Comprehensive Review of Perilla frutescens: Chemical Composition, Pharmacological Mechanisms, and Industrial Applications in Food and Health Products
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Chemical Composition
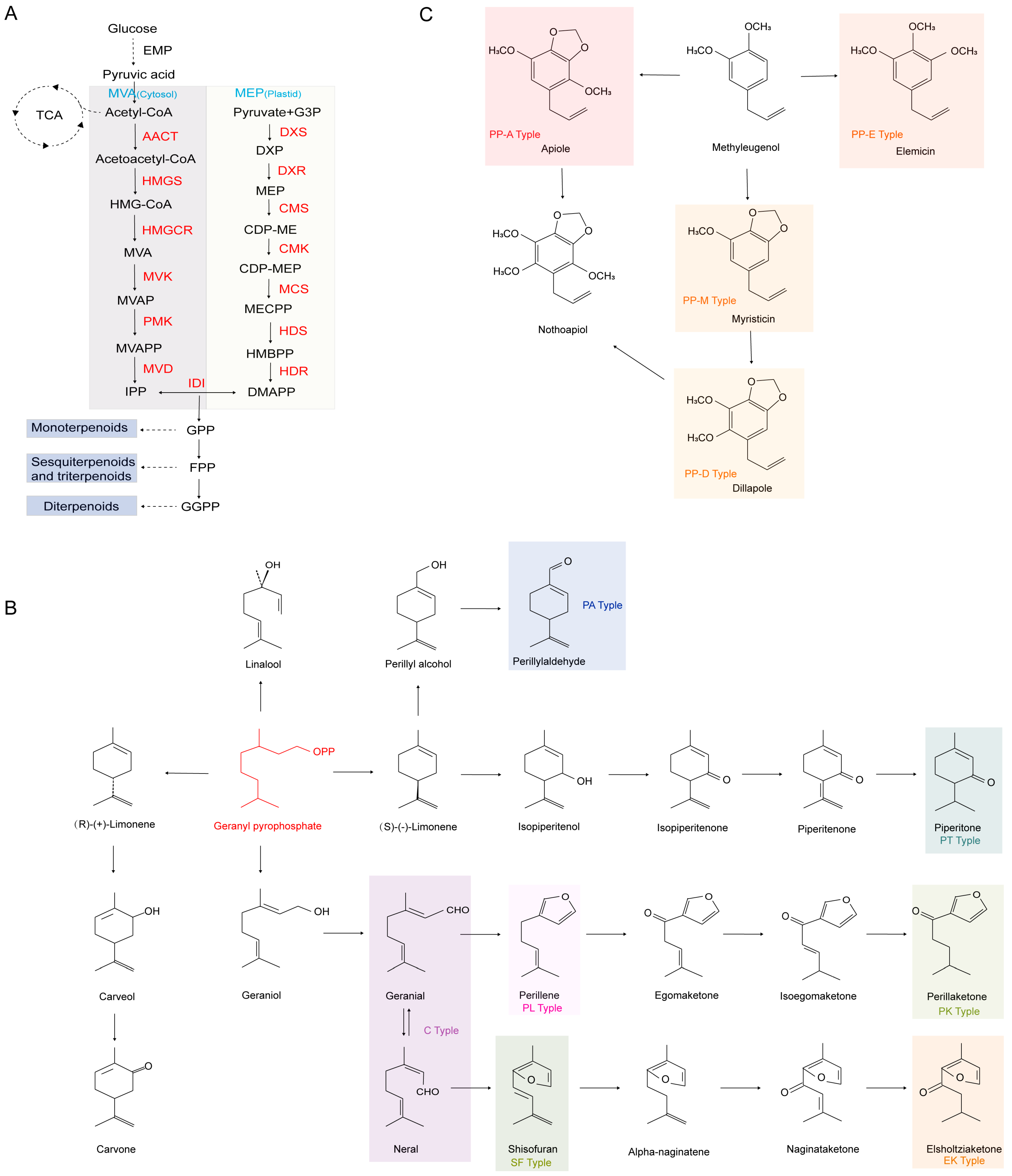
2.1. Volatile Oils
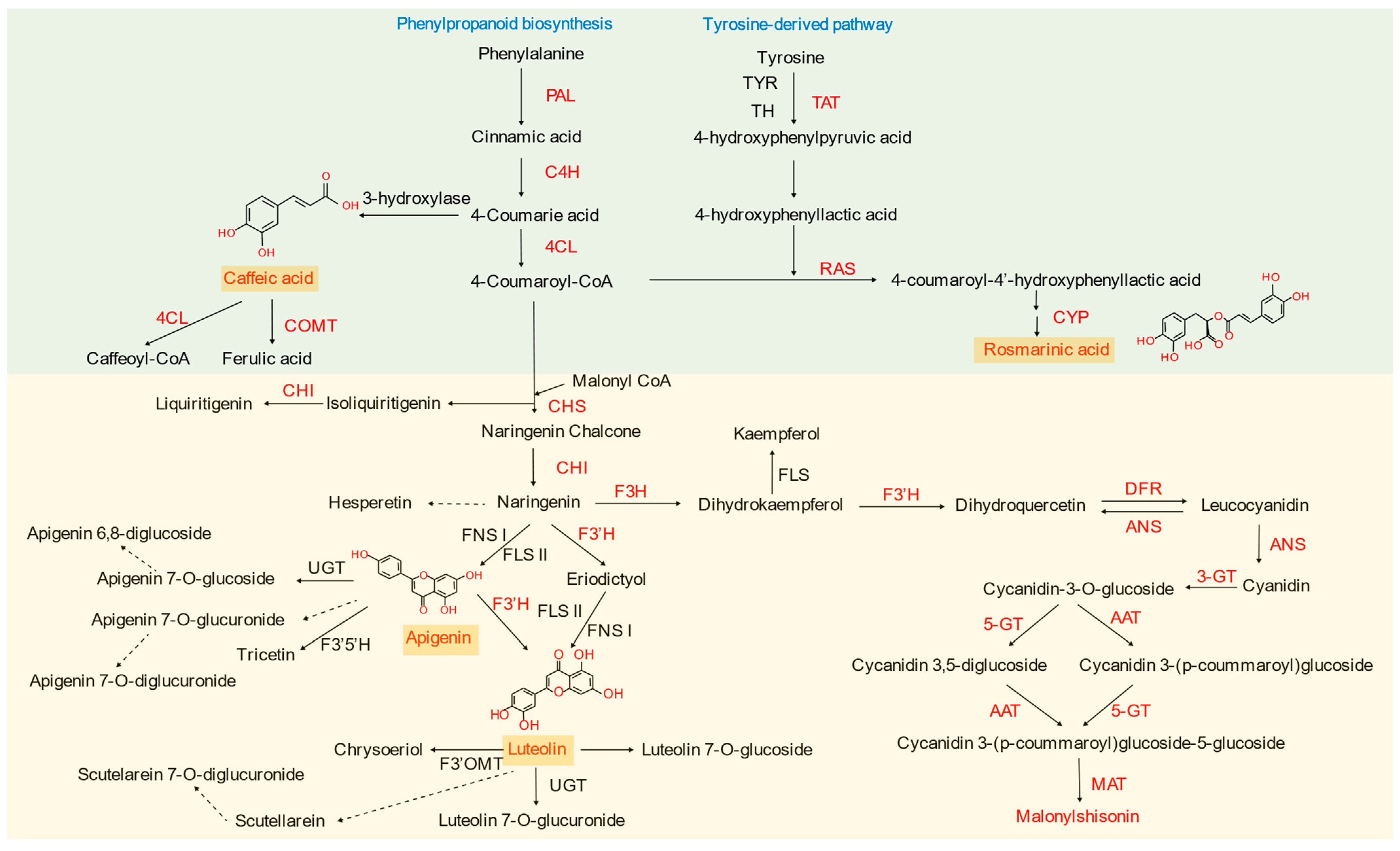
2.2. Flavonoids
2.3. Phenolic Acids
2.4. Anthocyanins
2.5. Fatty Acids
2.6. Polysaccharides
3. Functional Activity
3.1. Antioxidant
3.2. Anti-Inflammatory
3.3. Antiviral
3.4. Anticancer
3.5. Antibacterial
3.6. Lowers Blood Sugar
3.7. Others
| Function | Cell/Animal Model | Mechanism of Action | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Antioxidant | t-BHP-induced hepatotoxicity in rats | Modulates CYP1A1/2 activity and heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1) expression via nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (NRF2) activation, mitigating oxidative liver damage. | Kang et al. [88] |
| Anti-inflammatory | COPD mouse model | Inhibits leukocytosis and neutrophilia in BALF; suppresses p38 MAPK/NF-κB p65 signaling, reducing inflammatory mediator production and neutrophil infiltration. | Wei et al. [89] |
| Antiviral | PK15 cells and PRV-infected mice | Luteolin inhibits viral replication by downregulating viral mRNA/gB protein expression, reduces apoptosis in PRV-infected cells, and enhances survival rates post-lethal challenge. | Men et al. [90] |
| Anticancer | Huh-7, Hep3B cells, and xenograft mice | Isoegomaketone suppresses hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) growth via PI3K-Akt signaling pathway blockade. | Wang et al. [91] |
| Antimicrobial | Trichophyton mentagrophytes | Inhibits enolase expression, disrupting fungal glycolysis and energy metabolism, thereby suppressing growth. | Xu et al. [35] |
| Hypoglycemic | HFD/STZ-induced T2DM SD rats | Reduces hyperglycemia, ameliorates hepatic/intestinal tissue damage, and decreases glycogen accumulation via enhanced insulin signaling. | Wang et al. [75] |
| Anti-Alzheimer’s | 5XFAD transgenic mice | Blocks Aβ aggregation, dissociates preformed Aβ fibrils, and prevents Aβ-induced LTP impairment and memory deficits. | Cho et al. [92] |
| Antidepressant | CUMS-induced depressed rats | Modulates monoaminergic neurotransmission and activates BDNF/TrkB signaling pathways. | Zhong et al. [93] |
| Sleep Promotion | Pentobarbital-induced sleep mice | Exhibits adenosine A1 receptor (A1R) agonism, enhances neuronal activity in sleep-promoting brain regions, and reduces activity in wakefulness-associated regions. | Joy et al. [94] |
| Anti-asthmatic | OVA-induced allergic asthma mice | Suppresses airway inflammation and immune dysregulation via inhibition of ERK, JNK, and p38 MAPK phosphorylation. | Cao et al. [95] |
| Hypolipidemic | Hyperlipidemic rats | Reduces serum lipid levels, inhibits lipid peroxidation, normalizes lipoprotein metabolism, and enhances antioxidant enzyme activity. | Feng et al. [96] |
| Fertility Enhancement | Human endometrial Ishikawa cells | Upregulates integrin β3/β5 expression via leukemia inhibitory factor (LIF)-dependent pathways, enhancing adhesion between endometrial and trophoblast cells. | Kim et al. [97] |
4. Innovation in Food and Industrial Applications
4.1. Development of Functional Foods
4.2. Natural Preservatives and Preservatives
4.3. Novel Food Additives
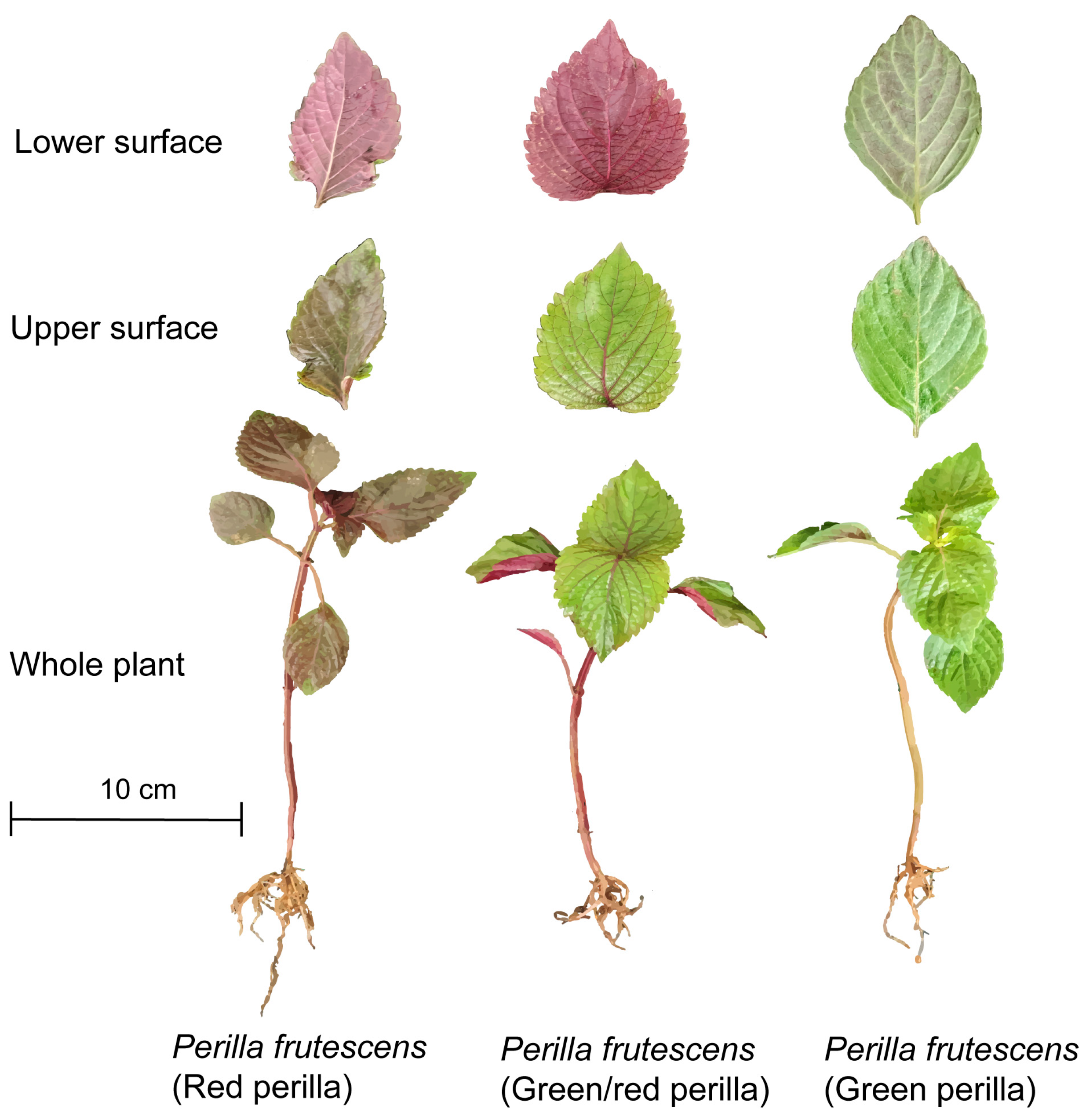
5. Biology and Genetic Improvement
6. Security and Standardization
6.1. Toxicity and Security
6.2. Standardization
7. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yu, H.; Qiu, J.F.; Ma, L.J.; Hu, Y.J.; Li, P.; Wan, J.B. Phytochemical and phytopharmacological review of Perilla frutescens L. (Labiatae), a traditional edible-medicinal herb in China. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2017, 108, 375–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dossou, S.S.K.; Deng, Q.; Li, F.; Wang, L.; Jiang, N.; Kefale, H.; Zhou, R.; Li, D.; Tan, M.; Wang, L. Metabolic profiling of Perilla leaves of different colors: Insights into metabolite variation and bioactive compound distribution. BMC Plant Biol. 2025, 25, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saini, R.K.; Keum, Y.-S.; Rengasamy, K.R.R. Profiling of nutritionally important metabolites in green/red and green perilla (Perilla frutescens Britt.) cultivars: A comparative study. Ind. Crops Prod. 2020, 151, 112441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, H.M. Ethnomedicinal, phytochemical and pharmacological investigations of Perilla frutescens (L.) Britt. Molecules 2018, 24, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akatsuka, R.; Ito, M. Content and distribution of prunasin in Perilla frutescens. J. Nat. Med. 2023, 77, 207–218. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Dong, S.; Chen, H.; Guo, M.; Sun, Z.; Luo, H. Perilla frutescens: A traditional medicine and food homologous plant. Chin. Herb. Med. 2023, 15, 369–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouphael, Y.; Kyriacou, M.C.; Carillo, P.; Pizzolongo, F.; Romano, R.; Sifola, M.I. Chemical Eustress Elicits Tailored Responses and Enhances the Functional Quality of Novel Food Perilla frutescens. Molecules 2019, 24, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Liu, S.; Zhao, Z.; Gao, W.; Ma, Y.; Wang, X.; Yan, S.; Luo, D. Ultrasound pre-treatment combined with microwave-assisted hydrodistillation of essential oils from Perilla frutescens (L.) Britt. leaves and its chemical composition and biological activity. Ind. Crops Prod. 2020, 143, 111908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayalakshmi, S.; Yoo, D.