Moisture Loss from Cheese During Baking: Influence of Cheese Type, Cheese Mass, and Temperature
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Sample Preparation
2.2.2. Moisture Content in Cheese Before Baking
2.2.3. Moisture Loss Rate During Baking of Cheese
2.2.4. Moisture Loss Rate During Baking of Pre-Dried Cheese
2.2.5. Image Acquisition and Color Analysis
2.2.6. Statistical Analysis
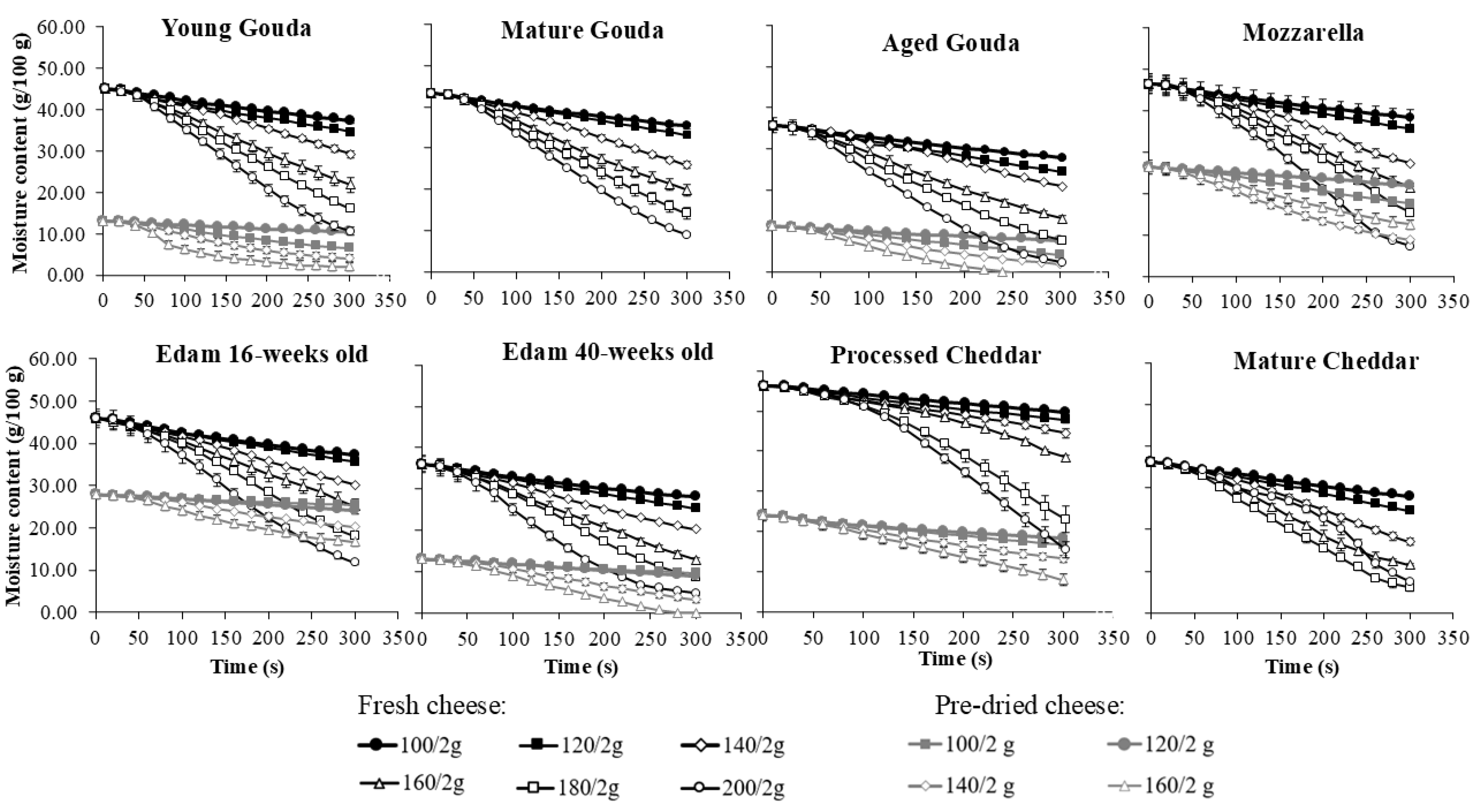
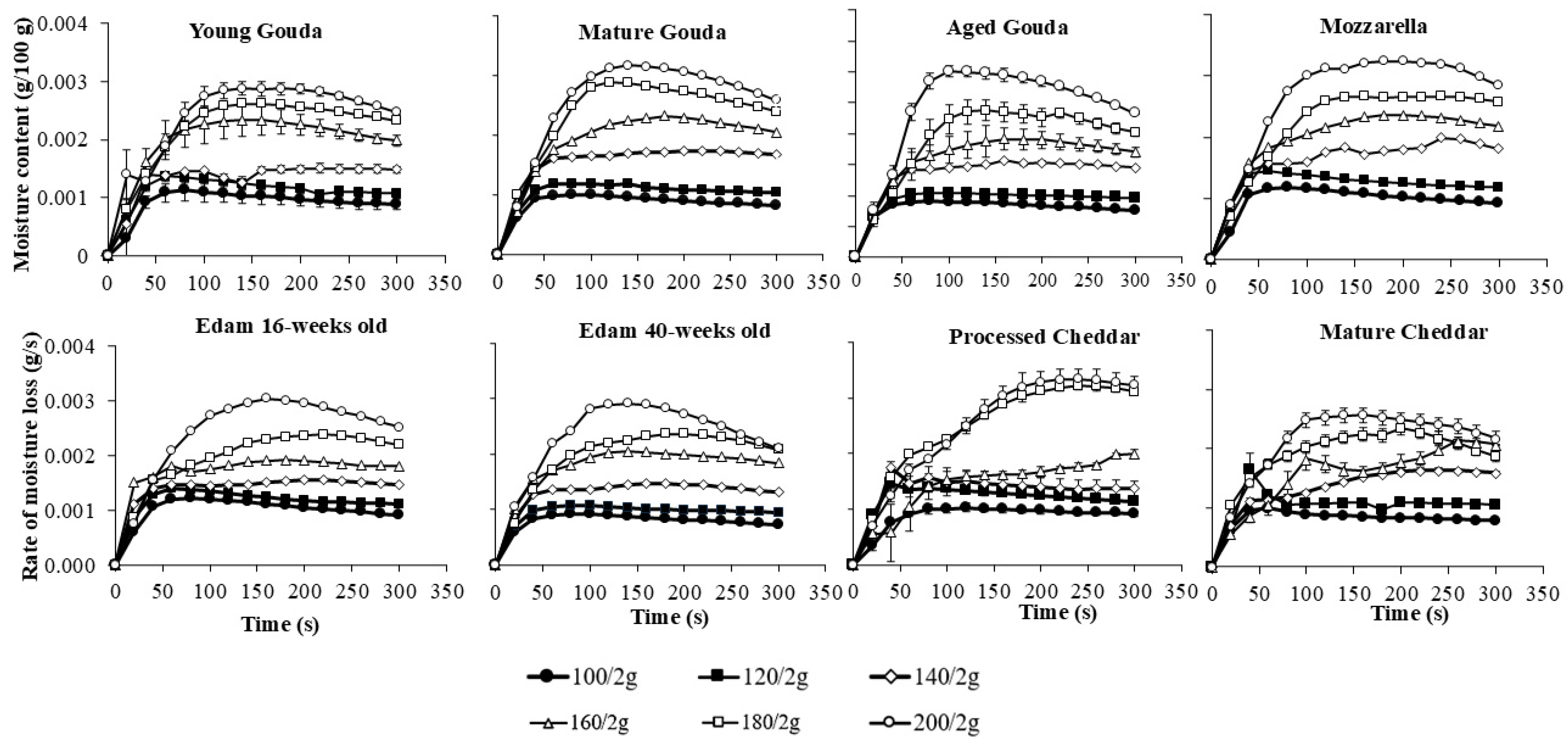
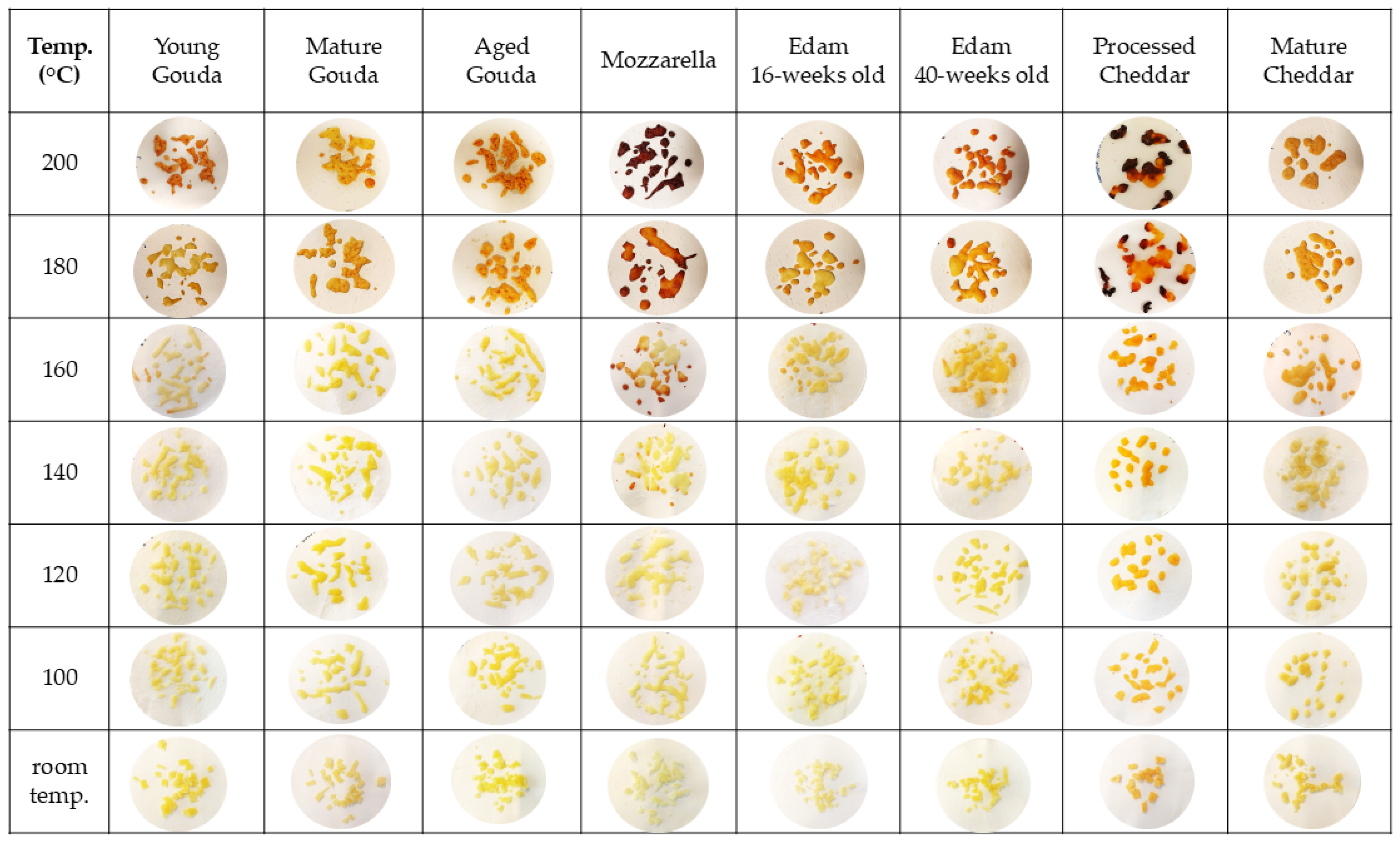
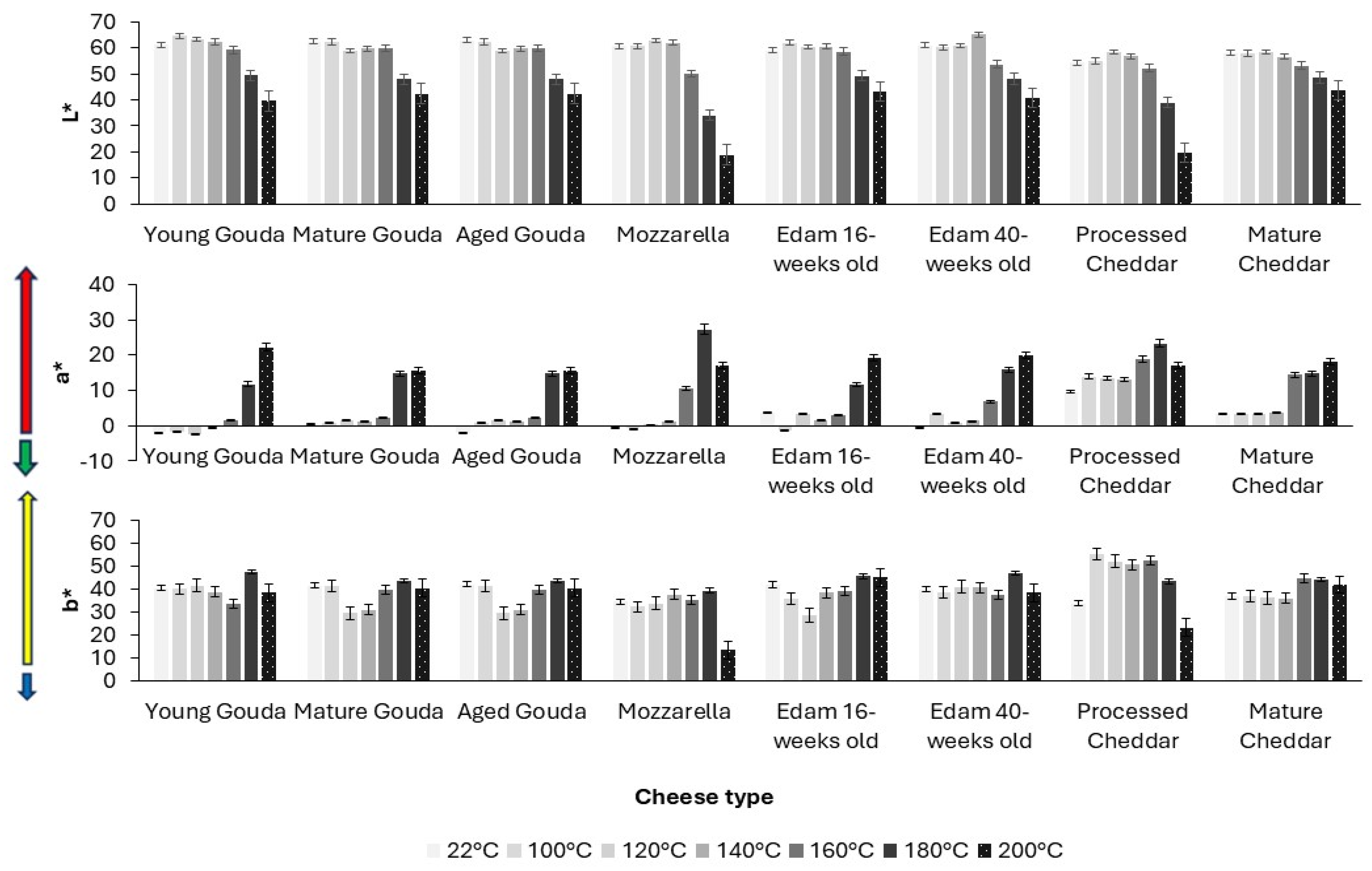
3. Results
4. Discussion
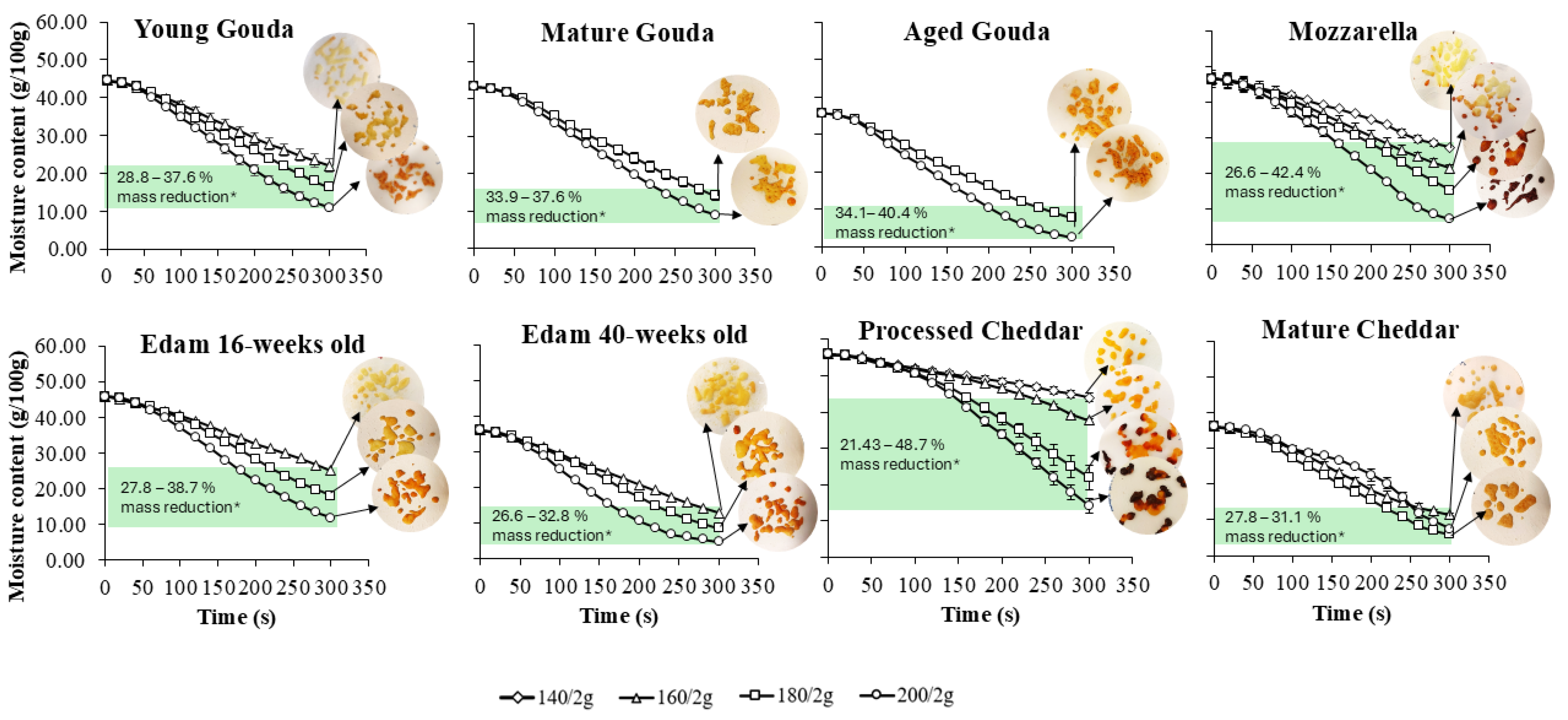
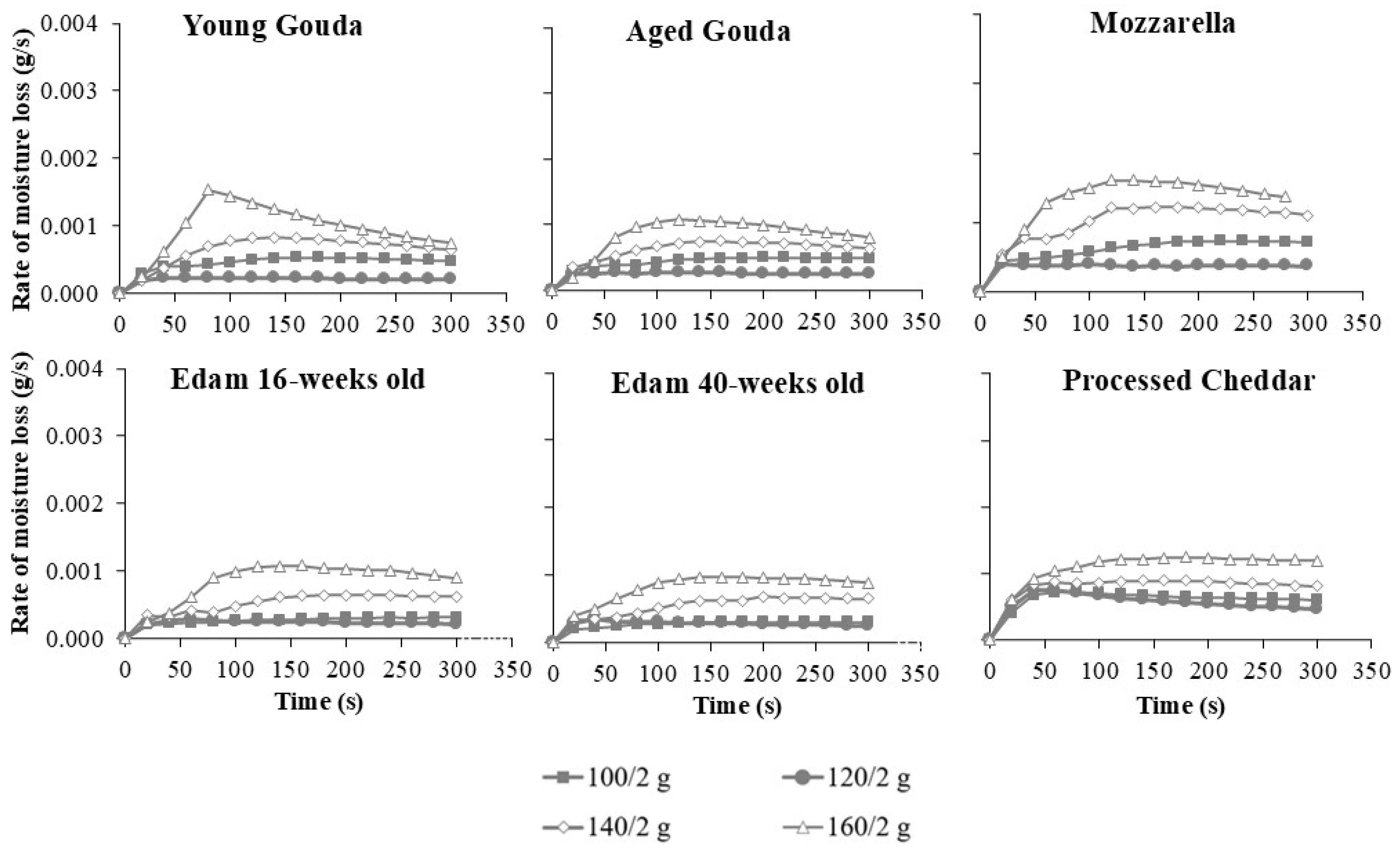
4.1. Moisture Loss Rate
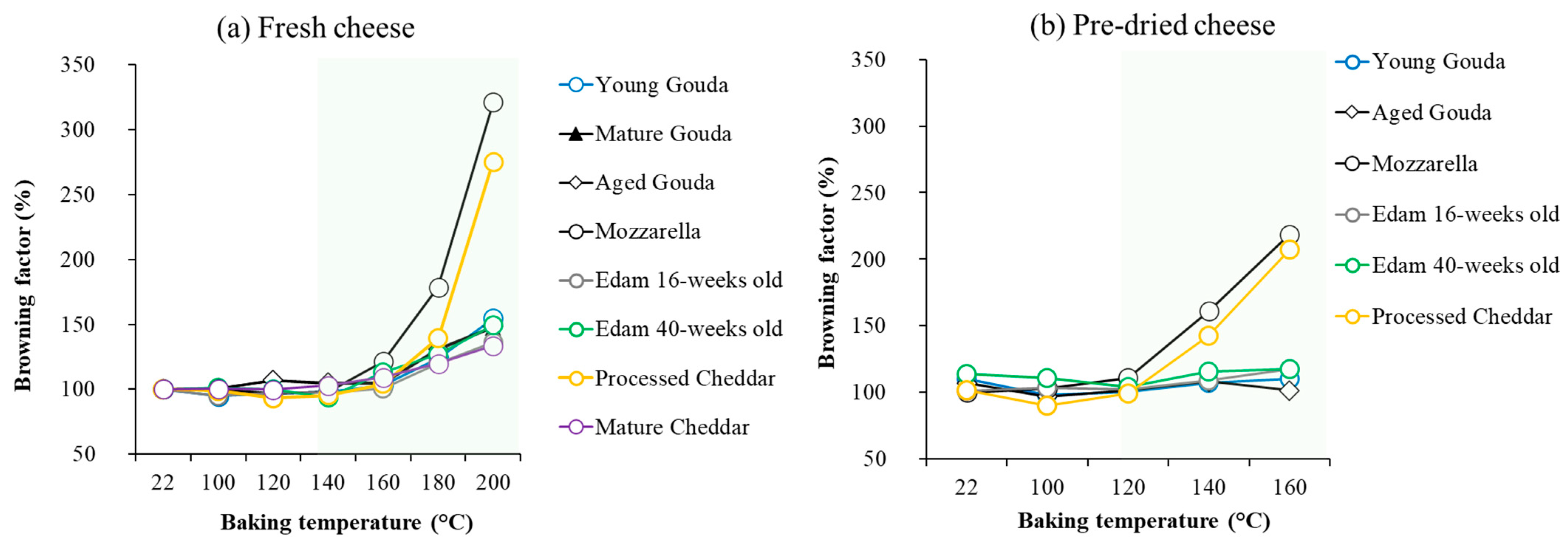
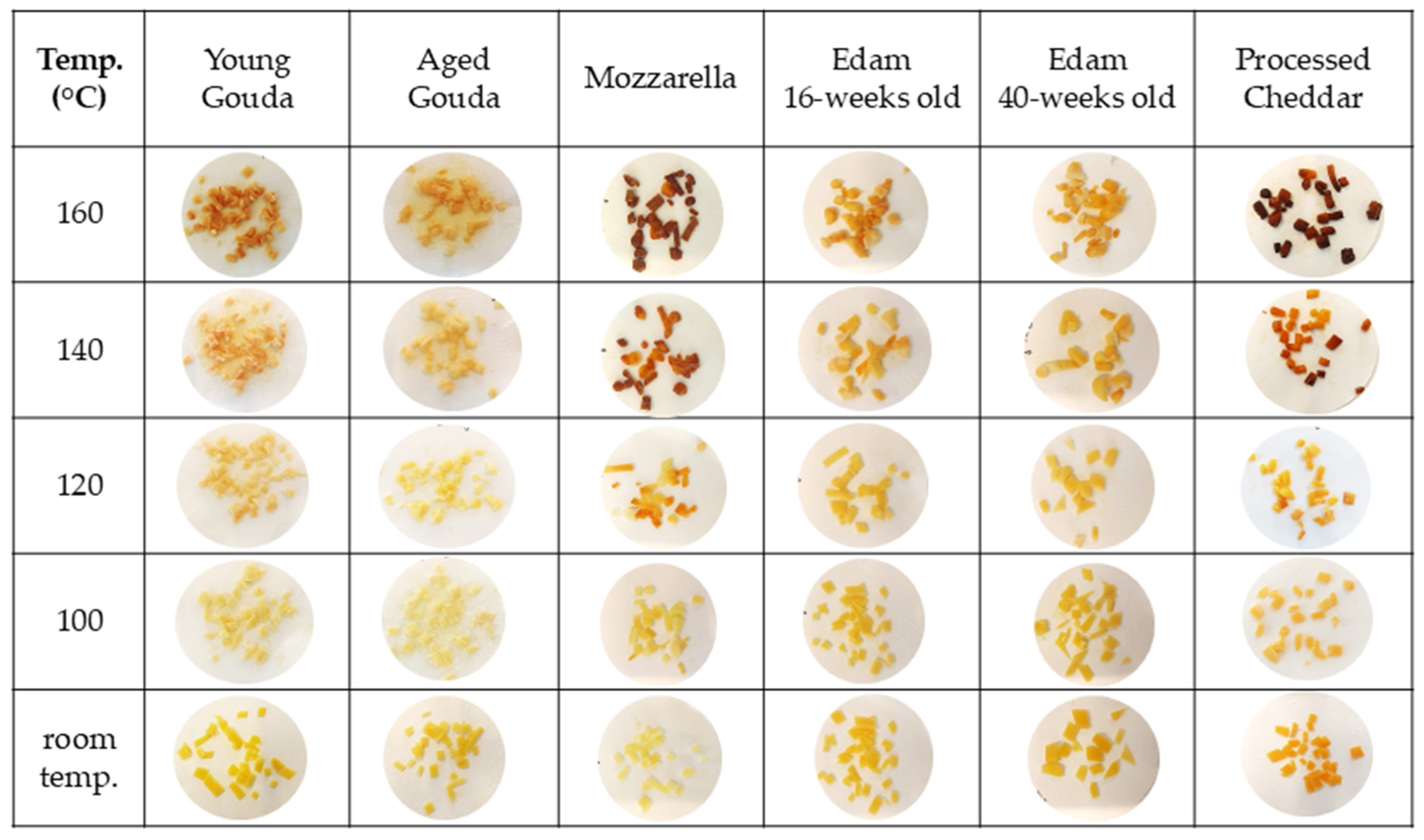
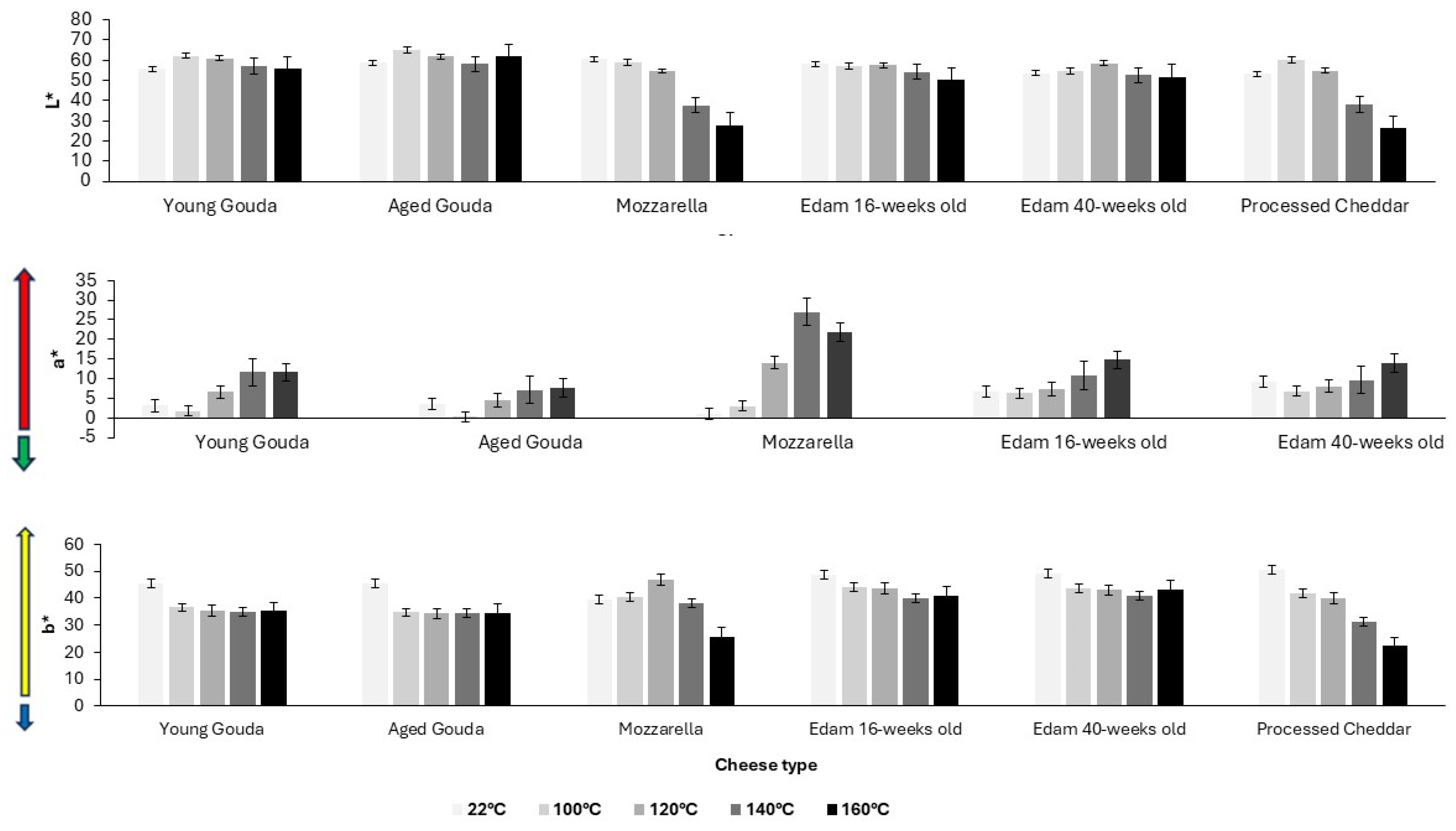
4.2. Browning
4.3. Comparison of Fresh and Pre-Dried Cheeses
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guinee, T.P. Cheese|Cheese as a Food Ingredient. In Encyclopedia of Dairy Sciences, 2nd ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011; pp. 822–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutariya, S.G.; Metzger, L.E.; Meletharayil, G.H. An Approach to Improve the Baking Properties and Determine the Onset of Browning in Fat-Free Mozzarella Cheese. J. Dairy Sci. 2022, 105, 2153–2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fox, P.F.; McSweeney, P.L.H. Cheese: An Overview. Cheese Chem. Phys. Microbiol. Fourth Ed. 2017, 1, 5–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Soda, M.; Awad, S. Cheese: Accelerated Cheese Ripening. In Encyclopedia of Dairy Sciences, 2nd ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011; pp. 795–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Balaban, M.O.; Zhang, L.; Emanuelsson-Patterson, E.A.C.; James, B. Quantification of Pizza Baking Properties of Different Cheeses, and Their Correlation with Cheese Functionality. J. Food Sci. 2014, 79, E1528–E1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banville, V.; Power, N.; Pouliot, Y.; Britten, M. Relationship