Effects of Discharge Parameters on the Thawing Characteristics and Physicochemical Properties of Beef in a Dielectric Barrier Discharge (DBD) System
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Materials and Device
2.2. Experimental Method
2.3. Measurement of Electric Field Discharge Characteristics
2.4. Specific Energy Consumption
2.5. Water-Holding Capacity (WHC)
2.5.1. Thawing Loss Determination
2.5.2. Centrifuge Loss Determination
2.5.3. Cooking Loss Measurement
2.6. Color Measurement
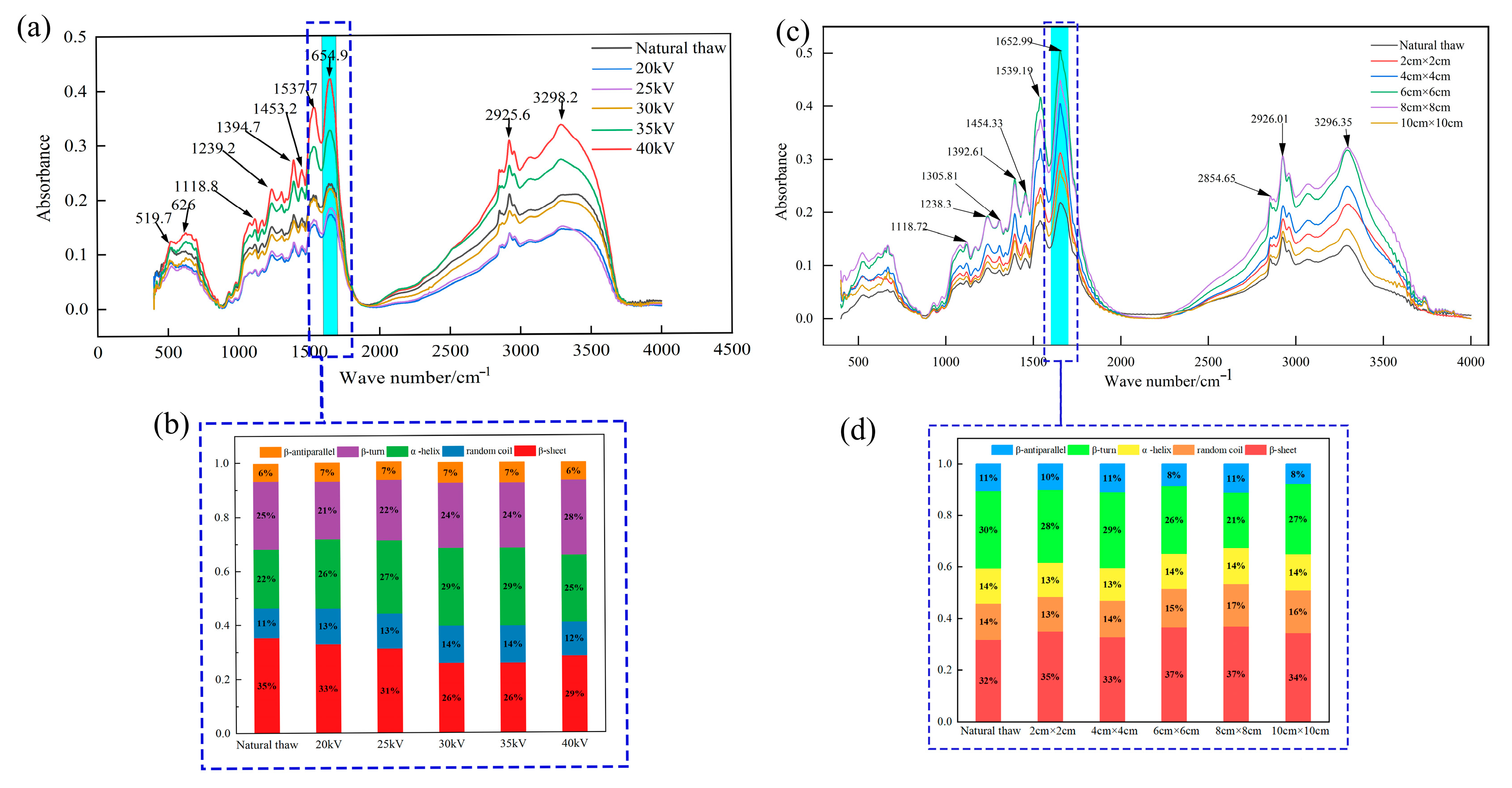
2.7. Fourier Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR) and Protein Secondary Structure Determination
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
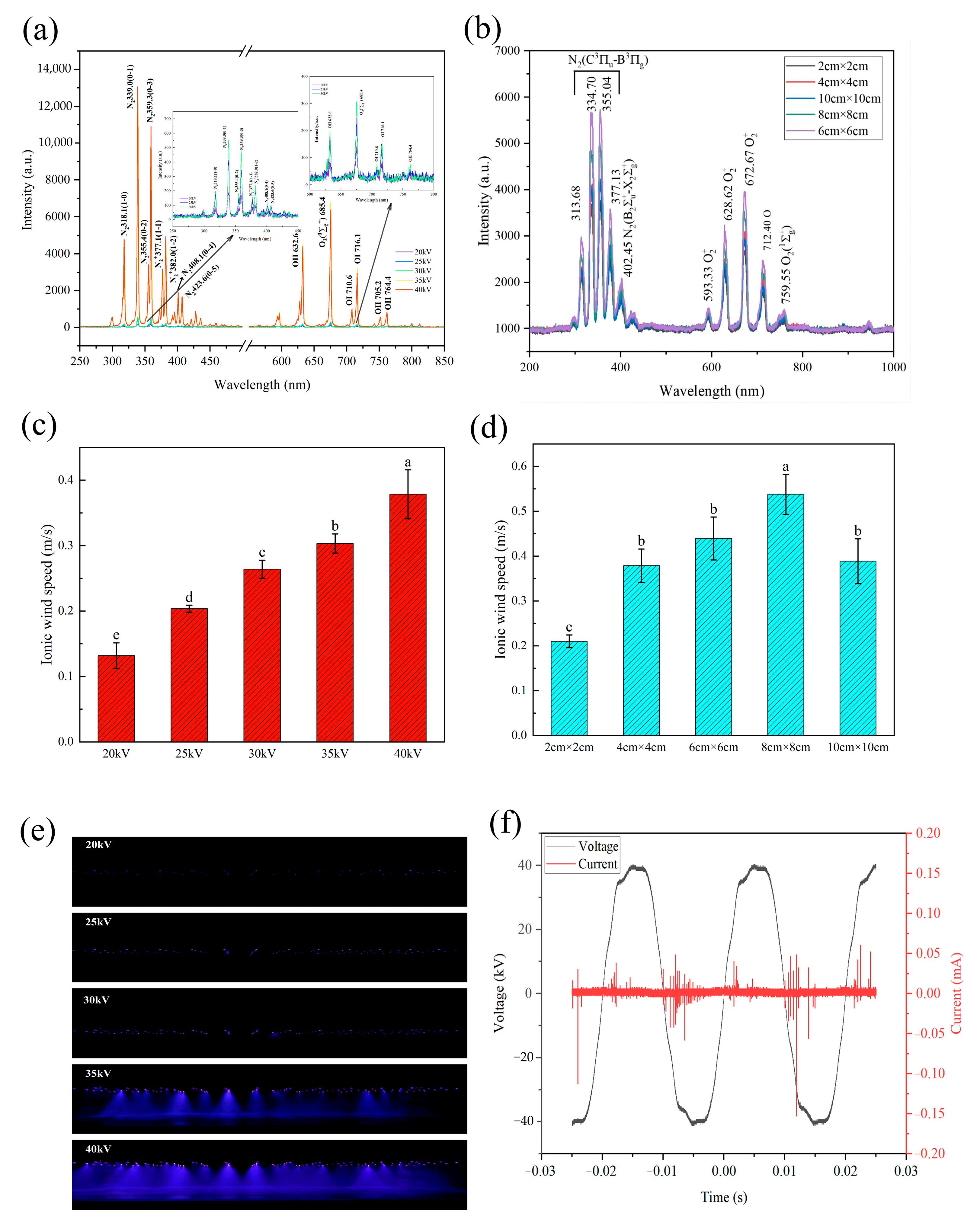
3.1. Plasma Emission Spectrum
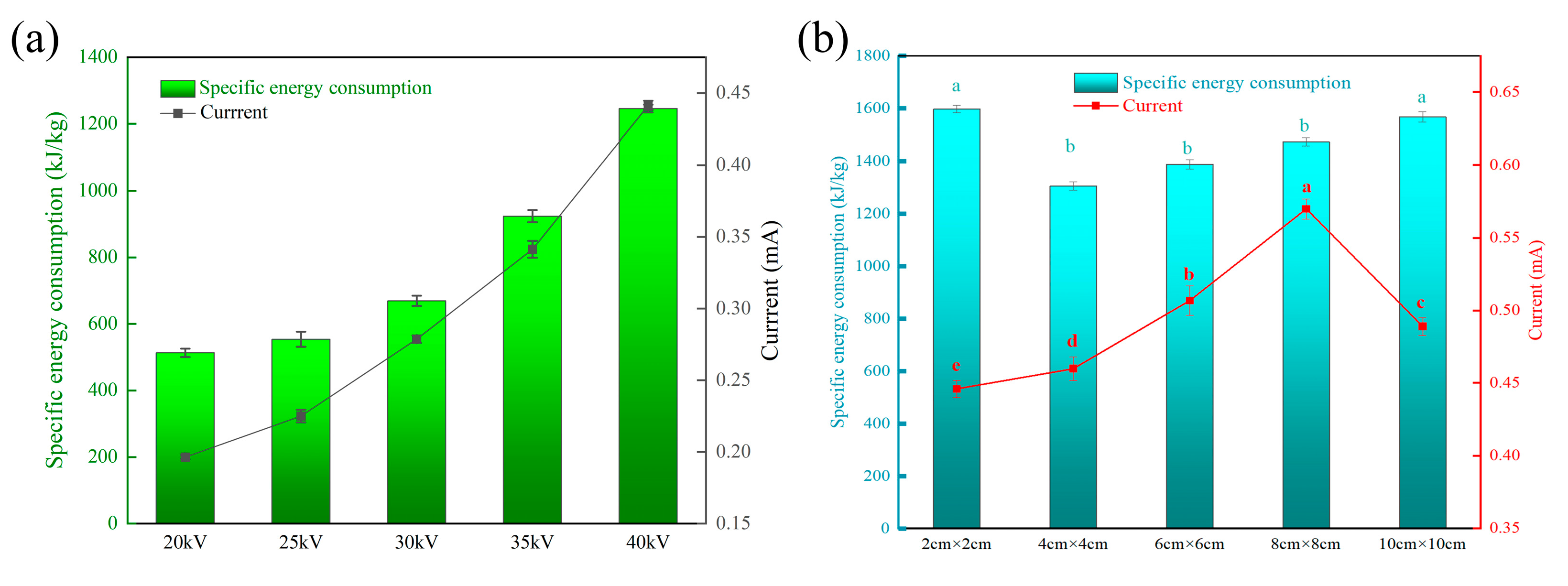
3.2. Specific Energy Consumption Analysis
3.3. Thawing Time and Central Temperature
3.4. WHC
3.5. Color
3.6. Protein Analysis
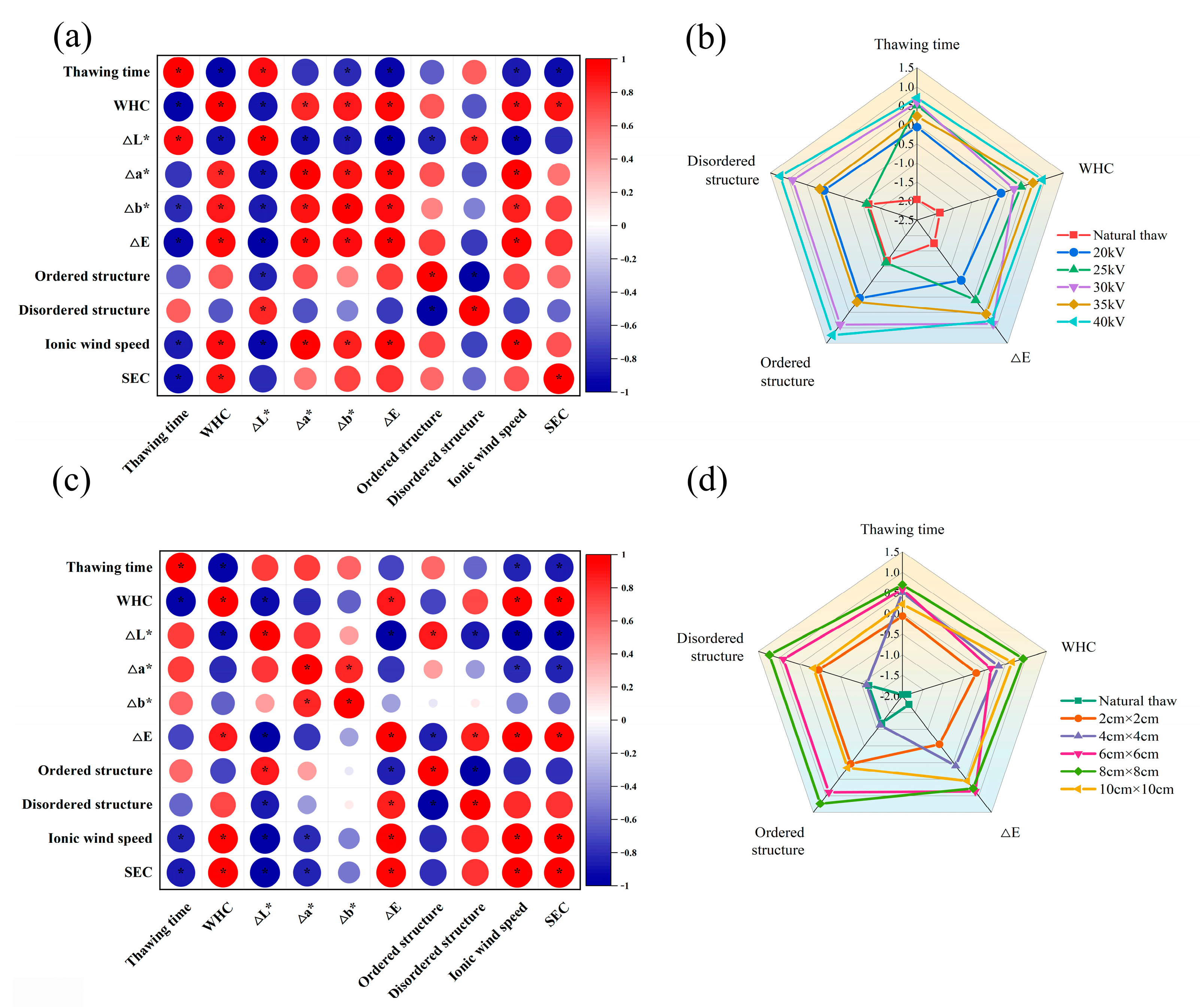
3.7. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wu, G. Important roles of dietary taurine, creatine, carnosine, anserine and 4-hydroxyproline in human nutrition and health. Amino Acids 2020, 52, 329–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, Y.; Xie, J. Quality of Cuttlefish as Affected by Different Thawing Methods. Int. J. Food Prop. 2022, 25, 33–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viji, P.; Rao, B.M.; Debbarma, J.; Ravishankar, C.N. Research developments in the applications of microwave energy in fish processing: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 123, 222–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, S.; Pu, Y.; Muhammad, A.I.; Hang, M.; Liu, D.; Ye, T. Ultrasound-assisted thawing of mango pulp: Effect on thawing rate, sensory, and nutritional properties. Food Chem. 2019, 286, 576–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.-X.; Sun, P.; Jia, J.-Z.; Cai, L.-Y.; Li, J.-R.; Lv, Y.