Development of a Sensitive and Specific Quantitative RT-qPCR Method for the Detection of Hepatitis E Virus Genotype 3 in Porcine Liver and Foodstuff
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Primer Design
2.2. Implementation of an Internal Amplification Contral (IAC)
2.3. Reverse Transcription Quantitative Real-Time PCR (RT-qPCR) Assay
2.4. Reference Method Used for Comparative Analysis of Samples
2.5. Analytical Specificity of the JBH4-HEV RT-qPCR Assay
2.6. Analytical Sensitivity of the JBH4-HEV RT-qPCR Assay
2.7. Quantification of HEV RNA by the JBH4-HEV RT-qPCR Assay under Field Conditions by a Spiking Experiment
2.8. Validation of the JBH4-HEV RT-qPCR Assay by Testing Naturally Contaminated Porcine Liver
3. Results
3.1. Analytical Specificity of the JBH4-HEV RT-qPCR Assay
3.2. Analytical Sensitivity of the JBH4-HEV RT-qPCR Assay
3.3. Analytical Sensitivity of the JBH4-HEV RT-qPCR Assay under Field Conditions in Spiked Liver Samples
3.4. Validation of the JBH4-HEV RT-qPCR Assay
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kamar, N.; Bendall, R.; Legrand-Abravanel, F.; Xia, N.-S.; Ijaz, S.; Izopet, J.; Dalton, H.R. Hepatitis E. Lancet 2012, 379, 2477–2488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, D.B.; Izopet, J.; Nicot, F.; Simmonds, P.; Jameel, S.; Meng, X.J.; Norder, H.; Okamoto, H.; van der Poel, W.H.M.; Reuter, G.; et al. Update: Proposed reference sequences for subtypes of hepatitis E virus (species Orthohepevirus A). J. Gen. Virol. 2020, 101, 692–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiry, D.; Mauroy, A.; Pavio, N.; Purdy, M.A.; Rose, N.; Thiry, E.; de Oliveira-Filho, E.F. Hepatitis E Virus and Related Viruses in Animals. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2017, 64, 37–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aslan, A.T.; Balaban, H.Y. Hepatitis E virus: Epidemiology, diagnosis, clinical manifestations, and treatment. World J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 26, 5543–5560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, H.C.; Wichmann, O.; Duizer, E. Transmission routes and risk factors for autochthonous hepatitis E virus infection in Europe: A systematic review. Epidemiol. Infect. 2010, 138, 145–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izopet, J.; Tremeaux, P.; Marion, O.; Migueres, M.; Capelli, N.; Chapuy-Regaud, S.; Mansuy, J.M.; Abravanel, F.; Kamar, N.; Lhomme, S. Hepatitis E virus infections in Europe. J. Clin. Virol. 2019, 120, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velavan, T.P.; Pallerla, S.R.; Johne, R.; Todt, D.; Steinmann, E.; Schemmerer, M.; Wenzel, J.J.; Hofmann, J.; Shih, J.W.K.; Wedemeyer, H.; et al. Hepatitis E: An update on One Health and clinical medicine. Liver Int. 2021, 41, 1462–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treagus, S.; Wright, C.; Baker-Austin, C.; Longdon, B.; Lowther, J. The Foodborne Transmission of Hepatitis E Virus to Humans. Food Environ. Virol. 