Enhancement of Dough Processing and Steamed Bread Quality with Modified Soybean Residue Dietary Fiber
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Modification and Extraction of Dietary Fiber from Soybean Residues
2.2.1. Extraction Methods
2.2.2. Modification Methods
2.3. Wheat Dough Preparation
2.4. Textural Properties of Wheat Dough
2.5. Measurement of Rheological Properties
2.5.1. Rheological Performance Test
2.5.2. Creep Recovery Measurement
2.6. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FT-IR) Analysis
2.7. Determination of Free Sulfhydryl and Disulfide Bond
2.7.1. Determination of Free Sulfhydryl
2.7.2. Determination of the Disulfide Bond
2.8. Low-Field Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (LF-NMR)
2.9. Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM)
2.10. Steamed Bread Preparation
2.11. Measurement of Specific Volume and Height-to-Diameter Ratio of Steamed Bread
2.12. Measurement of the Texture of Steamed Bread
2.13. Color Analysis of Steamed Bread Crumb
2.14. Sensory Evaluation of Steamed Bread
2.15. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Texture Property Test
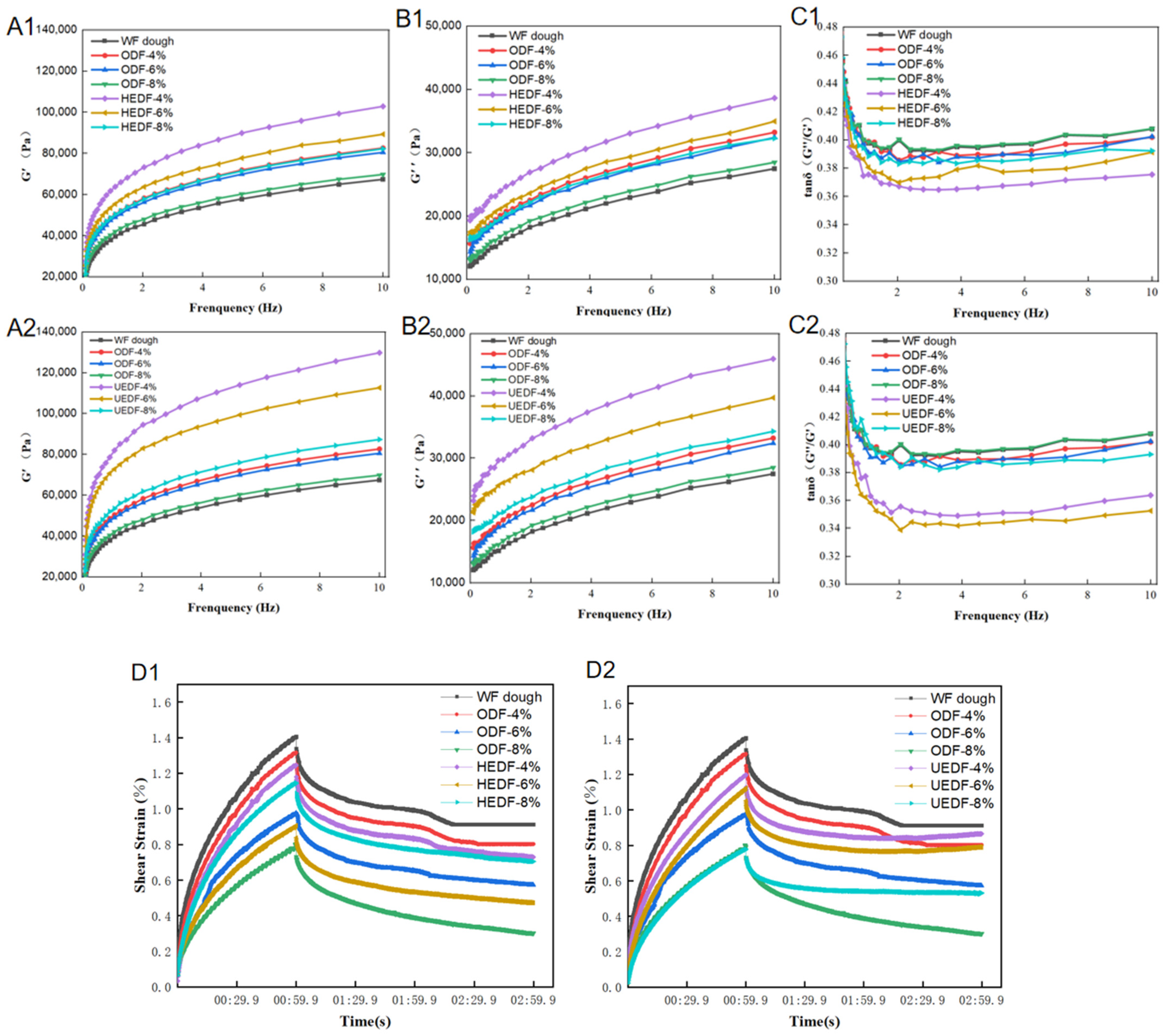
3.2. Rheological Properties
3.2.1. Rheological Characterization
3.2.2. Creep Recovery Measurement Results
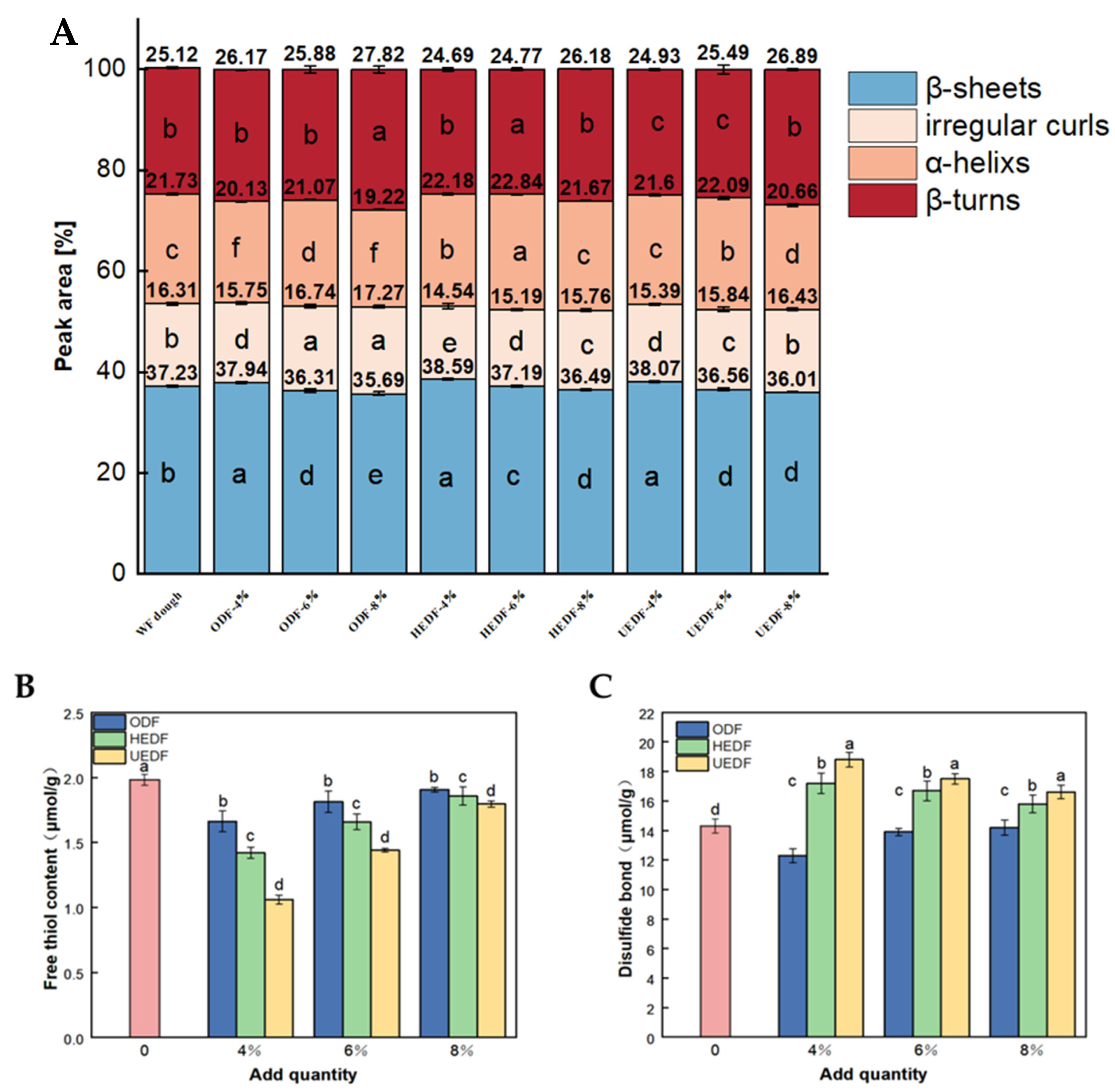
3.3. FT-IR Analysis
3.4. Free Hydrophobic and Disulfide Bond Content
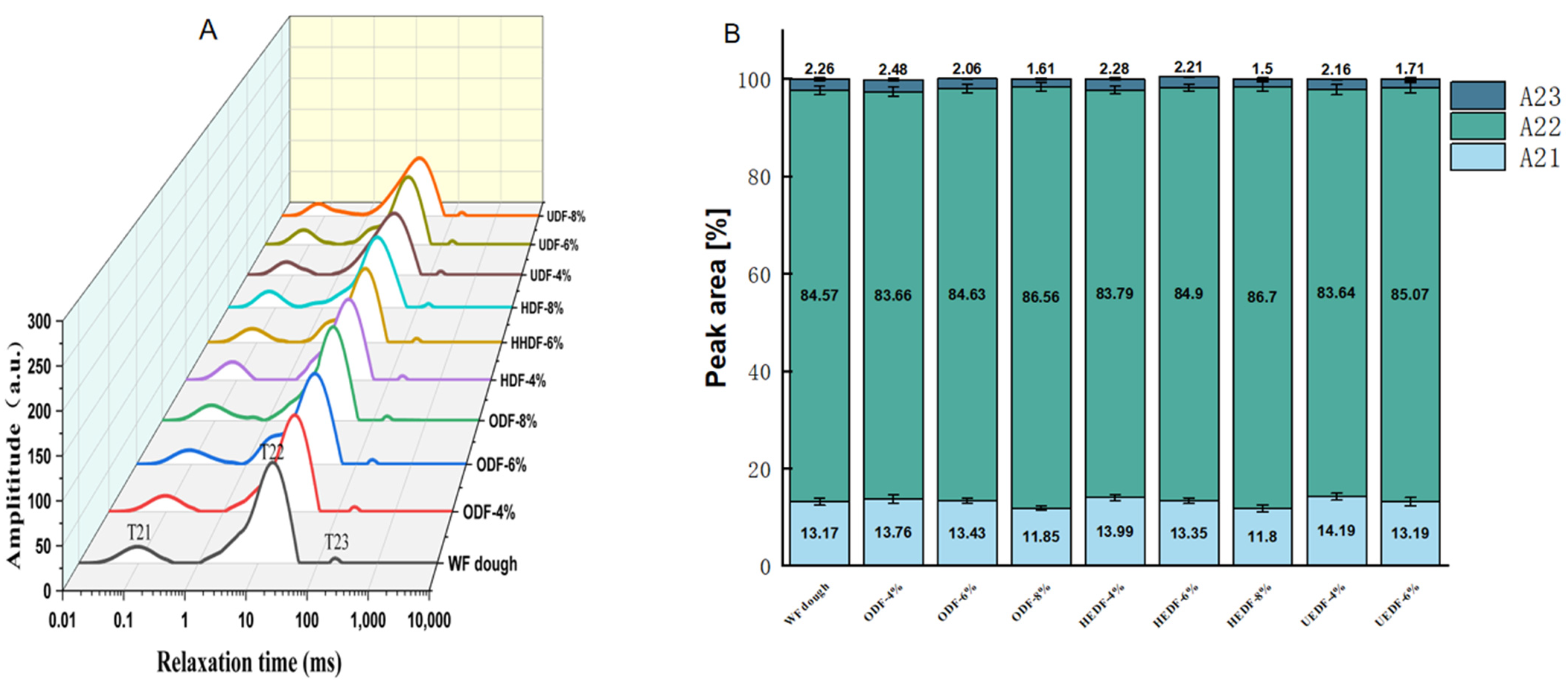
3.5. LF-NMR Analysis
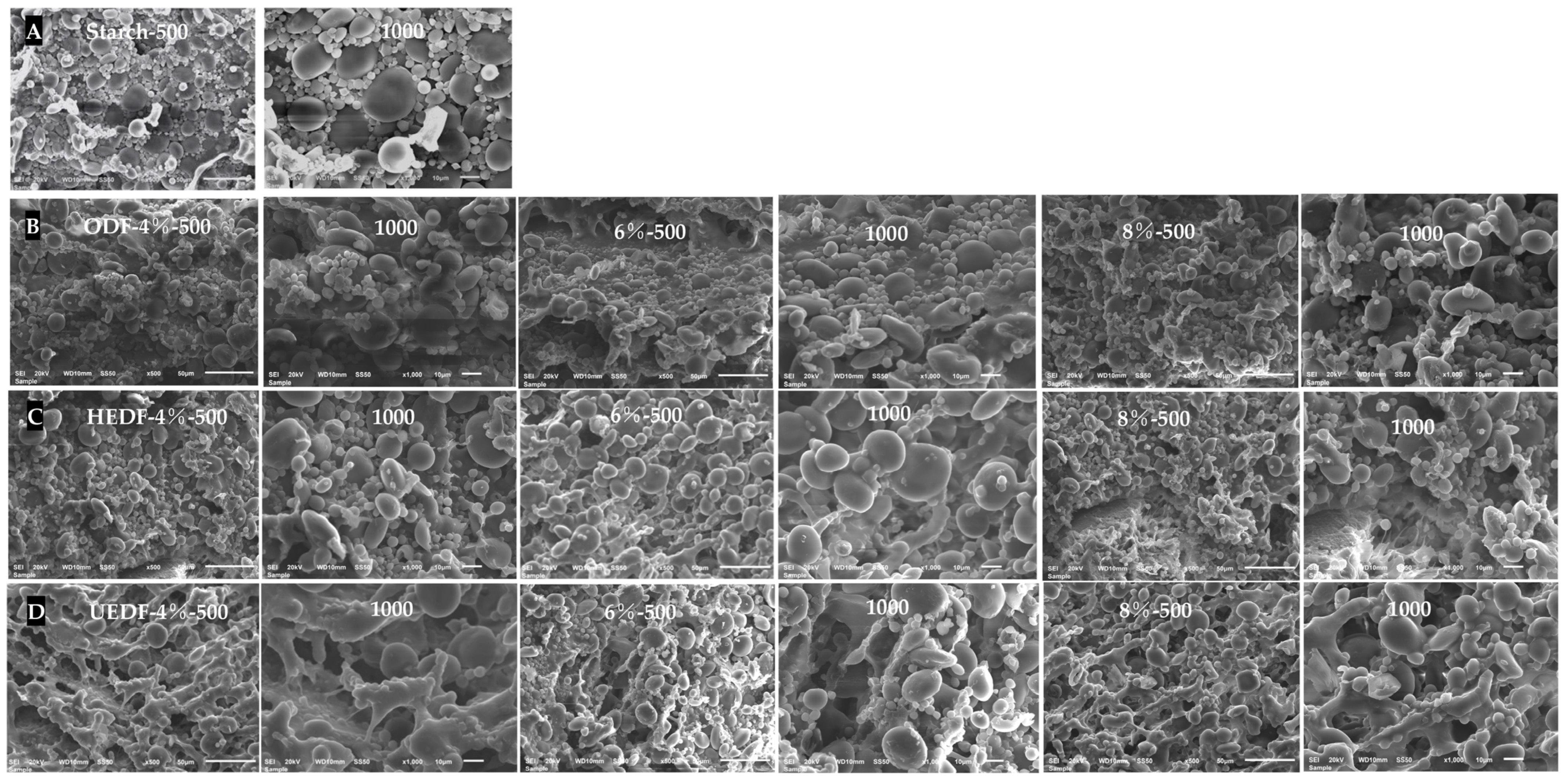
3.6. SEM Analysis
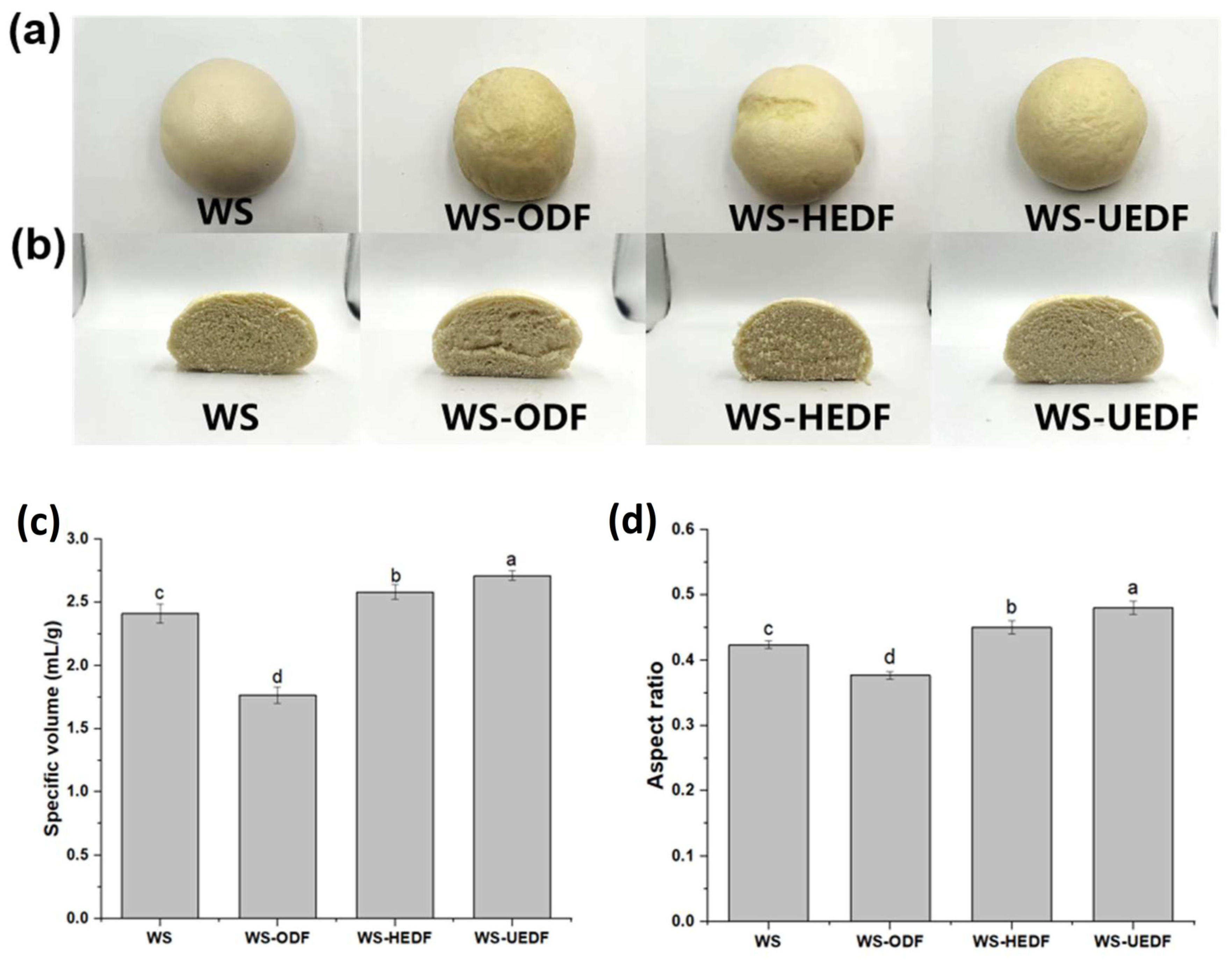
3.7. Height and Specific Volume of Steamed Bread
3.8. Textural Properties of Steamed Bread
3.9. Color of Steamed Bread
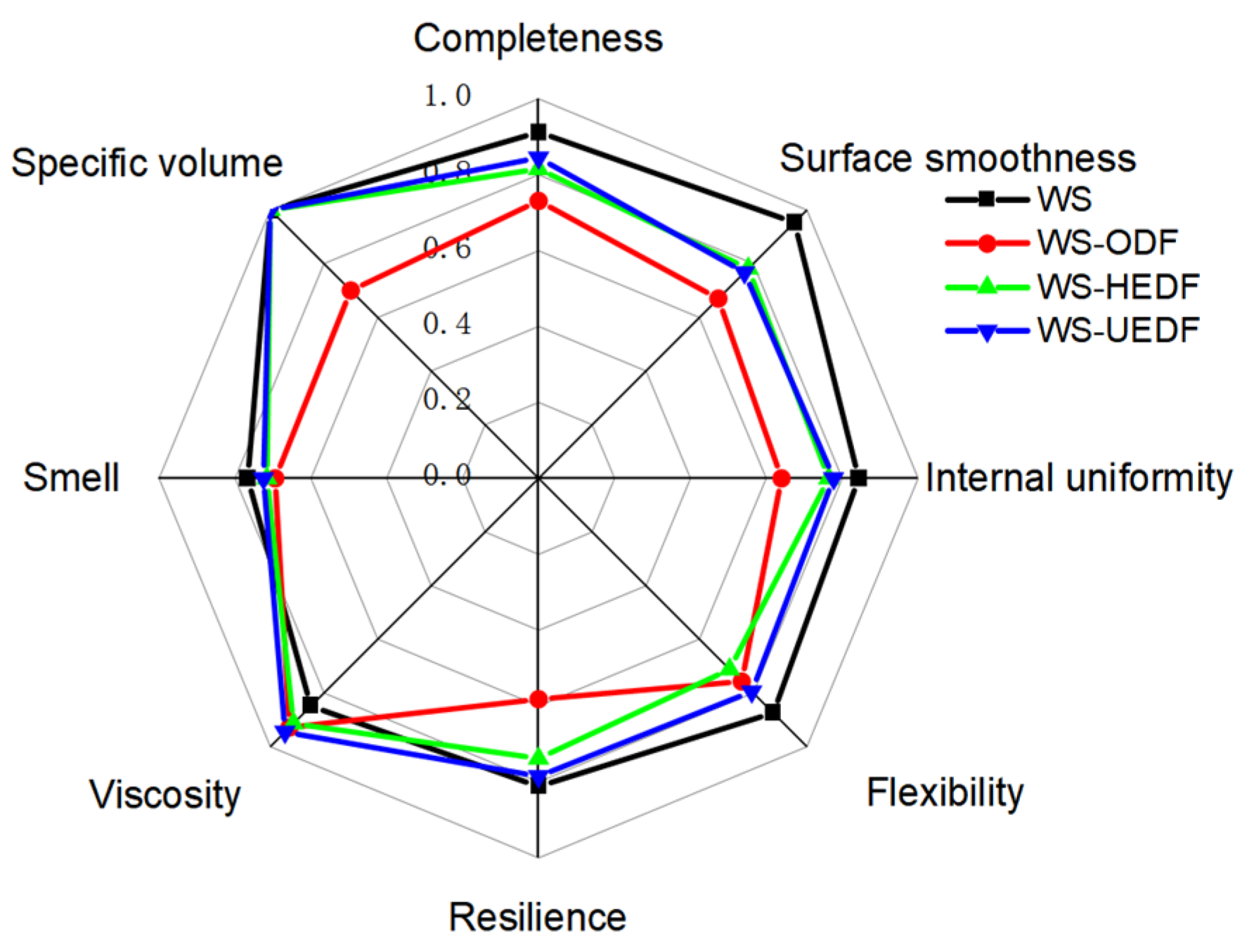
3.10. Sensory Evaluation
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, S.; Sun, H.; Ma, M.; Mu, T. Effects of dietary fibres, polyphenols and proteins on the estimated glycaemic index, physicochemical, textural and microstructural properties of steamed bread. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 59, 4041–4052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asghar, A.; Afzaal, M.; Saeed, F.; Ahmed, A.; Ateeq, H.; Shah, Y.A.; Islam, F.; Hussain, M.; Akram, N.; Shah, M.A. Valorization and food applications of okara (soybean residue): A concurrent review. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 11, 3631–3640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Ma, S. Effects of interaction between wheat bran dietary fiber and gluten protein on gluten protein aggregation behavior. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 283, 137692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Wu, S.; Sun, X. Improvement in the rheological properties and gas phase of dough, and overall quality of dietary fibre enriched products: Enzymatic modification on the composition and structure of dietary fibre. Food Hydrocoll. 