The Membrane-Targeting Synergistic Antifungal Effects of Walnut-Derived Peptide and Salicylic Acid on Prickly Pear Spoilage Fungus
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Reagents
2.2. Preservation Effect of FW on Prickly Pear
2.3. Structural Characterization of YW-5
2.3.1. FTIR Analysis of YW-5
2.3.2. CD Spectrum
2.4. Theoretical Calculation of Interaction Forces
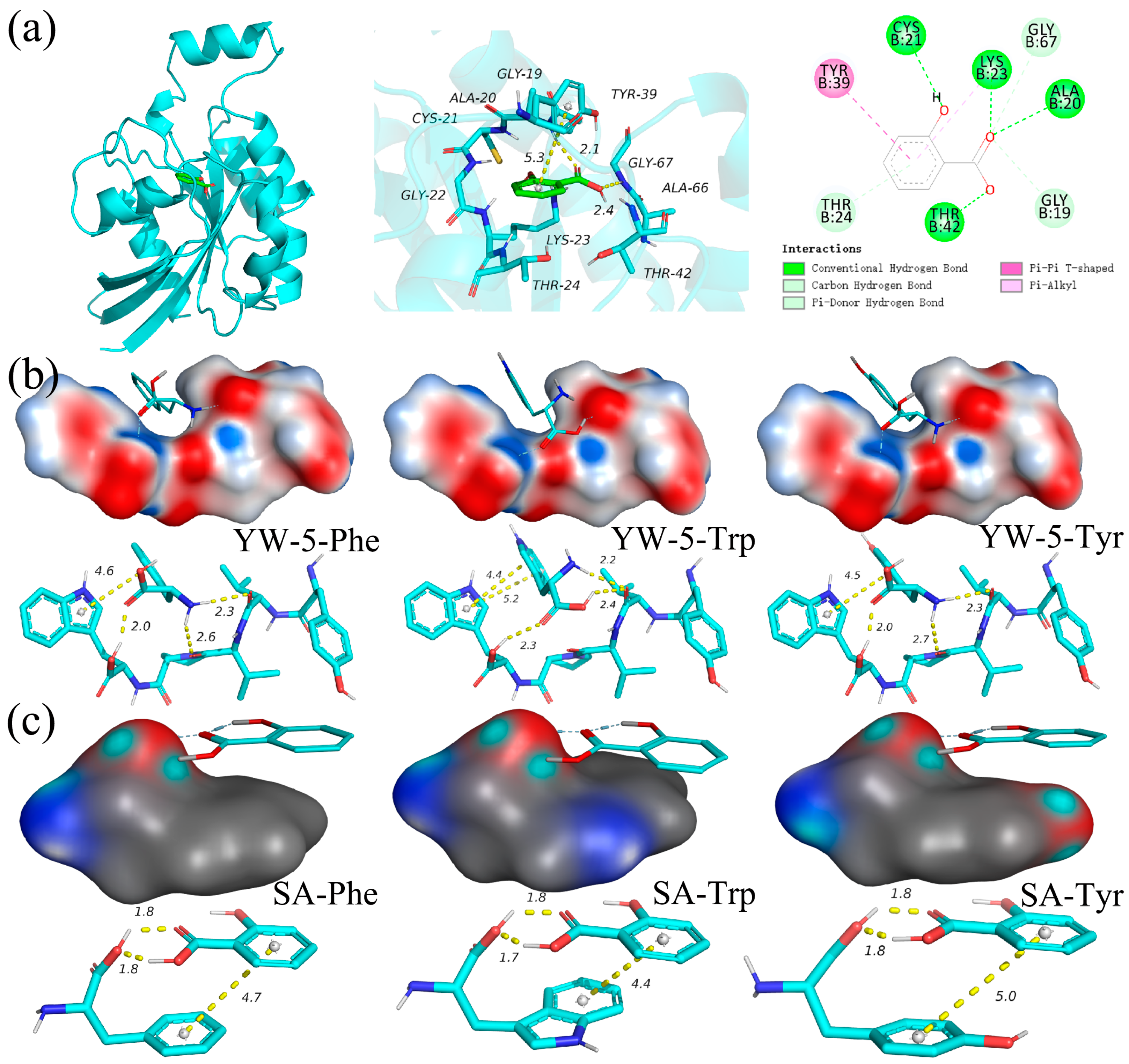
2.4.1. Molecular Docking with Rho1 GTPase
2.4.2. Molecular Docking with Amino Acids from Membrane Protein
2.5. Spectroscopic Analysis of the Interaction Site at the Cell Membrane
2.5.1. Mimic P. victoriae Membrane Liposome Preparation
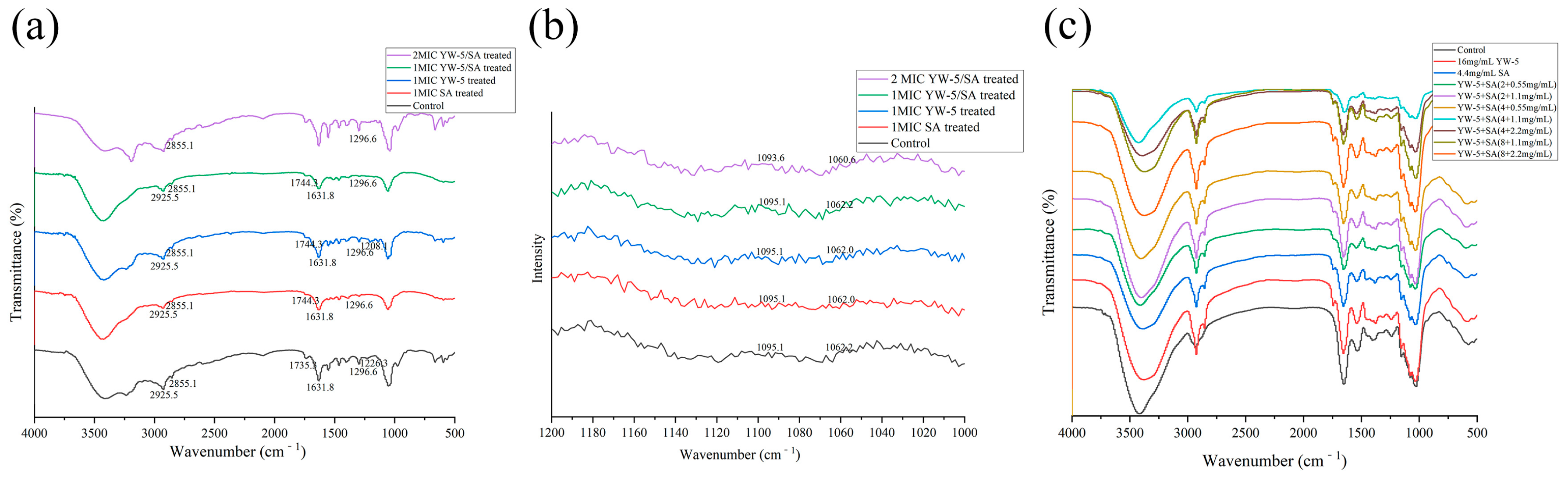
2.5.2. FTIR and Roman Interaction Site Analysis
2.6. Release of Cell Components
2.6.1. FTIR Analysis of Cell Components
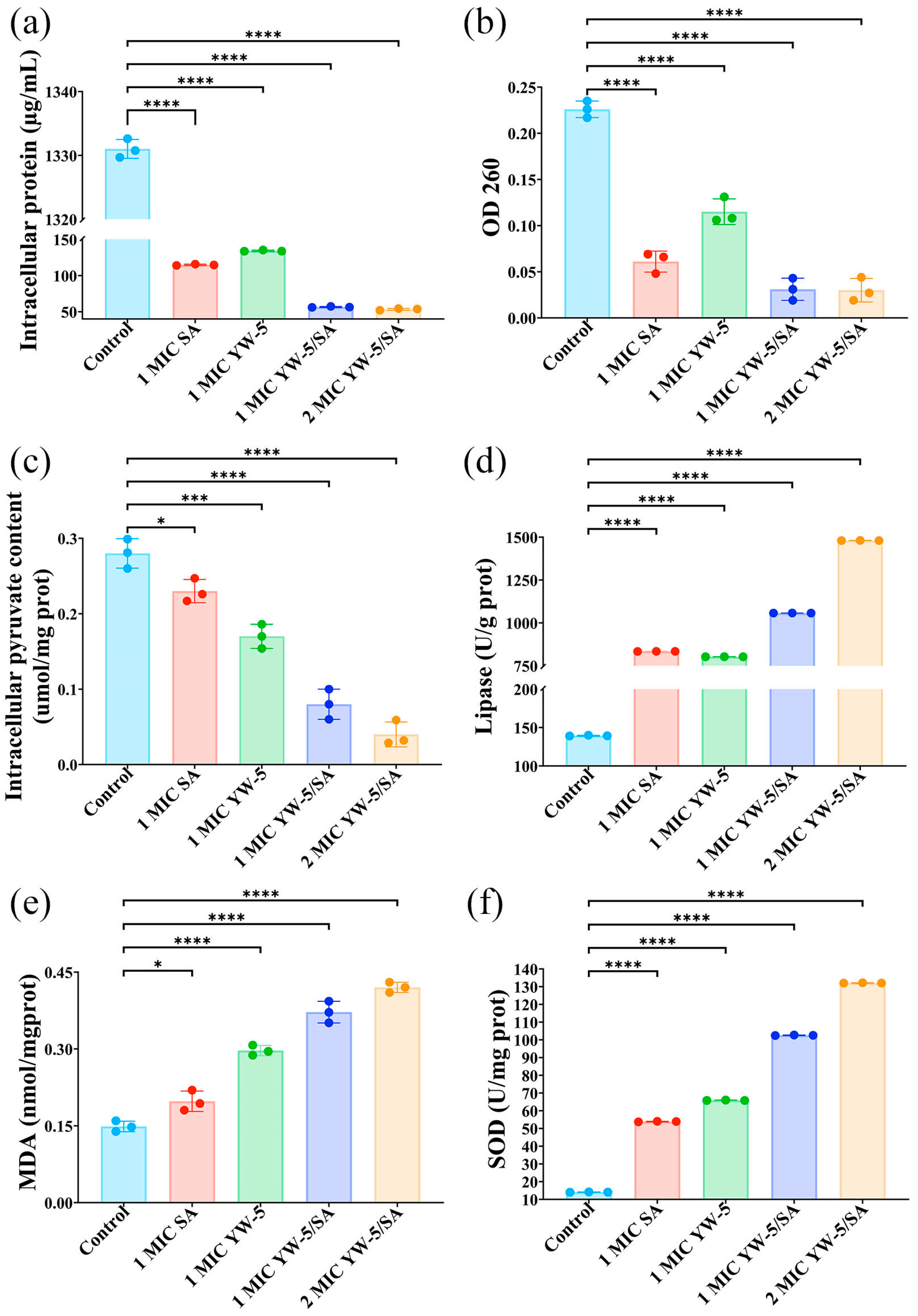
2.6.2. Intracellular Pyruvic Acid, Protein, and OD260
2.7. Malondialdehyde Content, Superoxide Dismutase Activity, and Lipase Activity Assay
2.8. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) and Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Enhancement of Freshness Capacity
3.2. Structural Characterization
3.3. Interaction Forces Determined via Molecular Docking
3.4. The Impact of YW-5 and SA on Cell Membrane Interactions
3.5. The Impact of YW-5 and SA on Cell Component Release
3.6. The Impact of YW-5 and SA on Membrane Lipid Peroxidation
3.7. The Impact of YW-5 and SA on Spore Morphology and Cell Ultrastructure
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| FW | Fermented walnut |
| SA | Salicylic acid |
| YW-5 | YVVPW |
References
- Zhao, F.; Du, G.; Huang, Y. Exploring the use of Near-infrared spectroscopy as a tool to predict quality attributes in prickly pear (Rosa roxburghii Tratt) with chemometrics variable strategy. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2022, 105, 104225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, B.; Xiao, J.; Huang, Q.; Li, C.; Fu, X. Physicochemical, functional, and biological properties of water-soluble polysaccharides from Rosa roxburghii Tratt fruit. Food Chem. 2018, 249, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanzani, S.M.; Reverberi, M.; Geisen, R. Mycotoxins in harvested fruits and vegetables: Insights in producing fungi, biological role, conducive conditions, and tools to manage postharvest contamination. Postharvest Biol. Tec. 2016, 122, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berman, J.; Krysan, D.J. Drug resistance and tolerance in fungi. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2020, 18, 319–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ou, D.; Zou, Y.; Zhang, X.; Jiao, R.; Zhang, D.; Ling, N. The potential of antifungal peptides derived from Lactiplantibacillus plantarum WYH for biocontrol of Aspergillus flavus contamination. Int. J. Food. Microbiol. 2024, 418, 110727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Luo, W.; Gao, Q.; Chen, C.; Li, L.; Liu, D.; Wang, S. Incorporating single-copper sites and host defense peptides into a nanoreactor for antibacterial therapy by bioinspired design. Engineering 2024, 43, 216–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.; Wang, H.; Su, W.; He, X.; Tan, M. Artificial intelligence in food bioactive peptides screening: Recent advances and future prospects. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2025, 156, 104845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, H.; Zhang, W.; Sun-Waterhouse, D.; Jiang, Y.; Li, F.; Waterhouse, G.I.N. Phenolic-protein interactions in foods and post ingestion: Switches empowering health outcomes. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 118, 71–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, R.; Brás, N.F.; Pérez-Gregorio, M.; Fernandes, I.; Mateus, N.; Freitas, V.A. Multi-spectroscopic study on the interaction of food polyphenols with a bioactive gluten peptide: From chemistry to biological implications. Food Chem. 2019, 299, 125051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, D.; Sun, L.C.; Huo, W.S.; Zhang, L.J.; Chen, Y.L.; Miao, S.; Cao, M. Improved functionality and safety of peptides by the formation of peptide-polyphenol complexes. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 141, 104193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sophie, G.; Holly, T.; Harjinder, S. In vitro gastric and intestinal digestion of a walnut oil body dispersion. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 410–417. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Y.; Wan, S.; Zhao, R.; Cao, L.; Fu, C.; Ren, D.F. Characterization of ultrasonic-assisted antifungal film loaded with fermented walnut meal on Rosa roxburghii Tratt during near-freezing temperature storage. J. Food Sci. 2024, 89, 6539–6552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Ling, Y.; Qin, Z.; Huang, J.; Jian, L.; Ren, D.F. Isolation, identification, and synergistic mechanism of a novel antimicrobial peptide and phenolic compound from fermented walnut meal and their application in Rosa roxbughii Tratt spoilage fungus. Food Chem. 2024, 433, 137333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 12293-1990; Fruit and Vegetable Products—Determination of Titrable Acidity. Ministry of Agriculture of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 1989.
- Hu, Y.; Yan, H.; Yin, Y.; Li, X.; Li, H.; Ren, D.F. Effect of microwave-assisted hydrothermal extraction on the bioactive compounds and antioxidant activities of dateplum persimmon juice and vinegar. Lwt-Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 154, 112642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB 4789.2-2016; Microbiological Examination of Food—Determination of Aerobic Plate Count. State Food and Drug Administration of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2016.
- Fazi, R.; Tintori, C.; Brai, A.; Botta, L.; Selvaraj, M.; Garbelli, A.; Maga, G.; Botta, M. Homology Model-Based Virtual Screening for the Identification of Human Helicase DDX3 Inhibitors. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2015, 55, 2443–2454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.; Zhang, H.; Wang, L.; Qian, H.; Qi, X. Targeted separation of antibacterial peptide from protein hydrolysate of anchovy cooking wastewater by equilibrium dialysis. Food Chem. 2015, 168, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ju, J.; Guo, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Yao, W. Analysis of the synergistic antifungal mechanism of small molecular combinations of essential oils at the molecular level. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2022, 188, 115612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bico, S.L.S.; Raposo, M.F.J.; Morais, R.M.S.C.; Morais, R.M.S.C. Combined effects of chemical dip and/or carrageenan coating and/or controlled atmosphere on quality of fresh-cut banana. Food Control 2009, 20, 508–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Zhang, C.; Chen, X.; Cui, H.; Lin, L. The interference mechanism of basil essential oil on the cell membrane barrier and respiratory metabolism of Listeria monocytogenes. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 855905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, Z.; Hu, K.; Song, C.; Ma, R.; Li, Z.; Zheng, J.; Fu, L.; Wei, Z.; Zhang, H. Hydrogen sulfide alleviates postharvest senescence of grape by modulating the antioxidant defenses. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2016, 2016, 4715651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, M.D.T.; Sothiselvam, S.; Lu, T.K.; de la Fuente-Nunez, C. Peptide design principles for antimicrobial applications. J. Mol. Biol. 2019, 431, 3547–3567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, L.; Xing, Y.; Kong, Y.; Sun, J.; Wei, Y. Impact of vacuum mixing on protein composition and secondary structure of noodle dough. Lwt-Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 85, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Huang, A.; He, L.; Huang, Z.; Zhao, Q.; Fan, J.; Tian, Y.; Huang, A. Isolation, identification and characterization of a novel antimicrobial peptide from Moringa oleifera seeds based on affinity adsorption. Food Chem. 2023, 398, 133923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, S.; Zhang, G.Y.; Zhang, H.J.; Kitajima, T.; Nakanishi, H.; Gao, X.D. Effects of Rho1, a small GTPase on the production of recombinant glycoproteins in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Microb. Cell Fact. 2016, 15, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirchmair, J.; Williamson, M.J.; Tyzack, J.D.; Tan, L.; Bond, P.J.; Bender, A.; Glen, R.C. Computational prediction of metabolism: Sites, products, SAR, P450 enzyme dynamics, and mechanisms. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2012, 52, 617–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manrique-Moreno, M.; Heinbockel, L.; Suwalsky, M.; Garidel, P.; Brandenburg, K. Biophysical study of the non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAID) ibuprofen, naproxen and diclofenac with phosphatidylserine bilayer membranes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2016, 1858, 2123–2131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Li, X.; Zhao, D.; Ni, J.; Chen, J.; Hwang, F. Interaction of scopolamine and cholesterol with sphingomyelin bilayers by ft-raman spectroscopy. Spectrosc. Lett. 1998, 31, 1825–1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saif, F.A.; Yaseen, S.A.; Alameen, A.S.; Mane, S.B.; Undre, P.B. Identification and characterization of Aspergillus species of fruit rot fungi using microscopy, ft-ir, raman and uv-vis spectroscopy. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2021, 246, 119010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gáplovská, K.; Šimonovičová, K.; Halko, R.; Okenicová, L.; Žemberyová, M.; Čerňanský, S.; Mackuľak, T. Study of the binding sites in the biomass of Aspergillus niger wild-type strains by FTIR spectroscopy. Chem. Pap. 2018, 7, 2228–2283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efstathia, K.A.; Sofoulis, M.; Natskoulis, P.; Tarantilis, P.; Christos, S.P.; Panagou, E.Z. Differentiation and identification of grape-associated black aspergilli using Fourier transform infrared (FT-IR) spectroscopic analysis of mycelia. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2017, 259, 22–28. [Google Scholar]
- Salman, A.; Lapidot, I.; Pomerantz, A.; Tsror, L.; Shufan, E.; Moreh, R.; Mordechai, S. Identification of fungal phytopathogens using fourier transform infrared-attenuated total reflection spectroscopy and advanced statistical methods. J. Biomed. Opt. 2012, 17, 017002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salgado, C.A.; dos Santos, C.I.A.; Vanetti, M.C.D. Microbial lipases: Propitious biocatalysts for the food industry. Food Biosci. 