Nutritional Composition and Safety Aspects of Deep-Sea Whelks (Buccinum tenuissimum Kuroda)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Samples
2.2. Proximate Composition Analysis
2.2.1. Mineral Content Analysis
2.2.2. Measurement of Dietary Fiber Content
2.2.3. Quantification of Free Sugars
2.2.4. Quantification of Cholesterol
2.2.5. Vitamin D3 Content Analysis
2.3. Amino Acid Analysis
2.3.1. Bound Amino Acid Analysis
2.3.2. Free Amino Acid Analysis
2.4. Fatty Acid Composition Analysis
2.5. Lipid Nutritional Quality Indices
2.6. Heavy Metal Analysis
2.7. Radioactivity Analysis
2.8. Microbial Analysis
2.9. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
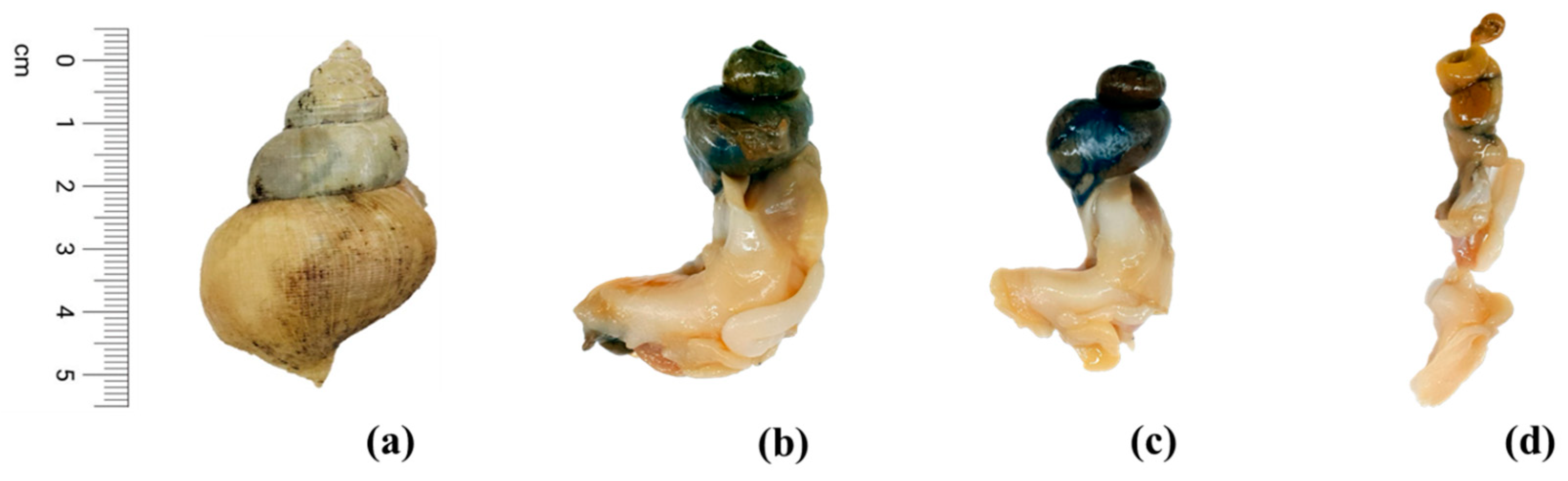
3.1. Physical Characteristics
3.2. Proximate Composition
3.3. Amino Acid Composition
3.4. Fatty Acid Composition
3.5. Heavy Metals
3.6. Radioactivity Analysis
3.7. Microbial Examination
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rogers, A. The Deep: The Hidden Wonders of Our Oceans and How We Can Protect Them; Headline Publishing Group: London, UK, 2019; pp. 1–368. [Google Scholar]
- Stel, J.H. Exploring and exploiting deep ocean space. In Ocean Literacy: Understanding the Ocean; Key Challenges in Geography; EUROGEO Book Series; Koutsopoulos, K.C., Stel, J.H., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; pp. 65–92. [Google Scholar]
- Ogbuagu, M.N. Amino acid composition of a species of whelk (Buccinum inclytum) meat protein. Food 2012, 6, 105–107. [Google Scholar]
- Ab Lah, R.; Smith, J.; Savins, D.; Dowell, A.; Bucher, D.; Benkendorff, K. Investigation of nutritional properties of three species of marine turban snails for human consumption. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017, 5, 14–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shirai, S.M.; Hirose, T.; Goto, T.; Kogure, Y.; Yosho, I. Three predominant species groups of deep-sea whelks (Gastropoda: Buccinidae) in the Sea of Japan: Their molecular taxonomy and geographic distribution. Plankton Benthos Res. 2010, 5, 17–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohn, M.H.; Lee, H.; Hong, B.K.; Chun, Y.Y. Seasonal variation of species composition by depths in deep sea ecosystem of the East Sea of Korea. J. Kor. Soc. Fish. Tech. 2010, 46, 376–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, D.K. Mollusks in Korea; Hangul Book Publishing: Seoul, Republic of Korea, 2004; pp. 1–235. (In Korean) [Google Scholar]
- Okutani, T. Marine Mollusks in Japan; Tokai University Press: Tokyo, Japan, 2017; pp. 1–1375. [Google Scholar]
- MFDS. Ministry of Food and Drug Administrant Approved Seafood Products; MFDS: Cheongju, Republic of Korea, 2022; Available online: https://various.foodsafetykorea.go.kr/fsd/#/ext/Document/FC (accessed on 10 March 2023).