2024, 160, 110742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šoronja-Simović, D.; Šereš, Z.; Maravić, N.; Djordjević, M.; Djordjević, M.; Luković, J.; Tepić, A. Enhancement of physicochemical properties of sugar beet fibres affected by chemical modification and vacuum drying. Food Bioprod. Process. 2016, 100, 432–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Ainiwan, D.; Liu, Y.; He, J.; Liu, T. Effects of steam explosion-modified rice bran dietary fiber on volatile flavor compounds retention and release of red date-flavored naan (ethnic specialty food of Xinjiang) during storage. Food Chem. X 2024, 22, 101438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ranasinghe, M.; Alghaithi, M.; Stathopoulos, C.; Sundarakani, B.; Maqsood, S. Valorizing date seeds through ultrasonication to enhance quality attributes of dough and biscuit: Part 2—Study on bioactive properties, sensory acceptance, in vitro gastrointestinal digestion and shelf life of biscuits. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2024, 112, 107160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, Y.; Wu, T.; Sheng, Y.; Li, L.; Wang, C. Effects of cavitation-jet technology combined with enzyme treatment on the structure properties and functional properties of OKARA insoluble dietary fiber. Food Chem. 2023, 423, 136286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, D.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, X.; Huang, Y.; Ni, L.; Chen, X.; Wu, Z.; Huang, C.; Yi, Q.; Li, J.; et al. Study on physicochemical properties, antioxidant and antimicrobial activity of okara soluble dietary fiber/sodium carboxymethyl cellulose/thyme essential oil active edible composite films incorporated with pectin. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 165, 1241–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Gu, S.; Shi, Y.; Chen, Q. Alleviative effects of mannosylerythritol lipid-A on the deterioration of internal structure and quality in frozen dough and corresponding steamed bread. Food Chem. 2024, 431, 137122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, B.; Guo, J.; Li, P.; Cheng, B.; Zhang, G.; Bai, Z.; Luo, D.; Cui, C. Moisture, rheology and structure of deacetylated konjac glucomannan-treated dough and the performance of steamed bread under frozen storage. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 197, 115941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranasinghe, M.; Stathopoulos, C.; Sundarakani, B.; Maqsood, S. Changes in the rheological, textural, microstructural and in vitro antioxidant properties of biscuit dough by incorporation of the extract and fiber-rich residue obtained through green extraction of defatted date seeds. Food Struct. 