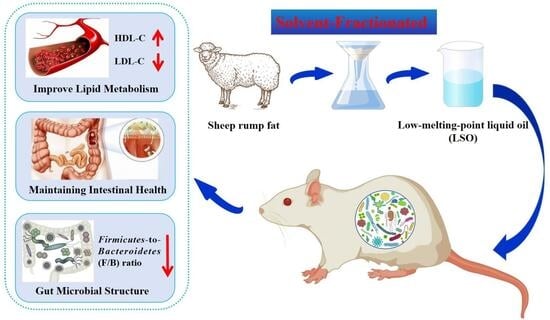
Solvent Fractionation Improves the Functional Properties of Sheep Rump Fat: Effects of Different Lipid Fractions on Lipid Metabolism and Gut Health in Mice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Physicochemical Indicator Analysis
2.3. Experimental Animals and Diet
2.4. Sample Collection
2.5. Determination of Growth Indicators
2.6. Determination of Blood Lipids and Histopathological Examination of Colon Tissues
2.7. Real-Time Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction (qPCR)
2.8. Gut Microbial Analysis
2.8.1. PCR Amplification and 16S rDNA Sequencing
2.8.2. Biological Analysis
2.9. Extraction and Analysis of SCFAs
2.10. Data Processing
3. Results
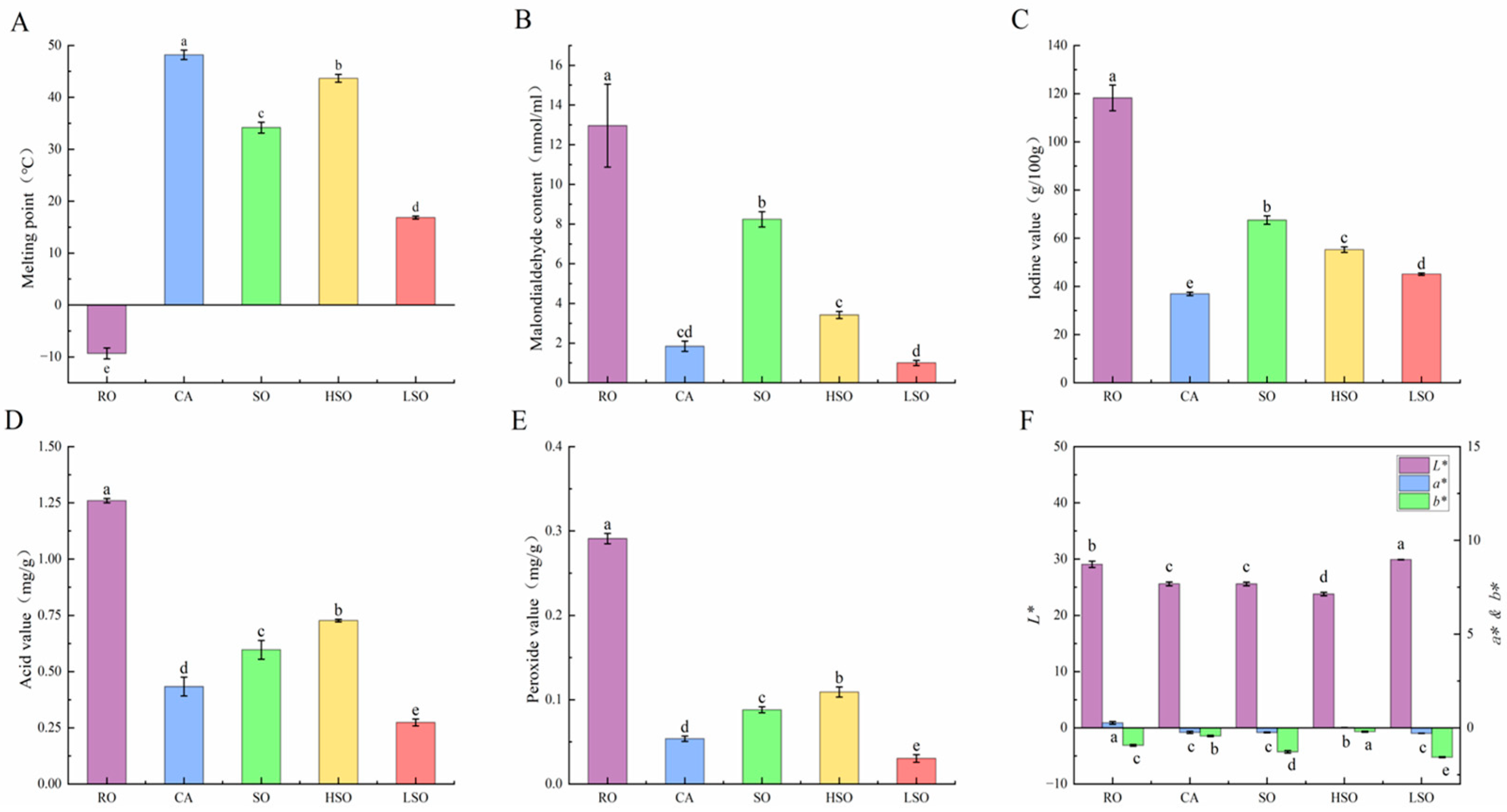
3.1. Physicochemical Property Analysis
3.2. Fatty Acid Analysis
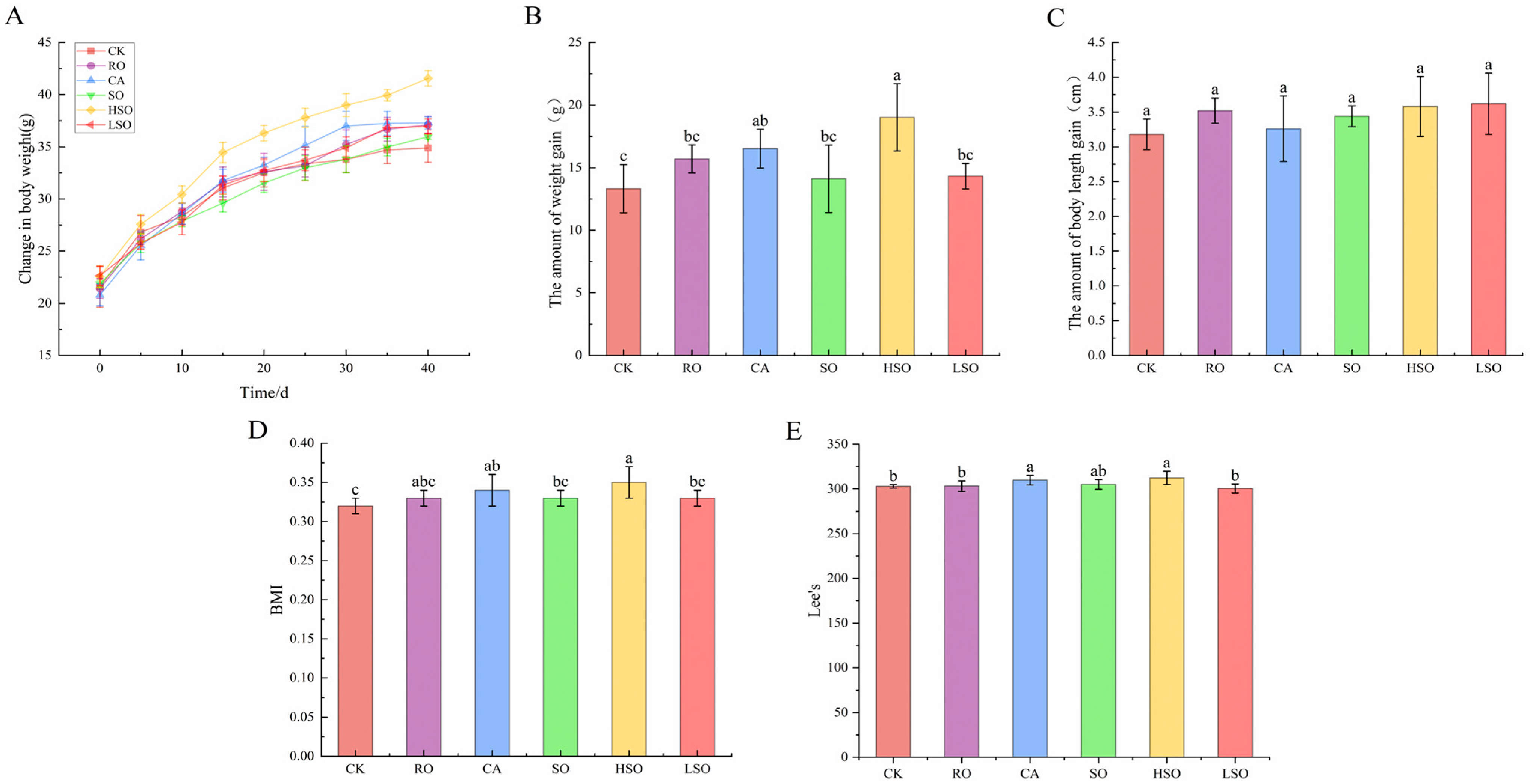
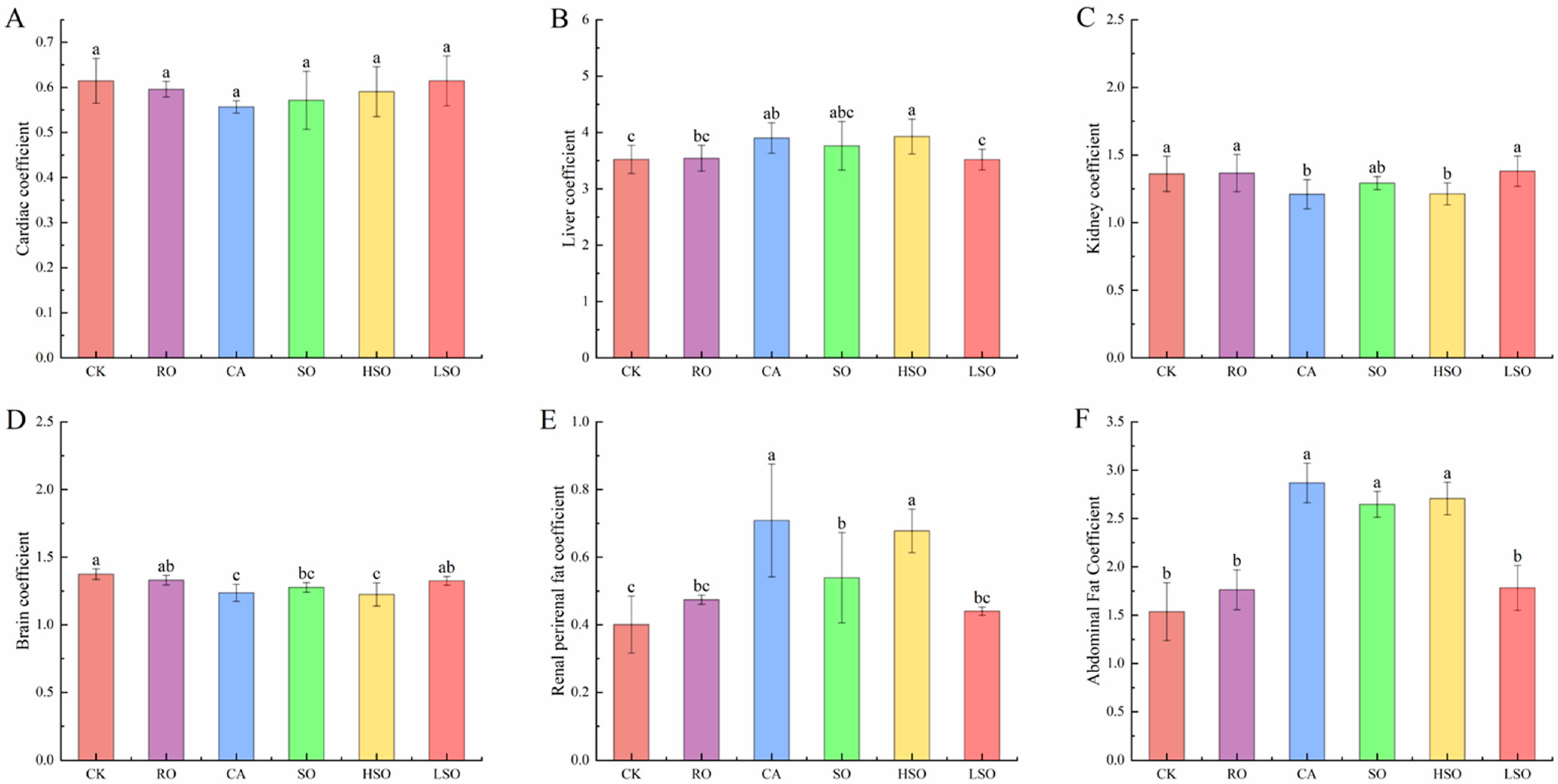
3.3. Growth and Organ Coefficient Indicators
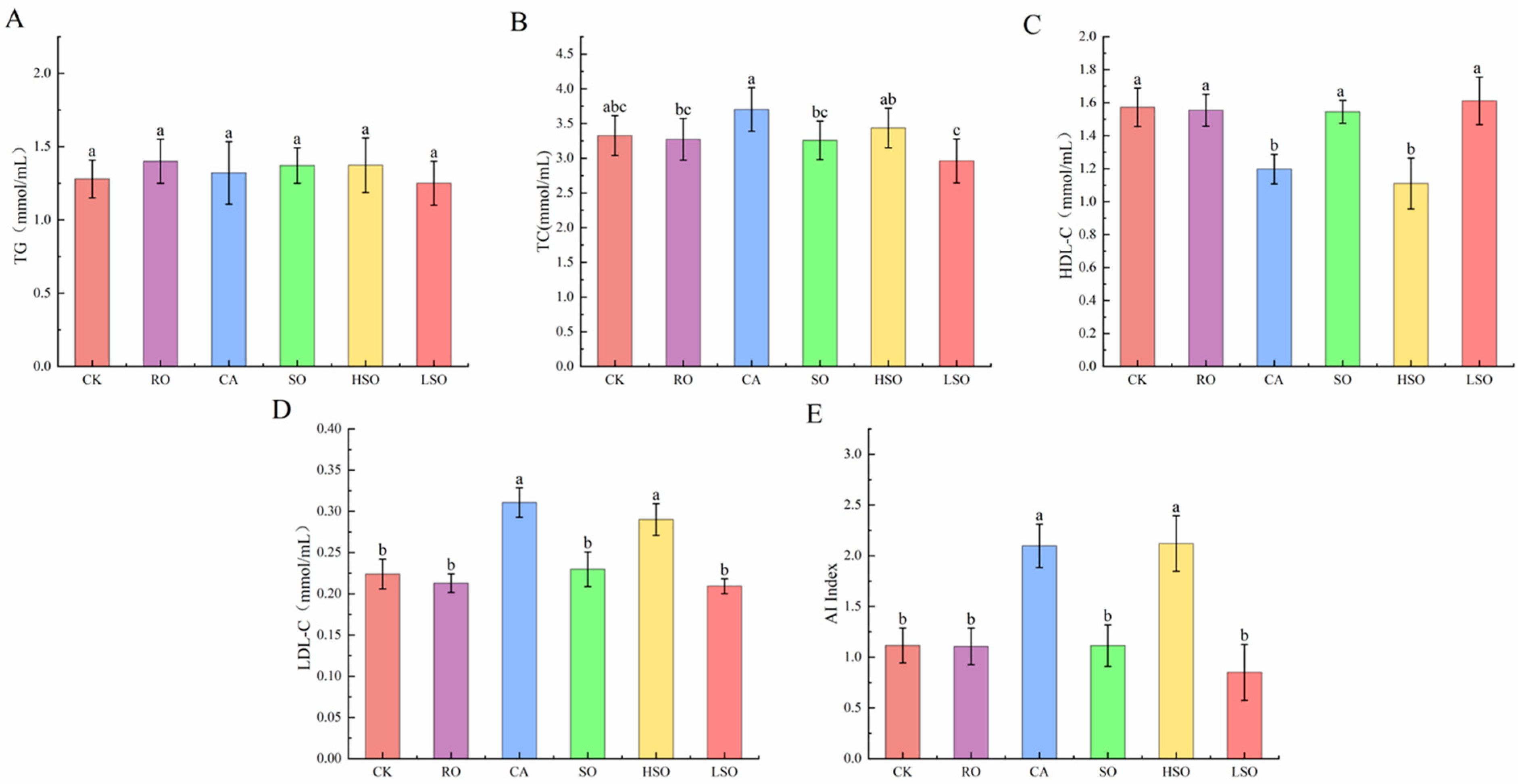
3.4. Serum Lipid Profiles
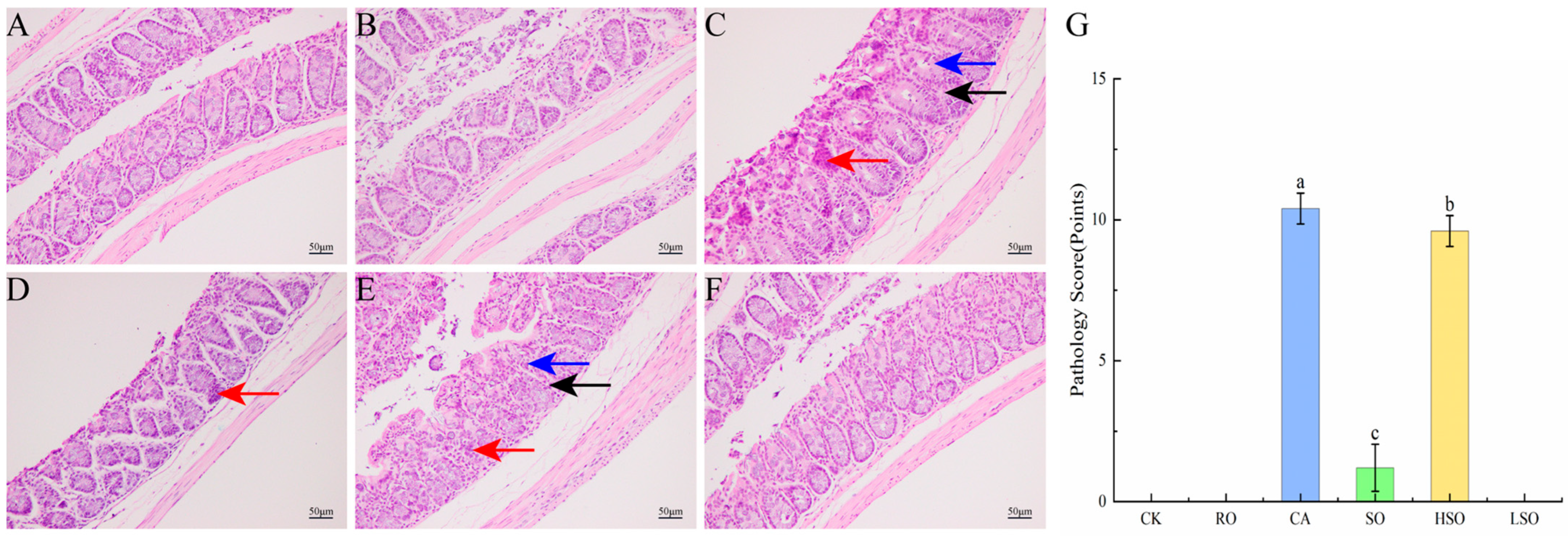
3.5. Histopathological Evaluation of the Colon
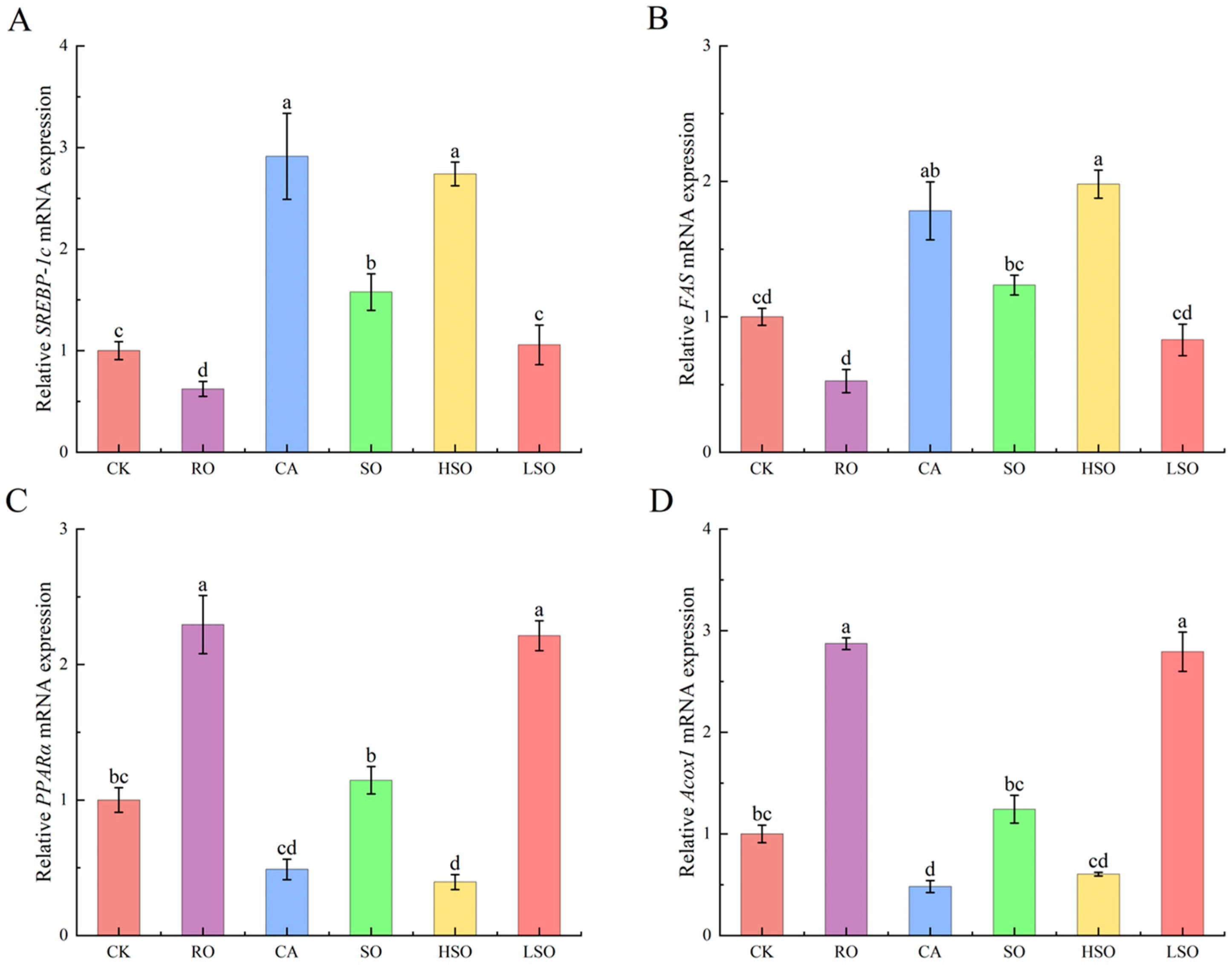
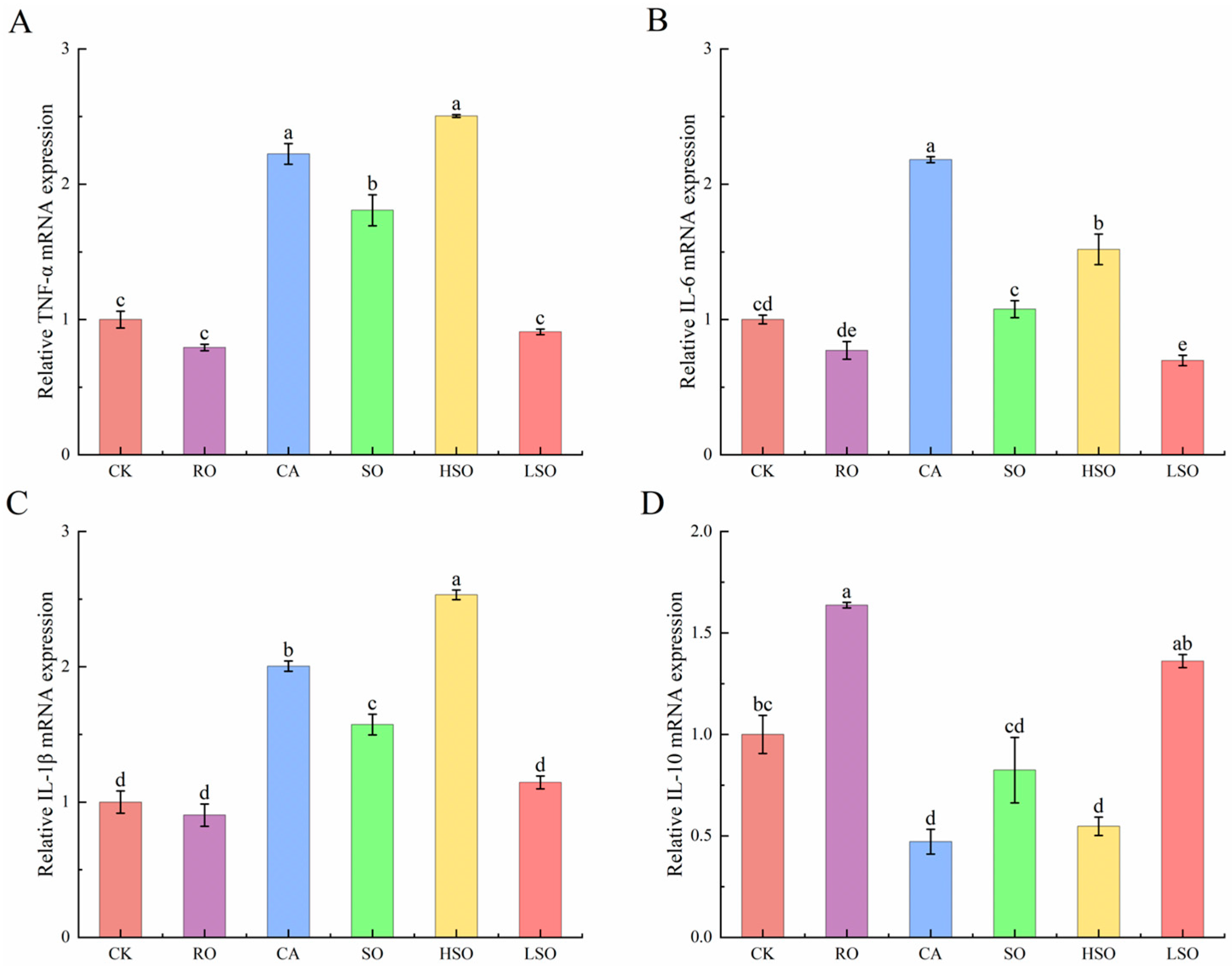
3.6. qPCR Results
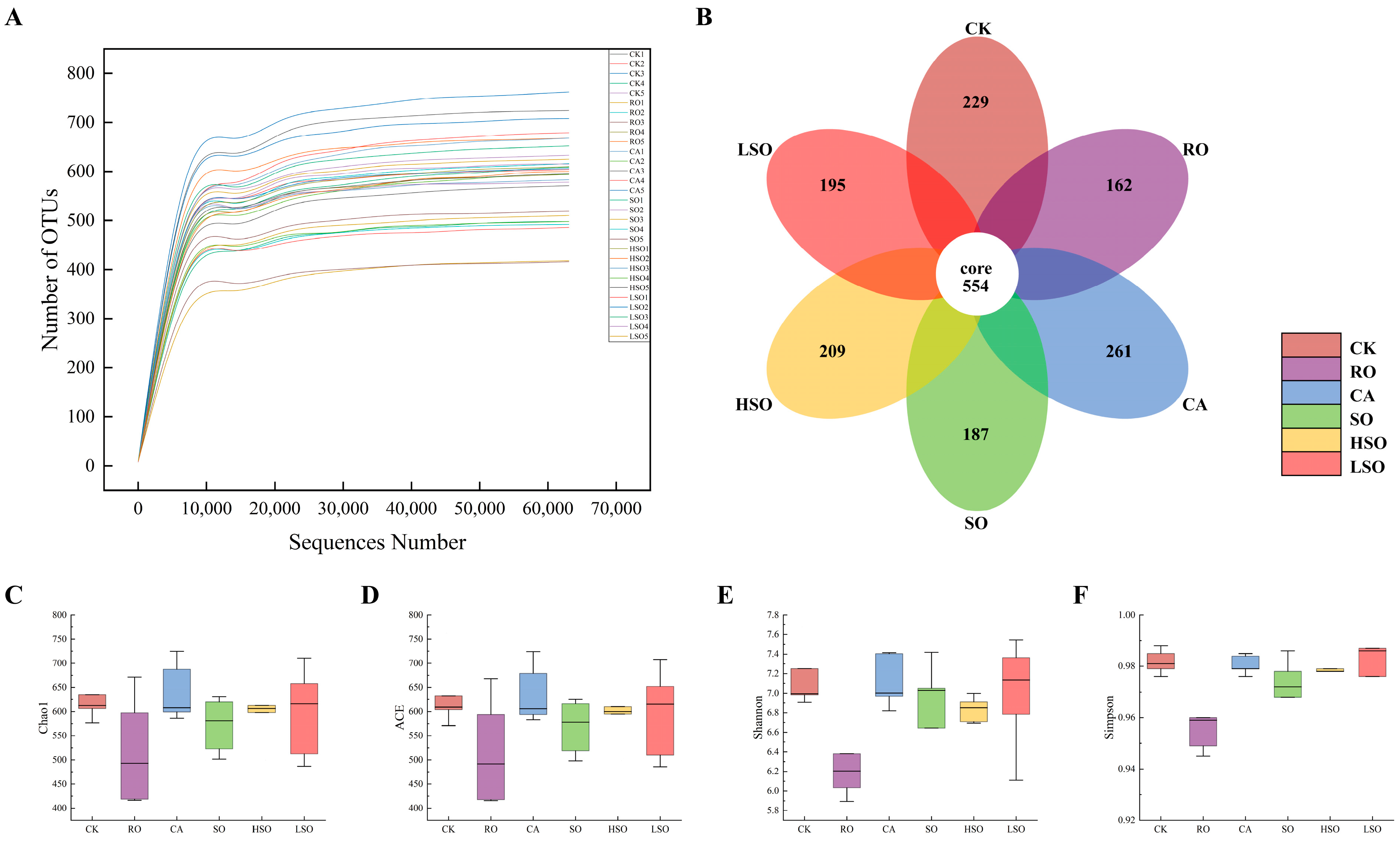
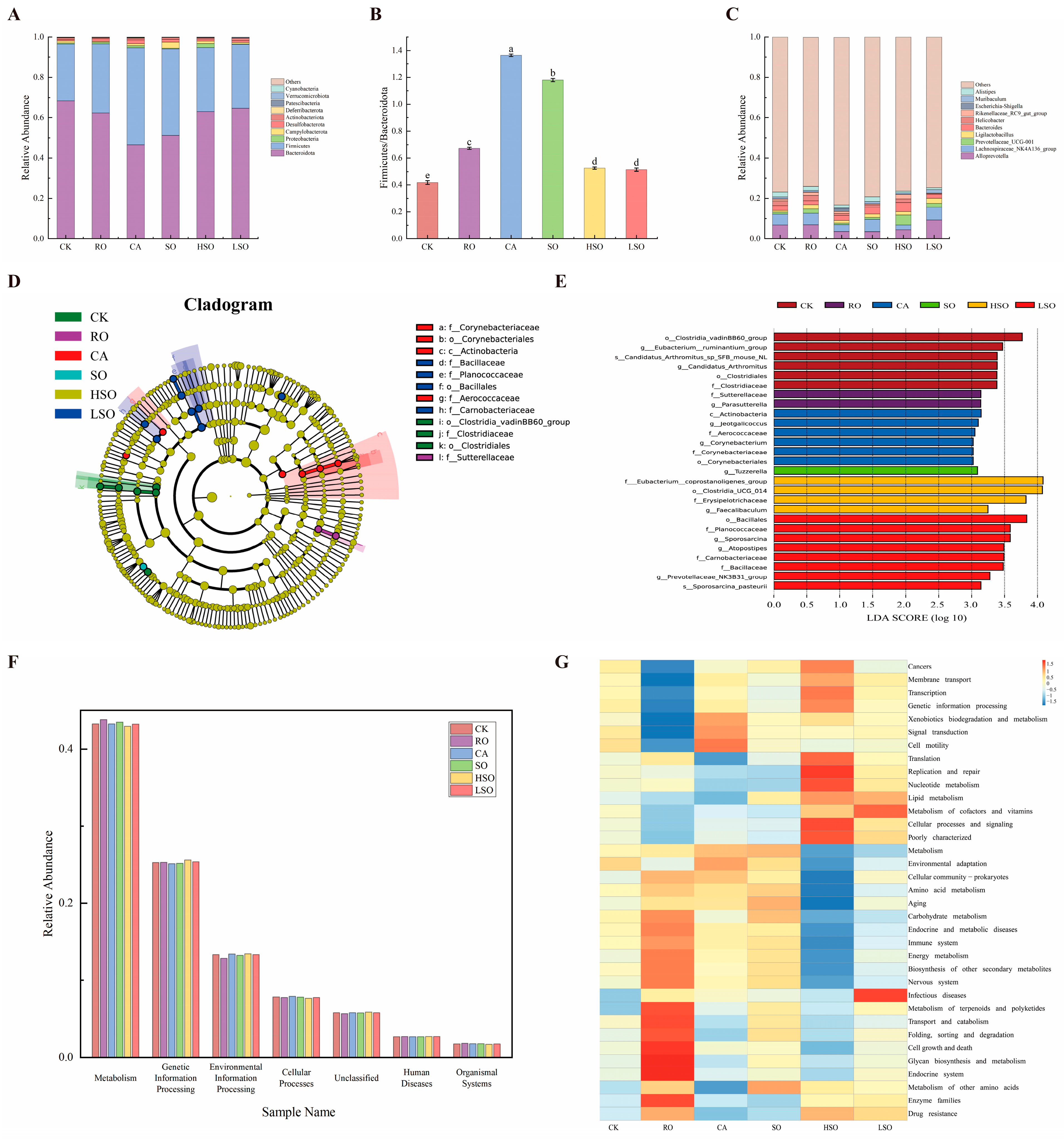
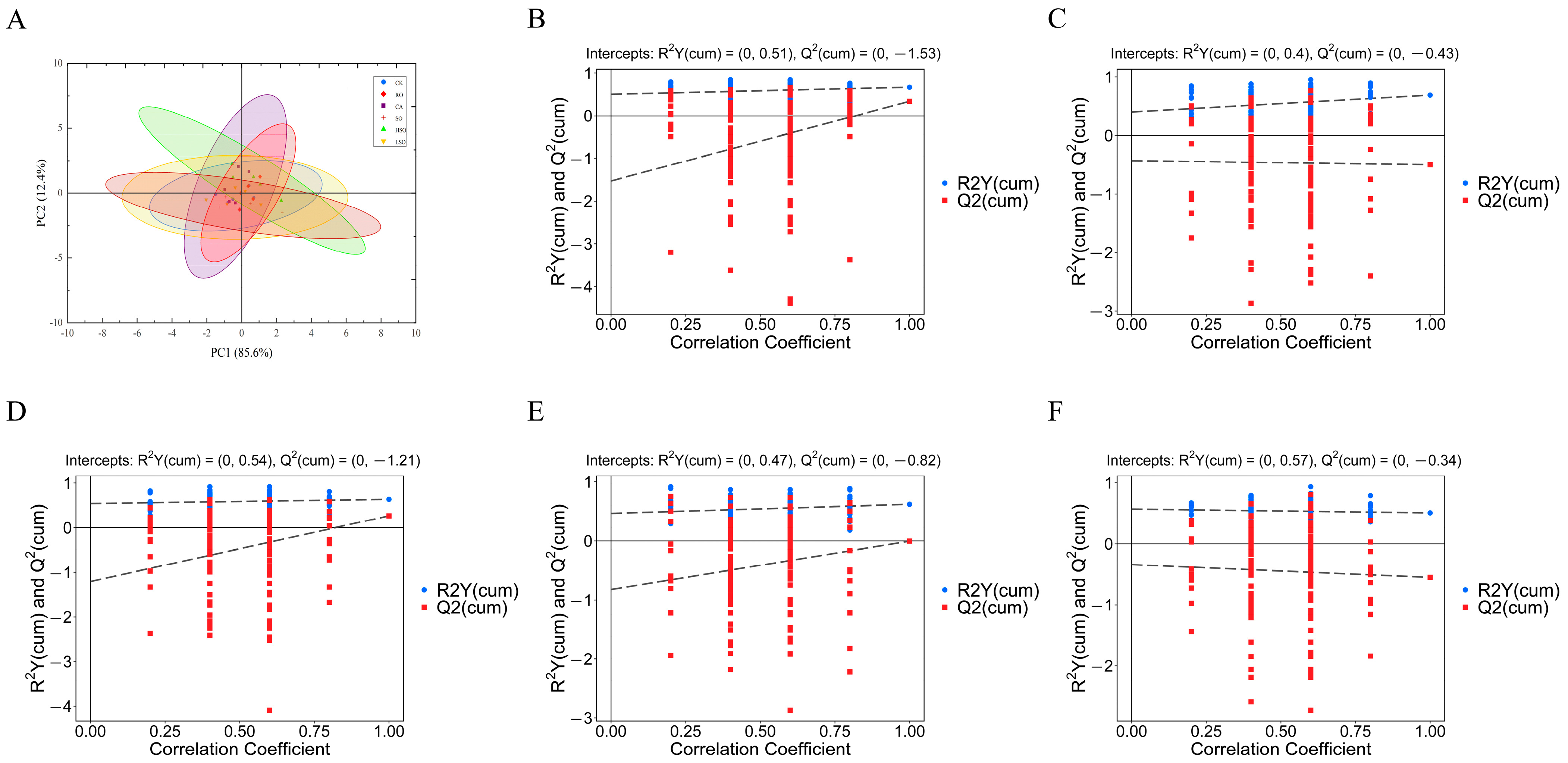
3.7. Gut Microbiota Composition Analysis
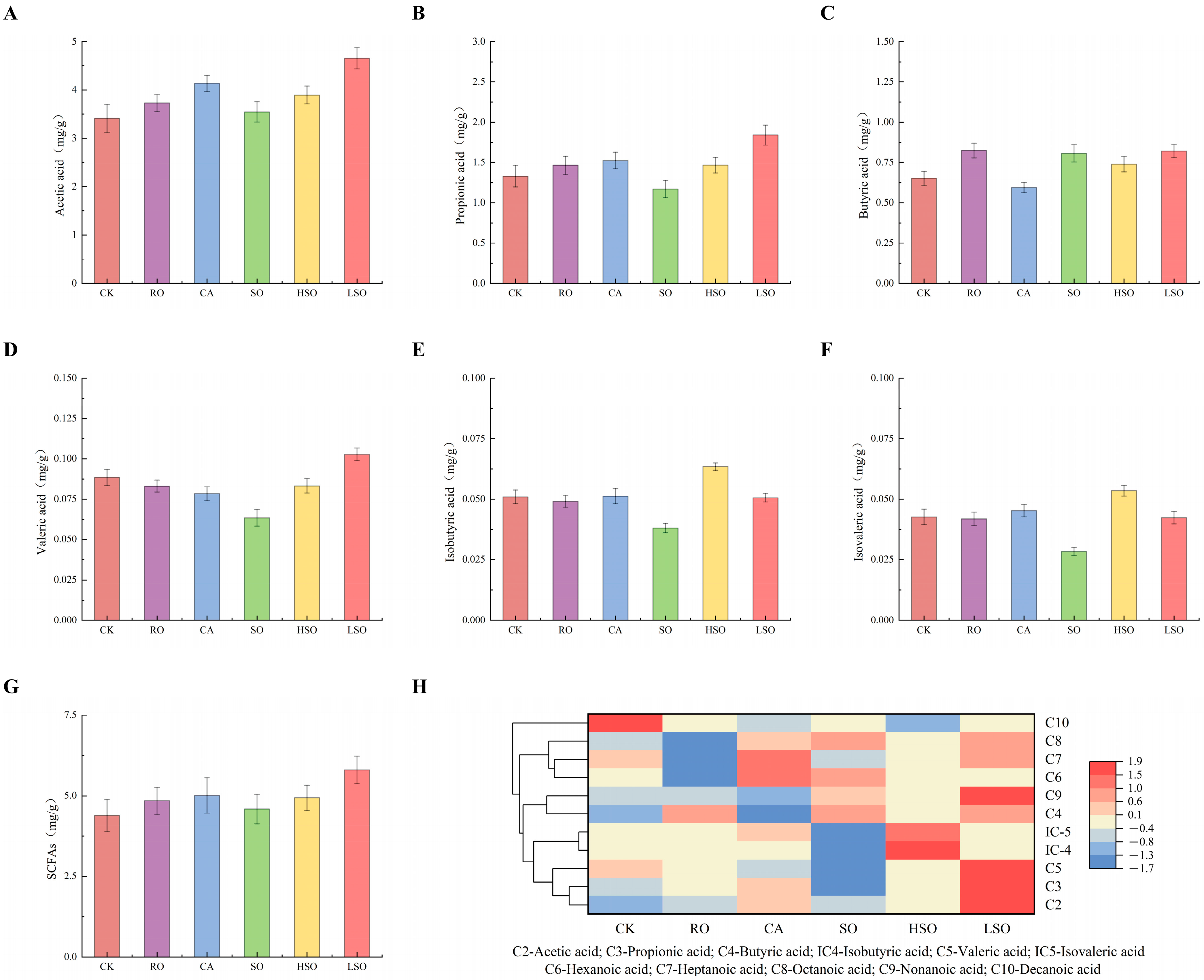
3.8. SCFAs Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Swinburn, B.A.; Sacks, G.; Hall, K.D.; McPherson, K.; Finegood, D.T.; Moodie, M.L.; Gortmaker, S.L. The global obesity pandemic: Shaped by global drivers and local environments. Lancet 2011, 378, 804–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalski, M.C.; Genot, C.; Gayet, C.; Lopez, C.; Fine, F.; Joffre, F.; Steering Committee of RMT LISTRAL. Multiscale structures of lipids in foods as parameters affecting fatty acid bioavailability and lipid metabolism. Prog. Lipid Res. 2013, 52, 354–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Micha, R.; Mozaffarian, D. Saturated fat and cardiometabolic risk factors, coronary heart disease, stroke, and diabetes: A fresh look at the evidence. Lipids 2010, 45, 893–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kellens, M.; Gibon, V.; Hendrix, M.; Greyt, W.D. Palm oil fractionation. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2007, 109, 336–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathiasen, S.S.; Frydenberg, R.P.; Kleinert, M.; Kiens, B.; Guo, Z.; Wiking, L. Novel milk fat fractions for health and functionality obtained by short-path distillation. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 201, 116255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salas, J.J.; Bootello, M.A.; Martínez-Force, E.; Garcés, R. Production of stearate-rich butters by solvent fractionation of high stearic-high oleic sunflower oil. Food Chem. 2010, 124, 450–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapseu, C.; Kayem, G.; Balesdent, D.; Schuffenecker, L. The viscosity of cottonseed oil, fractionation solvents and their solutions. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 1991, 68, 128–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malpuech-Brugere, C.; de Venne, W.P.V.; Mensink, R.P.; Arnal, M.A.; Morio, B.; Brandolini, M.; Beaufrere, B. Effects of two conjugated linoleic acid isomers on body fat mass in overweight humans. Obes. Res. 2004, 12, 591–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korver, O.; Katan, M.B. The elimination of trans fats from spreads: How science helped to turn an industry around. Nutr. Rev. 2006, 64, 275–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turnbaugh, P.J.; Ley, R.E.; Mahowald, M.A.; Magrini, V.; Mardis, E.R.; Gordon, J.I. An obesity-associated gut microbiome with increased capacity for energy harvest. Nature 2006, 444, 1027–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, Y.B.; Liu, C.J. Changes in lipid oxidation and fatty acids in Altay sheep fat during a long time of low temperature storage. J. Oleo Sci. 