-S.; Kim, D.-G.; Chelliah, R.; Barathikannan, K.; Aloo, S.-O.; Tyagi, A.; Yan, P.; Shan, L.; Gebre, T.S.; et al. Fermented Perilla frutescens leaves and their untargeted metabolomics by UHPLC-QTOF-MS reveal anticancer and immunomodulatory effects. Food Biosci. 2023, 56, 103065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Cho, Y.-S. Assessment of phenolic profiles from various organs in different species of perilla plant (Perilla frutescens (L.) Britt.) and their antioxidant and enzyme inhibitory potential. Ind. Crops Prod. 2021, 171, 113914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, S.; Seem, K.; Ali, A.; Jaiswal, S.; Gumachanamardi, P.; Kaur, G.; Singh, N.; Touthang, L.; Singh, S.K.; Bhardwaj, R.; et al. A comprehensive review on nutritional, nutraceutical, and industrial perspectives of perilla (Perilla frutscens L.) seeds—An orphan oilseed crop. Heliyon 2024, 10, e33281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Luo, F.; Qing, Z.; Yang, H.; Liu, X.; Yang, Z.; Zeng, J. Chemical Composition and Bioactivity of Essential Oil of Ten Labiatae Species. Molecules 2020, 25, 4862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Huang, J.; Lin, X.; Su, W.; Zhu, P.; Yang, N.; Adams, E. Recent progress in the extraction of terpenoids from essential oils and separation of the enantiomers by GC-MS. J. Chromatogr. A 2024, 1730, 465118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, H.M.; Tavaszi-Sarosi, S. Identification and quantification of essential oil content and composition, total polyphenols and antioxidant capacity of Perilla frutescens (L.) Britt. Food Chem. 2019, 275, 730–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, C.; Zhang, H.; Sun, C.; Cao, J.; Yang, H.; Chen, J.; Wang, Y.; Sun, C. The antifungal activity and mechanism of Perillaldehyde and its stabilized encapsulation technology for fruit preservation. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2024, 207, 112613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tashakor, A.H.; Rezaei, A.; Fouladseresht, H.; Mansury, D. Characterization and investigation of cytotoxicity and antimicrobial properties of coencapsulated limonene and thymol into the Ferula assafoetida gum microparticles. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 263, 130338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, W.; Wang, K.; Luo, J.; Liu, Y.; Tong, J.; Qi, M.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Ma, Z.; Feng, J.; et al. Limonene anti-TMV activity and its mode of action. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2023, 194, 105512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghimire, B.K.; Yoo, J.H.; Yu, C.Y.; Chung, I.M. GC-MS analysis of volatile compounds of Perilla frutescens Britton var. Japonica accessions: Morphological and seasonal variability. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Med. 2017, 10, 643–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Yang, X.; Chen, S.; Wu, L.; Zhou, J.; Jia, K.; Ju, W. Integrated Network Pharmacology and GC-MS-Based Metabolomics to Investigate the Effect of Xiang-Su Volatile Oil Against Menopausal Depression. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 765638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabanca, N.; Demirci, B.; Ali, A.; Ali, Z.; Blythe, E.K.; Khan, I.A. Essential oils of green and red Perilla frutescens as potential sources of compounds for mosquito management. Ind. Crops Prod. 2015, 65, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, C.X.; Yang, K.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, W.J.; Wang, Y.; Geng, Z.F.; Chen, H.P.; Jiang, H.Y.; Du, S.S.; Deng, Z.W.; et al. Chemical composition and insecticidal activities of the essential oil of Perilla frutescens (L.) Britt. aerial parts against two stored product insects. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2014, 239, 481–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, D.; Fang, J.; Song, Z.; Geng, J.; Zhao, J.; Fang, Y.; Wang, C.; Li, M. Green and efficient extraction of flavonoids from Perilla frutescens (L.) Britt. leaves based on natural deep eutectic solvents: Process optimization, component identification, and biological activity. Food Chem. 2024, 452, 139508. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhao, G.; Qin, G.W.; Wang, J.; Chu, W.J.; Guo, L.H. Functional activation of monoamine transporters by luteolin and apigenin isolated from the fruit of Perilla frutescens (L.) Britt. Neurochem. Int. 2010, 56, 168–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khandelwal, N.; Chander, Y.; Kumar, R.; Riyesh, T.; Dedar, R.K.; Kumar, M.; Gulati, B.R.; Sharma, S.; Tripathi, B.N.; Barua, S. Antiviral activity of Apigenin against buffalopox: Novel mechanistic insights and drug-resistance considerations. Antivir. Res. 2020, 181, 104870. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, K.A.; Piao, M.J.; Hyun, Y.J.; Zhen, A.X.; Cho, S.J.; Ahn, M.J.; Yi, J.M.; Hyun, J.W. Luteolin promotes apoptotic cell death via upregulation of Nrf2 expression by DNA demethylase and the interaction of Nrf2 with p53 in human colon cancer cells. Exp. Mol. Med. 2019, 51, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, M.; Pang, Z. Luteolin inhibits inflammation and M1 macrophage polarization in the treatment of Pseudomonas aeruginosa-induced acute pneumonia through suppressing EGFR/PI3K/AKT/NF-κB and EGFR/ERK/AP-1 signaling pathways. Phytomedicine 2025, 141, 156663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Lin, J.; Bai, B.; Bo, T.; He, Y.; Fan, S.; Zhang, J. Study on Purification, Identification and Antioxidant of Flavonoids Extracted from Perilla leaves. Molecules 2023, 28, 7273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paek, J.H.; Shin, K.H.; Kang, Y.H.; Lee, J.Y.; Lim, S.S. Rapid identification of aldose reductase inhibitory compounds from Perilla frutescens. Biomed. Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 679463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.J.; Yan, L.L.; Yin, P.P.; Shi, L.L.; Zhang, J.H.; Liu, Y.J.; Ma, C. Structural characterisation and antioxidant activity evaluation of phenolic compounds from cold-pressed Perilla frutescens var. arguta seed flour. Food Chem. 2014, 164, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.-Y.; Kim, J.-I.; Kim, S.-W.; Kim, S.; Oh, E.; Lee, J.; Lee, E.; An, Y.-J.; Han, C.-Y.; Lee, H. Influence of Secondary Metabolites According to Maturation of Perilla (Perilla frutescens) on Respiratory Protective Effect in Fine Particulate Matter (PM2.5)-Induced Human Nasal Cell. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 12119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Zhan, P.; Geng, J.; Wang, P.; He, W.; Tian, H. Identification and inhibition of key off-odorants in boiled greenfin horse-faced filefish (Thamnaconus septentrionalis) subjected to perilla polyphenols extract. LWT 2024, 199, 116120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.Y.; Hong, C.O.; Lee, G.P.; Kim, C.T.; Lee, K.W. The hepatoprotection of caffeic acid and rosmarinic acid, major compounds of Perilla frutescens, against t-BHP-induced oxidative liver damage. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2013, 55, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, S.H.; Wang, Z.; Hwang, S.H.; Kang, Y.-H.; Lee, J.-Y.; Lim, S.S. Comprehensive evaluation of the antioxidant capacity of Perilla frutescens leaves extract and isolation of free radical scavengers using step-wise HSCCC guided by DPPH-HPLC. Int. J. Food Prop. 2017, 20, 921–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Fan, Y.; Zhang, S.; Li, J.; Zhang, L.; Wu, H. Extraction of rosmarinic acid from Perilla seeds using green protic ionic liquids. Microchem. J. 2021, 170, 106667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.D.; Guo, Y.J.; Mao, H.R.; Xiong, Z.X.; Luo, M.Y.; Luo, R.Q.; Lu, S.; Huang, L.; Hong, Y. Integration of transcriptomics and proteomics to elucidate inhibitory effect and mechanism of rosmarinic acid from Perilla frutescens (L.) Britt. in treating Trichophyton mentagrophytes. Chin. Med. 2023, 18, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, G.; Zou, X.; Liang, Z.; Wu, D.; He, J.; Xie, K.; Jin, H.; Wang, H.; Shen, Q. Integrated metabolomic and transcriptomic analyses reveal molecular response of anthocyanins biosynthesis in perilla to light intensity. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 976449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimura, T.; Ohyama, K.; Goto, E.; Inagaki, N. Concentrations of perillaldehyde, limonene, and anthocyanin of Perilla plants as affected by light quality under controlled environments. Sci. Hortic. 2009, 122, 134–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharathy, P.; Thanikachalam, P.V. Pharmacological relevance of anthocyanin derivative: A review. Pharmacol. Res. Mod. Chin. Med. 2025, 14, 100565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, E.; Kim, E.-G.; Lee, J.-E.; Lee, S.; Lee, D.; Lee, G.-A. Genetic Variations in FAD3 and Its Influence on Agronomic Traits and Fatty Acid Composition in Perilla Germplasm. Plant Sci. 2025, 355, 112452. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, S.; Yan, Z.; Liu, H.; Chen, P.; Shi, S.; Chang, M. Structural characterization and antitumor activity of a polysaccharide extracted from Perilla frutescens var. frutescens. Ind. Crops Prod. 2022, 187, 115334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, H.M.; Mohan Al-Zubaidy, A.; Othman-Qadir, G. Biological investigations on macro-morphological characteristics, polyphenolic acids, antioxidant activity of Perilla frutescens (L.) Britt. grown under open field. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2022, 29, 3213–3222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.H.; Kim, B.; Kim, S.; Kim, M.S.; Kim, H.; Hwang, S.R.; Kim, K.; Lee, J.H. Characterization of metabolite profiles from the leaves of green perilla (Perilla frutescens) by ultra high performance liquid chromatography coupled with electrospray ionization quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry and screening for their antioxidant properties. J. Food Drug Anal. 2017, 25, 776–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jun, H.I.; Kim, B.T.; Song, G.S.; Kim, Y.S. Structural characterization of phenolic antioxidants from purple perilla (Perilla frutescens var. acuta) leaves. Food Chem. 2014, 148, 367–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.J.; Song, B.R.; Kim, J.E.; Bae, S.J.; Choi, Y.J.; Lee, S.J.; Gong, J.E.; Lee, H.S.; Lee, C.Y.; Kim, B.H.; et al. Therapeutic Effects of Cold-Pressed Perilla Oil Mainly Consisting of Linolenic acid, Oleic Acid and Linoleic Acid on UV-Induced Photoaging in NHDF Cells and SKH-1 Hairless Mice. Molecules 2020, 25, 989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuyuno, Y.; Uchi, H.; Yasumatsu, M.; Morino-Koga, S.; Tanaka, Y.; Mitoma, C.; Furue, M. Perillaldehyde Inhibits AHR Signaling and Activates NRF2 Antioxidant Pathway in Human Keratinocytes. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2018, 2018, 9524657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, H.