Steam Explosion Enhances the Powder Property, Instant Solubility, and Diffusivity of Superfine Ground Tea Powder
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Steam Explosion Process
2.3. Determination of Physicochemical Properties of Low-Grade Tea
2.3.1. Chemical Composition Determination
2.3.2. Crystallinity Degree Determination
2.3.3. Thermal Stability Determination
2.4. Preparation of Superfine Tea Powder
2.5. Microscopy Observation of Superfine Tea Powder
2.6. Particle Size Distribution and Cell Wall Breakage Ratio of Superfine Tea Powder
2.7. Sedimentation Performance and Dispersion Optimization of Superfine Tea Powder
2.8. Diffusion Property Rules of Bioactive Compounds of Superfine Tea Powder
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
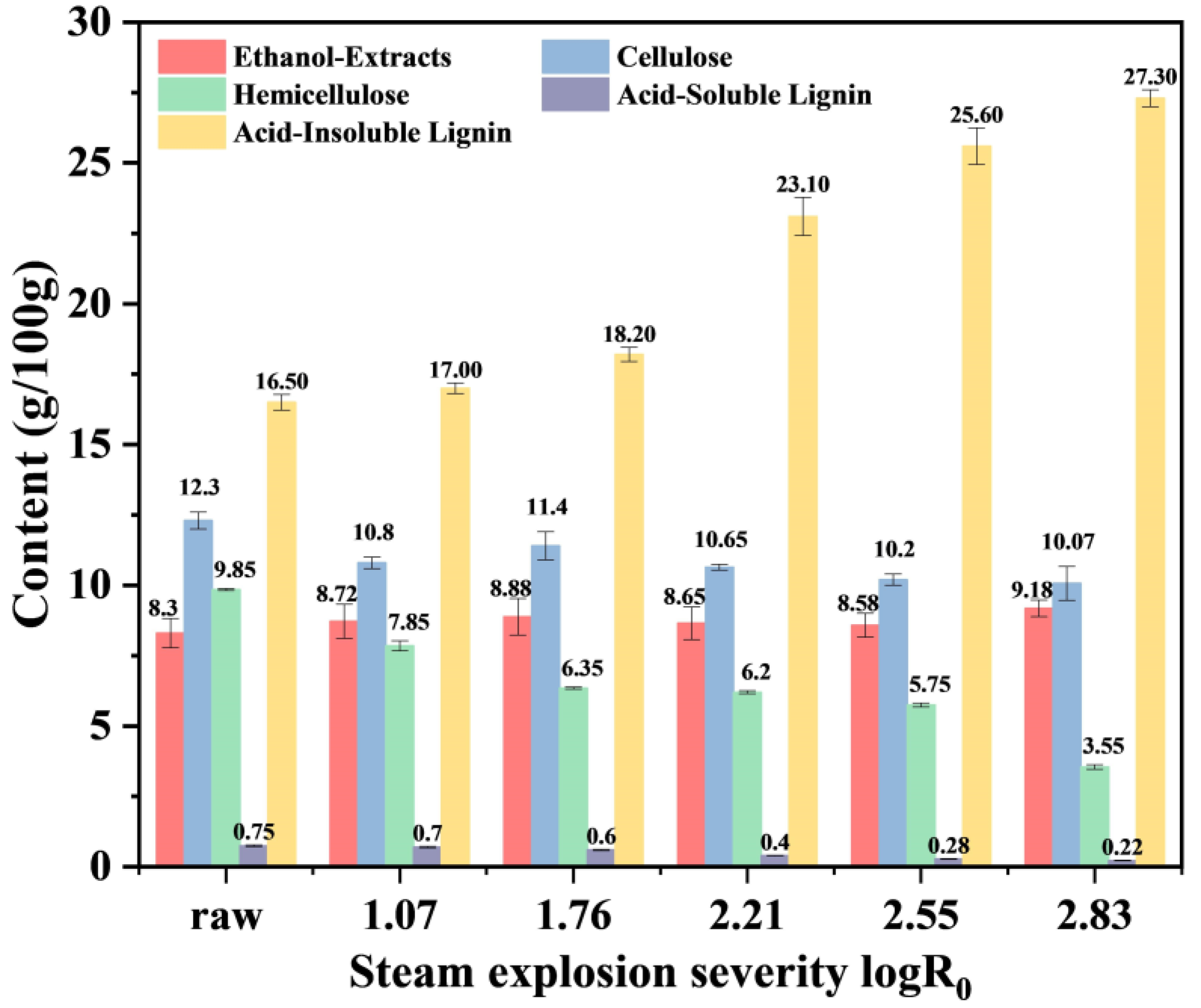
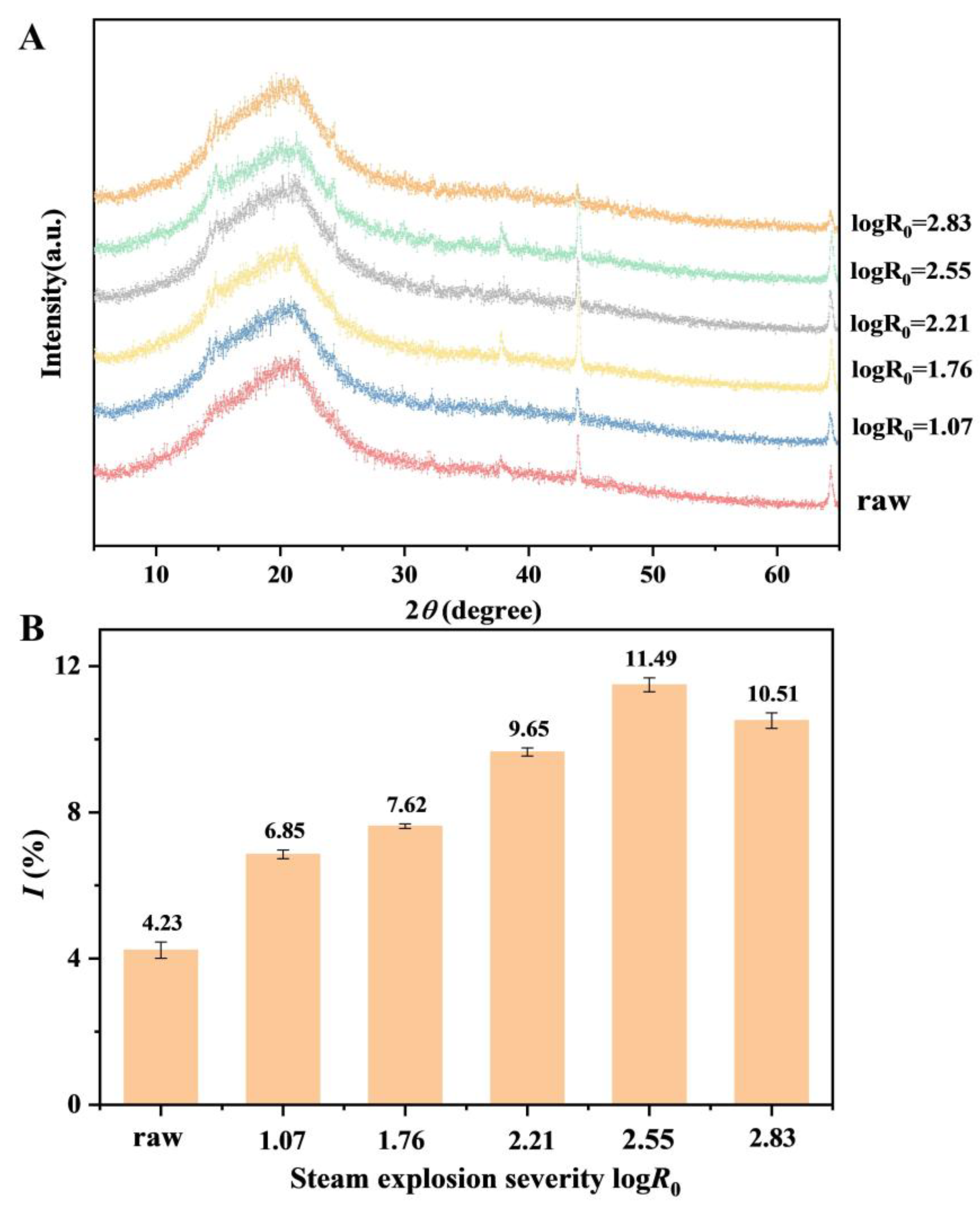
3.1. Effects of Steam Explosion on Chemical Properties of Low-Grade Tea
3.1.1. Chemical Composition
3.1.2. Crystallinity Index
3.1.3. Thermal Stability
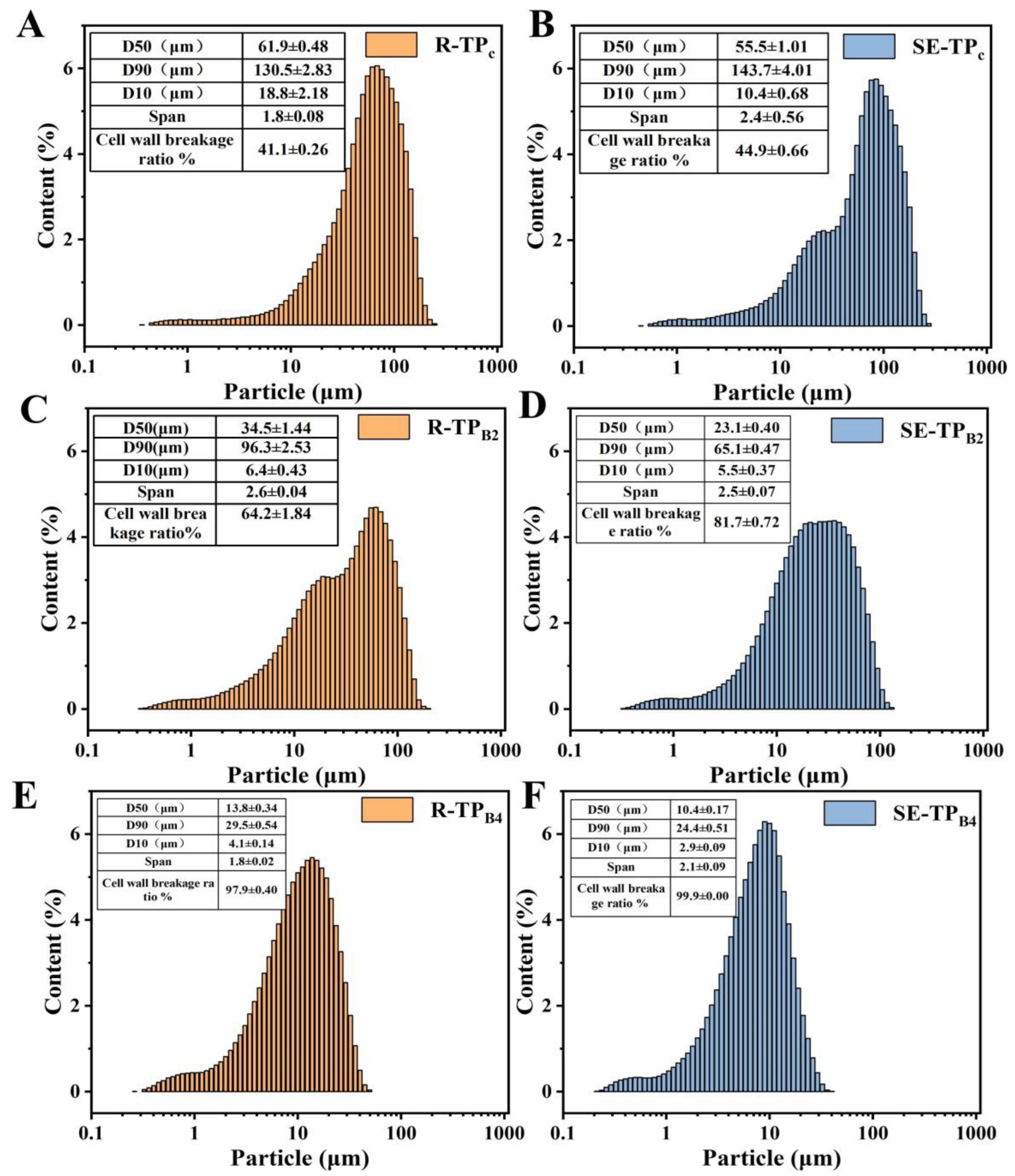
3.2. Powder Property and Solubilization Property of Low-Grade Tea After Steam Explosion and Superfine Grinding
3.2.1. Microstructure
3.2.2. Particle Size Distribution and Cell Wall Breakage Ratio
3.2.3. Sedimentation Performance and Dispersion Optimization
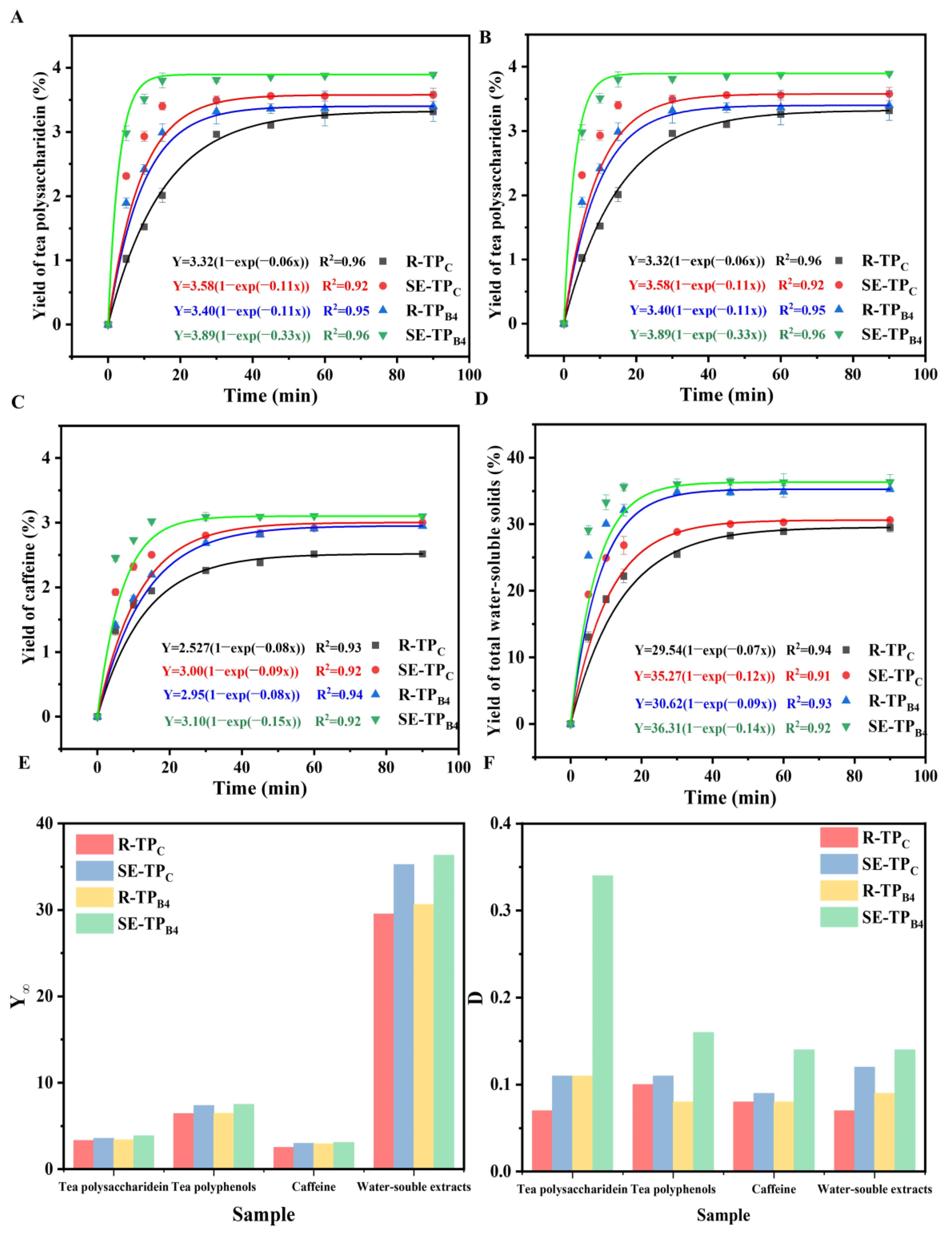
3.3. Diffusion Property of Bioactive Compounds of Low-Grade Tea Powder by Steam Explosion and Superfine Grinding
3.4. Industrial Scalability and Energy Consumption Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mozumder, N.H.M.R.; Lee, J.; Hong, Y. A Comprehensive Understanding of Camellia sinensis Tea Metabolome: From Tea Plants to Processed Teas. Annu. Rev. Food Sci. Technol. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, T.; Wu, S.