2022, 45, 101509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arokiyaraj, S.; Bharanidharan, R.; Agastian, P.; Shin, H. Chemical composition, antioxidant activity and antibacterial mechanism of action from Marsilea minuta leaf hexane: Methanol extract. Chem. Cent. J. 2018, 12, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

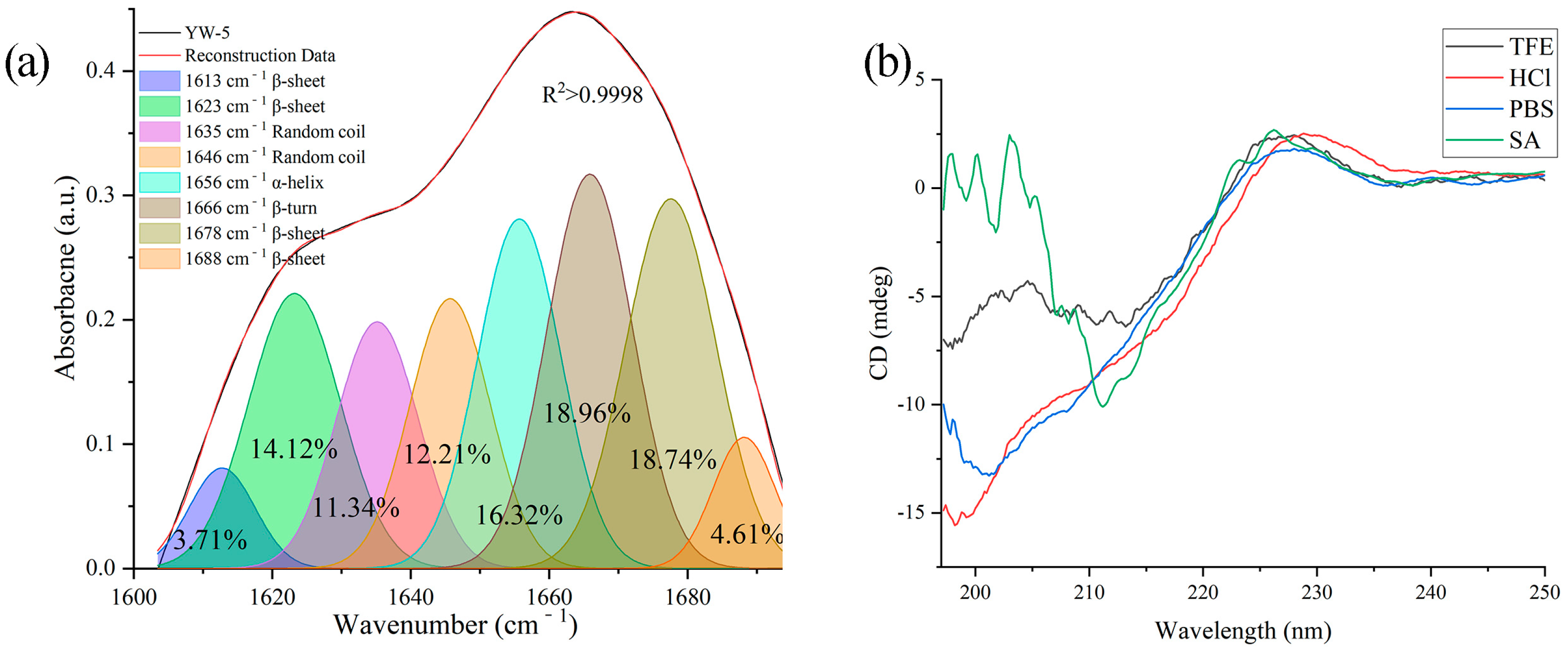

| Secondary Structure | α-Helix (%) | β-Sheet (%) | β-Turn (%) | Random (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FTIR | In its solid state | 16.32% | 41.18% | 18.96% | 23.54% |
| CD | In HCl | 3.0% | 32.9% | 21.8% | 42.3% |
| In PBS | 1.9% | 33.6% | 18.7% | 45.8% | |
| In TFE | 8.0% | 38.2% | 12.3% | 41.6% | |
| In SA | 0.7% | 49.0% | 26.6% | 23.8% | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, Y.; Liu, N.; Ma, C.; Ren, D.; Wang, D.; Shang, Y.; Li, F.; Lyu, Y.; Cai, C.; Chen, L.; et al. The Membrane-Targeting Synergistic Antifungal Effects of Walnut-Derived Peptide and Salicylic Acid on Prickly Pear Spoilage Fungus. Foods 2025, 14, 951. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14060951
Hu Y, Liu N, Ma C, Ren D, Wang D, Shang Y, Li F, Lyu Y, Cai C, Chen L, et al. The Membrane-Targeting Synergistic Antifungal Effects of Walnut-Derived Peptide and Salicylic Acid on Prickly Pear Spoilage Fungus. Foods. 2025; 14(6):951. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14060951
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Yue, Na Liu, Caiqing Ma, Difeng Ren, Dujun Wang, Yueling Shang, Fengwei Li, Yongmei Lyu, Chen Cai, Long Chen, and et al. 2025. "The Membrane-Targeting Synergistic Antifungal Effects of Walnut-Derived Peptide and Salicylic Acid on Prickly Pear Spoilage Fungus" Foods 14, no. 6: 951. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14060951
APA StyleHu, Y., Liu, N., Ma, C., Ren, D., Wang, D., Shang, Y., Li, F., Lyu, Y., Cai, C., Chen, L., Liu, W., & Yu, X. (2025). The Membrane-Targeting Synergistic Antifungal Effects of Walnut-Derived Peptide and Salicylic Acid on Prickly Pear Spoilage Fungus. Foods, 14(6), 951. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14060951






