Evaluation of a Standard Dietary Regimen Combined with Heat-Inactivated Lactobacillus gasseri HM1, Lactoferrin-Producing HM1, and Their Sonication-Inactivated Variants in the Management of Metabolic Disorders in an Obesity Mouse Model
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Probiotic Strain and Postbiotics Preparation
2.2. Animal, Experimental Design, and Sample Collection
2.3. Biochemical Analyses
2.4. Testing for Glucose Tolerance and Insulin Sensitivity
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Weight Fluctuations in Mice throughout the Entire Experimental Period
3.2. Glucose Tolerance among Treatments
3.3. Insulin Sensitivity across Treatments
3.4. Improvement Benefits of Dietary Control and Oral Probiotics in Tissue Pathological Changes in Obese Mice
3.5. Impact of Diverse Probiotic Formulations, Coupled with a Standard Chow Diet, on Serum Biochemical Values in Diet-Induced Obese Mice
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hou, Y.-P.; He, Q.-Q.; Ouyang, H.-M.; Peng, H.-S.; Wang, Q.; Li, J.; Lv, X.-F.; Zheng, Y.-N.; Li, S.-C.; Liu, H.-L. Human gut microbiota associated with obesity in Chinese children and adolescents. BioMed Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 7585989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chooi, Y.C.; Ding, C.; Magkos, F. The epidemiology of obesity. Metabolism 2019, 92, 6–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Li, H. Obesity: Epidemiology, pathophysiology, and therapeutics. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 706978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duggan, C.; Tapsoba, J.D.; Shivappa, N.; Harris, H.R.; Hebert, J.R.; Wang, C.Y.; McTiernan, A. Changes in Dietary Inflammatory Index Patterns with Weight Loss in Women: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Cancer Prev. Res. 2021, 14, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Souza Kraemer, M.; Moehlecke, M.; Rheinheimer, J.; Canani, L.H.; Leitao, C.B.; Nicoletto, B.B. Plasma progranulin levels in obese patients before and after Roux-en-Y gastric bariatric surgery: A longitudinal study. Surg. Obes. Relat. Dis. 2020, 16, 1655–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheen, A.J. Sodium–glucose cotransporter type 2 inhibitors for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2020, 16, 556–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bluher, M. Obesity: Global epidemiology and pathogenesis. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2019, 15, 288–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colman, R.J.; Anderson, R.M.; Johnson, S.C.; Kastman, E.K.; Kosmatka, K.J.; Beasley, T.M.; Allison, D.B.; Cruzen, C.; Simmons, H.A.; Kemnitz, J.W. Caloric restriction delays disease onset and mortality in rhesus monkeys. Science 2009, 325, 201–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, E.C.; Galuska, D.A.; Khan, L.K.; Gillespie, C.; Serdula, M.K. Weight regain in US adults who experienced substantial weight loss, 1999–2002. Am. J. Prev. Med. 2007, 33, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarlio-Lähteenkorva, S.; Rissanen, A.; Kaprio, J. A descriptive study of weight loss maintenance: 6 and 15 year follow-up of initially overweight adults. Int. J. Obes. 2000, 24, 116–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraschnewski, J.L.; Boan, J.; Esposito, J.; Sherwood, N.E.; Lehman, E.B.; Kephart, D.K.; Sciamanna, C.N. Long-term weight loss maintenance in the United States. Int. J. Obes. 2010, 34, 1644–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, J.W.; Konz, E.C.; Frederich, R.C.; Wood, C.L. Long-term weight-loss maintenance: A meta-analysis of US studies. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2001, 74, 579–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marlatt, K.L.; Redman, L.M.; Burton, J.H.; Martin, C.K.; Ravussin, E. Persistence of weight loss and acquired behaviors 2 y after stopping a 2-y calorie restriction intervention. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 105, 928–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, C.; Kong, L.; Shan, M.; Lu, Z.; Lu, Y. Protective and ameliorating effects of probiotics against diet-induced obesity: A review. Food Res. Int. 2021, 147, 110490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fabersani, E.; Abeijon-Mukdsi, M.C.; Ross, R.; Medina, R.; Gonzalez, S.; Gauffin-Cano, P. Specific Strains of Lactic Acid Bacteria Differentially Modulate the Profile of Adipokines In Vitro. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fabersani, E.; Russo, M.; Marquez, A.; Abeijon-Mukdsi, C.; Medina, R.; Gauffin-Cano, P. Modulation of intestinal microbiota and immunometabolic parameters by caloric restriction and lactic acid bacteria. Food Res. Int. 2019, 124, 188–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahiya, D.K.; Renuka; Puniya, M.; Shandilya, U.K.; Dhewa, T.; Kumar, N.; Kumar, S.; Puniya, A.K.; Shukla, P. Gut Microbiota Modulation and Its Relationship with Obesity Using Prebiotic Fibers and Probiotics: A Review. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobyliak, N.; Conte, C.; Cammarota, G.; Haley, A.P.; Styriak, I.; Gaspar, L.; Fusek, J.; Rodrigo, L.; Kruzliak, P. Probiotics in prevention and treatment of obesity: A critical view. Nutr. Metab. 2016, 13, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sivamaruthi, B.S.; Kesika, P.; Suganthy, N.; Chaiyasut, C. A Review on Role of Microbiome in Obesity and Antiobesity Properties of Probiotic Supplements. BioMed Res. Int. 2019, 2019, 3291367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, C.; Guarner, F.; Reid, G.; Gibson, G.R.; Merenstein, D.J.; Pot, B.; Morelli, L.; Canani, R.B.; Flint, H.J.; Salminen, S. Expert consensus document: The International Scientific Association for Probiotics and Prebiotics consensus statement on the scope and appropriate use of the term probiotic. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 11, 506–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinderola, G.; Sanders, M.E.; Salminen, S. The Concept of Postbiotics. Foods 2022, 11, 1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuevas-Gonzalez, P.F.; Liceaga, A.M.; Aguilar-Toala, J.E. Postbiotics and paraprobiotics: From concepts to applications. Food Res. Int. 2020, 136, 109502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aguilar-Toalá, J.; Garcia-Varela, R.; Garcia, H.; Mata-Haro, V.; González-Córdova, A.; Vallejo-Cordoba, B.; Hernández-Mendoza, A. Postbiotics: An evolving term within the functional foods field. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 75, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nataraj, B.H.; Ali, S.A.; Behare, P.V.; Yadav, H. Postbiotics-parabiotics: The new horizons in microbial biotherapy and functional foods. Microb. Cell Fact. 2020, 19, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourebaba, Y.; Marycz, K.; Mularczyk, M.; Bourebaba, L. Postbiotics as potential new therapeutic agents for metabolic disorders management. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 153, 113138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.; Yun, Y.R.; Choi, E.J.; Song, J.H.; Kang, J.Y.; Kim, D.; Lee, K.W.; Chang, J.Y. Anti-obesity effect of vegetable juice fermented with lactic acid bacteria isolated from kimchi in C57BL/6J mice and human mesenchymal stem cells. Food Funct. 