-F. Effect of low frequency ultrasound thawing method on the quality characteristics of Peru squid (Dosidicus gigas). Food Sci. Technol. Int. 2019, 25, 171–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, T.; Ando, Y. Evaluation of heating uniformity and quality attributes during vacuum microwave thawing of frozen apples. Lwt-Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 150, 111997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Liu, R.; Tatsumi, E.; Nirasawa, S.; Liu, H. Factors affecting the thawing characteristics and energy consumption of frozen pork tenderloin meat using high-voltage electrostatic field. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2014, 22, 110–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahbari, M.; Hamdami, N.; Mirzaei, H.; Jafari, S.M.; Kashaninejad, M.; Khomeiri, M. Effects of high voltage electric field thawing on the characteristics of chicken breast protein. J. Food Eng. 2018, 216, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Guo, Z.; Wang, B.; Liu, J.; Zhang, M. Effect of high-voltage electrostatic field-assisted freeze-thaw pretreatment on the microwave freeze drying process of hawthorn. Dry. Technol. 2024, 42, 477–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misra, N.N.; Pankaj, S.K.; Segat, A.; Ishikawa, K. Cold plasma interactions with enzymes in foods and model systems. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 55, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roobab, U.; Chacha, J.S.; Abida, A.; Rashid, S.; Madni, G.M.; Lorenzo, J.M.; Zeng, X.-A.; Aadil, R.M. Emerging Trends for Nonthermal Decontamination of Raw and Processed Meat: Ozonation, High-Hydrostatic Pressure and Cold Plasma. Foods 2022, 11, 2173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.-H.; Chen, L.; Zhao, S.; Huang, Y.; Zeng, X.-A.; Aadil, R.M. Inactivation efficacy and mechanisms of atmospheric cold plasma on Alicyclobacillus acidoterrestris: Insight into the influence of growth temperature on survival. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 1012901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Umair, M.; Jabbar, S.; Ayub, Z.; Aadil, R.M.; Abid, M.