Determination of Amino Acids of Novel Food in Food by HPLC Coupled with Pre-Column Derivatization
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Chemicals
2.2. Instrumentation and Materials
2.3. Preparation of Solution
2.4. Preparation and Extraction of Sample
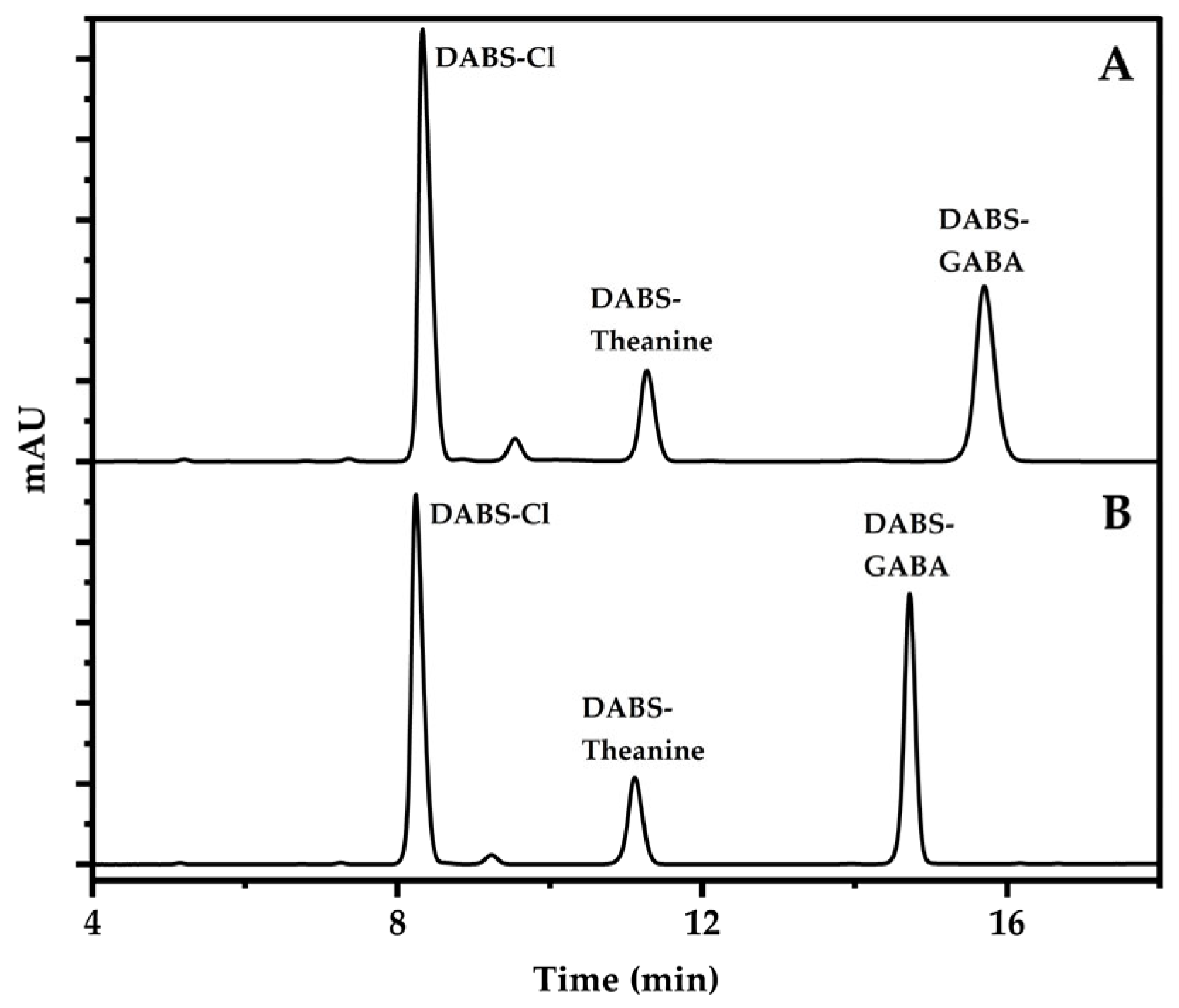
2.5. Pre-Column Derivatization
2.6. Chromatographic Conditions
2.7. Optimization of Chromatographic Conditions
2.8. Optimization of Derivatization Conditions
3. Results and Discussion
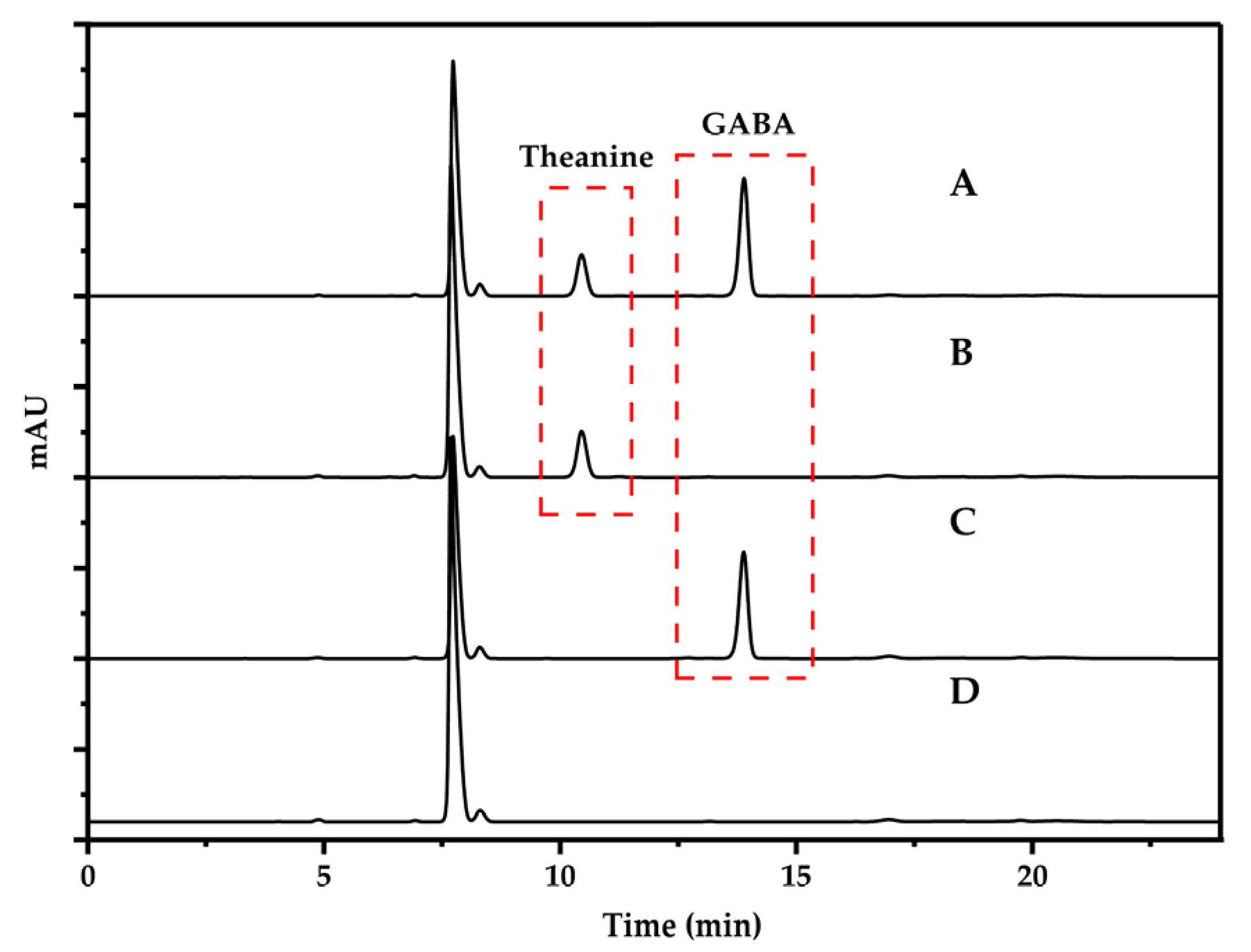
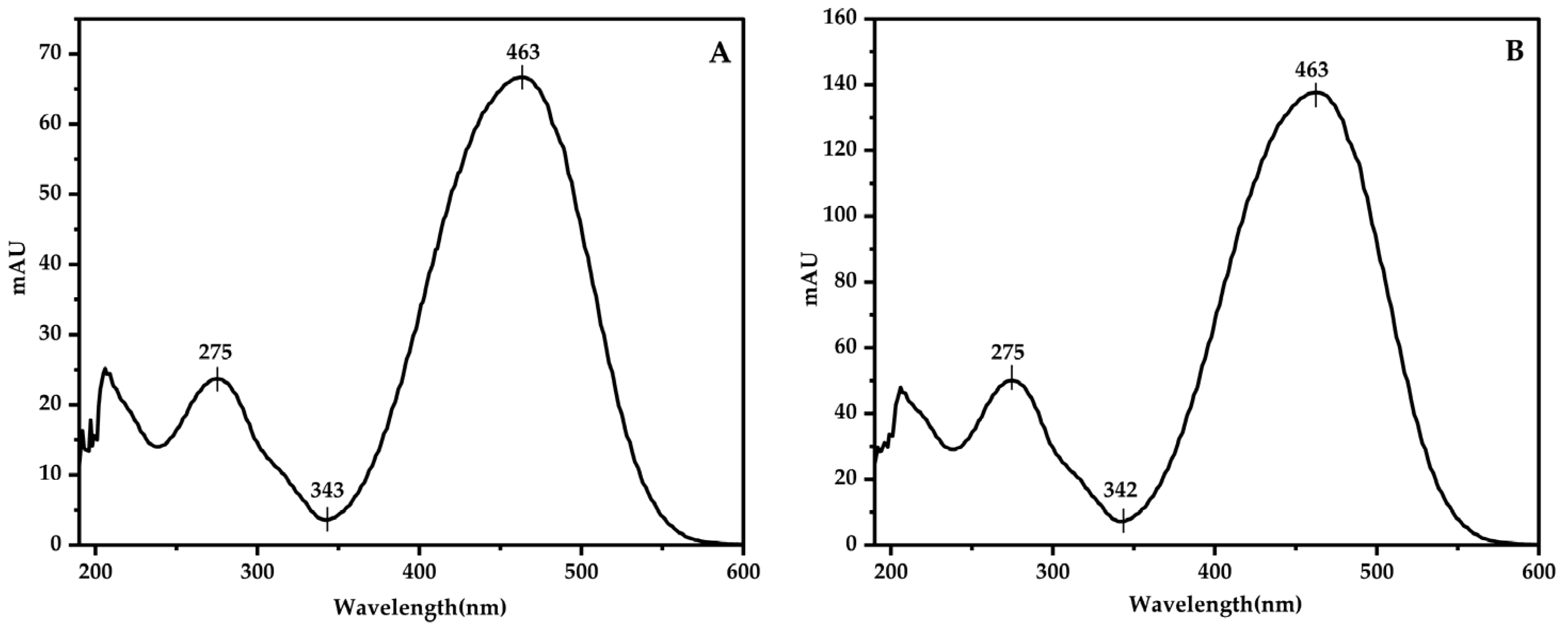
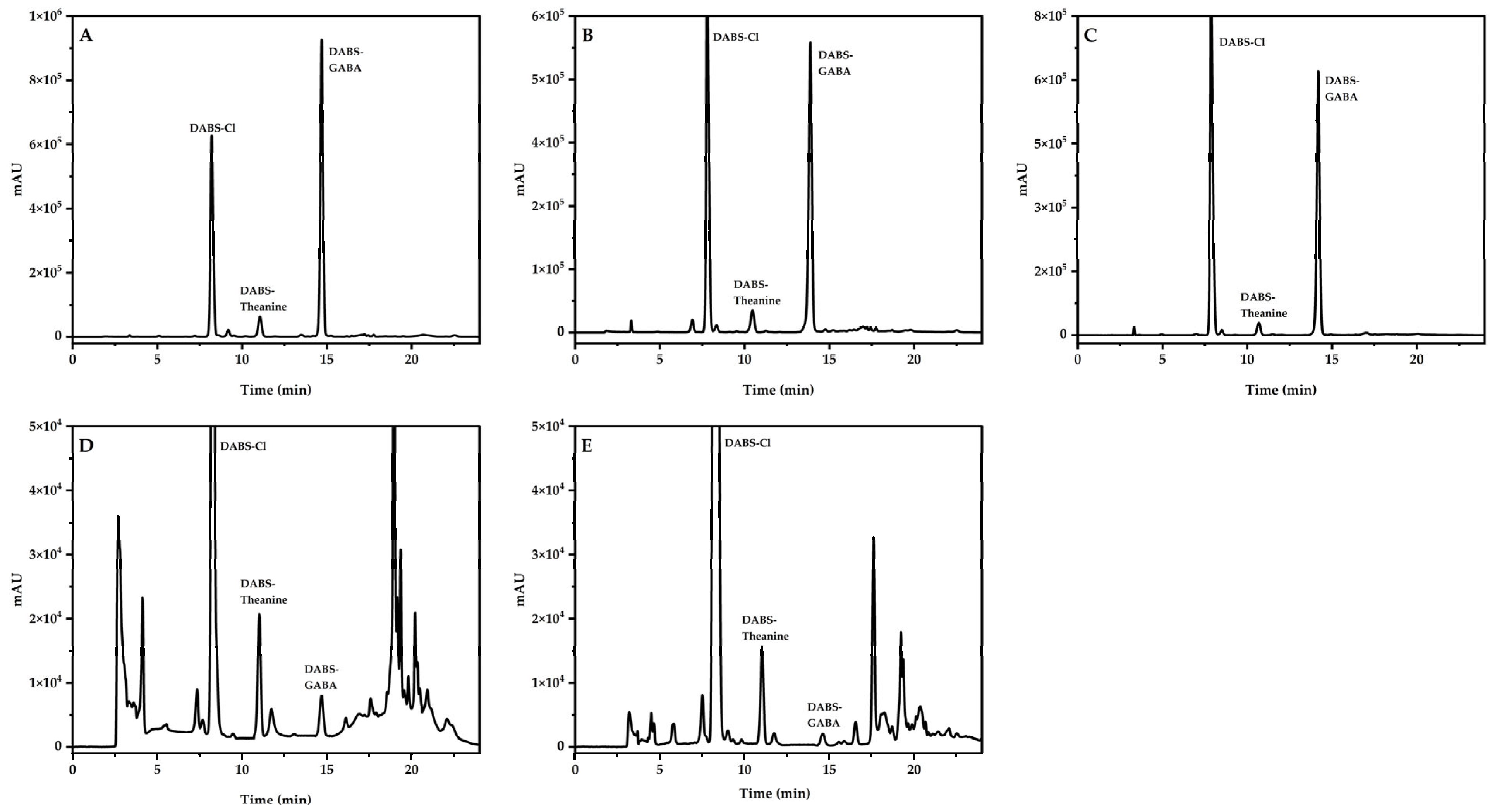
3.1. Classification of Chromatographic Peaks and Confirmation of Detection Wavelength
3.2. Selection of Chromatographic Column
3.3. Optimization of Gradient Elution Conditions
3.4. Optimization of Derivatization Conditions
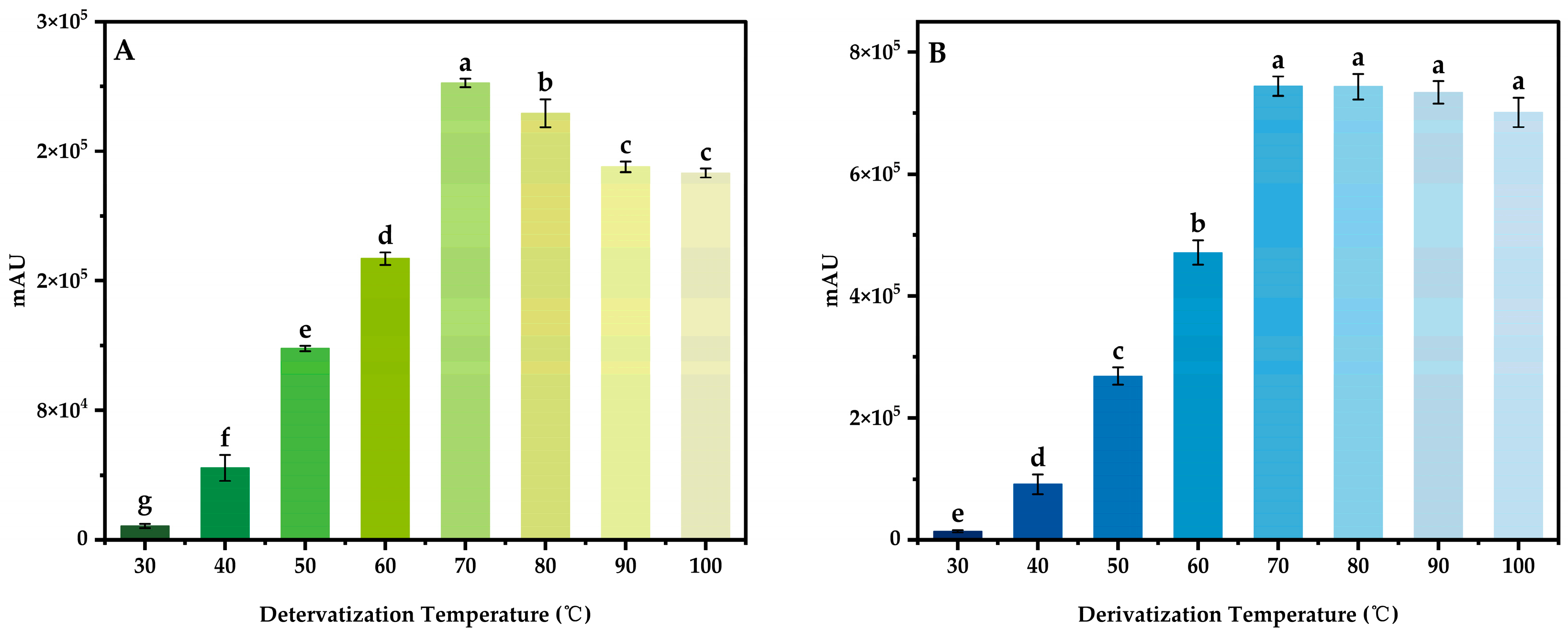
3.4.1. Derivatization Temperature
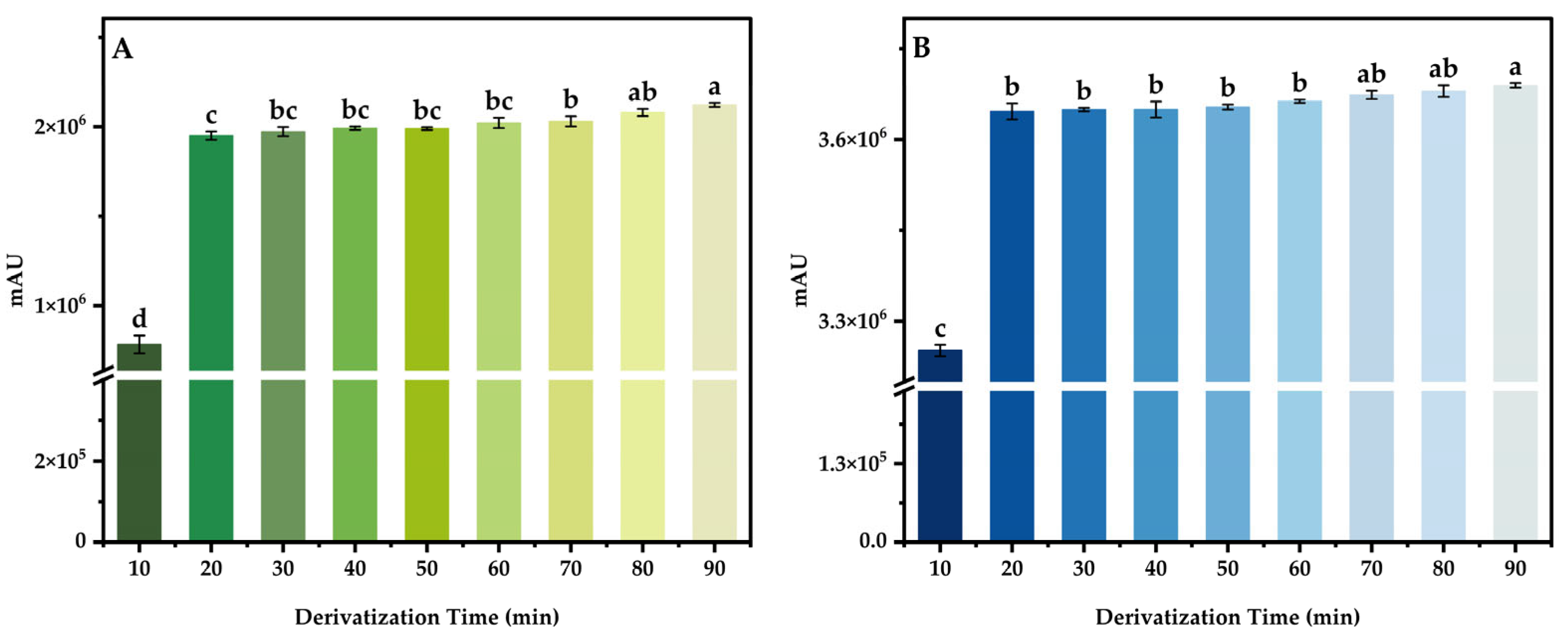
3.4.2. Derivatization Time
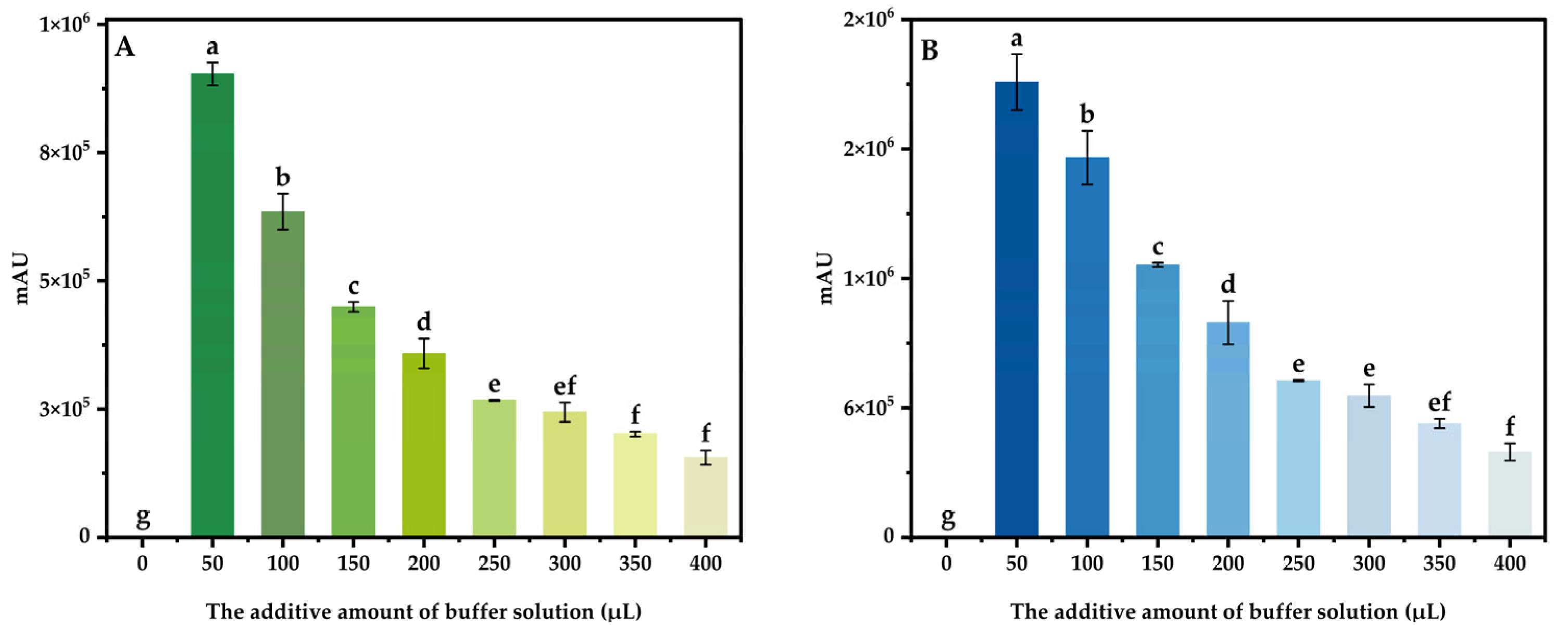
3.4.3. The Additive Amount of Buffer Solution
3.4.4. The Additive Amount of Derivatization Reagent
3.5. Method Validation
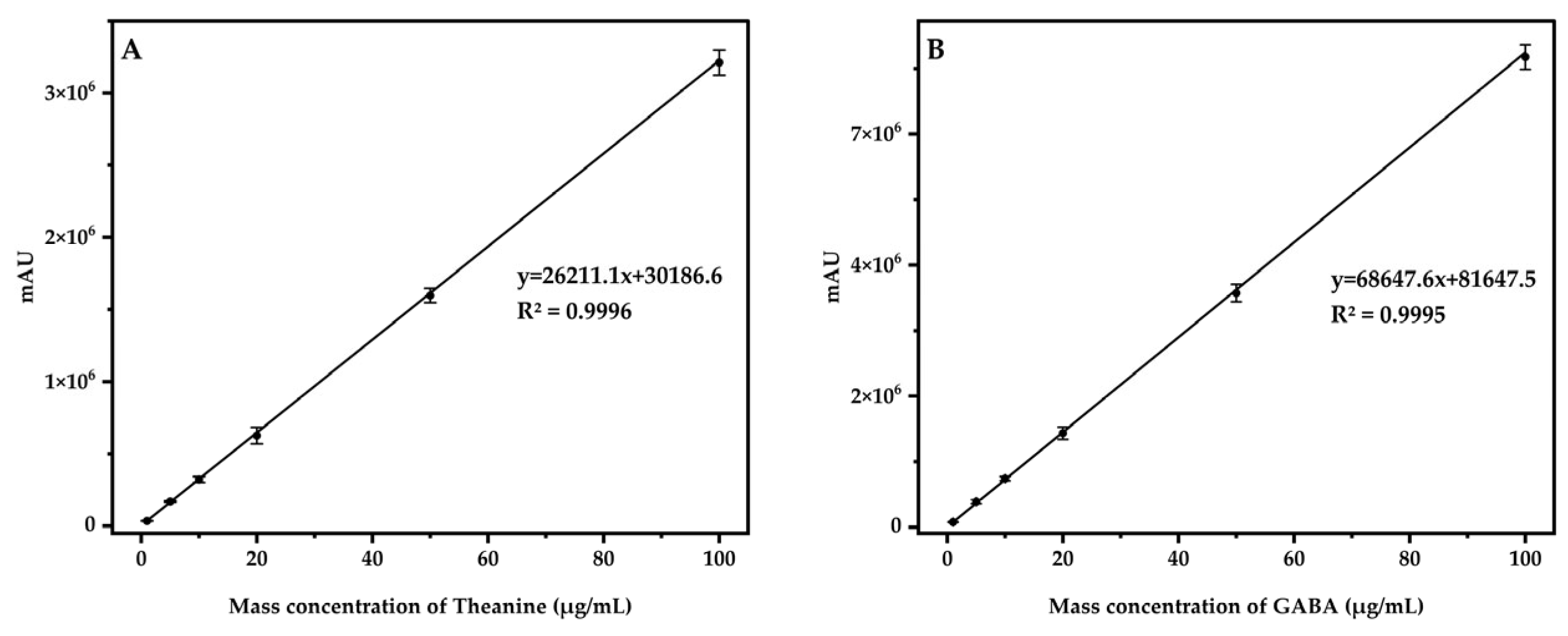
3.5.1. Linearity, LOD, and LOQ
3.5.2. Precision and Stability Test
3.5.3. Recovery and Repeatability
3.6. Method Application
3.7. Comparison with Other Methods
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhong, Y.Q.; Lu, Y.L.; Lv, L.S. Theanine in Tea: An Effective Scavenger of Single or Multiple Reactive Carbonyl Species at the Same Time. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2023, 71, 17153–17162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, Y.Q.; Yang, C.; Lu, Y.L.; Lv, L.S. Theanine Capture of Reactive Carbonyl Species in Humans after Consuming Theanine Capsules or Green Tea. