Developing High-Coloring Natural Systems Using Double Emulsions with Daucus carota L. Extract to Meet High-Performance Requirements
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Samples and Reagents
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Double Emulsion Production
2.4. Emulsion Characterization
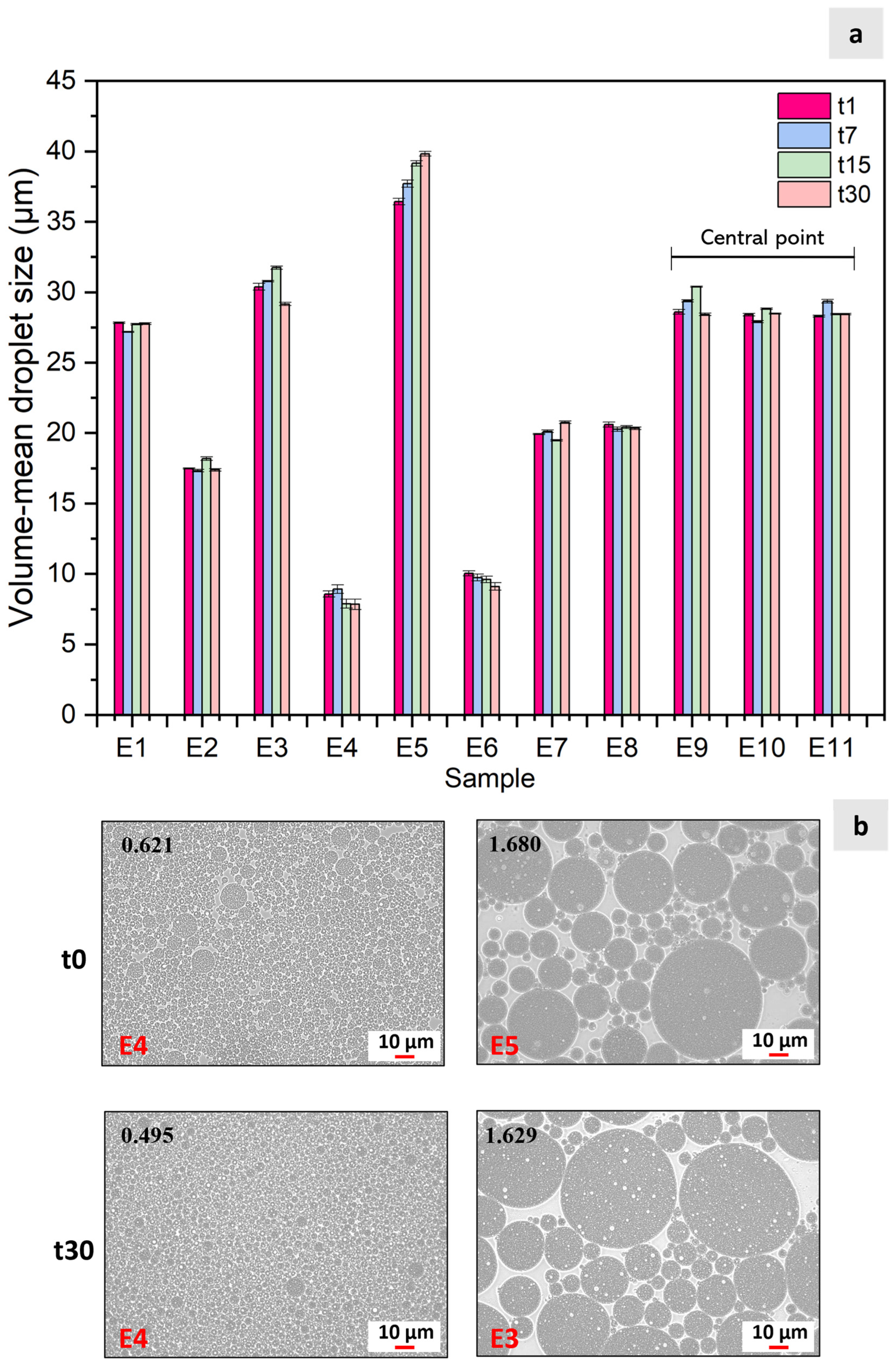
2.4.1. Droplet Size Analysis
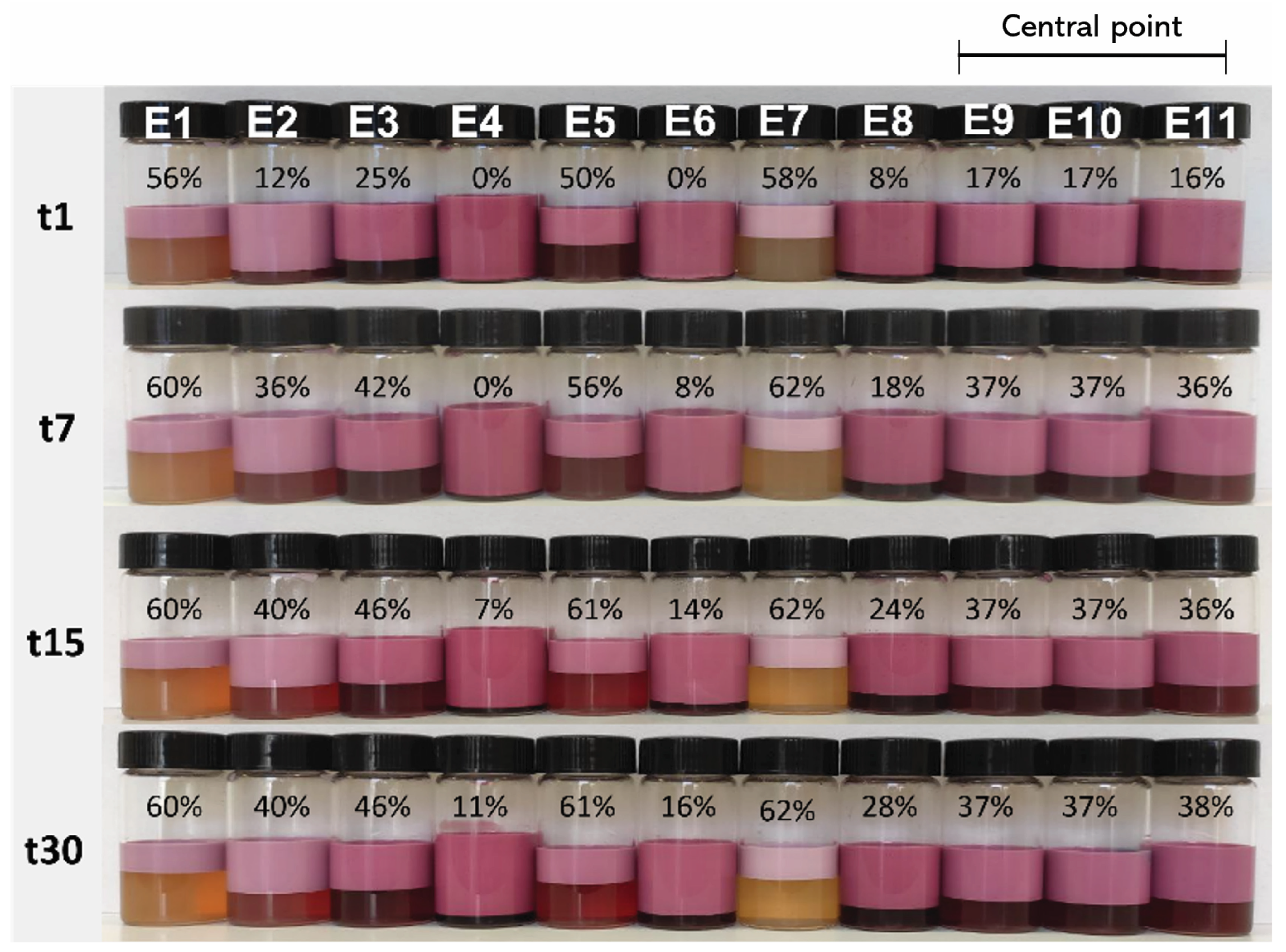
2.4.2. Creaming Index Evaluation
2.4.3. Emulsion Microstructure
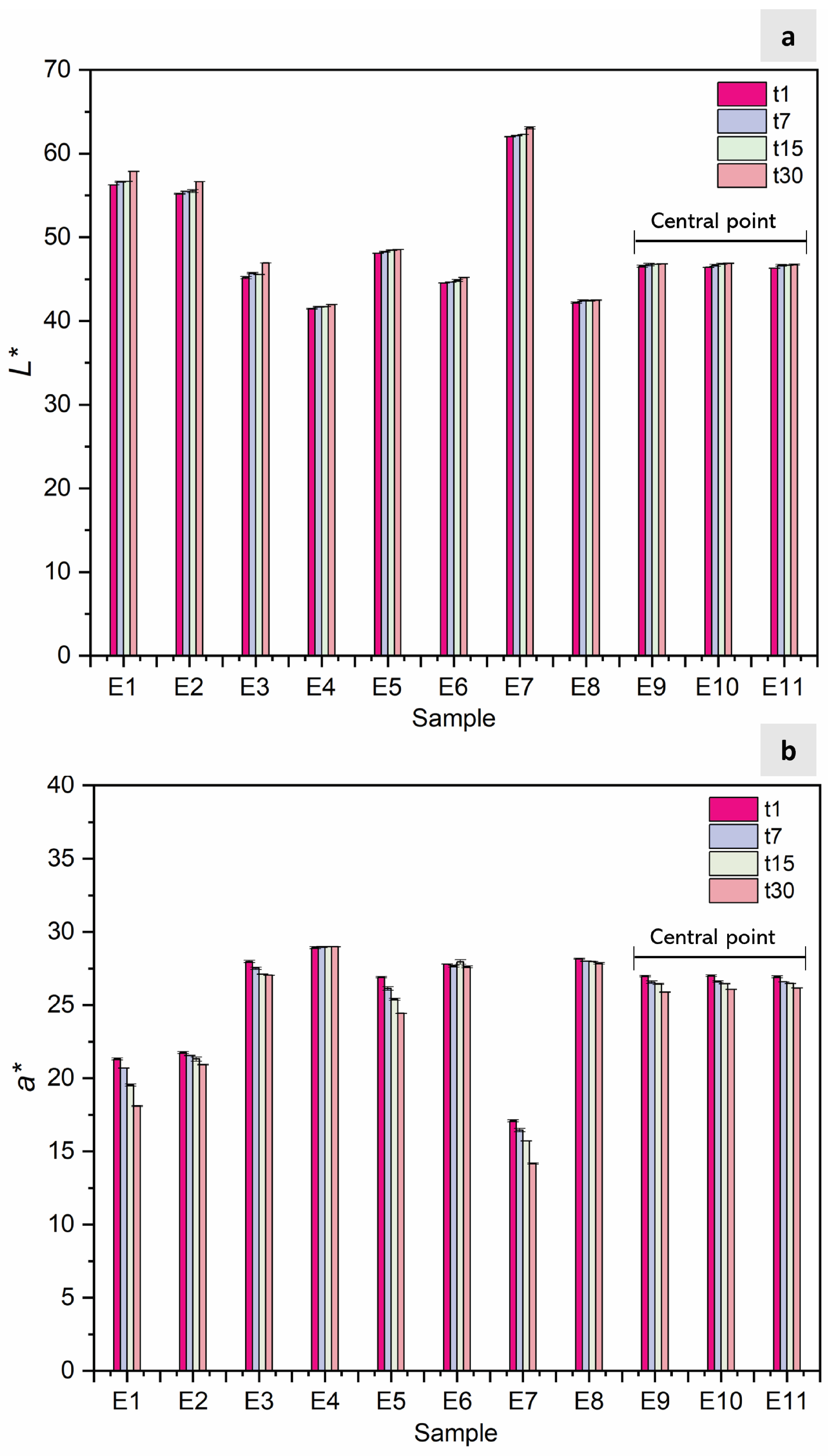
2.4.4. Color Determination
3. Results and Discussion
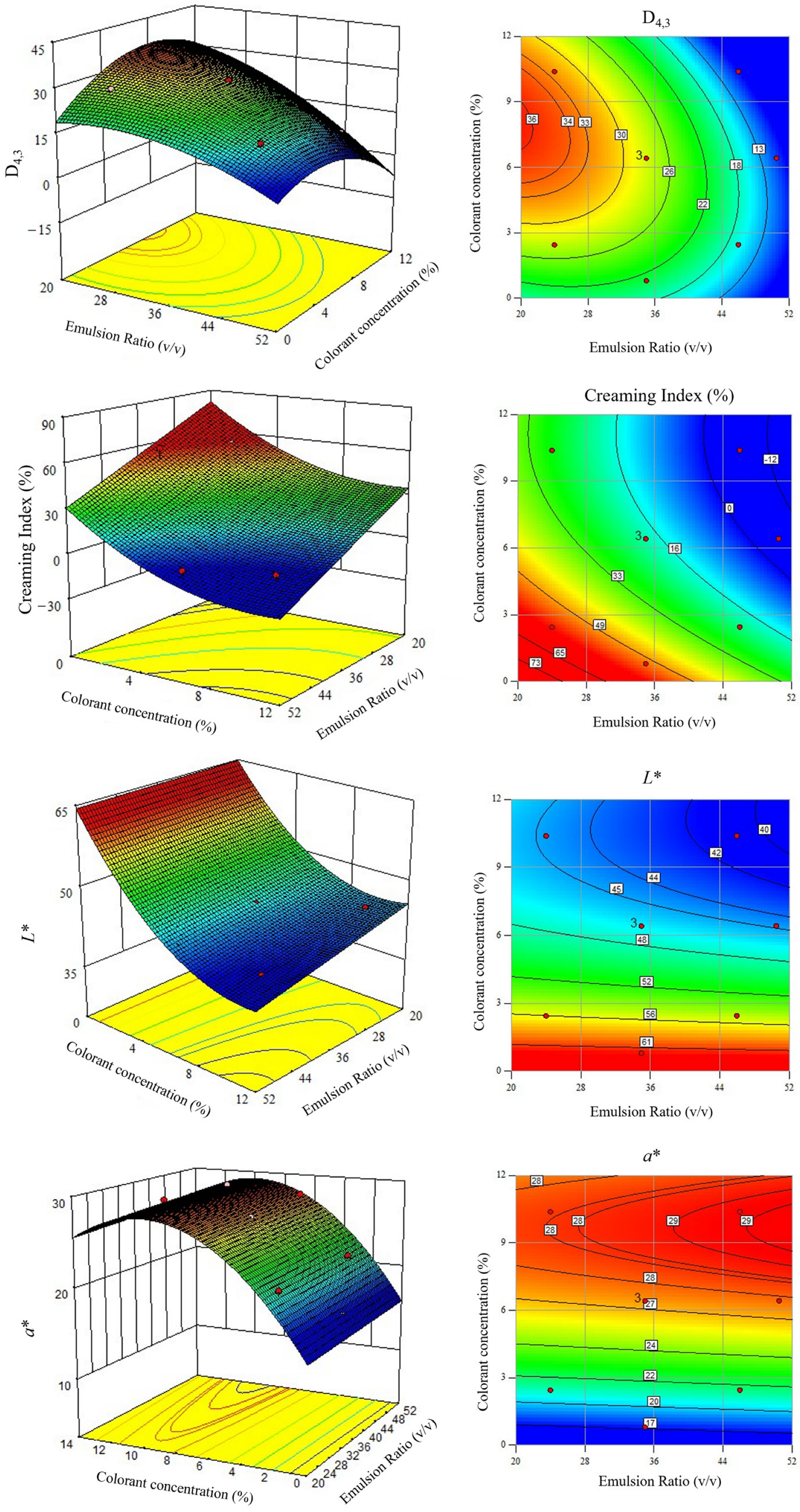
3.1. Emulsion Characterization
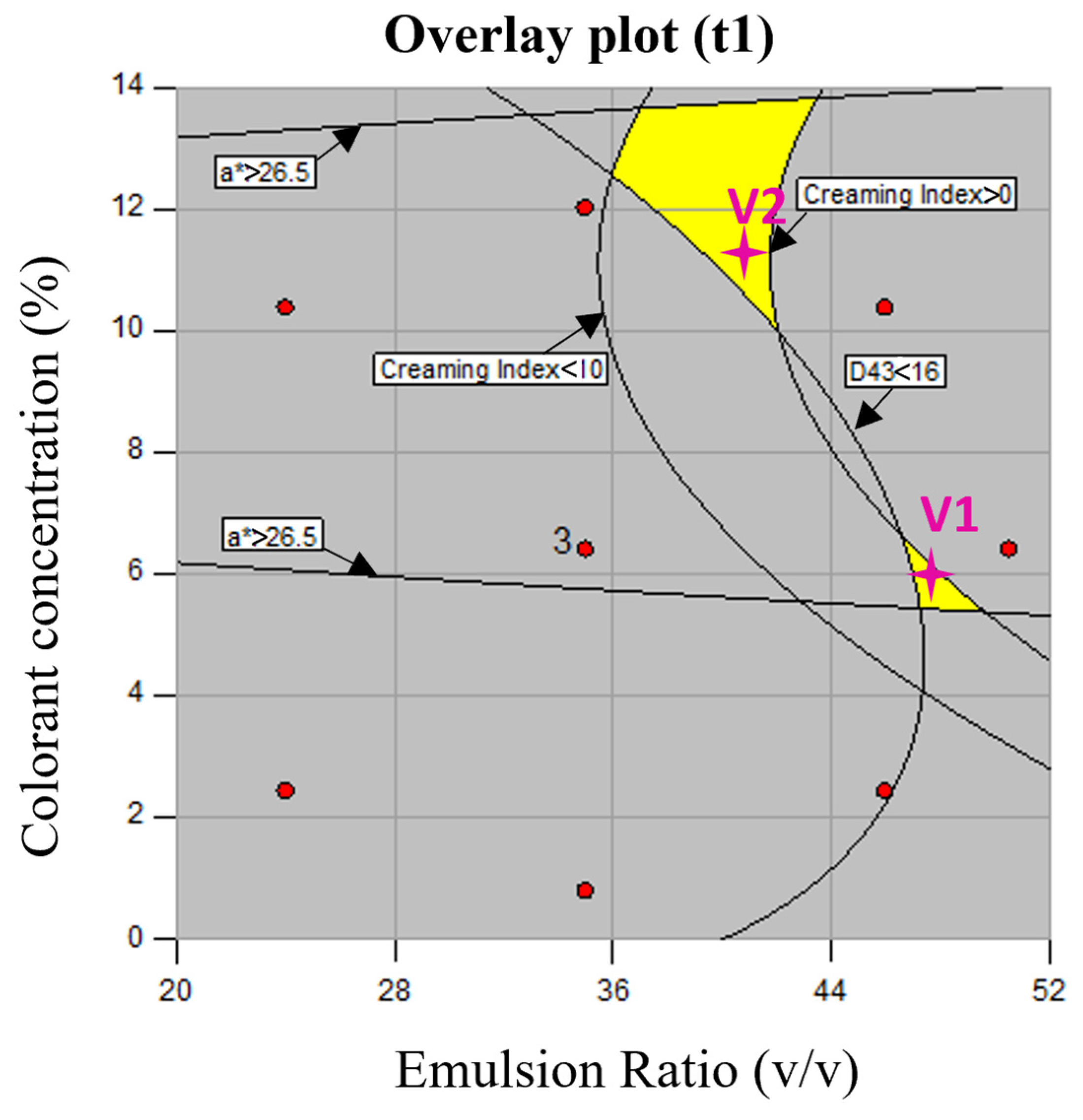
3.2. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Espinosa-Acosta, G.; Ramos-Jacques, A.; Molina, G.; Maya-Cornejo, J.; Esparza, R.; Hernandez-Martinez, A.; Sánchez-González, I.; Estevez, M. Stability Analysis of Anthocyanins Using Alcoholic Extracts from Black Carrot (Daucus carota ssp. Sativus Var. Atrorubens Alef.). Molecules 2018, 23, 2744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, H.; Sun, L.; Liu, R.; Si, X.; Li, D.; Wang, Y.; Shu, C.; Sun, X.; Jiang, Q.; Qiao, Y.; et al. Current Knowledge of Anthocyanin Metabolism in the Digestive Tract: Absorption, Distribution, Degradation, and Interconversion. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 63, 5953–5966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sampaio, S.L.; Lonchamp, J.; Dias, M.I.; Liddle, C.; Petropoulos, S.A.; Glamočlija, J.; Alexopoulos, A.; Santos-Buelga, C.; Ferreira, I.C.F.R.; Barros, L. Anthocyanin-Rich Extracts from Purple and Red Potatoes as Natural Colourants: Bioactive Properties, Application in a Soft Drink Formulation and Sensory Analysis. Food Chem. 2021, 342, 128526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nath, P.; Dukare, A.; Kumar, S.; Kale, S.; Kannaujia, P. Black Carrot (Daucus carota subsp. sativus) Anthocyanin-infused Potato Chips: Effect on Bioactive Composition, Color Attributes, Cooking Quality, and Microbial Stability. J. Food Process Preserv. 