The Impact of the Desugarization Process on the Physiochemical Properties of Duck Egg Mélange Powders
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Samples and Material
2.2. Desugarization of Duck Eggs
2.3. Freeze-Drying
2.4. Physiochemical Properties
2.4.1. Moisture Content
2.4.2. Ash Content
2.4.3. Fat Determination
2.4.4. Protein Content
2.4.5. Solubility
2.5. Carbohydrates
2.6. Mineral Composition
2.7. Vitamins
2.8. Fatty Acids
2.9. Amino Acid Content
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Physiochemical Properties
3.2. Carbohydrate Content
3.3. Mineral Content
3.4. Vitamin Content
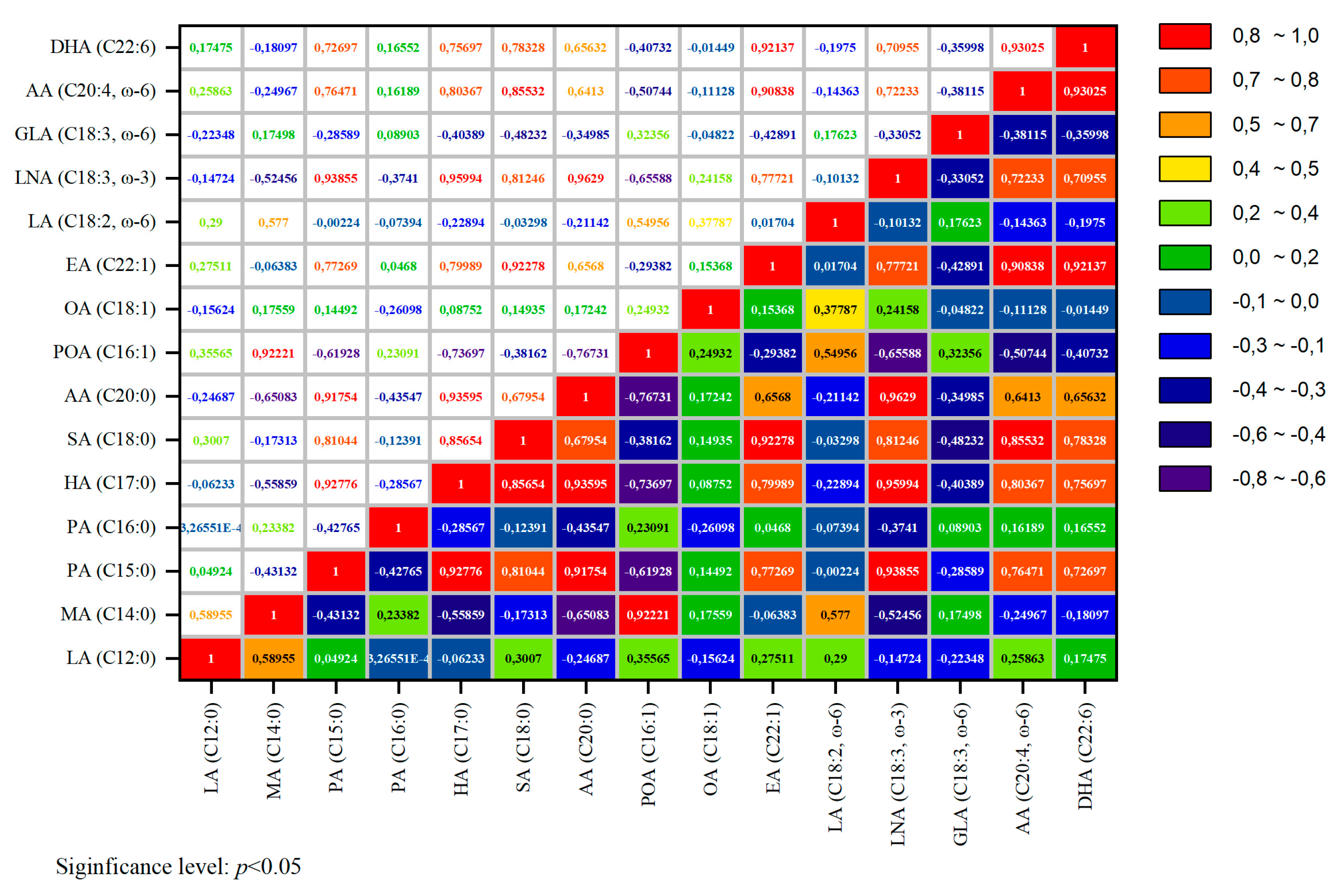
3.5. Fatty Acid Content
3.6. Amino Acid Composition
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tian, Y.; Zhang, R.; Li, G.; Zeng, T.; Chen, L.; Xu, W.; Gu, T.; Tao, Z.; Du, X.; Lu, L. Microbial fermented feed affects flavor amino acids and yolk trimethylamine of duck eggs via cecal microbiota–yolk metabolites crosstalk. Food Chem. 2024, 430, 137008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shibamoto, T.; Yeo, H. Flavor Compounds Formed from Lipids by Heat Treatment; ACS Publications: Washington, DC, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.-C.; Chang, H.-S.; Wang, C.-T.; Cheng, F.-Y. Antioxidative activities of hydrolysates from duck egg white using enzymatic hydrolysis. Asian-Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2009, 22, 1587–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganesan, P.; Kaewmanee, T.; Benjakul, S.; Baharin, B. Comparative study on the nutritional value of pidan and salted duck egg. Korean J. Food Sci. Anim. Resour. 2014, 34, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, N.; Zhao, Y.; Yao, Y.; Wu, N.; Xu, M.; Du, H.; Tu, Y. Biological activities of egg yolk lipids: A review. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 1948–1957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherian, G.; Quezada, N. Egg quality, fatty acid composition and immunoglobulin Y content in eggs from laying hens fed full fat camelina or flax seed. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2016, 7, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraeye, I.; Bruneel, C.; Lemahieu, C.; Buyse, J.; Muylaert, K.; Foubert, I. Dietary enrichment of eggs with omega-3 fatty acids: A review. Food Res. Int. 2012, 48, 961–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerver, J.M.; Park, Y.; Song, W.O. The role of eggs in American diets: Health implications and benefits. In Eggs and Health Promotion; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2002; pp. 9–18. [Google Scholar]
