Bitter Perception and Effects of Foods Rich in Bitter Compounds on Human Health: A Comprehensive Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. The Perception Mechanism of Bitterness
2.1. Bitter Receptors
2.2. Bitter Signal Delivery Pathway
2.3. Bitterness Perception and Health
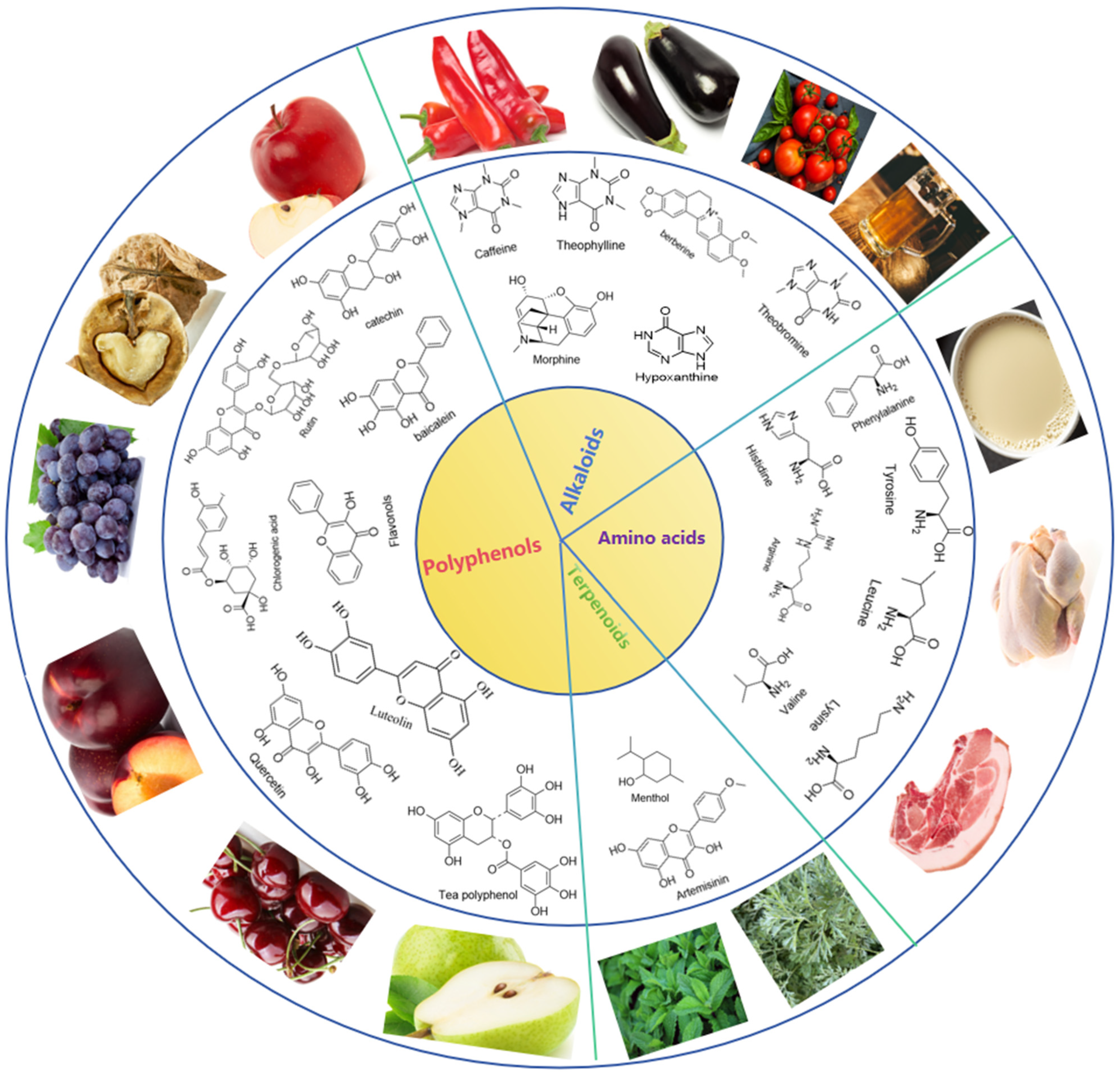
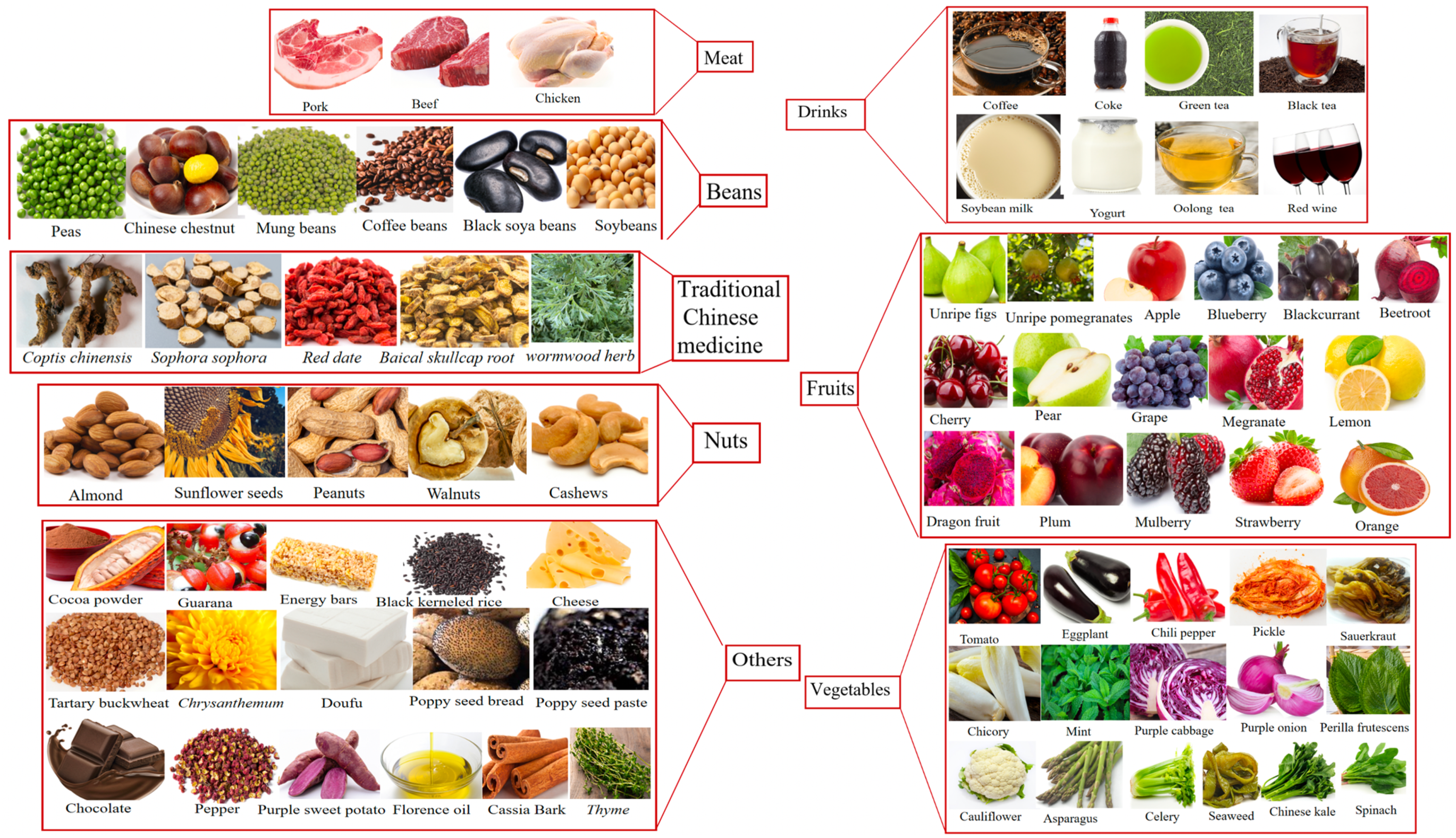
3. Bitter Compounds
3.1. Alkaloids
3.2. Polyphenols
3.3. Terpenoids
3.4. Amino Acids
4. Health Benefits of Bitter Compounds on the Human Body
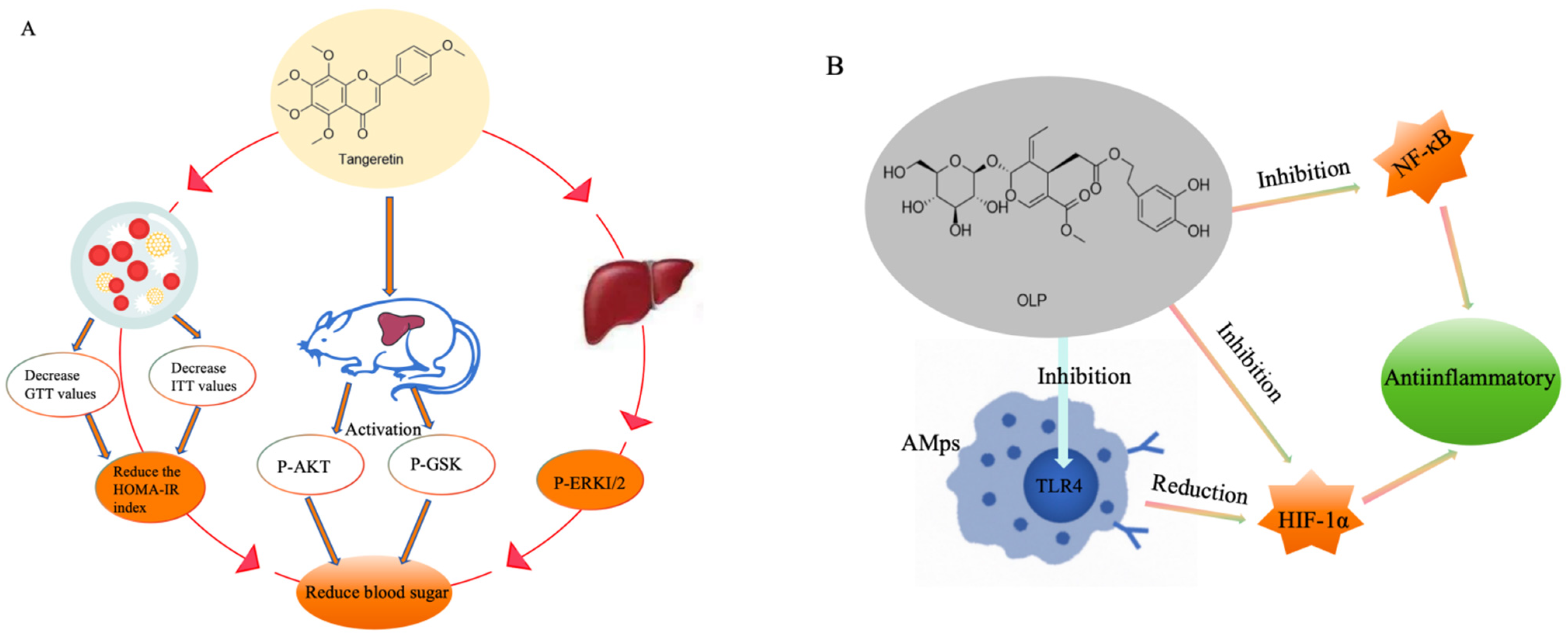
4.1. Prevent Hyperlipidemia, High Blood Pressure, and High Blood Sugar
4.2. Anti-Inflammatory
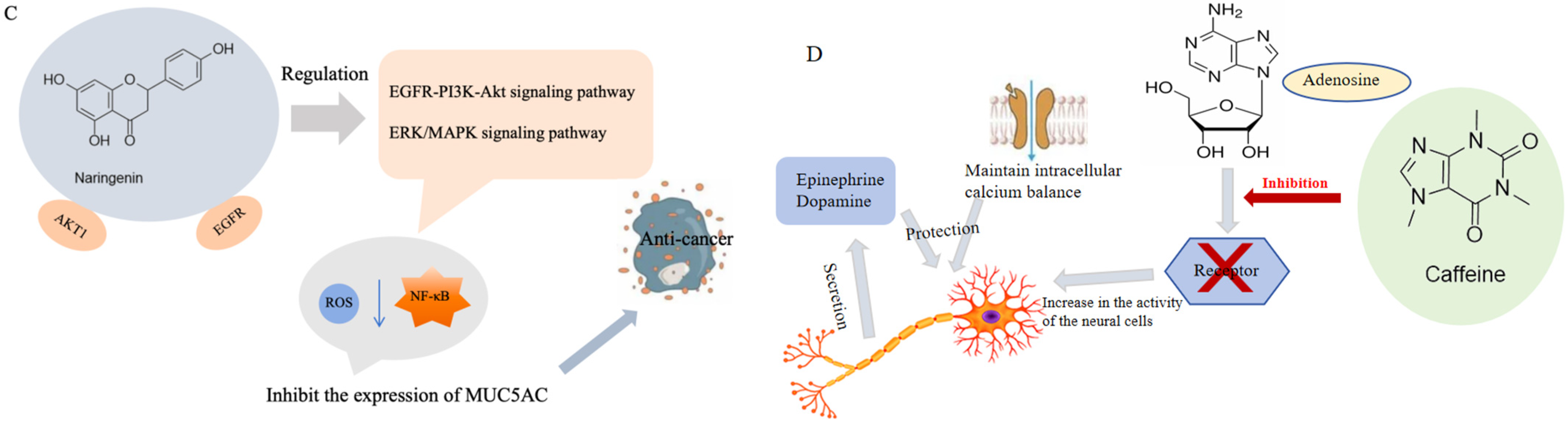
4.3. Antitumor
4.4. Antibacterial
4.5. Antioxidant
4.6. Neuroprotective Effect
5. Application of Bitter Taste Compounds in the Food Industry
6. Challenges and Future Trends
7. Conclusions and Outlook
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jiang, Z.; Han, Z.; Zhu, M.; Wan, X.; Zhang, L. Effects of Thermal Processing on Transformation of Polyphenols and Flavor Quality. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2023, 51, 101014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roper, S.D.; Chaudhari, N. Taste Buds: Cells, Signals and Synapses. