A Review on In Vitro Evaluation of Chemical and Physical Digestion for Controlling Gastric Digestion of Food
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Food Digestion Process in GI Tract

1.2. Controlling the Food Digestion Process
1.3. In Vitro Evaluation of Gastric Digestion
1.4. Objectives of This Review

2. Standardization of In Vitro Chemical Digestion Protocols
2.1. INFOGEST Static In Vitro Digestion Protocol
| INFOGEST Protocol | Proposed Paper | Subject | Static/Semi-dynamic * 3 | Static Protocol : Major Items Standardized Other Protocols : Major Differences from the Static Protocol | Recent Application Examples [Ref.] * 6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Static Protocol | [66,67] * 2 | Healthy adults | Static |
| |
| Semi-dynamic Protocol | [72] | Healthy adults | Semi-dynamic |
| |
| Static Infant Protocol * 1 | [76] | Full-term newborns (28 days old) | Static |
| |
| Static Older Adult Protocol | [80] | Adults over 65 years old | Static |
|
2.2. Variation of INFOGEST Protocol
3. Recent Studies on In Vitro Evaluation of Physical Digestion in the Stomach
3.1. Current GI Tract Devices Simulating Gastric Peristalsis
3.2. Utilization of Agar Gel Beads for Force Validation in GI Tract Devices
3.3. Possibility of Using Hydrogel Food and Gastric GI Tract Device to Study Gastric Digestion Control
4. Summary, Prospects, and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bornhorst, G.M.; Singh, R.P. Gastric Digestion in Vivo and in Vitro: How the Structural Aspects of Food Influence the Digestion Process. Annu. Rev. Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 5, 111–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Unger, A.L.; Astrup, A.; Feeney, E.L.; Holscher, H.D.; Gerstein, D.E.; Torres-Gonzalez, M.; Brown, K. Harnessing the Magic of the Dairy Matrix for Next-Level Health Solutions: A Summary of a Symposium Presented at Nutrition 2022. Curr. Dev. Nutr. 2023, 7, 100105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bornhorst, G.M.; Gouseti, O.; Wickham, M.S.J.; Bakalis, S. Engineering Digestion: Multiscale Processes of Food Digestion. J. Food Sci. 2016, 81, R534–R543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cichero, J.A.Y. Evaluating Chewing Function: Expanding the Dysphagia Field Using Food Oral Processing and the IDDSI Framework. J. Texture Stud. 2020, 51, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sensoy, I. A Review on the Food Digestion in the Digestive Tract and the Used in Vitro Models. Curr. Res. Food Sci. 2021, 4, 308–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abodi, M.; Mazzocchi, A.; Risé, P.; Marangoni, F.; Agostoni, C.; Milani, G.P. Salivary Fatty Acids in Humans: A Comprehensive Literature Review. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2025, 63, 14–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalabert-Malbos, M.-L.; Mishellany-Dutour, A.; Woda, A.; Peyron, M.-A. Particle Size Distribution in the Food Bolus after Mastication of Natural Foods. Food Qual. Prefer. 2007, 18, 803–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandhra, G.K.; Chaichanavichkij, P.; Birch, M.; Scott, S.M. Gastrointestinal Transit Times in Health as Determined Using Ingestible Capsule Systems: A Systematic Review. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 5272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, F.; Singh, R.P. Disintegration of Solid Foods in Human Stomach. J. Food Sci. 2008, 73, R67–R80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Jin, Y.; Wilde, P.J.; Hou, Y.; Wang, Y.; Han, J. Mechanisms, Physiology, and Recent Research Progress of Gastric Emptying. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 61, 2742–2755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baba, S.; Sasaki, A.; Nakajima, J.; Obuchi, T.; Koeda, K.; Wakabayashi, G. Assessment of Gastric Motor Function by Cine Magnetic Resonance Imaging. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2009, 24, 1401–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopirajah, R.; Raichurkar, K.P.; Wadhwa, R.; Anandharamakrishnan, C. The Glycemic Response to Fibre Rich Foods and Their Relationship with Gastric Emptying and Motor Functions: An MRI Study. Food Funct. 2016, 7, 3964–3972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Somaratne, G.; Ferrua, M.J.; Ye, A.; Nau, F.; Floury, J.; Dupont, D.; Singh, J. Food Material Properties as Determining Factors in Nutrient Release during Human Gastric Digestion: A Review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 60, 3753–3769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Kong, F. Simulating Human Gastrointestinal Motility in Dynamic in Vitro Models. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2022, 21, 3804–3833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwiatek, M.A.; Steingoetter, A.; Pal, A.; Menne, D.; Brasseur, J.G.; Hebbard, G.S.; Boesiger, P.; Thumshirn, M.; Fried, M.; Schwizer, W. Quantification of Distal Antral Contractile Motility in Healthy Human Stomach with Magnetic Resonance Imaging. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2006, 24, 1101–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Grady, G.; Gharibans, A.A.; Du, P.; Huizinga, J.D. The Gastric Conduction System in Health and Disease: A Translational Review. Am. J. Physiol. -Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2021, 321, G527–G542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivera del Rio, A.; Keppler, J.K.; Boom, R.M.; Janssen, A.E.M. Protein Acidification and Hydrolysis by Pepsin Ensure Efficient Trypsin-Catalyzed Hydrolysis. