Simultaneous Determination of Three Active Forms of Vitamin B12 In Situ Produced During Fermentation by LC-MS/MS
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Reagents
2.2. Activation of Bacteria and Fermentation of Rice Bran
2.3. Extraction of VB12
2.4. Purification of VB12
2.5. Determination of VB12 by LC-MS/MS and Validation of the Method
2.6. Determination of VB12 by Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
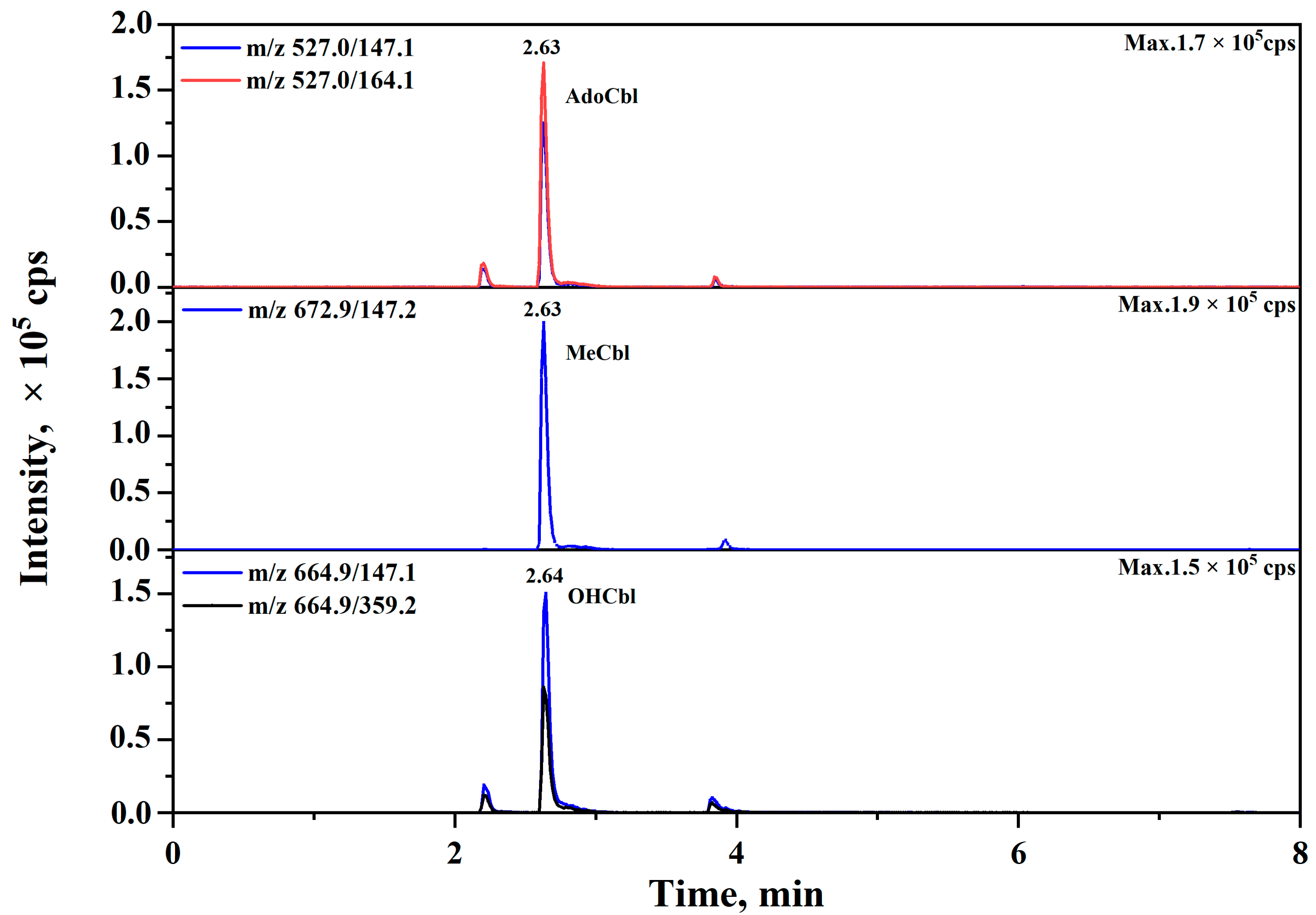
3.1. Method Development and Validation
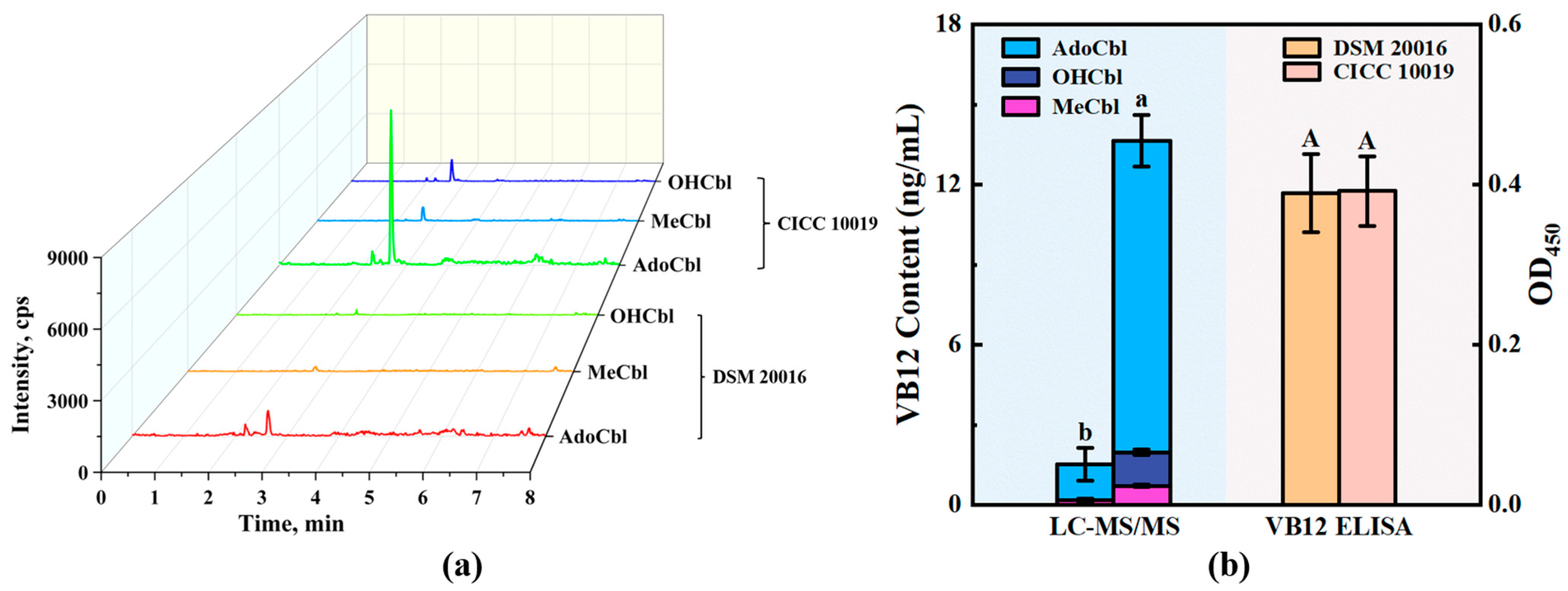
3.2. Distinguishing of VB12 and Pseudo-VB12
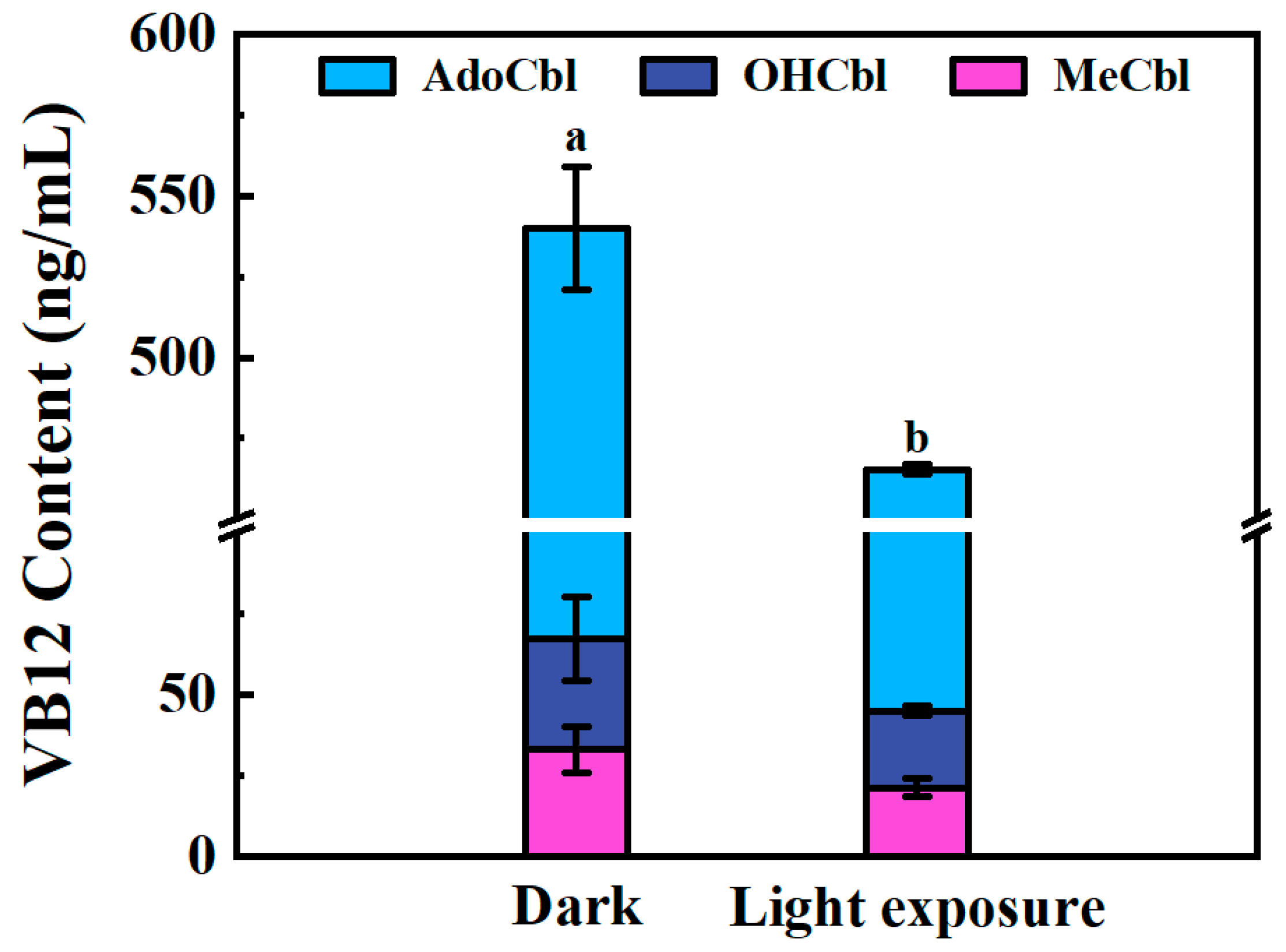
3.3. Light Stability
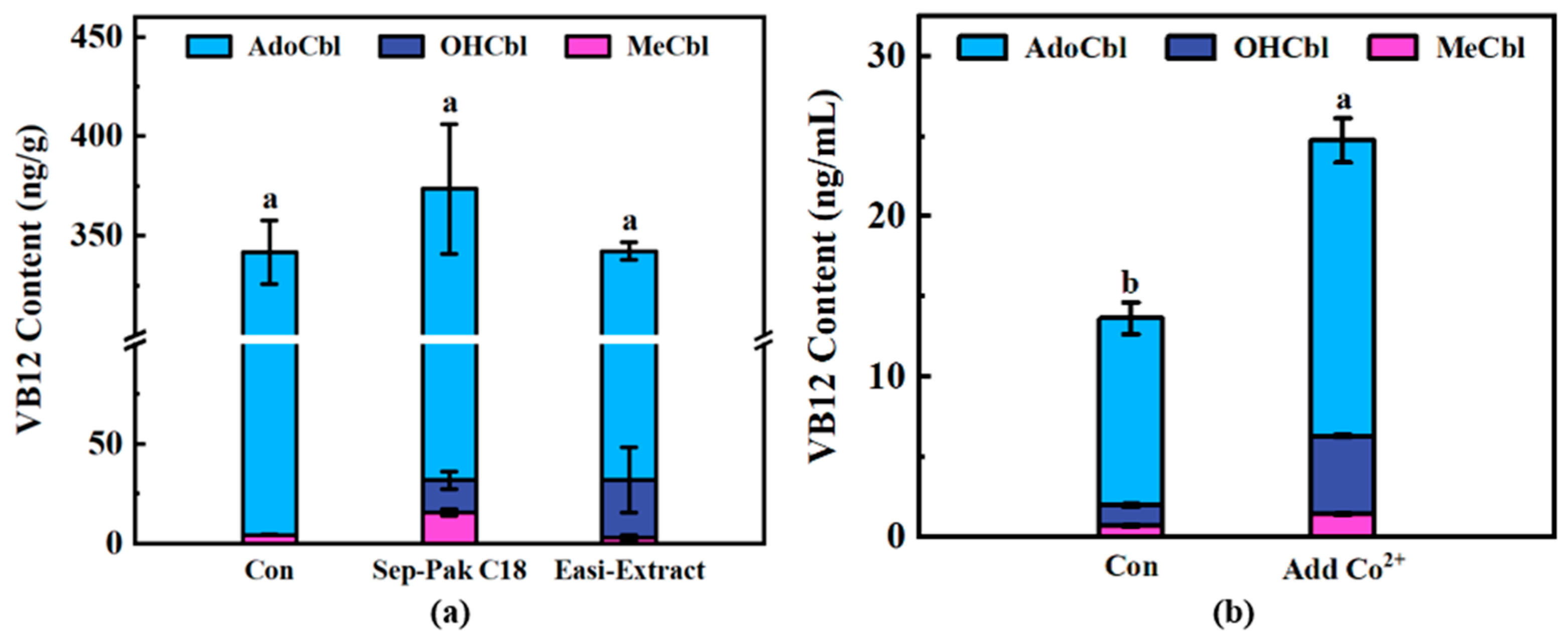
3.4. Application of Detection Methods
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nielsen, M.J.; Rasmussen, M.R.; Andersen, C.B.F.; Nexø, E.; Moestrup, S.K. Vitamin B12 transport from food to the body’s cells—A sophisticated, multistep pathway. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2012, 9, 345–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Wang, C.; Wang, Y.; Fu, L.; Zhang, N. Future foods, dietary factors and healthspan. J. Future Foods 2023, 3, 75–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martens, J.H.; Barg, H.; Warren, M.; Jahn, D. Microbial production of vitamin B12. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2002, 58, 275–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sobczyńska-Malefora, A.; Delvin, E.; McCaddon, A.; Ahmadi, K.R.; Harrington, D.J. Vitamin B12 status in health and disease: A critical review. Diagnosis of deficiency and insufficiency—Clinical and laboratory pitfalls. Crit. Rev. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2021, 58, 399–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Leary, F.; Samman, S. Vitamin B12 in health and disease. Nutrients 2010, 2, 299–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, H.; Kang, J.; Zhang, D. Microbial production of vitamin B(12): A review and future perspectives. Microb. Cell Factories 2017, 16, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xie, C.; Pulkkinen, M.; Edelmann, M.; Chamlagain, B.; Coda, R.; Sandell, M.A.; Piironen, V.; Maina, N.H.; Katina, K.J.L. In situ production of vitamin B12 and dextran in soya flour and rice bran: A tool to improve flavour and texture of B12-fortified bread. LWT 2022, 161, 113407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Signorini, C.; Carpen, A.; Coletto, L.; Borgonovo, G.; Galanti, E.; Capraro, J.; Magni, C.; Abate, A.; Johnson, S.K.; Duranti, M.; et al. Enhanced vitamin B12 production in an innovative lupin tempeh is due to synergic effects of Rhizopus and Propionibacterium in cofermentation. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2018, 69, 451–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tindjau, R.; Chua, J.Y.; Liu, S.Q. Co-culturing Propionibacterium freudenreichii and Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. lactis improves short-chain fatty acids and vitamin B(12) contents in soy whey. Food Microbiol. 2024, 121, 104525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsiminis, G.; Schartner, E.P.; Brooks, J.L.; Hutchinson, M.R. Measuring and tracking vitamin B12: A review of current methods with a focus on optical spectroscopy. Appl. Spectrosc. Rev. 2017, 52, 439–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamlagain, B.; Edelmann, M.; Kariluoto, S.; Ollilainen, V.; Piironen, V. Ultra-high performance liquid chromatographic and mass