between Baked-Cheese Sensory Properties and Melted-Cheese Physical Characteristics. J. Texture Stud. 2015, 46, 321–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atik, D.S.; Huppertz, T. Melting of Natural Cheese: A Review. Int. Dairy J. 2023, 142, 105648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AH, J.; Tagalpallewar, G.P. Functional Properties of Mozzarella Cheese for Its End Use Application. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 54, 3766–3778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fife, R.L.; McMahon, D.J.; Oberg, C.J. Functionality of Low Fat Mozzarella Cheese. J. Dairy Sci. 1996, 79, 1903–1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merrill, R.K.; Oberg, C.J.; McMahon, D.J. A Method for Manufacturing Reduced Fat Mozzarella Cheese. J. Dairy Sci. 1994, 77, 1783–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Rankin, S.A.; Fonseca, L.M.; Milani, F.X. Lactose and Galactose Content in Cheese Results in Overestimation of Moisture by Vacuum Oven and Microwave Methods. J. Dairy Sci. 2014, 97, 2567–2577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nooshkam, M.; Varidi, M.; Bashash, M. The Maillard Reaction Products as Food-Born Antioxidant and Antibrowning Agents in Model and Real Food Systems. Food Chem. 2019, 275, 644–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acton, J.C.; Dawson, P.L. Impact of Proteins on Food Colour. In Proteins in Food Processing; CIBA: Woodland, CA, USA, 2004; pp. 631–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, K.N.; Modi, R.B.; Patel, H.G.; Aparnathi, K.D. Browning, Its Chemistry and Implications in Dairy Products: A Review. Indo-Am. J. Agric. Vet. Sci. 2013, 1, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.H.; Sun, D.W. Melting Characteristics of Cheese: Analysis of Effects of Cooking Conditions Using Computer Vision Technology. J. Food Eng. 2002, 51, 305–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.H.; Sun, D.W. Assessment of Cheese Browning Affected by Baking Conditions