- Barboza, P.; Parker, K.; Hume, I. Metabolic constituents: Water, minerals and vitamins. In Integrative Wildlife Nutrition; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; pp. 157–206. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, W.-Y.; Majumder, K.; Wu, J. Oxygen radical absorbance capacity of peptides from egg white protein ovotransferrin and their interaction with phytochemicals. Food Chem. 2010, 123, 635–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asaithambi, N.; Singha, P.; Singh, S.K. Recent application of protein hydrolysates in food texture modification. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 63, 10412–10443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, D. Food stabilization, glucose conversion in preparation of albumen solids by glucose oxidase-catalase system. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1953, 1, 727–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lechevalier, V.; Nau, F.; Jeantet, R. Powdered egg. In Handbook of Food Powders; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 484–512. [Google Scholar]
- Katekhong, W.; Charoenrein, S. Influence of spray drying temperatures and storage conditions on physical and functional properties of dried egg white. Dry. Technol. 2018, 36, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, T.H.; Benjakul, S. Gelling properties of duck albumen powder as affected by desugarization and drying conditions. J. Texture Stud. 2018, 49, 520–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quan, T.H.; Benjakul, S. Impacts of desugarization and drying methods on physicochemical and functional properties of duck albumen powder. Dry. Technol. 2019, 37, 864–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, D.; Pan, X.; Zhang, W.; Bi, S.; Wu, J. Effect of glucose oxidase treatment on the aroma qualities and release of cooked off-odor components from heat-treated Hami melon juice. Food Chem. 2022, 371, 131166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Jia, J.; Xiong, D.; Xu, X.; Yang, Y.; Liu, X.; Duan, X. Effects of short-term fermentation with lactic acid bacteria on egg white: Characterization, rheological and foaming activities. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 101, 105507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sebring, M. Desugarization of egg products. In Egg Science and Technology; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017; pp. 323–334. [Google Scholar]
