Biological Activities and Phytochemical Profile of Hawm Gra Dang Ngah Rice: Water and Ethanolic Extracts
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods and Materials
2.1. Materials and Chemical Reagents
2.2. Extraction of Hawm Gra Dang Ngah Rice
2.3. Determine the Bioactive Compound Content in HDNR-W and HDNR-E
2.4. UHPLC-ESI-Q-TOF-MS/MS
2.5. Amino Acid Profile
2.6. Fatty Acid Profile
2.7. Heavy Metal and Trace Element in HDNR-W Extracts
2.8. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FT-IR) Analysis
2.9. Antioxidant Assay
2.10. Inhibition of HMG-CoA Reductase Activity of HDNR-W and HDNR-E
2.11. Inhibition of α-Glucosidase Activity of HDNR-W and HDNR-E
2.12. Inhibition of Monoamine Oxidases (MAO) Activity of HDNR-W and HDNR-E
2.13. Cell Culture and Cytotoxicity of HDNR-W and HDNR-E in Normal and Cancer Cell Lines
2.14. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Major Components of HDNR-W and HDNR-E
3.2. Amino Acid Profile in the HDNR-W and HDNR-E Extracts
3.3. Fatty Acid Profile in the HDNR-W and HDNR-E Extracts
3.4. Heavy Metal Concentration in HDNR-W
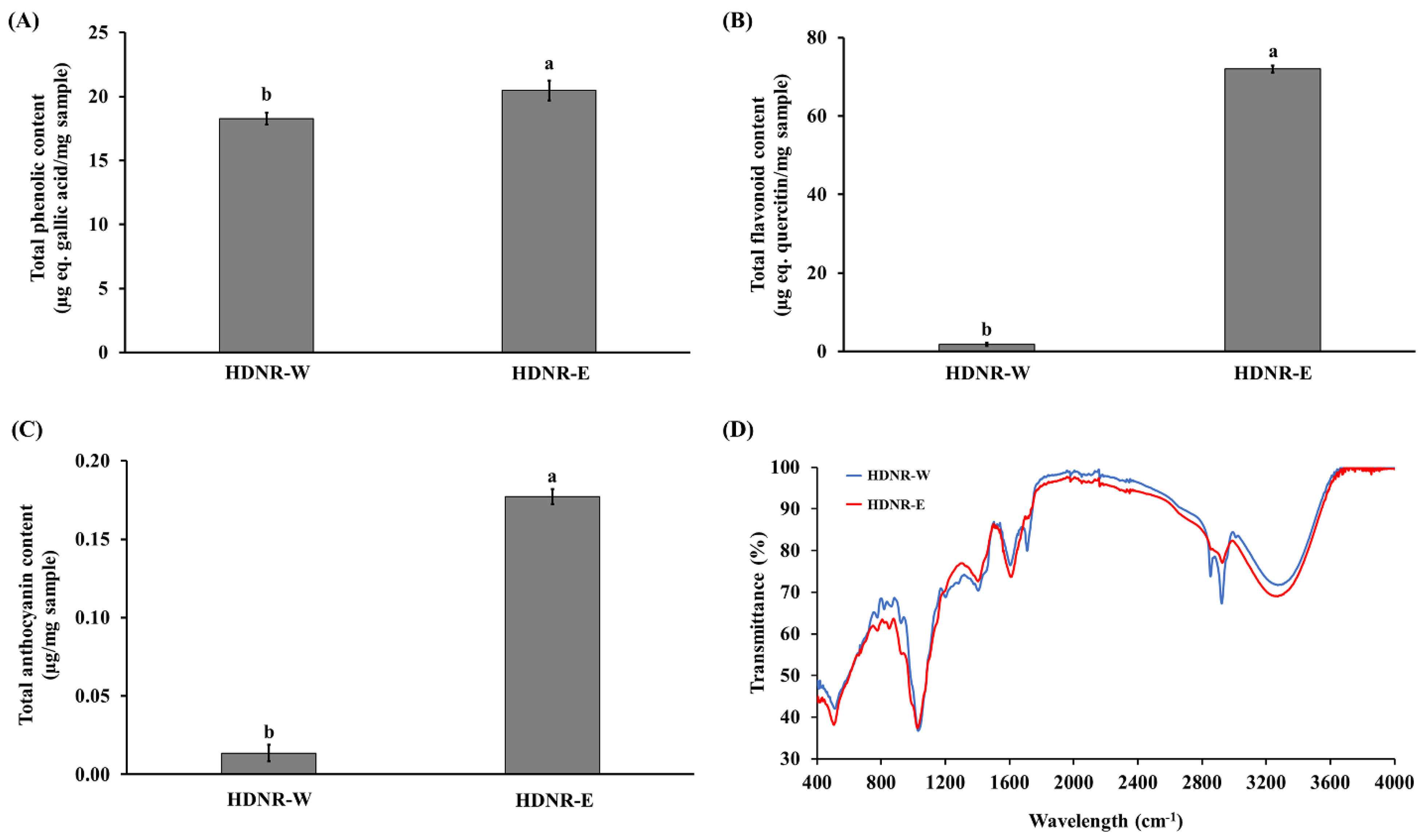
3.5. Total Phenolic, Total Flavonoid, and Total Anthocyanin Contents in the HDNR-W and HDNR-E Extracts
3.6. FT-IR in the HDNR-W and HDNR-E Extracts
3.7. Antioxidation Activity of HDNR-W and HDNR-E Extracts
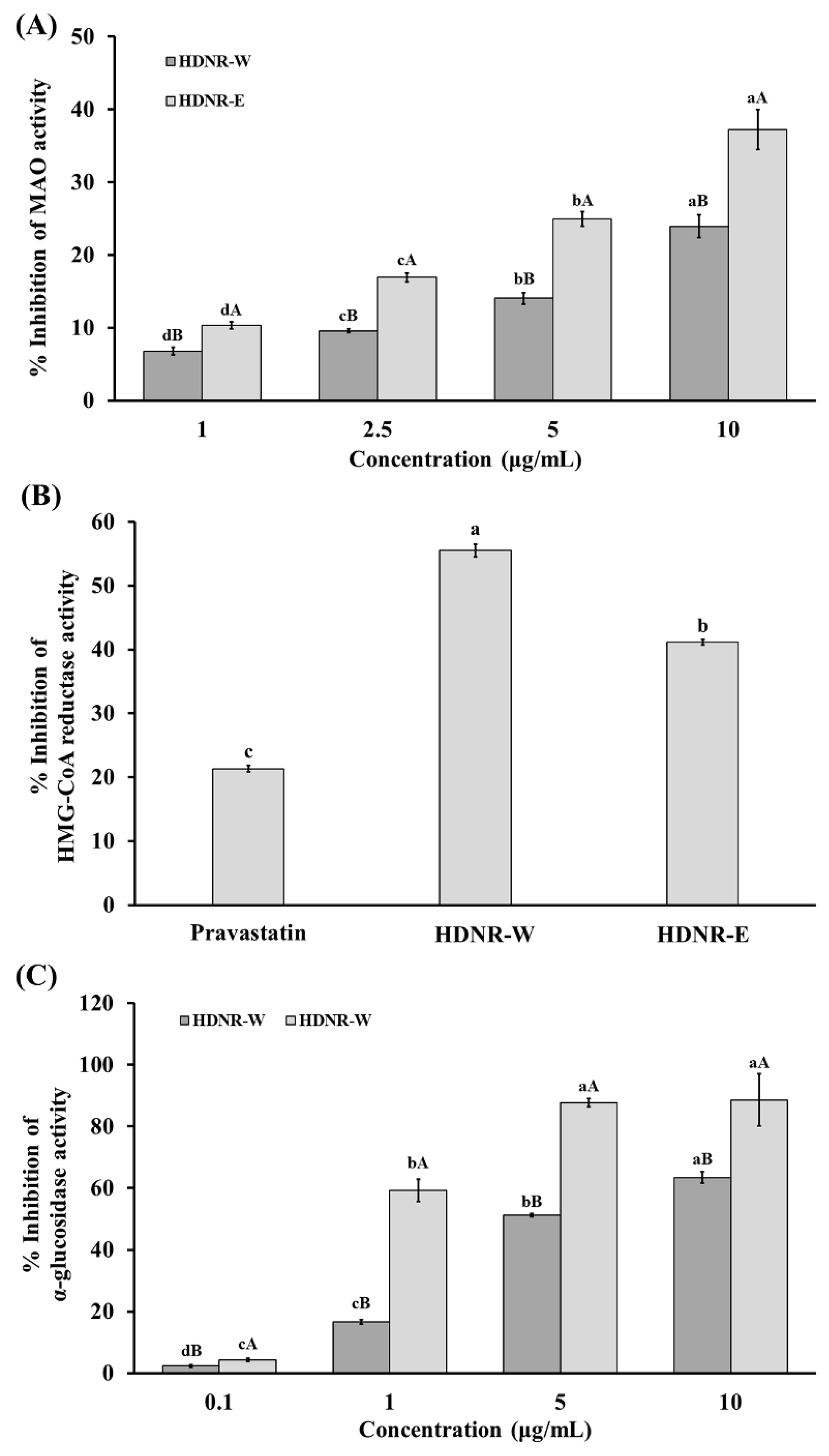
3.8. Inhibitory Activity of MAO, HMG-CoA Reductase, and α-Glucosidase in HDNR-W and HDNR-E Extracts
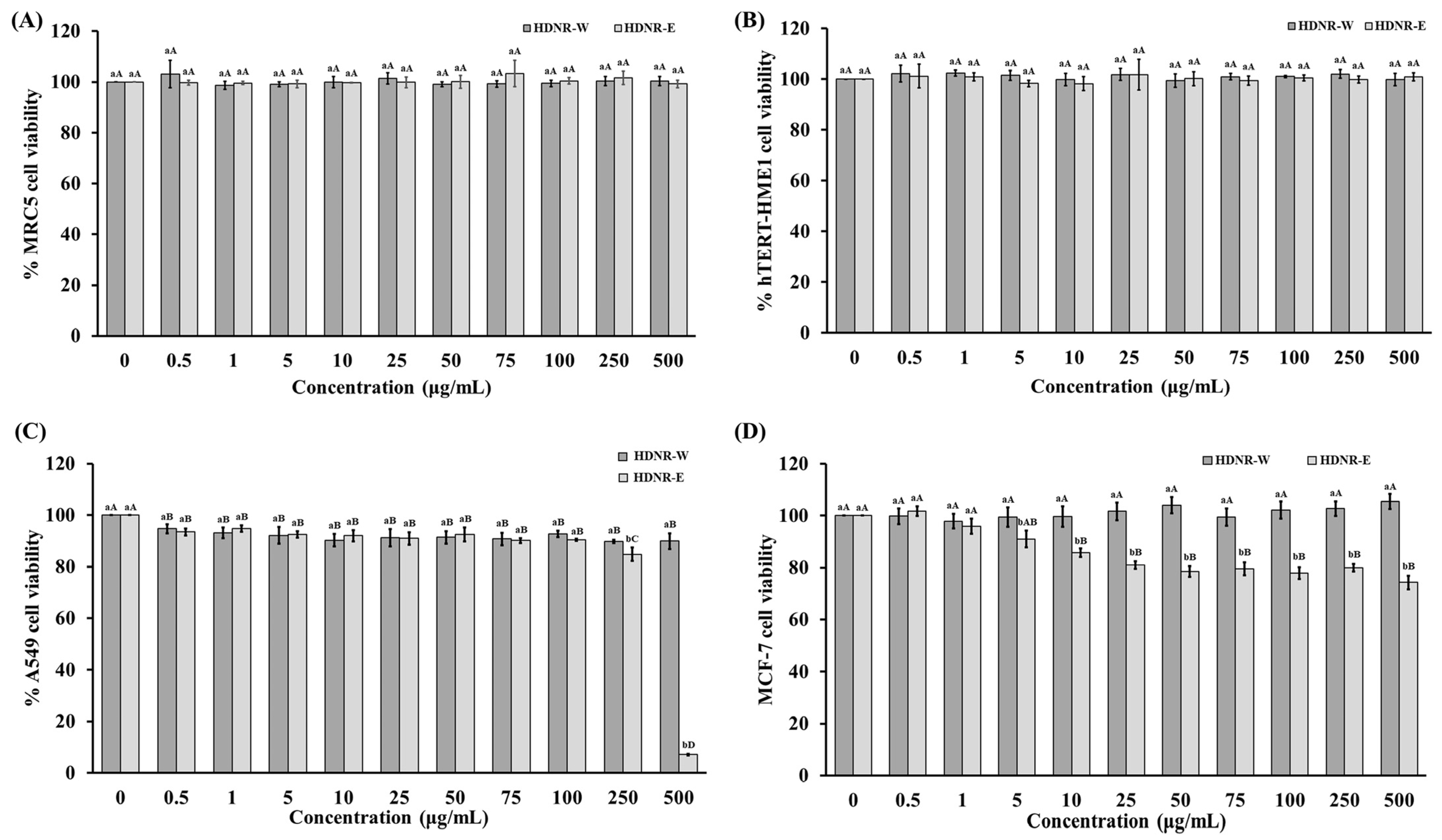
3.9. Cytotoxicity of HDNR-W and HDNR-E Extracts on Normal Cell Lines (MRC5 and hTERT-HME1) and Cancer Cell Lines (A549 and MCF7)
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Budreviciute, A.; Damiati, S.; Sabir, D.K.; Onder, K.; Schuller-Goetzburg, P.; Plakys, G.; Katileviciute, A.; Khoja, S.; Kodzius, R. Management and prevention strategies for non-communicable diseases (NCDs) and their risk factors. Front. Public Health 2020, 8, 574111. [Google Scholar]
- Noncommunicable Diseases Country Profiles; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021.