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2017, 18, 485–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alotaibi, S.S.; Alshoaibi, D.; Alamari, H.; Albogami, S.; Khan, E.; Alshanbari, A.; Darwish, H.; Alshanqiti, B.; Alghamdi, H.; Almalki, W. Potential Significance of Medicinal Plants in Forensic Analysis: A Review. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 28, 3929–3935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paul, A.K.; Smith, C.M.; Rahmatullah, M.; Nissapatorn, V.; Wilairatana, P.; Spetea, M.; Gueven, N.; Dietis, N. Opioid Analgesia and Opioid-Induced Adverse Effects: A Review. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuo, Y.; Akita, K.; Taguchi, H.; Fujii, S.; Yoshie-Stark, Y.; Araki, T. Utilization and Evaluation of Citrus Natsudaidai Peel Waste as a Source of Natural Food Additives. Food Chem. 2022, 373, 131464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortés, V.; Talens, P.; Barat, J.M.; Lerma-García, M.J. Discrimination of Intact Almonds According to Their Bitterness and Prediction of Amygdalin Concentration by Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2019, 148, 236–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolahdouzan, M.; Hamadeh, M.J. The Neuroprotective Effects of Caffeine in Neurodegenerative Diseases. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2017, 23, 272–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metwally, D.M.; Alajmi, R.A.; El-Khadragy, M.F.; Yehia, H.M.; AL-Megrin, W.A.; Akabawy, A.M.A.; Amin, H.K.; Abdel Moneim, A.E. Chlorogenic Acid Confers Robust Neuroprotection against Arsenite Toxicity in Mice by Reversing Oxidative Stress, Inflammation, and Apoptosis. J. Funct. Foods 2020, 75, 104202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lossow, K.; Hübner, S.; Roudnitzky, N.; Slack, J.P.; Pollastro, F.; Behrens, M.; Meyerhof, W. Comprehensive Analysis of Mouse Bitter Taste Receptors Reveals Different Molecular Receptive Ranges for Orthologous Receptors in Mice and Humans. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 15358–15377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyerhof, W.; Batram, C.; Kuhn, C.; Brockhoff, A.; Chudoba, E.; Bufe, B.; Appendino, G.; Behrens, M. The Molecular Receptive Ranges of Human TAS2R Bitter Taste Receptors. Chem. Senses 2010, 35, 157–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, K.; Guo, J.; Bu, B.; Pan, Y.; Li, J.; Liu, L.; Luo, M.; Deng, L. Naringin as a Plant-Derived Bitter Tastant Promotes Proliferation of Cultured Human Airway Epithelial Cells via Activation of TAS2R Signaling. Phytomedicine 2021, 84, 153491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- TAS2R38 Bitter Taste Receptor and Attainment of Exceptional Longevity|Scientific Reports. Available online: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-019-54604-1#citeas (accessed on 29 October 2024).