- Elhalis, H.; Cox, J.; Frank, D.; Zhao, J. The crucial role of yeasts in the wet fermentation of coffee beans and quality. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2020, 333, 108796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, H.K.; Singh, J.; Sarkar, B.C.; Singh, B.; Premi, M. Statistical optimization of desugarization process parameters of liquid whole egg using response surface methodology. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2012, 47, 208–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horwitz, W.; Latimer, G. Official Methods of Analysis; Association of Official Analytical Chemists: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- AOAC International. AOAC Official Method 2001.11 Protein (Crude) in Animal Feed, Forage (Plant Tissue), Grain and Oilseeds; AOAC International: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, K.; Zha, F.; Yang, Z.; Rao, J.; Chen, B. Structure characteristics and functionality of water-soluble fraction from high-intensity ultrasound treated pea protein isolate. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 125, 107409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.-G.; Sun, H.-M.; Wang, T.-L.; Liang, J.; Yang, B.-Y.; Kuang, H.-X. A modified GC-MS analytical procedure for separation and detection of multiple classes of carbohydrates. Molecules 2018, 23, 1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, L.; Zhang, S.-F.; Cheng, C.-M.; Su, Y.-T.; Xing, J.-L.; Shi, L.-L.; Ke, J.-J.; Zhang, S.-H. Investigation and analysis of mineral elements in infant formula milk powder sold in Ningbo in 2018. J. Food Saf. Qual. 2020, 11, 4267–4272. [Google Scholar]
- Nimalaratne, C.; Sun, C.; Wu, J.; Curtis, J.M.; Schieber, A. Quantification of selected fat soluble vitamins and carotenoids in infant formula and dietary supplements using fast liquid chromatography coupled with tandem mass spectrometry. Food Res. Int. 2014, 66, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Liu, X.; Li, S.; Dong, S.; Harlina, P.W.; Wang, J.; Geng, F. Research note: Changes in chicken egg yolk metabolome during its spray drying and storage. Poult. Sci. 2024, 103, 104453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Awogbemi, O.; Kallon, D.V.V.; Aigbodion, V.S.; Mzozoyana, V. Property determination, FA composition and NMR characterization