- Nguanchoo, V.; Balslev, H.; Sadgrove, N.J.; Phumthum, M. Medicinal plants used by rural Thai people to treat non-communicable diseases and related symptoms. Heliyon 2023, 9, e12758. [Google Scholar]
- Fukagawa, N.K.; Ziska, L.H. Rice: Importance for global nutrition. J. Nutr. Sci. Vitaminol. 2019, 65, S2–S3. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; Li, J.; Xue, Y.; Xu, Y.; Liu, C.; Su, D. Comprehensive improvement of nutrients and volatile compounds of black/purple rice by extrusion-puffing technology. Front. Nutr. 2023, 10, 1248501. [Google Scholar]
- Tapia-Hernández, J.A.; Del-Toro-Sánchez, C.L.; Cinco-Moroyoqui, F.J.; Juárez-Onofre, J.E.; Ruiz-Cruz, S.; Carvajal-Millan, E.; López-Ahumada, G.A.; Castro-Enriquez, D.D.; Barreras-Urbina, C.G.; Rodríguez-Felix, F. Prolamins from cereal by-products: Classification, extraction, characterization and its applications in micro- and nanofabrication. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 90, 111–132. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Yang, Y.; Yang, X.; Zhu, G.; Lu, X.; Jia, F.; Diao, B.; Yu, S.; Ali, A.; Zhang, H.; et al. Investigation of flavonoid components and their associated antioxidant capacity in different pigmented rice varieties. Food Res. Int. 2022, 161, 111726. [Google Scholar]
- Aenglong, C.; Woonnoi, W.; Tanasawet, S.; Klaypradit, W.; Sukketsiri, W. Impact of time and enzyme concentration on Sangyod rice bran hydrolysate: Phytochemicals, antioxidants, amino acids, and cytotoxicity. Rice 2024, 17, 13. [Google Scholar]
- Hanchang, W.; Woonnoi, W.; Saetan, J.; Suttithumsatid, W.; Tanasawet, S.; Sanprick, A.; Moolsup, F.; Sukketsiri, W. Sangyod rice extract mitigates insulin resistance in HepG2 cells and hepatic steatosis in diabetic rats via AMPK/mTOR/MAPK signaling pathways. Food Biosci. 2024, 61, 104662. [Google Scholar]
- Panomwan, P.; Temdee, W. Physical and nutritional properties of local Hawm Gra Dang Ngah Rice varieties. Curr. Res. Nutr. Food Sci. 2021, 9, 1074–1080. [Google Scholar]
- Woonnoi, W.; Suttithumsatid, W.; Muneerungsee, N.; Saetan, J.; Tanasawet, S.; Sukketsiri, W. Sangyod rice extract inhibits adipocyte growth and differentiation via mTOR, Akt, and AMPK pathways. J. Funct. Foods 2023, 111, 105913. [Google Scholar]
- Wisetkomolmat, J.; Arjin, C.; Hongsibsong, S.; Ruksiriwanich, W.; Niwat, C.; Tiyayon, P.; Jamjod, S.; Yamuangmorn, S.; Prom-U-Thai, C.; Sringarm, K. Antioxidant activities and characterization of polyphenols from selected oorthern Thai rice husks: Relation with seed attributes. Rice Sci. 2023, 30, 148–159. [Google Scholar]
- Hansakul, P.; Srisawat, U.; Itharat, A.; Lerdvuthisopon, N. Phenolic and flavonoid contents of Thai rice extracts and their correlation with antioxidant activities using chemical and cell assays. J. Med. Assoc. Thai. 2011, 94, S122–S130. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Durst, R.W.; Wrolstad, R.E. Determination of total monomeric anthocyanin pigment content of fruit juices, beverages, natural colorants, and wines by the pH differential method: Collaborative Study. J. AOAC Int. 2019, 88, 1269–1278. [Google Scholar]
- Curtis, J.M.; Berrigan, N.; Dauphinee, P. The determination of n-3 fatty acid levels in food products containing microencapsulated fish oil using the one-step extraction method. Part 1: Measurement in the raw ingredient and in dry powdered foods. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2008, 85, 297–305. [Google Scholar]
- Sneddon, E.J.; Hardaway, C.J.; Sneddon, J.; Kiran, B.; Tate, A.S.; Tidwell, S.L.; Gray, D.P.; Douvris, C. Determination of selected metals in rice and cereal by inductively coupled plasma-optical emission spectrometry (ICP-OES). Microchem. J. 2017, 134, 9–12. [Google Scholar]
- Chotphruethipong, L.; Sukketsiri, W.; Aluko, R.E.; Sae-Leaw, T.; Benjakul, S. Effect of hydrolyzed collagen from defatted Asian sea bass (Lates calcarifer) skin on fibroblast proliferation, migration and antioxidant activities. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 58, 541–551. [Google Scholar]
- Suttithumsatid, W.; Shah, M.A.; Bibi, S.; Panichayupakaranant, P. α-Glucosidase inhibitory activity of cannabidiol, tetrahydrocannabinol and standardized cannabinoid extracts from Cannabis sativa. Curr. Res. Food Sci. 2022, 5, 1091–1097. [Google Scholar]
- Boonruamkaew, P.; Sukketsiri, W.; Panichayupakaranant, P.; Kaewnam, W.; Tanasawet, S.; Tipmanee, V.; Hutamekalin, P.; Chonpathompikunlert, P. Apium graveolens extract influences mood and cognition in healthy mice. J. Nat. Med. 2017, 71, 492–505. [Google Scholar]
- Suttithumsatid, W.; Sukketsiri, W.; Panichayupakaranant, P. Cannabinoids and standardized cannabis extracts inhibit migration, invasion, and induce apoptosis in MCF-7 cells through FAK/MAPK/Akt/NF-κB signaling. Toxicol. In Vitro 2023, 93, 105667. [Google Scholar]
- Kukusamude, C.; Sricharoen, P.; Limchoowong, N.; Kongsri, S. Heavy metals and probabilistic risk assessment via rice consumption in Thailand. Food Chem. 2021, 334, 127402. [Google Scholar]
