Cultivar Differentiation and Origin Tracing of Panax quinquefolius Using Machine Learning Model-Driven Comparative Metabolomics
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Instruments
2.2. Sample Preparation and Metabolite Extraction for LC-MS
2.3. UHPLC-Q-TOFMS-Based Untargeted Metabolomics Analysis
2.4. LC-MS-Based Data Processing and Multivariate Data Analysis for Screening Differential Metabolites Between Wild and Cultivated American Ginseng
2.5. Differential Metabolites-Based Machine Learning Diagnostic Model for Differing Wild and Cultivated American Ginseng
3. Results
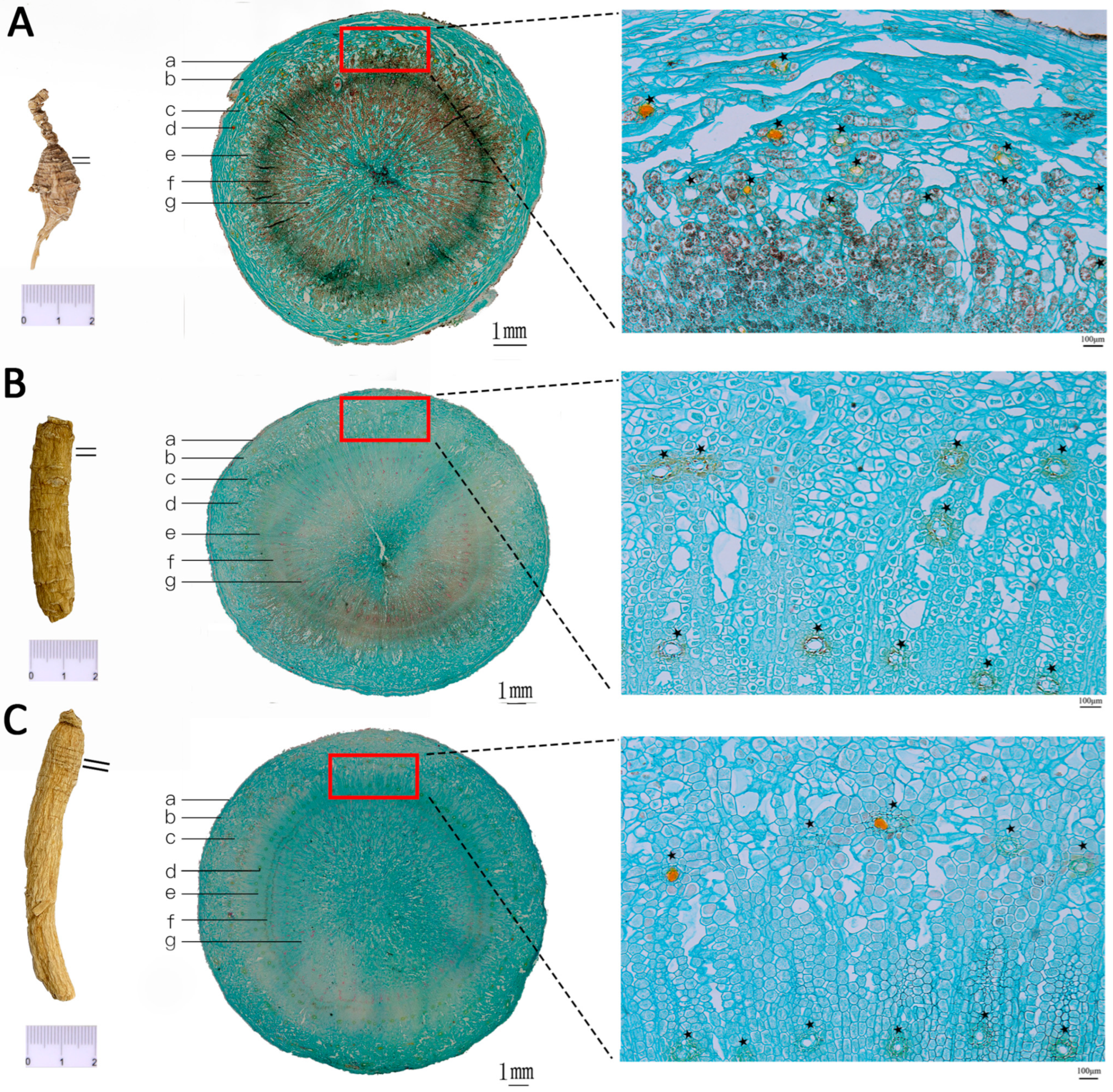
3.1. Differentiation and Identification of Wild and Cultivated American Ginseng Based on Microscopic Morphology
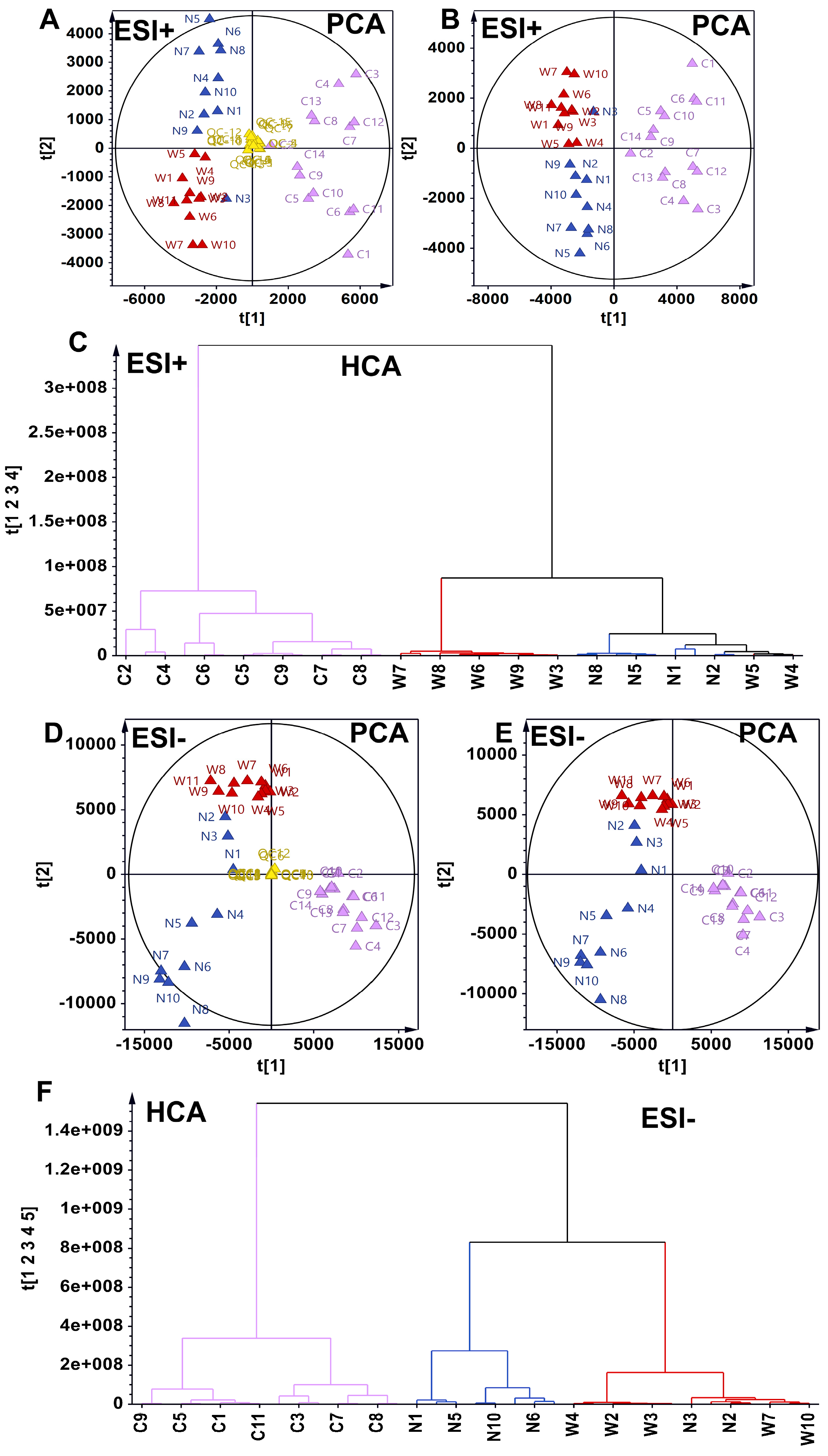
3.2. Discrimination of Metabolic Subtypes of American Ginsengs in Metabolomics Based on Unsupervised Analysis
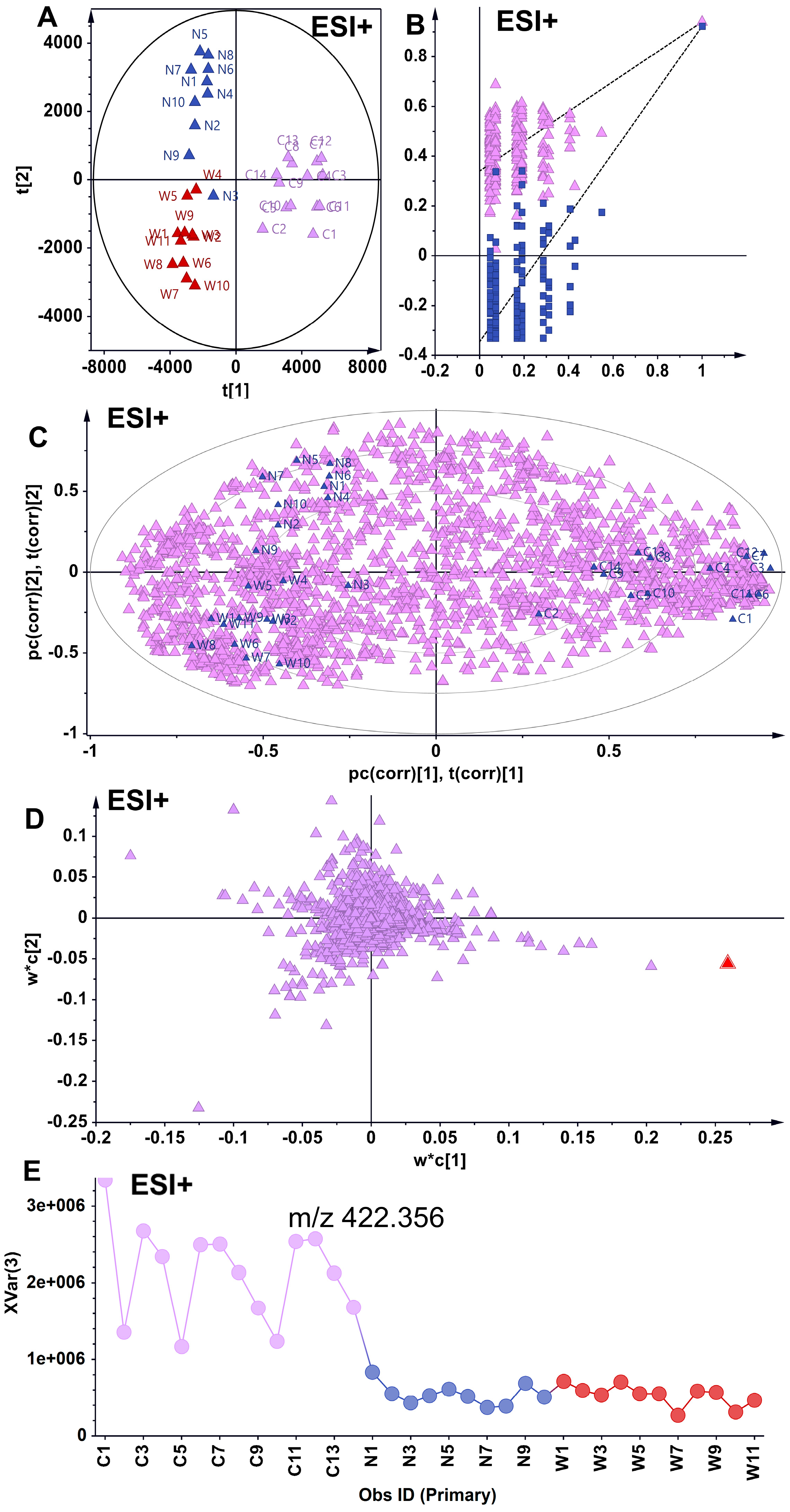
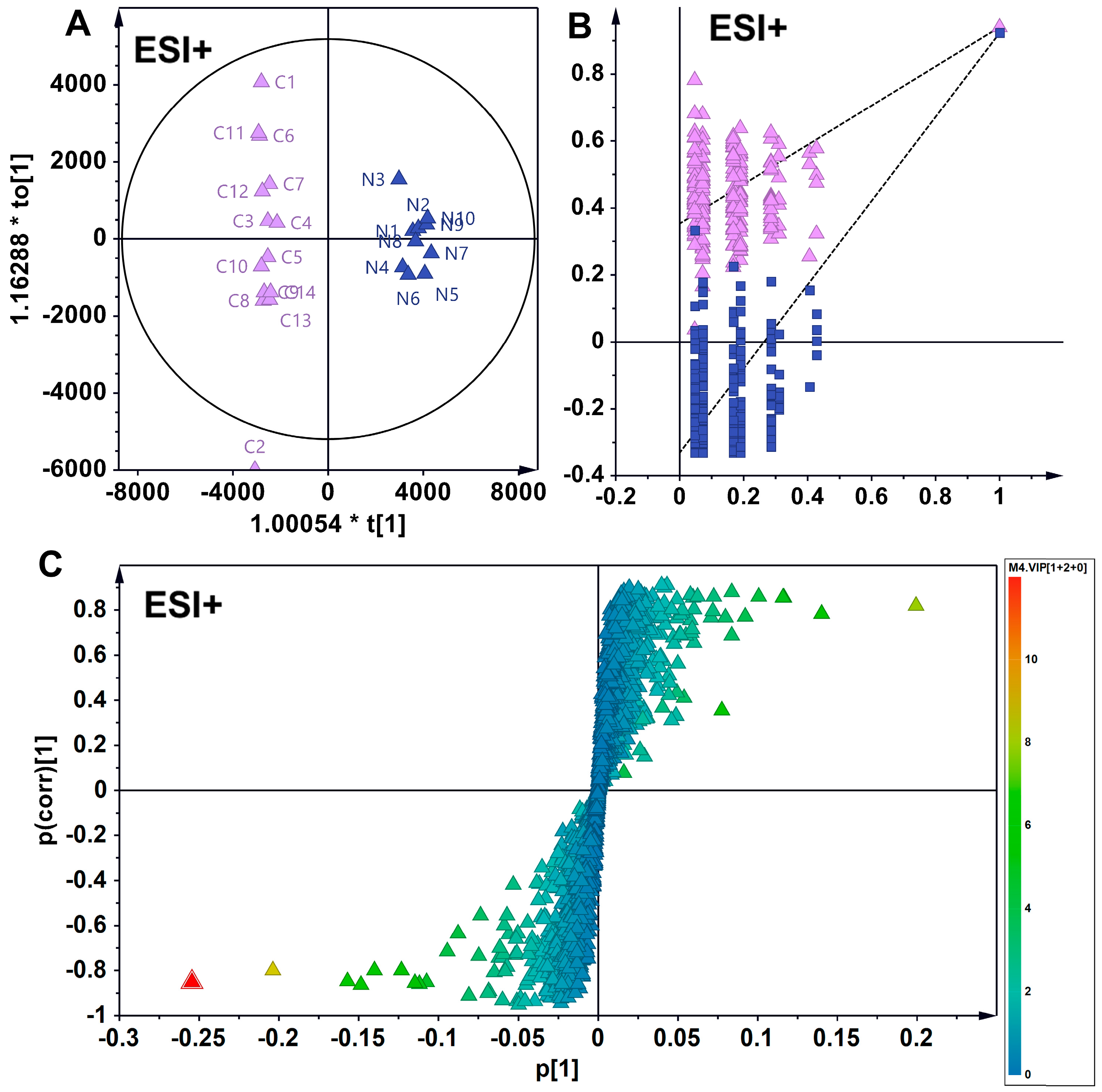
3.3. Supervised Analytical Screening of Differential Metabolites in Wild and Cultivated American Ginseng in ESI+ Mode
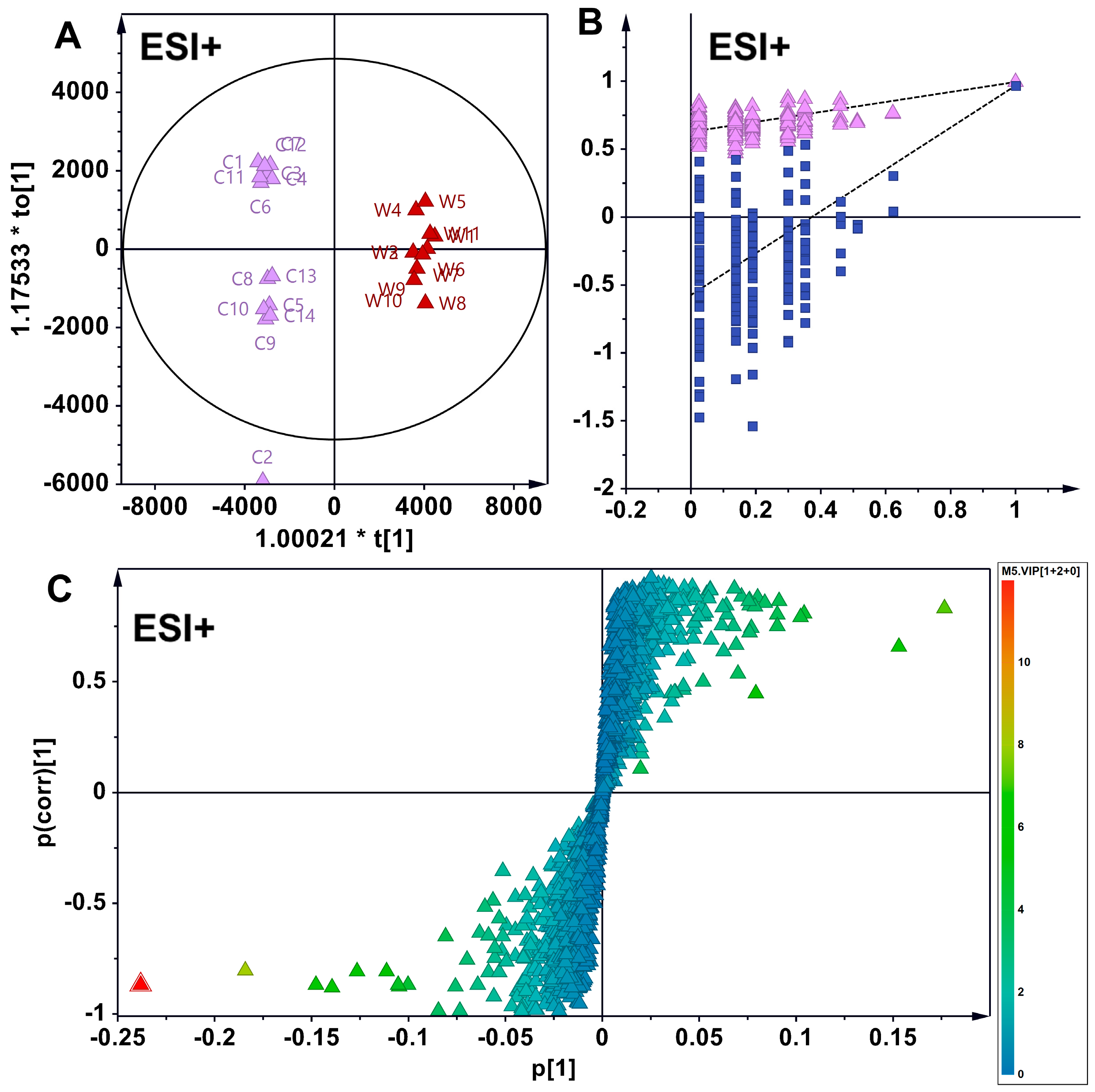
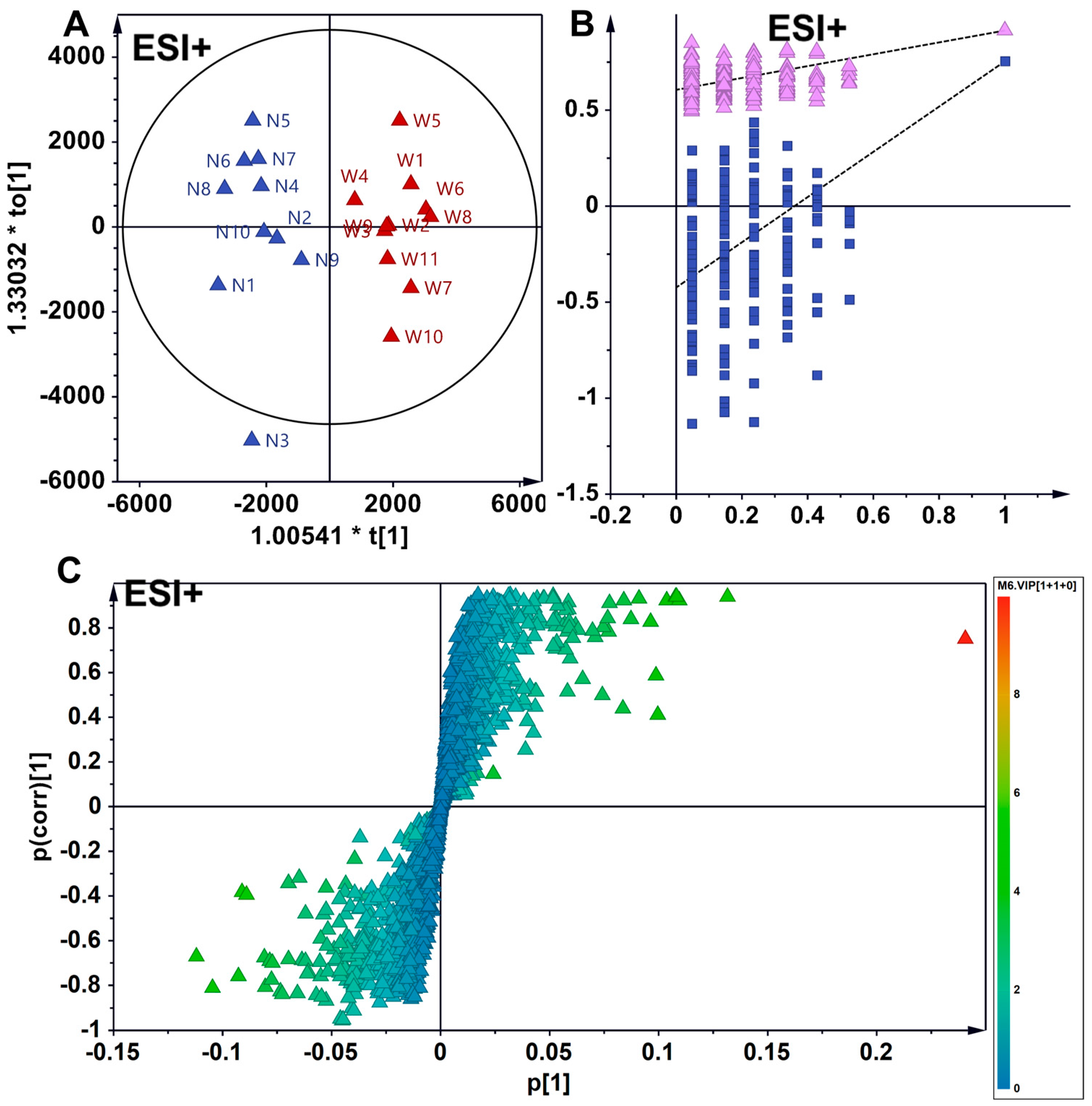
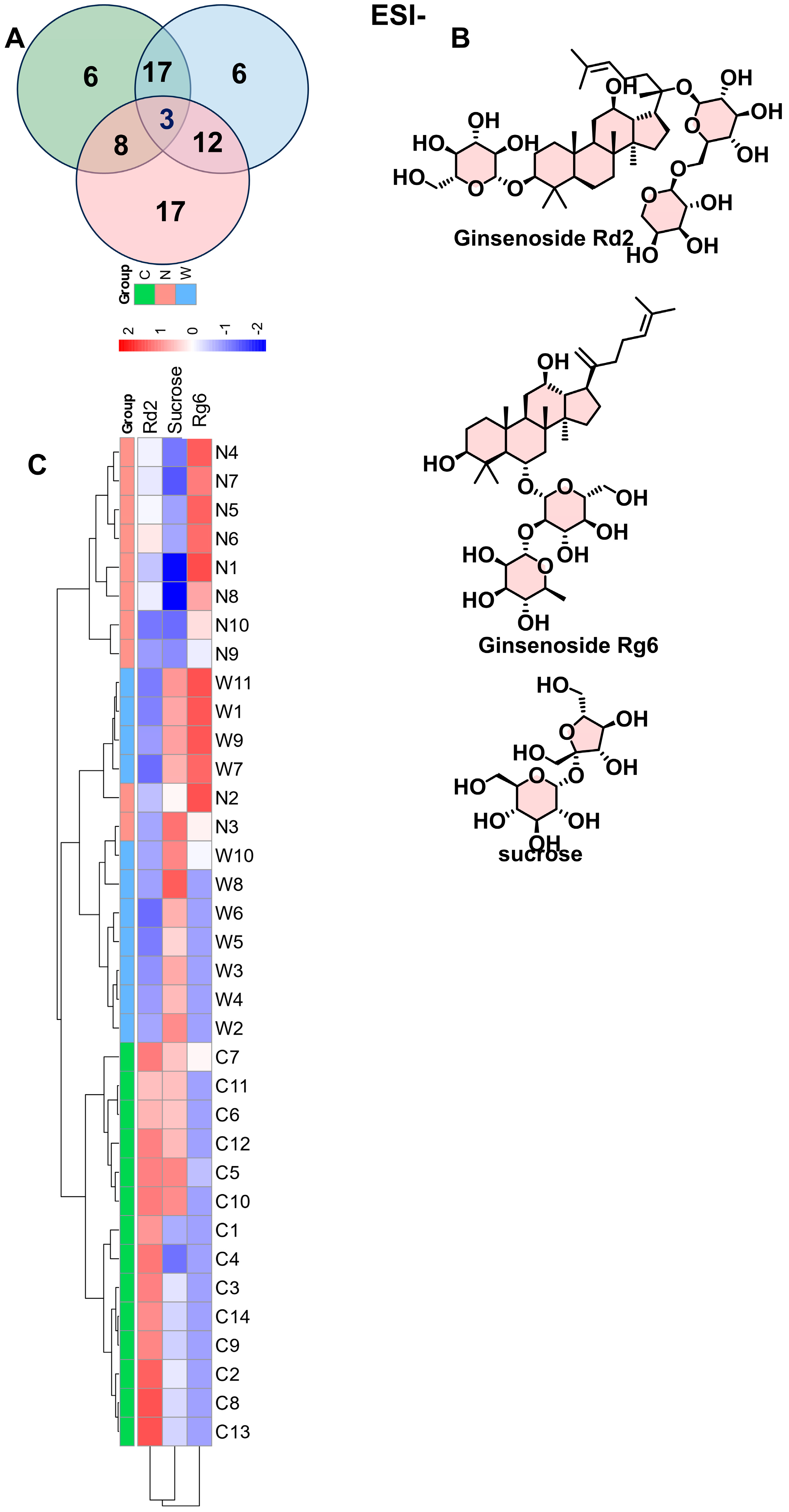
3.4. Supervised Analytical Screening of Differential Metabolites Between Wild and Cultivated American Ginseng in ESI- Mode