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2024, 72, 13240–13249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Liu, A.X.; Liu, K.H.; Zhang, S.; Gong, Z.H.; Xiao, W.J. L-Theanine Alleviates Ulcerative Colitis by Regulating Colon Immunity via the Gut Microbiota in an MHC-II-Dependent Manner. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2024, 72, 19852–19868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Jiang, Y.Y.; Zhang, Z.B.; Loake, V.I.P.; Bao, X.; Loake, G.J. Improvement of both human and animal memory by synergy between fructooligosaccharide and L-theanine function establishing a safe and effective food supplement. Food Sci. Nutr. 2024, 12, 4966–4980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srimaharaj, W.; Chaising, S.; Temdee, P. Identification of L-Theanine Acid Effectiveness in Oolong Tea on Human Brain Memorization and Meditation. ECTI Trans. Comput. Inf. Technol. 2019, 13, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Everett, J.M.; Gunathilake, D.; Dufficy, L.; Roach, P.; Thomas, J.; Upton, D.; Naumovski, N. Theanine consumption, stress and anxiety in human clinical trials: A systematic review. J. Nutr. Intermed. Metab. 2016, 4, 41–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, Y.S.; Wang, R. Determination of theanine in black tea. J. Henan Univ. (Med. Sci.) 2018, 37, 247–249. [Google Scholar]