- Dewan, M.F.; Ahiduzzaman, M.; Islam, M.N.; Shozib, H.B. Potential benefits of bioactive compounds of traditional rice grown in South and Southeast Asia: A review. Rice Sci. 2023, 30, 537–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.W.; Lin, L.G.; Ye, W.C. Techniques for extraction and isolation of natural products: A comprehensive review. Chin. Med. 2018, 13, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alara, O.R.; Abdurahman, N.H.; Olalere, O.A. Ethanolic extraction of flavonoids, phenolics and antioxidants from Vernonia amygdalina leaf using two-level factorial design. J. King Saud. Univ. Sci. 2020, 32, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaves, J.O.; de Souza, M.C.; da Silva, L.C.; Lachos-Perez, D.; Torres-Mayanga, P.C.; Machado, A.F.; Forster-Carneiro, T.; Vázquez-Espinosa, M.; González-de-Peredo, A.V.; Barbero, G.F.; et al. Extraction of flavonoids from natural sources using modern techniques. Front. Chem. 2020, 8, 507887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Zhao, W.; Yang, Z.; Subbiah, V.; Suleria, H.A.R. Extraction and characterization of phenolic compounds and their potential antioxidant activities. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 81112–81129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayaprakash, G.; Bains, A.; Chawla, P.; Fogarasi, M.; Fogarasi, S. A narrative review on rice proteins: Current scenario and food industrial application. Polymers 2022, 14, 3003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melgosa, R.; Marques, M.; Paiva, A.; Bernardo, A.; Fernández, N.; Sá-Nogueira, I.; Simões, P. Subcritical water extraction and hydrolysis of Cod (Gadus morhua) frames to produce bioactive protein extracts. Foods 2021, 10, 1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sitanggang, A.B.; Joshua, M.; Munarko, H.; Kusnandar, F.; Budijanto, S. Increased γ-aminobutyric acid content of germinated brown rice produced in membrane reactor. Food Technol. Biotechnol. 2021, 59, 295–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalman, D.S. Amino acid composition of an organic brown rice protein concentrate and isolate compared to soy and whey concentrates and isolates. Foods 2014, 3, 394–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribas, F.B.T.; Gasparetto, H.; Salau, N.P.G. Sustainable extraction of rice bran oil: Assessing renewable solvents, kinetics, and thermodynamics. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2023, 197, 342–354. [Google Scholar]
- Ilias, N.N.; Mohd Rozalli, N.H.; Mohamad Kassim, M.H. Characterizations of rice bran nanofibers produced by enzymatic treatment and their role in stabilizing oil-in-water pickering emulsions. Waste Biomass Valorization 2023, 14, 3401–3413. [Google Scholar]
- Özgül-Yücel, S.; Proctor, A. Rice bran FFA determination by diffuse reflectance IR spectroscopy. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2004, 81, 221–224. [Google Scholar]
- Prasad, P.; Savyasachi, S.; Reddy, L.P.A.; Sreedhar, R.V. Physico-chemical characterization, profiling of total lipids and triacylglycerol molecular species of omega-3 fatty acid rich B. arvensis seed oil from India. J. Oleo Sci. 2019, 68, 209–223. [Google Scholar]
- Falcioni, R.; Moriwaki, T.; Gibin, M.S.; Vollmann, A.; Pattaro, M.C.; Giacomelli, M.E.; Sato, F.; Nanni, M.R.; Antunes, W.C. Classification and prediction by pigment content in Lettuce (Lactuca sativa L.) varieties using machine learning and ATR-FTIR spectroscopy. Plants 2022, 11, 3413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, E.A.; Abdalla, I.G.; Alfawaz, M.A.; Mohammed, M.A.; Al Maiman, S.A.; Osman, M.A.; Yagoub, A.E.A.; Hassan, A.B. Effects of extraction solvents on the total phenolic content, total flavonoid content, and antioxidant activity in the aerial part of root vegetables. Agriculture 2022, 12, 1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, S.; Ubeyitogullari, A. Extraction of phenolic compounds from rice husk via ethanol-water-modified supercritical carbon dioxide. Heliyon 2023, 9, e14196. [Google Scholar]
- Wanyo, P.; Kaewseejan, N.; Meeso, N.; Siriamornpun, S. Bioactive compounds and antioxidant properties of different solvent extracts derived from Thai rice by-products. Appl. Biol. Chem. 2016, 59, 373–384. [Google Scholar]
- Scarano, A.; Laddomada, B.; Blando, F.; De Santis, S.; Verna, G.; Chieppa, M.; Santino, A. The chelating ability of plant polyphenols can affect iron homeostasis and gut microbiota. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del-Toro-Sánchez, C.L.; Rodríguez-Félix, F.; Cinco-Moroyoqui, F.J.; Juárez, J.; Ruiz-Cruz, S.; Wong-Corral, F.J.; Borboa-Flores, J.; Castro-Enríquez, D.D.; Barreras-Urbina, C.G.; Tapia-Hernández, J.A. Recovery of phytochemical from three safflower (Carthamus tinctorius L.) by-products: Antioxidant properties, protective effect of human erythrocytes and profile by UPLC-DAD-MS. J. Food Process Preserv. 2021, 45, e15765. [Google Scholar]
- Chaurasiya, N.D.; Leon, F.; Muhammad, I.; Tekwani, B.L. Natural products inhibitors of monoamine oxidases-potential new drug leads for neuroprotection, neurological disorders, and neuroblastoma. Molecules 2022, 27, 4297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ademosun, A.O.; Oboh, G. Comparison of the inhibition of monoamine oxidase and butyrylcholinesterase activities by infusions from green tea and some citrus peels. Int. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2014, 2014, 586407. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ganiyu, O.; Olunbamigbe, O.O.; Ogunsuyi, O.B.; Aro, O.P.; Oyeleye, I.S.; Ademosun, A.O. Evaluating the nutrient composition and antioxidant properties of orange (Citrus sinensis) peels through Penicillium camemberti-based solid-substrate fermentation. Discov. Food 2024, 4, 114. [Google Scholar]
