Effect of Whey Protein Changes on Milk Flavor and Sensory Characteristics During Heating
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Sample Collection and Preparation
2.3. Protein Analysis
2.3.1. Determination of the Protein Profile
2.3.2. Determination of Denaturation Rate of Active Protein
2.3.3. Determination of Secondary Structure of Whey Protein
2.4. Analysis and Identification of the VOCs
2.4.1. Extraction of VOCs in Milk Samples
2.4.2. GC-MS Analysis
2.5. Sensory Evaluation
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Protein Profile and Structural Changes
3.1.1. Protein Denaturation and Aggregation
3.1.2. Denaturation Rate of the Active Milk Proteins
3.1.3. Secondary Structures of the Whey Proteins
3.2. VOCs Characteristics of Different Heat-Treated Milk
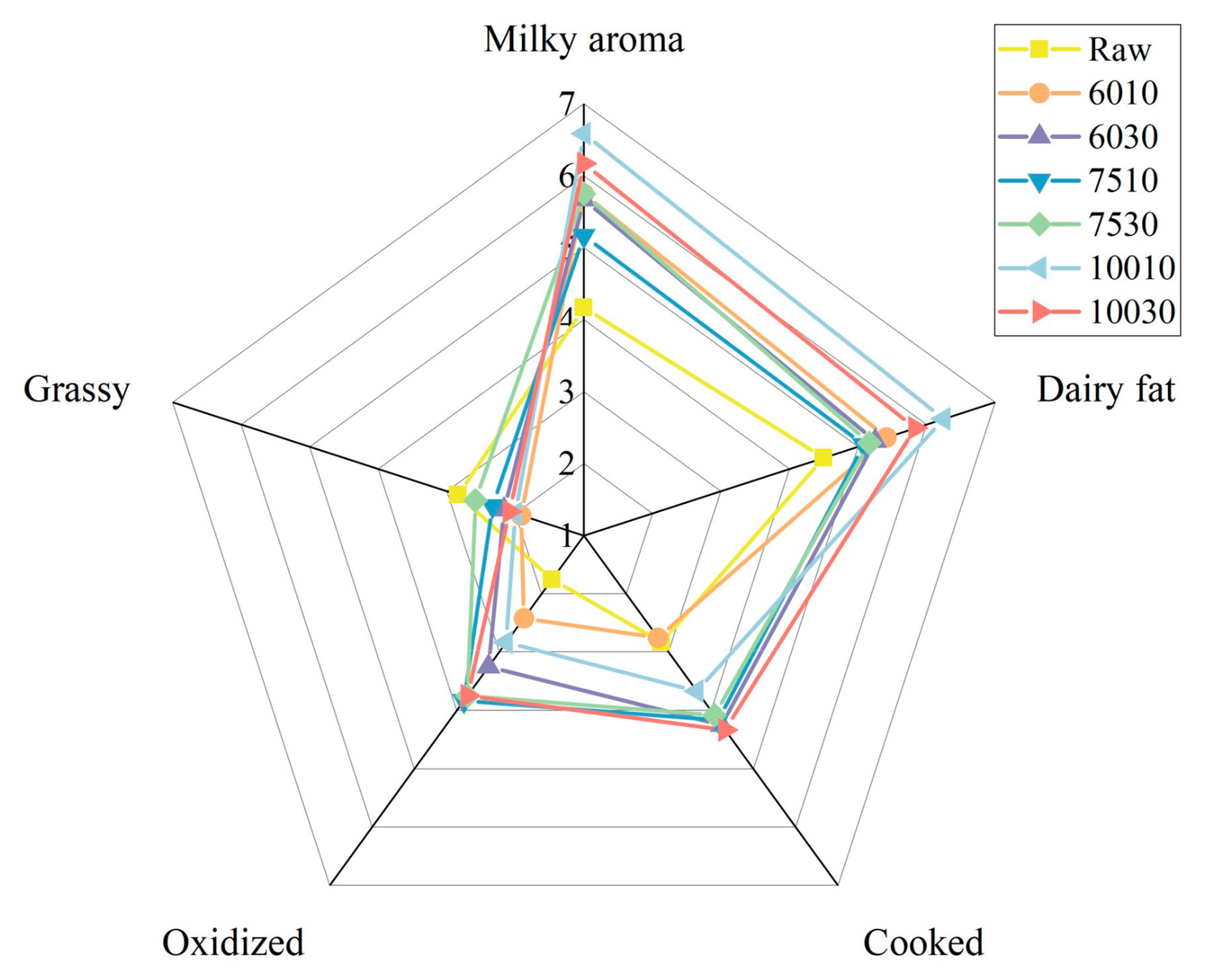
3.3. Sensory Characteristics
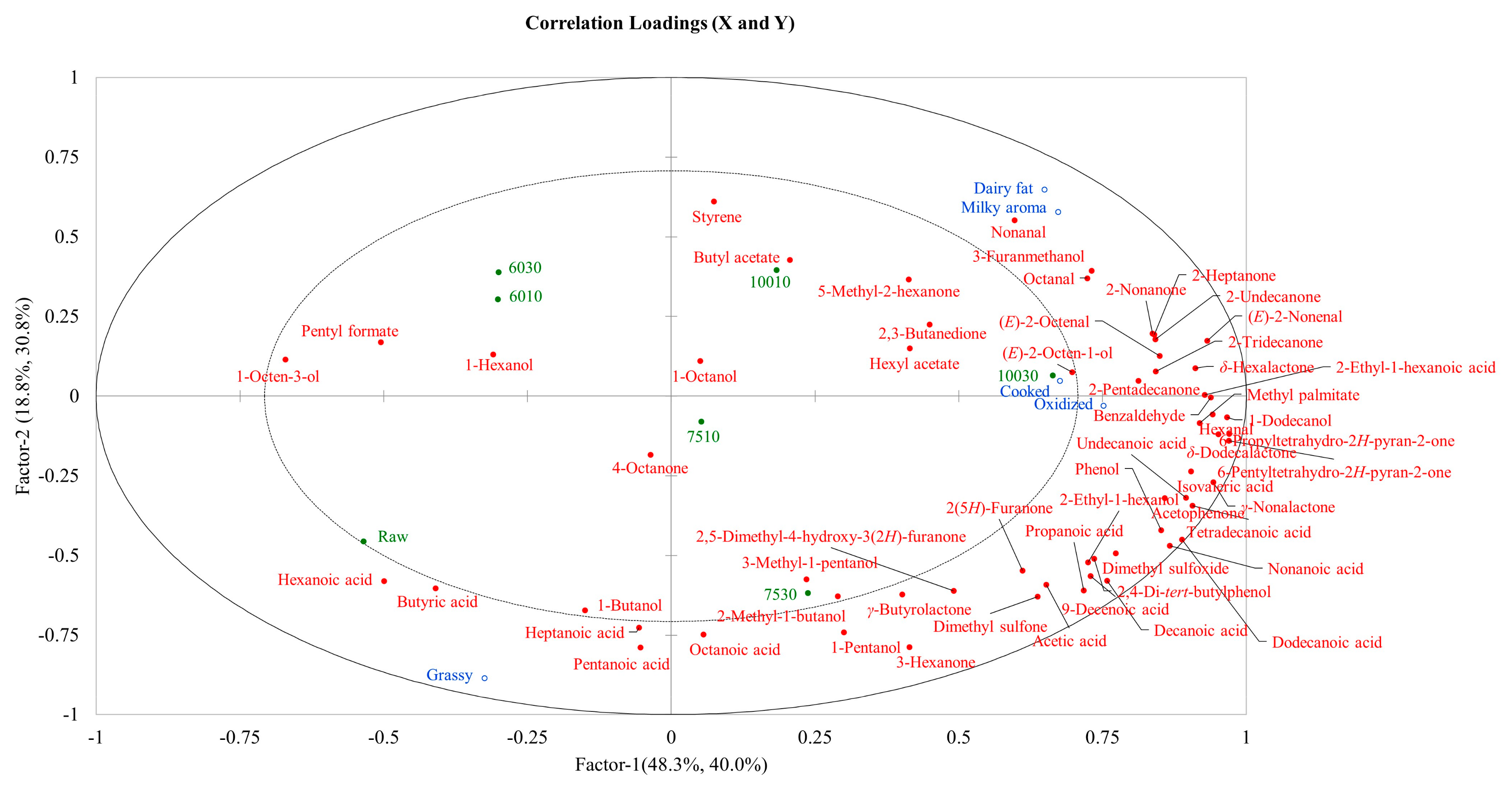
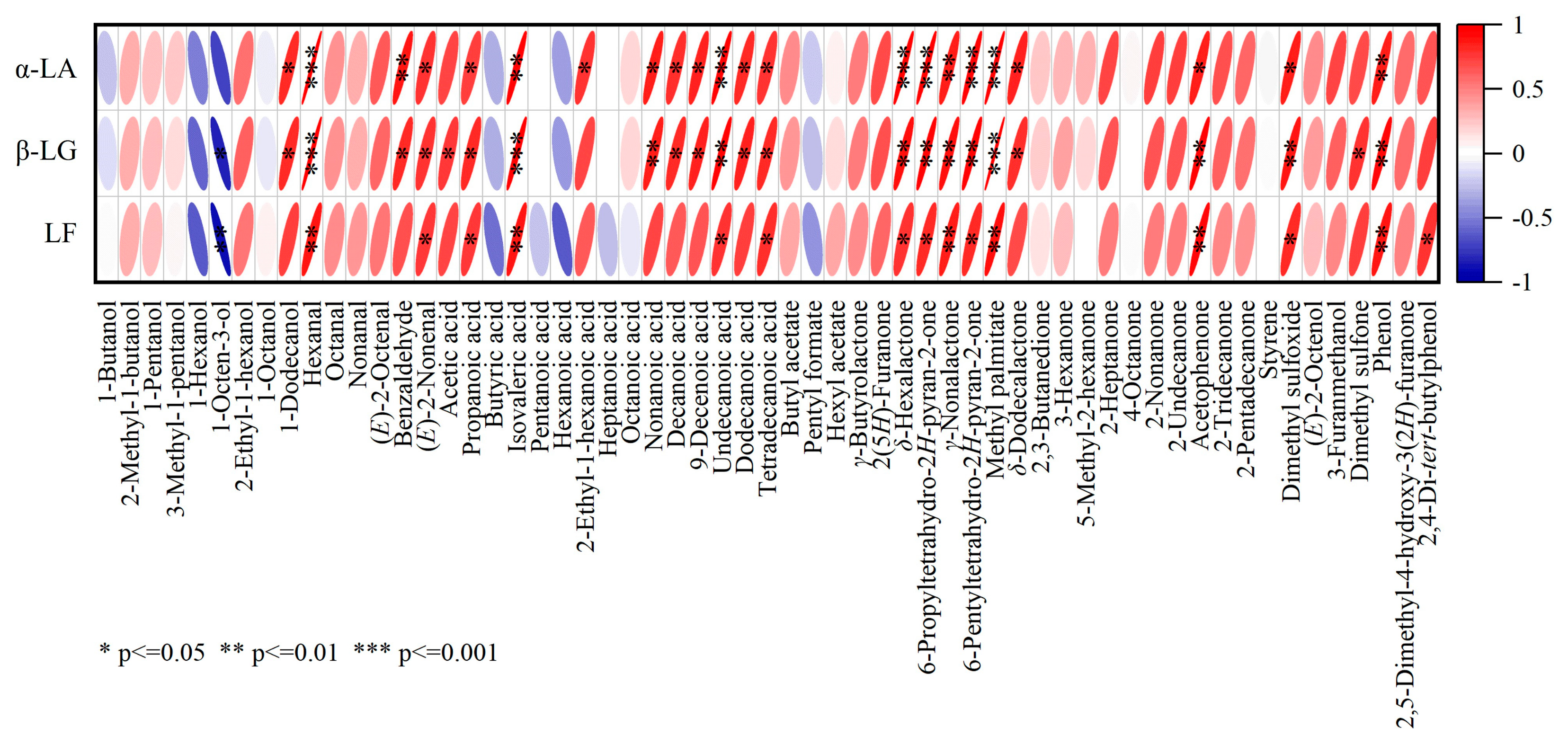
3.4. Correlation Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shao, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, P.; Li, K.; Li, C. Comparison and discrimination of the terpenoids in 48 species of huajiao according to variety and geographical origin by E-nose coupled with HS-SPME-GC-MS. Food Res. Int. 2023, 167, 112629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coolbear, T.; Janin, N.; Traill, R.; Shingleton, R. Heat-induced changes in the sensory properties of milk. Int. Dairy J. 2022, 126, 105199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Arntfield, S.D. Effect of protein-flavour binding on flavour delivery and protein functional properties: A special emphasis on plant-based proteins. Flavour. Fragr. J. 2017, 32, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cadwallader, K.R.; Singh, T.K. Flavours and Off-Flavours in Milk and Dairy Products. In Advanced Dairy Chemistry: Volume 3: Lactose, Water, Salts and Minor Constituents; McSweeney, P., Fox, P.F., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2009; pp. 631–690. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, N.; Chi, X.; Ye, Q.; Liu, H.; Zheng, N. Analysis of Volatile Organic Compounds in Milk during Heat Treatment Based on E-Nose, E-Tongue and HS-SPME-GC-MS. Foods 2023, 12, 1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yi, S.; Lu, J.; Pang, X.; Xu, X.; Lv, J.; Zhang, S. Effect of different heat treatments on the Maillard reaction products, volatile compounds and glycation level of milk. Int. Dairy J. 2021, 123, 105182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kühn, J.; Considine, T.; Singh, H. Binding of Flavor Compounds and Whey Protein Isolate as Affected by Heat and High Pressure Treatments. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 10218–10224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heng, L.; van Koningsveld, G.A.; Gruppen, H.; van Boekel, M.A.J.S.; Vincken, J.P.; Roozen, J.P.; Voragen, A.G.J. Protein–flavour interactions in relation to development of novel protein foods. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2004, 15, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Kang, D.; Zhang, W.; Lorenzo, J.M. Recent advantage of interactions of protein-flavor in foods: Perspective of theoretical models, protein properties and extrinsic factors. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 111, 405–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.-J.; Wu, J.-H.; Li, X.; Xu, X.-B.; Wang, Z.-Y.; Wu, C.; Du, M.; Song, L. Effect of alkyl distribution in pyrazine on pyrazine flavor release in bovine serum albumin solution. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 36951–36959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, S.; Dai, W.; Chong, Y.; Lyu, F.; Zhou, X.; Ding, Y. The binding of key fishy off-flavor compounds to silver carp proteins: A thermodynamic analysis. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 11292–11299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Sun, J.; Cao, D.; Cao, J.; Jiang, W. Distinction of different heat-treated bovine milks by native-PAGE fingerprinting of their whey proteins. Food Chem. 2010, 121, 803–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniloski, D.; McCarthy, N.A.; Vasiljevic, T. Impact of heating on the properties of A1/A1, A1/A2, and A2/A2 β-casein milk phenotypes. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 128, 107604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jovanovic, S.; Barac, M.; Macej, O.; Vucic, T.; Lacnjevac, C. SDS-PAGE Analysis of Soluble Proteins in Reconstituted Milk Exposed to Different Heat Treatments. Sensors 2007, 7, 371–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maćej, O.; Jovanović, S.; Denin-Djurdjević, J.D. The influence of high temperatures on milk proteins. Hem. Ind. 2002, 56, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anantharamkrishnan, V.; Hoye, T.; Reineccius, G.A. Covalent Adduct Formation Between Flavor Compounds of Various Functional Group Classes and the Model Protein β-Lactoglobulin. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 6395–6402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- On-Nom, N.; Grandison, A.S.; Lewis, M.J. Measurement of ionic calcium, pH, and soluble divalent cations in milk at high temperature. J. Dairy Sci. 2010, 93, 515–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, P.X.; Ren, D.; Xiao, Y.; Tomasula, P.M. Effect of homogenization and pasteurization on the structure and stability of whey protein in milk1. J. Dairy Sci. 2015, 98, 2884–2897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zenker, H.E.; Raupbach, J.; Boeren, S.; Wichers, H.J.; Hettinga, K.A. The effect of low vs. high temperature dry heating on solubility and digestibility of cow’s milk protein. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 109, 106098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordin, G.; Cordeiro Raposo, F.; de la Calle, B.; Rodriguez, A.R. Identification and quantification of major bovine milk proteins by liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2001, 928, 63–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rynne, N.M.; Beresford, T.P.; Kelly, A.L.; Guinee, T.P. Effect of milk pasteurization