- Kankanamge, D.; Ubeysinghe, S.; Tennakoon, M.; Pantula, P.D.; Mitra, K.; Giri, L.; Karunarathne, A. Dissociation of the G Protein Βγ from the Gq-PLCβ Complex Partially Attenuates PIP2 Hydrolysis. J. Biol. Chem. 2021, 296, 100702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Yang, D.; Li, L.; Wang, Y.; Chen, S.; Zhao, Y.; Lin, W. Comparison of the Taste Mechanisms of Umami and Bitter Peptides from Fermented Mandarin Fish (Chouguiyu) Based on Molecular Docking and Electronic Tongue Technology. Food Funct. 2023, 14, 9671–9680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mikoshiba, K. IP3 Receptor/Ca2+ Channel: From Discovery to New Signaling Concepts. J. Neurochem. 2007, 102, 1426–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godinho, R.O.; Duarte, T.; Pacini, E.S.A. New Perspectives in Signaling Mediated by Receptors Coupled to Stimulatory G Protein: The Emerging Significance of cAMP Efflux and Extracellular cAMP-Adenosine Pathway. Front. Pharmacol. 2015, 6, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wooding, S.P.; Ramirez, V.A.; Behrens, M. Bitter taste receptors: Genes, evolution and health. Evol. Med. Public Health 2021, 9, 431–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huffman, M.A. Animal self-medication and ethno-medicine: Exploration and exploitation of the medicinal properties of plants. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2003, 62, 371–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, A.A.; Dotson, C.D.; Elson, A.E.; Voigt, A.; Boehm, U.; Meyerhof, W.; Steinle, N.I.; Munger, S.D. TAS2R bitter taste receptors regulate thyroid function. FASEB J. 2015, 29, 164–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, P.; Zhang, C.H.; Lifshitz, L.M.; ZhuGe, R. Extraoral bitter taste receptors in health and disease. J. Gen. Physiol. 2017, 149, 181–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Tong, H. An Overview of Bitter Compounds in Foodstuffs: Classifications, Evaluation Methods for Sensory Contribution, Separation and Identification Techniques, and Mechanism of Bitter Taste Transduction. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2023, 22, 187–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lisko, J.G.; Lee, G.E.; Kimbrell, J.B.; Rybak, M.E.; Valentin-Blasini, L.; Watson, C.H. Caffeine Concentrations in Coffee, Tea, Chocolate, and Energy Drink Flavored E-Liquids. Nicotine Tob. Res. 2017, 19, 484–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saimaiti, A.; Zhou, D.-D.; Li, J.; Xiong, R.-G.; Gan, R.-Y.; Huang, S.-Y.; Shang, A.; Zhao, C.-N.; Li, H.-Y.; Li, H.-B. Dietary Sources, Health Benefits, and Risks of Caffeine. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 63, 9648–9666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faudone, G.; Arifi, S.; Merk, D. The Medicinal Chemistry of Caffeine. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 64, 7156–7178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodda, S.; Booth, N.; McKean, J.; Chung, A.; Park, J.J.; Ware, P. Mechanisms for the Reduction of Caffeine Consumption: What, How and Why. Drug Alcohol. Depend. 2020, 212, 108024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeszka-Skowron, M.; Frankowski, R.; Zgoła-Grześkowiak, A. Comparison of Methylxantines, Trigonelline, Nicotinic Acid and Nicotinamide Contents in Brews of Green and Processed Arabica and Robusta Coffee Beans—Influence of Steaming, Decaffeination and Roasting Processes on Coffee Beans. LWT 2020, 125, 109344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cinar, Z.Ö.; Atanassova, M.; Tumer, T.B.; Caruso, G.; Antika, G.; Sharma, S.; Sharifi-Rad, J.; Pezzani, R. Cocoa and Cocoa Bean Shells Role in Human Health: An Updated Review. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2021, 103, 104115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gawron-Gzella, A.; Chanaj-Kaczmarek, J.; Cielecka-Piontek, J. Yerba Mate—A Long but Current History. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sperkowska, B.; Murawska, J.; Przybylska, A.; Gackowski, M.; Kruszewski, S.; Durmowicz, M.; Rutkowska, D. Cardiovascular Effects of Chocolate and Wine—Narrative Review. Nutrients 2021, 13, 4269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engelhardt, U.H. Tea Chemistry—What Do and What Don’t We Know?—A Micro Review. Food Res. Int. 2020, 132, 109120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, G.L.; Wang, X.; Zhang, L.; Qiu, M.H. The Sources and Mechanisms of Bioactive Ingredients in Coffee. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 3113–3126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, E.A.F.S.; da, C. Pinaffi-Langley, A.C.; de Souza Figueira, M.; Cordeiro, K.S.; Negrão, L.D.; Soares, M.J.; da Silva, C.P.; Alfino, M.C.Z.; Sampaio, G.R.; de Camargo, A.C. Effects of the Consumption of Guarana on Human Health: A Narrative Review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2022, 21, 272–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López, P.; Pereboom-de Fauw, D.P.K.H.; Mulder, P.P.J.; Spanjer, M.; de Stoppelaar, J.; Mol, H.G.J.; de Nijs, M. Straightforward Analytical Method to Determine Opium Alkaloids in Poppy Seeds and Bakery Products. Food Chem. 2018, 242, 443–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Lin, L. Alkaloids in Diet. In Handbook of Dietary Phytochemicals; Xiao, J., Sarker, S.D., Asakawa, Y., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2019; pp. 1–35. ISBN 9789811317453. [Google Scholar]