Using Computer Vision. J. Food Eng. 2003, 56, 339–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; James, B.; Balaban, M.O.; Zhang, L.; Emanuelsson-Patterson, E.A.C. Quantifying Blistering and Browning Properties of Mozzarella Cheese. Part II: Cheese with Different Salt and Moisture Contents. Food Res. Int. 2013, 54, 917–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, C.J.; Barbin, D.F.; Sun, D.W. Quality Evaluation of Pizzas. In Computer Vision Technology for Food Quality Evaluation, 2nd ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2016; pp. 465–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purlis, E. Browning Development in Bakery Products—A Review. J. Food Eng. 2010, 99, 239–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulzar, N.; Sameen, A.; Rafiq, S.; Huma, N.; Murtaza, M.S. Influence of Mozzarella and Cheddar Cheese Blending on Baking Performance, Viscosity and Microstructure of Pizza Cheese Blends. J. Anim. Plant Sci. 2020, 30, 212–218. [Google Scholar]
- Milovanovic, B.; Djekic, I.; Miocinovic, J.; Djordjevic, V.; Lorenzo, J.M.; Barba, F.J.; Mörlein, D.; Tomasevic, I. What Is the Color of Milk and Dairy Products and How Is It Measured? Foods 2020, 9, 1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thornton, D.J. Browning and Blistering of Mozzarella During High Temperature Pizza Baking. Ph.D. Thesis, Massey University, Palmerston North, NZ, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Yates, M.D.; Drake, M.A. Texture Properties of Gouda Cheese. J. Sens. Stud. 2007, 22, 493–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudan, M.A.; Barbano, D.M. A Model of Mozzarella Cheese Melting and Browning During Pizza Baking. J. Dairy Sci. 1998, 81, 2312–2319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moskowitz, H.R. Sensory Directionals for Pizza: A Deeper Analysis. J. Sens. Stud. 2001, 16, 583–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metzger, L.E.; Barbano, D.M. Measurement of Postmelt Chewiness of Mozzarella Cheese. J. Dairy Sci. 1999, 82, 2274–2279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, S.; Jiang, F.; Shah, N.P.; Corke, H. Functional and Pizza Bake Properties of Mozzarella Cheese Made with Konjac Glucomannan as a Fat Replacer. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 92, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berta, M.; Muskens, E.; Schuster, E.; Stading, M. Rheology of Natural and Imitation Mozzarella Cheese at Conditions Relevant to Pizza Baking. Int. Dairy J. 2016, 57, 34–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Ling, X.; Jiang, K.; Zhao, X.; Gan, Y. Development of Low-Fat Mozzarella Cheeses Enriched with Soy or Pea Protein Hydrolysates: Composition, Texture and Functional Properties during Ageing. Int. J. Dairy Technol. 2024, 77, 165–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AOAC International. Official Methods of Analysis, 18th ed.; AOAC International: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Esteller, M.S.; De Lima, A.C.O.; Da Silva Lannes, S.C. Color Measurement in Hamburger Buns with Fat and Sugar Replacers. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2006, 39, 184–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, T.T.H.; Jaskulski, M.; Avila-Acevedo, J.G.; Tsotsas, E. Model Parameters for Single-Droplet Drying of Skim Milk and Its Constituents at Moderate and Elevated Temperatures. Dry. Technol. 2017, 35, 444–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitz-Schug, I.; Kulozik, U.; Foerst, P. Modeling Spray Drying of Dairy Products—Impact of Drying Kinetics, Reaction Kinetics and Spray Drying Conditions on Lysine Loss. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2016, 141, 315–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meda, V.; Anthony Opoku, M.G. Drying Kinetics and Quality Characteristics of Microwave-Vacuum Dried Saskatoon Berries. J. Microw. Power Electromagn. Energy 2007, 42, 4–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frías, J.M.; Bimbenet, J.J.; Bonazzi, C.; Foucat, L. Modeling of Moisture Profiles in Paddy Rice during