- Garsetti, M.; de Vries, J.; Smith, M.; Amosse, A.; Rolf-Pedersen, N.; ILSI Europe Aisbl. Nutrient profiling schemes: Overview and comparative analysis. Eur. J. Nutr. 2007, 46, 15–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, P.K.; Lee, S.S.; Zhang, M.; Tsang, Y.F.; Kim, K.-H. Heavy metals in food crops: Health risks, fate, mechanisms, and management. Environ. Int. 2019, 125, 365–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandion, K.; Khalith, S.B.M.; Ravindran, B.; Chandrasekaran, M.; Rajagopal, R.; Alfarhan, A.; Chang, S.W.; Ayyamperumal, R.; Mukherjee, A.; Arunachalam, K.D. Potential health risk caused by heavy metal associated with seafood consumption around coastal area. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 294, 118553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AOAC. International Official Methods of Analysis Official Methods, 18th ed.; Association of Official Analytical Chemists: Arlington, VA, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- KFDA. Korea Food and Drug Administration Food Code. Article 1-5-12; Korea Food and Drug Administration: Seoul, Republic of Korea, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Ministry of Food and Drug Administration. 8th General Analysis Method. Foodcode (Sik-Poom-Gong-Jeon); MFDS: Cheongju, Republic of Korea, 2020; pp. 259–260. Available online: https://www.foodsafetykorea.go.kr/foodcode/01_03.jsp?idx=11142 (accessed on 23 June 2021).
- Moore, S.; Stein, W.H. 117—Chromatographic determination of amino acids by the use of automatic recording equipment. Methods Enzymol. 1963, 6, 819–831. [Google Scholar]
- Hugli, T.E.; Moore, S. Determination of the tryptophan content of proteins by ion exchange chromatography of alkaline hydrolysates. J. Biol. Chem. 1972, 247, 2828–2834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folch, J.; Lees, M.; Sloane Stanley, G.H. A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipides from animal tissues. J. Biol. Chem. 1957, 226, 497–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulbricht, T.L.V.; Southgate, D.A.T. Coronary heart disease: Seven dietary factors. Lancet 1991, 338, 985–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mierliță, D. Effects of diets containing hemp seeds or hemp cake on fatty acid composition and oxidative stability of sheep milk. S. Afr. J. Anim. Sci. 2018, 48, 504–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MFDS. Ministry of Food and Drug Safety Administration Food Code. 2022-48; Ministry of Food and Drug Safety Administration: Seoul, Republic of Korea, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- KFSA. Reassessment Report on Food Heavy Metal Standards Specifications; Korea Food Safety Authority: Cheongju-si, Chungcheongbuk-do, Republic of Korea, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Dridi, S.; Romdhane, M.S.; Elcafsi, M. Seasonal variation in weight and biochemical composition of the Pacific oyster, Crassostrea gigas in relation to the gametogenic cycle and environmental conditions of the Bizert Lagoon. Tunisia. Aquaculture 2007, 263, 238–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Periyasamy, N.; Srinivasan, M.; Devanathan, K.; Balakrishnan, S. Nutritional value of gastropod Babylonia spirata (Linnaeus, 1758) from Thazhanguda, Southeast coast of India. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 2011, 12, 249–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, K.Y.; Gao, Q.F.; Yip, K.M.; Wong, W.H.; Shin, P.K.S.; Cheung, S.G. Lipid content and fatty acid composition in the green-lipped mussel Perna viridis (L.). J. Food Lipids 2004, 11, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laxmilatha, P. Proximate composition of the surf clam Mactra violacea (Gmelin 1791). Indian J. Fish. 2009, 56, 147–150. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, H.; Wang, R. Seasonal variation in metabolism of cultured pacific oyster, Crassostrea gigas, in Sanggou Bay. China. Aquaculture 2006, 253, 322–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiou, T.; Lai, M.; Shiau, C. Seasonal variations of chemical constituents in the muscle and viscera of small abalone fed different diets. Fish. Sci. 2001, 67, 146–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, S.L.; Shi, J.; Bekhit, A.E.; Gooneratne, R. Nutritional and toxicological studies of New Zealand Cookia sulcata. J. Food Composit. Anal. 2014, 36, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarai, Z.; Frikha, F.; Balti, R.; Miled, N.; Gargouri, Y.; Mejdoub, H. Nutrient composition of the marine snail (Hexaplex trunculus) from the Tunisian Mediterranean coasts. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2011, 91, 1265–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celik, M.Y.; Çulha, S.T.; Culha, M.; Yildiz, H.; Acarli, S.; Celik, I.; Celik, P. Comparative study on biochemical composition of some edible marine molluscs at Canakkale coasts, Turkey. Indian J. GeoMarine Sci. 2014, 43, 601–606. [Google Scholar]
- Smoothey, A.F. Habitat-associations of turban snails on intertidal and subtidal rocky reefs. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e0146911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramesh, R.; Ravichandran, S. Seasonal variation on the proximate composition of Turbo brunneus. Int. J. Zool. Res. 2008, 4, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasconcelos, P.; Gaspar, M.B.; Castro, M.; Nunes, M.L. Influence of growth and reproductive cycle on the meat yield and proximate composition of Hexaplex trunculus (Gastropoda: Muricidae). J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. 2009, 89, 1223–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merdzhanova, A.; Dobreva, D.A.; Stancheva, M.; Makedonski, L. Fat soluble vitamins and fatty acid composition of wild black sea mussel, rapana and shrimp. Ovidius Univ. Ann. Chem. 2014, 25, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, H.; Aono, H. Characteristics of lipid and fatty acid of marine gastropod Turbo cornutus: High levels of arachidonic and n-3 docosapentaenoic acid. Food Chem. 2014, 145, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwe, M.O. The Science and Technology of Soybean: Chemistry, Nutrition, Processing, Utilization; Rojoint Community Service Ltd.: Enugu, Nigeria, 2003; pp. 1–36. [Google Scholar]
- Aremu, A.O.; Olaofe, O.; Akintayo, T.E. A comparative study on the chemical and amino acid composition of some Nigerian under-utilized legume flours. Pak. J. Nutr. 2006, 5, 34–38. [Google Scholar]
- Pellett, P.L.; Young, V.R. Role of meat as a source of protein and essential amino acids in human nutrition. In Meat and Health, Advances in Meat Research; Pearson, A.M., Dutson, T.R., Eds.; Elsevier Applied Science: London, UK, 1990; pp. 329–370. [Google Scholar]
- Nelson, M.M.; Leighton, D.L.; Phleger, C.F.; Nichols, P.D. Comparison of growth and lipid composition in the green abalone, Haliotis fulgens, provided specific macroalgal diets. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part B 2002, 131, 695–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milinsk, M.C.; Padre, R.G.; Hayashi, C.; Souza, N.E.; Matsushita, M. Influence of diets enriched with different vegetable oils on the fatty acid profiles of Helix aspersa maxima. Food Chem. 2003, 82, 553–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martino, R.C.; Cruz, G.M. Proximate composition and fatty acid content of the mangrove oyster Crassostrea rhizophorae along the year seasons. Braz. Arch. Biol. Technol. 