- Si, X.; Li, Y.B.; Jiang, Y.G.; Shang, W.T.; Shui, G.H.; Lam, S.M.; Blanchard, C.; Strappe, P.; Zhou, Z. γ-Aminobutyric Acid Attenuates High-Fat Diet-Induced Cerebral Oxidative Impairment via Enhanced Synthesis of Hippocampal Sulfatides. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 1081–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Yu, L.X.; Liu, X.Y.; Liu, D.; Zhang, W.G. Research Progress on Improving Sleep Mechanism of γ-aminobutyric Acid. Sci. Technol. Food Ind. 2019, 40, 353–358. [Google Scholar]
- Toshiyuki, H.; Fatima, R.; Tomohide, H.; Justin, H.N. GABA, γ-Aminobutyric Acid, Protects Against Severe Liver Injury. J. Surg. Res. 2019, 236, 172–183. [Google Scholar]
- Bie, T.H.D.; Witkamp, R.F.; Balvers, M.G.J.; Jongsma, M.A. Effects of γ-aminobutyric acid supplementation on glucose control in adults with prediabetes A double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2023, 118, 708–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Geng, S.Y.; Han, H.F.; Liu, J.H.; Liu, G.H.; Zheng, B.Q.; Tu, J. Study on detection and changing rules of γ-aminobutyric acid in vinegar. J. Food Saf. Qual. 2024, 15, 197–204. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.B.; Lin, H.; Zhang, K.X.; Shao, X.K.; Kang, W.C.; Chen, Z.Y.; Wang, D.; Lin, R.X. Rapid Detection of Internal Component Content in Instant Tea Based on Near-Infrared Spectroscopy. Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 49, 307–314. [Google Scholar]
- Tu, Y.F.; Diao, C.H.; Zuo, X.B. Simultaneous Determination of Vitamin C, Theanine, Catechins and Theaflavins in Green Tea and Black Tea by HPLC. J. Guizhou Tea 2023, 1, 54–58. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Y.H.; Ding, T.; Sun, C.; Liu, B.; Teng, S. Determination of L-theanine, caffeine, tea polyphenols and palmitic acid in green tea by gas chromatography-tandem triple quadrupole mass spectrometry. Food Ferment. Ind. 2023, 49, 276–282. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, L.B.; Li, J.; Xu, J.; Cao, S.X. Determination of caffeine, theanine and catechin in Wuyi rock tea by ultra-high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. ChinaTea 2019, 41, 38–42. [Google Scholar]
- Yi, R.R.; Ma, Y.J.; Yang, N. Determination of Theanine Content in Tea Samples by Precolumn Derivatization CE-ECL Method. Guangdong Chem. Ind. 2017, 44, 202–203. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; You, J.M.; Sun, Z.W.; Ji, Z.Y.; Zhang, S.J.; Tan, J.K.; Luo, X.Z.; Wang, H.L. Using 4-(Carbazole-9-yl)-benzyl Chloroformate as a Derivatization Reagent for the Measurement of Amino Acids in Tea Samples by High-Performance Liquid Chromatography with Fluorescence Detection. Chromatographia 2020, 83, 487–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.W.; Li, X.H.; Bao, D.P.; Zhou, C.L.; Chen, H.Y.; Feng, Z.; Li, H.W.; Wang, R.J.; Shao, Y.R.; Wu, Y.Y. Rapid detection of γ-aminobutyric acid in the mycelia of Flammulina filiformis. Mycosystema 2024, 43, 230362. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Ma, J.J.; Hu, J.G.; Zhou, J.D.; Fu, C.H.; Qian, S.N.; Wu, J.; Zhuge, Q. Determination of γ-aminobutyric acid in alcoholic beverage by isotope-labeled internal standard liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. China Brew. 2023, 42, 239–244. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, W.W.; Zhou, T.; Wu, Y.; Lin, Q.L.; Ding, Y.Q.; Wang, X.Y. HPLC Analysis of γ-Amino Butyric Acid in Germinated Brown Rice. Food Sci. 2014, 35, 98–101. [Google Scholar]
