Enzymatic Preparation and Processing Properties of DPP-IV Inhibitory Peptides Derived from Wheat Gluten: Effects of Pretreatment Methods and Protease Types
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Pretreatment Methods
2.3. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy Determination
2.4. Soluble Protein Content Determination
2.5. Surface Hydrophobicity
2.6. Preparation of WGP Hydrolysates
2.7. Degree of Hydrolysis Determination
2.8. TCA-Soluble Peptide Content
2.9. DPP-IV Inhibition Assay
2.10. Foaming Properties
2.11. Emulsion Activity
2.12. Statistical Analysis
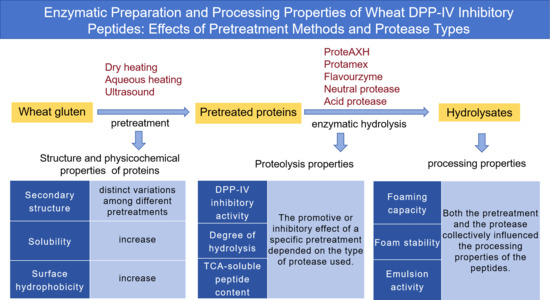
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Structure and Physicochemical Properties
3.1.1. Secondary Structure
3.1.2. Soluble Protein Content and Surface Hydrophobicity
3.2. Proteolysis Properties
3.2.1. Degree of Hydrolysis
3.2.2. TCA-Soluble Peptide Content
3.2.3. DPP-IV Inhibitory Activity
3.3. Processing Properties of the Hydrolysates
3.3.1. Foaming Properties
3.3.2. Emulsion Activity
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tanase, D.M.; Gosav, E.M.; Neculae, E.; Costea, C.F.; Ciocoiu, M.; Hurjui, L.L.; Tarniceriu, C.C.; Maranduca, M.A.; Lacatusu, C.M.; Floria, M.; et al. Role of Gut Microbiota on Onset and Progression of Microvascular Complications of Type 2 Diabetes (T2DM). Nutrients 2020, 12, 3719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rorsman, P.; Braun, M. Regulation of Insulin Secretion in Human Pancreatic Islets. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2013, 75, 155–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nongonierma, A.B.; FitzGerald, R.J. Features of Dipeptidyl Peptidase IV (DPP-IV) Inhibitory Peptides from Dietary Proteins. J. Food Biochem. 2019, 43, e12451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taga, Y.; Hayashida, O.; Kusubata, M.; Ogawa-Goto, K.; Hattori, S. Production of a Novel Wheat Gluten Hydrolysate Containing Dipeptidyl Peptidase-IV Inhibitory Tripeptides Using Ginger Protease. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2017, 81, 1823–1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nongonierma, A.B.; Cadamuro, C.; Le Gouic, A.; Mudgil, P.; Maqsood, S.; FitzGerald, R.J. Dipeptidyl Peptidase IV (DPP-IV) Inhibitory Properties of a Camel Whey Protein Enriched Hydrolysate Preparation. Food Chem. 2019, 279, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harnedy-Rothwell, P.A.; McLaughlin, C.M.; O’Keeffe, M.B.; Le Gouic, A.V.; Allsopp, P.J.; McSorley, E.M.; Sharkey, S.; Whooley, J.; McGovern, B.; O’Harte, F.P.M.; et al. Identification and Characterisation of Peptides from a Boarfish (Capros Aper) Protein Hydrolysate Displaying in Vitro Dipeptidyl Peptidase-IV (DPP-IV) Inhibitory and Insulinotropic Activity. Food Res. Int. 2020, 131, 108989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nongonierma, A.B.; FitzGerald, R.J. Prospects for the Management of Type 2 Diabetes Using Food Protein-Derived Peptides with Dipeptidyl Peptidase IV (DPP-IV) Inhibitory Activity. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2016, 8, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Zhu, L.; Wu, G.; Liu, T.; Qi, X.; Zhang, H. Food-Derived Dipeptidyl Peptidase IV Inhibitory Peptides: Production, Identification, Structure-Activity Relationship, and Their Potential Role in Glycemic Regulation. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nongonierma, A.B.; FitzGerald, R.J. An in Silico Model to Predict the Potential of Dietary Proteins as Sources of Dipeptidyl Peptidase IV (DPP-IV) Inhibitory Peptides. Food Chem. 2014, 165, 489–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacroix, I.M.E.; Li-Chan, E.C.Y. Evaluation of the Potential of Dietary Proteins as Precursors of Dipeptidyl Peptidase (DPP)-IV Inhibitors by an in Silico Approach. J. Funct. Foods 2012, 4, 403–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulug, S.K.; Jahandideh, F.; Wu, J. Novel Technologies for the Production of Bioactive Peptides. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 108, 27–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, P.-R.; Hu, F.; Ni, Z.-J.; Zhang, F.; Thakur, K.; Zhang, J.-G.; Wei, Z.-J. Effects of Phosphorylation Pretreatment and Subsequent Transglutaminase Cross-Linking on Physicochemical, Structural, and Gel Properties of Wheat Gluten. Food Chem. 2022, 392, 133296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; Li, S.; Ma, H.; Zhang, H. Mechanism Study of Multimode Ultrasound Pretreatment on the Enzymolysis of Wheat Gluten. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2018, 98, 1530–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; He, R.; Mintah, B.K.; Dabbour, M.; Qu, W.; Liu, D.; Ma, H. Proteolysis Efficiency and Structural Traits of Corn Gluten Meal: Impact of Different Frequency Modes of a Low-Power Density Ultrasound. Food Chem. 2021, 344, 128609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arrutia, F.; Puente, Á.; Riera, F.A.; Menéndez, C.; González, U.A. Influence of Heat Pre-Treatment on BSA Tryptic Hydrolysis and Peptide Release. Food Chem. 2016, 202, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Zheng, Z.; Zhu, G.; Luo, S.; Zhang, D.; Liu, F.; Shen, Y. Modification of the Structural and Functional Properties of Wheat Gluten Protein Using a Planetary Ball Mill. Food Chem. 2021, 363, 130251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, M.; Mantsch, H.H. The Use and Misuse of FTIR Spectroscopy in the Determination of Protein Structure. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 1995, 30, 95–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, X.-S.; Luo, S.-Z.; Cai, J.; Zhong, X.-Y.; Jiang, S.-T.; Zhao, Y.-Y.; Zheng, Z. Transglutaminase-Induced Gelation Properties of Soy Protein Isolate and Wheat Gluten Mixtures with High Intensity Ultrasonic Pretreatment. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2016, 31, 590–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Chen, G.; Liu, M.; Mei, X.; Yu, Q.; Kan, J. Effects of Multi-Frequency Ultrasound on Physicochemical Properties, Structural Characteristics of Gluten Protein and the Quality of Noodle. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2020, 67, 105135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.; Stephen Elmore, J.; Zhao, M.; Sun, W. Effect of Oxidation on the Gel Properties of Porcine Myofibrillar Proteins and Their Binding Abilities with Selected Flavour Compounds. Food Chem. 2020, 329, 127032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chelh, I.; Gatellier, P.; Santé-Lhoutellier, V. Technical Note: A Simplified Procedure for Myofibril Hydrophobicity Determination. Meat Sci. 2006, 74, 681–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Zheng, L.; Su, G.; Zeng, X.-A.; Sun, B.; Zhao, M. Evaluation and Exploration of Potentially Bioactive Peptides in Casein Hydrolysates against Liver Oxidative Damage in STZ/HFD-Induced Diabetic Rats. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 2393–2405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, K.; Zheng, Z.; Dai, Z. Identification of Antifreeze Peptides in Shrimp Byproducts Autolysate Using Peptidomics and Bioinformatics. Food Chem. 2022, 383, 132568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zielińska, E.; Karaś, M.; Baraniak, B. Comparison of Functional Properties of Edible Insects and Protein Preparations Thereof. LWT 2018, 91, 168–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Ma, M.; Yang, T.; Li, M.; Sun, Q. Dynamic Distribution and Transition of Gluten Proteins during Noodle Processing. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 123, 107114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.M.R.; Yu, P. Thermal Stability and Molecular Microstructure of Heat-Induced Cereal Grains, Revealed with Raman Molecular Microspectroscopy and Differential Scanning Calorimetry. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 6495–6504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scarsi, M.; Majeux, N.; Caflisch, A. Hydrophobicity at the Surface of Proteins. Proteins 1999, 37, 565–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, J.R.; Sorgentini, D.A.; Añón, M.C. Relation between Solubility and Surface Hydrophobicity as an Indicator of Modifications during Preparation Processes of Commercial and Laboratory-Prepared Soy Protein Isolates. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2000, 48, 3159–3165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schein, C.H. Solubility as a Function of Protein Structure and Solvent Components. Bio/Technology 1990, 8, 308–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossmann, L.; McClements, D.J. Current Insights into Protein Solubility: A Review of Its Importance for Alternative Proteins. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 137, 108416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, P.; Bagchi, S.; Sengupta, N. The Non-Uniform Early Structural Response of Globular Proteins to Cold Denaturing Conditions: A Case Study with Yfh1. J. Chem. Phys. 2014, 141, 205103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yvon, M.; Chabanet, C.; Pélissier, J.P. Solubility of Peptides in Trichloroacetic Acid (TCA) Solutions. Hypothesis on the Precipitation Mechanism. Int. J. Pept. Protein Res. 1989, 34, 166–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olson, B.J.S.C. Assays for Determination of Protein Concentration. Curr. Protoc. Pharmacol. 2016, 73, A.3A.1–A.3A.32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, R.; Cheng, J.; Wu, H. Discovery of Food-Derived Dipeptidyl Peptidase IV Inhibitory Peptides: A Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kokini, J.; Aken, G. van Discussion Session on Food Emulsions and Foams. Food Hydrocoll. 2006, 20, 438–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, T.; Xu, J.; Zhu, S.; Yao, X.; Guo, J.; Lv, W. Effects of Spray Drying, Freeze Drying, and Vacuum Drying on Physicochemical and Nutritional Properties of Protein Peptide Powder from Salted Duck Egg White. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 1026903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Zhao, M.; Yang, X.; Jiang, Y. Improvement on Functional Properties of Wheat Gluten by Enzymatic Hydrolysis and Ultrafiltration. J. Cereal Sci. 2006, 44, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Xiong, W.; Chen, B.; Zhu, J.; Wang, L. Enhancing the Solubility and Foam Ability of Rice Glutelin by Heat Treatment at pH12: Insight into Protein Structure. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 103, 105626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nura Ruhaya, A.H.; Sarbon, N. Characterization of Asian Swamp Eel (Monopterus sp.) Protein Hydrolysate Functional Properties Prepared Using Alcalase® Enzyme. Food Res. 2019, 4, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halim, N.R.A.; Yusof, H.M.; Sarbon, N.M. Functional and Bioactive Properties of Fish Protein Hydolysates and Peptides: A Comprehensive Review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 51, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nirmal, N.P.; Santivarangkna, C.; Rajput, M.S.; Benjakul, S.; Maqsood, S. Valorization of Fish Byproducts: Sources to End-Product Applications of Bioactive Protein Hydrolysate. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2022, 21, 1803–1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bozkurt, F.; Bekiroglu, H.; Dogan, K.; Karasu, S.; Sagdic, O. Technological and Bioactive Properties of Wheat Glutenin Hydrolysates Prepared with Various Commercial Proteases. LWT 2021, 149, 111787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wouters, A.G.B.; Rombouts, I.; Legein, M.; Fierens, E.; Brijs, K.; Blecker, C.; Delcour, J.A. Air–Water Interfacial Properties of Enzymatic Wheat Gluten Hydrolyzates Determine Their Foaming Behavior. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 55, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villamil, O.; Váquiro, H.; Solanilla, J.F. Fish Viscera Protein Hydrolysates: Production, Potential Applications and Functional and Bioactive Properties. Food Chem. 2017, 224, 160–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Pretreatment | β-Sheet (%) | α-Helix (%) | β-Turn (%) | α-Helix/β-Sheet |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 50.89 ± 0.02 c | 26.33 ± 0.14 b | 22.78 ± 0.14 b | 0.52 ± 0.00 b |
| DHT | 49.82 ± 0.29 d | 26.88 ± 0.11 a | 23.30 ± 0.18 a | 0.54 ± 0.01 a |
| AHT | 52.09 ± 0.31 a | 25.33 ± 0.08 d | 22.58 ± 0.23 b | 0.49 ± 0.00 d |
| UST | 51.36 ± 0.22 b | 26.00 ± 0.18 c | 22.64 ± 0.04 b | 0.51 ± 0.01 c |
| Protease | Pretreatment Method | Foaming Capacity (%) | Foam Stability (%) | Emulsion Activity (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ProteAXH | DHT | 126.00 ± 1.73 Fb | 10.07 ± 1.96 Ec | <10 |
| AHT | 106.67 ± 2.89 Gc | 10.89 ± 2.37 Ec | <10 | |
| UST | 139.00 ± 3.61 Ea | 16.52 ± 1.50 Db | <10 | |
| Control | 113.33 ± 7.64 Gc | 23.43 ± 2.17 Ca | <10 | |
| Protamex | DHT | 214.33 ± 4.04 Db | 35.15 ± 2.78 Aa | 49.82 ± 0.30 Ba |
| AHT | 216.00 ± 5.29 Db | 10.51 ± 1.31 Ed | 26.67 ± 1.61 Eb | |
| UST | 253.00 ± 5.57 ABa | 20.95 ± 0.31 Cc | 51.40 ± 0.80 Ba | |
| Control | 257.33 ± 0.58 Aa | 31.09 ± 0.83 Bb | 51.05 ± 0.53 Ba | |
| Flavourzyme | DHT | 245.67 ± 4.04 BCb | 17.23 ± 0.34 Da | 54.21 ± 1.39 Aa |
| AHT | 252.00 ± 3.46 ABa | 9.13 ± 0.76 Eb | 38.60 ± 1.22 Cb | |
| UST | 245.33 ± 2.52 BCb | 10.20 ± 2.09 Eb | 36.14 ± 0.61 Dc | |
| Control | 238.67 ± 1.15 Cc | 9.92 ± 1.39 Eb | 35.44 ± 1.22 Dc |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, R.; Lu, S.; Li, S.; Shen, H.; Wang, Y.; Gao, Y.; Shen, X.; Wang, F.; Wu, J.; Liu, W.; et al. Enzymatic Preparation and Processing Properties of DPP-IV Inhibitory Peptides Derived from Wheat Gluten: Effects of Pretreatment Methods and Protease Types. Foods 2024, 13, 216. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13020216
Zhao R, Lu S, Li S, Shen H, Wang Y, Gao Y, Shen X, Wang F, Wu J, Liu W, et al. Enzymatic Preparation and Processing Properties of DPP-IV Inhibitory Peptides Derived from Wheat Gluten: Effects of Pretreatment Methods and Protease Types. Foods. 2024; 13(2):216. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13020216
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Rui, Shuwen Lu, Shaozhen Li, Huifang Shen, Yao Wang, Yang Gao, Xinting Shen, Fei Wang, Jiawu Wu, Wenhui Liu, and et al. 2024. "Enzymatic Preparation and Processing Properties of DPP-IV Inhibitory Peptides Derived from Wheat Gluten: Effects of Pretreatment Methods and Protease Types" Foods 13, no. 2: 216. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13020216
APA StyleZhao, R., Lu, S., Li, S., Shen, H., Wang, Y., Gao, Y., Shen, X., Wang, F., Wu, J., Liu, W., Chen, K., Yao, X., & Li, J. (2024). Enzymatic Preparation and Processing Properties of DPP-IV Inhibitory Peptides Derived from Wheat Gluten: Effects of Pretreatment Methods and Protease Types. Foods, 13(2), 216. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13020216