of palm oil, used palm oil and their methyl esters. Processes 2021, 10, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun Jian, S.J.; Zhang Su, Z.S.; Hu Qing, H.Q.; Mao XiuHong, M.X.; Ji Shen, J.S. Determination of 16 kinds of amino acids in health foods by high performance liquid chromatography with pre-column derivatization. J. Food Saf. Qual. 2016, 7, 2715–2719. [Google Scholar]
- Šajbidor, J.; Čertík, M.; Grego, J. Lipid analysis of baker’s yeast. J. Chromatogr. A 1994, 665, 191–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J. Eggs and egg products processing. In Food Processing: Principles and Applications; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2014; pp. 437–455. [Google Scholar]
- Hawthorne, J. Dried albumen: Removal of sugar by yeast before drying. J. Sci. Food Agric. 1950, 1, 199–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Chen, C. Biosorption of heavy metals by Saccharomyces cerevisiae: A review. Biotechnol. Adv. 2006, 24, 427–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hencken, H. Chemical and physiological behavior of feed carotenoids and their effects on pigmentation. Poult. Sci. 1992, 71, 711–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irie, T.; Sugimoto, T.; Ueki, N.; Senoo, H.; Seki, T. Retinoid storage in the egg of reptiles and birds. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2010, 157, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karataş, F.; Tela, A.H.; Saydam, S. Comparison of vitamin, peptide and malondialdehyde content of different eggs. Gida 2019, 44, 216–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linster, C.L.; Van Schaftingen, E. Vitamin C: Biosynthesis, recycling and degradation in mammals. FEBS J. 2007, 274, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Julies, J.M. Evaluating the Vitamin Requirements of Wine-Related Yeasts and the Resultant Impact on Population Dynamics and Fermentation Kinetics; Stellenbosch University: Stellenbosch, South Africa, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Antón, M.; Gandemer, G. Composition, solubility and emulsifying properties of granules and plasma of egg yolk. J. Food Sci. 1997, 62, 484–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baucells, M.; Crespo, N.; Barroeta, A.; Lopez-Ferrer, S.; Grashorn, M.A. Incorporation of different polyunsaturated fatty acids into eggs. Poult. Sci. 2000, 79, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitfield, F.B.; Mottram, D.S. Volatiles from interactions of Maillard reactions and lipids. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 1992, 31, 1–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utzmann, C.M.; Lederer, M.O. Identification and quantification of aminophospholipid-linked Maillard compounds in model systems and egg yolk products. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2000, 48, 1000–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Xia, Y.; Wang, G.; Tao, L.; Yu, J.; Ai, L. Effects of boiling, ultra-high temperature and high hydrostatic pressure on free amino acids, flavor characteristics and sensory profiles in Chinese rice wine. Food Chem. 2019, 275, 407–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Treatment | Moisture Content, % | Fat, % | Protein, % | Ash Content, % | Solubility, % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 2.2 ± 0.043 a | 36.5 ± 0.264 a | 39.9 ± 0.002 j | 2.6 ± 0.02 a | 94.2 ± 1.037 cd |
| 3.6/5 | 3.3 ± 0.026 e | 36.5 ± 0.1 a | 39.6 ± 0.026 i | 2.7 ± 0.008 b | 92.7 ± 0.537 bc |
| 3.6/6 | 3.8 ± 0.029 f | 36.6 ± 0.305 a | 38.5 ± 0.09 g | 3.4 ± 0.007 c | 92.8 ± 0.771 bc |
| 3.6/7 | 2.8 ± 0.012 c | 36.7 ± 0.264 a | 37.5 ± 0.05 d | 3.4 ± 0.04 cd | 94.9 ± 0.141 de |
| 3.8/5 | 3.3 ± 0.033 e | 36.5 ± 0.01 a | 38.1 ± 0.13 f | 3.4 ± 0.016 c | 92.9 ± 0.848 bc |
| 3.8/6 | 3.4 ± 0.122 e | 36.6 ± 0.208 a | 35.6 ± 0.02 b | 3.4 ± 0.012 cd | 95.0 ± 0.0 de |
| 3.8/7 | 3.3 ± 0.032 e | 36.8 ± 0.136 ab | 34.0 ± 0.06 a | 3.5 ± 0.084 d | 96.3 ± 0.942 e |
| 4.0/5 | 2.9 ± 0.049 cd | 36.5 ± 0.236 a | 38.9 ± 0.12 h | 3.4 ± 0.012 cd | 88.2 ± 0.014 a |
| 4.0/6 | 2.9 ± 0.245 d | 36.8 ± 0.151 ab | 37.7 ± 0.032 e | 3.4 ± 0.004 cd | 89.2 ± 0.996 a |
| 4.0/7 | 2.6 ± 0.033 b | 37.1 ± 0.15 b | 35.8 ± 0.05 c | 3.5 ± 0.043 d | 92.4 ± 0.188 b |
| Treatment | Mannose | N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine | Glucose | Galactose | N-Acetyl-D-galactosamine | Total Content |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 559.2 ± 1.25 d | 46.3 ± 0.85 d | 135.2 ± 1.13 b | 408.3 ± 0.63 g | 227.8 ± 0.95 e | 1376.7 ± 0.96 g |
| 3.6/5 | 572.7 ± 0.34 e | Trace | 102.1 ± 0.91 a | 417.2 ± 0.01 h | 195.9 ± 1.03 d | 1287.8 ± 0.46 f |
| 3.6/6 | 1662.9 ± 2.58 f | 87.5 ± 1.07 e | 152.3 ± 0.57 c | 463.2 ± 1.42 k | 362.3 ± 0.79 f | 2728.3 ± 1.29 h |
| 3.6/7 | 81 ± 1.78 b | 38.8 ± 0.53 c | Trace | 237.0 ± 1.16 c | 138.3 ± 1.02 b | 495.1 ± 0.89 d |
| 3.8/5 | 4435.4 ± 3.42 i | 138.2 ± 1.39 i | 207.1 ± 0.89 f | 358.4 ± 0.32 f | 782.1 ± 1.26 i | 5921.2 ± 1.46 k |