- Moelands, S.V.; Lucassen, P.L.; Akkermans, R.P.; De Grauw, W.J.; Van de Laar, F.A. Alpha-glucosidase inhibitors for prevention or delay of type 2 diabetes mellitus and its associated complications in people at increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes mellitus. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2018, 12, Cd005061. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chaachouay, N.; Zidane, L. Plant-derived natural products: A source for drug discovery and development. Drugs Drug Candidates 2024, 3, 184–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhuyan, P.; Ganguly, M.; Baruah, I.; Borgohain, G.; Hazarika, J.; Sarma, S. Alpha glucosidase inhibitory properties of a few bioactive compounds isolated from black rice bran: Combined in vitro and in silico evidence supporting the antidiabetic effect of black rice. RSC Adv. 2022, 12, 22650–22661. [Google Scholar]
- Sansenya, S.; Payaka, A. Inhibitory potential of phenolic compounds of Thai colored rice (Oryza sativa L.) against α-glucosidase and α-amylase through in vitro and in silico studies. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2022, 102, 6718–6726. [Google Scholar]
- Laka, K.; Makgoo, L.; Mbita, Z. Cholesterol-lowering phytochemicals: Targeting the mevalonate pathway for anticancer interventions. Front. Genet. 2022, 13, 841639. [Google Scholar]
- Sukketsiri, W.; Daodee, S.; Parhira, S.; Malakul, W.; Tunsophon, S.; Sutthiwong, N.; Tanasawet, S.; Chonpathompikunlert, P. Chemical characterization of Passiflora edulis extracts and their in vitro antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, anti-lipid activities, and ex-vivo vasodilation effect. J. King Saud. Univ. Sci. 2023, 35, 102431. [Google Scholar]
- Heres, A.; Mora, L.; Toldrá, F. Inhibition of 3-hydroxy-3-methyl-glutaryl-coenzyme A reductase enzyme by dipeptides identified in dry-cured ham. Food Prod. Process Nutr. 2021, 3, 18. [Google Scholar]
- Rizeq, B.; Gupta, I.; Ilesanmi, J.; AlSafran, M.; Rahman, M.M.; Ouhtit, A. The power of phytochemicals combination in cancer chemoprevention. J. Cancer 2020, 11, 4521–4533. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, Z.; Liu, X.; Cheng, C.; Yu, W.; Yi, P. Metabolism of amino acids in cancer. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 603837. [Google Scholar]
- Lieu, E.L.; Nguyen, T.; Rhyne, S.; Kim, J. Amino acids in cancer. Exp. Mol. Med. 2020, 52, 15–30. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hardman, W.E. Omega-3 fatty acids to augment cancer therapy. J. Nutr. 2002, 132, 3508S–3512S. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
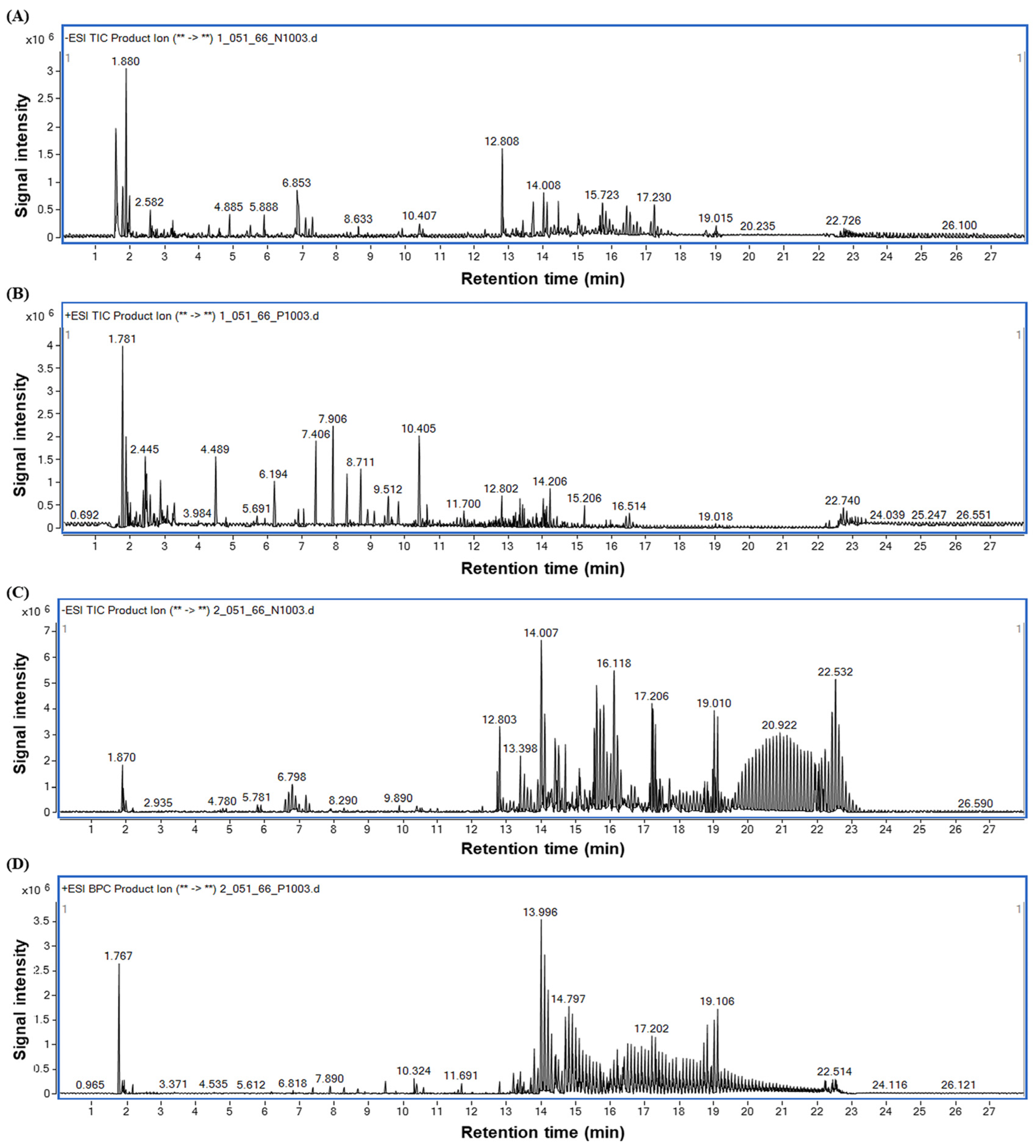

| No. | RT (min) | Identification | Molecular Formula | Experimental Mass (m/z) | Error (ppm) | Category |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Negative mode | ||||||
| 1 | 1.621 | Phytic acid | C6H18O246 | 658.854 | 0.38 | Phosphorus Compound |
| 2 | 1.646 | myo-Inositol pentakisphosphate | C6H17O21P5 | 578.8874 | 0.76 | Phosphorus Compound |
| 3 | 1.696 | 1D-myo-Inositol 1,3,4,6-tetrakisphosphate | C6H16O18P4 | 498.9212 | 0.58 | Phosphorus Compound |
| 4 | 1.822 | L-Iditol | C6H14O6 | 181.0713 | 2.7 | Sugar Alcohol |
| 5 | 1.897 | D-Mannonate | C6H12O7 | 195.051 | 0.43 | Sugar Acid |
| 6 | 1.922 | L-Xylonate | C5H10O6 | 165.0401 | 2.11 | Sugar Acid |
| 7 | 2.047 | Sucrose | C12H22O11 | 341.1082 | 1.43 | Disaccharide |
| 8 | 2.085 | Glyceric acid | C3H6O4 | 105.0189 | 3.87 | Sugar Acid |
| 9 | 2.26 | Malic acid | C4H6O5 | 133.0138 | 3.22 | Organic Acid |
| 10 | 2.423 | Sarmentosin epoxide | C11H17NO8 | 290.0872 | 3.17 | Alkaloid |
| 11 | 2.523 | Hypoxanthine | C5H4N4O | 135.0307 | 3.44 | Purine Derivative |
| 12 | 2.649 | Citric acid | C6H8O7 | 191.0199 | −0.45 | Organic Acid |
| 13 | 2.673 | 2,3-Dihydroxy-2,4-cyclopentadien-1-one | C5H4O3 | 111.0085 | 2.44 | Phenolic Compound |
| 14 | 2.786 | Pyroglutamic acid | C5H7NO3 | 128.035 | 2.48 | Amino Acid Derivative |
| 15 | 2.849 | Pseudouridine | C9H12N2O6 | 243.0617 | 2.14 | Nucleoside |
| 16 | 3.024 | Maleic acid | C4H4O4 | 115.0034 | 2.29 | Organic Acid |
| 17 | 3.049 | Meta-Tyrosine | C9H11NO3 | 180.0661 | 1.87 | Amino Acid Derivative |
| 18 | 3.275 | (R)-2,3-Dihydro-3,5-dihydroxy-2-oxo-3-indoleacetic acid | C10H9NO5 | 222.04 | 3.36 | Alkaloid |
| 19 | 4.102 | DIMBOA-Glc | C15H19NO10 | 372.0926 | 2.7 | Alkaloid Glycoside |
| 20 | 4.666 | L-Phenylalanine | C9H11NO2 | 164.0711 | 3.16 | Amino Acid |
| 21 | 4.929 | 4-Hydroxyisoleucine | C6H13NO3 | 146.0819 | 2.33 | Amino Acid |
| 22 | 4.954 | Pantothenic Acid | C9H17NO5 | 218.1036 | −0.86 | Vitamin |
| 23 | 5.706 | 6-Caffeoylsucrose | C21H28O14 | 503.1399 | 1.72 | Phenylpropanoid Glycoside |
| 24 | 5.831 | Mandelonitrile sophoroside | C20H27NO11 | 456.1502 | 2.03 | Cyanogenic Glycoside |
| 25 | 5.931 | 3,4-Dihydroxybenzoic acid | C7H6O4 | 153.0191 | 1.74 | Phenolic Acid |
| 26 | 5.956 | Pyrocatechol | C6H6O2 | 109.0293 | 2.05 | Phenolic Compound |
| 27 | 6.307 | L-Tryptophan | C11H12N2O2 | 203.082 | 3.04 | Amino Acid |
| 28 | 6.933 | Procyanidin B2 | C30H26O12 | 577.1345 | 1.4 | Flavonoid |
| 29 | 6.933 | Epigallocatechin 3-O-(4-hydroxybenzoate) | C22H18O9 | 425.087 | 2.25 | Flavonoid |
| 30 | 7.209 | Potassium 2-(1′-ethoxy) ethoxypropanoate | C7H144 | 161.0815 | 2.85 | Organic Salt |
| 31 | 7.334 | Epicatechin | C15H14O6 | 289.071 | 2.55 | Flavonoid |
| 32 | 7.359 | 3,4-Dihydroxybenzaldehyde | C7H6O3 | 137.0241 | 2.23 | Phenolic Compound |
| 33 | 8.261 | Phloracetophenone | C8H8O4 | 167.0346 | 2.48 | Phenolic Compound |
| 34 | 8.311 | Bisbynin | C15H22O5 | 281.1386 | 3.27 | Sesquiterpenoid |
| 35 | 8.524 | APIIN | C26H28O14 | 563.1395 | 2.03 | Flavonoid Glycoside |
| 36 | 8.913 | Dihydroferulic acid 4-O-glucuronide | C16H20O10 | 371.0977 | 2.13 | Phenylpropanoid Glycoside |
| 37 | 9.965 | Phloroacetophenone 6′-[xylosyl-(1->6)-glucoside] | C21H30O13 | 489.1606 | 1.86 | Phenolic Glycoside |