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, L. Recent Advances in Plasma Technology: Influence of Atmospheric Cold Plasma on Spore Inactivation. Food Rev. Int. 2022, 38, 789–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makari, M.; Hojjati, M.; Shahbazi, S.; Askari, H. Elimination of Aspergillus flavus from Pistachio Nuts with Dielectric Barrier Discharge (DBD) Cold Plasma and Its Impacts on Biochemical Indices. J. Food Qual. 2021, 2021, 9968711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.; Choudhury, B.; Johnson, J.; Schindler-Tyka, A. Application of dielectric barrier discharge for improving food shelf life and reducing spoilage. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 19200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Fu, Y.; Xue, M.; Lan, Y.; Xi, W.; Xu, Z.; Han, W.; Wu, D.; Cheng, C. Simultaneous removal of antibiotic-resistant Escherichia coli and its resistance genes by dielectric barrier discharge plasma. Environ. Res. 2023, 231, 116163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, A.; Ong, A.; Beck, N.; Meschke, J.S.; Novosselov, I. Surface Virus Inactivation by Impinging Flow Nonthermal Plasma Reactor. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 2024, 52, 1129–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalvi-Isfahan, M.; Havet, M.; Hamdami, N.; Le-Bail, A. Recent advances of high voltage electric field technology and its application in food processing: A review with a focus on corona discharge and static electric field. J. Food Eng. 2023, 353, 111551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, D.; Liu, J.; Wang, J.; Chen, Q.; Liu, Q.; Sun, F.; Kong, B. Ultrasound-assisted plasma-activated water thawing of porcine longissimus dorsi: Effects on physicochemical, thermal stability, rheological, and structural properties of myofibrillar protein. Food Chem. 2024, 459, 140430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, D.; Quan, C.; Xi, Q.; Han, R.; Li, P.; Du, Q.; Yang, Y.; Sun, J.; Tamplin, M.; Wang, J. Effects