2022, 46, e16180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, S.; Giusti, M.M. Comparing the Effect of Whey Protein Preheating Temperatures on the Color Expression and Stability of Anthocyanins from Different Sources. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 124, 107273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuevas Montilla, E.; Rodriguez Arzaba, M.; Hillebrand, S.; Winterhalter, P. Anthocyanin Composition of Black Carrot (Daucus carota ssp. Sativus Var. Atrorubens Alef.) Cultivars Antonina, Beta Sweet, Deep Purple, and Purple Haze. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 3385–3390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polat, S.; Guclu, G.; Kelebek, H.; Keskin, M.; Selli, S. Comparative Elucidation of Colour, Volatile and Phenolic Profiles of Black Carrot (Daucus carota L.) Pomace and Powders Prepared by Five Different Drying Methods. Food Chem. 2022, 369, 130941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albuquerque, B.R.; Pinela, J.; Barros, L.; Oliveira, M.B.P.P.; Ferreira, I.C.F.R. Anthocyanin-Rich Extract of Jabuticaba Epicarp as a Natural Colorant: Optimization of Heat- and Ultrasound-Assisted Extractions and Application in a Bakery Product. Food Chem. 2020, 316, 126364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatterjee, N.S.; Dara, P.K.; Perumcherry Raman, S.; Vijayan, D.K.; Sadasivam, J.; Mathew, S.; Ravishankar, C.N.; Anandan, R. Nanoencapsulation in Low-molecular-weight Chitosan Improves in Vivo Antioxidant Potential of Black Carrot Anthocyanin. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2021, 101, 5264–5271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khoo, H.E.; Azlan, A.; Tang, S.T.; Lim, S.M. Anthocyanidins and Anthocyanins: Colored Pigments as Food, Pharmaceutical Ingredients, and the Potential Health Benefits. Food Nutr. Res. 2017, 61, 1361779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monica, L.; Tundis, R.; Menichini, F. Anthocyanins from Vaccinium Species: Potential Health Effects, Bioaccessibility and Use in Food Industry. In Handbook of Anthocyanins: Food Sources, Chemical Applications and Health Benefits; Warner, L., Ed.; Nova Science Publishers Inc.: Hauppauge, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 175–196. ISBN 9781633217959. [Google Scholar]
- Swer, T.L.; Chauhan, K. Stability Studies of Enzyme Aided Anthocyanin Extracts from Prunus nepalensis L. LWT 2019, 102, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aditya, N.P.; Aditya, S.; Yang, H.; Kim, H.W.; Park, S.O.; Ko, S. Co-Delivery of Hydrophobic Curcumin and Hydrophilic Catechin by a Water-in-Oil-in-Water Double Emulsion. Food Chem. 2015, 173, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, L.; Huan, S.; Rojas, O.J.; McClements, D.J. Recent Innovations in Emulsion Science and Technology for Food Applications. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 8944–8963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elaine, E.; Bhandari, B.; Tan, C.P.; Nyam, K.L. Recent Advances in the Formation, Stability, and Emerging Food Application of Water-in-Oil-in-Water Double Emulsion Carriers. Food Bioproc. Tech. 2024, 17, 3440–3460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alouk, I.; Xu, D.; Cao, Y. Encapsulation of Natural Pigments by Double Emulsion: A Review. Food Biosci. 