Prevalence, Molecular Characterization, and Antimicrobial Resistance Profile of Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli Isolates from Pig Farms in China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Isolates
2.2. Investigation of Virulence
- Hemolytic activity of ETEC strains
- b.
- Hemolytic activity of ETEC supernatants
- c.
- Galleria mellonella infection model
- d.
- Cytotoxicity
2.3. Transcriptional Analysis of Virulence Genes by Quantitative Real-Time qPCR
2.4. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Test
2.5. Library Construction and DNA Sequencing
2.6. Analysis of AMR Genes, Virulence Genes, and Serogroups
2.7. Correlation Analysis
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
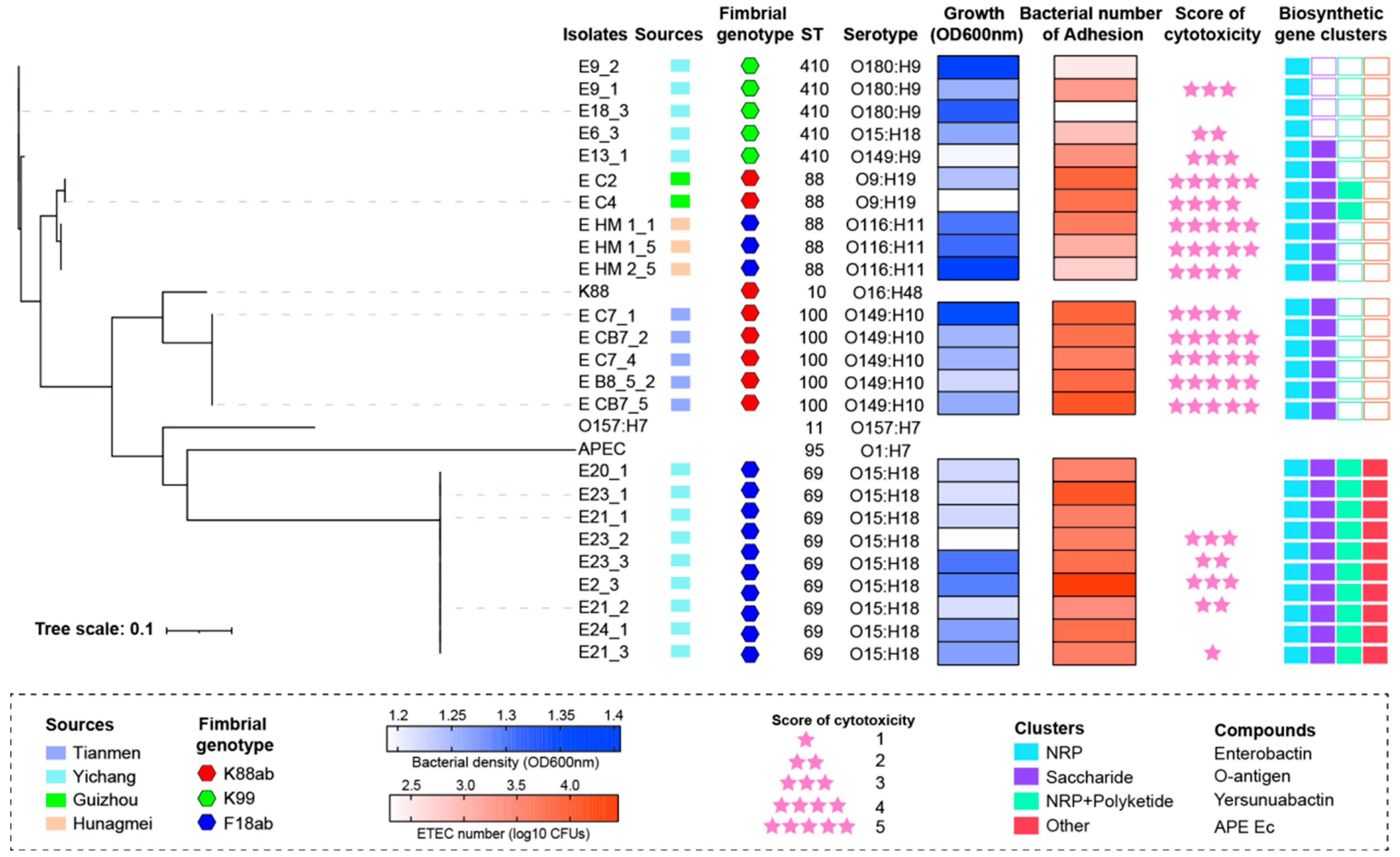
3.1. Characterization and Isolation of ETEC from Different Farms in China
3.2. Evaluation of ETEC Toxicity In Vitro and In Vivo
3.3. MLST and Serotype of ETEC Isolates
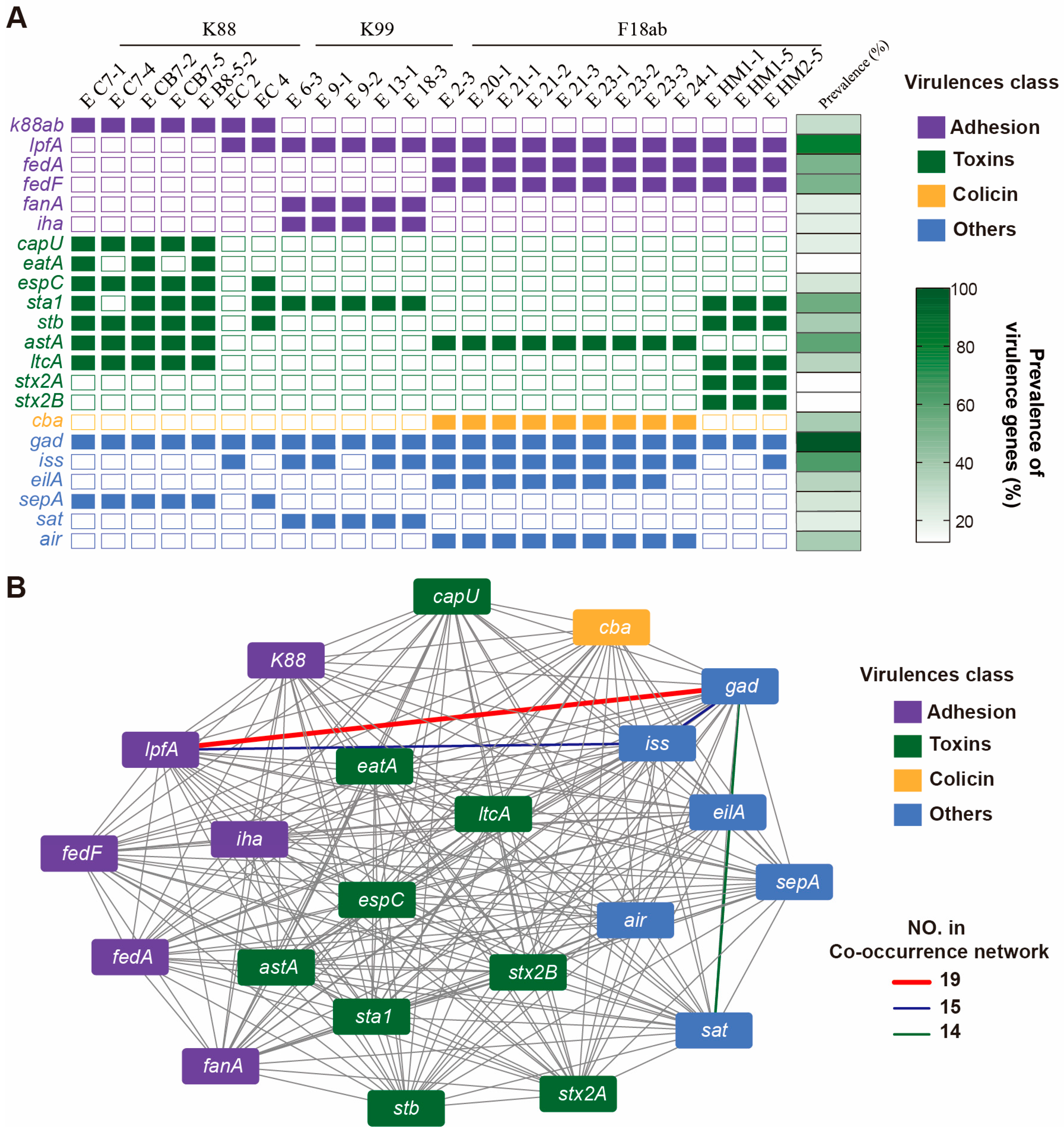
3.4. Toxin Genes Carried in ETEC Isolates
3.5. Correlation Analysis Among Bacterial Growth, Adhesion, and Cytotoxicity
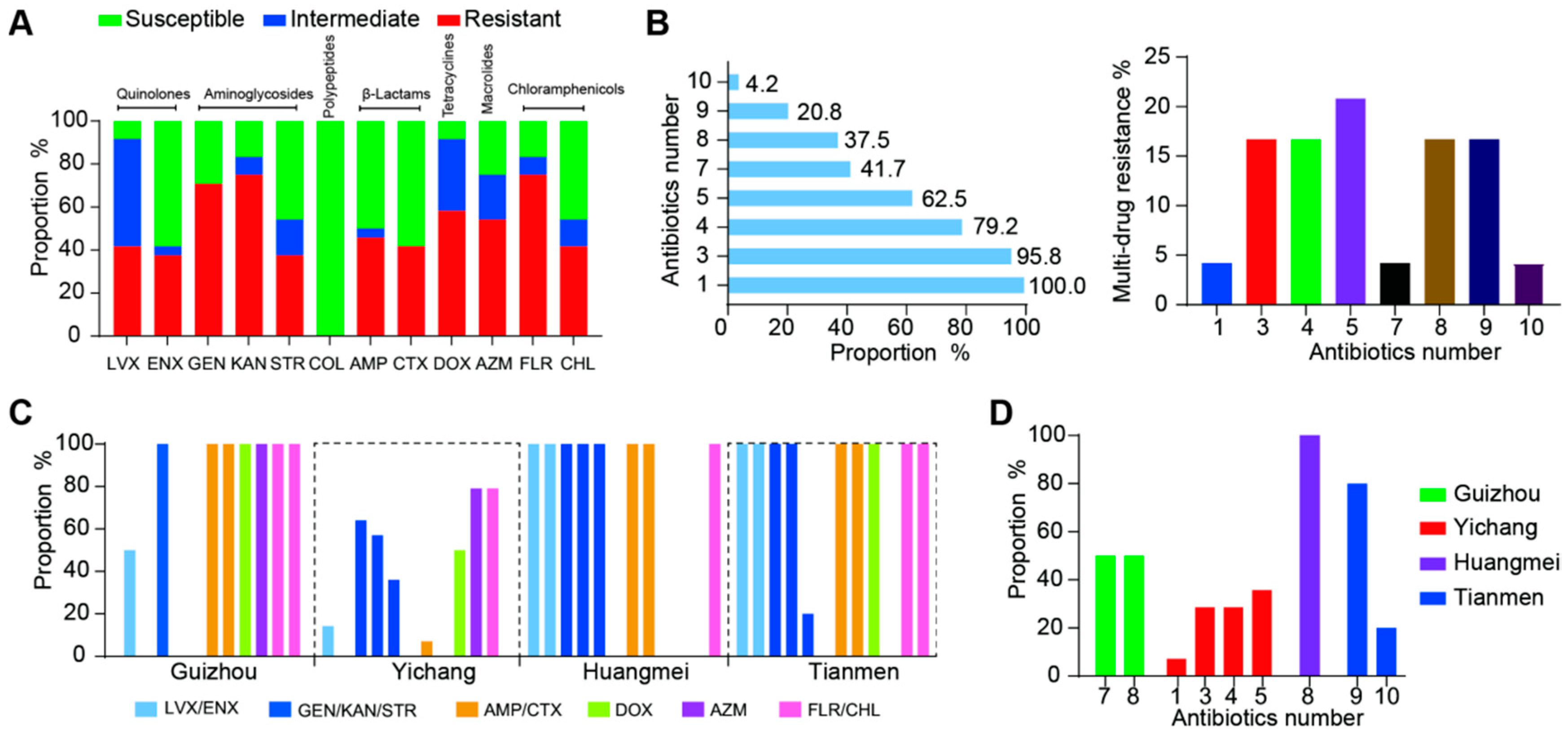
3.6. Antimicrobial Resistance of ETEC Isolates
3.7. Antibacterial Genes Carried in ETEC Isolates
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Underwood, W.J.; McGlone, J.J.; Swanson, J.; Anderson, K.A.; Anthony, R. Agricultural Animal Welfare. Lab. Anim. Welf. 2014, 46, 233–278. [Google Scholar]
- O’Meara, S. Antimicrobial resistance. Nature 2020, 586, S49. [Google Scholar]
- Murray, C.J.L.; Ikuta, K.S.; Sharara, F.; Swetschinski, L.; Robles Aguilar, G.; Gray, A.; Han, C.; Bisignano, C.; Rao, P.; Wool, E.; et al. Global burden of bacterial antimicrobial resistance in 2019: A systematic analysis. Lancet 2022, 399, 629–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olaf Mol, B.O. Molecular and structural aspects of fimbriae biosynthesis and assembly in Escherichia coli. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 1996, 19, 28. [Google Scholar]
- Luppi, A.; Gibellini, M.; Gin, T.; Vangroenweghe, F.; Vandenbroucke, V.; Bauerfeind, R.; Bonilauri, P.; Labarque, G.; Hidalgo, A. Prevalence of virulence factors in enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli isolated from pigs with post-weaning diarrhoea in Europe. Porc. Health Manag. 2016, 2, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco, J.; Blanco, M.; Garabal, J.I.; Gonzalez, E.A. Enterotoxins, colonization factors and serotypes of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli from humans and animals. Microbiologia 1991, 7, 57–73. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- von Mentzer, A.; Svennerholm, A.M. Colonization factors of human and animal-specific enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC). Trends Microbiol. 