2004, 47, 955–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freiji, A.M.; Awadh, M.N. Fatty acid compositions of Turbo coronatus Gmelin 1791. Brit. Food J. 2010, 112, 1049–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahaffey, K.R. Fish and shellfish as dietary sources of methylmercury and the omega-3 fatty acids, eicosahexaenoic acid and docosahexaenoic acid: Risks and benefits. Environ. Res. 2004, 95, 414–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahaffey, K.R.; Clickner, R.P.; Jeffries, R.A. Methylmercury and omega-3 fatty acids: Co-occurrence of dietary sources with emphasis on fish and shellfish. Environ. Res. 2008, 107, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morais, S.; Boaventura, D.; Narciso, L.; Re, P.; Hawkins, S.J. Gonad development and fatty acid composition of Patella depressa Pennat (Gastropoda: Prosobranchia) populations with different patterns of spatial distribution, in expressed and sheltered sites. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2003, 294, 61–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Comacho, A.; Delgado, M.; Fernandez-Reiriz, M.J.; Labarta, L.U. Energy balance, gonad development and biochemical composition in the clam Ruditapes decussatus. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2003, 258, 133–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, H. Lipid and FA composition of the pearl oyster Pinctada fucata martensii: Influence of season and maturation. Lipids 2004, 39, 997–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ersoy, B.; Sereflisan, H. The proximate composition and fatty acid profiles of edibles parts of two freshwater mussels. Turk. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2010, 10, 71–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, H.; Hashimoto, J. Characteristic of the fatty acid composition of the deep-sea vent gastropod, Ifremeria nautilei. Lipids 2010, 45, 537–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bautista-Teruel, M.; Koshio, S.S.; Ishikawa, M. Diet development and evaluation for juvenile abalone, Haliotis asinina Linne: Lipid and essential fatty acid levels. Aquaculture 2011, 312, 172–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mooney, B.D.; Nichols, P.D.; Elliot, N.G. Seafood the Good Food II: Oil Profiles for Further Australian Seafoods and Influencing Factors; Fisheries Research and Development Corporation: Deakin, Australia, 2002; pp. 1–126. [Google Scholar]
- Molversmyr, E.; Devle, H.M.; Naess-Andresen, C.F.; Ekeberg, D. Identification and quantification of lipids in wild and farmed Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar), and salmon feed by GC-MS. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 10, 3117–3127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouraji, H.; Shabanpour, B.; Abedian Kenari, A.; Shabani, A.; Nezami, S.; Sudagar, M.; Faghani, S. Total lipid, fatty acid composition and lipid oxidation of Indian white shrimp (Fenneropenaeus indicus) fed diets containing different lipid sources. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2009, 89, 993–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stancheva, M.; Merdzhanova, A.; Dobreva, D.; Makedonski, L. Common carp (Cyprinus caprio) and European Catfish (Sillurus glanis) from the Danube River as sources of fat soluble vitamins and fatty acids. Czech J. Food Sci. 2014, 32, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Liu, H. Nutritional Indices for Assessing Fatty Acids: A Mini-Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cravo, A.; Bebianno, M.J. Bioaccumulation of metals in the soft tissue of Patella aspera: Application of metal/shell weight indices. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2005, 65, 571–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozogul, Y.; Ozogul, F.; Olgunoglu, A.I. Fatty acid profile and mineral content of the wild snail (Helix pomatia) from the region of the south of the Turkey. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2005, 221, 547–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Health and Medical Research Council. Nutrient Reference Values for Australia and New Zealand: Including Recommended Dietary Intakes; National Health and Medical Research Council, Commonwealth of Australia: Canberra, Australia, 2006; pp. 1–126. [Google Scholar]