spectrometric analysis of active vitamin B12 in cells of Propionibacterium and fermented cereal matrices. Food Chem. 2015, 166, 630–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guetterman, H.M.; Huey, S.L.; Knight, R.; Fox, A.M.; Mehta, S.; Finkelstein, J.L. Vitamin B-12 and the Gastrointestinal Microbiome: A Systematic Review. Adv. Nutr. (Bethesda Md.) 2022, 13, 530–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, C.; Yuan, R.; Su, L.; Li, D.; Zhang, C.; Yin, Y.; Wang, P.; Yang, R. Improving nutritional and sensory properties of rice bran by germination and solid-state fermentation with fungi. Food Biosci. 2024, 59, 103992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, A.C.; Reinbold, G.W.; Vedamuthu, E.R. An evaluation of the taxonomy of Propionibacterium. Can. J. Microbiol. 1968, 14, 1185–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, C.; Coda, R.; Chamlagain, B.; Varmanen, P.; Piironen, V.; Katina, K. Co-fermentation of Propionibacterium freudenreichii and Lactobacillus brevis in Wheat Bran for in situ Production of Vitamin B12. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.; Xia, Y.; Wang, H.; Shi, L.; Yin, H.; Gu, M.; Yan, F. PM2.5 induced neurotoxicity through unbalancing vitamin B12 metabolism by gut microbiota disturbance. Gut Microbes 2023, 15, 2267186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Fernandez, V.; Gentili, A.; Martinelli, A.; Caretti, F.; Curini, R. Evaluation of oxidized buckypaper as material for the solid phase extraction of cobalamins from milk: Its efficacy as individual and support sorbent of a hydrophilic-lipophilic balance copolymer. J. Chromatogr. A 2016, 1428, 255–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomes Soares, M.; Bevilaqua, G.C.; Marcondes Tassi, É.M.; Reolon Schmidt, V.C. Fermented foods and beverages: A potential in situ vitamin B12 biofortification—A literature review. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 74, 655–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelleher, B.P.; Scott, J.M.; O’Broin, S.D. Cryo-preservation of Lactobacillus leichmannii for vitamin B12 microbiological assay. Med. Lab. Sci. 1990, 47, 90–96. [Google Scholar]
- Alcock, S.C.; Finglas, P.M.; Morgan, M.R.A. Production and purification of an R-protein-enzyme conjugate for use in a microtitration plate protein-binding assay for vitamin B12 in fortified food. Food Chem. 1992, 45, 199–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frenkel, E.P.; Kitchens, R.L.; Prough, R. High-performance liquid chromatographic separation of cobalamins. J. Chromatogr. 1979, 174, 393–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Honda, K.; Imanishi, M.; Takeda, T.; Kimura, M. Determination of Vitamin B12 in Serum by HPLC/ICP-MS. Anal. Sci. 2001, 17, i983–i985. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.; Schuster, K.; Asam, S.; Rychlik, M. Challenges in the determination of total vitamin B12 by cyanidation conversion: Insights from stable isotope dilution assays. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2023, 415, 5797–5807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Zhang, J.; Wang, M.; Cai, Z. Determination of Vitamin B12 in Milk and Dairy Products by Isotope-Dilution Liquid Chromatography Tandem Mass Spectrometry. J. Food Qual. 2022, 2022, 7649228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.N.; Yin, S.A.; Yang, Z.Y.; Yang, X.G.; Shao, B.; Ren, Y.P.; Zhang, J. Application of UPLC-MS/MS Method for Analyzing B-vitamins in Human