2024, 42, 100395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, S.; Chen, D.; Federici, E.; Jones, O.G.; Campanella, O.H. The effects of whey protein fibrils on the linear and non-linear rheological properties of a gluten-free dough. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 909877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, W.; Xu, D.; Zhang, H.; Guo, L.; Hong, T.; Zhang, W.; Jin, Y.; Xu, X. Effect of pigskin gelatin on baking, structural and thermal properties of frozen dough: Comprehensive studies on alteration of gluten network. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 102, 105591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.; Wu, D.; Wang, L.; Song, G.; Chi, R.; Ma, J.; Li, Z.; Wang, L.; Sun, W. Insoluble dietary fibers from Lentinus edodes stipes improve the gel properties of pork myofibrillar protein: A water distribution, microstructure and intermolecular interactions study. Food Chem. 2023, 411, 135386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almoumen, A.; Mohamed, H.; Ayyash, M.; Yuliarti, O.; Kamleh, R.; Al-Marzouqi, A.H.; Kamal-Eldin, A. Harnessing date fruit pomace: Extraction of high fibre dietary ingredient and its impact on high fibre wheat flour dough. NFS J. 2024, 35, 100178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Guo, J.; Lu, C.; Yue, C.; Wang, P. Effects of fish skin collagen peptide on physicochemical properties of frozen dough and quality and antioxidant activity of steamed bread. Food Hydrocoll. 2024, 157, 110420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Huang, H.; Zheng, B.; Xie, J.; Chen, Y.; Xie, J.; Dong, R.; Hu, X.; Yu, Q. Effect of modified grapefruit peel dietary fiber on bread: Baking quality, flavor characteristics, and starch digestive properties. Food Hydrocoll. 2025, 162, 110964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Fu, S.; Li, H.; Li, H.; Wang, Y.; Li, Z.; Liu, C. Quality evaluation of steam reheated frozen steamed bread. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 150, 112074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Qin, S.; Deng, Y.; Zhao, Y. Effect of dietary fiber-rich fractions on texture, thermal, water distribution, and gluten properties of frozen dough during storage. Food Chem. 2019, 297, 124902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curti, E.; Carini, E.; Diantom, A.; Vittadini, E. The use of potato fibre to improve bread physico-chemical properties during storage. Food Chem. 2015, 195, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Hu, H.; Liu, Q.; Dai, X.; Zhang, H. Rheological