| 38 | 9.99 | Lentialexin | C8H8O | 119.05 | 2.53 | Phenolic Compound |
| 39 | 10.441 | Sinapic acid | C11H12O5 | 223.0605 | 2.99 | Phenylpropanoid |
| 40 | 10.579 | Scytalone | C10H10O4 | 193.0499 | 3.79 | Phenolic Compound |
| 41 | 12.32 | p-Salicylic acid | C7H6O3 | 137.0242 | 1.92 | Phenolic Acid |
| 42 | 12.872 | 9S,10S,11R-trihydroxy-12Z-octadecenoic acid | C18H34O5 | 329.2331 | 0.03 | Fatty Acid |
| 43 | 13.347 | Isoleptospermone | C15H22O4 | 265.1435 | 3.73 | Sesquiterpenoid |
| 44 | 13.724 | Myrsinone | C17H26O4 | 293.1753 | 1.98 | Diterpenoid |
| 45 | 13.773 | Thyrotropin-releasing hormone | C16H22N6O4 | 361.1626 | 0.92 | Peptide Hormone |
| 46 | 14.074 | (±)12,13-DiHOME | C18H34O4 | 313.2381 | 1.05 | Fatty Acid |
| 47 | 14.112 | Val His Lys | C17H30N6O4 | 381.2249 | 1.47 | Tripeptide |
| 48 | 14.726 | 13(S)-HODE | C18H32O3 | 295.2272 | 2.51 | Fatty Acid |
| 49 | 19.098 | Vaccenic acid | C18H34O2 | 281.2477 | 2.76 | Fatty Acid |
| Positive mode | ||||||
| 1 | 1.897 | Betaine | C5H12NO2 | 118.0866 | −2.79 | Quaternary Ammonium Compound |
| 2 | 1.997 | Sucrose | C12H22O11 | 365.1057 | −1.76 | Carbohydrate |
| 3 | 2.072 | Cytosine | C4H5N3O | 112.0508 | −2.79 | Nucleobase |
| 4 | 2.147 | Epidermin | C11H19NO6 | 262.1285 | 0.31 | Lipopeptide |
| 5 | 2.348 | Niacin (Nicotinic acid) | C6H5NO2 | 124.0399 | −4.53 | Vitamin (B-complex) |
| 6 | 2.473 | Pro Leu | C11H20N2O3 | 229.1554 | −2.92 | Dipeptide |
| 7 | 2.523 | Hypoxanthine | C5H4N4O | 137.0462 | −3.61 | Purine Derivative |
| 8 | 2.548 | N-Methylanthranilic Acid | C8H9NO2 | 152.0709 | −2.64 | Alkaloid |
| 9 | 2.724 | (S)-2,3-Dihydro-3,5-dihydroxy-2-oxo-3-indoleacetic acid 5-glucoside | C16H19NO10 | 408.0902 | −0.02 | Indole Glucoside |
| 10 | 2.824 | Pyroglutamic acid | C5H7NO3 | 130.0498 | 0.71 | Amino Acid Derivative |
| 11 | 2.924 | Adenosine | C10H13N5O4 | 268.1045 | −0.36 | Nucleoside |
| 12 | 3.037 | Pirbuterol | C12H20N2O3 | 241.1549 | −1.12 | Beta-Agonist |
| 13 | 3.1 | Guanine | C5H5N5O | 152.0572 | −3.68 | Nucleobase |
| 14 | 3.325 | Pirbuterol | C12H20N2O3 | 241.1548 | −0.6 | Benzoxazinoid |
| 15 | 3.551 | Pirbuterol | C12H20N2O3 | 241.1548 | −0.58 | Vitamin (B-complex) |
| 16 | 4.002 | DIMBOA-Glc | C15H19NO10 | 374.1082 | 0.04 | Aminobenzoic Acid Derivative |
| 17 | 4.803 | Pantothenic Acid | C9H17NO5 | 242.1004 | −1.89 | Flavonoid |
| 18 | 6.282 | 3-Amino-2-naphthoic acid | C11H9NO2 | 188.0711 | −2.28 | Polysaccharide |
| 19 | 6.808 | Procyanidin B2 | C30H26O12 | 579.1491 | 1.19 | Alkaloid |
| 20 | 7.083 | Galactan | C20 H36O16 | 571.1626 | 1.07 | Phenylpropanoid |
| 21 | 9.564 | Gelsedine | C19H24 N2 O3 | 346.2128 | −0.8 | Alkaloid |
| 22 | 10.516 | 3-(3,4-Methylenedioxyphenyl)propenal | C10H8O3 | 177.0547 | −1.07 | Tripeptide |
| 23 | 10.541 | Compound IV | C20H26N2O3 | 360.2287 | −1.78 | Aminoglycoside |
| 24 | 13.084 | His Gln Glu | C16H24N6O7 | 413.1784 | −1.13 | Tripeptide |
| 25 | 13.159 | 1-O-[2-(Acetylamino)-2-deoxy-alpha-D-glucopyranosyl]-D-myo-Inositol | C14H25NO11 | 401.1782 | −4.58 | Peptide Toxin |
| 26 | 13.222 | Asn His Gly | C12H18N6O5 | 327.1419 | −3.03 | Sphingolipid |
| 27 | 13.272 | HC Toxin | C21H32N4O6 | 459.2199 | 3.23 | Sphingolipid |
| 28 | 13.323 | Phytosphingosine | C18H39NO3 | 318.301 | −1.76 | Tripeptide |
| 29 | 13.372 | C16 Sphinganine | C16H35NO2 | 274.2741 | −0.11 | Tripeptide |
| 30 | 13.423 | Gln Phe Met | C19H28N4O5S | 425.1849 | 0.93 | Sphingolipid |
| 31 | 13.448 | Thr His Gln | C15H24N6O6 | 385.1841 | −3.31 | Hydroxy Fatty Acid |
| 32 | 13.523 | C17 Sphinganine | C17H37NO2 | 288.2898 | −0.43 | Cytokinin Derivative |
| 33 | 13.748 | (3S,4S)-3-hydroxytetradecane-1,3,4-tricarboxylic acid | C17H30O7 | 369.1884 | 0.19 | Phosphonoglycine |
| 34 | 13.924 | trans-Zeatin-O-glucoside riboside | C21H31N5O10 | 531.2409 | −0.34 | Tripeptide |
| 35 | 14.187 | N-Acetylbialaphos | C13H24N3O7P | 383.1684 | 1.33 | Fatty Acid Amide |
| 36 | 14.387 | Tyr Asn Gln | C18H25N5O7 | 441.2094 | −1.22 | Ester |
| 37 | 14.75 | dodecanamide | C12H25NO | 200.2011 | −1.07 | Fatty Acid Amide |
| 38 | 15.327 | Dibutyl phthalate | C16H22O4 | 301.1421 | −3.45 | Fatty Acid Amide |
| 39 | 16.442 | 13E-Docosenamide | C22H43NO | 338.3422 | −1.14 | Bile Acid |
| 40 | 19.085 | N-stearoyl valine | C23H45NO3 | 406.3288 | 0.99 | Aminophenone Derivative |
| 41 | 22.355 | 6β-Hydroxy-3-oxo-5β-cholan-24-oic Acid | C24H38O4 | 413.266 | 0.67 | Quaternary Ammonium Compound |
| 42 | 22.568 | 2-(ethylamino)-4′-hydroxy-Propiophenone | C11H15NO2 | 194.1175 | 0.3 | Carbohydrate |
| No. | RT (min) | Identification | Molecular Formula | Experimental Mass (m/z) | Error (ppm) | Category |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Negative mode | ||||||
| 1 | 1.865 | D-Sorbitol | C6H14O6 | 181.0714 | 2.19 | Sugar Alcohol |
| 2 | 2.028 | Sucrose | C12H22O11 | 341.1091 | −0.43 | Carbohydrate |
| 3 | 2.04 | Glyceric acid | C3H6O4 | 105.019 | 3.04 | Organic Acid |
| 4 | 2.241 | Pyroglutamic acid | C5H7NO3 | 128.0351 | 1.62 | Amino Acid Derivative |
| 5 | 2.892 | 2,3-Dihydroxy-2-methylbutanoic acid | C5H10O4 | 133.0504 | 3.97 | Organic Acid |
| 6 | 4.809 | Pantothenic Acid | C9H17NO5 | 218.1029 | 2.17 | Vitamin (B-complex) |
| 7 | 5.874 | 3,4-Dihydroxybenzoic acid | C7H6O4 | 153.0192 | 0.93 | Phenolic Acid |
| 8 | 5.899 | Pyrocatechol | C6H6O2 | 109.0293 | 1.51 | Phenol |
| 9 | 6.701 | Procyanidin B2 | C30H26O12 | 577.1349 | 0.74 | Flavonoid |
| 10 | 6.851 | Epigallocatechin 3-O-(4-hydroxybenzoate) | C22H18O9 | 425.0867 | 2.48 | Flavonoid |
| 11 | 6.914 | Cinnamtannin A1 | C45H38O18 | 865.197 | 2.04 | Flavonoid (Tannin) |