- Zhuang, K.Y.; Zhang, J.L.; Fan, C.L.; Yao, Z.Y.; Zhang, Z.J. Determination of γ-aminobutyric acid in fermented soybean products by HPLC coupled with pre-column derivatization. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2023, 119, 105248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, Y.F.; Yang, X.F.; Zhang, S.K.; Zhu, Y.J. Determination of theanine and γ-aminobutyric acid in tea by high performance liquid chromatography with precolumn derivatization. Chin. J. Chromatogr. 2012, 30, 184–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pencheva, D.; Teneva, D.; Denev, P. Validation of HPLC method for analysis of gamma-aminobutyric and glutamic acids in plant foods and medicinal plants. Molecules 2022, 28, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, R.; Zhou, W.; He, H.Y. HPLC analysis of γ- amino butyric acid in solid beverages. Food Eng. 2016, 4, 59–63. [Google Scholar]
- Du, J.F.; Guo, H.H.; Tao, X.J.; Zhang, N.J.; Song, J. Determination of γ-Aminobuytric Acid in Germinated Brown Rice Powder by HPLC with DABS-Cl Precolumn Derivatization. Food Ind. 2021, 42, 468–472. [Google Scholar]
- Shao, J.L.; Yang, D.S.; Fan, J.L.; Liu, X.Y.; Du, L.J.; Wang, L.; Wang, L.X.; Liu, H.C. Optimization of DABS-Cl pre-column derivation-HPLC method for determination of γ-aminobutyric acid in rice. Crops 2016, 1, 129–134. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, W.; Lu, C.Z.; Liu, F.; Li, D.; Cao, Z. Determination of Theanine in Tea Liquor by Ultra High Pressure and High Performance Liquid Chromatography. J. Anhui Agric. Sci. 2016, 44, 70–71. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.L.; Gao, L.S.; Zhang, D.D.; Han, J.H.; Zhao, J.J.; Gao, W.H. Determination of γ-aminobutyric acid in lactic acid bacteria fermentation broth by HPLC. China Brew. 2022, 41, 233–238. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, N.F. Research on Optimization and Application of Determination Method of γ-Aminobutyric Acid in Jujube; Tarim University: Alar, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Q.F.; Wang, M.; Chen, H.P.; Chen, L.; Hu, Y.; Liu, Y.P. Determination of 17 amino acids in Coix lacryma-jobi seed by HPLC with pre-column derivatization of PITC. Food Ferment. Ind. 2021, 47, 274–279. [Google Scholar]
- He, W.Q.; Mo, Y.C. Determination of L-theanine in tea by precolumn derivatization. China Food Saf. Mag. 2017, 24, 117–119. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, Z.H.; Huang, Y.M.; Lv, Y.N.; Lian, L.Z.; Huang, Y.X.; Ye, H.; Ye, S.Q. Determination of γ-aminobutyric Acid in Sea Rice by HPLC-UV Method with 2,4-Dinitrofluorobenzene Pre-column Derivatization. Sci. Technol. Food Ind. 2019, 40, 257–261. [Google Scholar]
- Syu, K.Y.; Lin, C.L.; Huang, H.C.; Lin, J.K. Determination of Theanine, GABA, and Other Amino Acids in Green, Oolong, Black, and Pu-erh Teas with Dabsylation and High-Performance Liquid Chromatography. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 7637–7643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, X.H.; Liu, H.H.; Xu, Y.H.; Zhou, R.J.; Yu, Z.Q.; Zhang, X.Z. Determination of Hydroxyproline in sea cucumber with DABS-Cl pre-column derivatization by high performance liquid chromatography. Chin. Fish. Qual. Stand. 2012, 2, 45–49. [Google Scholar]
- SANTE/11312/2021. Analytical Quality Control and Method Validation Procedures for Pesticide Residues Analysis in Food and Feed. 2021. Available online: https://www.eurl-pesticides.eu/docs/public/tmplt_article.asp?CntID=727 (accessed on 30 September 2024).