2017, 66, 321–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Xu, Z.Q.; Zhu, M.R.; Wu, L.Y.; Wang, Z.R. Mechanistic studies on the effects of solvent fractionation on the fatty acid distribution of Altay sheep tail fat and blood lipids in mice. Food Sci. 2025, 46, 153–160, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Wu, W.; Zhang, Y.; Tang, X.; Zheng, X.; Huang, X. Lard reduces obesity in mice compared with corn oil and canola oil via modulating gut microbiota and bile acid metabolism. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2025, 14, 9250070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Lu, Y.; Chen, W.; Li, J.; Ma, X.; Liu, D.; Kaersaijiang; Wang, Z. Fractionated extractive property analysis of different parts of fat from Hazake sheep by solvent extraction. Mod. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 34, 81–87, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 24892; Animal and Vegetable Fats and Oils—Determination of Melting Point in Open Capillary Tubes (Slip Point). National Standards of the People’s Republic of China. General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People’s Republic of China, Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2010; pp. 1–9.
- GB/T 5532; Animal and Vegetable Fats and Oils—Determination of Iodine Value. National Standards of the People’s Republic of China. State Administration for Market Regulation and Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2022; pp. 1–13.
- Liu, J.; Liu, L.; Jia, Q.; Zhang, X.; Jin, X.; Shen, H. Effects of excessive iodine intake on blood glucose, blood pressure, and blood lipids in adults. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2019, 192, 136–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB 5009.227; National Food Safety Standard—Determination of Peroxide Value in Foods. National Standards of the People’s Republic of China. National Health Commission of the People’s Republic of China, State Administration for Market Regulation: Beijing, China, 2023; pp. 1–8.