2021, 13, 127–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavio, N.; Doceul, V.; Bagdassarian, E.; Johne, R. Recent knowledge on hepatitis E virus in Suidae reservoirs and transmission routes to human. Vet. Res. 2017, 48, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anheyer-Behmenburg, H.E.; Szabo, K.; Schotte, U.; Binder, A.; Klein, G.; Johne, R. Hepatitis E Virus in Wild Boars and Spillover Infection in Red and Roe Deer, Germany, 2013–2015. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2017, 23, 130–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faber, M.; Willrich, N.; Schemmerer, M.; Rauh, C.; Kuhnert, R.; Stark, K.; Wenzel, J.J. Hepatitis E virus seroprevalence, seroincidence and seroreversion in the German adult population. J. Viral Hepat. 2018, 25, 752–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.J.; Wiseman, B.; Elvinger, F.; Guenette, D.K.; Toth, T.E.; Engle, R.E.; Emerson, S.U.; Purcell, R.H. Prevalence of antibodies to hepatitis E virus in veterinarians working with swine and in normal blood donors in the United States and other countries. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2002, 40, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montagnaro, S.; De Martinis, C.; Sasso, S.; Ciarcia, R.; Damiano, S.; Auletta, L.; Iovane, V.; Zottola, T.; Pagnini, U. Viral and Antibody Prevalence of Hepatitis E in European Wild Boars (Sus scrofa) and Hunters at Zoonotic Risk in the Latium Region. J. Comp. Pathol. 2015, 153, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuda, H.; Okada, K.; Takahashi, K.; Mishiro, S. Severe hepatitis E virus infection after ingestion of uncooked liver from a wild boar. J. Infect. Dis. 2003, 188, 944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferri, G.; Vergara, A. Hepatitis E Virus in the Food of Animal Origin: A Review. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2021, 18, 368–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pallerla, S.R.; Schembecker, S.; Meyer, C.G.; Linh, L.T.K.; Johne, R.; Wedemeyer, H.; Bock, C.T.; Kremsner, P.G.; Velavan, T.P. Hepatitis E virus genome detection in commercial pork livers and pork meat products in Germany. J. Viral Hepat. 2021, 28, 196–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szabo, K.; Trojnar, E.; Anheyer-Behmenburg, H.; Binder, A.; Schotte, U.; Ellerbroek, L.; Klein, G.; Johne, R. Detection of hepatitis E virus RNA in raw sausages and liver sausages from retail in Germany using an optimized method. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2015, 215, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, L.; Ramos, T.M.; Wu, X.; DiCaprio, E. Presence of hepatitis E virus in commercially available pork products. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2021, 339, 109033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, C.; Chae, C. Localization of swine hepatitis E virus in liver and extrahepatic tissues from naturally infected pigs by in situ hybridization. J. Hepatol. 2003, 38, 827–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Said, B.; Ijaz, S.; Chand, M.A.; Kafatos, G.; Tedder, R.; Morgan, D. Hepatitis E virus in England and Wales: Indigenous infection is associated with the consumption of processed pork products. Epidemiol. Infect. 