- Announcement of the National Health and Family Planning Commission on the Approval of Tea Theanine as a Novel Food (No. 15, 2014). Available online: http://www.nhc.gov.cn/sps/s7890/201407/d388b72707fa4e978bea6a222b920cbf.shtml (accessed on 16 September 2024).
- Announcement of the Ministry of Health on the Approval of Gamma-Aminobutyric Acid and Other 6 Substances as New Resource Foods (Ministry of Health Announcement No. 12, 2009). Available online: http://www.nhc.gov.cn/bgt/s9513/200910/b9d3f11802bd40209782bdc7f080c2b2.shtml (accessed on 16 September 2024).


| Serial Number | The Peak Area of DABS-Theanine (mAU) | RSD (%) | The Peak Area of DABS-GABA (mAU) | RSD (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1,447,947 | 0.08 | 3,695,706 | 0.10 |
| 2 | 1,449,504 | 3,694,736 | ||
| 3 | 1,446,784 | 3,685,472 | ||
| 4 | 1,447,279 | 3,693,983 | ||
| 5 | 1,449,319 | 3,691,117 | ||
| 6 | 1,447,828 | 3,694,924 |
| Sample | Additive Amount (mg/kg) | Recovery (%) | RSD (%) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Crisps | 50 | Theanine | 95.18 | 96.68 | 102.18 | 99.08 | 99.18 | 100.28 | 2.54 |
| GABA | 101.97 | 99.77 | 95.77 | 98.27 | 101.87 | 100.97 | 2.41 | ||
| 100 | Theanine | 97.39 | 97.69 | 96.24 | 103.19 | 98.34 | 100.34 | 2.54 | |
| GABA | 98.13 | 100.78 | 101.13 | 98.08 | 99.88 | 102.13 | 1.65 | ||
| 200 | Theanine | 101.12 | 99.05 | 100.35 | 99.67 | 100.62 | 96.10 | 1.82 | |
| GABA | 102.54 | 101.72 | 102.07 | 103.24 | 99.67 | 98.57 | 1.78 | ||
| Coated Tofu | 50 | Theanine | 97.70 | 100.40 | 101.70 | 95.60 | 98.60 | 101.10 | 2.34 |
| GABA | 100.50 | 97.90 | 99.10 | 98.50 | 101.60 | 98.60 | 1.41 | ||
| 100 | Theanine | 97.40 | 96.10 | 103.65 | 102.25 | 101.70 | 99.70 | 2.94 | |
| GABA | 97.50 | 99.80 | 94.40 | 103.90 | 102.65 | 103.05 | 3.70 | ||
| 200 | Theanine | 101.45 | 95.23 | 98.15 | 101.15 | 102.18 | 93.95 | 3.53 | |
| GABA | 102.85 | 101.50 | 97.33 | 102.13 | 99.90 | 100.95 | 1.95 | ||
| GABA Candy | 50 | Theanine | 99.20 | 94.30 | 97.90 | 103.00 | 96.60 | 103.70 | 3.70 |
| GABA | 103.87 | 100.47 | 98.17 | 99.87 | 102.67 | 99.47 | 2.11 | ||
| 100 | Theanine | 98.85 | 98.75 | 98.55 | 97.95 | 100.90 | 97.10 | 1.28 | |
| GABA | 94.53 | 99.63 | 101.33 | 94.93 | 98.83 | 100.63 | 2.96 | ||
| 200 | Theanine | 102.43 | 97.60 | 99.25 | 97.93 | 98.43 | 98.75 | 1.76 | |
| GABA | 94.59 | 100.29 | 96.14 | 103.37 | 94.82 | 95.87 | 3.62 | ||
| Green Tea Beverage | 50 | Theanine | 99.70 | 95.30 | 102.40 | 99.50 | 103.40 | 99.20 | 2.84 |
| GABA | 101.60 | 96.10 | 98.50 | 96.90 | 103.80 | 98.80 | 2.93 | ||
| 100 | Theanine | 99.90 | 98.30 | 99.35 | 99.00 | 96.90 | 94.40 | 2.08 | |
| GABA | 98.40 | 98.65 | 97.90 | 102.40 | 97.45 | 98.75 | 1.79 | ||
| 200 | Theanine | 95.75 | 95.75 | 97.70 | 95.78 | 95.25 | 103.15 | 3.11 | |
| GABA | 99.13 | 98.08 | 103.58 | 98.10 | 100.70 | 101.45 | 2.15 | ||
| Matcha Cookie | 50 | Theanine | 98.98 | 97.08 | 97.88 | 101.68 | 100.08 | 98.88 | 1.64 |
| GABA | 98.82 | 94.02 | 98.92 | 98.42 | 95.82 | 96.92 | 2.01 | ||
| 100 | Theanine | 94.09 | 96.69 | 99.64 | 97.64 | 95.89 | 99.74 | 2.26 | |
| GABA | 94.76 | 98.01 | 97.06 | 99.46 | 99.71 | 96.56 | 1.92 | ||
| 200 | Theanine | 99.27 | 100.77 | 99.35 | 99.75 | 101.27 | 98.30 | 1.08 | |
| GABA | 98.30 | 96.23 | 99.80 | 99.88 | 94.85 | 98.75 | 2.07 | ||
| Solid Beverage | 50 | Theanine | 99.52 | 98.82 | 96.22 | 96.42 | 102.82 | 102.22 | 2.81 |
| GABA | 97.77 | 96.27 | 97.57 | 95.37 | 99.17 | 100.97 | 2.05 | ||
| 100 | Theanine | 98.26 | 101.16 | 94.81 | 96.81 | 96.51 | 101.51 | 2.73 | |
| GABA | 94.73 | 99.83 | 96.53 | 94.48 | 94.98 | 98.03 | 2.22 | ||
| 200 | Theanine | 97.10 | 100.48 | 96.73 | 99.60 | 97.13 | 96.85 | 1.66 | |
| GABA | 103.79 | 100.49 | 97.27 | 97.22 | 95.92 | 96.89 | 3.02 | ||
| Theanine and GABA Mixed drink | 50 | Theanine | 95.97 | 103.67 | 98.27 | 101.57 | 102.77 | 102.57 | 3.00 |
| GABA | 101.08 | 100.38 | 99.88 | 101.38 | 98.68 | 99.68 | 0.99 | ||
| 100 | Theanine | 102.83 | 96.83 | 101.83 | 96.58 | 94.13 | 103.43 | 3.93 | |
| GABA | 97.74 | 99.44 | 94.14 | 99.64 | 98.79 | 102.69 | 2.83 | ||
| 200 | Theanine | 102.67 | 101.59 | 95.29 | 99.99 | 99.34 | 97.59 | 2.70 | |