temperature and in situ whey protein denaturation on the composition, texture and heat-induced functionality of half-fat Cheddar cheese. Int. Dairy J. 2004, 14, 989–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, S.M.; Price, N.C. The use of circular dichroism in the investigation of protein structure and function. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 2000, 1, 349–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, Z.; Blank, I.; Zhong, F.; Wang, B.; Wang, Y.; Zeng, H. A comparative study to determine the key aroma components of yogurt aroma types based on Sensomics and Flavoromics. Food Chem. 2024, 460, 140618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kessler, J.C.; Vieira, V.; Martins, I.M.; Manrique, Y.A.; Ferreira, P.; Calhelha, R.C.; Afonso, A.; Barros, L.; Rodrigues, A.E.; Dias, M.M. The potential of almonds, hazelnuts, and walnuts SFE-CO2 extracts as sources of bread flavouring ingredients. Food Chem. 2023, 417, 135845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, H.L.A.; Balthazar, C.F.; Silva, R.; Vieira, A.H.; Costa, R.G.B.; Esmerino, E.A.; Freitas, M.Q.; Cruz, A.G. Sodium reduction and flavor enhancer addition in probiotic prato cheese: Contributions of quantitative descriptive analysis and temporal dominance of sensations for sensory profiling. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 8837–8846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.K.; Park, Y.W. SDS-PAGE of Proteins in Goat Milk Cheeses Ripened under Different Conditions. J. Food Sci. 1996, 61, 490–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van den Oever, S.P.; Mayer, H.K. Analytical assessment of the intensity of heat treatment of milk and dairy products. Int. Dairy J. 2021, 121, 105097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, H.A.; Singh, H.; Anema, S.G.; Creamer, L.K. Effects of Heat and High Hydrostatic Pressure Treatments on Disulfide Bonding Interchanges among the Proteins in Skim Milk. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 3409–3420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Qing, M.; Zang, J.; Shan, A.; Zhang, H.; Chi, Y.; Chi, Y.; Gao, X. Molecular interactions in the dry heat-facilitated hydrothermal gel formation of egg white protein. Food Res. Int. 2022, 162, 112058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Wit, J.N. Thermal behaviour of bovine β-lactoglobulin at temperatures up to 150 °C. a review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2009, 20, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, L.; Li, C.; Boeren, S.; Vervoort, J.; Hettinga, K. Effect of heat treatment on bacteriostatic activity and protein profile of bovine whey proteins. Food Res. Int. 2020, 127, 108688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Plancken, I.; Van Loey, A.; Hendrickx, M.E.G. Changes in Sulfhydryl Content of Egg White Proteins Due to Heat and Pressure Treatment. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 5726–5733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonfatti, V.; Grigoletto, L.; Cecchinato, A.; Gallo, L.; Carnier, P. Validation of a new reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography method for separation and quantification of bovine milk protein genetic variants. J. Chromatogr. A 2008, 1195, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halabi, A.; Deglaire, A.; Hennetier, M.; Violleau, F.; Burel, A.; Bouhallab, S.; Dupont, D.; Croguennec, T. Structural characterization of heat-induced protein aggregates in model infant milk formulas. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 107, 105928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stănciuc, N.; Aprodu, I.; Râpeanu, G.; van der Plancken, I.; Bahrim, G.; Hendrickx, M. Analysis of the Thermally Induced Structural Changes of Bovine Lactoferrin. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 2234–2243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, P.J.; Williams, S.C. Protein modification by thermal processing. Allergy 1998, 53, 102–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Ma, Y.; Li, H.; Yang, F.; Cheng, J. Identification and characterization of yak α-lactalbumin and β-lactoglobulin. J. Dairy Sci. 2021, 104, 2520–2528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, D.M.; Jasim, S.B.; Dyer, N.T.; Auvray, F.; Réfrégiers, M.; Hirst, J.D. Electronic Circular Dichroism Spectroscopy of Proteins. Chem 2019, 5, 2751–2774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristau, P.; Martin, M.-T.; Tran Huu Dau, M.-E.; Vors, J.-P.; Zhu, J. Strained-Cyclophane-Induced β-Turn Template: Design, Synthesis, and Spectroscopic Characterization. Org. Lett. 2004, 6, 3183–3186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Tolkach, A.; Kulozik, U. Quantitative Assessment of Thermal Denaturation of Bovine α-Lactalbumin via Low-Intensity Ultrasound, HPLC, and DSC. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 6501–6506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qie, X.; Chen, W.; Zeng, M.; Wang, Z.; Chen, J.; Goff, H.D.; He, Z. Interaction between β-lactoglobulin and chlorogenic acid and its effect on antioxidant activity and thermal stability. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 121, 107059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.H. Food-processing approaches to altering allergenic potential of milk-based formula. J. Pediatr. 1992, 121, S47–S50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Cao, H.; Pan, M.; Wang, C.; Sun, B.; Ai, N. Unraveling volatilomics profiles of milk products from diverse regions in China. Food Res. Int. 2024, 179, 114006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vagenas, G.; Roussis, I.G. Fat-Derived Volatiles of Various Products of Cows’, Ewes’, and Goats’ Milk. Int. J. Food Prop. 2012, 15, 665–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perkins, M.; Elliott, A.; D’Arcy, B.; Deeth, H. Stale flavour volatiles in Australian commercial UHT milk during storage. Aust. J. Dairy. Technol. 2005, 60, 231. [Google Scholar]