2023, 14, 1349–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aoun, A.; Darwish, F.; Hamod, N. The influence of the gut microbiome on obesity in adults and the role of probiotics, prebiotics, and synbiotics for weight loss. Prev. Nutr. Food Sci. 2020, 25, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sienkiewicz, M.; Jaskiewicz, A.; Tarasiuk, A.; Fichna, J. Lactoferrin: An overview of its main functions, immunomodulatory and antimicrobial role, and clinical significance. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 62, 6016–6033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kowalczyk, P.; Kaczynska, K.; Kleczkowska, P.; Bukowska-Osko, I.; Kramkowski, K.; Sulejczak, D. The Lactoferrin Phenomenon-A Miracle Molecule. Molecules 2022, 27, 2941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.S.; Chen, P.W. Featured Prebiotic Agent: The Roles and Mechanisms of Direct and Indirect Prebiotic Activities of Lactoferrin and Its Application in Disease Control. Nutrients 2023, 15, 2759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Zapata, R.C.; Pezeshki, A.; Chelikani, P.K. Dietary lactalbumin and lactoferrin interact with inulin to modulate energy balance in obese rats. Obesity 2017, 25, 1050–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zapata, R.C.; Singh, A.; Pezeshki, A.; Nibber, T.; Chelikani, P.K. Whey Protein Components—Lactalbumin and Lactoferrin—Improve Energy Balance and Metabolism. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 9917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.-S.; Lin, C.-F.; Lee, C.-P.; Hsieh, M.-C.; Lu, H.-F.; Chen, Y.-F.; Ku, Y.-W.; Chen, P.-W. A single plasmid of nisin-controlled bovine and human lactoferrin expressing elevated antibacterial activity of lactoferrin-resistant probiotic strains. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.-S.; Li, P.-L.; Ku, Y.-W.; Chen, P.-W. Oral Administration of Recombinant Lactoferrin-Expressing Probiotics Ameliorates Diet-Induced Lipid Accumulation and Inflammation in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Mice. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 2215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, P.W.; Lin, Y.L.; Huang, M.S. Profiles of commensal and opportunistic bacteria in human milk from healthy donors in Taiwan. J. Food Drug Anal. 2018, 26, 1235–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van, V.T.H.; Liu, Z.