2024, 32, 448–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joffre, E.; von Mentzer, A.; Svennerholm, A.M.; Sjoling, A. Identification of new heat-stable (STa) enterotoxin allele variants produced by human enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC). Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2016, 306, 586–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikh, A.; Tumala, B.; Vickers, T.J.; Martin, J.C.; Rosa, B.A.; Sabui, S.; Basu, S.; Simoes, R.D.; Mitreva, M.; Storer, C.; et al. Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli heat-labile toxin drives enteropathic changes in small intestinal epithelia. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 6886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleckenstein, J.M.; Hardwidge, P.R.; Munson, G.P.; Rasko, D.A.; Sommerfelt, H.; Steinsland, H. Molecular mechanisms of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli infection. Microbes Infect. 2010, 12, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubreuil, J.D. Pig vaccination strategies based on enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli toxins. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2021, 52, 2499–2509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, D.; Li, X.; Duan, X.; Yang, L.; Luo, B.; Wang, L.; Hu, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Qian, P. Recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae EBY100/pYD1-FaeG: A candidate for an oral subunit vaccine against F4+ ETEC infection. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2024, 91, e0181724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, C.; She, Y.; Fu, F.; Xu, C. Production of a new tetravalent vaccine targeting fimbriae and enterotoxin of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Can. J. Vet. Res. 2024, 88, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ruan, X.; Liu, M.; Casey, T.A.; Zhang, W. A tripartite fusion, FaeG-FedF-LT(192)A2:B, of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC) elicits antibodies that neutralize cholera toxin, inhibit adherence of K88 (F4) and F18 fimbriae, and protect pigs against K88ac/heat-labile toxin infection. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2011, 18, 1593–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Upadhyay, I.; Lauder, K.L.; Li, S.; Ptacek, G.; Zhang, W. Intramuscularly Administered Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC) Vaccine Candidate MecVax Prevented H10407 Intestinal Colonization in an Adult Rabbit Colonization Model. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e0147322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Food Safety Authority; European Centre for Disease, Prevention and Control. The European Union Summary Report on Antimicrobial Resistance in zoonotic and indicator bacteria from humans, animals and food in 2018/2019. EFSA J. 2021, 19, e06490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anueyiagu, K.N.; Agu, C.G.; Umar, U.; Lopes, B.S. Antimicrobial Resistance in Diverse Escherichia coli Pathotypes from Nigeria. Antibiotics 2024, 13, 922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayer, S.S.; Rovira, A.; Olsen, K.; Johnson, T.J.; Vannucci, F.; Rendahl, A.; Perez, A.; Alvarez, J. Prevalence and trend analysis of antimicrobial resistance in clinical Escherichia coli isolates collected from diseased pigs in the USA between 2006 and 2016. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2020, 67, 1930–1941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahms, C.; Hubner, N.O.; Kossow, A.; Mellmann, A.; Dittmann, K.; Kramer, A. Occurrence of ESBL-Producing Escherichia coli in Livestock and Farm Workers in Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania, Germany. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0143326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Li, J.; Huang, X.; Xia, J.; Cui, M.; Huang, Y.; Wen, Y.; Xie, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Cao, S.; et al. Genomic traits of multidrug resistant enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli isolates from diarrheic pigs. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1244026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Liu, D.; Li, R.; Fu, Y.; Zhai, W.; Liu, X.; He, T.; Wu, C.; Bai, L.; Wang, Y. Polymorphism Existence of Mobile Tigecycline Resistance Gene tet(X4) in Escherichia coli. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2020, 64, e01825-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sisay, A.; Asmare, Z.; Kumie, G.; Gashaw, Y.; Getachew, E.; Ashagre, A.; Nigatie, M.; Ayana, S.; Misganaw, T.; Dejazmach, Z.; et al. Prevalence of carbapenem-resistant gram-negative bacteria among neonates suspected for sepsis in Africa: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Infect. Dis. 2024, 24, 838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.Y.; Wang, Y.; Walsh, T.R.; Yi, L.X.; Zhang, R.; Spencer, J.; Doi, Y.; Tian, G.; Dong, B.; Huang, X.; et al. Emergence of plasmid-mediated colistin resistance mechanism MCR-1 in animals and human beings in China: A microbiological and molecular biological study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2016, 16, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, X.; Wu, Y.; Yan, Z.; Ju, X.; Huang, Y.; Zhou, H.; Wang, Z.; Wang, S.; et al. National genomic epidemiology investigation revealed the spread of carbapenem-resistant Escherichia coli in healthy populations and the impact on public health. Genome Med. 2024, 16, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jean, S.S.; Harnod, D.; Hsueh, P.R. Global Threat of Carbapenem-Resistant Gram-Negative Bacteria. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 823684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaufuss, P.; Steller, U. Haemolytic activities of Trichophyton species. Med. Mycol. 2003, 41, 511–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, F.; Chen, Y.; Sun, T.; Wu, Y.; Su, Y.; Liu, C.; Zhou, J.; Deng, Y.; Wen, J. Antimicrobial resistance, virulence characteristics and genotypes of Bacillus spp. from probiotic products of diverse origins. Food Res. Int. 2021, 139, 109949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- A, A.J.; Suresh, A. Oral microbial shift induced by probiotic Bacillus coagualans along with its clinical perspectives. J. Oral. Biol. Craniofac Res. 2023, 13, 398–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treangen, T.J.; Ondov, B.D.; Koren, S.; Phillippy, A.M. The Harvest suite for rapid core-genome alignment and visualization of thousands of intraspecific microbial genomes. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bortolaia, V.; Kaas, R.S.; Ruppe, E.; Roberts, M.C.; Schwarz, S.; Cattoir, V.; Philippon, A.; Allesoe, R.L.; Rebelo, A.R.; Florensa, A.F.; et al. ResFinder 4.0 for predictions of phenotypes from genotypes. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2020, 75, 3491–3500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Yang, J.; Yu, J.; Yao, Z.; Sun, L.; Shen, Y.; Jin, Q. VFDB: A reference database for bacterial virulence factors. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33, D325–D328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, P.; Markiel, A.; Ozier, O.; Baliga, N.S.; Wang, J.T.; Ramage, D.; Amin, N.; Schwikowski, B.; Ideker, T. Cytoscape: A software environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks. Genome Res. 2003, 13, 2498–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stenutz, R.; Weintraub, A.; Widmalm, G. The structures of Escherichia coli O-polysaccharide antigens. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2006, 30, 382–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro-Garcia, F.; Serapio-Palacios, A.; Vidal, J.E.; Salazar, M.I.; Tapia-Pastrana, G. EspC promotes epithelial cell detachment by enteropathogenic Escherichia coli via sequential cleavages of a cytoskeletal protein and then focal adhesion proteins. Infect. Immun. 