- Jakše, B.; Jakše, B.; Pajek, M.; Pajek, J. Uric Acid and Plant-Based Nutrition. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajput, A.; Sharma, R.; Bharti, R. Pharmacological Activities and Toxicities of Alkaloids on Human Health. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 48, 1407–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobhani, M.; Farzaei, M.H.; Kiani, S.; Khodarahmi, R. Immunomodulatory; Anti-Inflammatory/Antioxidant Effects of Polyphenols: A Comparative Review on the Parental Compounds and Their Metabolites. Food Rev. Int. 2021, 37, 759–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathod, N.B.; Elabed, N.; Punia, S.; Ozogul, F.; Kim, S.-K.; Rocha, J.M. Recent Developments in Polyphenol Applications on Human Health: A Review with Current Knowledge. Plants 2023, 12, 1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bondonno, N.P.; Bondonno, C.P.; Ward, N.C.; Hodgson, J.M.; Croft, K.D. The Cardiovascular Health Benefits of Apples: Whole Fruit vs. Isolated Compounds. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 69, 243–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pouille, C.L.; Ouaza, S.; Roels, E.; Behra, J.; Tourret, M.; Molinié, R.; Fontaine, J.-X.; Mathiron, D.; Gagneul, D.; Taminiau, B.; et al. Chicory: Understanding the Effects and Effectors of This Functional Food. Nutrients 2022, 14, 957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorzynik-Debicka, M.; Przychodzen, P.; Cappello, F.; Kuban-Jankowska, A.; Marino Gammazza, A.; Knap, N.; Wozniak, M.; Gorska-Ponikowska, M. Potential Health Benefits of Olive Oil and Plant Polyphenols. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, Y.C.; de Oliveira Santos, G.; Machado, N.M.; Otoboni, A.M.M.B.; Laurindo, L.F.; Bishayee, A.; Fimognari, C.; Bishayee, A.; Barbalho, S.M. Peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.) Seeds and by-Products in Metabolic Syndrome and Cardiovascular Disorders: A Systematic Review of Clinical Studies. Phytomedicine 2024, 123, 155170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, F.; Zhou, S. Phenolic Components and Health Beneficial Properties of Onions. Agriculture 2021, 11, 872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szabo, K.; Mitrea, L.; Călinoiu, L.F.; Teleky, B.-E.; Martău, G.A.; Plamada, D.; Pascuta, M.S.; Nemeş, S.-A.; Varvara, R.-A.; Vodnar, D.C. Natural Polyphenol Recovery from Apple-, Cereal-, and Tomato-Processing By-Products and Related Health-Promoting Properties. Molecules 2022, 27, 7977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dludla, P.V.; Cirilli, I.; Marcheggiani, F.; Silvestri, S.; Orlando, P.; Muvhulawa, N.; Moetlediwa, M.T.; Nkambule, B.B.; Mazibuko-Mbeje, S.E.; Hlengwa, N.; et al. Bioactive Properties, Bioavailability Profiles, and Clinical Evidence of the Potential Benefits of Black Pepper (Piper Nigrum) and Red Pepper (Capsicum annum) against Diverse Metabolic Complications. Molecules 2023, 28, 6569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vidović, B.B.; Milinčić, D.D.; Marčetić, M.D.; Djuriš, J.D.; Ilić, T.D.; Kostić, A.Ž.; Pešić, M.B. Health Benefits and Applications of Goji Berries in Functional Food Products Development: A Review. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borghi, S.M.; Pavanelli, W.R. Antioxidant Compounds and Health Benefits of Citrus Fruits. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitura, K.; Arntfield, S.D. Characteristics of Flavonol Glycosides in Bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) Seed Coats. Food Chem. 2019, 272, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Wu, H.; Sajid, A.; Li, Z. Whole Grain Cereals: The Potential Roles of Functional Components in Human Health. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 62, 8388–8402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.; Sheng, X.; Zhang, J.; Li, X.; Dai, Q.; Chen, Y.; Kang, A. Homeostatic Regulation of the Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor-Cytochrome P450 1a Axis by Scutellaria baicalensis-Coptis chinensis Herb Pair and Its Main Constituents. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2022, 297, 115545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, B.; Yang, Z.; Liu, H.; Liu, Y.; Wang, S. Advances in Flavonoid Research: Sources, Biological Activities, and Developmental Prospectives. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2024, 46, 2884–2925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yang, P.; Luo, Y.; Gao, B.; Sun, J.; Lu, W.; Liu, J.; Chen, P.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, L. Chemical Compositions of Chrysanthemum Teas and Their Anti-Inflammatory and Antioxidant Properties. Food Chem. 2019, 286, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duda-Chodak, A.; Tarko, T. Possible Side Effects of Polyphenols and Their Interactions with Medicines. Molecules 2023, 28, 2536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bader Ul Ain, H.; Tufail, T.; Javed, M.; Tufail, T.; Arshad, M.U.; Hussain, M.; Gull Khan, S.; Bashir, S.; Al Jbawi, E.; Abdulaali Saewan, S. Phytochemical Profile and Pro-Healthy Properties of Berries. Int. J. Food Prop. 2022, 25, 1714–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, A.; Kazemi, M.; Samani, S.A.; Simal-Gandara, J. Bioactive Compounds from By-Products of Eggplant: Functional Properties, Potential Applications and Advances in Valorization Methods. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 112, 518–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Su, X.; Lim, S.; Griffin, J.; Carey, E.; Katz, B.; Tomich, J.; Smith, J.S.; Wang, W. Characterisation and Stability of Anthocyanins in Purple-Fleshed Sweet Potato P40. Food Chem. 2015, 186, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Deng, P.; Xu, Y.; Lü, S.; Wang, J. Quantification and Analysis of Anthocyanin and Flavonoids Compositions, and Antioxidant Activities in Onions with Three Different Colors. J. Integr. Agric. 2016, 15, 2175–2181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emerging Approaches to Determine Maturity of Citrus Fruit: Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition: Volume 62, No 19. Available online: https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/10408398.2021.1883547 (accessed on 29 October 2024).