- Scherz, H.; Kirchhoff, E. Trace elements in foods: Zinc contents of raw foods-A comparison of data originating from different geographical regions of the world. J. Food Compost. Anal. 2006, 19, 420–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilic, O.; Belivermis, M. Spatial and seasonal distribution of trace metal concentrations in mussel (Mytilus galloprovincialis) and sediment of Bosphorus and Golden Horn. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2013, 91, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bilandžić, N.; Sedak, M.; Đokić, M.; Varenina, I.; Kolanović, B.S.; Božić, Đ.; Brstilo, M.; Šimić, B. Determination of zinc concentrations in foods of animal origin, fish and shellfish from Croatia and assessment of their contribution to dietary intake. J. Food Composit. Anal. 2014, 35, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Characteristic | Large-Sized Whelks | Medium-Sized Whelks | Small-Sized Whelks |
|---|---|---|---|
| Shell height (mm) | 78.22 ± 4.99 a | 60.31 ± 6.24 b | 44.06 ± 3.63 c |
| Shell breadth (mm) | 47.69 ± 6.71 a | 34.99 ± 5.82 b | 28.98 ± 3.60 b |
| Total weight (g) | 55.90 ± 5.97 a | 31.88 ± 8.63 b | 14.41 ± 2.42 c |
| Shell weight (g) | 9.06 ± 2.09 a | 6.69 ± 1.70 ab | 3.87 ± 0.74 b |
| Muscle weight (g) | 20.18 ± 3.68 a | 12.42 ± 3.68 b | 5.51 ± 1.40 c |
| Gut weight (g) | 23.94 ± 4.17 a | 11.66 ± 5.59 b | 3.74 ± 0.91 b |
| Component | Unit | Large-Sized Whelks | Medium-Sized Whelks | Small-Sized Whelks | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Muscle | Gut | Muscle | Gut | Muscle | Gut | ||
| Crude protein | g/100 g | 13.54 ± 0.04 | 16.38 ± 0.07 | 13.82 ± 0.05 | 16.75 ± 0.06 | 15.24 ± 0.05 | 20.47 ± 0.08 |
| Carbohydrate | g/100 g | 12.81 ± 0.04 | 2.84 ± 0.02 | 4.53 ± 0.02 | 2.48 ± 0.02 | 2.48 ± 0.01 | 1.55 ± 0.02 |
| Sugars | g/100 g | 0.80 ± 0.004 | 1.17 ± 0.02 | 1.18 ± 0.01 | 1.04 ± 0.03 | 1.10 ± 0.02 | 1.40 ± 0.03 |
| Fat | g/100 g | 0.94 ± 0.005 | 7.18 ± 0.01 | 0.85 ± 0.01 | 8.39 ± 0.04 | 1.18 ± 0.01 | 8.59 ± 0.01 |
| Saturated fat | g/100 g | 0.46 ± 0.002 | 1.90 ± 0.02 | 0.32 ± 0.01 | 2.14 ± 0.05 | 0.42 ± 0.01 | 2.12 ± 0.04 |
| Trans fat | g/100 g | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. |
| Cholesterol | mg/100 g | 110.30 ± 0.54 | 367.30 ± 1.81 | 117.78 ± 0.53 | 366.19 ± 1.76 | 116.38 ± 0.52 | 469.57 ± 2.41 |
| Crude ash | g/100 g | 2.66 ± 0.02 | 2.31 ± 0.02 | 2.18 ± 0.03 | 2.15 ± 0.03 | 2.48 ± 0.01 | 2.81 ± 0.01 |
| Energy | kJ/100 g | 476.39 ± 2.32 | 592.04 ± 2.97 | 339.11 ± 1.64 | 637.77 ± 3.18 | 341.00 ± 1.72 | 692.00 ± 3.21 |
| Sodium | mg/100 g | 715.87 ± 3.62 | 572.77 ± 2.93 | 609.26 ± 3.14 | 507.63 ± 2.55 | 669.24 ± 3.32 | 482.69 ± 2.45 |
| Calcium | mg/100 g | 115.34 ± 0.64 | 86.96 ± 0.44 | 57.72 ± 0.30 | 76.00 ± 0.37 | 68.97 ± 0.33 | 284.58 ± 1.53 |
| Cholecalciferol | IU/100 g | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. |
| Potassium | g/100 g | 0.37 ± 0.002 | 0.35 ± 0.002 | 0.35 ± 0.001 | 0.37 ± 0.002 | 0.38 ± 0.001 | 0.37 ± 0.002 |
| Dietary fiber | g/100 g | 1.25 ± 0.006 | 1.81 ± 0.007 | 1.46 ± 0.009 | 1.94 ± 0.010 | 1.33 ± 0.008 | 1.95 ± 0.009 |
| Iron | mg/100 g | 1.28 ± 0.004 | 4.11 ± 0.006 | 0.87 ± 0.007 | 5.60 ± 0.029 | 0.92 ± 0.005 | 6.09 ± 0.04 |
| Amino Acid Content (%) | Large-Sized Whelks | Medium-Sized Whelks | Small-Sized Whelks | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Muscle | Gut | Muscle | Gut | Muscle | Gut | |
| Aspartic acid | 1.24 ± 0.006 | 1.55 ± 0.008 | 1.21 ± 0.005 | 1.52 ± 0.008 | 1.31 ± 0.006 | 1.89 ± 0.009 |
| Threonine | 0.54 ± 0.007 | 0.68 ± 0.008 | 0.56 ± 0.007 | 0.74 ± 0.009 | 0.58 ± 0.006 | 0.87 ± 0.008 |
| Serine | 0.58 ± 0.006 | 0.53 ± 0.007 | 0.62 ± 0.006 | 0.68 ± 0.003 | 0.61 ± 0.004 | 0.72 ± 0.004 |
| Glutamic acid | 1.87 ± 0.009 | 1.99 ± 0.010 | 1.80 ± 0.007 | 1.95 ± 0.008 | 1.96 ± 0.014 | 2.42 ± 0.015 |
| Proline | 0.53 ± 0.005 | 0.61 ± 0.003 | 0.55 ± 0.002 | 0.62 ± 0.003 | 0.55 ± 0.004 | 0.73 ± 0.006 |
| Glycine | 0.86 ± 0.007 | 0.76 ± 0.004 | 0.86 ± 0.003 | 0.79 ± 0.003 | 0.84 ± 0.003 | 0.93 ± 0.003 |