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Q.; Guo, Y.; Guan, H.; Wang, D.; Dong, R.; et al. Vine tea (Ampelopsis grossedentata)—A different kind of tea hidden deep in the mountains of China: A comprehensive review of the nutritional profile, functional effect, and diverse applications as a novel raw material in food practices. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2025, 159, 104939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Saadony, M.T.; Yang, T.; Saad, A.M.; Alkafaas, S.S.; Elkafas, S.S.; Eldeeb, G.S.; Mohammed, D.M.; Salem, H.M.; Korma, S.A.; Loutfy, S.A.; et al. Polyphenols: Chemistry, bioavailability, bioactivity, nutritional aspects and human health benefits: A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 277, 134223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, Q.; Xiao, G.; Wang, L.; Xu, J.; Hou, C.; Liao, T.; Rao, X.; Mao, J.; Chen, L. Effect of steam explosion pretreatment on the fermentation characteristics of polysaccharides from tea residue. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 279, 134920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, M.; Sirisena, S.; Ng, K. Phytochemical profile of differently processed tea: A review. J. Food Sci. 2022, 87, 1925–1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, Y.; Wang, L.; Chen, H. Recalcitrant structure analysis of the enzymatic residues in corn stover pretreated with steam explosion. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2024, 222, 119772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Wang, J.; Zhao, L.; Cui, Z.; Yao, S.; Li, G.; Yuan, J. Compost tea: Preparation, utilization mechanisms, and agricultural applications potential—A comprehensive review. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2025, 38, 104137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auxenfans, T.; Cronier, D.; Chabbert, B.; Paes, G. Understanding the structural and chemical changes of plant biomass following steam explosion pretreatment. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2017, 10, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imcharoen, U.; Rachtanapun, P.; Thipchai, P.; Sae Eng, R.; Chinvorarat, S.; Jearanaisilawong, P. Effects of Steam Explosion on Curcumin Extraction from Fresh Turmeric Chips. Plants 2024, 13, 3417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duguma, H.T.; Zhang, L.; Ofoedu, C.E.; Chacha, J.S.; Agunbiade, A.O. Potentials of superfine grinding in quality modification of food powders. CYTA J. Food 2023, 21, 530–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Guo, X.; Bai, X.; Zhang, J.; Huo, R.; Zhang, Y. Improving the adsorption characteristics and antioxidant activity of oat bran by superfine grinding. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 11, 216–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, M.; Hou, G.G.; Wang, L.; Chen, Z. Effects of superfine grinding on the quality characteristics of whole-wheat flour and its raw noodle product. J. Cereal Sci. 2014, 60, 382–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Guo, W.; Gao, X.; Wang, Y.; Sun, S. Effect of superfine grinding on physicochemical and antioxidant properties of soybean residue powder. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 8, 1208–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, F.; Wang, L.; Gao, H.; Chen, H. Process of steam explosion assisted superfine grinding on particle size, chemical composition and physico-chemical properties of wheat bran powder. Powder Technol. 2020, 371, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraljić, K.; Škevin, D.; Čukelj Mustač, N.; Benković, M.; Drakula, S.; Balbino, S.; Mandura Jarić, A.; Mamilović, K.; Ramljak, I.; Ćurić, D. Influence of Cryogenic Grinding on the Nutritional and Antinutritional Components of Rapeseed Cake. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 5841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, N.; Fan, J.; Chen, N.; Chen, H. Effect of ball milling treatment on the structural, physicochemical and digestive properties of wheat starch, A- and B-type starch granules. J. Cereal Sci. 2022, 104, 103439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Dai, Z.; Jiang, X.; Yu, L.; Hu, M.; Peng, J.; Zhou, F. Influence and optimization of long-time superfine grinding on the physicochemical features of green tea powder. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2023, 117, 105124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, W.; Chen, H. Effects of water states on steam explosion of lignocellulosic biomass. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 199, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, W.; Chen, H. Multi-stage energy analysis of steam explosion process. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2014, 116, 254–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, W.; Li, S.; Zhou, X.; Dou, Z.; Liu, R.; Wu, T.; Jia, H.; Wang, G.; Zhang, M. Potential Hydrothermal-Humification of Vegetable Wastes by Steam Explosion and Structural Characteristics of Humified Fractions. Molecules 2021, 26, 3841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Chen, Z.; Lin, X.; Ren, Z.; Li, B.; Zhang, Y. Preparation and characterization of microcrystalline cellulose (MCC) from tea waste. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 184, 164–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Xiao, W.; Ji, G.; Gao, C.; Chen, X.; Cao, Y.; Han, L. Effects of multiscale-mechanical grinding process on physicochemical properties of black tea particles and their water extracts. Food Bioprod. Process. 