| GABA | 101.15 | 97.70 | 98.20 | 99.47 | 96.90 | 98.47 | 1.51 | ||
| Samples | Content (mg/kg) | Average Value (mg/kg) | RSD (%) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Theanine and GABA bonbon | Theanine | 1330.10 | 1313.75 | 1336.80 | 1309.65 | 1264.05 | 1318.40 | 1312.13 | 1.96 |
| GABA | 7088.40 | 7012.10 | 6528.75 | 6687.05 | 6563.10 | 6587.90 | 6744.55 | 3.61 | |
| Theanine and GABA gummy candy | Theanine | 1093.10 | 1100.20 | 1118.15 | 1110.80 | 1100.90 | 1130.15 | 1108.88 | 1.23 |
| GABA | 5282.20 | 5134.90 | 5299.75 | 5211.30 | 5129.65 | 5158.25 | 5202.68 | 1.43 | |
| Theanine and GABA mixed drink | Theanine | 768.75 | 768.20 | 774.40 | 785.20 | 762.90 | 773.85 | 772.22 | 0.99 |
| GABA | 5778.50 | 5744.25 | 5800.25 | 5817.75 | 5785.55 | 5826.35 | 5792.11 | 0.51 | |
| Black tea beverage | Theanine | 375.60 | 366.85 | 370.20 | 371.95 | 366.80 | 373.65 | 370.84 | 0.97 |
| GABA | 22.90 | 22.50 | 22.60 | 23.30 | 23.35 | 23.25 | 22.98 | 1.62 | |
| Solid beverage | Theanine | 302.40 | 302.55 | 312.75 | 305.70 | 307.55 | 314.00 | 307.49 | 1.62 |
| GABA | 93.50 | 90.65 | 91.90 | 94.35 | 91.70 | 91.50 | 92.27 | 1.50 | |
| Analytes | Samples | LOD (mg/kg) | LOQ (mg/kg) | Linear Range (µg/mL) | Derivatization Reagent | Derivatization Time (min) | Separation Time (min) | RSD (%) | Method | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Theanine | Green tea | 3 × 10−3 | 0.01 | 0.02–1.0 | - | - | 16 | 3.0–10.5 | GC-MS/MS | Gao et al. 2023 [15] |
| Theanine | Tea | 9.8 × 10−2 | - | 0.87–34.8 | Formaldehyde and sodium borohydride | - | 5 | - | CE-ECL | Yi et al. 2017 [17] |
| Theanine | Tea | 5.7 × 10−4 | 1.88 × 10−3 | 10–200 | CBBC-Cl | 6 | 14 | 2.24–4.85 | HPLC-FLD | Wang et al. 2020 [18] |
| GABA | Alcoholic beverage | 0.1–8.2 | 0.25–27.3 | 10–500 | - | - | 6 | 1.17–7.93 | LC-MS/MS | Liu et al. 2023 [20] |
| GABA | Germinated brown rice | 9.8 × 10−4 | - | 5–60 | OPA | 2 | 20 | - | HPLC-DAD | Cheng et al. 2014 [21] |
| GABA | Fermented soybean products | 3 | 10 | 1–100 | FMOC-Cl | 5 | 45 | 0.56–4.21 | HPLC-DAD | Zhuang et al. 2023 [22] |
| GABA | Plants foods and medicinal plants | 9 | - | 2–1000 | Dansyl-Cl | 60 | - | 0.73–3.72 | HPLC-DAD | Pencheva et al. 2022 [24] |
| Theanine and GABA | Tea | 2.6 and 4.1 | 8.7 and 13.7 | 1.74–69.6 and 1.03–41.2 | OPA and NAC | 1 | 19 and 18 | - | HPLC-FLD | Tu et al. 2012 [23] |
| Theanine and GABA | Tea | 1.162 × 10−2 and 3.4 × 10−3 | - | - | DABS-Cl | 10 | 20 and 40 | - | HPLC-DAD | Syu et al. 2008 [34] |
| Theanine and GABA | Food | 0.6 and 0.2 | 1.7 and 0.6 | 1–100 | DABS-Cl | 20 | 11 and 15 | 0.99–3.93 | HPLC-DAD | This method |
| Time (h) | The Peak Area of DABS-Theanine (mAU) | RSD (%) | The Peak Area of DABS-GABS (mAU) | RSD (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1,447,947 | 0.37 | 3,695,706 | 0.49 |
| 2 | 1,447,828 | 3,694,924 | ||
| 4 | 1,441,699 | 3,647,233 | ||
| 6 | 1,447,330 | 3,679,871 | ||
| 8 | 1,449,575 | 3,659,602 | ||
| 12 | 1,434,174 | 3,681,925 | ||
| 24 | 1,443,504 | 3,681,633 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xiao, C.; Xiao, J.; Wu, Y.; Pang, J.; Chen, F.; Zhang, W.; Xu, D. Determination of Amino Acids of Novel Food in Food by HPLC Coupled with Pre-Column Derivatization. Foods 2024, 13, 4012. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13244012
Xiao C, Xiao J, Wu Y, Pang J, Chen F, Zhang W, Xu D. Determination of Amino Acids of Novel Food in Food by HPLC Coupled with Pre-Column Derivatization. Foods. 2024; 13(24):4012. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13244012
Chicago/Turabian StyleXiao, Cenjun, Jing Xiao, Yuan Wu, Jie Pang, Fuhong Chen, Wenhua Zhang, and Dunming Xu. 2024. "Determination of Amino Acids of Novel Food in Food by HPLC Coupled with Pre-Column Derivatization" Foods 13, no. 24: 4012. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13244012
APA StyleXiao, C., Xiao, J., Wu, Y., Pang, J., Chen, F., Zhang, W., & Xu, D. (2024). Determination of Amino Acids of Novel Food in Food by HPLC Coupled with Pre-Column Derivatization. Foods, 13(24), 4012. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13244012





