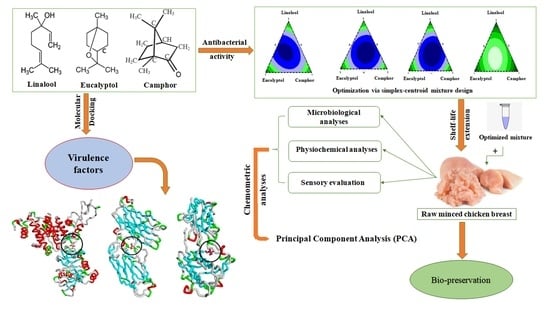
Disclosing the Functional Potency of Three Oxygenated Monoterpenes in Combating Microbial Pathogenesis: From Targeting Virulence Factors to Chicken Meat Preservation
Abstract
Share and Cite
Akermi, S.; Chaari, M.; Elhadef, K.; Fourati, M.; Chakchouk Mtibaa, A.; Agriopoulou, S.; Smaoui, S.; Mellouli, L. Disclosing the Functional Potency of Three Oxygenated Monoterpenes in Combating Microbial Pathogenesis: From Targeting Virulence Factors to Chicken Meat Preservation. Foods 2024, 13, 965. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13060965
Akermi S, Chaari M, Elhadef K, Fourati M, Chakchouk Mtibaa A, Agriopoulou S, Smaoui S, Mellouli L. Disclosing the Functional Potency of Three Oxygenated Monoterpenes in Combating Microbial Pathogenesis: From Targeting Virulence Factors to Chicken Meat Preservation. Foods. 2024; 13(6):965. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13060965
Chicago/Turabian StyleAkermi, Sarra, Moufida Chaari, Khaoula Elhadef, Mariam Fourati, Ahlem Chakchouk Mtibaa, Sofia Agriopoulou, Slim Smaoui, and Lotfi Mellouli. 2024. "Disclosing the Functional Potency of Three Oxygenated Monoterpenes in Combating Microbial Pathogenesis: From Targeting Virulence Factors to Chicken Meat Preservation" Foods 13, no. 6: 965. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13060965
APA StyleAkermi, S., Chaari, M., Elhadef, K., Fourati, M., Chakchouk Mtibaa, A., Agriopoulou, S., Smaoui, S., & Mellouli, L. (2024). Disclosing the Functional Potency of Three Oxygenated Monoterpenes in Combating Microbial Pathogenesis: From Targeting Virulence Factors to Chicken Meat Preservation. Foods, 13(6), 965. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13060965