2014, 142, 1467–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motte, A.; Roquelaure, B.; Galambrun, C.; Bernard, F.; Zandotti, C.; Colson, P. Hepatitis E in three immunocompromized children in southeastern France. J. Clin. Virol. 2012, 53, 162–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansuy, J.M.; Gallian, P.; Dimeglio, C.; Saune, K.; Arnaud, C.; Pelletier, B.; Morel, P.; Legrand, D.; Tiberghien, P.; Izopet, J. A nationwide survey of hepatitis E viral infection in French blood donors. Hepatology 2016, 63, 1145–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Rosa, G.; Muscillo, M.; Vennarucci, V.S.; Garbuglia, A.R.; La Scala, P.; Capobianchi, M.R. Hepatitis E virus in Italy: Molecular analysis of travel-related and autochthonous cases. J. Gen. Virol. 2011, 92, 1617–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ripellino, P.; Pianezzi, E.; Martinetti, G.; Zehnder, C.; Mathis, B.; Giannini, P.; Forrer, N.; Merlani, G.; Dalton, H.R.; Petrini, O.; et al. Control of Raw Pork Liver Sausage Production Can Reduce the Prevalence of HEV Infection. Pathogens 2021, 10, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Poel, W.H.M.; Dalton, H.R.; Johne, R.; Pavio, N.; Bouwknegt, M.; Wu, T.; Cook, N.; Meng, X.J. Knowledge gaps and research priorities in the prevention and control of hepatitis E virus infection. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2018, 65 (Suppl. 1), 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, R.M.; Decker, C.C.; Dao Thi, V.L. Cell Culture Models for Hepatitis E Virus. Viruses 2019, 11, 608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jothikumar, N.; Cromeans, T.L.; Robertson, B.H.; Meng, X.J.; Hill, V.R. A broadly reactive one-step real-time RT-PCR assay for rapid and sensitive detection of hepatitis E virus. J. Virol. Methods 2006, 131, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, N.; D’Agostino, M.; Wood, A.; Scobie, L. Real-Time PCR-Based Methods for Detection of Hepatitis E Virus in Pork Products: A Critical Review. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vina-Rodriguez, A.; Schlosser, J.; Becher, D.; Kaden, V.; Groschup, M.H.; Eiden, M. Hepatitis E virus genotype 3 diversity: Phylogenetic analysis and presence of subtype 3b in wild boar in Europe. Viruses 2015, 7, 2704–2726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizuo, H.; Suzuki, K.; Takikawa, Y.; Sugai, Y.; Tokita, H.; Akahane, Y.; Itoh, K.; Gotanda, Y.; Takahashi, M.; Nishizawa, T.; et al. Polyphyletic strains of hepatitis E virus are responsible for sporadic cases of acute hepatitis in Japan. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2002, 40, 3209–3218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erker, J.C.; Desai, S.M.; Mushahwar, I.K. Rapid detection of Hepatitis E virus RNA by reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction using universal oligonucleotide primers. J. Virol. Methods 1999, 81, 109–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, X.; Yang, B.; Li, B.Y.; Yin, X.P.; Li, X.R.; Liu, J.X. Reverse transcription-loop-mediated isothermal amplification assay for rapid detection of hepatitis E virus. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2009, 47, 2304–2306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.Q.; Zhao, F.R.; Liu, Z.G.; Kong, W.L.; Wang, H.; Ouyang, Y.; Liang, H.B.; Zhang, C.Y.; Qi, H.T.; Huang, C.L.; et al. Simple and rapid detection of swine hepatitis E virus by reverse transcription loop-mediated isothermal amplification. Arch. Virol. 2012, 157, 2383–2388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, H.; Yan, S.; Wang, Y.; Lu, X.; Fu, H. Development of a One Step Reverse Transcription-Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification System for a Highly Sensitive Detection of Rabbit Hepatitis E Virus. Clin. Lab. 2017, 63, 901–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, P.; Poitras, E.; Leblanc, D.; Letellier, A.; Brassard, J.; Plante, D.; Houde, A. Comparative analysis of different TaqMan real-time RT-PCR assays for the detection of swine Hepatitis E virus and integration of Feline calicivirus as internal control. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2009, 106, 1360–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baylis, S.A.; Hanschmann, K.O.; Matsubayashi, K.; Sakata, H.; Roque-Afonso, A.M.; Kaiser, M.; Corman, V.M.; Kamili, S.; Aggarwal, R.; Trehanpati, N.; et al. Development of a World Health Organization International Reference Panel for different genotypes of hepatitis E virus for nucleic acid amplification testing. J. Clin. Virol. 2019, 119, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Germer, J.J.; Ankoudinova, I.; Belousov, Y.S.; Mahoney, W.; Dong, C.; Meng, J.; Mandrekar, J.N.; Yao, J.D. Hepatitis E Virus (HEV) Detection and Quantification by a Real-Time Reverse Transcription-PCR Assay Calibrated to the World Health Organization Standard for HEV RNA. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2017, 55, 1478–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frías, M.; López-López, P.; Zafra, I.; Caballero-Gómez, J.; Machuca, I.; Camacho, Á.; Risalde, M.A.; Rivero-Juárez, A.; Rivero, A. Development and Clinical Validation of a Pangenotypic PCR-Based Assay for the Detection and Quantification of Hepatitis E Virus (Orthohepevirus A Genus). J. Clin. Microbiol. 2021, 59, e02075-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, A.; Pietsch, K.; Zucker, R.; Mayr, A.; Müller-Hohe, E.; Messelhäusser, U.; Sing, A.; Busch, U.; Huber, I. Validation of a Duplex Real-Time PCR for the Detection of Salmonella spp. in Different Food Products. Food Anal. Methods 2011, 4, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.Y.; Li, D. Optimization and Implementation of the Virus Extraction Method for Hepatitis E Virus Detection from Raw Pork Liver. Food Environ. Virol. 2021, 13, 74–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schotte, U.; Martin, A.; Brogden, S.; Schilling-Loeffler, K.; Schemmerer, M.; Anheyer-Behmenburg, H.E.; Szabo, K.; Müller-Graf, C.; Wenzel, J.J.; Kehrenberg, C.; et al. Phylogeny and spatiotemporal dynamics of hepatitis E virus infections in wild boar and deer from six areas of Germany during 2013–2017. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2022, 69, e1992–e2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wist, V.; Kubacki, J.; Lechmann, J.; Steck, M.; Fraefel, C.; Stephan, R.; Bachofen, C. Complete Genome Sequence of a Swiss Hepatitis E Virus Isolate from the Liver of a Fattening Pig. Genome Announc. 2018, 6, e00113-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gremmel, N.; Keuling, O.; Becher, P.; Baechlein, C. Isolation of 15 hepatitis E virus strains lacking ORF1 rearrangements from wild boar and pig organ samples and efficient replication in cell culture. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2022, 69, e2617–e2628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicot, F.; Dimeglio, C.; Migueres, M.; Jeanne, N.; Latour, J.; Abravanel, F.; Ranger, N.; Harter, A.; Dubois, M.; Lameiras, S.; et al. Classification of the Zoonotic Hepatitis E Virus Genotype 3 into Distinct Subgenotypes. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 634430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baylis, S.A.; Ma, L.; Padley, D.J.; Heath, A.B.; Yu, M.W.; Collaborative Study Group. Collaborative study to establish a World Health Organization International genotype panel for parvovirus B19 DNA nucleic acid amplification technology (NAT)-based assays. Vox Sang. 2012, 102, 204–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozyra, I.; Bigoraj, E.; Jabłoński, A.; Politi, K.; Rzeżutka, A. Genetic Diversity and Epidemiological Significance of Wild Boar HEV-3 Strains Circulating in Poland. Viruses 2021, 13, 1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, J.; Takahashi, M.; Yazaki, Y.; Tsuda, F.; Okamoto, H. Development and validation of an improved RT-PCR assay with nested universal primers for detection of hepatitis E virus strains with significant sequence divergence. J. Virol. Methods 2006, 137, 325–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaba, M.; Davoust, B.; Marié, J.-L.; Barthet, M.; Henry, M.; Tamalet, C.; Raoult, D.; Colson, P. Frequent transmission of hepatitis E virus among piglets in farms in Southern France. J. Med. Virol. 2009, 81, 1750–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin-Latil, S.; Hennechart-Collette, C.; Delannoy, S.; Guillier, L.; Fach, P.; Perelle, S. Quantification of Hepatitis E Virus in Naturally-Contaminated Pig Liver Products. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, J.M.; Rayamajhi, N.; Gyun Kang, S.; Sang Yoo, H. Comparison of real-time reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction and nested or commercial reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction for the detection of hepatitis E virus particle in human serum. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2006, 56, 269–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gyarmati, P.; Mohammed, N.; Norder, H.; Blomberg, J.; Belák, S.; Widén, F. Universal detection of hepatitis E virus by two real-time PCR assays: TaqMan® and Primer-Probe Energy Transfer. J. Virol. Methods 2007, 146, 226–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enouf, V.; Dos Reis, G.; Guthmann, J.P.; Guerin, P.J.; Caron, M.; Marechal, V.; Nicand, E. Validation of single real-time TaqMan® PCR assay for the detection and quantitation of four major genotypes of hepatitis E virus in clinical specimens. J. Med. Virol. 2006, 78, 1076–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hennechart-Collette, C.; Fraisse, A.; Guillier, L.; Perelle, S.; Martin-Latil, S. Evaluation of methods for elution of HEV particles in naturally contaminated sausage, figatellu and pig liver. Food Microbiol. 2019, 84, 103235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenzel, J.J.; Preiss, J.; Schemmerer, M.; Huber, B.; Plentz, A.; Jilg, W. Detection of hepatitis E virus (HEV) from porcine livers in Southeastern Germany and high sequence homology to human HEV isolates. J. Clin. Virol. 2011, 52, 50–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baechlein, C.; Seehusen, F.; Nathues, H.; Grosse Beilage, E.; Baumgärtner, W.; Grummer, B. Molecular detection of hepatitis E virus in German domestic pigs. Berl. Munch. Tierarztl. Wochenschr. 2013, 126, 25–31. [Google Scholar]
- Boxman, I.L.A.; Verhoef, L.; Dop, P.Y.; Vennema, H.; Dirks, R.A.M.; Opsteegh, M. High prevalence of acute hepatitis E virus infection in pigs in Dutch slaughterhouses. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2022, 379, 109830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schielke, A.; Sachs, K.; Lierz, M.; Appel, B.; Jansen, A.; Johne, R. Detection of hepatitis E virus in wild boars of rural and urban regions in Germany and whole genome characterization of an endemic strain. Virol. J. 2009, 6, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, A.; Collineau, L.; Stephan, R.; Müller, A.; Stärk, K.D.C. Assessment of the risk of foodborne transmission and burden of hepatitis E in Switzerland. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2017, 242, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, N.; D’Agostino, M.; Johne, R. Potential Approaches to Assess the Infectivity of Hepatitis E Virus in Pork Products: A Review. Food Environ. Virol. 2017, 9, 243–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Primer: | Sequence 5′ → 3′ | Region | GC% | Tm (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JBH4-HEV | ORF1 (FJ705359) | |||
| ForwardPrimer: Fw_JBH4-HEV | 5′-TAAGGCTCCTGGCATTACTACT-3′ | 45–67 | 45.45 | 58.35 |
| ReversePrimer: Rv_JBH4-HEV | 5′-GCCGAACCACCACAGCATT-3′ | 113–131 | 57.89 | 61.27 |
| Probe: P_JBH4-HEV | 5′-[FAM]-CTGCTCTGGCTGCGGCCAA-[BHQ1]-3′ | 81–99 | 68.42 | 59.96 |
| IPC-ntb2 | Source: Anderson et al., (2011) [39] | |||
| ForwardPrimer: IPC-ntb2-fw | 5′-ACCACAATGCCAGAGTGACAAC-3′ | 50 | 68 | |
| ReversePrimer: IPC-ntb2-re | 5′-TACCTGGTCTCCAGCTTTCAGTT-3′ | 47.82 | 68 | |
| Probe: IPC-ntb2 | 5′-[HEX]-CACGCGCATGAAGTTAGGGGACCA-[BHQ1]-3′ | 58.3 | 74 | |
| Virus | Origin | Reactivity |
|---|---|---|
| Inclusivity | ||
| HEV-Subtype 3b | HEV reference material PEI (Baylis et al., 2012) [45] | + |