| 3.8/6 | 2761.7 ± 1.21 g | 123.2 ± 0.77 h | 175.1 ± 0.66 d | 431.3 ± 1.04 j | 524.4 ± 1.44 g | 4015.6 ± 1.02 i |
| 3.8/7 | 182.0 ± 0.69 c | 33.1 ± 0.82 b | Trace | 421.1 ± 1.23 i | 158.9 ± 0.38 c | 795.2 ± 0.62 e |
| 4.0/5 | 4777.2 ± 4.76 j | 115.6 ± 0.67 g | 188.8 ± 1.37 e | 419.8 ± 1.51 i | 808.4 ± 1.45 j | 6309.8 ± 1.95 l |
| 4.0/6 | 3914.3 ± 4.35 h | 96.9 ± 1.14 f | 188.8 ± 0.45 e | 323.9 ± 0.86 e | 683.9 ± 0.99 h | 5207.7 ± 1.56 j |
| 4.0/7 | 78.5 ± 1.01 b | 27.5 ± 0.74 a | Trace | 304.8 ± 0.97 d | 139.6 ± 0.45 b | 424.3 ± 0.63 a |
| Albumin | 63.3 ± 0.94 a | 38.8 ± 0.72 c | Trace | 220.4 ± 0.65 b | 132.1 ± 1.25 a | 454.6 ± 0.71 c |
| Yolk | 61.6 ± 1.12 a | 27.5 ± 0.47 a | Trace | 205.1 ± 0.73 a | 140.2 ± 1.01 b | 434.4 ± 0.67 b |
| Treatment | P | Zn | Fe | Mg | Cu | Ca | Total Composition |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 6565.5 ± 7.9 a | 63.9 ± 0.3 e | 192.3 ± 3.4 d | 404.5 ± 2.9 b | 6.1 ± 0.2 f | 2101.8 ± 23.1 b | 9334.1 ± 6.3 b |
| 3.6/5 | 7054.2 ± 24.5 b | 52.1 ± 0.3 c | 203.5 ± 2.6 e | 414.3 ± 6.9 bc | 8.7 ± 0 g | 2172.5 ± 20.1 c | 9905.3 ± 9.1 e |
| 3.6/6 | 7346.2 ± 46.8 e | 51.2 ± 0.9 bc | 243.8 ± 3.3 h | 433.9 ± 2.4 de | 1.2 ± 0 c | 2198.5 ± 24.5 cd | 10,274.8 ± 12.9 j |
| 3.6/7 | 7296.7 ± 28.8 d | 50.6 ± 0.7 abc | 93.5 ± 1.4 a | 424.0 ± 4 cd | 1.2 ± 0 c | 2265.8 ± 8.8 g | 10,131.8 ± 7.3 g |
| 3.8/5 | 7216.0 ± 17 c | 55.1 ± 0.8 d | 212.0 ± 2.3 f | 379.8 ± 1.6 a | 3.4 ± 0.2 e | 1960.5 ± 28.5 a | 9826.8 ± 8.4 c |
| 3.8/6 | 7354.0 ± 24.3 e | 50.4 ± 1.5 abc | 152.8 ± 3.6 c | 417.8 ± 8.6 c | 0.9 ± 0.1 b | 2254.8 ± 11.8 fg | 10,230.7 ± 8.3 i |
| 3.8/7 | 7214.8 ± 11.3 c | 49.3 ± 0.3 a | 92.5 ± 0.6 a | 438.0 ± 1.6 e | 0.8 ± 0 b | 2244.6 ± 1.1 efg | 10,040.0 ± 2.5 f |
| 4.0/5 | 7253.5 ± 22.5 cd | 50.7 ± 1.5 abc | 222.5 ± 7.1 g | 418.3 ± 12.5 c | 1.2 ± 0.1 c | 2224.5 ± 19.5 def | 10,170.7 ± 10.5 h |
| 4.0/6 | 7076.6 ± 22.1 b | 50.4 ± 0.4 abc | 109.4 ± 4 b | 422.2 ± 12.2 cd | 1.4 ± 0 d | 2210.7 ± 6.4 de | 9870.7 ± 7.5 d |
| 4.0/7 | 7274.7 ± 26.5 d | 49.4 ± 0.7 ab | 90.4 ± 0.4 a | 433.8 ± 7.3 de | 0.5 ± 0 a | 2267.8 ± 39.3 g | 101.8 ± 12.3 a |
| Treatment | Vitamin A | Vitamin D3 | Vitamin E | Vitamin B1 | Vitamin B2 | Vitamin B3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 1.7 ± 0.07 e | 0.8 ± 0.08 d | 12.1 ± 0.01 d | 0.9 ± 0.2 d | 8.3 ± 0.13 bc | 1.2 ± 0.25 bcd |
| 3.6/5 | 1.3 ± 0.04 b | 0.8 ± 0.01 d | 12.5 ± 0.08 e | 0.8 ± 0.03 cd | 8.6 ± 0.01 c | 1.4 ± 0.22 cd |