- Chi, X.; Shao, Y.; Pan, M.; Yang, Q.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Ai, N.; Sun, B. Distinction of volatile flavor profiles in various skim milk products via HS-SPME–GC–MS and E-nose. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2021, 247, 1539–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goss, M.B.; Kroll, J.H. Chamber studies of OH + dimethyl sulfoxide and dimethyl disulfide: Insights into the dimethyl sulfide oxidation mechanism. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2024, 24, 1299–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valero, E.; Villamiel, M.; Miralles, B.; Sanz, J.; Martínez-Castro, I. Changes in flavour and volatile components during storage of whole and skimmed UHT milk. Food Chem. 2001, 72, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melini, F.; Melini, V.; Luziatelli, F.; Ruzzi, M. Raw and Heat-Treated Milk: From Public Health Risks to Nutritional Quality. Beverages 2017, 3, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalač, P. The effects of silage feeding on some sensory and health attributes of cow’s milk: A review. Food Chem. 2011, 125, 307–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yayota, M.; Tsukamoto, M.; Yamada, Y.; Ohtani, S. Milk composition and flavor under different feeding systems: A survey of dairy farms. J. Dairy Sci. 2013, 96, 5174–5183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornu, A.; Rabiau, N.; Kondjoyan, N.; Verdier-Metz, I.; Pradel, P.; Tournayre, P.; Berdagué, J.L.; Martin, B. Odour-active compound profiles in Cantal-type cheese: Effect of cow diet, milk pasteurization and cheese ripening. Int. Dairy J. 2009, 19, 588–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di, C.; Jia, W. Capture modes evaluation of four flavor constituents in β-lactoglobulin by high-resolution mass spectrometry and molecular dynamics simulation approaches. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 145, 109157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
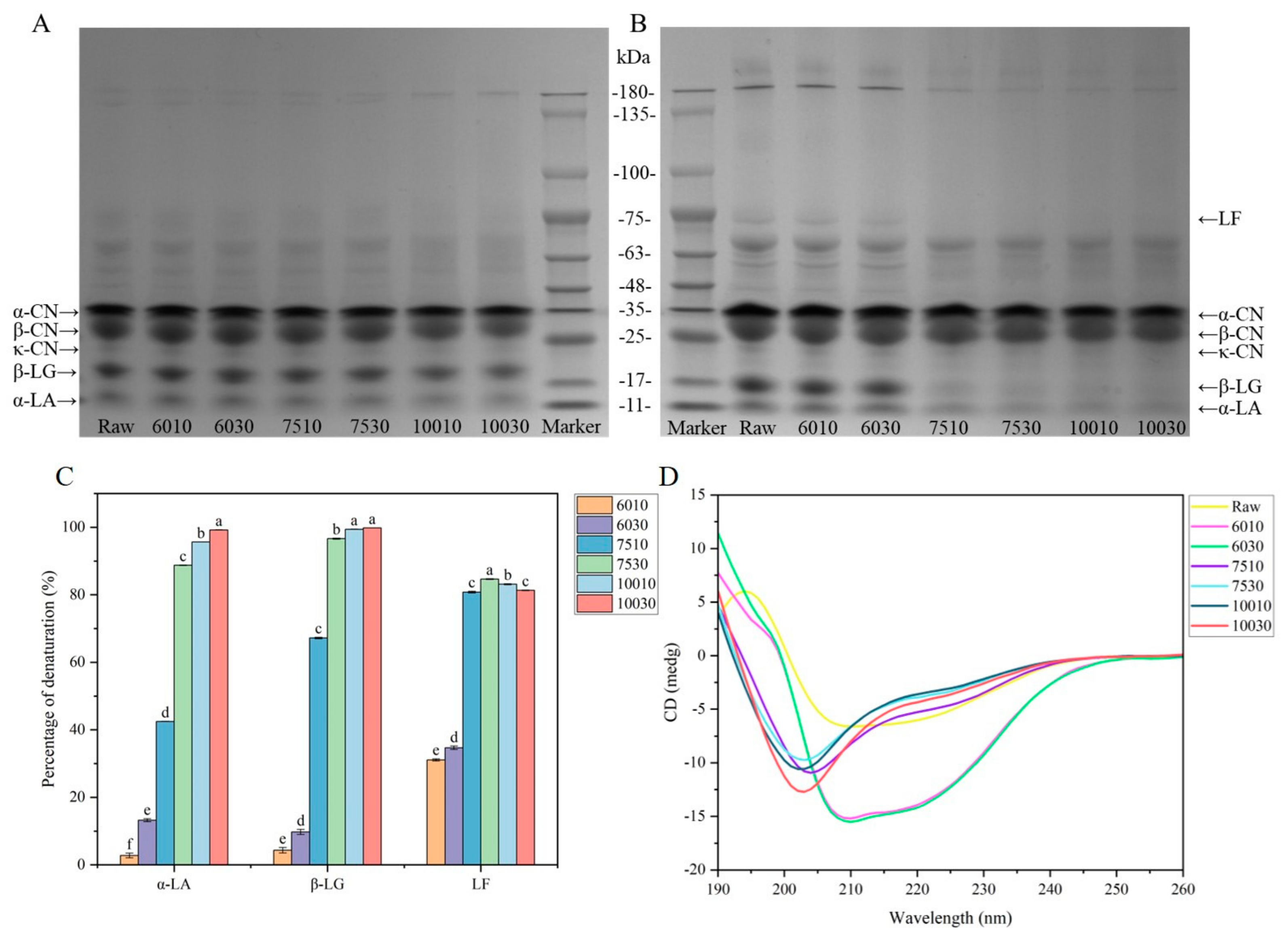

| Sample | α-Helix (%) | β-Sheet (%) | β-Turn (%) | Random Coil (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Raw | 15.5 ± 0.08 c | 34.6 ± 0.08 a | 19.6 ± 0.00 g | 30.3 ± 0.08 e |