and microstructural properties of wheat flour dough systems added with potato granules. Int. J. Food Prop. 2017, 20, S1145–S1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Jin, X.; Gao, J.; Qiu, Z.; Ying, J.; Wang, Y.; Dong, Z.; Zhou, W. Impact of wheat bran micronization on dough properties and bread quality: Part I—Bran functionality and dough properties. Food Chem. 2021, 353, 129407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Gao, W.; Liang, J.; Fan, H.; Yang, Y.; Suo, B.; Ai, Z. Mechanism underlying the weakening effect of β-glucan on the gluten system. Food Chem. 2023, 420, 136002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mei, Z.; Wang, W.; Feng, X.; Liu, M.; Peng, S.; Chen, L.; Chen, H.; Lin, S. Effect of soluble oat β-glucan and tea polyphenols on the rheological properties and microstructure of wheat dough. LWT 2024, 198, 116004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Peng, H.; Li, B.; Tian, J. Impact of pomegranate fruit powder on dough, textural and functional properties of fresh noodle. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2023, 103, 6895–6904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Sun, X.; Du, Y.; Su, A.; Fang, Y.; Hu, Q.; Pei, F. Effects of co-fermentation on the release of ferulic acid and the rheological properties of whole wheat dough. J. Cereal Sci. 2023, 111, 103669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.-C.; Yang, Z.; Xing, J.-J.; Guo, X.-N.; Zhu, K.-X. Effects and underlying mechanisms of insoluble dietary fiber and ferulic acid on the crumb structure of steamed bread. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 125, 107448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dangi, N.; Yadav, B.S.; Yadav, R.B. Pasting, rheological and dough mixing behavior of rice flour as affected by the addition of native and partially hydrolyzed β-glucan concentrate. J. Texture Stud. 2020, 51, 650–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Correa, M.J.; Ferrer, E.; Añón, M.C.; Ferrero, C. Interaction of modified celluloses and pectins with gluten proteins. Food Hydrocoll. 2014, 35, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, N.; Yang, Q.; Zhang, C.-C.; Chen, H.-Q. Impact of basil seed gum on the textural, rheological properties, water state, gluten depolymerization and microstructure of frozen dough. J. Cereal Sci. 2023, 112, 103728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Chen, J.; Zhai, J.; Zhang, P.; Peng, L. Reduced fat content of fried batter-breaded fish nuggets by adding dietary fibers: Insight into wheat starch and gluten conformations, fiber properties and anti-fat absorption capacities. Food Chem. 2025, 463, 141251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Q.; Yan, J.; Ma, S. Effect of heat treatment on conformation and aggregation properties of wheat bran dietary fiber-gluten protein. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 253, 127164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, J.; Jiang, L.; Qi, M.; Han, F.; Li, L.; Xu, M.; Li, Y.; Zhang, D.; Yu, S.; Li, H. Influence of magnetic field on gluten aggregation behavior and quality characteristics of dough enriched with potato pulp. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 254, 128082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Z.; Huang, J.; Mei, X.; Sui, Y.; Li, S.; Zhu, Z. Noncovalent Conjugates of Anthocyanins to Wheat Gluten: Unraveling Their Microstructure and Physicochemical Properties. Foods 2024, 13, 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, L.; Lu, L.; Zhao, L.; Peng, J.; Zhou, W. Improvement of okara noodle quality by modifying the soluble/insoluble dietary fibre ratio. Food Chem. 2024, 464, 141566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hemdane, S.; Langenaeken, N.A.; Jacobs, P.J.; Verspreet, J.; Delcour, J.A.; Courtin, C.M. Study of the role of bran water binding and the steric hindrance by bran in straight dough bread making. Food Chem. 2018, 253, 262–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gangadharappa, G.H.; Ramakrishna, R.; Prabhasankar, P. Chemical and scanning electron microscopic studies of wheat whole-meal and its streams from roller flour mill. J. Food Eng. 2008, 85, 366–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, M.; Yu, Q.; Chen, J.; He, Z.; Chen, Y.; Xie, J.; Nie, S.; Xie, M. Physical quality and in vitro starch digestibility of biscuits as affected by addition of soluble dietary fiber from defatted rice bran. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 99, 105349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, M.; Jia, J.; Wu, Q. Effects of rice bran soluble dietary fiber on the physicochemical properties of frozen dough and the quality of steamed bread. LWT 2024, 214, 117120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, C.; Nie, L.; Chen, H.; Li, J.; Li, B. Effect of degree of substitution of carboxymethyl cellulose sodium on the state of water, rheological and baking performance of frozen bread dough. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 80, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krekora, M.; Miś, A.; Nawrocka, A. Molecular interactions between gluten network and phenolic acids studied during overmixing process with application of FT-IR spectroscopy. J. Cereal Sci. 2021, 99, 103203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Guo, J.