| 12 | 7.264 | Epicatechin | C15H14O6 | 289.0716 | 0.86 | Flavonoid |
| 13 | 7.352 | 3,4-Dihydroxybenzaldehyde | C7H6O3 | 137.0244 | 0.38 | Phenolic Aldehyde |
| 14 | 8.329 | Bisbynin | C15H22O5 | 281.1387 | 2.81 | Phenolic Compound |
| 15 | 8.705 | APIIN | C26H28O14 | 563.1397 | 1.9 | Flavonoid Glycoside |
| 16 | 9.958 | Phloroacetophenone 6′-[xylosyl-(1->6)-glucoside] | C21H30O13 | 489.1602 | 2.26 | Phenolic Glycoside |
| 17 | 9.958 | Lentialexin | C8H8O | 119.0501 | 1.48 | Phenylpropanoid |
| 18 | 10.434 | Sinapic acid | C11H12O5 | 223.0607 | 2.33 | Phenolic Acid |
| 19 | 10.572 | Scytalone | C10H10O4 | 193.0498 | 4.31 | Phenolic Compound |
| 20 | 10.584 | Phloridzin | C21H24O10 | 435.1281 | 3.66 | Flavonoid Glycoside |
| 21 | 11.01 | Natsudaidain 3-(4-O-3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaroylglucoside) | C33H40O18 | 723.2127 | 2.3 | Phenolic Glycoside |
| 22 | 12.313 | p-Salicylic acid | C7H6O3 | 137.0242 | 1.84 | Phenolic Acid |
| 23 | 12.514 | Luteolin | C15H10O6 | 285.0397 | 2.54 | Flavonoid |
| 24 | 12.802 | 9,10,13-Trihydroxystearic acid | C18H36O5 | 331.2484 | 2.09 | Hydroxy Fatty Acid |
| 25 | 12.865 | 9S,10S,11R-trihydroxy-12Z-octadecenoic acid | C18H34O5 | 329.2336 | −0.31 | Hydroxy Fatty Acid |
| 26 | 12.964 | Diosmetin | C16H12O6 | 299.0555 | 2.07 | Flavonoid |
| 27 | 13.015 | 9,10-dihydroxy-hexadecanoic acid | C16H32O4 | 287.2224 | 1.38 | Hydroxy Fatty Acid |
| 28 | 13.34 | N-Oleoyl-L-Serine | C21H39NO4 | 368.28 | 1.63 | Fatty Acid Amide |
| 29 | 13.441 | Obliquine | C26H28N2O5 | 447.1921 | 0.92 | Alkaloid |
| 30 | 13.566 | Lipomycin | C32H45NO9 | 586.2997 | 4.59 | Polyketide |
| 31 | 13.716 | Myrsinone | C17H26O4 | 293.175 | 2.74 | Phenolic Compound |
| 32 | 13.766 | S-cucujolide V | C14H22O2 | 221.1538 | 4 | Macrolide Compound |
| 33 | 13.967 | LysoPE(0:0/14:0) | C19H40NO7P | 424.2465 | 1.26 | Lysophospholipid |
| 34 | 14.142 | (±)12,13-DiHOME | C18H34O4 | 313.2382 | 0.84 | Hydroxy Fatty Acid |
| 35 | 14.418 | 9,14-dihydroxy-octadecanoic acid | C18H36O4 | 315.253 | 3.56 | Hydroxy Fatty Acid |
| 36 | 14.455 | PE(18:2(9Z,12Z)/0:0) | C23H44NO7P | 476.2774 | 2.35 | Phospholipid |
| 37 | 14.543 | 8-HpODE | C18H32O4 | 311.2229 | −0.09 | Hydroxy Fatty Acid |
| 38 | 14.769 | 13(S)-HODE | C18H32O3 | 295.2275 | 1 | Hydroxy Fatty Acid |
| 39 | 14.919 | (S)-Nerolidol 3-O-[a-L-rhamnopyranosyl-(1->2)-b-D-glucopyranoside] | C27H46O10 | 529.3019 | 0.38 | Glycoside |
| 40 | 15.019 | Ricinoleic acid | C18H34O3 | 297.2431 | 1.78 | Hydroxy Fatty Acid |
| 41 | 16.046 | cholesterol sulfate | C27H46O4S | 465.3063 | −4.06 | Steroid Sulfate |
| 42 | 16.948 | cis-9,10-Epoxystearic acid | C18H34O3 | 297.2427 | 2.94 | Epoxy Fatty Acid |
| 43 | 17.324 | 10E,12Z-Octadecadienoic acid | C18H32O2 | 279.2321 | 2.91 | Unsaturated Fatty Acid |
| 44 | 18.276 | 19-hydroxy-nonadecanoic acid | C19H38O3 | 313.2741 | 2.61 | Hydroxy Fatty Acid |
| 45 | 18.715 | DL-2-hydroxy stearic acid | C18H36O3 | 299.2587 | 1.8 | Hydroxy Fatty Acid |
| 46 | 18.74 | PG(18:2(9Z,12Z)/0:0) | C24H45O9P | 507.2726 | 0.91 | Phospholipid |
| 47 | 19.053 | Vaccenic acid | C18H34O2 | 281.2482 | 1.33 | Unsaturated Fatty Acid |
| 48 | 19.291 | Elaidic Acid | C18H34O2 | 281.2484 | 0.86 | Unsaturated Fatty Acid |
| 49 | 21.458 | 15-methoxy-tricosanoic acid | C24H48O3 | 383.3523 | 2.19 | Methoxy Fatty Acid |
| 50 | 22.336 | PG(16:0/0:0) | C22H45O9P | 483.2726 | 0.65 | Phospholipid |
| Positive mode | ||||||
| 1 | 1.887 | Betaine | C5H12NO2 | 118.0866 | −3.36 | Quaternary Ammonium Compound |
| 2 | 1.974 | Sucrose | C12H22O11 | 365.1057 | −1.05 | Disaccharide |
| 3 | 3.39 | Pro Leu | C11H20N2O3 | 229.1552 | −1.75 | Dipeptide |
| 4 | 6.197 | 3-Amino-2-naphthoic acid | C11H9NO2 | 188.0709 | −1.36 | Amino Acid Derivative |
| 5 | 6.698 | Procyanidin B2 | C30H26O12 | 579.1492 | 1.12 | Flavonoid |
| 6 | 7.073 | Galactan | C20H36O16 | 571.163 | 0.64 | Polysaccharide |
| 7 | 9.103 | Ceanothine E | C34H40N4O4 | 569.3138 | −2.73 | Alkaloid |
| 8 | 9.554 | Gelsedine | C19H24N2O3 | 346.2129 | −1.08 | Alkaloid |
| 9 | 9.905 | Coumarin | C9H6O2 | 147.044 | −0.23 | Benzopyrone |
| 10 | 10.381 | Compound IV | C20H26N2O3 | 360.2288 | −2.47 | Alkaloid |
| 11 | 10.456 | Eugenin | C11H10O4 | 207.0653 | −0.67 | Phenolic Compound |
| 12 | 12.072 | Pro Asp Arg | C15H26N6O6 | 387.1991 | −1.34 | Tripeptide |
| 13 | 12.21 | Quinoline | C9H7N | 130.0653 | −3.54 | Heterocyclic Compound |
| 14 | 12.36 | Patuletin 3-rhamnoside-7-(3′′′,4′′′-diacetylrhamnoside) | C32H36O18 | 709.194 | 4.96 | Flavonoid Glycoside |
| 15 | 12.41 | Berberine | C20H18NO4 | 336.1231 | −0.03 | Alkaloid |
| 16 | 12.811 | 6-Epi-7-isocucurbic acid glucoside | C18H30O8 | 397.1836 | −0.64 | Glycoside |
| 17 | 12.836 | HC Toxin | C21H32N4O6 | 459.22 | 2.18 | Cyclic Tetrapeptide |
| 18 | 12.861 | 9S,10S,11R-trihydroxy-12Z-octadecenoic acid | C18H34O5 | 353.2301 | −0.42 | Hydroxy Fatty Acid |
| 19 | 13.012 | Leu Lys Asp | C16H30N4O6 | 413.1786 | −0.06 | Tripeptide |
| 20 | 13.061 | Glucosyl (E)-2,6-Dimethyl-2,5-heptadienoate | C15H24O7 | 339.1415 | −0.18 | Glycoside |
| 21 | 13.212 | C16 Sphinganine | C16H35NO2 | 274.2748 | −2.57 | Sphingolipid |
| 22 | 13.362 | Thr His Gln | C15H24N6O6 | 385.1835 | −1.79 | Tripeptide |
| 23 | 13.538 | Dehydrophytosphingosine | C18H37NO3 | 316.2851 | −1.54 | Sphingolipid |
| 24 | 13.613 | PI(16:1(9Z)/0:0) | C25H47O12P | 588.3145 | −0.02 | Phosphatidylinositol |
| 25 | 13.763 | Glucosyl sphingosine | C24H47NO7 | 462.3431 | −1.36 | Glycosphingolipid |
| 26 | 13.776 | Linoleamide | C18H33NO | 280.2641 | −1.83 | Fatty Acid Amide |
| 27 | 13.801 | (Z)-N-(2-hydroxyethyl)hexadec-7-enamide | C18H35NO2 | 298.275 | −2.92 | Amide Compound |