Milk. Biomed. Environ. Sci. 2015, 28, 738–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zia, H.; Fischbach, N.; Hofsommer, M.; Slatnar, A. Development and validation of HPLC-MS/MS method for simultaneous analysis of B vitamins present naturally or after fortification in fruit juices. LWT 2023, 184, 115103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Wang, Y.; Liu, J. Simultaneous determination of four cobalamins in rat plasma using online solid phase extraction coupled to high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry: Application to pentylenetetrazole-induced seizures in Sprague-Dawley rats. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0269645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, X.; Zhang, H.; Yin, Y.; Brandes, H.; Marsala, T.; Stenerson, K.; Cramer, H.; You, H. Determination of active vitamin B12 (cobalamin) in dietary supplements and ingredients by reversed-phase liquid chromatography: Single-laboratory validation. Food Chem. 2019, 298, 125010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Zhou, B.; Zheng, C. The Fast Quantification of Vitamin B12 in Milk Powder by High-Performance Liquid Chromatography-Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry. Molecules 2024, 29, 1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, F.; Vera, J.L.; Lamosa, P.; de Valdez, G.F.; de Vos, W.M.; Santos, H.; Sesma, F.; Hugenholtz, J. Pseudovitamin B12 is the corrinoid produced by Lactobacillus reuteri CRL1098 under anaerobic conditions. FEBS Lett. 2007, 581, 4865–4870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van den Oever, S.P.; Mayer, H.K. Biologically active or just “pseudo”-vitamin B12 as predominant form in algae-based nutritional supplements? J. Food Compos. Anal. 2022, 109, 104464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edelmann, M.; Aalto, S.; Chamlagain, B.; Kariluoto, S.; Piironen, V. Riboflavin, niacin, folate and vitamin B12 in commercial microalgae powders. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2019, 82, 103226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temova Rakuša, Ž.; Roškar, R.; Hickey, N.; Geremia, S. Vitamin B(12) in Foods, Food Supplements, and Medicines-A Review of Its Role and Properties with a Focus on Its Stability. Molecules 2022, 28, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shell, T.A.; Lawrence, D.S. A New Trick (Hydroxyl Radical Generation) for an Old Vitamin (B12). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 2148–2150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padmanabhan, S.; Jost, M.; Drennan, C.L.; Elías-Arnanz, M. A New Facet of Vitamin B12: Gene Regulation by Cobalamin-Based Photoreceptors. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2017, 86, 485–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jost, M.; Simpson, J.H.; Drennan, C.L. The Transcription Factor CarH Safeguards Use of Adenosylcobalamin as a Light Sensor by Altering the Photolysis Products. Biochemistry 2015, 54, 3231–3234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hogenkamp, H.P.C. A Cyclic Nucleoside Derived from Coenzyme B12. J. Biol. Chem. 1963, 238, 477–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, P.Y.; Wood, J.M. The photolysis of 5′-deoxyadenosylcobalamin under anaerobic conditions. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)—Nucleic Acids Protein Synth. 1973, 331, 451–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, P.A.; Frey, P.A. 5‘-Peroxyadenosine and 5‘-Peroxyadenosylcobalamin as Intermediates in the Aerobic Photolysis of Adenosylcobalamin. Biochemistry 2007, 46, 7284–7292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juzeniene, A.; Nizauskaite, Z. Photodegradation of cobalamins in aqueous solutions and in human blood. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2013, 122, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohail, M.; Rakha, A.; Butt, M.S.; Iqbal, M.J.; Rashid, S. Rice bran nutraceutics: A comprehensive review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017, 57, 3771–3780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, C.; Coda, R.; Chamlagain, B.; Edelmann, M.; Varmanen, P.; Piironen, V.; Katina, K. Fermentation of cereal, pseudo-cereal and legume materials with Propionibacterium freudenreichii and Levilactobacillus brevis for vitamin B12 fortification. LWT 2021, 137, 110431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marley, E.C.; Mackay, E.; Young, G. Characterisation of vitamin B12 immunoaffinity columns and method development for determination of vitamin B12 in a range of foods, juices and pharmaceutical products using immunoaffinity clean-up and high performance liquid chromatography with UV detection. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2009, 26, 282–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, S.J.; Lawrence, A.D.; Biedendieck, R.; Deery, E.; Frank, S.; Howard, M.J.; Rigby, S.E.J.; Warren, M.J. Elucidation of the anaerobic pathway for the corrin component of cobalamin (vitamin B12). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 14906–14911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, C.; Coda, R.; Chamlagain, B.; Edelmann, M.; Deptula, P.; Varmanen, P.; Piironen, V.; Katina, K. In situfortification of vitamin B12 in wheat flour and wheat bran by fermentation with Propionibacterium freudenreichii. J. Cereal Sci. 2018, 81, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