- Osojnik Črnivec, I.G.; Skrt, M.; Šeremet, D.; Sterniša, M.; Farčnik, D.; Štrumbelj, E.; Poljanšek, A.; Cebin, N.; Pogačnik, L.; Smole Možina, S.; et al. Waste Streams in Onion Production: Bioactive Compounds, Quercetin and Use of Antimicrobial and Antioxidative Properties. Waste Manag. 2021, 126, 476–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.; Singh, J.P.; Kaur, A.; Singh, N. Phenolic Composition, Antioxidant Potential and Health Benefits of Citrus Peel. Food Res. Int. 2020, 132, 109114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambra, R.; Lucchetti, S.; Pastore, G. A Review of the Effects of Olive Oil-Cooking on Phenolic Compounds. Molecules 2022, 27, 661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vejarano, R.; Luján-Corro, M. Red Wine and Health: Approaches to Improve the Phenolic Content During Winemaking. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 890066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Chen, L.; Mao, C.; Jin, L.; Wu, S.; Zheng, Y.; Cui, Z.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, S.; et al. Natural Extracts for Antibacterial Applications. Small 2024, 20, e2306553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musial, C.; Kuban-Jankowska, A.; Gorska-Ponikowska, M. Beneficial Properties of Green Tea Catechins. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nascimento, M.M.; Santos, H.M.; Coutinho, J.P.; Lôbo, I.P.; da Silva Junior, A.L.S.; Santos, A.G.; de Jesus, R.M. Optimization of Chromatographic Separation and Classification of Artisanal and Fine Chocolate Based on Its Bioactive Compound Content through Multivariate Statistical Techniques. Microchem. J. 2020, 152, 104342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, Y. Novel Uses of Catechins in Foods. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2006, 17, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arts, I.C.; van de Putte, B.; Hollman, P.C. Catechin Contents of Foods Commonly Consumed in The Netherlands. 1. Fruits, Vegetables, Staple Foods, and Processed Foods. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2000, 48, 1746–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Li, S.; Ho, C.-T. Dietary Bioactives and Essential Oils of Lemon and Lime Fruits. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2022, 11, 753–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsayed, N.; El-Din, H.S.; Altemimi, A.B.; Ahmed, H.Y.; Pratap-Singh, A.; Abedelmaksoud, T.G. In Vitro Antimicrobial, Antioxidant and Anticancer Activities of Egyptian Citrus Beebread. Molecules 2021, 26, 2433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shilpa, V.S.; Shams, R.; Dash, K.K.; Pandey, V.K.; Dar, A.H.; Ayaz Mukarram, S.; Harsányi, E.; Kovács, B. Phytochemical Properties, Extraction, and Pharmacological Benefits of Naringin: A Review. Molecules 2023, 28, 5623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Ren, S.; Yang, H.; Tang, S.; Guo, C.; Liu, M.; Tao, Q.; Ming, T.; Xu, H. Peppermint Essential Oil: Its Phytochemistry, Biological Activity, Pharmacological Effect and Application. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 154, 113559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazemi, A.; Iraji, A.; Esmaealzadeh, N.; Salehi, M.; Hashempur, M.H. Peppermint and Menthol: A Review on Their Biochemistry, Pharmacological Activities, Clinical Applications, and Safety Considerations. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2024, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, Q.; Zhang, L. The Distinctive Role of Menthol in Pain and Analgesia: Mechanisms, Practices, and Advances. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2022, 15, 1006908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, W.; Tan, X.; Xu, X.; Li, G.; Wang, Z.; Du, M. Relationship between Enzyme, Peptides, Amino Acids, Ion Composition, and Bitterness of the Hydrolysates of Alaska Pollock Frame. J. Food Biochem. 2019, 43, e12801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.; Li, N.; Chen, F.; Zhang, J.; Sun, X.; Xu, L.; Fang, F. Review on the Release Mechanism and Debittering Technology of Bitter Peptides from Protein Hydrolysates. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2022, 21, 5153–5170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Xin, X.; Wu, H.; Zhang, H. Debittering Effect of Partially Purified Proteases from Soybean Seedlings on Soybean Protein Isolate Hydrolysate Produced by Alcalase. Food Chem. 2021, 362, 130190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, W.; Wu, X.; Jia, G.; Zhao, H.; Chen, X.; Tang, J.; Wu, C.; Cai, J.; Tian, G.; Wang, J.; et al. Roles of Dietary Supplementation with Arginine or N-Carbamylglutamate in Modulating the Inflammation, Antioxidant Property, and mRNA Expression of Antioxidant-Relative Signaling Molecules in the Spleen of Rats under Oxidative Stress. Anim. Nutr. 2018, 4, 322–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Górska-Warsewicz, H.; Laskowski, W.; Kulykovets, O.; Kudlińska-Chylak, A.; Czeczotko, M.; Rejman, K. Food Products as Sources of Protein and Amino Acids-The Case of Poland. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shipelin, V.A.; Trusov, N.V.; Apryatin, S.A.; Shumakova, A.A.; Balakina, A.S.; Riger, N.A.; Gmoshinski, I.V.; Nikityuk, D.B. Effects of Tyrosine and Tryptophan in Rats with Diet-Induced Obesity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dietary Valine Improved Growth, Immunity, Enzymatic Activities and Expression of TOR Signaling Cascade Genes in Rainbow Trout, Oncorhynchus Mykiss Fingerlings|Scientific Reports. Available online: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-021-01142-4 (accessed on 29 October 2024).