| HEV-Subtype 3c | HEV reference material PEI (Baylis et al., 2012) [45] | + |
| HEV-Subtype 3c | Eluate isolated from pigliver (Schotte et al., 2022) [41] | + |
| HEV-Subtype 3c | Eluate isolated from pigliver (Schotte et al., 2022) [41] | + |
| HEV-Subtype 3c | Eluate isolated from pigliver (Schotte et al., 2022) [41] | + |
| HEV-Subtype 3c | Eluate isolated from pigliver (Schotte et al., 2022) [41] | + |
| HEV-Subtype 3c | Eluate isolated from pigliver (Schotte et al., 2022) [41] | + |
| HEV-Subtype 3c | Eluate isolated from pigliver (Schotte et al., 2022) [41] | + |
| HEV-Subtype 3c | Eluate isolated from pigliver (Schotte et al., 2022) [41] | + |
| HEV-Subtype 3c | Eluate isolated from pigliver (Schotte et al., 2022) [41] | + |
| HEV-Subtype 3c | Eluate isolated from pigliver (Schotte et al., 2022) [41] | + |
| HEV-Subtype 3c | Eluate isolated from pigliver (Schotte et al., 2022) [41] | + |
| HEV-Subtype 3c | Eluate isolated from pigliver (Schotte et al., 2022) [41] | + |
| HEV-Subtype 3c | Eluate isolated from pigliver (Schotte et al., 2022) [41] | + |
| HEV-Subtype 3c | Eluate isolated from pigliver (Schotte et al., 2022) [41] | + |
| HEV-Subtype 3c | Eluate isolated from pigliver (Schotte et al., 2022) [41] | + |
| HEV-Subtype 3c | Eluate isolated from pigliver (Schotte et al., 2022) [41] | + |
| HEV-Subtype 3c | Eluate isolated from pigliver (Schotte et al., 2022) [41] | + |
| HEV-Subtype 3c | Eluate isolated from pigliver (Gremmel et al., 2022) [43] | + |
| HEV-Subtype 3c | Eluate isolated from pigliver (Gremmel et al., 2022) [43] | + |
| HEV-Subtype 3c | Eluate isolated from pigliver (Gremmel et al., 2022) [43] | + |
| HEV-Subtype 3c | Eluate isolated from pigliver (Gremmel et al., 2022) [43] | + |
| HEV-Subtype 3e | HEV reference material PEI (Baylis et al., 2012) [45] | + |
| HEV-Subtype 3e | Eluate isolated from pigliver (Gremmel et al., 2022) [43] | + |
| HEV-Subtype 3f | HEV reference material PEI (Baylis et al., 2012) [45] | + |
| HEV-Subtype 3f | Eluate isolated from pigliver (Schotte et al., 2022) [41] | + |
| HEV-Subtype 3f | Eluate isolated from pigliver (Schotte et al., 2022) [41] | + |
| HEV-Subtype 3f | Eluate isolated from pigliver (Schotte et al., 2022) [41] | + |
| HEV-Subtype 3f | Eluate isolated from pigliver (Schotte et al., 2022) [41] | + |
| HEV-Subtype 3f | Eluate isolated from pigliver (Schotte et al., 2022) [41] | + |
| HEV-Subtype 3f | Eluate isolated from pigliver (Schotte et al., 2022) [41] | + |
| HEV-Subtype 3f | Eluate isolated from pigliver (Schotte et al., 2022) [41] | + |
| HEV-Subtype 3h | Eluate isolated from pigliver (Wist et al., 2018) [42] | + |
| HEV-Subtype 3i | Eluate isolated from pigliver (Schotte et al., 2022) [41] | + |
| HEV-Subtype 3i | Eluate isolated from pigliver (Schotte et al., 2022) [41] | + |
| HEV-Subtype 3i | Eluate isolated from pigliver (Schotte et al., 2022) [41] | + |
| HEV-Subtype 3i | Eluate isolated from pigliver (Schotte et al., 2022) [41] | + |
| HEV-Subtype 3i | Eluate isolated from pigliver (Schotte et al., 2022) [41] | + |
| HEV-Subtype 3i | Eluate isolated from pigliver (Schotte et al., 2022) [41] | + |