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, L. Insight into konjac glucomannan-retarding deterioration of steamed bread during frozen storage: Quality characteristics, water status, multi-scale structure, and flavor compounds. Food Res. Int. 2024, 195, 114962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, F. Frozen steamed breads and boiled noodles: Quality affected by ingredients and processing. Food Chem. 2021, 349, 129178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, P.; Guo, J.; Fan, J.; Wang, P.; Yan, X. Combined effect of konjac glucomannan addition and ultrasound treatment on the physical and physicochemical properties of frozen dough. Food Chem. 2023, 411, 135516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Li, H.; Guo, J.; Zhang, C.; Li, X.; Geng, M.; Lan, H.; Luo, D.; Han, S. Effects of red kidney bean polysaccharide on the physicochemical properties of frozen dough and the resulting steamed bread quality. J. Agric. Food Res. 2024, 16, 101063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Luo, D.; Yue, C.; Wang, L.; Xiang, J.; Guo, J.; Li, P.; Huang, J.; Zhang, K. Effect of phosphorylated long-chain inulin on the dough rheology and steamed bread quality. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 58, 730–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, D.; Liang, X.; Xu, B.; Kou, X.; Li, P.; Han, S.; Liu, J.; Zhou, L. Effect of inulin with different degree of polymerization on plain wheat dough rheology and the quality of steamed bread. J. Cereal Sci. 2017, 75, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Luo, D.; Li, X.; Xu, B.; Zhang, X.; Liu, J. Effects of inulin on the structure and emulsifying properties of protein components in dough. Food Chem. 2016, 210, 235–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Attribute | Marking Scheme | Value of a Score |
|---|---|---|
| Completeness | Complete shape, no cracks on the surface | 6–10 |
| Incomplete shape with surface cracks | 0–5 | |
| Surface smoothness | The surface is very smooth, with no wrinkles, no bubbles or hard lumps | 7–10 |
| Smooth surface, a few folds, no bubbles or hard lumps | 4–6 | |
| The surface is not smooth, wrinkles are obvious, there are bubbles and hard lumps | 0–3 | |
| Internal uniformity | The stomata are fine and evenly distributed, with good layering and no large holes | 12–15 |
| Stomata are fine and more evenly distributed, better layered, and have slightly larger pores | 8–11 | |
| Uneven porosity, rough structure, more large pores | 0–7 | |
| Flexibility | Bite-sized, chewy, no crumbs | 7–10 |
| More substantial, more chewy, not easy to fall out of the crumbs | 4–6 | |
| Poor bite, very easy to fall out | 0–3 | |
| Resilience | Soft, elastic, immediate recovery after pressing, fast rebound | 16–20 |