2017, 105, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, W.; Zhang, Y.; Fan, C.; Han, L. A method for producing superfine black tea powder with enhanced infusion and dispersion property. Food Chem. 2017, 214, 242–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levoguer, C. Using laser diffraction to measure particle size and distribution. Met. Powder Rep. 2013, 68, 15–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xiao, W.; Cao, Y.; Ji, G.; Gao, C.; Han, L. The effect of ultrafine and coarse grinding on the suspending and precipitating properties of black tea powder particles. J. Food Eng. 2018, 223, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, W.; Zhou, X.; Su, H.; Wang, G.; Jiang, W.; Liu, R.; Wu, T.; Wang, S.; Jin, Y.; Zhang, M. Multi-fractal structure features of corn stalks and their correlation with pretreatment homogeneity and efficacy. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 346, 126573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besserer, A.; Mougnala Moukagni, E.; Ziegler-Devin, I.; Brosse, N. Extraction of polymeric hemicelluloses from okoumé sapwood by steam explosion: Use of non-destructive characterization methods. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2024, 208, 117808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Liu, X.; Zhang, J.; Sui, W.; Jang, J.; Si, C. One-pot lignin depolymerization and activation by solid acid catalytic phenolation for lightweight phenolic foam preparation. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2018, 124, 216–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, W.; Chen, H. Extraction enhancing mechanism of steam exploded Radix Astragali. Process Biochem. 2014, 49, 2181–2190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Chen, H. Air–steam explosion enhancing the extraction efficiency of chlorogenic acid from leaves of Eucommia ulmoides Oliver. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2015, 146, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, X.; Li, S.; Zhang, T.; Sui, W.; Zhang, M.; Yang, S.; Chen, H. Physical properties, phenolic profile and antioxidant capacity of Java tea (Clerodendranthus spicatus) stems as affected by steam explosion treatment. Food Chem. 2024, 440, 138190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, X.; Su, Y.; Wu, Y.; Li, M.; Lu, Y.; Xue, H.; Li, G. Comprehensive understanding of impacts of steam explosion on facilitated extraction and transformation of flavonoids from Astragali Radix. Food Chem. 2025, 463, 141410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, S.; Li, Y.; Chen, H.; Liu, Y.; Yin, L. Effects of high-pressure homogenization on thermal and electrical properties of wheat starch. J. Food Eng. 2014, 128, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, C.; Li, F.; Liu, L.; Tan, Z. Deep eutectic solvents used as the green media for the efficient extraction of caffeine from Chinese dark tea. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 227, 115723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, J.; Li, X.; Wang, S.; Wu, T.; Liu, P. Steam explosion pretreatment of Achyranthis bidentatae radix: Modified polysaccharide and its antioxidant activities. Food Chem. 2022, 375, 131746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, A.; Hou, C.; Sun, J.; Wan, F. Effect of steam explosion on phenolic compounds and antioxidant capacity in adzuki beans. J. Sci. Food. Agric. 2020, 100, 4495–4503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Deng, Z.; Yu, C.; Wu, J.; Luo, T. Effects of steam explosion on raspberry leaf structure and the release of water-soluble nutrients and phenolics. Food Chem. 2024, 445, 138708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H. Gas Explosion Technology and Biomass Refinery; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2015; ISBN 9401774129;9789401774123. [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez-Gloria, K.D.; Rodriguez-Jasso, R.M.; Rosero-Chasoy, G.; Shiva; Kostas, E.T.; Aparicio, E.; Sanchez, A.; Lopez-Sandin, I.; Ruiz, H.A. Scale-up of hydrothermal processing: Liquid hot water and pilot-scale tubular steam explosion batch reactor for bioethanol production using macroalgae Sargassum spp biomass. Bioresour. Technol. 