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 4570–4581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iddir, M.; Porras Yaruro, J.F.; Larondelle, Y.; Bohn, T. Gastric Lipase Can Significantly Increase Lipolysis and Carotenoid Bioaccessibility from Plant Food Matrices in the Harmonized INFOGEST Static in Vitro Digestion Model. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 9043–9053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gardner, J.D.; Ciociola, A.A.; Robinson, M. Measurement of Meal-Stimulated Gastric Acid Secretion by in Vivo Gastric Autotitration. J. Appl. Physiol. 2002, 92, 427–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malagelada, J.-R.; Longstreth, G.F.; Summerskill, W.H.J.; Go, V.L.W. Measurement of Gastric Functions During Digestion of Ordinary Solid Meals in Man. Gastroenterology 1976, 70, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camilleri, M.; Malagelada, J.R.; Brown, M.L.; Becker, G.; Zinsmeister, A.R. Relation between Antral Motility and Gastric Emptying of Solids and Liquids in Humans. Am. J. Physiol. 1985, 249, G580–G585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graff, J.; Brinch, K.; Madsen, J.L. Simplified Scintigraphic Methods for Measuring Gastrointestinal Transit Times. Clin. Physiol. 2000, 20, 262–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.C.; Prather, C.; Fisher, R.S.; Meyer, J.H.; Summers, R.W.; Pimentel, M.; Mccallum, R.W.; Akkermans, L.M.A.; Loening-Baucke, V.; Transit, A.T.F.C. on G. Measurement of Gastrointestinal Transit. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2005, 50, 989–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, K.A. Gastric Emptying of Liquids and Solids: Roles of Proximal and Distal Stomach. Am. J. Physiol. 1980, 239, G71–G76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coupe, A.J.; Davis, S.S.; Evans, D.F.; Wilding, I.R. Correlation of the Gastric Emptying of Nondisintegrating Tablets with Gastrointestinal Motility. Pharm. Res. 1991, 8, 1281–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, D.F.; Pye, G.; Bramley, R.; Clark, A.G.; Dyson, T.J.; Hardcastle, J.D. Measurement of Gastrointestinal PH Profiles in Normal Ambulant Human Subjects. Gut 1988, 29, 1035–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalantzi, L.; Goumas, K.; Kalioras, V.; Abrahamsson, B.; Dressman, J.B.; Reppas, C. Characterization of the Human Upper Gastrointestinal Contents Under Conditions Simulating Bioavailability/Bioequivalence Studies. Pharm. Res. 2006, 23, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinch, K.; Larsson, H.B.; Madsen, J.L. A Deconvolution Technique for Processing Small Intestinal Transit Data. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. 1999, 26, 272–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Feunteun, S.; Verkempinck, S.; Floury, J.; Janssen, A.; Kondjoyan, A.; Marze, S.; Mirade, P.-S.; Pluschke, A.; Sicard, J.; van Aken, G.; et al. Mathematical Modelling of Food Hydrolysis during in Vitro Digestion: From Single Nutrient to Complex Foods in Static and Dynamic Conditions. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 116, 870–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dima, C.; Assadpour, E.; Dima, S.; Jafari, S.M. Bioavailability and Bioaccessibility of Food Bioactive Compounds; Overview and Assessment by in Vitro Methods. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2020, 19, 2862–2884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbonell-Capella, J.M.; Buniowska, M.; Barba, F.J.; Esteve, M.J.; Frígola, A. Analytical Methods for Determining Bioavailability and Bioaccessibility of Bioactive Compounds from Fruits and Vegetables: A Review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2014, 13, 155–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bornet, F.R.; Billaux, M.S.; Messing, B. Glycaemic Index Concept and Metabolic Diseases. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 1997, 21, 207–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Granfeldt, Y.; Bjorck, I.; Hagander, B. On the Importance of Processing Conditions, Product Thickness and Egg Addition for the Glycaemic and Hormonal Responses to Pasta: A Comparison with Bread Made from “Pasta Ingredients”. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 1991, 45, 489–499. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Musa-Veloso, K.; Poon, T.; Harkness, L.S.; O’Shea, M.; Chu, Y. The Effects of Whole-Grain Compared with Refined Wheat, Rice, and Rye on the Postprandial Blood Glucose Response: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 108, 759–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.; Qiao, D.; Zhao, S.; Zhang, B.; Lin, Q.; Xie, F. Whole Grain Rice: Updated Understanding of Starch Digestibility and the Regulation of Glucose and Lipid Metabolism. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2022, 21, 3244–3273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norton, J.E.; Gonzalez Espinosa, Y.; Watson, R.L.; Spyropoulos, F.; Norton, I.T. Functional Food Microstructures for Macronutrient Release and Delivery. Food Funct. 