| Soft, slow recovery after pressing, slow rebound | 10–15 | |
| Viscosity | Chewable and non-sticky | 7–10 |
| medium | 4–6 | |
| Unpleasant to chew, sticky teeth | 0–3 | |
| Smell | Wheat aroma, bean aroma, no bad taste | 12–15 |
| Bland flavor, slightly off flavor There is an odor | 9–11 0–8 | |
| Specific volume | 2.30 mL/g full marks, 1 mark for every 0.2 less | 0–10 |
| Samples | Hardness/N | Springiness | Chewiness/N | Cohesiveness |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WF-dough | 765.64 ± 13.28 e | 0.72 ± 0.02 e | 380.36 ± 9.45 h | 0.69 ± 0.03 bc |
| ODF-4% | 1265.64 ± 13.28 e | 0.87 ± 0.02 bc | 781.78 ± 9.45 f | 0.71 ± 0.03 bc |
| ODF-6% | 1738.76 ± 13.39 b | 0.81 ± 0.02 d | 1098.54 ± 23.78 b | 0.78 ± 0.02 a |
| ODF-8% | 1938.73 ± 17.54 a | 0.76 ± 0.01 e | 1134.54 ± 16.81 a | 0.77 ± 0.01 a |
| HEDF-4% | 1164.10 ± 12.49 f | 0.89 ± 0.03 ab | 621.62 ± 23.78 g | 0.60 ± 0.03 f |
| HEDF-6% | 1475.52 ± 10.15 d | 0.82 ± 0.03 cd | 919.43 ± 16.90 d | 0.76 ± 0.03 a |
| HEDF-8% | 1640.09 ± 16.65 c | 0.79 ± 0.02 d | 816.27 ± 18.47 e | 0.63 ± 0.02 f |
| UEDF-4% | 1245.85 ± 12.70 e | 0.92 ± 0.03 a | 631.88 ± 14.11 g | 0.70 ± 0.02 bc |
| UEDF-6% | 1471.59 ± 19.89 d | 0.89 ± 0.09 ab | 971.86 ± 223.03 c | 0.74 ± 0.03 ab |
| UEDF-8% | 1651.73 ± 15.60 c | 0.81 ± 0.02 d | 896.39 ± 16.59 d | 0.67 ± 0.01 cd |
| Samples | Relaxation Time [ms] | Peak Area [%] | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T21 | T22 | T23 | A21 | A22 | A23 | |
| WF dough | 0.12 ± 0.003 a | 18.32 ± 0.21 a | 228.14 ± 3.41 a | 13.17 ± 0.16 b | 84.57 ± 2.03 c | 2.26 ± 0.03 a |
| ODF-4% | 0.10 ± 0.002 a | 18.11 ± 0.45 a | 224.31 ± 4.73 a | 13.76 ± 0.25 b | 83.66 ± 1.41 c | 2.48 ± 0.06 a |
| ODF-6% | 0.09 ± 0.01 b | 18.04 ± 0.55 a | 215.52 ± 4.51 b | 13.43 ± 0.05 c | 84.63 ± 2.15 b | 2.06 ± 0.05 b |
| ODF-8% | 0.08 ± 0.004 b | 16.61 ± 0.53 b | 202.30 ± 3.76 e | 11.85 ± 0.13 e | 86.56 ± 3.20 a | 1.61 ± 0.02 d |
| HEDF-4% | 0.08 ± 0.003 b | 15.60 ± 0.46 d | 217.34 ± 2.75 b | 13.99 ± 0.03 a | 83.79 ± 2.12 c | 2.28 ± 0.02 a |
| HEDF-6% | 0.07 ± 0.004 c | 16.67 ± 0.42 b | 210.39 ± 1.21 c | 13.35 ± 0.21 d | 84.90 ± 3.14 b | 2.21 ± 0.10 c |
| HEDF-8% | 0.07 ± 0.003 c | 13.61 ± 0.91 c | 197.50 ± 2.17 f | 11.80 ± 0.40 e | 86.70 ± 4.11 a | 1.52 ± 0.03 d |
| UEDF-4% | 0.08 ± 0.004 b | 15.46 ± 0.40 c | 214.43 ± 2.12 b | 14.19 ± 0.07 a | 83.64 ± 3.06 c | 2.16 ± 0.05 b |
| UEDF-6% | 0.07 ± 0.003 c | 16.55 ± 0.48 b | 207.94 ± 2.54 d | 13.19 ± 0.08 d | 85.07 ± 2.08 b | 1.71 ± 0.03 d |
| UEDF-8% | 0.06 ± 0.006 d | 16.88 ± 0.10 b | 193.10 ± 3.68 f | 12.07 ± 0.10 e | 86.65 ± 1.07 a | 1.28 ± 0.05 e |