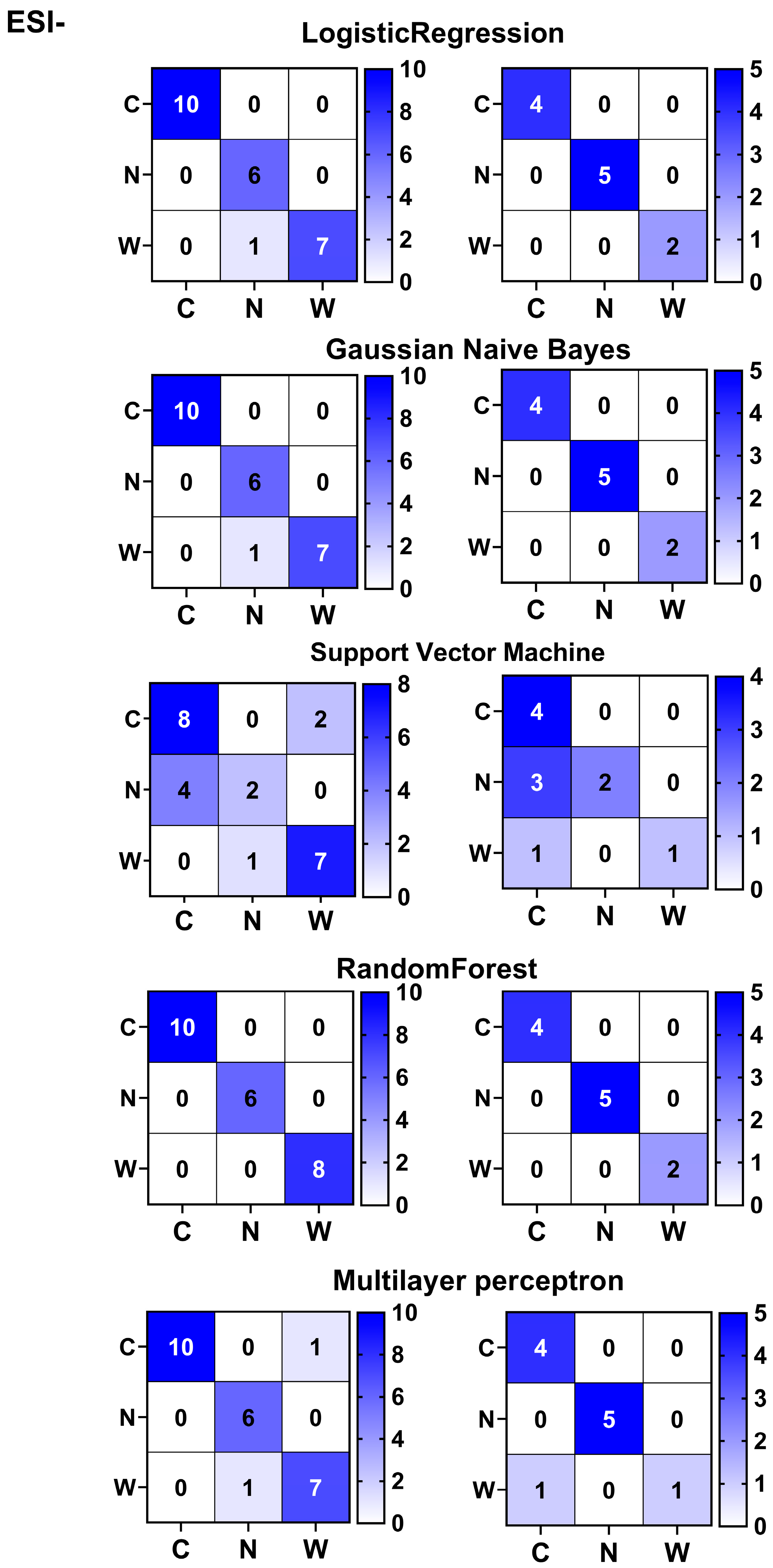
3.5. Differentiation and Origin Tracing of American Ginseng Species Using Five Machine Learning Classifiers Based on Differential Metabolites
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Correction Statement
References
- Szczuka, D.; Nowak, A.; Zakłos-Szyda, M.; Kochan, E.; Szymańska, G.; Motyl, I.; Blasiak, J. American Ginseng (Panax quinquefolium L.) as a Source of Bioactive Phytochemicals with Pro-Health Properties. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Hou, A.; Zhang, J.; Wang, S.; Man, W.; Yu, H.; Zheng, S.; Wang, X.; Liu, S.; Jiang, H. Panacis Quinquefolii Radix: A Review of the Botany, Phytochemistry, Quality Control, Pharmacology, Toxicology and Industrial Applications Research Progress. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 602092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Choi, H.-K.; Brinckmann, J.A.; Jiang, X.; Huang, L. Chemical analysis of Panax quinquefolius (North American ginseng): A review. J. Chromatogr. A 2015, 1426, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Ju, Z.