2015, 6, 663–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, C.; Jiang, P.; Chai, J.; Jiang, Y.; Li, D.; Bao, W.; Liu, B.; Liu, B.; Norde, W.; Li, Y. The Delivery of Sensitive Food Bioactive Ingredients: Absorption Mechanisms, Influencing Factors, Encapsulation Techniques and Evaluation Models. Food Res. Int. 2019, 120, 130–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qazi, H.J.; Ye, A.; Acevedo-Fani, A.; Singh, H. Delivery of Encapsulated Bioactive Compounds within Food Matrices to the Digestive Tract: Recent Trends and Future Perspectives. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2024, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, I.H.; Matia-Merino, L.; Huffman, L.M. Use of Viscous Fibres in Beverages for Appetite Control: A Review of Studies. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2015, 66, 479–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristensen, M.; Jensen, M.G. Dietary Fibres in the Regulation of Appetite and Food Intake. Importance of Viscosity. Appetite 2011, 56, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Wilde, P.J.; Hou, Y.; Wang, Y.; Han, J.; Liu, W. An Evolving View on Food Viscosity Regulating Gastric Emptying. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 63, 5783–5799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norton, J.E.; Wallis, G.A.; Spyropoulos, F.; Lillford, P.J.; Norton, I.T. Designing Food Structures for Nutrition and Health Benefits. Annu. Rev. Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 5, 177–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourlieu, C.; Menard, O.; Bouzerzour, K.; Mandalari, G.; Macierzanka, A.; Mackie, A.R.; Dupont, D. Specificity of Infant Digestive Conditions: Some Clues for Developing Relevant in Vitro Models. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2014, 54, 1427–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oustamanolakis, P.; Tack, J. Dyspepsia: Organic versus Functional. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2012, 46, 175–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calligaris, S.; Moretton, M.; Melchior, S.; Mosca, A.C.; Pellegrini, N.; Anese, M. Designing Food for the Elderly: The Critical Impact of Food Structure. Food Funct. 2022, 13, 6467–6483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kido, Y. The Issue of Nutrition in an Aging Society. J. Nutr. Sci. Vitaminol. 2015, 61, S176–S177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muramatsu, N.; Akiyama, H. Japan: Super-Aging Society Preparing for the Future. Gerontologist 2011, 51, 425–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Pillidge, C.; Harrison, B.; Adhikari, B. Pathways in Formulating Foods for the Elderly. Food Res. Int. 2024, 186, 114324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugie, M.; Harada, K.; Nara, M.; Kugimiya, Y.; Takahashi, T.; Kitagou, M.; Kim, H.; Kyo, S.; Ito, H. Prevalence, Overlap, and Interrelationships of Physical, Cognitive, Psychological, and Social Frailty among Community-Dwelling Older People in Japan. Arch. Gerontol. Geriatr. 2022, 100, 104659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovat, L.B. Age Related Changes in Gut Physiology and Nutritional Status. Gut 1996, 38, 306–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baron, J.H. Studies of Basal and Peak Acid Output with an Augmented Histamine Test. Gut 1963, 4, 136–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vellas, B.; Balas, D.; Moreau, J.; Bouisson, M.; Senegas-Balas, F.; Guidet, M.; Ribet, A. Exocrine Pancreatic Secretion in the Elderly. Int. J. Pancreatol. 1988, 3, 497–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldman, M.; Cryer, B.; McArthur, K.E.; Huet, B.A.; Lee, E. Effects of Aging and Gastritis on Gastric Acid and Pepsin Secretion in Humans: A Prospective Study. Gastroenterology 1996, 110, 1043–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, T.L.; Berardi, R.R.; Barnett, J.L.; Dermentzoglou, L.C.; Jarvenpaa, K.M.; Schmaltz, S.P.; Dressman, J.B. Upper Gastrointestinal PH in Seventy-Nine Healthy, Elderly, North American Men and Women. Pharm. Res. 1993, 10, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Jonge, C.S.; Smout, A.J.P.M.; Nederveen, A.J.; Stoker, J. Evaluation of Gastrointestinal Motility with MRI: Advances, Challenges and Opportunities. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2018, 30, e13257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, K.-H.; Liu, Z.; Jaffey, D.; Wo, J.M.; Mosier, K.M.; Cao, J.; Wang, X.; Powley, T.L. Automatic Assessment of Human Gastric Motility and Emptying from Dynamic 3D Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2022, 34, e14239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Alkaabi, F.; Choi, M.; Di Natale, M.R.; Scheven, U.M.; Noll, D.C.; Furness, J.B.; Liu, Z. Surface Mapping of Gastric Motor Functions Using MRI: A Comparative Study between Humans and Rats. Am. J. Physiol. -Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2024, 327, G345–G359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishida, S.; Miyagawa, T.; O’Grady, G.; Cheng, L.K.; Imai, Y. Quantification of Gastric Emptying Caused by Impaired Coordination of Pyloric Closure with Antral Contraction: A Simulation Study. J. R. Soc. Interface 2019, 16, 20190266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhar, S.; Lee, J.H.; Seo, J.