| 3.6/6 | 1.8 ± 0.08 f | 0.6 ± 0 c | 12.6 ± 0.19 e | 0.7 ± 0.11 abcd | 7.9 ± 0.14 b | 1.1 ± 0.07 bc |
| 3.6/7 | 1.7 ± 0.01 e | 0.6 ± 0 c | 13.4 ± 0.01 g | 0.6 ± 0.08 a | 7.9 ± 0.15 b | 1.4 ± 0.12 d |
| 3.8/5 | 1.3 ± 0.01 c | 0.2 ± 0.01 a | 9.3 ± 0.03 b | 3.1 ± 0.15 e | 13.4 ± 0.1 f | 0.1 ± 0.02 a |
| 3.8/6 | 1.1 ± 0.07 a | 0.6 ± 0.02 c | 8.3 ± 0.25 a | 0.8 ± 0.07 bcd | 6.9 ± 0.16 a | 0.9 ± 0.06 b |
| 3.8/7 | 2.0 ± 0.05 g | 0.7 ± 0 d | 12.1 ± 0.29 d | 0.6 ± 0.01 ab | 8.7 ± 0.66 cd | 1.5 ± 0.12 de |
| 4.0/5 | 1.5 ± 0.01 d | 0.6 ± 0.01 c | 12.6 ± 0.18 e | 0.8 ± 0.06 cd | 9.0 ± 0.17 de | 1.2 ± 0.23 bcd |
| 4.0/6 | 1.2 ± 0.01 b | 0.6 ± 0.01 c | 10.8 ± 0.31 c | 0.8 ± 0.09 cd | 9.4 ± 0.15 e | 1.4 ± 0.18 cd |
| 4.0/7 | 1.9 ± 0.11 g | 0.5 ± 0.06 b | 12.9 ± 0.13 f | 0.7 ± 0.02 abc | 8.4 ± 0.06 c | 1.8 ± 0.21 e |
| Treatment | Lauric Acid (C12:0) | Myristic Acid (C14:0) | Pentadecanoic Acid(C15:0) | Palmitic Acid (C16:0) | Heptadecanoic Acid (C17:0) | Stearic Acid (C18:0) | Palmitoleic Acid (C16:1) | Arachidic Acid (C20:0) | Oleic Acid (C18:1) | Erucic Acid (C22:1) | Linoleic Acid (C18:2, ω − 6) | Linolenic Acid (C18:3, ω − 3) | Gamma-Linolenic Acid (GLA) (C18:3, ω − 6) | Arachidonic Acid (C20:4, ω − 6) | Docosahexaenoic Acid (DHA) (C22:6, ω − 3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 124.96 ± 2.7 h | 1059.02 ± 39.4 bcd | 462.62 ± 6.3 e | 77,272.39 ± 368.4 d | 1366.38 ± 124.76 d | 16,025.25 ± 437.66 g | 3672.79 ± 50.02 a | 426.38 ± 3.64 cd | 139,396.34 ± 374.67 a | 535.42 ± 12.1 e | 162.56 ± 9.09 a | 32,927.85 ± 17.04 d | 1004.72 ± 4.41 cd | 3556.9 ± 89.25 f | 556.41 ± 10.08 e |
| 3.6/5 | 96.58 ± 0.02 f | 1104.27 ± 4.14 def | 448.39 ± 3.55 de | 78,378.1 ± 434.23 e | 1282.48 ± 11.49 cd | 15,418.21 ± 41.6 f | 4085.34 ± 47.97 c | 434.44 ± 0.44 d | 153,311.56 ± 264.56 bc | 526.38 ± 2.44 de | 232.91 ± 1.46 e | 34,952.71 ± 101.93 f | 1016.1 ± 3.61 de | 3182.59 ± 1.36 e | 479.97 ± 0.37 cd |
| 3.6/6 | 91.37 ± 1.56 e | 1129.31 ± 25.85 ef | 471.79 ± 4.69 ef | 84,921.61 ± 349.98 g | 1315.75 ± 22.81 cd | 16,053.87 ± 108.9 g | 4308.34 ± 18.71 d | 473.13 ± 11.47 e | 157,777.68 ± 269.1 bc | 573.21 ± 0.03 f | 204.66 ± 1.24 cd | 35,714.73 ± 671.82 g | 1037.79 ± 12.84 e | 3564.81 ± 13.45 f | 611.95 ± 20.01 f |
| 3.6/7 | 112.83 ± 2.56 g | 1132.83 ± 37.29 f | 487.72 ± 20.79 f | 46,611.64 ± 886.21 a | 1303.29 ± 4.34 cd | 15,640.97 ± 20.47 f | 4349.37 ± 8.03 d | 505.77 ± 18.74 f | 172,202.25 ± 761.78 c | 515.63 ± 4.3 d | 218.68 ± 11.95 de | 36,213.11 ± 205.25 h | 992.48 ± 17.5 c | 2793.6 ± 70.66 c | 469.81 ± 13.03 c |