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, L.; Wang, Z. Phytochemical analysis of Panax species: A review. J Ginseng Res. 2021, 45, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flagg, A.J. Traditional and Current Use of Ginseng. Nurs. Clin. N. Am. 2021, 56, 109–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, J.; Chen, L.; Guo, Y.H.; Zhang, M.; Gao, Y. Simultaneous Determination and Analysis of Major Ginsenosides in Wild American Ginseng Grown in Tennessee. Chem. Biodivers. 2019, 16, e1900203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheban, K.C.; Woodbury, D.J.; Duguid, M.C. Importance of environmental factors on plantings of wild-simulated American Ginseng. Agrofor. Syst. 2022, 96, 147–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuai, M.; Yang, Y.; Bai, F.; Cao, L.; Hou, R.; Peng, C.; Cai, H. Geographical origin of American ginseng (Panax quinquefolius L.) based on chemical composition combined with chemometric. J. Chromatogr. A 2022, 1676, 463284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abaya, A.; Zaro, G.C.; De la Mora Pena, A.; Hsiang, T.; Goodwin, P.H. Phenotypic and Genotypic Variation of Cultivated Panax quinquefolius. Plants 2024, 13, 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plumb, R.S.; Gethings, L.A.; Rainville, P.D.; Isaac, G.; Trengove, R.; King, A.M.; Wilson, I.D. Advances in high throughput LC/MS based metabolomics: A review. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2023, 160, 116954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Liang, Y.