-H.; Pasricha, P.J.; Mittal, R. Effect of Stomach Motility on Food Hydrolysis and Gastric Emptying: Insight from Computational Models. Phys. Fluids 2022, 34, 111909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmada, N.; Hosseini, S.; Avci, R.; Cater, J.E.; Suresh, V.; Cheng, L.K. A Systematic Review of Computational Fluid Dynamics Models in the Stomach and Small Intestine. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 6092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClements, D.J.; Li, Y. Review of in Vitro Digestion Models for Rapid Screening of Emulsion-Based Systems. Food Funct. 2010, 1, 32–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerra, A.; Etienne-Mesmin, L.; Livrelli, V.; Denis, S.; Blanquet-Diot, S.; Alric, M. Relevance and Challenges in Modeling Human Gastric and Small Intestinal Digestion. Trends Biotechnol. 2012, 30, 591–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duijsens, D.; Pälchen, K.; Guevara-Zambrano, J.M.; Verkempinck, S.H.E.; Infantes-Garcia, M.R.; Hendrickx, M.E.; Van Loey, A.M.; Grauwet, T. Strategic Choices for in Vitro Food Digestion Methodologies Enabling Food Digestion Design. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 126, 61–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, I.; Kozu, H.; Wang, Z.; Isoda, H.; Ichikawa, S. Development and Fundamental Characteristics of a Human Gastric Digestion Simulator for Analysis of Food Disintegration. Jpn. Agric. Res. Q. JARQ 2017, 51, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; He, X.; Zhao, R.; Shi, Q.; Nian, Y.; Hu, B. Hydrogels as Promising Carriers for the Delivery of Food Bioactive Ingredients. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 1006520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodkorb, A.; Egger, L.; Alminger, M.; Alvito, P.; Assunção, R.; Ballance, S.; Bohn, T.; Bourlieu-Lacanal, C.; Boutrou, R.; Carrière, F.; et al. INFOGEST Static in Vitro Simulation of Gastrointestinal Food Digestion. Nat. Protoc. 2019, 14, 991–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minekus, M.; Alminger, M.; Alvito, P.; Ballance, S.; Bohn, T.; Bourlieu, C.; Carrière, F.; Boutrou, R.; Corredig, M.; Dupont, D.; et al. A Standardised Static in Vitro Digestion Method Suitable for Food-an International Consensus. Food Funct. 2014, 5, 1113–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hur, S.J.; Lim, B.O.; Decker, E.A.; McClements, D.J. In Vitro Human Digestion Models for Food Applications. Food Chem. 2011, 125, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abik, F.; Ho, T.M.; Lehtonen, M.; Philo, M.; Booth, C.; Mandalari, G.; Wilde, P.J.; Mikkonen, K.S. The Two-Faced Functionality of Birch Glucuronoxylan in an Emulsion-Based Carrier of Vitamin D3. Food Hydrocoll. 2024, 157, 110442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Matos, F.M.; Rasera, G.B.; de Castro, R.J.S. Multifunctional Properties of Peptides Derived from Black Cricket (Gryllus Assimilis) and Effects of in Vitro Digestion Simulation on Their Bioactivities. Food Res. Int. 2024, 196, 115134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Janssen, A.E.M.; Smeets, P.A.M.; Stieger, M. Impact of Microstructure of Whey Protein Gels on in Vitro Gastric Protein Digestion Is Sustained after Oral Structural Breakdown by Mastication. Food Hydrocoll. 2025, 159, 110619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulet-Cabero, A.-I.; Egger, L.; Portmann, R.; Ménard, O.; Marze, S.; Minekus, M.; Le Feunteun, S.; Sarkar, A.; Grundy, M.M.-L.; Carrière, F.; et al. A Standardised Semi-Dynamic in Vitro Digestion Method Suitable for Food—An International Consensus. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 1702–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duijsens, D.; Verkempinck, S.H.E.; Somers, E.; Hendrickx, M.E.G.; Grauwet, T. From Static to Semi-Dynamic in Vitro Digestion Conditions Relevant for the Older Population: Starch and Protein Digestion of Cooked Lentils. Food Funct. 2024, 15, 591–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daniloski, D.; Page, R.M.; Lamichhane, P.; Fitzpatrick, C.J.; Vasiljevic, T.; Brodkorb, A.; Timlin, M.; Murphy, J.P.; O’Callaghan, T.F.; McCarthy, N.A. Cheddar Cheese Production, Structure and in-Vitro Semi-Dynamic Gastric Digestion: The Role of β-Casein Phenotype. Food Res. Int. 2024, 196, 115008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, C.; Xu, Z.; Wu, K.; Wang, J.; Guo, J.; Yang, X. Study on Gastric Digestion Behavior of Phytase-Treated Soybean Protein: A Semi-Dynamic Digestion Method. Food Chem. 2025, 463, 141118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ménard, O.; Bourlieu, C.; De Oliveira, S.C.; Dellarosa, N.; Laghi, L.; Carrière, F.; Capozzi, F.; Dupont, D.; Deglaire, A. A First Step towards a Consensus Static in Vitro Model for Simulating Full-Term Infant Digestion. Food Chem. 2018, 240, 338–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Wichers, H.J.; Hettinga, K.A. Glycation of Soy and Pea Proteins Influences Infant Gastric Digestibility More than Intestinal Digestibility. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 136, 108251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miltenburg, J.; Bastiaan-Net, S.; Hoppenbrouwers, T.; Wichers, H.; Hettinga, K. Gastric Clot Formation and Digestion of Milk Proteins in Static in Vitro Infant Gastric Digestion Models Representing Different Ages. Food Chem. 2024, 432, 137209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komatsu, Y.; Wada, Y.; Shibasaki, T.; Kitamura, Y.; Ehara, T.; Nakamura, H.; Miyaji, K. Comparison of Protein Digestibility of Human Milk and Infant Formula Using the INFOGEST Method under Infant Digestion Conditions. Br. J. Nutr. 2024, 132, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ménard, O.; Lesmes, U.; Shani-Levi, C.S.; Araiza Calahorra, A.; Lavoisier, A.; Morzel, M.; Rieder, A.; Feron, G.; Nebbia, S.; Mashiah, L.; et al. Static in Vitro Digestion Model Adapted to the General Older Adult Population: An INFOGEST International Consensus. Food Funct. 2023, 14, 4569–4582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-García, J.; Muñoz-Pina, S.; García-Hernández, J.; Tárrega, A.; Heredia, A.; Andrés, A. Protein Digestibility and ACE Inhibitory Activity of Fermented Flours in Older Adults and Standard Gastrointestinal Simulation. Food Res. Int. 2024, 180, 114080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavoisier, A.; Chevalier, S.; Henry, G.; Ossemond, J.; Harel-Oger, M.; Garric, G.; Dupont, D.; Morzel, M. Impact of Age on the Digestion of Cream Cheese Formulated with Opposite Caseins to Whey Proteins Ratios: An in Vitro Study. Food Res. Int. 2024, 190, 114621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Z.; Shi, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Shi, W.; Zhang, L.; Yin, M.; Wang, X. Comparison of in Vitro Digestive Characteristics of Proteins from Different Sources in Simulated Elderly Gastrointestinal Conditions. Food Chem. 2025, 463, 141299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egger, L.; Ménard, O.; Delgado-Andrade, C.; Alvito, P.; Assunção, R.; Balance, S.; Barberá, R.; Brodkorb, A.; Cattenoz, T.; Clemente, A.; et al. The Harmonized INFOGEST in Vitro Digestion Method: From Knowledge to Action. Food Res. Int. 2016, 88, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quiroz-Eraso, S.; Paola Rodriguez-Castaño, G.; Quintanilla-Carvajal, M.X.; Acosta-González, A. Microencapsulation of Fat-Removing Lactobacillales and Polyphenols from Theobroma cacao L. as a Combined Strategy for Intestinal Removal of Free Fatty Acids Evaluated by Simulated in Vitro Digestion. J. Funct. Foods 2024, 118, 106258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, R.; Xu, M. Metabolomics Analysis for Unveiling the Toxicological Mechanism of Silver Nanoparticles Using an In Vitro Gastrointestinal Digestion Model. ACS Nanosci. Au 2024, 4, 327–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sartori, A.G.d.O.; Saliba, A.S.M.C.; Bitencourt, B.S.; Guedes, J.S.; Torres, L.C.R.; de Alencar, S.M.; Augusto, P.E.D. Anthocyanin Bioaccessibility and Anti-Inflammatory Activity of a Grape-Based 3D Printed Food for Dysphagia. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2023, 84, 103289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Nan, X.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, L.; Chen, J.; Li, J.; Wang, H.; Ruan, Z. Effect of 3D Food Printing Processing on Polyphenol System of Loaded Aronia Melanocarpa and Post-Processing Evaluation of 3D Printing Products. Foods 2023, 12, 2068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Tan, Y.; McClements, D.J. Applications of the INFOGEST In Vitro Digestion Model to Foods: A Review. Annu. Rev. Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 14, 135–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombo, R.; Ferron, L.; Frosi, I.; Papetti, A. Advances in Static in Vitro Digestion Models after the COST Action Infogest Consensus Protocol. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 7619–7636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramanian, P.; Nadia, J.; Paul Singh, R.; Bornhorst, G.M. Comparison of Four Digestion Protocols on the Physical Characteristics of Gastric Digesta from Cooked Couscous Using the Human Gastric Simulator. Food Funct. 2023, 14, 8229–8247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Xu, R.; Xiu, H.; Feng, J.; Jin Park, H.; Prabhakar, H.; Kong, F. Effect of Cinnamon on Starch Hydrolysis of Rice Pudding: Comparing Static and Dynamic in Vitro Digestion Models. Food Res. Int. 2022, 161, 111813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavoisier, A.; Morzel, M.; Chevalier, S.; Henry, G.; Jardin, J.; Harel-Oger, M.; Garric, G.; Dupont, D. In Vitro Digestion of Two Protein-Rich Dairy Products in the Ageing Gastrointestinal Tract. Food Funct. 2023, 14, 9377–9390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Liu, D.; Tao, X.; Zhang, J.; Huppertz, T.; Regenstein, J.M.; Liu, X.; Zhou, P. Decalcification Strongly Affects in Vitro Gastrointestinal Digestion of Bovine Casein Micelles under Infant, Adult and Elderly Conditions. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 139, 108515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, B.S.T.; Garcia-Rojas, E.E. Double Emulsions as Delivery Systems for Iron: Stability Kinetics and Improved Bioaccessibility in Infants and Adults. Curr. Res. Food Sci. 2022, 5, 718–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marques, M.C.; Perina, N.P.; Mosquera, E.M.B.; Tomé, T.M.; Lazarini, T.; Mariutti, L.R.B. DHA Bioaccessibility in Infant Formulas and Preschool Children Milks. Food Res. Int. 2021, 149, 110698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torcello-Gómez, A.; Dupont, D.; Jardin, J.; Briard-Bion, V.; Deglaire, A.; Risse, K.; Mechoulan, E.; Mackie, A. Human Gastrointestinal Conditions Affect in Vitro Digestibility of Peanut and Bread Proteins. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 6921–6932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torcello-Gómez, A.; Dupont, D.; Jardin, J.; Briard-Bion, V.; Deglaire, A.; Risse, K.; Mechoulan, E.; Mackie, A. The Pattern of Peptides Released from Dairy and Egg Proteins Is Highly Dependent on the Simulated Digestion Scenario. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 5240–5256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Fan, R.; Wang, X.; Zhang, L.; Wang, C.; Hou, Z.; Li, C.; Liu, L.; He, J. In Vitro Digestion and Functional Properties of Bovine β-Casein: A Comparison between Adults and Infants. Food Res. Int. 2024, 194, 114914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Liu, D.; Hong, X.; Tao, X.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, J.; Hou, Y.; Wu, T.; Liu, X.; Zhou, P. Calcium Binding Affects in Vitro Gastrointestinal Digestion of Bovine α-Lactalbumin under Infant, Adult and Elderly Conditions. Int. Dairy J. 2024, 154, 105943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Shi, J.; Xu, Y.-J.; Tan, C.-P.; Liu, Y. The Digestion Fates of Lipids with Different Unsaturated Levels in People with Different Age Groups. Food Chem. 2024, 438, 137400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnal, M.; Salcedo, L.; Talens, P.; Ribes, S. Role of Food Texture, Oral Processing Responses, Bolus Properties, and Digestive Conditions on the Nutrient Bioaccessibility of Al Dente and Soft-Cooked Red Lentil Pasta. Foods 2024, 13, 2341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez-García, J.; Muñoz-Pina, S.; García-Hernández, J.; Tárrega, A.; Heredia, A.; Andrés, A. In Vitro Digestion Assessment (Standard vs. Older Adult Model) on Antioxidant Properties and Mineral Bioaccessibility of Fermented Dried Lentils and Quinoa. Molecules 2023, 28, 7298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsukiashi, M.; Koyama, T.; Iwamoto, H.; Sonoki, H.; Miyaji, K. Evaluation of the Effect of Thickeners in Enteral Formulas on the Gastric Emptying Rate of Proteins and Carbohydrates Using a Semi-Dynamic Gastric Model. Nutrients 2024, 16, 2115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wu, K.; Guo, W.; Guo, J.; Wang, J.; Yang, X. Digestion Behavior of Plant-Based Meat Analogs with Anisotropic Fibrous Structure in a Semi-Dynamic Gastric Digestion System. Food Res. Int. 2024, 190, 114631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaeim, D.; Liu, W.; Han, J.; Wilde, P.J. Effect of Non-Starch Polysaccharides on the in Vitro Gastric Digestion of Soy-Based Milk Alternatives. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 133, 107875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shani-Levi, C.; Levi-Tal, S.; Lesmes, U. Comparative Performance of Milk Proteins and Their Emulsions under Dynamic in Vitro Adult and Infant Gastric Digestion. Food Hydrocoll. 2013, 32, 349–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dupont, D.; Mandalari, G.; Mollé, D.; Jardin, J.; Rolet-Répécaud, O.; Duboz, G.; Léonil, J.; Mills, C.E.N.; Mackie, A.R. Food Processing Increases Casein Resistance to Simulated Infant Digestion. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2010, 54, 1677–1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levi, C.S.; Lesmes, U. Bi-Compartmental Elderly or Adult Dynamic Digestion Models Applied to Interrogate Protein Digestibility. Food Funct. 2014, 5, 2402–2409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Olivas, E.; Muñoz-Pina, S.; Andrés, A.; Heredia, A. Impact of Elderly Gastrointestinal Alterations on in Vitro Digestion of Salmon, Sardine, Sea Bass and Hake: Proteolysis, Lipolysis and Bioaccessibility of Calcium and Vitamins. Food Chem. 2020, 326, 127024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvo-Lerma, J.; Fornés-Ferrer, V.; Heredia, A.; Andrés, A. In Vitro Digestion Models to Assess Lipolysis: The Impact of the Simulated Conditions of Gastric and Intestinal PH, Bile Salts and Digestive Fluids. Food Res. Int. 2019, 125, 108511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Callanan, M.; Giblin, L.; Tobin, J.; Brodkorb, A. Comparison of Conventional Heat-Treated and Membrane Filtered Infant Formulas Using an in Vitro Semi-Dynamic Digestion Method. Food Funct. 2022, 13, 8158–8167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Zhang, T.; Pan, Y.; Yang, H.; Xu, X.; Han, J.; Liu, W. Thermal Stability and in Vitro Biological Fate of Lactoferrin-Polysaccharide Complexes. Food Res. Int. 2024, 182, 114182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lajterer, C.; Shani Levi, C.; Lesmes, U. An in Vitro Digestion Model Accounting for Sex Differences in Gastro-Intestinal Functions and Its Application to Study Differential Protein Digestibility. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 132, 107850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickham, M.; Faulks, R.; Mills, C. In Vitro Digestion Methods for Assessing the Effect of Food Structure on Allergen Breakdown. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2009, 53, 952–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vardakou, M.; Mercuri, A.; Barker, S.A.; Craig, D.Q.; Faulks, R.M.; Wickham, M.S. Achieving Antral Grinding Forces in Biorelevant in Vitro Models: Comparing the USP Dissolution Apparatus II and the Dynamic Gastric Model with Human in Vivo Data. AAPS PharmSciTech 2011, 12, 620–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minekus, M.; Marteau, P.; Havenaar, R.; Veld, J.H.H.I.T. A Multicompartmental Dynamic Computer-Controlled Model Simulating the Stomach and Small Intestine. Altern. Lab. Anim. 1995, 23, 197–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, F.; Singh, R.P. A Human Gastric Simulator (HGS) to Study Food Digestion in Human Stomach. J. Food Sci. 2010, 75, E627–E635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozu, H.; Nakata, Y.; Nakajima, M.; Neves, M.A.; Uemura, K.; Sato, S.; Kobayashi, I.; Ichikawa, S. Development of a Human Gastric Digestion Simulator Equipped with Peristalsis Function for the Direct Observation and Analysis of the Food Digestion Process. Food Sci. Technol. Res. 2014, 20, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, C.; Langrish, T. A Comparison of Different Physical Stomach Models and an Analysis of Shear Stresses and Strains in These System. Food Res. Int. 2020, 135, 109296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mennah-Govela, Y.A.; Swackhamer, C.; Bornhorst, G.M. Gastric Secretion Rate and Protein Concentration Impact Intragastric PH and Protein Hydrolysis during Dynamic in Vitro Gastric Digestion. Food Hydrocoll. Health 2021, 1, 100027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Xu, Y.; Fan, T.; Liao, Z.; Wu, P.; Wu, X.; Chen, X.D. Gastric Emptying and Morphology of a ‘near Real’ in Vitro Human Stomach Model (RD-IV-HSM). J. Food Eng. 2016, 183, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Greco, I.; Ménard, O.; Lee, J.; Jeantet, R.; Dupont, D.; Le Feunteun, S. Dynamic in Vitro Gastric Digestion of Skimmed Milk Using the NERDT, an Advanced Human Biomimetic Digestion System. Food Res. Int. 2024, 195, 114898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swackhamer, C.; Bedane, T.; Keppler, S.; Poltorak, A.; Cheung, K.; Awais, N.; Marra, F.; Bornhorst, G.M. Development and Analysis of a Multi-Module Peristaltic Simulator for Gastrointestinal Research. Food Res. Int. 2023, 170, 112877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Z.; Wu, P.; Wang, J.; Dupont, D.; Menard, O.; Jeantet, R.; Chen, X.D. Achieving Realistic Gastric Emptying Curve in an Advanced Dynamic in Vitro Human Digestion System: Experiences with Cheese—A Difficult to Empty Material. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 3965–3977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madalena, D.A.; Araújo, J.F.; Ramos, Ó.L.; Vicente, A.A.; Pinheiro, A.C. Assessing the In Vitro Digestion of Lactoferrin-Curcumin Nanoparticles Using the Realistic Gastric Model. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 2237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Zhang, T.; Jin, Y.; Li, Z.; Han, J.; Tian, S. Development Details of an Artificial Gastric Digestive System (AGDS) and Analysis of Model Food Disintegration and Degradation. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 59, 1738–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barros, L.; Retamal, C.; Torres, H.; Zúñiga, R.N.; Troncoso, E. Development of an in Vitro Mechanical Gastric System (IMGS) with Realistic Peristalsis to Assess Lipid Digestibility. Food Res. Int. 2016, 90, 216–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Hashem, R.; Bhattacharya, D.; Allen, J.; Stommel, M.; Cheng, L.K.; Xu, W. SoGut: A Soft Robotic Gastric Simulator. Soft Robot. 2020, 8, 273–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payal, A.; Elumalai, A.; Murugan, S.V.; Moses, J.A.; Anandharamakrishnan, C. An Investigation on Gastric Emptying Behavior of Apple in the Dynamic Digestion Model ARK® and Its Validation Using MRI of Human Subjects—A Pilot Study. Biochem. Eng. J. 2021, 175, 108134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakita, Y.; Takahashi, M.; Tamiya, S.; Kobayashi, I. Effect of Marination in Lemon Juice on Beef Tenderization and Gastric Digestibility. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2024, 104, 809–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marciani, L.; Gowland, P.A.; Fillery-Travis, A.; Manoj, P.; Wright, J.; Smith, A.; Young, P.; Moore, R.; Spiller, R.C. Assessment of Antral Grinding of a Model Solid Meal with Echo-Planar Imaging. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2001, 280, G844–G849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Kozu, H.; Uemura, K.; Kobayashi, I.; Ichikawa, S. Effect of Hydrogel Particle Mechanical Properties on Their Disintegration Behavior Using a Gastric Digestion Simulator. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 110, 106166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wu, P.; Liu, M.; Liao, Z.; Wang, Y.; Dong, Z.; Chen, X.D. An Advanced near Real Dynamic in Vitro Human Stomach System to Study Gastric Digestion and Emptying of Beef Stew and Cooked Rice. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 2914–2925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Ye, A.; Lad, M.; Dalgleish, D.; Singh, H. Behaviour of Whey Protein Emulsion Gel during Oral and Gastric Digestion: Effect of Droplet Size. Soft Matter 2014, 10, 4173–4183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Q.; Ye, A.; Lad, M.; Ferrua, M.; Dalgleish, D.; Singh, H. Disintegration Kinetics of Food Gels during Gastric Digestion and Its Role on Gastric Emptying: An in Vitro Analysis. Food Funct. 