2014, 82, 2255–2265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarr, P.I.; Bilge, S.S.; Vary, J.C., Jr.; Jelacic, S.; Habeeb, R.L.; Ward, T.R.; Baylor, M.R.; Besser, T.E. Iha: A novel Escherichia coli O157:H7 adherence-conferring molecule encoded on a recently acquired chromosomal island of conserved structure. Infect. Immun. 2000, 68, 1400–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loos, S.; Oh, J.; van de Loo, L.; Kemper, M.J.; Blohm, M.; Schild, R. Hemoconcentration and predictors in Shiga toxin-producing E. coli-hemolytic uremic syndrome (STEC-HUS). Pediatr. Nephrol. 2021, 36, 3777–3783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Paruch, L.; Chen, X.; van Eerde, A.; Skomedal, H.; Wang, Y.; Liu, D.; Liu Clarke, J. Antibiotic Application and Resistance in Swine Production in China: Current Situation and Future Perspectives. Front. Vet. Sci. 2019, 6, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, T.; Peng, W.; Liu, Z.; Gao, T.; Liu, W.; Zhou, D.; Yang, K.; Guo, R.; Duan, Z.; Liang, W.; et al. Tea polyphenols inhibit the growth and virulence of ETEC K88. Microb. Pathog. 2021, 152, 104640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, C.; Zhang, H.; Guo, Q.; Duan, Y.; Chen, S.; Han, M.; Li, F.; Jin, M.; Wang, Y. Engineered Bacillus subtilis alleviates intestinal oxidative injury through Nrf2-Keap1 pathway in enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC) K88-infected piglet. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 2023, 24, 496–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Chen, Y.; Imre, K.; Arslan-Acaroz, D.; Istanbullugil, F.R.; Fang, Y.; Ros, G.; Zhu, K.; Acaroz, U. Mechanisms of probiotic Bacillus against enteric bacterial infections. One Health Adv. 2023, 1, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Peng, K.; She, Y.; Fu, F.; Shi, Q.; Lin, Y.; Xu, C. Preparation of novel trivalent vaccine against enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli for preventing newborn piglet diarrhea. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2023, 84, ajvr.22.10.0183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubreuil, J.D.; Isaacson, R.E.; Schifferli, D.M. Animal Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Eco. Sal. Plus 2016, 7, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Liu, H.; Cao, S.; Cheng, P.; Li, F.; Ishfaq, M.; Sun, J.; Zhang, X. Resistance Detection and Transmission Risk Analysis of Pig-Derived Pathogenic Escherichia coli in East China. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 614651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, F.; Wang, J.; Li, D.; Gao, S.; Ren, J.; Ma, L.; Liu, F.; Zhuge, X.; Yan, G.; Lu, Y.; et al. Comparative genomic analysis of 127 Escherichia coli strains isolated from domestic animals with diarrhea in China. BMC Genomics 2019, 20, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helgerson, A.F.; Sharma, V.; Dow, A.M.; Schroeder, R.; Post, K.; Cornick, N.A. Edema disease caused by a clone of Escherichia coli O147. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2006, 44, 3074–3077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parreira, V.R.; Liao, J.H.; Kim, S.H.; Gyles, C.L. A homolog of the O157 urease-encoding O island 48 is present in porcine O149:H10 enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Vet. Res. 2008, 39, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orskov, I.; Orskov, F.; Wittig, W.; Sweeney, E.J. A new E. coli serotype O149:K9 (B), K88ac (L): H10 isolated from diseased swine. Acta Pathol. Microbiol. Scand. 1969, 75, 491–498. [Google Scholar]
- Chung, S.Y.; Kwon, T.; Bak, Y.S.; Park, J.J.; Kim, C.H.; Cho, S.H.; Kim, W. Comparative genomic analysis of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli O159 strains isolated from diarrheal patients in Korea. Gut Pathog. 2019, 11, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, D.; Choi, C.; Jung, T.; Chung, H.K.; Kim, J.P.; Bae, S.S.; Cho, W.S.; Kim, J.; Chae, C. Genotypic prevalence of the fimbrial adhesins (F4, F5, F6, F41 and F18) and toxins (LT, STa, STb and STx2e) in Escherichia coli isolated from postweaning pigs with diarrhoea or oedema disease in Korea. Vet. Rec. 2002, 150, 35–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zajacova, Z.S.; Konstantinova, L.; Alexa, P. Detection of virulence factors of Escherichia coli focused on prevalence of EAST1 toxin in stool of diarrheic and non-diarrheic piglets and presence of adhesion involving virulence factors in astA positive strains. Vet. Microbiol. 2012, 154, 369–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, D.J.; Choi, S.; Jeon, S.B.; Jeong, S.; Park, H.; Lee, B.H.; Kim, G.B.; Yang, S.J.; Nishikawa, Y.; Choi, C. Comparative sequence analysis of enteroaggregative Escherichia coli heat-stable enterotoxin 1 identified in Korean and Japanese Escherichia coli strains. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2017, 243, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, K.; Kansal, R.; Bartels, S.R.; Hamilton, D.J.; Shaaban, S.; Fleckenstein, J.M. Adhesin degradation accelerates delivery of heat-labile toxin by enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 29771–29779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheutz, F.; Teel, L.D.; Beutin, L.; Pierard, D.; Buvens, G.; Karch, H.; Mellmann, A.; Caprioli, A.; Tozzoli, R.; Morabito, S.; et al. Multicenter evaluation of a sequence-based protocol for subtyping Shiga toxins and standardizing Stx nomenclature. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2012, 50, 2951–2963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Do, K.H.; Byun, J.W.; Lee, W.K. Prevalence of O-serogroups, virulence genes, and F18 antigenic variants in Escherichia coli isolated from weaned piglets with diarrhea in Korea during 2008–2016. J. Vet. Sci. 2019, 20, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bugarel, M.; Beutin, L.; Martin, A.; Gill, A.; Fach, P. Micro-array for the identification of Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli (STEC) seropathotypes associated with Hemorrhagic Colitis and Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome in humans. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2010, 142, 318–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kariminik, A.; Saeidi, M.; Parsia, P. Cloning and expression of rice glutamate decarboxylase (GAD) in Escherichia coli. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand) 2017, 63, 106–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matussek, A.; Jernberg, C.; Einemo, I.M.; Monecke, S.; Ehricht, R.; Engelmann, I.; Lofgren, S.; Mernelius, S. Genetic makeup of Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli in relation to clinical symptoms and duration of shedding: A microarray analysis of isolates from Swedish children. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2017, 36, 1433–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doekes, H.M.; de Boer, R.J.; Hermsen, R. Toxin production spontaneously becomes regulated by local cell density in evolving bacterial populations. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2019, 15, e1007333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sturbelle, R.T.; de Avila, L.F.; Roos, T.B.; Borchardt, J.L.; da Conceicao Rde, C.; Dellagostin, O.A.; Leite, F.P. The role of quorum sensing in Escherichia coli (ETEC) virulence factors. Vet. Microbiol. 2015, 180, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, C.; Borges, A.; Flament-Simon, S.C.; Simoes, M. Quorum sensing architecture network in Escherichia coli virulence and pathogenesis. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2023, 47, fuad031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puvaca, N.; de Llanos Frutos, R. Antimicrobial Resistance in Escherichia coli Strains Isolated from Humans and Pet Animals. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bassi, P.; Bosco, C.; Bonilauri, P.; Luppi, A.; Fontana, M.C.; Fiorentini, L.; Rugna, G. Antimicrobial Resistance and Virulence Factors Assessment in Escherichia coli Isolated from Swine in Italy from 2017 to 2021. Pathogens 2023, 12, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luppi, A. Swine enteric colibacillosis: Diagnosis, therapy and antimicrobial resistance. Porcine Health Manag. 