| HEV-Subtype 3i | Eluate isolated from pigliver (Schotte et al., 2022) [41] | + |
| HEV-Subtype 3i-like | Eluate isolated from pigliver (Schotte et al., 2022) [41] | + |
| HEV-Subtype 3i-like | Eluate isolated from pigliver (Schotte et al., 2022) [41] | + |
| HEV-Subtype 3i-like | Eluate isolated from pigliver (Schotte et al., 2022) [41] | + |
| HEV-Subtype 3ra | HEV reference material PEI (Baylis et al., 2012) [45] | + |
| HEV-Subtype 4c | HEV reference material PEI (Baylis et al., 2012) [45] | - |
| HEV-Subtype 4g | HEV reference material PEI (Baylis et al., 2012) [45] | - |
| Exclusivity | ||
| PCV3 | IoV 1 | - |
| PPV | IoV 1 | - |
| SIV | IoV 1 | - |
| PRV | IoV 1 | - |
| APPV | IoV 1 | - |
| TGEV | IoV 1 | - |
| PRRSV EU | IoV 1 | - |
| PRRSV US | IoV 1 | - |
| GE/µL | Positive/Tested | Average Cq-Value | Average Deviation |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 × 107 | 6/6 | 13.24 | 0.217 |
| 1 × 106 | 6/6 | 16.90 | 0.168 |
| 1 × 105 | 6/6 | 20.46 | 0.059 |
| 1 × 104 | 6/6 | 23.84 | 1.193 |
| 1 × 103 | 6/6 | 26.92 | 0.132 |
| 1 × 102 | 6/6 | 31.62 | 1.995 |
| 1 × 101 | 6/6 | 33.83 | 0.880 |
| 1 × 100 | 2/6 | 35.47 | 0.311 |
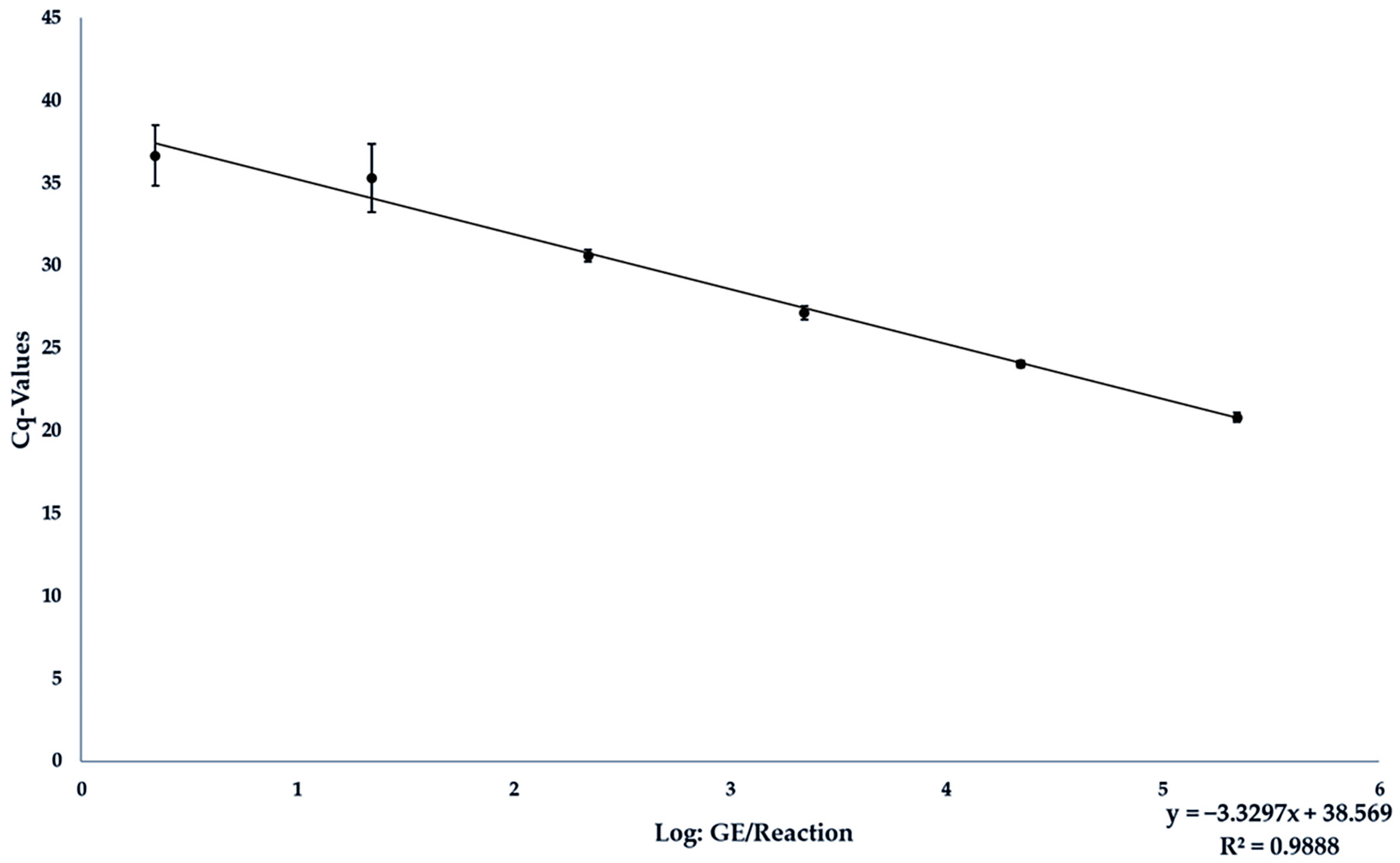
| GE/25 mg Sample | Tested/Positive | Average Cq-Value | Average Deviation |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 × 107 | 9/9 | 20.805 | 0.285 |
| 1 × 106 | 9/9 | 24.058 | 0.220 |
| 1 × 105 | 9/9 | 27.165 | 0.415 |
| 1 × 104 | 9/9 | 30.611 | 0.353 |
| 1 × 103 | 7/9 | 35.324 | 2.072 |
| 1 × 102 | 2/9 | 36.665 | 1.831 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hinrichs, J.B.; Kreitlow, A.; Plötz, M.; Schotte, U.; Becher, P.; Gremmel, N.; Stephan, R.; Kemper, N.; Abdulmawjood, A. Development of a Sensitive and Specific Quantitative RT-qPCR Method for the Detection of Hepatitis E Virus Genotype 3 in Porcine Liver and Foodstuff. Foods 2024, 13, 467. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13030467
Hinrichs JB, Kreitlow A, Plötz M, Schotte U, Becher P, Gremmel N, Stephan R, Kemper N, Abdulmawjood A. Development of a Sensitive and Specific Quantitative RT-qPCR Method for the Detection of Hepatitis E Virus Genotype 3 in Porcine Liver and Foodstuff. Foods. 2024; 13(3):467. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13030467
Chicago/Turabian StyleHinrichs, Jan Bernd, Antonia Kreitlow, Madeleine Plötz, Ulrich Schotte, Paul Becher, Nele Gremmel, Roger Stephan, Nicole Kemper, and Amir Abdulmawjood. 2024. "Development of a Sensitive and Specific Quantitative RT-qPCR Method for the Detection of Hepatitis E Virus Genotype 3 in Porcine Liver and Foodstuff" Foods 13, no. 3: 467. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13030467
APA StyleHinrichs, J. B., Kreitlow, A., Plötz, M., Schotte, U., Becher, P., Gremmel, N., Stephan, R., Kemper, N., & Abdulmawjood, A. (2024). Development of a Sensitive and Specific Quantitative RT-qPCR Method for the Detection of Hepatitis E Virus Genotype 3 in Porcine Liver and Foodstuff. Foods, 13(3), 467. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13030467