of ultrasound-assisted slightly acidic electrolyzed water thawing on myofibrillar protein conformation and gel properties of chicken breasts. Food Chem. 2023, 404, 134738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Lin, H.; Guan, W.; Song, Y.; He, X.; Zhang, D. Effect of static magnetic field-assisted thawing on the quality, water status, and myofibrillar protein characteristics of frozen beef steaks. Food Chem. 2024, 436, 137709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, H.; Jin, Y.; Zhang, X.; Yang, N.; Xu, X. Influence of pulsed electric field on thawing of frozen pork: Physical properties, fat oxidation and protein structure. Food Biosci. 2023, 56, 103175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Shi, W.; Wang, Y.; Meng, X.; Dabbour, M.; Mintah, B.K.; Chen, X.; Chen, X.; He, R.; Ma, H. Mono-frequency ultrasonic-assisted thawing of frozen goose meat Influence on thawing efficiency, product quality and microstructure. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2023, 98, 106489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, X.; Kong, B.; Liu, J.; Diao, X.; Liu, Q. Influence of different thawing methods on physicochemical changes and protein oxidation of porcine longissimus muscle. Lwt-Food Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 280–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, C.H.; Cheng, H.; Yu, H.J.; Mei, J.; Xie, J. Effect of multi-frequency ultrasound assisted thawing on the quality of large yellow croaker (Larimichthys crocea). Ultrason. Sonochem. 2022, 82, 105907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, S.; Li, X.; Wang, H.; Mehmood, W.; Zhong, M.; Zhang, C.; Blecker, C. Effects of low voltage electrostatic field thawing on the changes in physicochemical properties of myofibrillar proteins of bovine Longissimus dorsi muscle. J. Food Eng. 2019, 261, 140–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Ding, C.; Lu, J.; Wang, H.; Bao, Y.; Han, B.; Duan, S.; Song, Z.; Chen, H. Influence of electrohydrodynamics on the drying characteristics and volatile components of iron stick yam. Food Chem. -X 2023, 20, 101026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, W.; Sun, D.