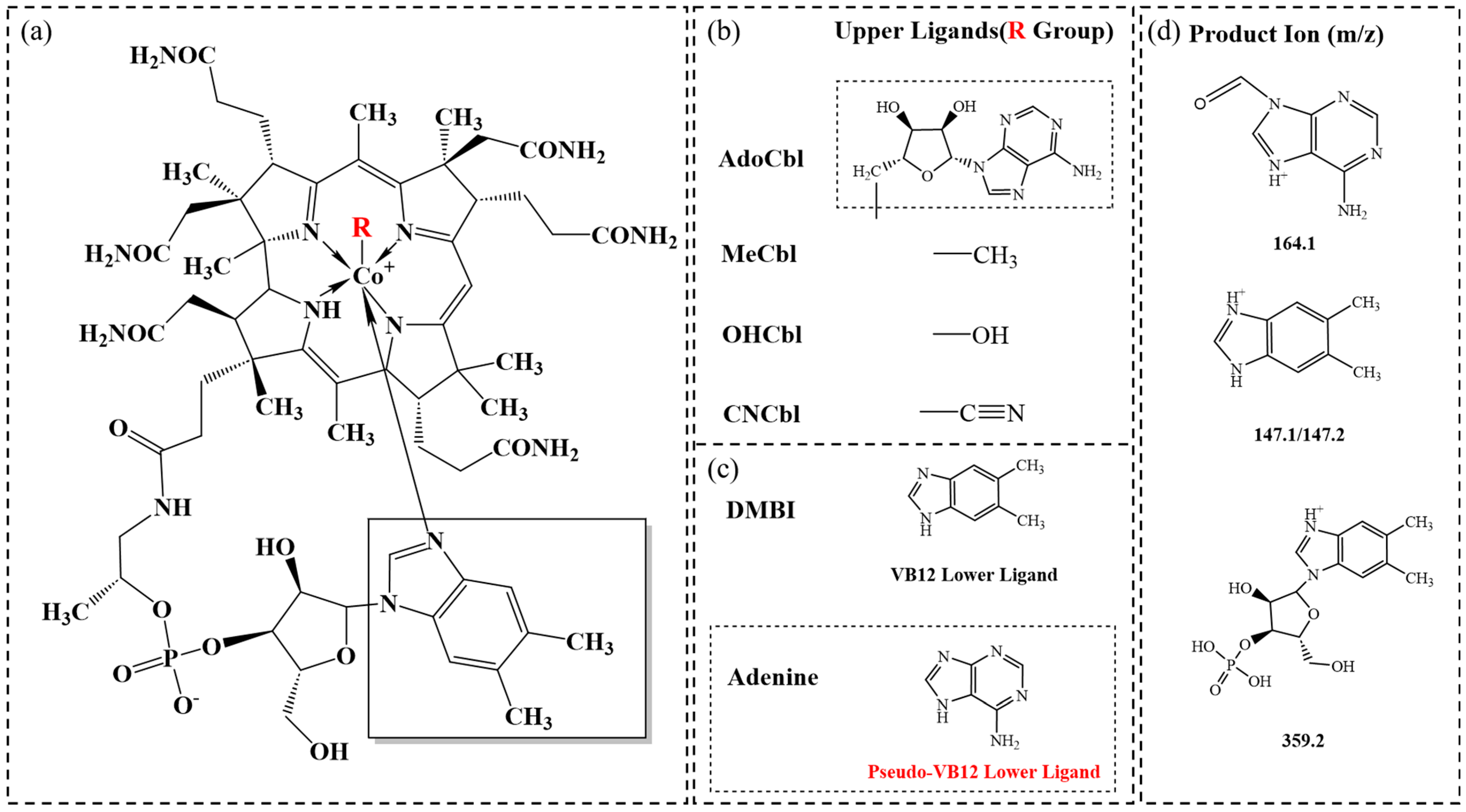
| Analytes | MRM Transition | RT (min) | DP (V) | CE (V) | Linear Range (ng/mL) | Limit of Detection |
| OHCbl | 664.9 → 147.1 | 2.65 | 125.0 | 66.0 | 0.10–400 | 0.01 ng/mL |
| 664.9 → 359.2 a | 2.65 | 100.0 | 32.0 | 0.10–400 | ||
| AdoCbl | 527.0 → 147.1 a | 2.63 | 52.5 | 74.0 | 0.50–400 | 0.01 ng/mL |
| 527.0 → 164.1 | 2.63 | 64.0 | 60.0 | 0.50–400 | ||
| MeCbl | 672.9 → 147.2 a | 2.63 | 60.0 | 20.5 | 0.50–400 | 0.01 ng/mL |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fan, Z.; Li, Y.; Fan, X.; Wang, P.; Yang, R.; Xie, C. Simultaneous Determination of Three Active Forms of Vitamin B12 In Situ Produced During Fermentation by LC-MS/MS. Foods 2025, 14, 309. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14020309
Fan Z, Li Y, Fan X, Wang P, Yang R, Xie C. Simultaneous Determination of Three Active Forms of Vitamin B12 In Situ Produced During Fermentation by LC-MS/MS. Foods. 2025; 14(2):309. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14020309
Chicago/Turabian StyleFan, Zhihao, Yajie Li, Xia Fan, Pei Wang, Runqiang Yang, and Chong Xie. 2025. "Simultaneous Determination of Three Active Forms of Vitamin B12 In Situ Produced During Fermentation by LC-MS/MS" Foods 14, no. 2: 309. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14020309
APA StyleFan, Z., Li, Y., Fan, X., Wang, P., Yang, R., & Xie, C. (2025). Simultaneous Determination of Three Active Forms of Vitamin B12 In Situ Produced During Fermentation by LC-MS/MS. Foods, 14(2), 309. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14020309