| Alanine | 0.76 ± 0.004 | 0.84 ± 0.006 | 0.75 ± 0.006 | 0.84 ± 0.007 | 0.80 ± 0.006 | 1.00 ± 0.009 |
| Valine | 0.56 ± 0.003 | 0.80 ± 0.004 | 0.52 ± 0.004 | 0.73 ± 0.005 | 0.60 ± 0.002 | 0.98 ± 0.008 |
| Isoleucine | 0.45 ± 0.003 | 0.69 ± 0.006 | 0.40 ± 0.001 | 0.63 ± 0.002 | 0.48 ± 0.002 | 0.86 ± 0.005 |
| Leucine | 0.91 ± 0.003 | 1.18 ± 0.009 | 0.88 ± 0.004 | 1.13 ± 0.008 | 0.98 ± 0.004 | 1.45 ± 0.007 |
| Tyrosine | 0.29 ± 0.001 | 0.33 ± 0.001 | 0.33 ± 0.001 | 0.43 ± 0.002 | 0.31 ± 0.001 | 0.47 ± 0.002 |
| Phenylalanine | 0.40 ± 0.003 | 0.67 ± 0.004 | 0.40 ± 0.002 | 0.63 ± 0.003 | 0.44 ± 0.003 | 0.84 ± 0.005 |
| Histidine | 0.25 ± 0.001 | 0.44 ± 0.002 | 0.25 ± 0.001 | 0.42 ± 0.002 | 0.26 ± 0.001 | 0.51 ± 0.003 |
| Lysine | 0.82 ± 0.004 | 1.14 ± 0.008 | 0.80 ± 0.007 | 1.11 ± 0.010 | 0.89 ± 0.008 | 1.41 ± 0.012 |
| Arginine | 1.11 ± 0.009 | 0.92 ± 0.007 | 1.08 ± 0.006 | 0.94 ± 0.005 | 1.15 ± 0.008 | 1.13 ± 0.007 |
| Cystine | 0.20 ± 0.001 | 0.45 ± 0.002 | 0.20 ± 0.001 | 0.42 ± 0.002 | 0.21 ± 0.001 | 0.54 ± 0.004 |
| Methionine | 0.33 ± 0.002 | 0.52 ± 0.003 | 0.34 ± 0.002 | 0.45 ± 0.003 | 0.37 ± 0.002 | 0.57 ± 0.004 |
| Tryptophan | 0.07 ± 0.001 | 0.83 ± 0.004 | 0.07 ± 0.001 | 0.73 ± 0.004 | 0.08 ± 0.001 | 0.21 ± 0.001 |
| Total amount | 11.77 ± 0.05 | 14.93 ± 0.072 | 11.62 ± 0.061 | 14.76 ± 0.065 | 12.42 ± 0.052 | 17.53 ± 0.073 |
| Free Amino Acids (mg/kg) | Large-Sized Whelks | Medium-Sized Whelks | Small-Sized Whelks | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Muscle | Gut | Muscle | Gut | Muscle | Gut | |
| Phosphoserine | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. |
| Taurine | 1558.81 ± 7.80 | 1251.29 ± 6.24 | 1566.77 ± 7.62 | 1357.99 ± 6.53 | 1697.33 ± 8.32 | 1493.12 ± 6.79 |
| Phospho ethanol amine | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. |
| Urea | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. |
| Aspartic acid | 566.43 ± 2.77 | 473.23 ± 1.83 | 544.31 ± 2.44 | 478.17 ± 1.85 | 476.35 ± 1.87 | 619.50 ± 3.10 |
| Threonine | 256.70 ± 1.15 | 222.60 ± 1.08 | 254.56 ± 2.02 | 246.22 ± 1.89 | 240.12 ± 2.34 | 298.78 ± 2.13 |
| Serine | 373.93 ± 1.92 | 293.67 ± 1.83 | 367.94 ± 2.11 | 296.06 ± 1.98 | 347.66 ± 2.25 | 355.70 ± 3.03 |
| Glutamic acid | 754.11 ± 4.03 | 751.34 ± 4.14 | 741.02 ± 3.87 | 824.52 ± 4.19 | 662.21 ± 3.62 | 1017.92 ± 5.67 |
| Glutamine | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. |
| Sarcosine | 1663.61 ± 8.12 | 1025.02 ± 5.11 | 1590.42 ± 7.85 | 166.32 ± 0.84 | 1514.75 ± 6.98 | 1269.15 ± 6.17 |
| α-amino adipic acid | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. |
| Hydroxy proline | 130.45 ± 0.63 | 45.79 ± 0.25 | 121.91 ± 0.64 | 48.12 ± 0.14 | 69.47 ± 0.54 | 35.84 ± 0.08 |
| Proline | 391.85 ± 1.94 | 475.03 ± 1.98 | 351.22 ± 1.85 | 486.61 ± 2.34 | 307.14 ± 1.87 | 445.34 ± 2.55 |
| Glycine | 427.26 ± 3.12 | 363.36 ± 1.74 | 396.16 ± 2.52 | 345.61 ± 1.95 | 338.34 ± 2.35 | 391.01 ± 1.87 |
| Alanine | 628.99 ± 3.52 | 584.17 ± 3.13 | 650.31 ± 4.23 | 649.75 ± 3.94 | 597.17 ± 4.31 | 661.01 ± 4.16 |
| Citrulline | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. |
| α-amino-n-butyric acid | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. |
| Valine | 270.25 ± 1.13 | 278.05 ± 1.05 | 276.08 ± 1.24 | 288.25 ± 2.13 | 269.31 ± 2.53 | 371.37 ± 2.44 |
| Cystine | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. |
| Methionine | 181.40 ± 0.94 | 150.57 ± 0.85 | 194.64 ± 0.99 | 143.15 ± 0.74 | 185.28 ± 1.04 | 189.87 ± 0.87 |
| Cystathionine | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. |
| Isoleucine | 177.34 ± 0.85 | 204.49 ± 1.12 | 184.90 ± 0.89 | 215.66 ± 0.98 | 185.08 ± 0.97 | 284.03 ± 1.07 |
| Leucine | 383.72 ± 1.76 | 423.31 ± 2.13 | 392.92 ± 1.85 | 431.30 ± 2.24 | 385.90 ± 1.53 | 575.09 ± 2.38 |
| Tyrosine | 235.46 ± 1.11 | 277.45 ± 1.03 | 231.17 ± 1.14 | 269.24 ± 1.21 | 228.32 ± 1.55 | 336.61 ± 1.92 |
| Phenylalanine | 157.29 ± 0.74 | 208.36 ± 0.95 | 170.11 ± 0.84 | 214.12 ± 0.94 | 161.30 ± 0.73 | 277.88 ± 1.02 |