-Y.; Nam, M.-H.; Lee, H.-S.; Jun, W.; Hendrich, S.; Lee, K.-W. Isolation of caffeic acid from Perilla frutescens and its role in enhancing γ-glutamylcysteine synthetase activity and glutathione level. Food Chem. 2010, 119, 724–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Yao-Yue, C.; Qin, G.W.; Guo, L.H. Luteolin from Purple Perilla mitigates ROS insult particularly in primary neurons. Neurobiol. Aging 2012, 33, 176–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Lee, J.; Ju, J. Perilla frutescens Britton var. frutescens leaves attenuate dextran sulfate sodium-induced acute colitis in mice and lipopolysaccharide-stimulated angiogenic processes in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2020, 29, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, D.D.; Yum, H.W.; Zhong, X.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, D.H.; Kim, S.J.; Na, H.K.; Sato, A.; Miura, T.; et al. Perilla frutescens Extracts Protects against Dextran Sulfate Sodium-Induced Murine Colitis: NF-kappaB, STAT3, and Nrf2 as Putative Targets. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.Y.; Leu, Y.L.; Fang, Y.; Lin, C.F.; Kuo, L.M.; Sung, W.C.; Tsai, Y.F.; Chung, P.J.; Lee, M.C.; Kuo, Y.T.; et al. Anti-inflammatory effects of Perilla frutescens in activated human neutrophils through two independent pathways: Src family kinases and Calcium. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 18204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paradee, N.; Koonyosying, P.; Kusirisin, W.; Janthip, R.; Kanjanapothi, D.; Pattanapanyasat, K.; Srichairatanakool, S. Analgesic, anti-inflammatory and anti-ulcer properties of Thai Perilla frutescence fruit oil in animals. Biosci. Rep. 2021, 41, BSR20203166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.D.; Lee, Y.M.; Kang, M.A.; Lee, H.J.; Jin, C.H.; Choi, D.S.; Kim, D.S.; Kang, S.-Y.; Kim, W.-G.; Jeong, I.Y. Phytochemical profiles and in vitro anti-inflammatory properties of Perilla frutescens cv. Chookyoupjaso mutants induced by mutagenesis with γ-ray. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2010, 19, 305–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, A.; Ye, Y.; Han, B.; Zhu, X.; Xue, F.; Yang, L.; Zhang, C. Effect of Perilla frutescens polyphenols against tight junction alterations and intestinal inflammation: A Caco-2/macrophage co-culture model-based study integrated with network pharmacology. Food Biosci. 2024, 62, 105459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zi, Y.; Yao, M.; Lu, Z.; Lu, F.; Bie, X.; Zhang, C.; Zhao, H. Glycoglycerolipids from the leaves of Perilla frutescens (L.) Britton (Labiatae) and their anti-inflammatory activities in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated RAW264.7 cells. Phytochemistry 2021, 184, 112679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, C.H.; So, Y.; Kim, H.Y.; Han, S.N.; Kim, J.B. Anti-Arthritic Activities of Supercritical Carbon Dioxide Extract Derived from Radiation Mutant Perilla frutescens Var. Crispa in Collagen Antibody-Induced Arthritis. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Zhao, Y.; Cheng, J.; Wang, H.; Pan, S.; Liu, Y. The Antiviral Potential of Perilla frutescens: Advances and Perspectives. Molecules 2024, 29, 3328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.F.; Tsai, H.P.; Chang, Y.H.; Chang, T.Y.; Hsieh, C.F.; Lin, C.Y.; Lin, G.H.; Chen, Y.L.; Jheng, J.R.; Liu, P.C.; et al. Perilla (Perilla frutescens) leaf extract inhibits SARS-CoV-2 via direct virus inactivation. Biomed. J. 2021, 44, 293–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Guo, Y.; Song, Z.; Chang, H.; Kuang, Q.; Zheng, Z.; Wang, H.; Zhang, G. Luteolin restricts ASFV replication by regulating the NF-κB/STAT3/ATF6 signaling pathway. Vet. Microbiol. 2022, 273, 109527. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, G.-S.; Qin, J.-C.; Qin, Y.-L.; Wang, Y.; Yang, B.; Liu, X.; Ling, F.; Wang, G.-X. Evaluation on the antiviral activity of luteolin against largemouth bass virus. Aquaculture 2025, 595, 741573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mello, C.P.; Quirico-Santos, T.; Amorim, L.F.; Silva, V.G.; Fragel, L.M.; Bloom, D.C.; Paixao, I.P. Perillyl alcohol and perillic acid exert efficient action upon HSV-1 maturation and release of infective virus. Antivir. Ther. 2020, 25, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Nan, Y.; Chen, G.; Ning, N.; Du, Y.; Lu, D.; Yang, Y.; Meng, F.; Yuan, L. The Role and Mechanism of Perilla frutescens in Cancer Treatment. Molecules 2023, 28, 5883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, J.H.; Park, H.J.; Chi, G.Y.; Choi, Y.H.; Park, S.H. An Ethanol Extract of Perilla frutescens Leaves Suppresses Adrenergic Agonist-Induced Metastatic Ability of Cancer Cells by Inhibiting Src-Mediated EMT. Molecules 2023, 28, 3414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, P.J.B.; Huang, S.K.; De Castro-Cruz, K.A.; Leron, R.B.; Tsai, P.W. An In Vitro Evaluation and Network Pharmacology Analysis of Prospective Anti-Prostate Cancer Activity from Perilla frutescens. Plants 2023, 12, 3006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osakabe, N.; Yasuda, A.; Natsume, M.; Yoshikawa, T. Rosmarinic acid inhibits epidermal inflammatory responses: Anticarcinogenic effect of Perilla frutescens extract in the murine two-stage skin model. Carcinogenesis 2004, 25, 549–557. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.; Shi, R.; Wang, X.; Shen, H.