2023, 56, 2212–4292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Tan, Y.; Zhou, H.; Muriel Mundo, J.L.; McClements, D.J. Protection of Anthocyanin-Rich Extract from PH-Induced Color Changes Using Water-in-Oil-in-Water Emulsions. J. Food Eng. 2019, 254, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frountzas, M.; Karanikki, E.; Toutouza, O.; Sotirakis, D.; Schizas, D.; Theofilis, P.; Tousoulis, D.; Toutouzas, K.G. Exploring the Impact of Cyanidin-3-Glucoside on Inflammatory Bowel Diseases: Investigating New Mechanisms for Emerging Interventions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 9399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akinnusi, P.A.; Olubode, S.O.; Alade, A.A.; Ashimi, A.A.; Onawola, O.L.; Agbolade, A.O.; Emeka, A.P.; Shodehinde, S.A.; Adeniran, O.Y. Potential Inhibitory Biomolecular Interactions of Natural Compounds with Different Molecular Targets of Diabetes. Bioinform. Biol. Insights 2023, 17, 11779322231167970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, D.; Patel, C. Revisiting the Use of Quantum Chemical Calculations in LogPoctanol-Water Prediction. Molecules 2023, 28, 801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sebben, D.A.; MacWilliams, S.V.; Yu, L.; Spicer, P.T.; Bulone, V.; Krasowska, M.; Beattie, D.A. Influence of Aqueous Phase Composition on Double Emulsion Stability and Colour Retention of Encapsulated Anthocyanins. Foods 2021, 11, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teixeira, L.G.; Rezende, S.; Fernandes, Â.; Fernandes, I.P.; Barros, L.; Barreira, J.C.M.; Leimann, F.V.; Ferreira, I.C.F.R.; Barreiro, M.-F. Water-in-Oil-in-Water Double Emulsions as Protective Carriers for Sambucus nigra L. Coloring Systems. Molecules 2022, 27, 552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Guo, C.; Cai, S.; Yi, J.; Zhou, L. Fabrication of Anthocyanin–Rich W1/O/W2 Emulsion Gels Based on Pectin–GDL Complexes: 3D Printing Performance. Food Res. Int. 2023, 168, 112782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teixé-Roig, J.; Oms-Oliu, G.; Velderrain-Rodríguez, G.R.; Odriozola-Serrano, I.; Martín-Belloso, O. The Effect of Sodium Carboxymethylcellulose on the Stability and Bioaccessibility of Anthocyanin Water-in-Oil-in-Water Emulsions. Food Bioproc. Technol. 