-S.; Hsieh, Y.J.; Shiu, W.-C.; Chen, B.-Y.; Ku, Y.-W.; Chen, P.-W. Therapeutic effects of orally administration of viable and inactivated probiotic strains against murine urinary tract infection. J. Food Drug Anal. 2023, 31, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunt, E.M.; Janney, C.G.; Di Bisceglie, A.M.; Neuschwander-Tetri, B.A.; Bacon, B.R. Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: A proposal for grading and staging the histological lesions. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 1999, 94, 2467–2474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benedé-Ubieto, R.; Estévez-Vázquez, O.; Ramadori, P.; Cubero, F.J.; Nevzorova, Y.A. Guidelines and considerations for metabolic tolerance tests in mice. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2020, 13, 439–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brehm, B.J.; Seeley, R.J.; Daniels, S.R.; D’Alessio, D.A. A randomized trial comparing a very low carbohydrate diet and a calorie-restricted low fat diet on body weight and cardiovascular risk factors in healthy women. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2003, 88, 1617–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davoodi, S.H.; Ajami, M.; Ayatollahi, S.A.; Dowlatshahi, K.; Javedan, G.; Pazoki-Toroudi, H.R. Calorie shifting diet versus calorie restriction diet: A comparative clinical trial study. Int. J. Prev. Med. 2014, 5, 447. [Google Scholar]
- Masuo, K.; Rakugi, H.; Ogihara, T.; Lambert, G.W. Different mechanisms in weight loss-induced blood pressure reduction between a calorie-restricted diet and exercise. Hypertens. Res. 2012, 35, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Million, M.; Angelakis, E.; Paul, M.; Armougom, F.; Leibovici, L.; Raoult, D. Comparative meta-analysis of the effect of Lactobacillus species on weight gain in humans and animals. Microb. Pathog. 2012, 53, 100–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ezema, C. Probiotics in animal production: A review. J. Vet. Med. Anim. Health 2013, 5, 308–316. [Google Scholar]