| 6010 | 25.1 ± 0.05 b | 8.4 ± 0.05 e | 21.4 ± 0.12 e | 45.1 ± 0.21 a |
| 6030 | 27.2 ± 0.05 a | 8.3 ± 0.05 e | 20.5 ± 0.00 f | 43.9 ± 0.05 b |
| 7510 | 12.5 ± 0.05 d | 30.4 ± 0.19 d | 25.3 ± 0.05 b | 31.8 ± 0.19 c |
| 7530 | 9.8 ± 0.05 f | 34.8 ± 0.05 a | 24.0 ± 0.05 d | 31.3 ± 0.00 d |
| 10010 | 9.4 ± 0.05 g | 33.6 ± 0.12 b | 25.0 ± 0.08 c | 32.0 ± 0.08 c |
| 10030 | 11.0 ± 0.05 e | 32.1 ± 0.29 c | 26.3 ± 0.09 a | 30.6 ± 0.26 e |
| Descriptors | Raw | 6010 | 6030 | 7510 | 7530 | 10010 | 10030 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Milky aroma | 4.17 d | 5.75 b | 5.67 bc | 5.17 c | 5.75 b | 6.58 a | 6.17 ab |
| Dairy fat | 4.50 d | 5.42 bc | 5.25 bc | 5.08 c | 5.17 c | 6.25 a | 5.83 ab |
| Cooked | 2.83 c | 2.75 c | 4.25 a | 4.17 a | 4.08 a | 3.67 b | 4.33 a |
| Oxidized | 1.75 e | 2.42 d | 3.25 bc | 3.83 a | 3.75 ab | 2.83 cd | 3.75 ab |
| Grassy | 2.83 a | 1.92 c | 2.17 bc | 2.33 bc | 2.58 ab | 2.00 c | 2.08 c |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Z.; Jiang, K.; Yang, A.; Xu, K.; Meng, F.; Zhong, F.; Wang, B. Effect of Whey Protein Changes on Milk Flavor and Sensory Characteristics During Heating. Foods 2025, 14, 33. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14010033
Zhang Z, Jiang K, Yang A, Xu K, Meng F, Zhong F, Wang B. Effect of Whey Protein Changes on Milk Flavor and Sensory Characteristics During Heating. Foods. 2025; 14(1):33. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14010033
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Zheting, Kexin Jiang, Aolin Yang, Kunli Xu, Fanyu Meng, Fang Zhong, and Bei Wang. 2025. "Effect of Whey Protein Changes on Milk Flavor and Sensory Characteristics During Heating" Foods 14, no. 1: 33. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14010033
APA StyleZhang, Z., Jiang, K., Yang, A., Xu, K., Meng, F., Zhong, F., & Wang, B. (2025). Effect of Whey Protein Changes on Milk Flavor and Sensory Characteristics During Heating. Foods, 14(1), 33. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14010033