-W.; Pu, H.; Wei, Q. Heterospectral two-dimensional correlation analysis with near-infrared hyperspectral imaging for monitoring oxidative damage of pork myofibrils during frozen storage. Food Chem. 2018, 248, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, S.; Kim, H.J.; Park, S.; Yong, H.I.; Choe, J.H.; Jeon, H.-J.; Choe, W.; Jo, C. The use of atmospheric pressure plasma-treated water as a source of nitrite for emulsion-type sausage. Meat Sci. 2015, 108, 132–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Zhang, D.; Liu, H.; Wang, Z.; Hui, T. Potential Alternative to Nitrite in Roasted Lamb for Sensory Attributes: Atmospheric Nonthermal Plasma Treatment. Foods 2021, 10, 1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayasena, D.D.; Kim, H.J.; Yong, H.I.; Park, S.; Kim, K.; Choe, W.; Jo, C. Flexible thin-layer dielectric barrier discharge plasma treatment of pork butt and beef loin: Effects on pathogen inactivation and meat-quality attributes. Food Microbiol. 2015, 46, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grosse, S.; Angland, D. Parametric investigation of the fluid mechanic performance of an AC dielectric barrier discharge plasma actuator. J. Phys. D-Appl. Phys. 2020, 53, 455202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoeft, H.; Kettlitz, M.; Weltmann, K.D.; Brandenburg, R. The bidirectional character of O2 concentration in pulsed dielectric barrier discharges in O2N2 gas mixtures. J. Phys. D-Appl. Phys. 2014, 47, 455202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, J.-B.; Zhang, J.-S.; Bhandari, B.; Xiao, H.-W.; Ding, C.-J.; Peng, W.-J.; Fang, X.-M. Effects of dielectric barrier discharge (DBD) plasma on the drying kinetics, color, phenolic compounds, energy consumption and microstructure of lotus pollen. Dry. Technol. 