2018, 11, 2229–2241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, J.; Trujillo-Cayado, L.A.; Carrillo, F.; López-Castejón, M.L.; Alfaro-Rodríguez, M.C. Relation between Droplet Size Distributions and Physical Stability for Zein Microfluidized Emulsions. Polymers 2022, 14, 2195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Luo, Z.; Wang, J.; Ruan, Q.; Guo, J.; Yang, X. Fabrication of Stable Pickering Double Emulsion with Edible Chitosan/Soy β-Conglycinin Complex Particles via One-Step Emulsification Strategy. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 138, 108465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parralejo-Sanz, S.; Quereda-Moraleda, I.; Requena, T.; Cano, M.P. Encapsulation of Indicaxanthin-Rich Opuntia Green Extracts by Double Emulsions for Improved Stability and Bioaccessibility. Foods 2024, 13, 1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Li, C.; Yang, Y.; He, X.; Zhang, B.; Fu, X.; Tan, C.P.; Huang, Q. Starch Granules as Pickering Emulsifiers: Role of Octenylsuccinylation and Particle Size. Food Chem. 2019, 283, 437–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Wang, Y.-Q.; Li, L.; Song, H.-L.; Wu, H.-T.; Zhu, B.-W. Fabrication and Characterization of Salidroside W/O/W Emulsion with Sodium Alginate. Food Chem. X 2024, 22, 101260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eisinaité, V.; Leskauskaité, D.; Pukalskiené, M.; Venskutonis, P.R. Freeze-Drying of Black Chokeberry Pomace Extract—Loaded Double Emulsions to Obtain Dispersible Powders. J. Food Sci. 2020, 85, 628–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandenius, C.; Brundin, A. Bioprocess Optimization Using Design-of-experiments Methodology. Biotechnol. Prog. 2008, 24, 1191–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montgomery, D.C.; McAuley, R. Response Surface Methods and Other Approaches to Process Optimization. Des. Anal. Exp. 1997, 427–510. [Google Scholar]
