Comprehensive Insights of Biochemical and Sensory Characterization in Takifugu obscurus by Environmental Modulation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Method
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Sample Collections
2.3. Preparation of T. obscurus
2.4. Quantitation of Proximate Composition
2.4.1. Crude Protein
2.4.2. Crude Lpid
2.4.3. Ash and Moisture
2.5. Quantitation of Free Amino Acid
2.6. Quantitation of Nucleotides
2.7. Quantitation of Inorganic Ions
2.8. Sensory Evaluation
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Distribution and Content of Parameters
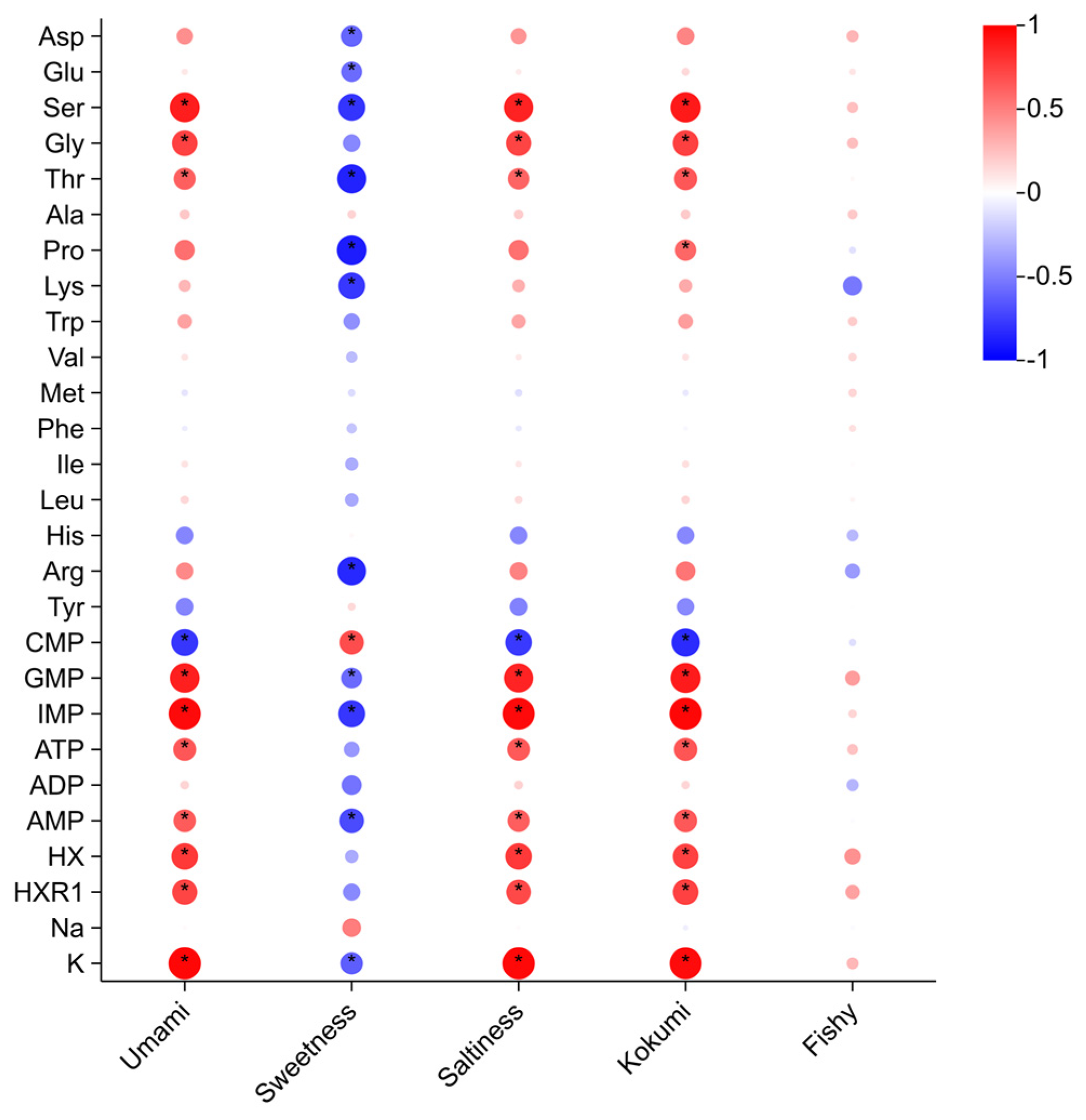
3.2. Correlation Analysis Between Chemical Components and Sensory Attributes
3.3. Environmental Factor Stratification
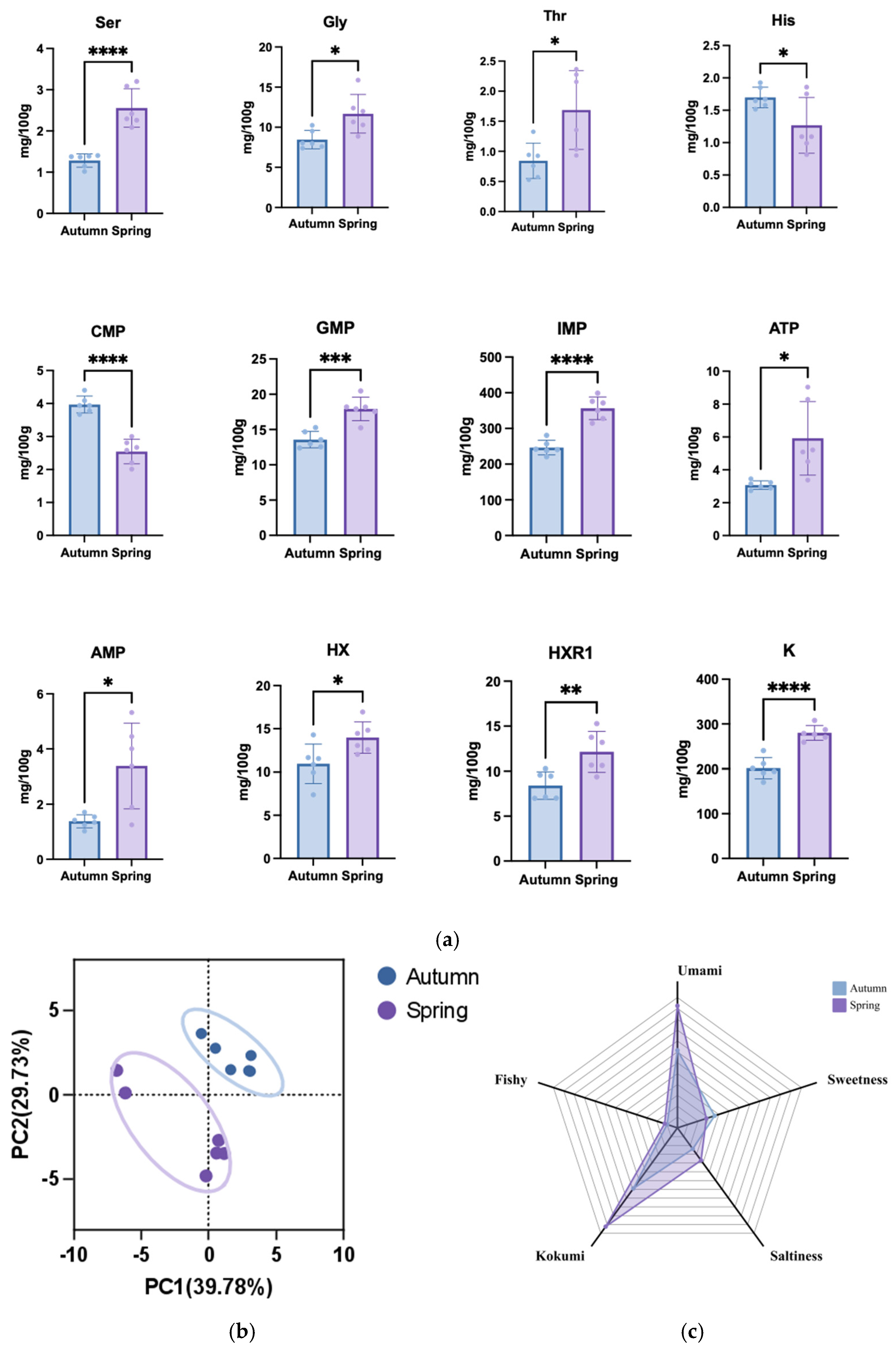
3.3.1. Insights into Seasonal Variations
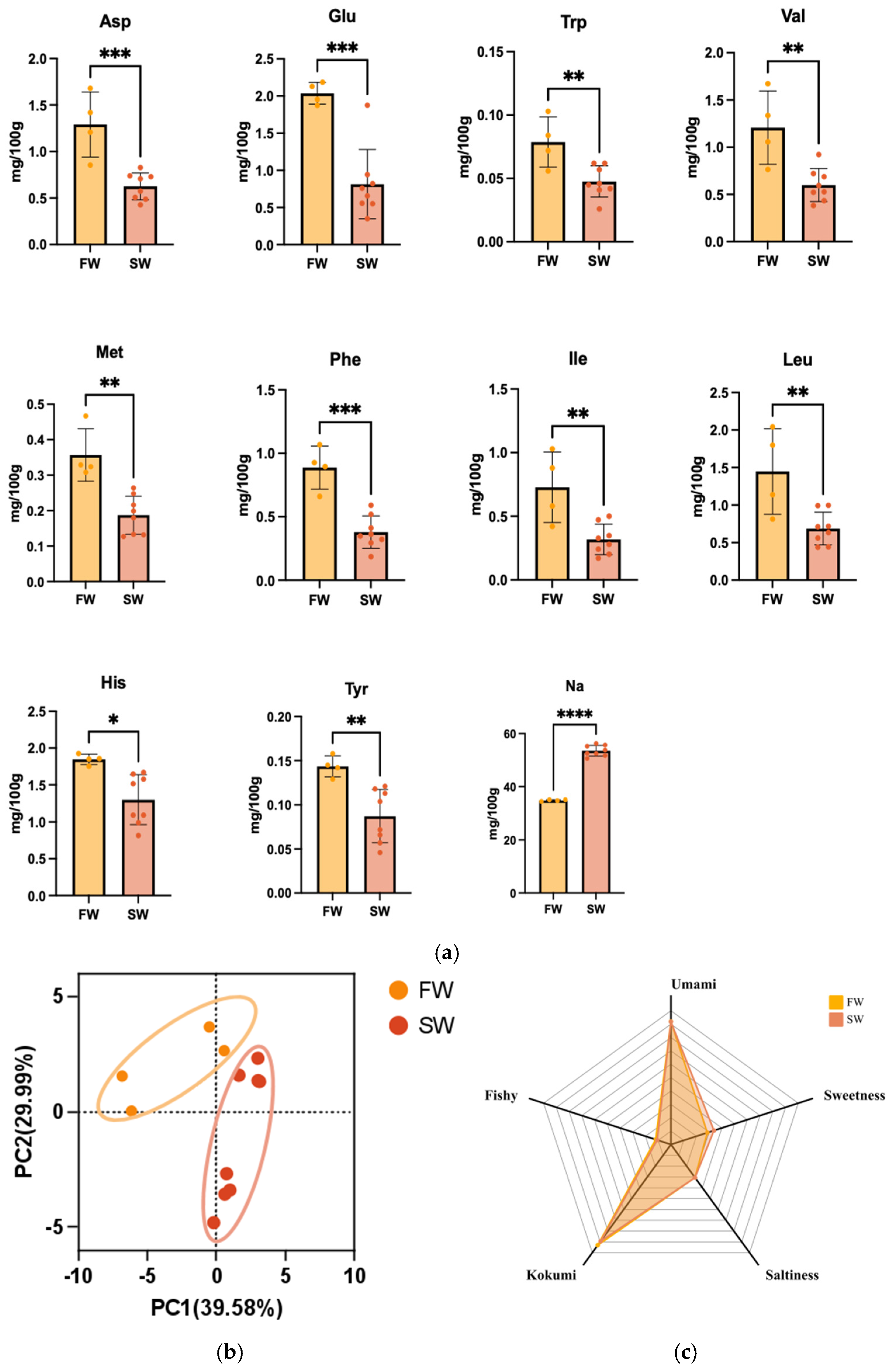
3.3.2. Insights into Salinity Conditions
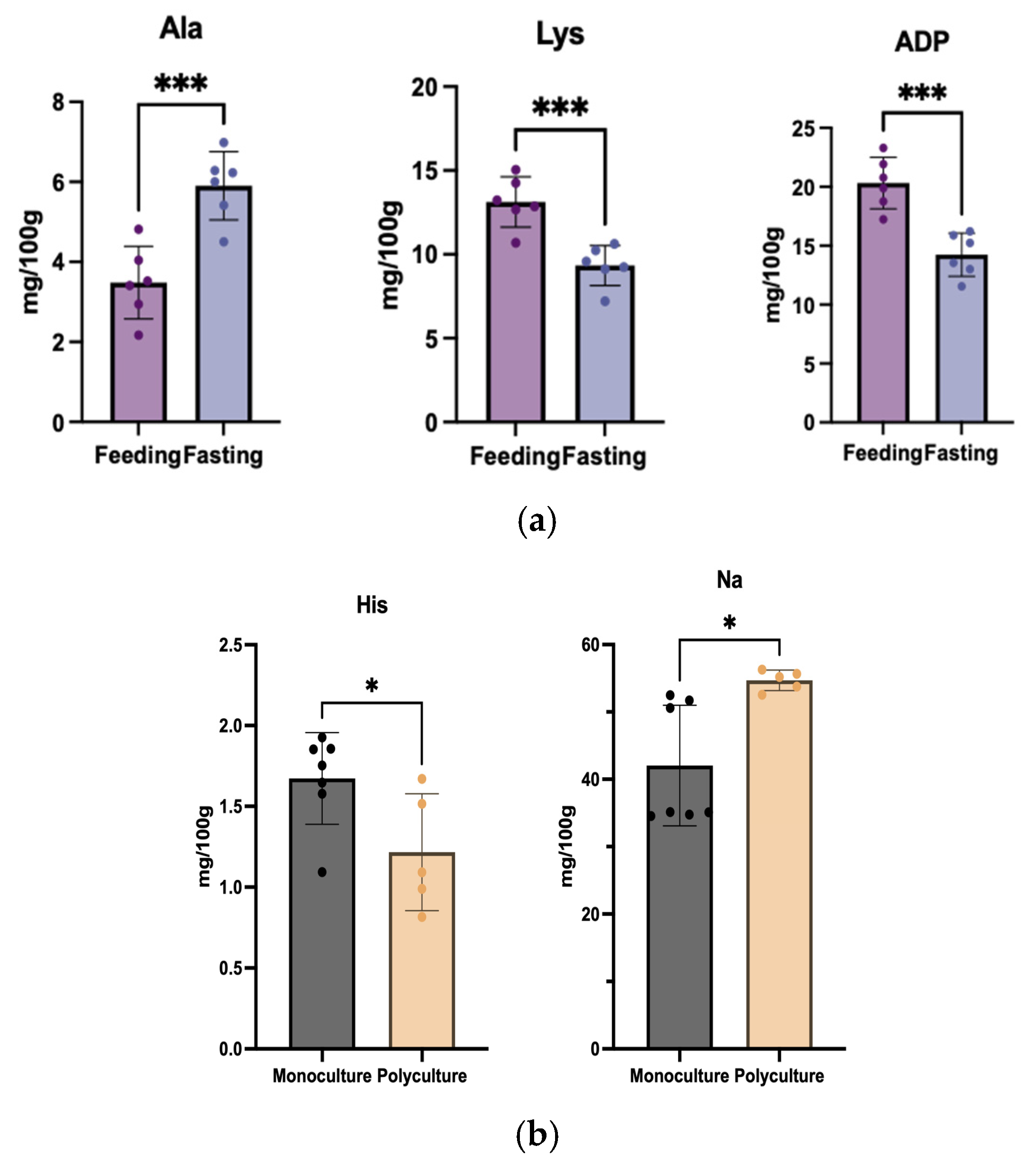
3.3.3. Insights into Nutritional Regime
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tao, N.; Wang, L.; Gong, X.; Liu, Y. Comparison of nutritional composition of farmed pufferfish muscles among Fugu obscurus, Fugu flavidus and Fugu rubripes. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2012, 28, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, L.; Tao, N. Analysis and Evaluation of Nutritional Composition of Farmed Male Pufferfish (Takifugu Obscurus). SHS Web Conf. 2014, 6, 03010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Qiu, J.; Tang, Y.; Xu, J.; Huang, S.; Liu, Y.; Ouyang, G. Rapid in vivo determination of tetrodotoxin in pufferfish (Fugu) muscle by solid-phase microextraction coupled to high-performance liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. Talanta 2017, 171, 179–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, D.F.; Chen, T.Y.; Shiau, C.Y.; Jeng, S.S. Seasonal variations of free amino acids and nucleotiderelated compounds in the muscle of cultured Taiwanese puffer Takifugu rubripes. Fish. Sci. 2000, 66, 1123–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Wang, X.; Liu, Y.; Xu, X.L.; Zhou, G. Isolation and identification of flavour peptides from Puffer fish (Takifugu obscurus) muscle using an electronic tongue and MALDI-TOF/TOF MS/MS. Food Chem. 2012, 135, 1463–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Ayed, C.; Wang, W.; Liu, Y. Sensory-Guided Analysis of Key Taste-Active Compounds in Pufferfish (Takifugu obscurus). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 13809–13816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siman Li, D.F.; Tang, Y.; Shi, Y.; Huang, D. Nutritional Quality of Takifugu obscurus and Related Research Progress. Qual. Saf. Agric. Prod. 2022, 1, 99–104. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, N.; Sakakibara, T.; Liang, J.; Hamada, Y.; Murata, M.; Taniyama, S.; Yagi, M.; Tachibana, K. Influence of Diluted Seawater Rearing on Flesh Quality of Cultured Tiger Puffer Takifugu rubripes. Aquac. Sci. 2013, 61, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, G.-Y.; Lee, J.-Y. The effect of feeding frequency, water temperature, and stocking density on the growth of river puffer Takifugu obscurus reared in a zero-exchange water system. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2016, 19, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexi, N.; Byrne, D.V.; Nanou, E.; Grigorakis, K. Investigation of sensory profiles and hedonic drivers of emerging aquaculture fish species. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2018, 98, 1179–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matuha, M.; Fornshell, G.; Kumar, G.; Cain, K.D. Sensory profiles and market potential of burbot Lota lota maculosa-An emerging aquaculture species. Int. J. Gastron. Food Sci. 2024, 36, 100950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyldig, G.; Nielsen, D. A eview of sensory and instrumental methods used to evaluate the texture of fish muscle. J. Texture Stud. 2001, 32, 219–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Wang, W.; Li, B.; Liu, Y. Non-volatile taste active compounds and umami evaluation in two aquacultured pufferfish (Takifugu obscurus and Takifugu rubripes). Food Biosci. 2019, 32, 100468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardo, Y.A.A.; Rosario, D.K.A.; Delgado, I.F.; Conte-Junior, C.A. Fish Quality Index Method: Principles, weaknesses, validation, and alternatives—A review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2020, 19, 2657–2676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, M.K.; Issac, A.; Minhas, N.; Sarkar, B. Image processing based method to assess fish quality and freshness. J. Food Eng. 2016, 177, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassoun, A.; Karoui, R. Quality evaluation of fish and other seafood by traditional and nondestructive instrumental methods: Advantages and limitations. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017, 57, 1976–1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 27624-2011; Processing Specifications for Fresh and Frozen Products of Farmed Takifugu rubripes. Standardization Administration of China: Beijing, China, 2011.