2015, 6, 756–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Q.; Ye, A.; Lad, M.; Dalgleish, D.; Singh, H. Impact of Colloidal Structure of Gastric Digesta on In-Vitro Intestinal Digestion of Whey Protein Emulsion Gels. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 54 Pt B, 255–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Ye, A.; Lad, M.; Dalgleish, D.; Singh, H. The Breakdown Properties of Heat-Set Whey Protein Emulsion Gels in the Human Mouth. Food Hydrocoll. 2013, 33, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Kozu, H.; Uemura, K.; Kobayashi, I.; Ichikawa, S. Effect of Mechanical Properties on in Vitro Dynamic Digestion of Starch Contained in Hydrogels. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2024, 104, 3498–3506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mella, C.; Quilaqueo, M.; Zúñiga, R.N.; Troncoso, E. Impact of the Simulated Gastric Digestion Methodology on the In Vitro Intestinal Proteolysis and Lipolysis of Emulsion Gels. Foods 2021, 10, 321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, M.; Ritzoulis, C.; Liu, J.; Zhang, X.; Han, J.; Liu, W. In Vitro Digestion of Tofu with Different Textures Using an Artificial Gastric Digestive System. Food Res. Int. 2022, 157, 111458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shibasaki, M.; Maeda, T.; Tanaka, T.; Sugiyama, K.; Kozu, H.; Noguchi, R.; Umeda, T.; Araki, T.; Kobayashi, I. Observation and Analysis of In Vitro Digestibility of Different Breads Using a Human Gastric Digestion Simulator. Foods 2024, 13, 3244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Ichikawa, S.; Kozu, H.; Neves, M.A.; Nakajima, M.; Uemura, K.; Kobayashi, I. Direct Observation and Evaluation of Cooked White and Brown Rice Digestion by Gastric Digestion Simulator Provided with Peristaltic Function. Food Res. Int. 2015, 71, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Mungure, T.; Ye, A.; Loveday, S.M.; Ellis, A.; Weeks, M.; Singh, H. Intragastric Restructuring Dictates the Digestive Kinetics of Heat-Set Milk Protein Gels of Contrasting Textures. Food Res. Int. 2024, 195, 114944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somaratne, G.; Ye, A.; Nau, F.; Ferrua, M.J.; Dupont, D.; Paul Singh, R.; Singh, J. Egg White Gel Structure Determines Biochemical Digestion with Consequences on Softening and Mechanical Disintegration during in Vitro Gastric Digestion. Food Res. Int. 2020, 138, 109782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
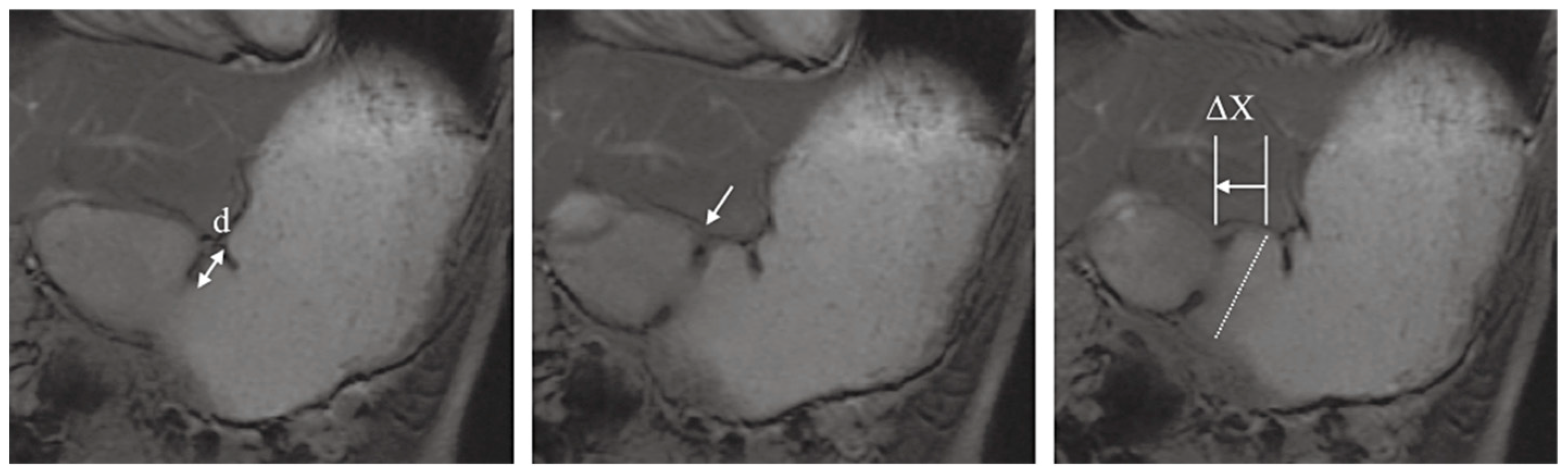
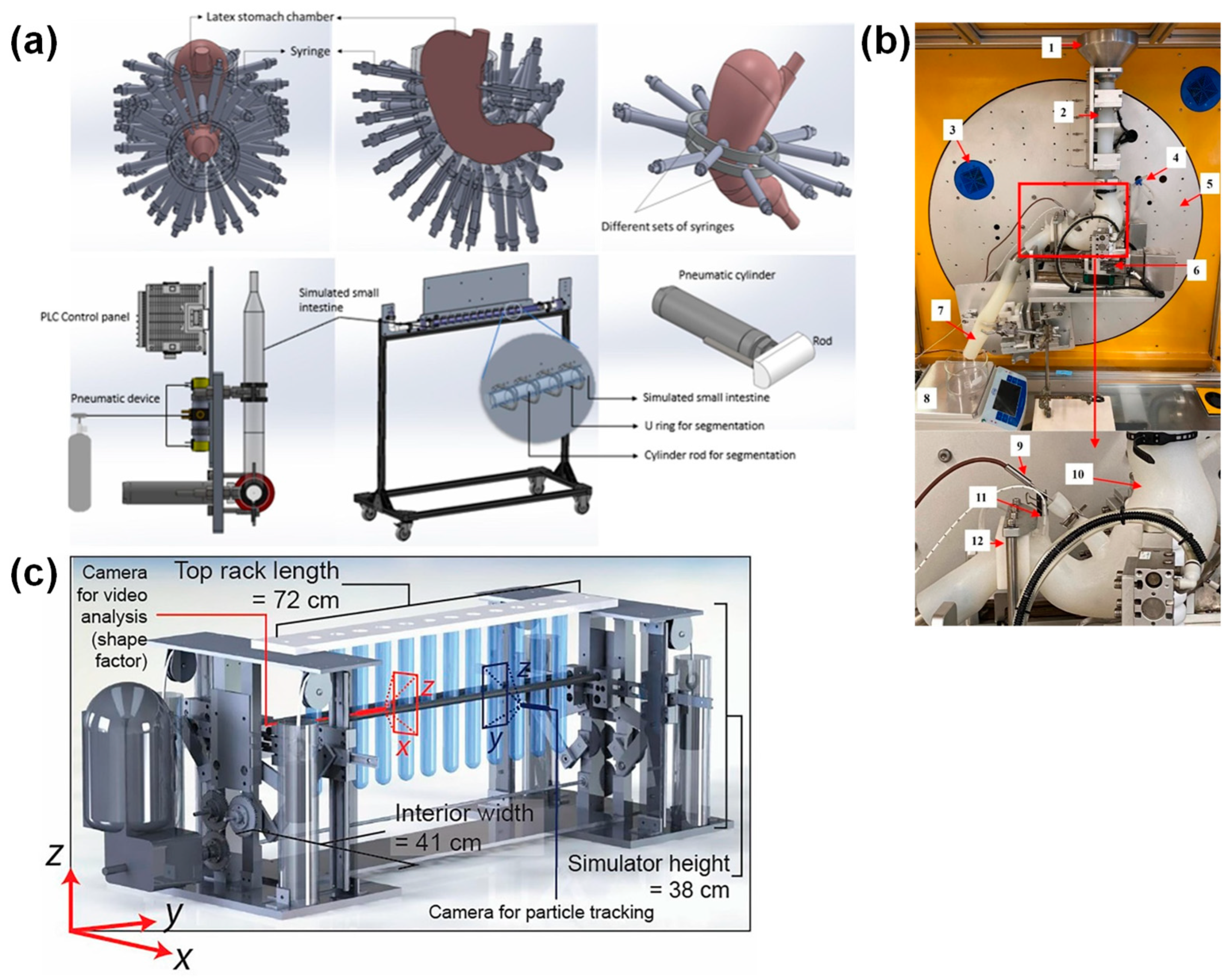
| Gastric GI Tract Device | Methods for Simulating Peristalsis | Agar Gel Beads Used for Validation * 1 | Ref. | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Diameter (mm) | Agar Concentration (wt%) | Fracture Strength (N) | |||
| Cf. Human stomach | Progressing wave: antral contraction wave | 12.7 | 0.75–3 | 0.15–0.90 | [132] |
| Dynamic Gastric Model (DGM) | Up-and-down stoke of piston | 12.7 | 1.51, 1.89, 2.39, 3.0 | 0.53, 0.65, 0.78, 0.90 | [116] |
| Rope-driven in vitro Human Stomach (RD-IV-HSM) | Progressing wave: rope-driven system | 12 | - | 0.15–0.65 | [122] |
| Gastric Digestion Simulator (GDS) | Progressing wave: roller-driven system | 12.7 | 1.50, 1.89, 2.39, 3.00 | - | [133] |
| Artificial Gastric Digestive System (AGDS) | Progressing wave: roller-driven system | 12.7 | 2.0, 2.5, 3.0, 3.5, 4.0 | 0.35, 0.50, 0.65, 0.80, 0.95 | [127] |
| Hydrogel Food to Be Digested | Gastric GI tract Device * 6 | Major Experimental Results | Ref. | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Name (Major Materials) | Mechanical Characteristics | Oral Phase * 1 | ||||
| Factors That Vary the Characteristics | Characteristics Reported * 1,2 | |||||
| Whey protein isolated (WPI) emulsion gel (soybean oil emulsion; whey protein isolated) |
|
|
| Human Gastric Simulator (HGS) |
| [135] |
| WPI emulsion gel (soybean oil emulsion; whey protein isolated) |
|
|
| HGS |
| [136,137] |
| Hydrogel (agar; native-type gellan gum) |
|
|
| Gastric Digestion Simulator (GDS) |
| [133] |
| Hydrogel containing starch (agar; native-type gellan gum; corn starch) |
|
|
| GDS |
| [139] |
| WPI emulsion gel (sunflower oil emulsion; whey protein isolated) |
|
|
| In vitro Mechanical Gastric System (IMGS) |
| [140] |
| Tofu (gel-like food made of soy curd) |
|
|
| Artificial Gastric Digestive System (AGDS) |
| [141] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kozu, H.; Kobayashi, I.; Ichikawa, S. A Review on In Vitro Evaluation of Chemical and Physical Digestion for Controlling Gastric Digestion of Food. Foods 2025, 14, 1435. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14081435
Kozu H, Kobayashi I, Ichikawa S. A Review on In Vitro Evaluation of Chemical and Physical Digestion for Controlling Gastric Digestion of Food. Foods. 2025; 14(8):1435. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14081435
Chicago/Turabian StyleKozu, Hiroyuki, Isao Kobayashi, and Sosaku Ichikawa. 2025. "A Review on In Vitro Evaluation of Chemical and Physical Digestion for Controlling Gastric Digestion of Food" Foods 14, no. 8: 1435. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14081435
APA StyleKozu, H., Kobayashi, I., & Ichikawa, S. (2025). A Review on In Vitro Evaluation of Chemical and Physical Digestion for Controlling Gastric Digestion of Food. Foods, 14(8), 1435. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14081435