2022, 40, 3100–3114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, L.; Cao, M.; Regenstein, J.; Cao, A. Recent Advances in Food Thawing Technologies. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2019, 18, 953–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, S.; Lee, J.; Lim, Y.; Choe, W.; Yong, H.I.; Jo, C. Direct infusion of nitrite into meat batter by atmospheric pressure plasma treatment. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2017, 39, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stadnik, J.; Dolatowski, Z.J.; Baranowska, H.M. Effect of ultrasound treatment on water holding properties and microstructure of beef (m. semimembranosus) during ageing. Lwt-Food Sci. Technol. 2008, 41, 2151–2158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henriott, M.L.; Herrera, N.J.; Ribeiro, F.A.; Hart, K.B.; Bland, N.A.; Eskridge, K.; Calkins, C.R. Impact of myoglobin oxygenation state prior to frozen storage on color stability of thawed beef steaks through retail display. Meat Sci. 2020, 170, 108232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, G.; Liu, H.; Nirasawa, S.; Liu, H. Effects of high-voltage electrostatic field treatment on the thawing rate and post-thawing quality of frozen rabbit meat. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2017, 41, 348–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Zhang, D.; Xie, F.; Li, X.; Schroyen, M.; Chen, L.; Hou, C. Changes in water holding capacity of chilled fresh pork in controlled freezing-point storage assisted by different modes of electrostatic field action. Meat Sci. 2023, 204, 109269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holman, B.W.B.; van de Ven, R.J.; Mao, Y.; Coombs, C.E.O.; Hopkins, D.L. Using instrumental (CIE and reflectance) measures to predict consumers’ acceptance of beef colour. Meat Sci. 2017, 127, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, B.; Yun, H.; Jung, S.; Jung, Y.; Jung, H.; Choe, W.; Jo, C. Effect of atmospheric pressure plasma on inactivation of pathogens inoculated onto bacon using two different gas compositions. Food Microbiol. 