- Marcó, A.; Rubio, R.; Compañó, R.; Casals, I. Comparison of the Kjeldahl method and a combustion method for total nitrogen determination in animal feed. Talanta 2002, 57, 1019–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mariotti, F.; Tomé, D.; Mirand, P.P. Converting Nitrogen into Protein—Beyond 6.25 and Jones’ Factors. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2008, 48, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.M.; Trevino, B.; Chaiyawat, M. A Simple and Rapid Solvent ExtractionMethod for Determining Total Lipids in Fish Tissue. J. AOAC Int. 1996, 79, 487–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sluiter, A.; Hames, B.; Ruiz, R.; Scarlata, C.; Sluiter, J.; Templeton, D. Determination of Ash in Biomass: LAP-005 NREL Analytical Procedure; National Renewable Energy Laboratory: Golden, CO, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Sluiter, A.; Hames, B.; Ruiz, R.; Scarlata, C.; Sluiter, J.; Templeton, D.; Crocker, D.L. Determination of structural carbohydrates and lignin in biomass. Lab. Anal. Proced. 2008, 1617, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Łozowicka, B.; Kaczyński, P.; Iwaniuk, P. Analysis of 22 free amino acids in honey from Eastern Europe and Central Asia using LC-MS/MS technique without derivatization step. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2021, 98, 103837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranogajec, A.; Beluhan, S.; Šmit, Z. Analysis of nucleosides and monophosphate nucleotides from mushrooms with reversed-phase HPLC. J. Sep. Sci. 2010, 33, 1024–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Palacios, T.; Salas, A.; Muñoz, A.; Ocaña, E.-R.; Antequera, T. Sodium chloride determination in meat products: Comparison of the official titration-based method with atomic absorption spectrometry. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2022, 108, 104425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, M.J. Practical Handbook Sensory Analysis; Instituto Politecnico de Beja: Beja, Portugal, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Meyer, S.; Dunkel, A.; Hofmann, T. Sensomics-Assisted Elucidation of the Tastant Code of Cooked Crustaceans and Taste Reconstruction Experiments. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 1164–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eldridge, S.M.; Ashby, D.; Kerry, S. Sample size for cluster randomized trials: Effect of coefficient of variation of cluster size and analysis method. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2006, 35, 1292–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fallah, A.A.; Nematollahi, A.; Saei-Dehkordi, S.S. Proximate composition and fatty acid profile of edible tissues of Capoeta damascina (Valenciennes, 1842) reared in freshwater and brackish water. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2013, 32, 150–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosain, M.E.; Amin, S.M.N.; Kamarudin, M.S.; Arshad, A.; Karim, M.; Romano, N. Effect of salinity on growth, survival, and proximate composition of Macrobrachium rosenbergii post larvae as well as zooplankton composition reared in a maize starch based biofloc system. Aquaculture 2021, 533, 736235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo-Vargasmachuca, S.; Ponce-Palafox, J.; Arambul-Muñoz, E.; Lopez-Gomez, C.; Arredondo-Figueroa, J.L.; Spanopoulos-Hernandez, M. The combined effects of salinity and temperature on the proximate composition and energetic value of spotted rose snapper Lutjanus guttatus (Steindachner, 1869). Lat. Am. J. Aquat. Res. 2017, 45, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horie, R.; Imagawa, T.; Uchida, K.; Taoka, Y.; Tanaka, R. Effect of seasons and fishing ban period on umami-related and functional components of greeneye (Chlorophthalmus albatrossis) from Japanese coast. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2025, 139, 107163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, M.; Wang, S.; Wang, J.; Chang, Q.; Mai, K. Comparison of flavor components in shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei cultured in sea water and low salinity water. Fish. Sci. 2008, 74, 1173–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Monroig, Ó.; Zhou, Q.; Tocher, D.R.; Yuan, Y.; Zhu, T.; Lu, J.; Song, D.; Jiao, L.; Jin, M. Environmental salinity and dietary lipid nutrition strategy: Effects on flesh quality of the marine euryhaline crab Scylla paramamosain. Food Chem. 2021, 361, 130160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyake, Y.; Roy, B.C.; Ando, M.; Okada, T.; Sawada, Y.; Seoka, M.; Kawasaki, K.-I.; Tsukamasa, Y. Effects of Brief Summer or Winter Fasting on the Muscle Quality of Cultured Pacific Bluefin Tuna (Thunnus orientalis). J. Aquat. Food Prod. Technol. 2011, 20, 196–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šimat, V.; Hamed, I.; Petričević, S.; Bogdanović, T. Seasonal Changes in Free Amino Acid and Fatty Acid Compositions of Sardines, Sardina pilchardus (Walbaum, 1792): Implications for Nutrition. Foods 2020, 9, 867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, S.; Chen, L.; Sun, Z.; Wen, Y.; Xue, Q.; Xue, C.; Li, Z.; Sun, C.; Wei, Z.; Liu, H. Investigating influence of aquaculture seawater with different salinities on non-volatile taste-active compounds in Pacific oyster (Crassostrea gigas). J. Food Meas. Charact. 2021, 15, 2078–2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajeb, P.; Jinap, S. Umami Taste Components and Their Sources in Asian Foods. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2015, 55, 778–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzeja, P.; Terzic, A. Adenylate Kinase and AMP Signaling Networks: Metabolic Monitoring, Signal Communication and Body Energy Sensing. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2009, 10, 1729–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Luo, N.; Guo, C.; Luo, J.; Wei, J.; Zhang, N.; Yin, X.; Feng, X.; Wang, X.; Cao, J. Current trends and perspectives on salty and salt taste–enhancing peptides: A focus on preparation, evaluation and perception mechanisms of salt taste. Food Res. Int. 2024, 190, 114593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Liu, K.; Yu, X.; Yang, H.; Han, W. Building a Kokumi Database and Machine Learning-Based Prediction: A Systematic Computational Study on Kokumi Analysis. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2024, 64, 2670–2680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Zhang, L.; Lametsch, R. Current progress in kokumi-active peptides, evaluation and preparation methods: A review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 62, 1230–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, T.; Inui-Yamamoto, C. The flavor-enhancing action of glutamate and its mechanism involving the notion of kokumi. npj Sci. Food 2023, 7, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Huang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Cai, S.; Zhu, B.; Dong, X. Recent advances in fishy odour in aquatic fish products, from formation to control. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 56, 4959–4969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lü, H.; Xu, J.; Haegen, G.V. Supplementing Marine Capture Fisheries in the East China Sea: Sea Ranching of Prawn Penaeus orientalis, Restocking of Large Yellow Croaker Pseudosciaena crocea, and Cage Culture. Rev. Fish. Sci. 2008, 16, 366–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, G.; Jiang, S.; Song, Y.; Yang, L.; Zhao, H.; Ding, H.; Xu, J.; Ma, A.; Cheng, Y.; Muhammad, L.Y. Impact of Overwintering Hoard on the Edible Tissues, Muscle Quality, Hepatopancreas Color, and Proximate Biochemical and Amino Acid Compositions of Male Eriocheir sinensis. Aquac. Res. 2023, 1, 8143352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, K.; Zhu, G.; Shi, C.; Ye, Y.; Li, R.; Mu, C.; Ren, Z.; Wu, Q.; Wang, C. Overwintering temperature affects the nutrient composition and non-volatile flavor substances of female adult mud crab Scylla paramamosain in recirculating aquaculture systems (RASs). Aquaculture 2024, 578, 740053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco, S.L.; Suárez, M.P.; Juan, F.S. Seasonal changes of nucleotides in mussel (Mytilus galloprovincialis) mantle tissue. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2006, 143, 384–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Gao, Q.; Yang, X.; Jiang, W.; Hao, L.; Yu, Y.; Tian, Y.; Huang, M.; Gao, Q.; Yang, X.; et al. Free amino acids in response to salinity changes in fishes: Relationships to osmoregulation. Fish. Physiol. Biochem. 2023, 49, 1031–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crockett, E.L.; Sidell, B.D. Some Pathways of Energy Metabolism Are Cold Adapted in Antarctic Fishes. Physiol. Zool. 1990, 63, 0156223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berthelot, C.; Clarke, J.; Desvignes, T.; William Detrich, H.; Flicek, P.; Peck, L.S.; Peters, M.; Postlethwait, J.H.; Clark, M.S. Adaptation of Proteins to the Cold in Antarctic Fish: A Role for Methionine? Genome Biol. Evol. 2019, 11, 220–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, M.; Li, Z.; Xiong, B.; Zhu, J. Effects of salinity on food intake, growth, and survival of pufferfish (Fugu obscurus). J. Appl. Ichthyol. 2004, 20, 146–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Li, X.; Qin, K.; Gao, T.; Wang, C.; Wang, H. Effects of low salinity on fatty acid and free amino acid composition of muscle tissues in Portunus trituberculatus. Aquac. Res. 2022, 53, 1627–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Niu, M.; Qin, K.; Hu, Y.; Li, Y.; Che, C.; Wang, C.; Mu, C.; Wang, H. Enhancement of Nutrient Composition and Non-Volatile Flavor Substances in Muscle Tissue of Red Drum (Sciaenops ocellatus) Through Inland Low Salinity Saline-Alkaline Water Culture. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2024, 72, 7326–7335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Hou, J.; Liu, H.; Zhu, H.; Xu, G.; Xu, J. Adaptive evolution of low-salinity tolerance and hypoosmotic regulation in a euryhaline teleost, Takifugu obscurus. Mar. Biol. 2020, 167, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, K.; Feng, W.; Ji, Z.; Jiang, X.; Hu, Y.; Li, Y.; Che, C.; Wang, C.; Mu, C.; Wang, H. Shrimp Cultured in Low-Salt Saline–Alkali Water has a Better Amino Acid Nutrition and Umami─Comparison of Flavors between Saline–Alkali Water- and Seawater-Cultured Litopenaeus vannamei. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2024, 72, 6585–6592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, X.; Zhang, W.; He, J.; Zhao, M.; Wang, J.; Dong, X.; Fu, Y.; Xie, X.; Miao, S. The Impact of Rearing Salinity on Flesh Texture, Taste, and Fatty Acid Composition in Largemouth Bass Micropterus salmoides. Foods 2022, 11, 3261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangiao-Alvarellos, S.; Guzmán, J.M.; Láiz-Carrión, R.; Míguez, J.M.; Río, M.P.M.D.; Mancera, J.M.; Soengas, J.L. Interactive effects of high stocking density and food deprivation on carbohydrate metabolism in several tissues of gilthead sea bream Sparus auratus. J. Exp. Zool. Part A Comp. Exp. Biol. 2005, 303A, 761–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viegas, I.; Rito, J.; González, J.D.; Jarak, I.; Carvalho, R.A.; Metón, I.; Pardal, M.A.; Baanante, I.V.; Jones, J.G. Effects of food-deprivation and refeeding on the regulation and sources of blood glucose appearance in European seabass (Dicentrarchus labrax L.). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2013, 166, 399–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, C.; Ye, J.; Yang, J.; Gao, C.; Yan, H.; Li, H.; Wang, X. mTORC1 Mediates Lysine-Induced Satellite Cell Activation to Promote Skeletal Muscle Growth. Cells 2019, 8, 1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.; Lu, X.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Ma, H.; Tan, Y.; Guan, Y.; Jia, R.; Xie, E.; Feng, A.; et al. Effects of fasting on golden pompano Trachinotus ovatus: Physiological and biochemical responses. Aquaculture 2025, 595, 741637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grigorakis, K.; Alexis, M.N. Effects of fasting on the meat quality and fat deposition of commercial-size farmed gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata, L.) fed different dietary regimes. Aquac. Nutr. 2005, 11, 341–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansour, A.T.; Allam, B.W.; Srour, T.M.; Omar, E.A.; Nour, A.A.M.; Khalil, H.S. The Feasibility of Monoculture and Polyculture of Striped Catfish and Nile Tilapia in Different Proportions and Their Effects on Growth Performance, Productivity, and Financial Revenue. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, S.; Li, S.; Li, Q.; Sun, Y.; Zheng, Z.; Nie, Z.; Tang, Z.; Wang, P.; Gao, J.; Xu, G. Polyculture Affects the Growth, Antioxidant Status, Nutrient Content, and Flavor of Chinese Mitten Crabs (Eriocheir sinensis) and Largemouth Bass (Micropterus salmoides). Fishes 2022, 7, 355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Collection Season | Water Environment | Pre-Harvest Treatment | Group Code |
|---|---|---|---|
| Autumn | Freshwater (0‰) | Regular feeding | AUN |
| Autumn | Freshwater (0‰) | 5-day fasting | AUY |
| Autumn | Saline (3‰) | Regular feeding(mixed) | ASN-M |
| Autumn | Saline (3‰) | 5-day fasting(mixed) | ASY-M |
| Autumn | Saline (3‰) | Regular feeding | ASN |
| Autumn | Saline (3‰) | 5-day fasting | ASY |
| Spring | Freshwater (0‰) | Regular feeding | SUN |
| Spring | Freshwater (0‰) | 5-day fasting | SUY |
| Spring | Saline (3‰) | Regular feeding (mixed) | SSN-M |
| Spring | Saline (3‰) | 5-day fasting (mixed) | SSY-M |
| Spring | Saline (3‰) | Regular feeding | SSN |
| Spring | Saline (3‰) | 5-day fasting | SSY |
| Parameter | Range | Mean | CV (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Moisture (%) | 74.17–79.25 | 76.16 | 2.20 |
| Ash (%) | 3.38–4.39 | 3.84 | 8.45 |
| Crude protein (mg/100 g) | 17.60–22.46 | 19.50 | 8.17 |
| Crude lipid (mg/100 g) | 0.60–2.10 | 1.13 | 39.63 |
| Asp (mg/100 g) | 0.43–1.68 | 0.87 | 45.94 |
| Glu (mg/100 g) | 0.35–2.19 | 1.16 | 60.69 |
| Ser (mg/100 g) | 1.02–3.20 | 1.98 | 35.85 |
| Gly (mg/100 g) | 7.38–15.87 | 10.27 | 26.64 |
| Thr (mg/100 g) | 0.53–2.37 | 1.19 | 51.97 |
| Ala (mg/100 g) | 2.17–6.98 | 4.50 | 46.06 |
| Pro (mg/100 g) | 0.47–4.63 | 1.79 | 88.85 |
| Lys (mg/100 g) | 7.20–15.04 | 11.45 | 23.54 |
| Trp (mg/100 g) | 0.026–0.10 | 0.061 | 36.29 |
| Val (mg/100 g) | 0.38–1.67 | 0.93 | 45.06 |
| Met (mg/100 g) | 0.13–0.47 | 0.27 | 39.07 |
| Phe (mg/100 g) | 0.18–1.07 | 0.53 | 64.65 |
| Ile (mg/100 g) | 0.17–1.03 | 0.53 | 62.42 |
| Leu (mg/100 g) | 0.44–2.04 | 0.98 | 60.28 |
| His (mg/100 g) | 0.82–1.93 | 1.58 | 30.12 |
| Arg (mg/100 g) | 4.02–8.66 | 6.44 | 26.55 |
| Tyr (mg/100 g) | 0.046–0.14 | 0.099 | 31.60 |
| CMP (mg/100 g) | 2.01–4.40 | 3.18 | 26.64 |
| GMP (mg/100 g) | 12.56–20.47 | 15.33 | 16.17 |
| IMP (mg/100 g) | 220.48–398.78 | 288.53 | 19.70 |
| ATP (mg/100 g) | 2.73–9.04 | 4.20 | 49.72 |
| ADP (mg/100 g) | 11.56–23.31 | 16.80 | 26.94 |
| AMP (mg/100 g) | 1.02–5.32 | 2.89 | 52.17 |
| HX (mg/100 g) | 7.38–16.94 | 12.65 | 26.83 |
| HXR1 (mg/100 g) | 6.99–15.28 | 10.72 | 25.19 |
| Na (mg/100 g) | 34.55–56.29 | 47.14 | 15.83 |
| K (mg/100 g) | 170.28–307.80 | 236.29 | 17.65 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, S.; Huang, X.; Fang, C.; Shi, Y.; Lou, X.; Huang, D.; Tang, Y. Comprehensive Insights of Biochemical and Sensory Characterization in Takifugu obscurus by Environmental Modulation. Foods 2025, 14, 1386. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14081386
Li S, Huang X, Fang C, Shi Y, Lou X, Huang D, Tang Y. Comprehensive Insights of Biochemical and Sensory Characterization in Takifugu obscurus by Environmental Modulation. Foods. 2025; 14(8):1386. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14081386
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Siman, Xuanyun Huang, Changling Fang, Yongfu Shi, Xiaoyi Lou, Dongmei Huang, and Yunyu Tang. 2025. "Comprehensive Insights of Biochemical and Sensory Characterization in Takifugu obscurus by Environmental Modulation" Foods 14, no. 8: 1386. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14081386
APA StyleLi, S., Huang, X., Fang, C., Shi, Y., Lou, X., Huang, D., & Tang, Y. (2025). Comprehensive Insights of Biochemical and Sensory Characterization in Takifugu obscurus by Environmental Modulation. Foods, 14(8), 1386. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14081386