-Z.; Liu, H.-t. Chemometrics applied to quality control and metabolomics for traditional Chinese medicines. J. Chromatogr. B 2016, 1015–1016, 82–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, J.-L.; Zhang, A.-H.; Kong, L.; Wang, X.-J. Advances in mass spectrometry-based metabolomics for investigation of metabolites. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 22335–22350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, L.; Xu, J.; Liang, Z.-T.; Dong, X.-P.; Chen, H.-B.; Zhao, Z.-Z. Tissue-Specific Analysis of Secondary Metabolites Creates a Reliable Morphological Criterion for Quality Grading of Polygoni Multiflori Radix. Molecules 2018, 23, 1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ludwiczuk, A.; Weryszko-Chmielewska, E.; Wolski, T. Localization of ginsenosides in Panax quinquefolium root tissues. Acta Agrobot. 2006, 59, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.-S.; Lee, S.; Park, S.M.; Yun, S.H.; Gab, H.-S.; Kim, S.S.; Kim, H.-J. Comparative Metabolomics Analysis of Citrus Varieties. Foods 2021, 10, 2826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, P.; He, N.; Umer, M.J.; Zhao, S.; Diao, W.; Zhu, H.; Dou, J.; Kaseb, M.O.; Kuang, H.; Lu, X.; et al. Comparative Metabolomic Profiling of Citrullus