- Siqueira Leite, C.B.; Coelho, J.M.; Muehlmann, L.A.; Azevedo, R.B.; Sousa, M.H. Microemulsions as Platforms for Transdermal Delivery of Hydrophilic Drugs—A Review. Curr. Nanosci. 2017, 14, 170–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, M.I.; Iemma, A.F. Experimental Design and Process Optimization; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2014; ISBN 9780429161865. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, S.C.; Almeida, T.; Colucci, G.; Santamaria-Echart, A.; Manrique, Y.A.; Dias, M.M.; Barros, L.; Fernandes, Â.; Colla, E.; Barreiro, M.F. Spirulina (Arthrospira platensis) Protein-Rich Extract as a Natural Emulsifier for Oil-in-Water Emulsions: Optimization through a Sequential Experimental Design Strategy. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng. Asp. 2022, 648, 129264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muschiolik, G.; Dickinson, E. Double Emulsions Relevant to Food Systems: Preparation, Stability, and Applications. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2017, 16, 532–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leister, N.; Karbstein, H.P. Evaluating the Stability of Double Emulsions—A Review of the Measurement Techniques for the Systematic Investigation of Instability Mechanisms. Colloids Interfaces 2020, 4, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Central Composite Rotatable Design 22 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| −1.41 | −1 | 0 | +1 | +1.41 | ||
| Emulsion ratio (W1/O)/W2 (v/v) | 20/80 | 24/76 | 35/65 | 46/54 | 50/50 | |
| Colorant concentration (wt.%) | 0.80 | 2.43 | 6.40 | 10.37 | 12.00 | |
| Run | Independent Variables | |
|---|---|---|
| Emulsion Ratio (W1/O)/W2 (v/v) | Colorant Concentration (wt.%) | |