-M. Luteolin, a flavonoid with potential for cancer prevention and therapy. Curr. Cancer Drug Targets 2008, 8, 634–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, T.; Guo, Y.; Han, W.; Zhou, Y.; Netala, V.R.; Li, H.; Li, H.; Zhang, Z. Exploring the Biomedical Applications of Biosynthesized Silver Nanoparticles Using Perilla frutescens Flavonoid Extract: Antibacterial, Antioxidant, and Cell Toxicity Properties against Colon Cancer Cells. Molecules 2023, 28, 6431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Netala, V.R.; Hou, T.; Sana, S.S.; Li, H.; Zhang, Z. Rosmarinic Acid-Rich Perilla frutescens Extract-Derived Silver Nanoparticles: A Green Synthesis Approach for Multifunctional Biomedical Applications including Antibacterial, Antioxidant, and Anticancer Activities. Molecules 2024, 29, 1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, H.M.; Al-Zubaidy, A.M.A. Exploring natural essential oil components and antibacterial activity of solvent extracts from twelve Perilla frutescens L. Genotypes. Arab. J. Chem. 2020, 13, 7390–7402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.; Zeng, X.; Zhang, S.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, P.; Lü, A.; Peng, X. Regional variation in components and antioxidant and antifungal activities of Perilla frutescens essential oils in China. Ind. Crops Prod. 2014, 59, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Lu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Tong, W.; Du, L.; Liu, F. Proteomic analysis of Aspergillus flavus reveals the antifungal action of Perilla frutescens essential oil by interfering with energy metabolism and defense function. LWT 2022, 154, 112660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, X.; Zhang, T.; Bai, B.; Yang, Y.; Bo, T.; Chen, M.; Fan, S. Study on the bacteriostatic property and bacteriostatic mechanism of rosemarinic acid compounded bacteriostatic agent. Food Biosci. 2024, 59, 103820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Wang, Y.; Wang, K.; Zhao, H.; Liu, M.; Liang, W.; Li, D. Perillaldehyde functions as a potential antifungal agent by triggering metacaspase-independent apoptosis in Botrytis cinerea. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e00526-23. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, W.; Cheng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, M.; Teng, Y.; Gu, Y.; Wang, H.; Xia, X. Antibiofilm efficacies and mechanism of perillaldehyde against Shewanella putrefaciens. Food Microbiol. 2025, 128, 104699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Wang, W.; Li, J.; Ai, Y.; Wang, H.; Han, Y.; Wang, W.; Hou, W. Unlocking the antibacterial activity and mechanisms of ε-poly-l-Lysine and perilla combination against Pseudomonas fluorescens: Insights from non-targeted metabolomic analyses. LWT 2024, 208, 116572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Tu, Z.; Xie, X.; Cui, H.; Kong, K.W.; Zhang, L. Perilla frutescens Leaf Extract and Fractions: Polyphenol Composition, Antioxidant, Enzymes (alpha-Glucosidase, Acetylcholinesterase, and Tyrosinase) Inhibitory, Anticancer, and Antidiabetic Activities. Foods 2021, 10, 315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; He, Y.; Yu, D.; Jin, L.; Gong, X.; Zhang, B. Perilla oil regulates intestinal microbiota and alleviates insulin resistance through the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway in type-2 diabetic KKAy mice. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2020, 135, 110965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, Q.-Q.; Fu, Z.-Z.; Mao, B.-Y.; Zhang, X.; Wang, H.-D.; Li, P.; Lin, L.-B.; Xi, Y.-T.; Yin, Y.-L.; Kamal, N.N.S.N.M. Perillaldehyde targeting PARP1 to inhibit TRPM2-CaMKII/CaN signal transduction in diabetic cardiomyopathy. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2025, 150, 114291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.R.; Kim, S.Y. Perilla frutescens Sprout Extract Protect Renal Mesangial Cell Dysfunction against High Glucose by Modulating AMPK and NADPH Oxidase Signaling. Nutrients 2019, 11, 356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.H.; Kim, S.J.; Yu, K.Y.; Jeong, S.I.; Kim, S.Y. Anti-hyperglycemic effects and signaling mechanism of Perilla frutescens sprout extract. Nutr. Res. Pract. 2018, 12, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Tian, G.; Tang, W.; Luo, W.; Liu, P.; Ma, Z. Protective effect of luteolin on streptozotocin-induced diabetic renal damage in mice via the regulation of RIP140/NF-κB pathway and insulin signalling pathway. J. Funct. Foods 2016, 22, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, J.; Guo, P.; Chen, M.; Wang, W.; Chen, X.; Li, Q.; He, Y.; Liang, J.; Yu, N.; Gao, P.; et al. Ultrasound-assisted extraction, purification, sulfation of Perilla leaves polysaccharide and hypoglycemic and hypolipidemic activities. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2025, 107269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, D.; Jee, H.J.; Kim, S.Y.; Hwang, S.H.; Pil, G.B.; Jung, Y.S. Luteolin-7-O-Glucuronide Improves Depression-like and Stress Coping Behaviors in Sleep Deprivation Stress Model by Activation of the BDNF Signaling. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.J.; Li, Z.; Gu, L.J.; Choi, K.J.; Kim, D.S.; Kim, H.K.; Sung, C.K. The promotion of hair regrowth by topical application of a Perilla frutescens extract through increased cell viability and antagonism of testosterone and dihydrotestosterone. J. Nat. Med. 2018, 72, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, M.; Luo, L.