spp. Fruits Provides Evidence for Metabolomic Divergence during Domestication. Metabolites 2021, 11, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alseekh, S.; Bermudez, L.; de Haro, L.A.; Fernie, A.R.; Carrari, F. Crop metabolomics: From diagnostics to assisted breeding. Metabolomics 2018, 14, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razzaq, A.; Sadia, B.; Raza, A.; Khalid Hameed, M.; Saleem, F. Metabolomics: A Way Forward for Crop Improvement. Metabolites 2019, 9, 303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.R.; Leung, C.Y.; Ho, H.M.; Chai, S.; Yau, L.F.; Zhao, Z.Z.; Jiang, Z.H. Quantitative comparison of ginsenosides and polyacetylenes in wild and cultivated American ginseng. Chem. Biodivers. 2010, 7, 975–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torun, F.M.; Virreira Winter, S.; Doll, S.; Riese, F.M.; Vorobyev, A.; Mueller-Reif, J.B.; Geyer, P.E.; Strauss, M.T. Transparent Exploration of Machine Learning for Biomarker Discovery from Proteomics and Omics Data. J. Proteome Res. 2023, 22, 359–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foschi, M.; Biancolillo, A.; Vellozzi, S.; Marini, F.; D’Archivio, A.A.; Boqué, R. Spectroscopic fingerprinting and chemometrics for the discrimination of Italian Emmer landraces. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2021, 215, 104348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.-Q.; Yi, L.-W.; Zhao, L.; Zhou, Y.-Z.; Guo, F.; Huo, Y.-S.; Zhao, D.-Q.; Xu, F.; Wang, X.; Cai, S.-Q. 177 Saponins, Including 11 New Compounds in Wild Ginseng Tentatively Identified via HPLC-IT-TOF-MSn, and Differences among Wild Ginseng, Ginseng under Forest, and Cultivated Ginseng. Molecules 2021, 26, 3371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu-Huynh, K.L.; Nguyen, H.T.; Van Le, T.H.; Ma, C.T.; Lee, G.J.; Kwon, S.W.; Park, J.H.; Nguyen, M.D. Accumulation of Saponins in Underground Parts of Panax vietnamensis at Different Ages Analyzed by HPLC-UV/ELSD. Molecules 2020, 25, 3086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Moore, R.; Gao, Y.; Chen, P.; Yu, L.; Zhang, M.; Sun, J. Comparison of Phytochemical Profiles of Wild and Cultivated American Ginseng Using Metabolomics by Ultra-High Performance Liquid Chromatography-High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry. Molecules 2023, 28, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, R.; Yang, P.; Jing, C.; Fu, B.; Teng, X.; Zhao, D.; Sun, L. Comparison of the metabolomic and proteomic profiles associated with triterpene and phytosterol accumulation between wild and cultivated ginseng. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2023, 195, 288–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacheco-Londoño, L.C.; Warren, E.; Galán-Freyle, N.J.; Villarreal-González, R.; Aparicio-Bolaño, J.A.; Ospina-Castro, M.L.; Shih, W.-C.; Hernández-Rivera, S.P. Mid-Infrared Laser Spectroscopy Detection and Quantification of Explosives in Soils Using Multivariate Analysis and Artificial Intelligence. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 4178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Qian, J.; Chen, J.; Ruiz-Garcia, L.; Dong, C.; Chen, Q.; Liu, Z.; Xiao, P.; Zhao, Z. Recent advances of machine learning in the geographical origin traceability of food and agro-products: A review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2025, 24, e70082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, T.L.; Yeap, Z.Q.; Tan, C.S.; Chen, Y.; Chen, J.; Yam, M.F. A novel machine learning scheme for classification of medicinal herbs based on 2D-FTIR fingerprints. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2022, 266, 120440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.Y.; Ren, Y.F.; Ye, Z.H.; Zhu, H.Y.; Liu, X.Q.; Chen, X.T.; Hou, R.Y.; Granato, D.; Cai, H.M. A comparative UHPLC-Q/TOF-MS-based metabolomics approach coupled with machine learning algorithms to differentiate Keemun black teas from narrow-geographic origins. Food Res. Int. 2022, 158, 111512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, R.; Wang, Y.; Zhen, L.; Shen, B.; Long, H.; Huang, L. Cultivar Differentiation and Origin Tracing of Panax quinquefolius Using Machine Learning Model-Driven Comparative Metabolomics. Foods 2025, 14, 1340. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14081340
Zhou R, Wang Y, Zhen L, Shen B, Long H, Huang L. Cultivar Differentiation and Origin Tracing of Panax quinquefolius Using Machine Learning Model-Driven Comparative Metabolomics. Foods. 2025; 14(8):1340. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14081340
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Rongrong, Yikun Wang, Lanping Zhen, Bingbing Shen, Hongping Long, and Luqi Huang. 2025. "Cultivar Differentiation and Origin Tracing of Panax quinquefolius Using Machine Learning Model-Driven Comparative Metabolomics" Foods 14, no. 8: 1340. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14081340
APA StyleZhou, R., Wang, Y., Zhen, L., Shen, B., Long, H., & Huang, L. (2025). Cultivar Differentiation and Origin Tracing of Panax quinquefolius Using Machine Learning Model-Driven Comparative Metabolomics. Foods, 14(8), 1340. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14081340