| 28 | 13.814 | Phytosphingosine | C18H39NO3 | 318.301 | −2.14 | Sphingolipid |
| 29 | 13.914 | Asp Phe Trp | C24H26N4O6 | 467.1946 | −4.71 | Tripeptide |
| 30 | 13.939 | 6-Hydroxyfluvastatin | C24H26FNO5 | 445.2129 | 1.24 | Statin |
| 31 | 14.001 | PI(20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)/0:0) | C29H51O12P | 640.346 | −0.44 | Phosphatidylinositol |
| 32 | 14.114 | Buprenorphine | C29H41NO4 | 468.3103 | 1.74 | Opioid |
| 33 | 14.151 | PC(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/0:0) | C26H49NO7P | 518.3247 | −1.01 | Phosphatidylcholine |
| 34 | 14.239 | PE(17:0/0:0) | C22H46NO7P | 490.2911 | −1.14 | Phosphatidylethanolamine |
| 35 | 14.364 | Sphinganine | C18H39NO2 | 302.306 | −0.74 | Sphingolipid |
| 36 | 14.49 | Dihydroceramide C2 | C20H41NO3 | 344.3169 | −2.76 | Sphingolipid |
| 37 | 14.565 | PI(18:1(9Z)/0:0) | C27H51O12P | 616.3462 | −0.73 | Phosphatidylinositol |
| 38 | 14.59 | PE(18:2(9Z,12Z)/0:0) | C23H44NO7P | 478.2935 | −1.28 | Phosphatidylethanolamine |
| 39 | 15.943 | Linoleoyl Ethanolamide | C20H37NO2 | 324.2906 | −2.58 | Fatty Acid Amide |
| 40 | 16.131 | SLF | C30H40N2O6 | 542.3224 | −0.06 | Sphingolipid |
| 41 | 16.218 | 20:2(5Z,9Z)(11Me,15Me,19Me) | C23H42O2 | 368.3528 | −1.28 | Fatty Acid Derivative |
| 42 | 17.17 | Oleoyl Ethanolamide | C20H39NO2 | 326.3056 | −0.88 | Fatty Acid Amide |
| 43 | 17.434 | PE(19:0/0:0) | C24H50NO7P | 518.3225 | −2.44 | Phosphatidylethanolamine |
| 44 | 22.382 | Prostaglandin F2α-biotin | C35H60N4O6S | 687.4138 | −1.94 | Biotinylated Compound |
| Amino Acid | Abbreviation | HPL/HPB | Amino Acid Content (mg/100 g Sample) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HDNR-W | HDNR-E | |||
| Essential amino acids (EAAs) | ||||
| Histidine | His | HPL | 0.48 a | 0.12 b |
| Isoleucine | Ile | HPB | 0.41 a | 0.37 b |
| Leucine | Leu | HPB | 0.69 b | 0.76 a |
| Lysine | Lys | HPL | 0.93 a | 0.27 b |
| Methionine | Met | HPB | 0.29 a | 0.13 b |
| Phenylalanine | Phe | HPB | 0.43 b | 0.50 a |
| Threonine | Thr | HPL | 1.13 a | 0.62 b |
| Tryptophan | Trp | HPB | ND | ND |
| Valine | Val | HPB | 1.22 a | 0.98 b |
| Total EAAs | 5.58 a | 3.75 b | ||
| Non-essential amino acids (NEAAs) | ||||
| Alanine | Ala | HPB | 2.40 a | 1.64 b |
| Arginine | Arg | HPL | 1.01 a | 0.48 b |
| Asparagine | Asn | HPL | ND | ND |
| Aspartic acid | Asp | HPL | 3.82 a | 1.51 b |
| Cystine | Cys | HPB | 0.44 a | 0.13 b |
| Glutamic acid | Glu | HPL | 4.46 a | 1.99 b |
| Glutamine | Gln | HPL | ND | ND |
| Glycine | Gly | HPB | 2.08 a | 1.04 b |
| Hydroxy proline | HyPro | HPL | 0.23 | ND |
| Hydroxylysine | HyLys | HPL | 0.60 | ND |
| Proline | Pro | HPB | 0.55 | ND |
| Serine | Ser | HPL | 1.09 a | 0.69 b |
| Tyrosine | Tyr | HPB | 0.54 b | 0.56 a |
| Total NEAAs | 17.22 a | 8.04 b | ||
| Total hydrophobic amino acids (HPBs) | 9.05 a | 6.11 b | ||
| Total hydrophilic amino acids (HPLs) | 13.75 a | 5.68 b | ||
| Nonprotein Amino Acids (NPAAs) | ||||
| Ornithine | Orn | 0.05 a | 0.04 a | |
| Taurine | Tau | 0.06 b | 0.10 a | |
| α-Amino-n-butyric acid | AABA | 0.06 | ND | |
| β-Alanine | β-Ala | 0.27 a | 0.18 b | |
| β-Amino isobutyric acid | BAIBA | 0.05 a | 0.05 a | |
| γ-Amino-n-butyric acid | GABA | 1.57 a | 0.94 b | |
| Total NPAAs | 2.06 a | 1.31 b | ||
| Fatty Acid | Fatty Acid Content (%) | |
|---|---|---|
| HDNR-W | HDNR-E | |
| Saturated fatty acid (SFA) | ||
| C14:0 | 1.03 | 1.02 |
| C16:0 | 21.87 | 24.23 |
| C18:0 | 2.78 | 2.13 |
| C20:0 | ND | 0.40 |
| C21:0 | ND | 0.01 |
| C22:0 | ND | 0.10 |
| C24:0 | ND | 0.17 |
| Monounsaturated fatty acid (MUFA) | ||
| C18:1n9t | ND | ND |
| C18:1n9c | 40.19 | 30.57 |
| Polyunsaturated fatty acid (PUFA) | ||
| C18:2n6c | 34.13 | 39.83 |
| C18:3n6 | ND | ND |
| C18:3n3 | ND | 1.52 |
| C20:2 | ND | 0.02 |
| Total SFA | 25.68 | 28.05 |
| Total USFA * | 74.32 | 71.95 |
| Total MUFA | 40.19 | 30.57 |
| Total PUFA | 34.13 | 41.37 |
| Concentration (mg/kg) | As | Cd | Cr | Cu | Mn | Ni | Pb | Zn | Fe |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HDNR-W | 0.026 | 0.002 | 0.030 | 0.114 | 1.913 | 0.118 | 0.006 | 0.257 | 0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chaithong, S.; Sukkarn, P.; Aenglong, C.; Woonnoi, W.; Klaypradit, W.; Suttithumsatid, W.; Chinfak, N.; Seatan, J.; Tanasawet, S.; Sukketsiri, W. Biological Activities and Phytochemical Profile of Hawm Gra Dang Ngah Rice: Water and Ethanolic Extracts. Foods 2025, 14, 1119. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14071119
Chaithong S, Sukkarn P, Aenglong C, Woonnoi W, Klaypradit W, Suttithumsatid W, Chinfak N, Seatan J, Tanasawet S, Sukketsiri W. Biological Activities and Phytochemical Profile of Hawm Gra Dang Ngah Rice: Water and Ethanolic Extracts. Foods. 2025; 14(7):1119. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14071119
Chicago/Turabian StyleChaithong, Suchanat, Pinwadee Sukkarn, Chakkapat Aenglong, Wanwipha Woonnoi, Wanwimol Klaypradit, Wiwit Suttithumsatid, Narainrit Chinfak, Jirawat Seatan, Supita Tanasawet, and Wanida Sukketsiri. 2025. "Biological Activities and Phytochemical Profile of Hawm Gra Dang Ngah Rice: Water and Ethanolic Extracts" Foods 14, no. 7: 1119. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14071119
APA StyleChaithong, S., Sukkarn, P., Aenglong, C., Woonnoi, W., Klaypradit, W., Suttithumsatid, W., Chinfak, N., Seatan, J., Tanasawet, S., & Sukketsiri, W. (2025). Biological Activities and Phytochemical Profile of Hawm Gra Dang Ngah Rice: Water and Ethanolic Extracts. Foods, 14(7), 1119. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14071119