Drying Mapped with Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Chem. Eng. J. 2002, 86, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malafronte, L.; Ahrné, L.; Schuster, E.; Innings, F.; Rasmuson, A. Exploring Drying Kinetics and Morphology of Commercial Dairy Powders. J. Food Eng. 2015, 158, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhikari, B.; Howes, T.; Bhandari, B.R.; Troung, V. Surface Stickiness of Drops of Carbohydrate and Organic Acid Solutions During Convective Drying: Experiments and Modeling. Dry. Technol. 2003, 21, 839–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.D.; Mujumdar, A.S. Drying Technologies in Food Processing; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2009; ISBN 1444309420. [Google Scholar]
- Constantin, G.-A.; Munteanu, M.-G.; Voicu, G.; Paraschiv, G.; Ștefan, E.-M. An Analysis of Air Flow in the Baking Chamber of a Tunnel-Type Electric Oven. Computation 2023, 11, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wadhwani, R.; McManus, W.R.; McMahon, D.J. Improvement in Melting and Baking Properties of Low-Fat Mozzarella Cheese. J. Dairy Sci. 2011, 94, 1713–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, M.E.; Olson, N.F. Nonenzymatic Browning of Mozzarella Cheese. J. Dairy Sci. 1985, 68, 3143–3147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McSweeney, P.L.H.; Fox, P.F. Metabolism of Residual Lactose and of Lactate and Citrate. Cheese Chem. Phys. Microbiol. 2004, 1, 361–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akarca, G.; Atik, A.; Atik, İ.; Denizkara, A.J. A Comparison Study on Functional and Textural Properties of Mozzarella Cheeses Made from Bovine and Buffalo Milks Using Different Starter Cultures. Int. Dairy J. 2023, 141, 105622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baskaran, D.; Sivakumar, S. Galactose Concentration in Pizza Cheese Prepared by Three Different Culture Techniques. Int. J. Dairy Technol. 2003, 56, 229–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristensen, D.; Hansen, E.; Arndal, A.; Trinderup, R.A.; Lieberman, S. Influence of Light and Temperature on the Colour and Oxidative Stability of Processed Cheese. Int. Dairy J. 2001, 11, 837–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, M.A. Browning Reaction in Cheddar Cheese. Aust. J. Dairy Technol. 1969, 24, 185–189. [Google Scholar]