2011, 28, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.-J.; Yong, H.I.; Park, S.; Choe, W.; Jo, C. Effects of dielectric barrier discharge plasma on pathogen inactivation and the physicochemical and sensory characteristics of pork loin. Curr. Appl. Phys. 2013, 13, 1420–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candogan, K.; Altuntas, E.G.; Igci, N. Authentication and Quality Assessment of Meat Products by Fourier-Transform Infrared (FTIR) Spectroscopy. Food Eng. Rev. 2021, 13, 66–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vahed, S.; Ahangar, H.A.; Nourani, M.; Dinani, S.T.; Nasr-Esfahani, M. Assessment of electrohydrodynamic (EHD) pretreatment effects on functional and structural properties of protein isolate from sprouted mung bean. J. Food Process Eng. 2023, 46, e14284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Thawing Loss (%) | Cooking Loss (%) | Centrifuge Loss (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Natural thaw | 6.00 ± 0.02 d | 49.96 ± 0.69 a | 13.05 ± 0.03 a |
| 20 kV | 4.79 ± 0.24 c | 44.86 ± 0.54 b | 9.55 ± 0.85 b |
| 25 kV | 4.87 ± 0.03 c | 44.60 ± 0.35 bc | 10.49 ± 0.41 bc |
| 30 kV | 5.42 ± 0.11 b | 43.09 ± 0.47 bc | 9.49 ± 0.31 bc |
| 35 kV | 5.75 ± 0.03 ab | 43.02 ± 0.62 c | 10.40 ± 0.44 c |
| 40 kV | 4.91 ± 0.09 a | 43.22 ± 0.22 c | 10.17 ± 0.63 c |
| 2 cm × 2 cm | 5.34 ± 0.03 ab | 44.00 ± 0.07 ab | 10.85 ± 0.05 ab |
| 4 cm × 4 cm | 4.98 ± 0.05 b | 43.18 ± 0.02 b | 10.46 ± 0.08 ab |
| 6 cm × 6 cm | 4.80 ± 0.05 b | 44.79 ± 0.06 ab | 9.57 ± 0.08 bc |
| 8 cm × 8 cm | 4.18 ± 0.03 b | 44.20 ± 0.09 ab | 8.58 ± 0.01 d |
| 10 cm × 10 cm | 5.10 ± 0.04 b | 44.47 ± 0.02 ab | 8.14 ± 0.09 cd |
| Natural thaw | −3.85 ± 0.21 a | 1.32 ± 0.53 c | 1.35 ± 0.54 a | 4.30 ± 0.53 e |
| 20 kV | −3.92 ± 0.43 b | 2.54 ± 0.24 b | 1.83 ± 0.42 a | 5.09 ± 0.12 e |
| 25 kV | −4.27 ± 0.25 bc | 3.07 ± 0.15 ab | 1.95 ± 0.17 a | 5.61 ± 0.34 c |