- Hong, C.-O.; Rhee, C.H.; Pyo, M.C.; Lee, K.-W. Anti-Inflammatory Effect of Glucose-Lysine Maillard Reaction Products on Intestinal Inflammation Model in Vivo. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2017, 52, 324–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seal, C.J.; Courtin, C.M.; Venema, K.; de Vries, J. Health Benefits of Whole Grain: Effects on Dietary Carbohydrate Quality, the Gut Microbiome, and Consequences of Processing. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2021, 20, 2742–2768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahwish, R.; Saeed, F.; Arshad, M.S.; Nisa, M.U.; Nadeem, M.T.; Arshad, M.U. Hypoglycemic and Hypolipidemic Effects of Different Parts and Formulations of Bitter Gourd (Momordica Charantia). Lipids Health Dis. 2017, 16, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Li, Z.; Zeng, T.; Zhan, J.; Wang, S.; Ho, C.-T.; Li, S. Bioactives of Momordica charantia as Potential Anti-Diabetic/Hypoglycemic Agents. Molecules 2022, 27, 2175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, Y.J.; Koo, H.J.; Sohn, E.-H.; Kang, S.C.; Rhee, D.-K.; Pyo, S. Theobromine Inhibits Differentiation of 3T3-L1 Cells during the Early Stage of Adipogenesis via AMPK and MAPK Signaling Pathways. Food Funct. 2015, 6, 2365–2374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aprotosoaie, A.C.; Luca, S.V.; Miron, A. Flavor Chemistry of Cocoa and Cocoa Products-An Overview. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2016, 15, 73–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ried, K.; Fakler, P.; Stocks, N.P. Effect of Cocoa on Blood Pressure. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2017, 4, CD008893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Shi, X.; Li, Y.; Peng, L.; Li, C.; Yang, X.; Ye, C.; Li, J.; He, Y.; Huang, H.; et al. Studies of Cocoa Tea, a Wild Tea Tree Containing Theobromine. Front. Biol. China 2009, 4, 460–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farag, M.A.; Abib, B.; Ayad, L.; Khattab, A.R. Sweet and Bitter Oranges: An Updated Comparative Review of Their Bioactives, Nutrition, Food Quality, Therapeutic Merits and Biowaste Valorization Practices. Food Chem. 2020, 331, 127306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.; Chen, J.; Ren, W.; Zhu, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Zhang, K.; Su, D.; Qiu, C.; Zhang, W.; Li, K. Citrus Flavone Tangeretin Is a Potential Insulin Sensitizer Targeting Hepatocytes through Suppressing MEK-ERK1/2 Pathway. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2020, 529, 277–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sulaimani, N.; Houghton, M.J.; Bonham, M.P.; Williamson, G. Effects of (Poly)Phenols on Circadian Clock Gene–Mediated Metabolic Homeostasis in Cultured Mammalian Cells: A Scoping Review. Adv. Nutr. 2024, 15, 100232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugiura, R.; Satoh, R.; Takasaki, T. ERK: A Double-Edged Sword in Cancer. ERK-Dependent Apoptosis as a Potential Therapeutic Strategy for Cancer. Cells 2021, 10, 2509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selim, S.; Albqmi, M.; Al-Sanea, M.M.; Alnusaire, T.S.; Almuhayawi, M.S.; AbdElgawad, H.; Al Jaouni, S.K.; Elkelish, A.; Hussein, S.; Warrad, M.; et al. Valorizing the Usage of Olive Leaves, Bioactive Compounds, Biological Activities, and Food Applications: A Comprehensive Review. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 1008349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, T.; Okumura, T.; Matsuo, Y.; Okuyama, T.; Michiura, T.; Kaibori, M.; Umezaki, N.; Bono, H.; Hirota, K.; Sekimoto, M. Activation of Transcription Factor HIF Inhibits IL-1β-Induced NO Production in Primary Cultured Rat Hepatocytes. Nitric Oxide 2022, 124, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liang, X.; Bao, X.; Xiao, W.; Chen, G. Toll-like Receptor 4 (TLR4) Inhibitors: Current Research and Prospective. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 235, 114291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Li, X.; Lin, J.; Zheng, W.; Hu, Z.; Xuan, J.; Ni, W.; Pan, X. Oleuropein Inhibits the IL-1β-Induced Expression of Inflammatory Mediators by Suppressing the Activation of NF-κB and MAPKs in Human Osteoarthritis Chondrocytes. Food Funct. 2017, 8, 3737–3744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naveed, M.; Hejazi, V.; Abbas, M.; Kamboh, A.A.; Khan, G.J.; Shumzaid, M.; Ahmad, F.; Babazadeh, D.; FangFang, X.; Modarresi-Ghazani, F.; et al. Chlorogenic Acid (CGA): A Pharmacological Review and Call for Further Research. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 97, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, J.; He, W.; Li, X.; Ji, X.; Liu, J. Anti-Acne Vulgaris Effects of Chlorogenic Acid by Anti-Inflammatory Activity and Lipogenesis Inhibition. Exp. Dermatol. 2021, 30, 865–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Xie, M.; He, L.; Song, X.; Cao, T. Chlorogenic Acid: A Review on Its Mechanisms of Anti-Inflammation, Disease Treatment, and Related Delivery Systems. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elia, I.; Haigis, M.C. Metabolites and the Tumor Microenvironment: From Cellular Mechanisms to Systemic Metabolism. Nat. Metab. 2021, 3, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motofei, I.G. Biology of Cancer; from Cellular and Molecular Mechanisms to Developmental Processes and Adaptation. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2022, 86, 600–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oleuropein Induces Apoptosis in Colorectal Tumor Spheres via Mitochondrial Fission | Molecular & Cellular Toxicology. Available online: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s13273-022-00260-y (accessed on 29 October 2024).
- Zhou, W.; Dong, M.; Wu, H.; Li, H.-L.; Xie, J.; Ma, R.-Y.; Su, W.-W.; Dai, J.-Y. Common Mechanism of Citrus Grandis Exocarpium in Treatment of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease and Lung Cancer. Chin. Herb. Med. 2021, 13, 525–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatri, S.; Kumar, M.; Phougat, N.; Chaudhary, R.; Chhillar, A.K. Perspectives on Phytochemicals as Antibacterial Agents: An Outstanding Contribution to Modern Therapeutics. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2016, 16, 290–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biharee, A.; Sharma, A.; Kumar, A.; Jaitak, V. Antimicrobial Flavonoids as a Potential Substitute for Overcoming Antimicrobial Resistance. Fitoterapia 2020, 146, 104720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Wang, P.; Guo, W.; Huang, X.; Tian, X.; Wu, G.; Xu, B.; Li, F.; Yan, C.; Liang, X.-J.; et al. Natural Berberine-Based Chinese Herb Medicine Assembled Nanostructures with Modified Antibacterial Application. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 6770–6781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.; Zhang, X.; Dong, L.; Zhang, C.; Guo, P.; Wu, C. The Triterpenoids of the Bitter Gourd (Momordica Charantia) and Their Pharmacological Activities: A Review. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2021, 96, 103726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Yang, W.; Deng, H.; Li, D.; Wang, Q.; Yi, L.; Kuang, Q.; Xu, R.; Li, D.; Li, R.; et al. Matrine Reverses the Resistance of Haemophilus Parasuis to Cefaclor by Inhibiting the Mutations in Penicillin-Binding Protein Genes (ftsI and mrcA). Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1364339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liguori, I.; Russo, G.; Curcio, F.; Bulli, G.; Aran, L.; Della-Morte, D.; Gargiulo, G.; Testa, G.; Cacciatore, F.; Bonaduce, D.; et al. Oxidative Stress, Aging, and Diseases. Clin. Interv. Aging 2018, 13, 757–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharifi-Rad, M.; Anil Kumar, N.V.; Zucca, P.; Varoni, E.M.; Dini, L.; Panzarini, E.; Rajkovic, J.; Tsouh Fokou, P.V.; Azzini, E.; Peluso, I.; et al. Lifestyle, Oxidative Stress, and Antioxidants: Back and Forth in the Pathophysiology of Chronic Diseases. Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, G.N.; Gupta, G.; Sharma, P. A Comprehensive Review of Free Radicals, Antioxidants, and Their Relationship with Human Ailments. Crit. Rev. Eukaryot. Gene Expr. 2018, 28, 139–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tumilaar, S.; Hardianto, A.; Dohi, H.; Dikdik, K. A Comprehensive Review of Free Radicals, Oxidative Stress, and Antioxidants: Overview, Clinical Applications, Global Perspectives, Future Directions, and Mechanisms of Antioxidant Activity of Flavonoid Compounds. J. Chem. 2024, 2024, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grzesik, M.; Naparło, K.; Bartosz, G.; Sadowska-Bartosz, I. Antioxidant Properties of Catechins: Comparison with Other Antioxidants. Food Chem. 2018, 241, 480–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Görgüç, A.; Gençdağ, E.; Yılmaz, F.M. Bioactive Peptides Derived from Plant Origin By-Products: Biological Activities and Techno-Functional Utilizations in Food Developments—A Review. Food Res. Int. 2020, 136, 109504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treml, J.; Šmejkal, K. Flavonoids as Potent Scavengers of Hydroxyl Radicals. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2016, 15, 720–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Pandey, A.K. Chemistry and Biological Activities of Flavonoids: An Overview. Sci. World J. 2013, 2013, 162750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akbari, B.; Baghaei-Yazdi, N.; Bahmaie, M.; Mahdavi Abhari, F. The Role of Plant-Derived Natural Antioxidants in Reduction of Oxidative Stress. Biofactors 2022, 48, 611–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruffini, N.; Klingenberg, S.; Schweiger, S.; Gerber, S. Common Factors in Neurodegeneration: A Meta-Study Revealing Shared Patterns on a Multi-Omics Scale. Cells 2020, 9, 2642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cellular Stress Responses, The Hormesis Paradigm, and Vitagenes: Novel Targets for Therapeutic Intervention in Neurodegenerative Disorders|Antioxidants & Redox Signaling. Available online: https://www.liebertpub.com/doi/full/10.1089/ars.2009.3074 (accessed on 29 October 2024).
- Caffeine and Its Neuroprotective Role in Ischemic Events: A Mechanism Dependent on Adenosine Receptors|Cellular and Molecular Neurobiology. Available online: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s10571-021-01077-4 (accessed on 29 October 2024).
- Sc, Y. Muralidhara Beneficial Role of Coffee and Caffeine in Neurodegenerative Diseases: A Minireview. AIMS Public Health 2016, 3, 407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dragicevic, N.; Delic, V.; Cao, C.; Copes, N.; Lin, X.; Mamcarz, M.; Wang, L.; Arendash, G.W.; Bradshaw, P.C. Caffeine Increases Mitochondrial Function and Blocks Melatonin Signaling to Mitochondria in Alzheimer’s Mice and Cells. Neuropharmacology 2012, 63, 1368–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruggiero, M.; Calvello, R.; Porro, C.; Messina, G.; Cianciulli, A.; Panaro, M.A. Neurodegenerative Diseases: Can Caffeine Be a Powerful Ally to Weaken Neuroinflammation? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 12958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabavi, S.F.; Tejada, S.; Setzer, W.N.; Gortzi, O.; Sureda, A.; Braidy, N.; Daglia, M.; Manayi, A.; Nabavi, S.M. Chlorogenic Acid and Mental Diseases: From Chemistry to Medicine. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2017, 15, 471–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murai, T.; Matsuda, S. The Chemopreventive Effects of Chlorogenic Acids, Phenolic Compounds in Coffee, against Inflammation, Cancer, and Neurological Diseases. Molecules 2023, 28, 2381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, R.; Gao, D.; Stoika, R.; Liu, K.; Sik, A.; Jin, M. Potential Implications of Polyphenolic Compounds in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2024, 64, 5491–5514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Socała, K.; Szopa, A.; Serefko, A.; Poleszak, E.; Wlaź, P. Neuroprotective Effects of Coffee Bioactive Compounds: A Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 22, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Tang, Z.; Wen, L.; Jiang, C.; Feng, Q. Matrine: A Review of Its Pharmacology, Pharmacokinetics, Toxicity, Clinical Application and Preparation Researches. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2021, 269, 113682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spence, C. Multisensory Flavour Perception: Blending, Mixing, Fusion, and Pairing Within and Between the Senses. Foods 2020, 9, 407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Sources of Caffeine | Mean Concentration |
|---|---|
| Espresso | 143 mg/43 mL |
| Coffee | 72.8 mg/125 mL |
| Tea | 13.8 mg/120 mL |
| Chicory beverage | 16.1 mg/125 mL |
| Cola | 17.6 mg/330 mL |
| Chocolate candy | 2.1 mg/30 g |
| Plain chocolate | 17.8 mg/30 g |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qiao, K.; Zhao, M.; Huang, Y.; Liang, L.; Zhang, Y. Bitter Perception and Effects of Foods Rich in Bitter Compounds on Human Health: A Comprehensive Review. Foods 2024, 13, 3747. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13233747
Qiao K, Zhao M, Huang Y, Liang L, Zhang Y. Bitter Perception and Effects of Foods Rich in Bitter Compounds on Human Health: A Comprehensive Review. Foods. 2024; 13(23):3747. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13233747
Chicago/Turabian StyleQiao, Kaina, Mingxia Zhao, Yan Huang, Li Liang, and Yuyu Zhang. 2024. "Bitter Perception and Effects of Foods Rich in Bitter Compounds on Human Health: A Comprehensive Review" Foods 13, no. 23: 3747. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13233747
APA StyleQiao, K., Zhao, M., Huang, Y., Liang, L., & Zhang, Y. (2024). Bitter Perception and Effects of Foods Rich in Bitter Compounds on Human Health: A Comprehensive Review. Foods, 13(23), 3747. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13233747