- Daly, D.; Mcsweeney, P.; Sheehan, J.; Daly, D.F.M.; Mcsweeney, P.L.H.; Sheehan, J.J. Pink Discolouration Defect in Commercial Cheese: A Review. Dairy Sci. Technol. 2012, 92, 439–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spanneberg, R.; Salzwedel, G.; Glomb, M.A. Formation of Early and Advanced Maillard Reaction Products Correlates to the Ripening of Cheese. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 600–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, P.F.; Guinee, T.P.; Cogan, T.M.; McSweeney, P.L.H. (Eds.) Biochemistry of Cheese Ripening. In Fundamentals of Cheese Science; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2017; pp. 391–442. ISBN 978-1-4899-7681-9. [Google Scholar]

| Cheese Type | Chemical Composition | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| FDM (%) | Salt in Dry Matter (%) | Moisture * (%) | |
| Mozzarella (4 wk) | 41 | 2.2 | 46.6 b ± 0.4 |
| Edam (16 wk) | 43 | 3.6 | 45.9 b,c ± 0.3 |
| Edam (40 wk) | 43 | 3.6 | 36.0 d ± 0.1 |
| Young Gouda (4 wk) | 55 | 3.4 | 44.5 c ± 0.5 |
| Mature Gouda (8 wk) | 55 | 3.4 | 43.3 c ± 0.2 |
| Aged Gouda (52 wk) | 55 | 3.4 | 35.7 d ± 0.3 |
| Mature Cheddar (52 wk) | 54 | 3.2 | 36.3 d ± 0.1 |
| Processed Cheddar | 38 | 8.6 | 56.0 a ± 0.1 |
| Temperature of Baking (°C) | YG | MG | AG | M | E16 | E40 | PC | MC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 100 | 3.5 ± 0.3 | 0.5 ± 0.1 | 3.1 ± 0.1 | 2.3 ± 0.1 | 36.4 ± 0.1 | 4.3 ± 0.1 | 22.0 ± 1.1 | 0.2 ± 0.0 |
| 120 | 2.5 ± 0.1 | 12.6 ± 0.4 | 13.8 ± 0.3 | 2.2 ± 0.1 | 28.7 ± 0.7 | 1.8 ± 0.1 | 19.3 ± 0.8 | 0.8 ± 0.0 |
| 140 | 2.5 ± 0.1 | 10.9 ± 0.4 | 12.0 ± 0.3 | 3.8 ± 0.1 | 38.7 ± 0.1 | 4.7 ± 0.4 | 17.7 ± 0.8 | 2.0 ± 0.1 |