| 30 kV | −5.19 ± 0.53 cd | 3.01 ± 0.45 a | 2.17 ± 0.04 a | 6.38 ± 0.27 a |
| 35 kV | −6.83 ± 0.21 d | 2.90 ± 0.25 b | 2.21 ± 0.11 a | 7.76 ± 0.20 c |
| 40 kV | −8.12 ± 0.28 e | 2.88 ± 0.46 c | 2.19 ± 0.06 a | 8.88 ± 0.08 b |
| 2 cm × 2 cm | −6.75 ± 0.58 b | 1.38 ± 0.21 c | 1.72 ± 0.23 b | 7.11 ± 0.47 d |
| 4 cm × 4 cm | −7.18 ± 0.71 | 2.75 ± 0.06 b | 2.29 ± 0.38 a | 8.61 ± 0.60 c |
| 6 cm × 6 cm | −9.56 ± 0.13 e | 3.44 ± 0.23 a | 2.37 ± 0.09 a | 10.43 ± 0.12 a |
| 8 cm × 8 cm | −9.19 ± 0.37 de | 3.81 ± 0.34 a | 2.30 ± 0.19 a | 10.22 ± 0.19 ab |
| 10 cm × 10 cm | −8.61 ± 0.38 cd | 3.48 ± 0.24 a | 2.72 ± 0.27 a | 9.69 ± 0.28 b |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, J.; Zhao, R.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, H.; Song, Z.; Xing, R.; Lu, J.; Ding, C. Effects of Discharge Parameters on the Thawing Characteristics and Physicochemical Properties of Beef in a Dielectric Barrier Discharge (DBD) System. Foods 2024, 13, 3360. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13213360
Zhang J, Zhao R, Zhang Y, Wang H, Song Z, Xing R, Lu J, Ding C. Effects of Discharge Parameters on the Thawing Characteristics and Physicochemical Properties of Beef in a Dielectric Barrier Discharge (DBD) System. Foods. 2024; 13(21):3360. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13213360
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Jie, Rui Zhao, Yaming Zhang, Huixin Wang, Zhiqing Song, Ru Xing, Jingli Lu, and Changjiang Ding. 2024. "Effects of Discharge Parameters on the Thawing Characteristics and Physicochemical Properties of Beef in a Dielectric Barrier Discharge (DBD) System" Foods 13, no. 21: 3360. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13213360
APA StyleZhang, J., Zhao, R., Zhang, Y., Wang, H., Song, Z., Xing, R., Lu, J., & Ding, C. (2024). Effects of Discharge Parameters on the Thawing Characteristics and Physicochemical Properties of Beef in a Dielectric Barrier Discharge (DBD) System. Foods, 13(21), 3360. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13213360