- GB 5009.229; National Food Safety Standard—Determination of Acid Value in Foods. National Standards of the People’s Republic of China. National Health and Family Planning Commission of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2016; pp. 1–15.
- Liu, X.; Sun, W.; Luo, Y. Decolorization and Flavor Analysis of Fragrant Rapeseed Oil in the Qinghai Plateau. Cereals Oils 2025, 38, 46–53, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebechi, S.R.; Vélez, M.A.; Vaira, S.; Perotti, M.C. Adulteration of Argentinean milk fats with animal fats: Detection by fatty acids analysis and multivariate regression techniques. Food Chem. 2016, 192, 1025–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henmi, A.; Shoji, M.; Nomura, M.; Inoue, T. Fatty acid composition and applications of Eriobotrya japonica seed oil. J. Oleo Sci. 2019, 68, 599–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.; Wang, P.; Xing, H.; Huang, Z.; Liu, P.; Li, T.; Huang, J. Consumer Preferences and Willingness to Pay for High-Quality Vegetable Oils: A Cross-Sectional Analysis of Chinese Residents. Foods 2024, 13, 1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majumder, K.; Fukuda, T.; Zhang, H.; Sakurai, T.; Taniguchi, Y.; Watanabe, H. Intervention of isomaltodextrin mitigates intestinal inflammation in a dextran sodium sulfate-induced mouse model of colitis via inhibition of toll-like receptor-4. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 810–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdi, T.; Desmons, A.; Krasniqi, P.; Lacorte, J.M.; Kapel, N.; Lamazière, A.; Eguether, T. Effect of stool sampling on a routine clinical method for the quantification of six short chain fatty acids in stool using gas chromatography–mass spectrometry. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, X.; Guo, J.; You, Y.; Yin, M.; Ren, C.; Zhan, J.; Huang, W. A fast and accurate way to determine short chain fatty acids in mouse feces based on GC–MS. J. Chromatogr. B 2018, 1099, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wang, J.; Dong, G.; Chen, X.; Wang, S.; Lei, F.; Bai, Q. Effect of different extraction methods on quality characteristics of rapeseed and flaxseed oils. J. Food Qual. 2022, 2022, 8296212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pădureţ, S. The effect of fat content and fatty acids composition on color and textural properties of butter. Molecules 2021, 26, 4565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, M.; Bai, Y.; Tian, H.; Zhao, X. The Chemical Composition and Health-Promoting Benefits of Vegetable Oils—A Review. Molecules 2023, 28, 6393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, H.Y.; Roy, P.K.; Chattopadhyay, S. Thermal degradation in edible oils by surface enhanced raman spectroscopy calibrated with iodine values. Vib. Spectrosc. 2020, 106, 103018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatouh, A.E.; Singh, R.K.; Koehler, P.E.; Mahran, G.A.; Metwally, A.E. Physical, chemical and stability properties of buffalo butter oil fractions obtained by multi-step dry fractionation. Food Chem. 2005, 89, 243–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galli, F.; Azzi, A.; Birringer, M.; Cook-Mills, J.M.; Eggersdorfer, M.; Frank, J.; Cruciani, G.; Lorkowski, S.; Özer, N.K. Vitamin E: Emerging aspects and new directions. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2016, 96, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahidi, F.; Zhong, Y. Lipid oxidation and improving the oxidative stability. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2010, 39, 4067–4079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, Y.; Zhou, C.; Fan, R.; Benazzouz, S.; Shen, J.; Xiao, R.; Ma, W. Altered intestinal microbiota induced by high-fat diets affect cognition differently in mice. Nutr. Res. 2024, 132, 67–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koliada, A.; Syzenko, G.; Moseiko, V.; Budovska, L.; Puchkov, K.; Perederiy, V.; Vaiserman, A. Association between body mass index and Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes ratio in an adult Ukrainian population. BMC Microbiol. 