| 160 | 7.7 ± 0.6 | 3.7 ± 0.3 | 5.8 ± 0.3 | 15.3 ± 1.6 | 39.2 ± 0.1 | 10.6 ± 1.1 | 20.9 ± 0.9 | 14.5 ± 0.7 |
| 180 | 19.4 ± 0.6 | 20.5 ± 2.3 | 22.5 ± 2.2 | 38.8 ± 4.5 | 47.5 ± 2.1 | 22.0 ± 1.5 | 22.7 ± 2.3 | 16.7 ± 0.6 |
| 200 | 32.4 ± 0.8 | 25.2 ± 4.5 | 27.1 ± 4.3 | 49.9 ± 4.3 | 50.4 ± 2.7 | 28.8 ± 3.5 | 36.9 ± 2.1 | 21.4 ± 0.6 |
| Temperature of Baking (°C) | YG | AG | M | E16 | E40 | PC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 100 | 11.2 ± 0.9 | 12.8 ± 0.1 | 2.8 ± 0.1 | 4.9 ± 0.2 | 6.4 ± 0.4 | 13.7 ± 0.3 |
| 120 | 11.8 ± 0.7 | 11.7 ± 0.5 | 16.1 ± 0.2 | 5.2 ± 0.3 | 8.0 ± 0.3 | 12.4 ± 0.7 |
| 140 | 13.5 ± 0.8 | 11.7 ± 0.7 | 34.6 ± 3.2 | 10.5 ± 0.1 | 8.4 ± 0.6 | 24.6 ± 1.5 |
| 160 | 13.3 ± 0.8 | 12.3 ± 0.5 | 41.1 ± 2.0 | 14.0 ± 0.4 | 7.8 ± 0.4 | 39.1 ± 3.8 |
| Factor | DF Number | DF Den | F-Value | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature of baking (°C) | 5.00 | 4290.89 | 2008.54 | <0.0001 |
| Mass of cheese (g) | 2.00 | 4294.47 | 1973.28 | <0.0001 |
| Time of baking (s) | 14.00 | 4288.64 | 278.49 | <0.0001 |
| Term | Coefficient | SE | DF | T-Value | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Constant | 0.002538 | 0.000096 | 8.64 | 26.36 | <0.0001 |
| Temp. (°C) | |||||
| 100 | −0.001178 | 0.000020 | 4291.77 | −60.41 | <0.0001 |
| 120 | −0.000856 | 0.000020 | 4291.77 | −43.90 | <0.0001 |
| 140 | −0.000333 | 0.000019 | 4290.07 | −17.15 | <0.0001 |
| 160 | 0.000237 | 0.000019 | 4289.63 | 12.20 | <0.0001 |
| 180 | 0.000794 | 0.000019 | 4291.67 | 40.75 | <0.0001 |
| Mass (g) | |||||
| 2 | −0.000755 | 0.000012 | 4295.21 | −60.70 | <0.0001 |
| 4 | 0.000164 | 0.000012 | 4295.21 | 13.20 | <0.0001 |
| Time (s) | |||||
| 20 | −0.001577 | 0.000032 | 4288.63 | −48.62 | <0.0001 |
| 40 | −0.000835 | 0.000032 | 4288.63 | −25.73 | <0.0001 |
| 60 | −0.000440 | 0.000032 | 4288.63 | −13.56 | <0.0001 |
| 80 | −0.000198 | 0.000032 | 4288.63 | −6.11 | <0.0001 |
| 100 | −0.000001 | 0.000032 | 4288.63 | −0.04 | 0.966 |
| 120 | 0.000136 | 0.000032 | 4288.63 | 4.18 | <0.0001 |
| 140 | 0.000237 | 0.000032 | 4288.63 | 7.32 | <0.0001 |
