZFP90 drives the initiation of colitis-associated colorectal cancer via a microbiota-dependent strategy. Gut Microbes 2021, 13, 1917269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guarino, A.; Guandalini, S.; Vecchio, A.L. Probiotics for prevention and treatment of diarrhea. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2015, 49, S37–S45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Górska, A.; Przystupski, D.; Niemczura, M.J.; Kulbacka, J. Probiotic bacteria: A promising tool in cancer prevention and therapy. Curr. Microbiol. 2019, 76, 939–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drago, L. Probiotics and colon cancer. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thirabunyanon, M.; Boonprasom, P.; Niamsup, P. Probiotic potential of lactic acid bacteria isolated from fermented dairy milks on antiproliferation of colon cancer cells. Biotechnol. Lett. 2009, 31, 571–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Meng, L.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, F.; Fang, Y. Extracellular vesicles of Lacticaseibacillus paracasei PC-H1 induce colorectal cancer cells apoptosis via PDK1/AKT/Bcl-2 signaling pathway. Microbiol. Res. 2022, 255, 126921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosa, L.S.; Santos, M.L.; Abreu, J.P.; Balthazar, C.F.; Rocha, R.S.; Silva, H.L.; Esmerino, E.A.; Duarte, M.C.K.; Pimentel, T.C.; Freitas, M.Q. Antiproliferative and apoptotic effects of probiotic whey dairy beverages in human prostate cell lines. Food Res. Int. 2020, 137, 109450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajoka, M.S.R.; Zhao, H.; Mehwish, H.M.; Li, N.; Lu, Y.; Lian, Z.; Shao, D.; Jin, M.; Li, Q.; Zhao, L. Anti-tumor potential of cell free culture supernatant of Lactobacillus rhamnosus strains isolated from human breast milk. Food Res. Int. 2019, 123, 286–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hata, A.N.; Engelman, J.A.; Faber, A.C. The BCL2 Family: Key mediators of the apoptotic response to targeted anticancer therapeutics. Cancer Discov. 2015, 5, 475–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- West, N.R.; McCuaig, S.; Franchini, F.; Powrie, F. Emerging cytokine networks in colorectal cancer. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2015, 15, 615–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, D.; Wu, P.; Huang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Ye, J.; Huang, J. Interleukin-17: A promoter in colorectal cancer progression. Clin. Dev. Immunol. 2013, 2013, 436307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, N.S.; Lee, J.Y.; Kim, Y.T.; Kim, S.H.; Lee, J.H. Cancer-protective effect of a synbiotic combination between Lactobacillus gasseri 505 and a Cudrania tricuspidata leaf extract on colitis-associated colorectal cancer. Gut Microbes 2020, 12, 1785803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.; San Yeoh, B.; Walker, R.E.; Xiao, X.; Saha, P.; Golonka, R.M.; Cai, J.; Bretin, A.C.A.; Cheng, X.; Liu, Q. Microbiota fermentation-NLRP3 axis shapes the impact of dietary fibres on intestinal inflammation. Gut 2019, 68, 1801–1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, P.A.; Morón, B.; Becker, H.M.; Lang, S.; Atrott, K.; Spalinger, M.R.; Scharl, M.; Wojtal, K.A.; Fischbeck-Terhalle, A.; Frey-Wagner, I. Titanium dioxide nanoparticles exacerbate DSS-induced colitis: Role of the NLRP3 inflammasome. Gut 2017, 66, 1216–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ligumsky, M.; Simon, P.; Karmeli, F.; Rachmilewitz, D. Role of interleukin 1 in inflammatory bowel disease-enhanced production during active disease. Gut 1990, 31, 686–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Chai, N.; Wei, Z.; Li, Z.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, M.; Ren, J.; Xu, R.; Pang, X.; Zhang, B. YYFZBJS inhibits colorectal tumorigenesis by enhancing Tregs-induced immunosuppression through HIF-1α mediated hypoxia in vivo and in vitro. Phytomedicine 2022, 98, 153917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Zhang, H.J.; Guan, L.; Zhang, Y.N.; Li, Y.; Sun, M.J. Mechanism and therapeutic effects of Saccharomyces boulardii on experimental colitis in mice. Mol. Med. Rep. 2018, 18, 5652–5662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sui, H.; Zhao, J.; Zhou, L.; Wen, H.; Deng, W.; Li, C.; Ji, Q.; Liu, X.; Feng, Y.; Chai, N. Tanshinone IIA inhibits β-catenin/VEGF-mediated angiogenesis by targeting TGF-β1 in normoxic and HIF-1α in hypoxic microenvironments in human colorectal cancer. Cancer Lett. 2017, 403, 86–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zihni, C.; Mills, C.; Matter, K.; Balda, M.S. Tight junctions: From simple barriers to multifunctional molecular gates. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2016, 17, 564–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, G.; Tang, Q.; Ma, J.; Liu, X.; Zhou, B.; Sun, Y.; Pang, X.; Guo, Z.; Xie, R.; Liu, T. Maternal emulsifier P80 intake induces gut dysbiosis in offspring and increases their susceptibility to colitis in adulthood. Msystems 2021, 6, 10–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.B.; Uppada, S.B.; Dhawan, P. Claudin proteins, outside-in signaling, and carcinogenesis. Eur. J. Physiol. 2017, 469, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hegazy, S.K.; El-Bedewy, M.M. Effect of probiotics on pro-inflammatory cytokines and NF-κB activation in ulcerative colitis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2010, 16, 4145–4151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caruso, R.; Lo, B.C.; Núñez, G. Host-microbiota interactions in inflammatory bowel disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2020, 20, 411–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganji-Arjenaki, M.; Rafieian-Kopaei, M. Probiotics are a good choice in remission of inflammatory bowel diseases: A meta analysis and systematic review. J. Cell. Physiol. 2018, 233, 2091–2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahran, W.E.; Elsonbaty, S.M.; Moawed, F.S. Lactobacillus rhamnosus ATCC 7469 exopolysaccharides synergizes with low level ionizing radiation to modulate signaling molecular targets in colorectal carcinogenesis in rats. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 92, 384–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, A.; Shukla, G. Synbiotic (Lactobacillus rhamnosus+Lactobacillus acidophilus+inulin) attenuates oxidative stress and colonic damage in 1,2 dimethylhydrazine dihydrochloride-induced colon carcinogenesis in Sprague-Dawley rats: A long-term study. Eur. J. Cancer Prev. 2014, 23, 550–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derrien, M.; Collado, M.C.; Ben-Amor, K.; Salminen, S.; de Vos, W.M. The Mucin degrader Akkermansia muciniphila is an abundant resident of the human intestinal tract. Appl. Environ. Microb. 2008, 74, 1646–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derrien, M.; Belzer, C.; de Vos, W.M. Akkermansia muciniphila and its role in regulating host functions. Microb. Pathog. 2017, 106, 171–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allali, I.; Boukhatem, N.; Bouguenouch, L.; Hardi, H.; Boudouaya, H.A.; Cadenas, M.B.; Ouldim, K.; Amzazi, S.; Azcarate-Peril, M.A.; Ghazal, H. Gut microbiome of Moroccan colorectal cancer patients. Med. Microbiol. Immun. 2018, 207, 211–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weir, T.L.; Manter, D.K.; Sheflin, A.M.; Barnett, B.A.; Heuberger, A.L.; Ryan, E.P. Stool microbiome and metabolome differences between colorectal cancer patients and healthy adults. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e70803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Cai, K.; Xiao, Q.; He, L.; Xie, L.; Liu, Z. Akkermansia muciniphila administration exacerbated the development of colitis-associated colorectal cancer in mice. J. Cancer 2022, 13, 124–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augustus, G.J.; Ellis, N.A. Colorectal cancer disparity in African Americans: Risk factors and carcinogenic mechanisms. Am. J. Pathol. 2018, 188, 291–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yachida, S.; Mizutani, S.; Shiroma, H.; Shiba, S.; Nakajima, T.; Sakamoto, T.; Watanabe, H.; Masuda, K.; Nishimoto, Y.; Kubo, M. Metagenomic and metabolomic analyses reveal distinct stage-specific phenotypes of the gut microbiota in colorectal cancer. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 968–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shang, J.; Liu, L.; Yang, S.; Duan, B.; Xie, S.; Meng, X. A New Combination of Bifidobacterium bifidum and Lactococcus lactis Strains with Synergistic Effects Alleviates Colitis-Associated Colorectal Cancer. Foods 2024, 13, 3054. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13193054
Shang J, Liu L, Yang S, Duan B, Xie S, Meng X. A New Combination of Bifidobacterium bifidum and Lactococcus lactis Strains with Synergistic Effects Alleviates Colitis-Associated Colorectal Cancer. Foods. 2024; 13(19):3054. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13193054
Chicago/Turabian StyleShang, Jiacui, Lijun Liu, Shuo Yang, Bofan Duan, Shuiqi Xie, and Xiangchen Meng. 2024. "A New Combination of Bifidobacterium bifidum and Lactococcus lactis Strains with Synergistic Effects Alleviates Colitis-Associated Colorectal Cancer" Foods 13, no. 19: 3054. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13193054
APA StyleShang, J., Liu, L., Yang, S., Duan, B., Xie, S., & Meng, X. (2024). A New Combination of Bifidobacterium bifidum and Lactococcus lactis Strains with Synergistic Effects Alleviates Colitis-Associated Colorectal Cancer. Foods, 13(19), 3054. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13193054