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Y.; Yan, Y.; Wang, F.; Zou, Y.; Zhu, H.; Wu, X.; Jin, Z.; et al. Perillaldehyde Improves Parkinson-Like Deficits by Targeting G3BP Mediated Stress Granule Assembly in Preclinical Models. Adv. Sci. 2025, e2412152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, N.; Hao, J.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, B.; Lin, J.; Song, J.; Wang, M.; Luo, Z. A Novel Natural Penetration Enhancer for Transdermal Drug Delivery: In Vitro/In Vivo Evaluation and Penetration Enhancement Mechanism. Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.-R.; Nam, B.; Han, A.-R.; Kim, J.-B.; Jin, C.H. Isoegomaketone from Perilla frutescens (L.) Britt stimulates MAPK/ERK pathway in human keratinocyte to promote skin wound healing. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2021, 2021, 6642606. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Gao, C.; Yang, J.; Du, R.; Zeng, F.; Bing, H.; Xia, B.; Shen, Y.; Liu, C. Endophytic Streptomyces sp. NEAU-ZSY13 from the leaf of Perilla frutescens, as a promising broad-spectrum biocontrol agent against soil-borne diseases. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1243610. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, J.H.; Yang, S.-Y.; Ha, J.; Lee, K.-W. Perilla frutescens modulates CYP1A1/2 and HO-1 and activates Nrf2 in oxidative stress-induced hepatotoxicity. J. Korean Soc. Appl. Biol. Chem. 2015, 58, 305–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, K.; Zhang, X.; Yang, J.; Chen, J. Tobacco introduced Perilla frutescens and Ocimum basilicum genes attenuates neutrophilic inflammation in lung tissues of COPD rats. Ecotoxicol. Env. Saf. 2024, 271, 115956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Men, X.; Li, S.; Cai, X.; Fu, L.; Shao, Y.; Zhu, Y. Antiviral Activity of Luteolin against Pseudorabies Virus In Vitro and In Vivo. Animals 2023, 13, 761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Huang, X.; Han, J.; Zheng, W.; Ma, W. Extract of Perilla frutescens inhibits tumor proliferation of HCC via PI3K/AKT signal pathway. Afr. J. Tradit. Complement. Altern. Med. 2013, 10, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, E.; Lee, J.; Sin, J.S.; Kim, S.K.; Kim, C.J.; Park, M.H.; Cho, W.S.; Moon, M.; Kim, D.H.; Jung, J.W. Effects of Perilla frutescens var. acuta in amyloid beta toxicity and Alzheimer’s disease-like pathology in 5XFAD mice. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2022, 161, 112847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, Y.; Du, Q.; Wang, Z.; Zheng, Q.; Yang, M.; Hu, P.; Yang, Q.; Xu, H.; Wu, Z.; Huang, X. Antidepressant effect of Perilla frutescens essential oil through monoamine neurotransmitters and BDNF/TrkB signal pathway. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2024, 318, 116840. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Joy Bormate, K.; Kyung Lee, B.; Kim, T.-H.; James Perez Custodio, R.; Hoon Cheong, J.; Jin Kim, H.; Hee Shim, S.; Bang Pil, G.; Jun Kim, H.; Ho Son, R.; et al. Involvement of adenosine A1 receptor in the sleep-promoting effect of fermented Perilla frutescens. J. Funct. Foods 2024, 120, 106345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, M.; Zhan, M.; Jing, H.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Miao, M. Network pharmacology and experimental evidence: MAPK signaling pathway is involved in the anti-asthma roles of Perilla frutescens leaf. Heliyon 2024, 10, e22971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.-J.; Yu, C.-H.; Ying, K.-J.; Hua, J.; Dai, X.-Y. Hypolipidemic and antioxidant effects of total flavonoids of Perilla frutescens leaves in hyperlipidemia rats induced by high-fat diet. Food Res. Int. 2011, 44, 404–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.Y.; Choi, H.J.; Chung, T.W.; Choi, J.Y.; Kim, H.S.; Jung, Y.S.; Lee, S.O.; Ha, K.T. Water-extracted Perilla frutescens increases endometrial receptivity though leukemia inhibitory factor-dependent expression of integrins. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2016, 131, 259–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Jiang, N.; Guo, G.; Lu, S.; Li, Z.; Mu, Y.; Xia, X.; Xu, Z.; Hu, Y.; Xiang, X. Perilla Seed Oil: A Review of Health Effects, Encapsulation Strategies and Applications in Food. Foods 2024, 13, 3615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhiman, A.; Chopra, R.; Singh, P.K.; Singh, A.; Homroy, S. Enzymatic interesterification of perilla seed oil and palm stearin: A sustainable approach to develop a novel zero-trans-fat margarine rich in omega-3 fatty acids. J. Food Sci. 2024, 89, 8504–8523. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, H.U.; Lee, K.-R.; Jeon, I.; Jung, H.E.; Heo, J.B.; Kim, T.-Y.; Chen, G.Q. Fatty acid composition and oil content of seeds from perilla (Perilla frutescens (L.) var. frutescens) germplasm of Republic of Korea. Genet. Resour. Crop Evol. 2019, 66, 1615–1624. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, K.; Ma, T. Study on the lipid-lowering capacity of α-linolenic acid from Perilla seed oil in oleic acid-induced HepG2 cells. Food Chem. Adv. 2025, 6, 100871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, S.S.; Kim, M.; Lee, S.J.; Cha, Y.S. Antiobesity Effects of Purple Perilla (Perilla frutescens var. acuta) on Adipocyte Differentiation and Mice Fed a High-fat Diet. J. Food Sci. 2018, 83, 2384–2393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, N.T.Y.; Duong, N.A.; Huynh, N.N.Y.; Nguyen, V.K.; Nguyen, T.T.K. Effects of storage temperature on biologically active ingredients of perilla drink. Food Chem. Adv. 2025, 6, 100897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, E.S.; Noh, Y.; Jeong, H.Y.; Lee, J.J.; Ahn, B.M.; Lee, J.; Jang, Y.J. Improved skeletal muscle mass and strength through Protamex-mediated hydrolysis of perilla seed cake: Elevated rosmarinic acid levels as a contributing factor. Food Chem. 2025, 463, 141369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Luo, H.; Netala, V.R.; Li, H.; Zhang, Z.; Hou, T. Comprehensive Review of Biological Functions and Therapeutic Potential of Perilla Seed Meal Proteins and Peptides. Foods 2024, 14, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, H.; Zhou, B.; Hu, X.; Wang, X.; Wang, M. Protective effect of Perilla (Perilla frutescens)leaf essential oil on the quality of a surimi-based food. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2018, 42, e13540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, Z.; Sun, Z.; Wang, D.; Liu, F. A novel gelatin/chitosan-based “sandwich” antibacterial nanofiber film loaded with perillaldehyde for the preservation of chilled chicken. Food Chem. 2025, 465, 142025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Guo, Y.; Han, W.; Zhang, Z.; Hou, T.; Li, H.; Li, H.; Wang, Q. Preparation of Perilla frutescens L. essential oil hydrogel beads and preservation application research in strawberry. Heliyon 2024, 10, e33689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tai, Z.; Zheng, M.; Yang, Y.; Xie, C.; Li, Z.; Xu, C. Temperature controlled microcapsule loaded with Perilla essential oil and its application in preservation of peaches. Front. Nutr. 2023, 10, 1087605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Cao, Y.; Zhang, L.; Yu, Q. Preservation of chilled beef using active films based on bacterial cellulose and polyvinyl alcohol with the incorporation of Perilla essential oil Pickering emulsion. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 271, 132118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Kong, H.; Zhang, X.; Hu, X.; Wang, M. The effect of Perilla (Perilla frutescens) leaf extracts on the quality of surimi fish balls. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 7, 2083–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, Z.; Yang, Y.; Lin, S.; Xu, L.; Chen, S.; Lv, W.; Wang, N.; Dong, S.; Lin, C.; Xie, Y.; et al. Development and antimicrobial activity of composite edible films of chitosan and nisin incorporated with perilla essential oil-glycerol monolaurate emulsions. Food Chem. 2025, 462, 141006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, I.A.; Shi, B.; Shi, H.; Nawaz, A.; Zhu, Z.; Ijaz, M.U.; Hussain, M.; Khan, A.; Wang, M.; Chen, F.; et al. Perilla frutescens seed meal as a fat substitute mitigates heterocyclic amine formation and protein oxidation and improves fatty acid profile of pan-fried chicken patties. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 975831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, Y.J.; Yoon, K.Y. Enzymatic hydrolysis of perilla seed meal yields water-soluble dietary fiber as a potential functional carbohydrate source. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2020, 29, 987–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Zhang, B.; Jiang, X.; Cui, Y.; Luo, H.; Stergiadis, S.; Wang, B. Exploring the metabolomic landscape: Perilla frutescens as a promising enhancer of production, flavor, and nutrition in Tan lamb meat. Meat Sci. 2024, 209, 109419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Sun, Z.; Tu, Y.; Si, B.; Liu, Y.; Yang, L.; Luo, H.; Yu, Z. Untargeted metabolomic investigate milk and ruminal fluid of Holstein cows supplemented with Perilla frutescens leaf. Food Res. Int. 2021, 140, 110017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liqi, H.; Chuanfeng, H.; Yiting, L.; Xuan, L.; Lingyun, W.; Yu, Q.; Lan, W.; Wenjing, W.; Liu, S. Effect of Perilla Essential Oil and Ginger Juice on the Flavor of Grilled Wuchang Fish. Mod. Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 40, 193–202. [Google Scholar]
- Fujiwara, Y.; Kono, M.; Ito, A.; Ito, M. Anthocyanins in perilla plants and dried leaves. Phytochemistry 2018, 147, 158–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klisurova, D.; Petrova, I.; Ognyanov, M.; Georgiev, Y.; Kratchanova, M.; Denev, P. Co-pigmentation of black chokeberry (Aronia melanocarpa) anthocyanins with phenolic co-pigments and herbal extracts. Food Chem. 2019, 279, 162–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hur, S. Quality Characteristics of Fermented Perilla Leaves Ice Cream Using Probiotics. J. Korean Appl. Sci. Technol. 2024, 41, 375–385. [Google Scholar]
- Trang, P.N.; Trâm, N.T.B.; Anh, N.P. NGHIÊN CỨU CHẾ BIẾN KẸO MỀM SỮA BỔ SUNG SIRO TỪ LÁ TÍA TÔ (Perilla frutescens (L.) Britt.). TNU J. Sci. Technol. 2024, 229, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karthik, S.; Chae, J.; Han, S.J.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, H.J.; Chung, Y.S.; Kim, H.U.; Heo, J.B. Improving the Traits of Perilla frutescens (L.) Britt Using Gene Editing Technology. Plants 2024, 13, 1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, W.; Kwon, S.J.; Lee, J.; Choi, I.Y.; Park, Y.J.; Choi, S.H.; Sa, K.J.; Kim, B.W.; Lee, J.K. Gene set by de novo assembly of Perilla species and expression profiling between P. frutescens (L.) var. frutescens and var. crispa. Gene 2015, 559, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, P.; Yin, M.; Dai, S.; Bao, K.; Song, C.; Liu, C.; Wu, Q. Multi-omics analysis of the bioactive constituents biosynthesis of glandular trichome in Perilla frutescens. BMC Plant Biol. 2021, 21, 277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, W.; Shi-Mei, Y.; Zhi-Wei, S.; Jing, X.; De-Gang, Z.; Hong-Bin, W.; Qi, S. Genome-wide analysis of the fatty acid desaturase gene family reveals the key role of PfFAD3 in α-linolenic acid biosynthesis in perilla seeds. Front. Genet. 