| 160 | 0.000299 | 0.000032 | 4288.63 | 9.21 | <0.0001 |
| 180 | 0.000338 | 0.000032 | 4288.63 | 10.44 | <0.0001 |
| 200 | 0.000366 | 0.000032 | 4288.63 | 11.29 | <0.0001 |
| 220 | 0.000371 | 0.000032 | 4288.63 | 11.43 | <0.0001 |
| 240 | 0.000361 | 0.000032 | 4288.65 | 11.14 | <0.0001 |
| 260 | 0.000344 | 0.000032 | 4288.65 | 10.60 | <0.0001 |
| 280 | 0.000318 | 0.000032 | 4288.65 | 9.82 | <0.0001 |
| Baking Temperature (°C) | N | Mean Moisture Loss Rate (g/s) | Grouping | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 200 | 720 | 0.0039 | A | |||||
| 180 | 720 | 0.0033 | B | |||||
| 160 | 720 | 0.0028 | C | |||||
| 140 | 720 | 0.0022 | D | |||||
| 120 | 720 | 0.0017 | E | |||||
| 100 | 720 | 0.0014 | F | |||||
| Cheese Mass (g) | N | Mean Moisture Loss Rate (g/s) | Grouping | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6 | 1440 | 0.0031 | A | ||
| 4 | 1440 | 0.0027 | B | ||
| 2 | 1440 | 0.0018 | C | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tarapata, J.; Szymańska, E.; van der Meulen, L.; Miltenburg, J.; Huppertz, T. Moisture Loss from Cheese During Baking: Influence of Cheese Type, Cheese Mass, and Temperature. Foods 2025, 14, 165. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14020165
Tarapata J, Szymańska E, van der Meulen L, Miltenburg J, Huppertz T. Moisture Loss from Cheese During Baking: Influence of Cheese Type, Cheese Mass, and Temperature. Foods. 2025; 14(2):165. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14020165
Chicago/Turabian StyleTarapata, Justyna, Ewa Szymańska, Liesbeth van der Meulen, Joost Miltenburg, and Thom Huppertz. 2025. "Moisture Loss from Cheese During Baking: Influence of Cheese Type, Cheese Mass, and Temperature" Foods 14, no. 2: 165. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14020165
APA StyleTarapata, J., Szymańska, E., van der Meulen, L., Miltenburg, J., & Huppertz, T. (2025). Moisture Loss from Cheese During Baking: Influence of Cheese Type, Cheese Mass, and Temperature. Foods, 14(2), 165. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14020165