- Angelakis, E. Weight gain by gut microbiota manipulation in productive animals. Microb. Pathog. 2017, 106, 162–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rouxinol-Dias, A.L.; Pinto, A.R.; Janeiro, C.; Rodrigues, D.; Moreira, M.; Dias, J.; Pereira, P. Probiotics for the control of obesity—Its effect on weight change. Porto Biomed. J. 2016, 1, 12–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, R.M.; da Cruz Rodrigues, K.C.; Sant’Ana, M.R.; Peruca, G.F.; Morelli, A.P.; Simabuco, F.M.; da Silva, A.S.; Cintra, D.E.; Ropelle, E.R.; Pauli, J.R. Strength exercise reduces hepatic pyruvate carboxylase and gluconeogenesis in DIO mice. J. Endocrinol. 2020, 247, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, M.; Pan, Q.; Dong, H.; Yuan, X.; Li, Y.; Sun, Z.; Dong, X.; Wang, H. Adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells improve glucose homeostasis in high-fat diet-induced obese mice. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2015, 6, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreno-Navarrete, J.; Ortega, F.; Bassols, J.; Ricart, W.; Fernández-Real, J. Decreased circulating lactoferrin in insulin resistance and altered glucose tolerance as a possible marker of neutrophil dysfunction in type 2 diabetes. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2009, 94, 4036–4044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maekawa, Y.; Sugiyama, A.; Takeuchi, T. Lactoferrin potentially facilitates glucose regulation and enhances the incretin effect. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2017, 95, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Navarrete, J.M.; Ortega, F.J.; Bassols, J.; Castro, A.; Ricart, W.; Fernández-Real, J.M. Association of circulating lactoferrin concentration and 2 nonsynonymous LTF gene polymorphisms with dyslipidemia in men depends on glucose-tolerance status. Clin. Chem. 2008, 54, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, W.A.; Schaalan, M.F. Antidiabetic efficacy of lactoferrin in type 2 diabetic pediatrics; controlling impact on PPAR-gamma, SIRT-1, and TLR4 downstream signaling pathway. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2018, 10, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, Y.; Li, D.; Chen, J.; Li, Y.H.; Zhang, Z.; Hidayat, K.; Wan, Z.; Xu, J.Y.; Qin, L.Q. Lactoferrin improves hepatic insulin resistance and pancreatic dysfunction in high-fat diet and streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice. Nutr. Res. 2022, 103, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, C.; Xue, H.; Guo, T.; Zhang, W.; Xuan, W.-Q.; Ren, Y.-T.; Wang, D.; Chen, Y.-H.; Meng, Y.-H.; Gao, H.-L.J.F.; et al. Recombinant human lactoferrin attenuates the progression of hepatosteatosis and hepatocellular death by regulating iron and lipid homeostasis in ob/ob mice. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 7183–7196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thaiss, C.A.; Itav, S.; Rothschild, D.; Meijer, M.T.; Levy, M.; Moresi, C.; Dohnalová, L.; Braverman, S.; Rozin, S.; Malitsky, S. Persistent microbiome alterations modulate the rate of post-dieting weight regain. Nature 2016, 540, 544–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, I.; Irmler, M.; Meyer, C.; Sachs, S.; Neff, F.; Hrabě de Angelis, M.; Beckers, J.; Tschöp, M.; Hofmann, S.; Ussar, S. A history of obesity leaves an inflammatory fingerprint in liver and adipose tissue. Int. J. Obes. 2018, 42, 507–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Wang, S.; Li, Y.; Zhao, M.; Kuang, J.; Liang, D.; Wang, J.; Wei, M.; Rajani, C.; Ma, X. Gut microbiota-bile acid crosstalk contributes to the rebound weight gain after calorie restriction in mice. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
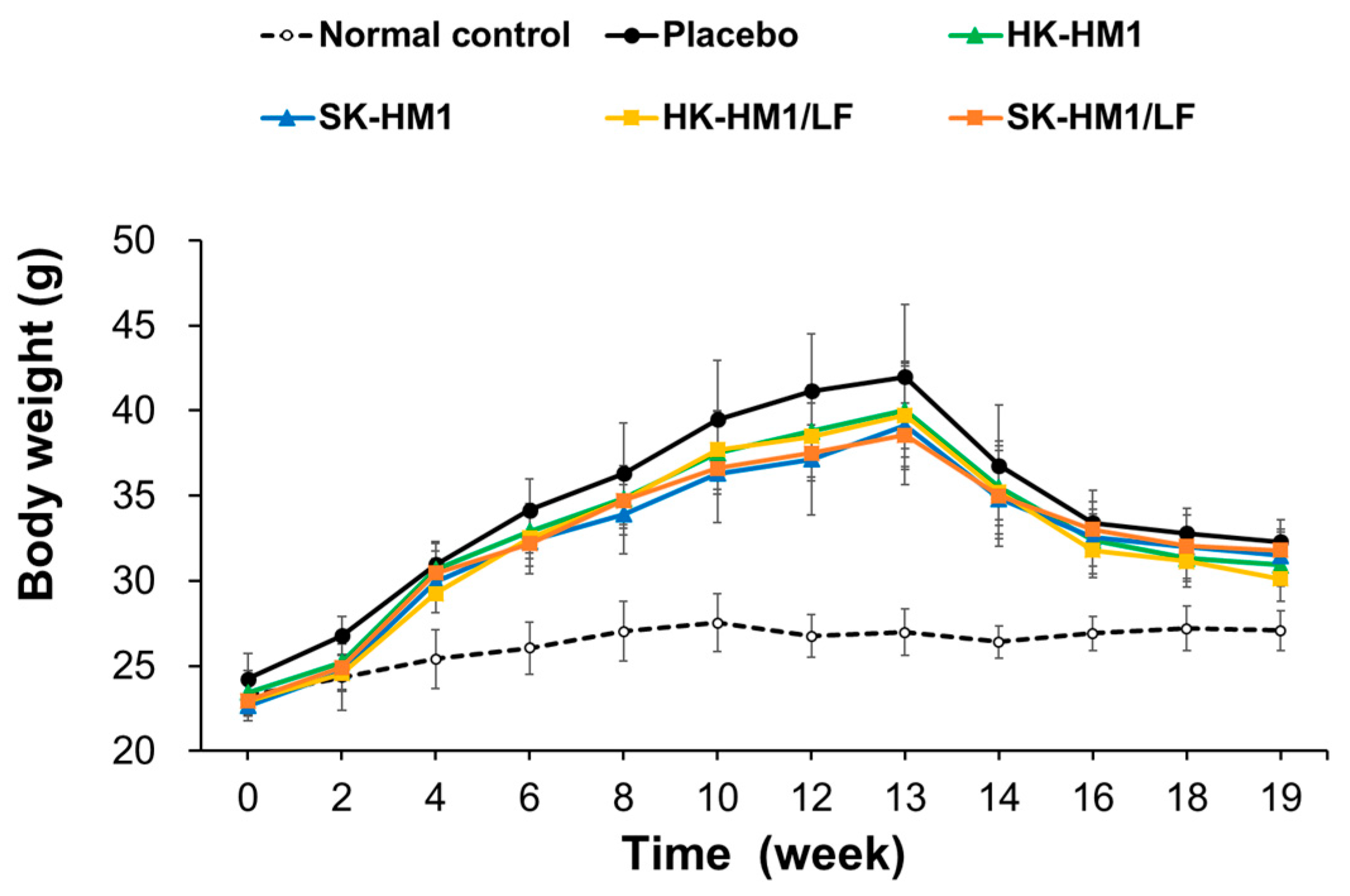
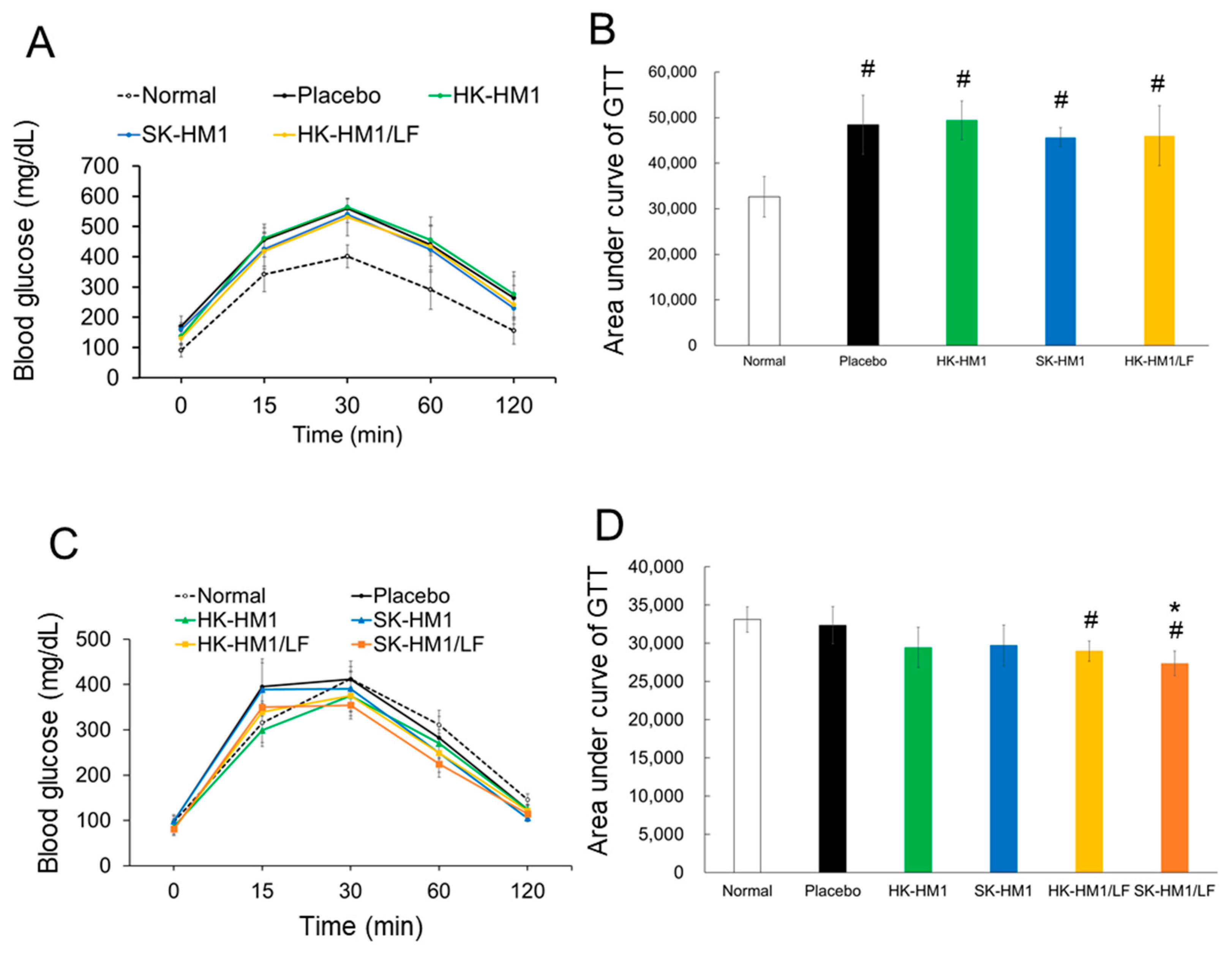
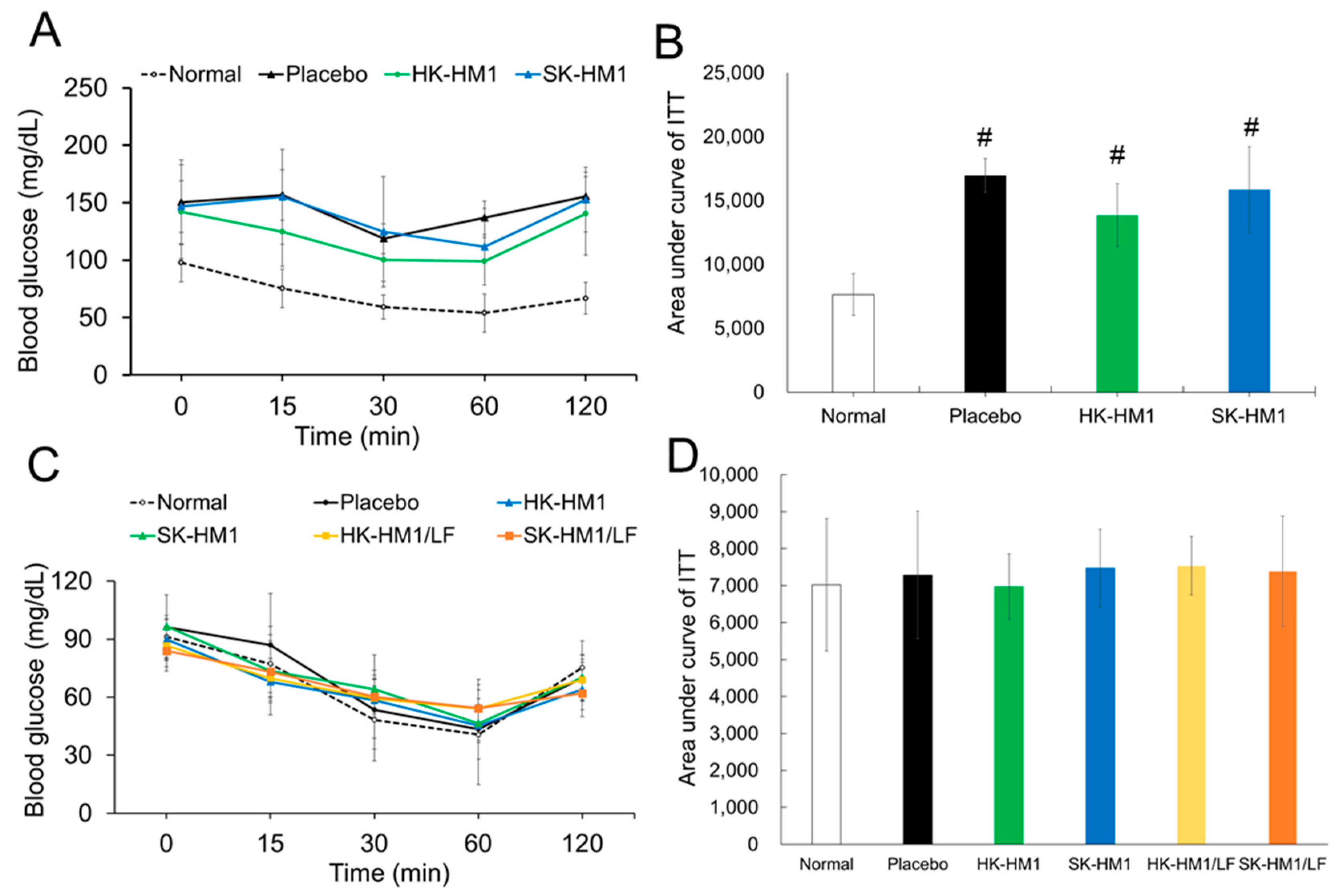

| Weight (g) | Normal Control | HFD Groups a | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Placebo | HK-HM1 | SK-HM1 | HK-HM1/LF | SK-HM1/LF | ||
| 0 week | 23.24 ± 1.2 | 24.25 ± 1.49 | 23.44 ± 1.31 | 22.65 ± 0.61 | 22.94 ± 1.18 | 22.96 ± 0.36 |
| 13 weeks | 26.98 ± 1.39 | 41.99 ± 4.24 # | 40.02 ± 2.74 # | 39.12 ± 3.48 # | 39.74 ± 3.17 # | 38.56 ± 1.86 # |
| 19 weeks—I | 27.09 ± 1.18 | 32.3 ± 1.29 # | 30.92 ± 1.23 # | 31.49 ± 1.56 # | 30.12 ± 1.34 #* | 31.8 ± 1.09 # |
| 19 weeks—II (weight gain) | 0.1 ± 0.46 | −9.69 ± 3.16 # | −9.1 ± 2.95 # | −7.63 ± 2.16 # | −9.62 ± 2.74 # | −6.76 ± 1.45 # |
| Normal | Standard Chow Diet | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Placebo | HK-HM1 | SK-HM1 | HK-HM1/LF | SK-HM1/LF | |||
| Liver fatty change or inflammation | Incidence rate 1 | 0/6 | 0/6 | 0/6 | 0/6 | 0/6 | 0/6 |
| Mean score 2 | 0 ± 0 2,3 | 0 ± 0 | 0 ± 0 | 0 ± 0 | 0 ± 0 | 0 ± 0 | |
| Epididymis fat inflammation, Multifocal | Incidence rate | 0/6 1 | 4/6 | 1/6 | 0/6 | 3/6 | 3/6 |
| Mean score | 0 ± 0 2,3 | 1.00 ± 0.89 # | 0.17 ± 0.41 | 0 ± 0 * | 0.5 ± 0.55 | 0.5 ± 0.55 | |
| Perirenal fat inflammation, Multifocal | Incidence rate | 0/6 1 | 4/6 | 1/6 | 0/6 | 2/6 | 3/6 |
| Mean score | 0 ± 0 2,3 | 0.83 ± 0.75 # | 0.17 ± 0.41 | 0 ± 0 * | 0.5 ± 0.84 | 0.5 ± 0.55 | |