| Samples | Hardness/N | Springiness | Chewiness/N | Viscosity/pa.s | Cohesiveness | Resilience |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WS | 566.66 ± 13.94 d | 0.88 ± 0.01 a | 440.65 ± 19.45 d | 498.74 ± 17.61 d | 0.82 ± 0.03 a | 0.49 ± 0.01 a |
| WS-ODF | 1508.47 ± 18.26 a | 0.70 ± 0.03 d | 964.60 ± 22.95 a | 735.57 ± 33.85 c | 0.64 ± 0.02 d | 0.28 ± 0.02 d |
| WS-HEDF | 1149.29 ± 18.68 c | 0.77 ± 0.04 c | 519.47 ± 12.78 c | 944.51 ± 8.77 a | 0.77 ± 0.05 b | 0.42 ± 0.05 b |
| WS-UEDF | 1324.91 ± 39.18 b | 0.82 ± 0.06 b | 727.66 ± 30.46 b | 1171.52 ± 26.94 b | 0.71 ± 0.07 c | 0.35 ± 0.05 c |
| Samples | L* | a* | b* | ΔE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WS | 34.35 ± 0.25 a | 5.26 ± 0.12 d | 11.17 ± 0.21 d | - |
| WS-ODF | 20.70 ± 0.11 d | 10.22 ± 0.09 a | 21.90 ± 0.20 a | 18.05 ± 0.43 a |
| WS-HEDF | 23.36 ± 0.22 c | 6.49 ± 0.16 c | 16.52 ± 0.19 b | 12.28 ± 0.24 b |
| WS-UEDF | 25.39 ± 0.25 c | 8.32 ± 0.08 b | 15.08 ± 0.17 c | 10.24 ± 0.36 c |
| Samples | Completeness | Surface Smoothness | Internal Uniformity | Flexibility | Resilience | Viscosity | Smell | Specific Volume | Totals |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WS | 9.12 ± 0.94 a | 9.54 ± 0.78 a | 12.65 ± 1.45 a | 8.74 ± 0.61 a | 16.23 ± 0.83 a | 8.49 ± 0.71 c | 11.49 ± 0.57 a | 10 | 86.26 ± 4.76 c |
| WS-ODF | 7.31 ± 1.26 d | 6.70 ± 0.83 c | 9.60 ± 0.95 d | 7.57 ± 0.85 c | 11.64 ± 0.62 d | 9.28 ± 0.52 b | 10.41 ± 0.46 b | 7 | 62.51 ± 5.31 c |
| WS-HEDF | 8.15 ± 1.68 c | 7.82 ± 0.64 b | 11.47 ± 0.78 b | 7.12 ± 0.77 d | 14.77 ± 0.75 b | 9.13 ± 0.95 b | 10.74 ± 0.74 b | 10 | 80.2 ± 6.23 c |
| WS-UEDF | 8.45 ± 1.18 b | 7.67 ± 0.76 b | 11.66 ± 0.86 b | 7.94 ± 0.94 b | 15.71 ± 0.97 c | 9.45 ± 1.05 a | 10.87 ± 1.01 b | 10 | 83.75 ± 5.89 c |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, J.; Xie, W.; Chen, Z.; Zheng, Y.; Li, S. Enhancement of Dough Processing and Steamed Bread Quality with Modified Soybean Residue Dietary Fiber. Foods 2025, 14, 346. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14030346
Zhao J, Xie W, Chen Z, Zheng Y, Li S. Enhancement of Dough Processing and Steamed Bread Quality with Modified Soybean Residue Dietary Fiber. Foods. 2025; 14(3):346. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14030346
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Jun, Wenlong Xie, Zhilong Chen, Yuqian Zheng, and Sheng Li. 2025. "Enhancement of Dough Processing and Steamed Bread Quality with Modified Soybean Residue Dietary Fiber" Foods 14, no. 3: 346. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14030346
APA StyleZhao, J., Xie, W., Chen, Z., Zheng, Y., & Li, S. (2025). Enhancement of Dough Processing and Steamed Bread Quality with Modified Soybean Residue Dietary Fiber. Foods, 14(3), 346. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14030346