2021, 12, 735862. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, B.; Hao, Y.; Lu, J.; Bai, H.; Guan, L.; Zhang, T. Transcriptomic analysis of Perilla frutescens seed to insight into the biosynthesis and metabolic of unsaturated fatty acids. BMC Genom. 2018, 19, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Cao, X.; Zhang, M.; Wei, S.; Zhu, Y.; Ouyang, H.; He, J. Quantitative comparison and chemical profile analysis of different medicinal parts of Perilla frutescens (L.) Britt. from different varieties and harvest periods. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 8838–8853. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhou, P.; Shao, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Dang, J.; Qu, C.; Wu, Q. The revealing of a novel double bond reductase related to perilla ketone biosynthesis in Perilla frutescens. BMC Plant Biol. 2023, 23, 345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, F.; Xiao, Q.; Gul, H.; Liu, T.; Cao, W.; Zhang, Y.; Duan, H.; Li, Y.; Liang, J.; Zhang, X.; et al. Comparative global profiling of Perilla leaf and stem via transcriptomics and metabolomics. Gene 2024, 929, 148828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinese Pharmacopoeia Commission. Chinese Pharmacopoeia; China Medical Science and Technology Press: Beijing, China, 2020.
- Wang, M.; Shen, R.; Wang, X.; Zhang, J.; Ma, J.; Shi, Y.; Xu, Q.; Guo, C.; Di, J.; Liu, A.; et al. Evaluation of edible and medicinal varieties based on multidimensional quantitative data: A case study of perilla leaf. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2025, 140, 107196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yu, M.; Wei, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Guo, Y.; Yuan, M.; Jin, J.; Li, J.; Shen, H.; Wu, D. Risk assessment of developmental and neurotoxicity by the flavoring agent perillaldehyde: NAC (N-acetylcysteine) mitigation of oxidative stress-mediated inhibition of the Nrf2 pathway. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2025, 288, 110071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erhunmwunsee, F.; Pan, C.; Yang, K.; Li, Y.; Liu, M.; Tian, J. Recent development in biological activities and safety concerns of perillaldehyde from perilla plants: A review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 62, 6328–6340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, S.; Lee, W.Y.; Yong, S.J.; Shin, K.C.; Kim, C.W.; Lee, J.-H.; Jung, Y.-R.; Kim, H.S.; Yu, T.-S.; Kim, S.-H. Occupational asthma caused by inhaling smoke from roasting perilla seeds. Allergy Asthma Respir. Dis. 2013, 1, 90–93. [Google Scholar]
- Jeong, K.; Lee, S.; Jeon, S.; Gantulga, P.; Nam, J.; Hong, S.; Lee, S. Clinical and Immunological Characterization of Perilla Seed Allergy in Children. J. Investig. Allergol. Clin. Immunol. 2021, 33, 14–20. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.X.; Guan, J.; Tian, Y.H.; Su, G.Y.; Zhao, Y.Q. Acute and sub-chronic 90-day oral toxicity study of Perilla seed oil in rodents and Beagle dogs. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2019, 103, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Huang, L.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Nie, L.; Kang, S.; Wei, F.; Ma, S. Rapid and accurate detection of cinnamon oil adulteration in perilla leaf oil using atmospheric solids analysis probe-mass spectrometry. Food Chem. 2025, 462, 140965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DB15/T 3207-2024; Technical Code of Practice for Planting and Turning Green Manure to Fertilize in Degenerated Black Soil. Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region Market Supervision Administration: Hohhot, China, 2024.
| Year | Total Publications | Primary Research Areas | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chemical Composition Research | Pharmacological Activity Research | Food Industry Applications | Genetic Improvement Research | Other Studies (Safety Standards/Heavy Metals/Stresses/Environment/ Quality/Pests, and Diseases/Clinical) | ||
| 2025 | 16 | 5 | 4 | 1 | 3 | 3 |
| 2024 | 143 | 19 | 44 | 16 | 19 | 45 |
| 2023 | 154 | 26 | 47 | 24 | 20 | 37 |
| 2022 | 148 | 29 | 38 | 25 | 17 | 39 |
| 2021 | 120 | 28 | 38 | 10 | 17 | 27 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yi, D.; Wang, Z.; Peng, M. Comprehensive Review of Perilla frutescens: Chemical Composition, Pharmacological Mechanisms, and Industrial Applications in Food and Health Products. Foods 2025, 14, 1252. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14071252
Yi D, Wang Z, Peng M. Comprehensive Review of Perilla frutescens: Chemical Composition, Pharmacological Mechanisms, and Industrial Applications in Food and Health Products. Foods. 2025; 14(7):1252. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14071252
Chicago/Turabian StyleYi, Dandan, Zhiyong Wang, and Mu Peng. 2025. "Comprehensive Review of Perilla frutescens: Chemical Composition, Pharmacological Mechanisms, and Industrial Applications in Food and Health Products" Foods 14, no. 7: 1252. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14071252
APA StyleYi, D., Wang, Z., & Peng, M. (2025). Comprehensive Review of Perilla frutescens: Chemical Composition, Pharmacological Mechanisms, and Industrial Applications in Food and Health Products. Foods, 14(7), 1252. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14071252