2017, 17, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turnbaugh, P.J.; Hamady, M.; Yatsunenko, T.; Cantarel, B.L.; Duncan, A.; Ley, R.E.; Gordon, J.I. A core gut microbiome in obese and lean twins. Nature 2009, 457, 480–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Xu, S.; Zhou, Q.; Zhao, T.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, X.; Wang, F. HBOT alleviates diet-induced MASH by reprograming gut microbiota and liver metabolism in mice. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2025, 237, 600–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.F. Free fatty acid receptors in the endocrine regulation of glucose metabolism: Insight from gastrointestinal-pancreatic-adipose interactions. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 956277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rios-Covian, D.; Salazar, N.; Gueimonde, M.; de Los Reyes-Gavilan, C.G. Shaping the metabolism of intestinal Bacteroides population through diet to improve human health. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Zhong, J.; Cui, Z.; Shen, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, Y. Branched-chain fatty acids from goat milk alleviate ulcerative colitis via the TLR4/NF-κB/NLRP3 pathway. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2024, 13, 3624–3632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Zhu, W.; Ge, Q.; Zhou, X. Effect of different types of oil intake on the blood index and the intestinal flora of rats. AMB Express 2022, 12, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zha, H.; Si, G.; Wang, C.; Zhang, H.; Li, L. Multiple intestinal bacteria associated with the better protective effect of Bifidobacterium pseudocatenulatum LI09 against rat liver injury. Biomed. Res. Int. 2022, 2022, 8647483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafar, H.; Saier, M.H., Jr. Gut Bacteroides species in health and disease. Gut Microbes 2021, 13, 1848158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Angelis, M.; Ferrocino, I.; Calabrese, F.M.; De Filippis, F.; Cavallo, N.; Siragusa, S.; Rampelli, S.; Di Cagno, R.; Rantsiou, K.; Vannini, L.; et al. Diet influences the functions of the human intestinal microbiome. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 4247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Tang, H.; Zhang, C.; Zhao, Y.; Derrien, M.; Rocher, E.; van-Hylckama Vlieg, J.E.T.; Strissel, K.; Zhao, L.; Obin, M.; et al. Modulation of gut microbiota during probiotic-mediated attenuation of metabolic syndrome in high fat diet-fed mice. ISME J. 2015, 9, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cani, P.D.; Van Hul, M.; Lefort, C.; Depommier, C.; Rastelli, M.; Everard, A. Microbial regulation of organismal energy homeostasis. Nat. Metab. 2019, 1, 34–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Liu, Z.; Yu, H.; Shen, Y.; Lu, L.; Kong, F.; Sun, W.; Wei, X.; Jin, L.; Ge, L.; et al. Dynamic changes in the gut microbiota of SPF Bama piglets during breast and formula feeding. Front. Microbiol. 2025, 16, 1537286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Parameter | Content | Parameter | Content |
|---|---|---|---|
| Calories | 3766 KJ/Kg | Ash | 4.17% |
| Calories from Protein | 19.3% | Calcium (Ca) | 0.046% |
| Calories from Fat | 16.7% | Total Phosphorus (P) | 0.036% |
| Moisture | 6.6% | Ca:P Ratio | 1.28 |
| Crude Fat | 7.0% | Lysine | 0.028% |
| Carbohydrates | 64.3% | Methionine + Cystine | 0.017% |
| Fatty Acid | RO | CA | SO | HSO | LSO |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C14:0 | - | 2.35 ± 0 d | 7.35 ± 0.02 b | 10.17 ± 0.01 a | 5.2 ± 0.02 c |
| C16:0 | 3.98 ± 0 e | 43.75 ± 0.01 a | 25.19 ± 0.01 c | 33.4 ± 0.02 b | 21.62 ± 0.09 d |
| C16:1 | - | 1.11 ± 0 d | 3.1 ± 0.01 b | 2.14 ± 0 c | 3.45 ± 0.01 a |
| C18:0 | 2.03 ± 0.03 e | 19.44 ± 0.01 a | 11.38 ± 0.02 c | 17.2 ± 0.01 b | 9.23 ± 0.04 d |
| C18:1n-9t | - | 1.59 ± 0.02 c | 4.62 ± 0 ab | 4.52 ± 0.01 b | 4.83 ± 0.21 a |