2023, 369, 128448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serrano-Martínez, V.M.; Pérez-Aguilar, H.; Carbonell-Blasco, M.P.; Arán-Ais, F.; Orgilés-Calpena, E. Steam Explosion-Based Method for the Extraction of Cellulose and Lignin from Rice Straw Waste. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.Y.; Liu, J.F.; Wu, N.N.; Tan, B. Effect of steam explosion treatment on structural and physicochemical properties, and potential application of soluble dietary fiber from grain and oil processing by-products: A review. Cereal Chem. 2024, 101, 437–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhuang, X.; Chen, Y.; Wang, S.; Zhong, K.; Sui, W.; Ma, C.; Wu, M. Steam Explosion Enhances the Powder Property, Instant Solubility, and Diffusivity of Superfine Ground Tea Powder. Foods 2025, 14, 1345. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14081345
Zhuang X, Chen Y, Wang S, Zhong K, Sui W, Ma C, Wu M. Steam Explosion Enhances the Powder Property, Instant Solubility, and Diffusivity of Superfine Ground Tea Powder. Foods. 2025; 14(8):1345. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14081345
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhuang, Xin, Yue Chen, Shuiqing Wang, Kai Zhong, Wenjie Sui, Chao Ma, and Maoyu Wu. 2025. "Steam Explosion Enhances the Powder Property, Instant Solubility, and Diffusivity of Superfine Ground Tea Powder" Foods 14, no. 8: 1345. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14081345
APA StyleZhuang, X., Chen, Y., Wang, S., Zhong, K., Sui, W., Ma, C., & Wu, M. (2025). Steam Explosion Enhances the Powder Property, Instant Solubility, and Diffusivity of Superfine Ground Tea Powder. Foods, 14(8), 1345. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14081345