| Normal | Standard Chow Diet | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Placebo | HK-HM1 | SK-HM1 | HK-HM1/LF | SK-HM1/LF | ||
| Serum total triglyceride (mg/dL) | 11.4 ± 4.49 | 29.57 ± 9.62 #,a | 24.17 ± 4.03 a | 28.08 ± 8.12 #,a | 26.1 ± 11.01 #,a | 33.65 ± 4.65 #,a |
| Serum total cholesterol (mg/dL) | 61.68 ± 9.45 | 86.32 ± 12.79 #,a | 79.47 ± 5.98 #,a | 82.52 ± 4.24 #,a | 78.43 ± 14.33 a | 79.03 ± 6.77 #,a |
| Serum HDL-C (mg/dL) | 50.27 ± 8.27 | 66.9 ± 6.39 #,a | 66.78 ± 5.46 #,a | 68.85 ± 4.37 #,a | 64.72 ± 13.59 | 63.8 ± 5.25 a |
| Serum LDL-C (mg/dL) | 9.68 ± 2.74 | 13.07 ± 4.64 a | 9.83 ± 0.98 a | 9.68 ± 2.02 a | 10.58 ± 2.57 a | 10.85 ± 3.37 a |
| Serum glucose (mg/dL) | 106.47 ± 12.98 | 157.77 ± 54.87 a | 146.33 ± 39.56 a | 180.97 ± 45.38 a | 201.03 ± 54.31 #,a | 155.88 ± 38.66 a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shiu, W.-C.; Liu, Z.-S.; Chen, B.-Y.; Ku, Y.-W.; Chen, P.-W. Evaluation of a Standard Dietary Regimen Combined with Heat-Inactivated Lactobacillus gasseri HM1, Lactoferrin-Producing HM1, and Their Sonication-Inactivated Variants in the Management of Metabolic Disorders in an Obesity Mouse Model. Foods 2024, 13, 1079. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13071079
Shiu W-C, Liu Z-S, Chen B-Y, Ku Y-W, Chen P-W. Evaluation of a Standard Dietary Regimen Combined with Heat-Inactivated Lactobacillus gasseri HM1, Lactoferrin-Producing HM1, and Their Sonication-Inactivated Variants in the Management of Metabolic Disorders in an Obesity Mouse Model. Foods. 2024; 13(7):1079. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13071079
Chicago/Turabian StyleShiu, Wei-Chen, Zhen-Shu Liu, Bo-Yuan Chen, Yu-We Ku, and Po-Wen Chen. 2024. "Evaluation of a Standard Dietary Regimen Combined with Heat-Inactivated Lactobacillus gasseri HM1, Lactoferrin-Producing HM1, and Their Sonication-Inactivated Variants in the Management of Metabolic Disorders in an Obesity Mouse Model" Foods 13, no. 7: 1079. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13071079
APA StyleShiu, W.-C., Liu, Z.-S., Chen, B.-Y., Ku, Y.-W., & Chen, P.-W. (2024). Evaluation of a Standard Dietary Regimen Combined with Heat-Inactivated Lactobacillus gasseri HM1, Lactoferrin-Producing HM1, and Their Sonication-Inactivated Variants in the Management of Metabolic Disorders in an Obesity Mouse Model. Foods, 13(7), 1079. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13071079