| β-Alanine | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. |
| β-Amino isobutyric acid | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. |
| γ-Amino-n-butyric acid | 2.07 ± 0.001 | n.d. | 3.17 ± 0.003 | n.d. | 2.89 ± 0.002 | n.d. |
| Ethanol amine | 27.54 ± 0.13 | 105.45 ± 0.53 | 26.25 ± 0.12 | 117.97 ± 0.62 | 35.25 ± 0.22 | 157.47 ± 0.86 |
| Tryptophan | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. |
| Ammonia | 86.16 ± 0.43 | 121.10 ± 0.61 | 87.84 ± 0.45 | 145.83 ± 0.78 | 99.79 ± 0.50 | 170.26 ± 0.85 |
| Hydroxylysine | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. |
| Ornithine | 23.75 ± 0.14 | 51.67 ± 0.23 | 32.31 ± 0.16 | 46.91 ± 0.24 | 102.96 ± 0.50 | 45.01 ± 0.28 |
| Lysine | 299.65 ± 1.45 | 396.54 ± 1.98 | 329.49 ± 1.65 | 427.29 ± 2.24 | 329.47 ± 1.65 | 537.61 ± 2.86 |
| 1-Methylhistidine | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. |
| Histidine | 176.67 ± 0.87 | 219.05 ± 1.03 | 196.35 ± 0.97 | 251.37 ± 1.24 | 143.15 ± 0.72 | 216.39 ± 1.08 |
| 3-Methylhistidine | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. |
| Anserine | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. |
| Carnosine | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. |
| Arginine | 1400.78 ± 7.15 | 828.49 ± 4.12 | 1314.95 ± 6.53 | 737.86 ± 3.75 | 1291.95 ± 6.44 | 931.94 ± 4.44 |
| Total amount | 10,174.22 ± 40.77 | 8750.03 ± 34.73 | 10,024.8 ± 40.11 | 8188.32 ± 29.82 | 9671.19 ± 37.32 | 10,680.9 ± 37.93 |
| Fatty Acids (g/100 g Fatty Acid) | Shorthand | Large-Sized Whelks | Medium-Sized Whelks | Small-Sized Whelks | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Muscle | Gut | Muscle | Gut | Muscle | Gut | ||
| Caprylic acid | C8:0 | 0.25 ± 0.001 | n.d. | 0.19 ± 0.001 | n.d. | 0.17 ± 0.001 | n.d. |
| Capric acid | C10:0 | 0.05 ± 0.000 | 0.01 ± 0.000 | 0.10 ± 0.001 | 0.01 ± 0.000 | 0.10 ± 0.001 | 0.02 ± 0.000 |
| Lauric acid | C12:0 | 0.80 ± 0.002 | 0.02 ± 0.000 | 0.06 ± 0.000 | 0.02 ± 0.000 | 0.07 ± 0.000 | 0.03 ± 0.000 |
| Myristic acid | C14:0 | 3.47 ± 0.017 | 3.09 ± 0.016 | 2.90 ± 0.014 | 3.09 ± 0.014 | 2.36 ± 0.012 | 3.11 ± 0.013 |
| Pentadecanoic acid | C15:0 | 0.51 ± 0.003 | 0.56 ± 0.003 | 0.36 ± 0.002 | 0.48 ± 0.003 | 0.33 ± 0.001 | 0.47 ± 0.002 |
| Palmitic acid | C16:0 | 20.28 ± 0.110 | 15.25 ± 0.074 | 12.11 ± 0.065 | 14.83 ± 0.074 | 11.52 ± 0.054 | 14.03 ± 0.065 |
| Magaric acid | C17:0 | 1.43 ± 0.006 | 0.73 ± 0.004 | 1.50 ± 0.007 | 0.58 ± 0.003 | 0.14 ± 0.001 | 0.68 ± 0.002 |
| Stearic acid | C18:0 | 17.15 ± 0.101 | 4.21 ± 0.015 | 13.44 ± 0.044 | 3.72 ± 0.013 | 14.58 ± 0.053 | 3.91 ± 0.013 |
| Arachidic acid | C20:0 | 0.17 ± 0.001 | 0.10 ± 0.000 | 0.06 ± 0.000 | 0.09 ± 0.000 | 0.06 ± 0.000 | 0.08 ± 0.000 |
| Lignoceric acid | C24:0 | 4.61 ± 0.012 | 2.54 ± 0.008 | 6.41 ± 0.014 | 2.73 ± 0.095 | 6.20 ± 0.021 | 2.35 ± 0.004 |
| Myristoleic acid | C14:1 | 0.20 ± 0.001 | 0.11 ± 0.000 | 0.08 ± 0.000 | 0.13 ± 0.000 | 0.09 ± 0.000 | 0.12 ± 0.000 |
| Pentadecenoic acid | C15:1 | 0.13 ± 0.000 | 0.14 ± 0.001 | 0.05 ± 0.000 | 0.14 ± 0.001 | 0.05 ± 0.000 | 0.12 ± 0.000 |
| Palmitoleic acid | C16:1 | 2.20 ± 0.013 | 3.63 ± 0.014 | 1.34 ± 0.008 | 4.05 ± 0.025 | 0.73 ± 0.001 | 2.76 ± 0.004 |
| Magaoleic acid | C17:1 | 0.37 ± 0.001 | 0.51 ± 0.002 | 0.08 ± 0.000 | 0.41 ± 0.002 | 0.18 ± 0.001 | 0.34 ± 0.002 |
| Oleic acid | C18:1 n-9 | 17.17 ± 0.104 | 23.39 ± 0.124 | 9.45 ± 0.042 | 25.82 ± 0.135 | 8.27 ± 0.035 | 20.90 ± 0.113 |
| Linoleic acid | C18:2 n-6 | 0.75 ± 0.003 | 1.30 ± 0.005 | 0.71 ± 0.003 | 1.25 ± 0.006 | 0.52 ± 0.002 | 1.11 ± 0.006 |
| γ-Linolenic acid | C18:3 n-6 | 0.20 ± 0.001 | 0.21 ± 0.001 | 0.10 ± 0.000 | 0.23 ± 0.001 | 0.08 ± 0.000 | 0.13 ± 0.001 |
| Linolenic acid | C18:3 n-3 | 0.24 ± 0.001 | 0.90 ± 0.002 | 0.20 ± 0.001 | 0.92 ± 0.003 | 0.12 ± 0.001 | 0.74 ± 0.004 |
| Eicosenoic acid | C20:1 n-9 | 5.04 ± 0.024 | 6.82 ± 0.013 | 4.54 ± 0.014 | 7.00 ± 0.025 | 5.00 ± 0.013 | 8.60 ± 0.053 |
| Eicosadienoic acid | C20:2 n-6 | 4.66 ± 0.012 | 1.68 ± 0.008 | 5.39 ± 0.025 | 1.59 ± 0.004 | 5.16 ± 0.014 | 1.71 ± 0.005 |