| X1 (x1) | X2 (x2) | |
| E1 | −1 (24/76) | −1 (2.43) |
| E2 | +1 (46/54) | −1 (2.43) |
| E3 | −1 (24/76) | +1 (10.37) |
| E4 | +1 (46/54) | +1 (10.37) |
| E5 | −1.41 (20/80) | 0 (6.40) |
| E6 | +1.41(50/50) | 0 (6.40) |
| E7 | 0 (35/65) | −1.41 (0.80) |
| E8 | 0 (35/65) | +1.41 (12.00) |
| E9 | 0 (35/65) | 0 (6.40) |
| E10 | 0 (35/65) | 0 (6.40) |
| E11 | 0 (35/65) | 0 (6.40) |
| Source | Droplet Size (D4,3) | Creaming Index (CI) | L* | a* | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a’s Coefficients # (Actual Factors) | p-Value | a’s Coefficients # (Actual Factors) | p-Value | a’s Coefficients # (Actual Factors) | p-Value | a’s Coefficients # (Actual Factors) | p-Value | |
| Model | -- | 0.0001 | -- | 0.0002 | -- | <0.0001 | -- | <0.0001 |
| Intercept | +3.74 | <0.0001 | +113.4 | <0.0001 | +65.1 | <0.0001 | +14.4 | <0.0001 |
| x1—Emulsion Ratio | +1.21 | <0.0001 | −1.59 | 0.0001 | −0.0135 | 0.0005 | +0.0298 | 0.0209 |
| x2—Colorant Concentration | +5.59 | 0.2744 | −8.46 | 0.0005 | −3.50 | <0.0001 | +2.74 | <0.0001 |
| x1×2 | −0.0654 | 0.0128 | -- | n.s. | −0.0153 | 0.0371 | -- | n.s. |
| (x1)2 | −0.0226 | 0.0077 | -- | n.s. | -- | n.s. | -- | n.s. |
| (x2)2 | −0.270 | 0.0011 | +0.380 | 0.0567 | +0.185 | <0.0001 | −0.141 | <0.0001 |
| Quality Parameter | Values | Values | Values | Values | ||||
| Adequate Precision | 23.38 | 16.10 | 61.31 | 60.73 | ||||
| R2 | 0.9852 | 0.9348 | 0.9964 | 0.9951 | ||||
| R2adj | 0.9704 | 0.9069 | 0.9939 | 0.9931 | ||||
| R2pred | 0.8950 | 0.7893 | 0.9776 | 0.9826 | ||||
| Effect | D4,3 | CI | L* | a* | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Emulsion composition | V1 (48/52, 6%) | 9.85 ± 0.44 b | 7.12 ± 5.20 a | 44.00 ± 0.14 a | 26.01 ± 0.19 |
| V2 (41/59, 11%) | 17.72 ± 0.53 a | 7.83 ± 6.30 a | 37.40 ± 012 b | 26.61 ± 0.27 | |
| p-value | <0.0001 | 0.1025 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | |
| Time | t1 | 13.68 ± 3.96 a | 0.00 ± 0.00 c | 40.56 ± 3.24 c | 26.47± 0.35 a |
| t7 | 13.84 ± 3.64 a | 6.24 ± 1.35 b | 40.64 ± 3.40 b,c | 26.51 ± 0.39 a | |
| t15 | 13.93 ± 4.13 a | 7.72 ± 0.72 b | 40.76 ± 3.28 a,b | 26.11 ± 0.23 b | |
| t30 | 13.70 ± 4.12 a | 15.92 ± 1.60 a | 40.83 ± 3.28 a | 26.14 ± 0.36 b | |
| p-value | 0.8275 | <0.0001 | 0.0001 | 0.0007 | |
| Emulsion composition × Time | p-value | 0.3320 | 0.1026 | 0.0184 | 0.5325 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gracher-Teixeira, L.; Pituco, S.C.S.; Colucci, G.; Santamaria-Echart, A.; Peres, A.M.; Dias, M.M.; Barreiro, M.F. Developing High-Coloring Natural Systems Using Double Emulsions with Daucus carota L. Extract to Meet High-Performance Requirements. Foods 2024, 13, 4147. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13244147
Gracher-Teixeira L, Pituco SCS, Colucci G, Santamaria-Echart A, Peres AM, Dias MM, Barreiro MF. Developing High-Coloring Natural Systems Using Double Emulsions with Daucus carota L. Extract to Meet High-Performance Requirements. Foods. 2024; 13(24):4147. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13244147
Chicago/Turabian StyleGracher-Teixeira, Liandra, Samara C. Silva Pituco, Giovana Colucci, Arantzazu Santamaria-Echart, António M. Peres, Madalena M. Dias, and M. Filomena Barreiro. 2024. "Developing High-Coloring Natural Systems Using Double Emulsions with Daucus carota L. Extract to Meet High-Performance Requirements" Foods 13, no. 24: 4147. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13244147
APA StyleGracher-Teixeira, L., Pituco, S. C. S., Colucci, G., Santamaria-Echart, A., Peres, A. M., Dias, M. M., & Barreiro, M. F. (2024). Developing High-Coloring Natural Systems Using Double Emulsions with Daucus carota L. Extract to Meet High-Performance Requirements. Foods, 13(24), 4147. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13244147