2017, 3, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Z.; Hu, Z.; Li, Z.; Zhang, X.; Jia, C.; Li, T.; Dai, M.; Tan, C.; Xu, Z.; Wu, B.; et al. Antimicrobial resistance and population genomics of multidrug-resistant Escherichia coli in pig farms in mainland China. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, L.H.; Sorensen, S.J.; Jorgensen, H.S.; Jensen, L.B. The prevalence of the OqxAB multidrug efflux pump amongst olaquindox-resistant Escherichia coli in pigs. Microb. Drug Resist. 2005, 11, 378–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Gene Name | Sequences | Length (bp) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| K88 | F | TGGTAGTATCACTGCAGAT | 343 |
| R | CACTTTCACTGAACCAACT | ||
| K99 | F | GCTCGTATTGACTGGTCT | 157 |
| R | CAGCCGTAGTGAATGAAG | ||
| F18ab | F | ATAACTTGGAGCGGGCAGTTA | 252 |
| R | TTGTAAGTAACCGCGTAAGC | ||
| F41 | F | TGCTGATTGGACGGAAGGTC | 580 |
| R | GGTTGAAGCACTTTGCCCTG | ||
| 987P | F | TTCAGTGGTTACTCGCTCGC | 495 |
| R | AGTGACAGTACCGGCCGTAA | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, J.; Liu, Z.; Wang, S.; Gao, T.; Liu, W.; Yang, K.; Yuan, F.; Wu, Q.; Li, C.; Guo, R.; et al. Prevalence, Molecular Characterization, and Antimicrobial Resistance Profile of Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli Isolates from Pig Farms in China. Foods 2025, 14, 1188. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14071188
Zhu J, Liu Z, Wang S, Gao T, Liu W, Yang K, Yuan F, Wu Q, Li C, Guo R, et al. Prevalence, Molecular Characterization, and Antimicrobial Resistance Profile of Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli Isolates from Pig Farms in China. Foods. 2025; 14(7):1188. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14071188
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Jiajia, Zewen Liu, Siyi Wang, Ting Gao, Wei Liu, Keli Yang, Fangyan Yuan, Qiong Wu, Chang Li, Rui Guo, and et al. 2025. "Prevalence, Molecular Characterization, and Antimicrobial Resistance Profile of Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli Isolates from Pig Farms in China" Foods 14, no. 7: 1188. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14071188
APA StyleZhu, J., Liu, Z., Wang, S., Gao, T., Liu, W., Yang, K., Yuan, F., Wu, Q., Li, C., Guo, R., Tian, Y., & Zhou, D. (2025). Prevalence, Molecular Characterization, and Antimicrobial Resistance Profile of Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli Isolates from Pig Farms in China. Foods, 14(7), 1188. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14071188