| Dihomoδ-Linoleicacid | C20:3 n-6 | 0.06 ± 0.000 | 0.44 ± 0.001 | 0.10 ± 0.001 | 0.60 ± 0.002 | 0.09 ± 0.000 | 0.16 ± 0.001 |
| Eicosatrienoicacid | C20:3 n-3 | 0.10 ± 0.000 | 0.65 ± 0.002 | 0.73 ± 0.003 | 0.65 ± 0.002 | 0.71 ± 0.004 | 0.98 ± 0.005 |
| Arachidonic acid | C20:4 n-6 | 4.19 ± 0.015 | 2.89 ± 0.011 | 6.56 ± 0.024 | 2.63 ± 0.014 | 6.16 ± 0.025 | 2.91 ± 0.013 |
| EPA | C20:5 n-3 | 9.69 ± 0.047 | 11.33 ± 0.053 | 23.73 ± 0.15 | 10.60 ± 0.05 | 26.73 ± 0.15 | 12.72 ± 0.06 |
| Erucic acid | C22:1 n-9 | 0.97 ± 0.005 | 1.92 ± 0.007 | 0.35 ± 0.002 | 1.91 ± 0.012 | 0.34 ± 0.001 | 2.09 ± 0.013 |
| DHA | C22:6 n-3 | 5.30 ± 0.02 | 17.58 ± 0.06 | 9.46 ± 0.046 | 16.54 ± 0.040 | 10.24 ± 0.05 | 19.92 ± 0.15 |
| ΣSAFAs | 48.72 ± 0.24 | 26.5 ± 0.13 | 37.13 ± 0.14 | 25.55 ± 0.13 | 35.53 ± 0.17 | 24.68 ± 0.13 | |
| ΣMUFAs | 26.08 ± 0.15 | 36.52 ± 0.14 | 15.89 ± 0.12 | 39.46 ± 0.10 | 14.66 ± 0.08 | 34.93 ± 0.09 | |
| ΣPUFAs | 25.19 ± 0.12 | 36.98 ± 0.13 | 46.98 ± 0.13 | 35.01 ± 0.12 | 49.81 ± 0.12 | 40.38 ± 0.15 | |
| Σω3 | n-3 | 15.33 ± 0.09 | 30.46 ± 0.08 | 34.12 ± 0.07 | 28.71 ± 0.06 | 37.8 ± 0.11 | 34.36 ± 0.13 |
| Σω6 | n-6 | 5.2 ± 0.025 | 4.84 ± 0.024 | 7.47 ± 0.034 | 4.71 ± 0.025 | 6.85 ± 0.023 | 4.31 ± 0.014 |
| ω6/ω3 | n-6/n-3 | 0.34 ± 0.0002 | 0.16 ± 0.0001 | 0.22 ± 0.0001 | 0.16 ± 0.0001 | 0.18 ± 0.0001 | 0.13 ± 0.0001 |
| TI | 0.12 ± 0.0001 | 0.04 ± 0.000 | 0.07 ± 0.001 | 0.03 ± 0.000 | 0.02 ± 0.000 | 0.03 ± 0.000 | |
| AI | 0.08 ± 0.001 | 0.01 ± 0.0000 | 0.01 ± 0.000 | 0.01 ± 0.000 | 0.01 ± 0.000 | 0.01 ± 0.000 | |
| h/H | 1.58 ± 0.008 | 3.16 ± 0.016 | 3.35 ± 0.017 | 3.27 ± 0.016 | 3.76 ± 0.019 | 3.42 ± 0.016 | |
| Heavy Metal Content (ppm) | Large-Sized Whelks | Medium-Sized Whelks | Small-Sized Whelks | Standard * | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Muscle | Gut | Muscle | Gut | Muscle | Gut | ||
| Pb | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.5 |
| Cd | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | 0.5 |
| Hg | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | 0.5 |
| As | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.1 |
| Radioisotope (Bq/kg) | Large-Sized Whelks | Medium-Sized Whelks | Small-Sized Whelks | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Muscle | Gut | Muscle | Gut | Muscle | Gut | |
| 131I | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. |
| 134Cs/137Cs | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. |
| Pathogenic Microorganism (log CFU/g) | Large-Sized Whelks | Medium-Sized Whelks | Small-Sized Whelks | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Muscle | Gut | Muscle | Gut | Muscle | Gut | |
| TBC | 2.09 ± 0.12 b | 2.21 ± 0.20 b | 2.49 ± 0.27 ab | 2.51 ± 0.46 ab | 2.71 ± 0.52 ab | 2.92 ± 0.19 a |
| Escherichia coli | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. |
| Coliforms | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mansoor, S.; Lee, J.-H.; Bashir, K.M.I.; Sohn, J.-H.; Choi, J.-S. Nutritional Composition and Safety Aspects of Deep-Sea Whelks (Buccinum tenuissimum Kuroda). Foods 2024, 13, 1169. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13081169
Mansoor S, Lee J-H, Bashir KMI, Sohn J-H, Choi J-S. Nutritional Composition and Safety Aspects of Deep-Sea Whelks (Buccinum tenuissimum Kuroda). Foods. 2024; 13(8):1169. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13081169
Chicago/Turabian StyleMansoor, Sana, Jin-Hwa Lee, Khawaja Muhammad Imran Bashir, Jae-Hak Sohn, and Jae-Suk Choi. 2024. "Nutritional Composition and Safety Aspects of Deep-Sea Whelks (Buccinum tenuissimum Kuroda)" Foods 13, no. 8: 1169. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13081169
APA StyleMansoor, S., Lee, J.-H., Bashir, K. M. I., Sohn, J.-H., & Choi, J.-S. (2024). Nutritional Composition and Safety Aspects of Deep-Sea Whelks (Buccinum tenuissimum Kuroda). Foods, 13(8), 1169. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13081169