| C18:1n-9c | 59.64 ± 0.13 a | 26.25 ± 0 d | 35.61 ± 0.01 c | 22.5 ± 0.02 e | 41.83 ± 0 b |
| C18:2n-6t | 3.14 ± 0.01 a | 0.55 ± 0 e | 0.84 ± 0 c | 0.59 ± 0 d | 0.95 ± 0.01 b |
| C18:2n-6c | 19.56 ± 0.09 a | 3.56 ± 0 b | 2.56 ± 0 d | 1.44 ± 0 e | 3 ± 0.01 c |
| C18:3n-3c | 6.07 ± 0.04 a | - | 1.94 ± 0.01 c | 1.08 ± 0 d | 2.26 ± 0.01 b |
| SFA | 6.01 ± 0.03 e | 65.54 ± 0.02 a | 43.91 ± 0.01 c | 60.77 ± 0.03 b | 36.05 ± 0.15 d |
| UFA | 88.41 ± 0.05 a | 33.06 ± 0.01 d | 48.67 ± 0.01 c | 32.27 ± 0.03 e | 56.32 ± 0.18 b |
| MUFA | 59.64 ± 0.13 a | 27.36 ± 0 d | 38.7 ± 0.01 c | 24.65 ± 0.02 e | 45.28 ± 0.01 b |
| PUFA | 28.77 ± 0.11 a | 5.7 ± 0.01 e | 9.97 ± 0.01 c | 7.63 ± 0.01 d | 11.04 ± 0.19 b |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, X.; Yu, J.; Xu, Z.; Wei, J.; Wu, L.; Han, H.; Zhou, J.; Wang, Z. Solvent Fractionation Improves the Functional Properties of Sheep Rump Fat: Effects of Different Lipid Fractions on Lipid Metabolism and Gut Health in Mice. Foods 2025, 14, 3641. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14213641
Ma X, Yu J, Xu Z, Wei J, Wu L, Han H, Zhou J, Wang Z. Solvent Fractionation Improves the Functional Properties of Sheep Rump Fat: Effects of Different Lipid Fractions on Lipid Metabolism and Gut Health in Mice. Foods. 2025; 14(21):3641. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14213641
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Xin, Junfei Yu, Zequan Xu, Jian Wei, Lingyan Wu, Hongjiao Han, Jianzhong Zhou, and Zirong Wang. 2025. "Solvent Fractionation Improves the Functional Properties of Sheep Rump Fat: Effects of Different Lipid Fractions on Lipid Metabolism and Gut Health in Mice" Foods 14, no. 21: 3641. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14213641
APA StyleMa, X., Yu, J., Xu, Z., Wei, J., Wu, L., Han, H., Zhou, J., & Wang, Z. (2025). Solvent Fractionation Improves the Functional Properties of Sheep Rump Fat: Effects of Different Lipid Fractions on Lipid Metabolism and Gut Health in Mice. Foods, 14(21), 3641. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14213641