| 3.8/5 | 113.96 ± 0.79 g | 1279.6 ± 4.39 g | 284.43 ±7.18 a | 85,809.54 ± 429.57 h | 505.8 ± 13.04 a | 11,948.16 ± 62.73 a | 5374.31 ± 58.8 e | 25.1 ± 3.06 a | 142,741.71 ± 634.32 bc | 428.69 ± 21.54 a | 215.3 ± 21.54 d | 18,452.1 ± 7.83 a | 1335.08 ± 3.51 f | 2169.68 ± 9.27 a | 366.55 ± 18.52 a |
| 3.8/6 | 72.92 ± 0.2 c | 1027.98 ± 11.59 ab | 417.75 ± 15.77 c | 80,434.47 ± 235.63 f | 1269.59 ± 15.79 c | 15,089.88 ± 165.58 e | 3975.57 ± 48.2 b | 439.95 ± 1.54 d | 153,330.95 ± 243.94 bc | 498.02 ± 9.03 c | 174.72 ± 2.18 ab | 33,260.5 ± 370.06 de | 957.84 ± 23.36 b | 2825.65 ± 62.05 c | 474.21 ± 13.74 c |
| 3.8/7 | 60.48 ± 0.22 a | 1045.36 ± 14.3 abc | 419.12 ± 20.55 c | 70,435.6 ± 284.79 c | 1090.08 ± 2.46 b | 12,861.6 ± 172.86 c | 4086.73 ± 71.7 c | 401.23 ± 14.24 b | 143,430.9 ± 243.93 bc | 454.35 ± 5.14 b | 190.45 ± 10.02 bc | 31,535.63 ± 33.74 c | 1857.34 ± 7.61 g | 2596.9 ± 27.83 b | 434.24 ± 7.32 b |
| 4.0/5 | 92.46 ± 0.03 e | 1129.84 ± 4.8 ef | 423.27 ± 12.42 c | 77,362.49 ± 264.12 d | 1250.46 ± 17.18 c | 14,726.86 ± 70.84 d | 4267.28 ± 12.23 d | 459.74 ± 1.2 e | 152,685.94 ± 108.28 bc | 537.85 ± 3.43 e | 174.95 ± 10.05 ab | 34,169.42 ± 277.59 e | 1033.3 ± 4.9 e | 3038.41 ± 16.42 d | 547.73 ± 13.34 e |
| 4.0/6 | 79.36 ± 0.34 d | 1083.88 ± 34.35 cde | 438.62 ± 4.45 cd | 69,945.33 ± 343.04 c | 1334.94 ± 27.88 cd | 16,158.5 ± 26.43 g | 4109.34 ± 42.27 c | 435.8 ± 3.61 d | 157,357.6 ± 552.24 bc | 533.89 ± 0.02 e | 174.61 ± 1.48 ab | 35,308.9 ± 154.6 fg | 967.03 ± 5.03 b | 3073.73 ± 41.91 d | 498.49 ± 4.88 d |
| 4.0/7 | 66.36 ± 2.45 b | 1005.7 ± 35.56 a | 394.77 ± 19.42 b | 68,326.51 ± 339.45 b | 1062.2 ± 54.79 b | 12,530.21 ± 108.32 b | 3700.93 ± 58.83 a | 414.2 ± 23.29 bc | 135,067.45 ± 382.41 ab | 445.88 ± 13.2 b | 171.86 ± 2.5 a | 29,486.07 ± 177.11 b | 821.3 ± 20.88 a | 2573.11 ± 30.89 b | 433.44 ± 9.79 b |
| Treatment | Alanine | Arginine | Aspartic Acid | L-Cysteine | Glutamic Acid | Glycine | Histidine | Isoleucine | Leucine | Lysine | Methionine | Phenylalanine | Proline | Serine | Threonine | Tyrosine | Valine |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 2.41 ± 0.06 ab | 15.03 ± 0.04 a | 7.38 ± 0 a | 0.57 ± 0.01 a | 11.7 ± 0.22 a | 7.88 ± 0.27 a | 7.61 ± 0.17 a | 17.71 ± 0.2 a | 29.76 ± 0.58 a | 17.4 ± 0.04 a | 7.47 ± 0.02 a | 20.74 ± 0.05 a | 15.47 ± 0.07 a | 15.2 ± 0.16 a | 2.36 ± 0.04 a | 12.17 ± 0.16 a | 20.33 ± 0.24 a |
| 3.6/5 | 2.51 ± 0.1 bc | 21.13 ± 0.27 ef | 9.04 ± 0.08 bc | 2 ± 0.05 de | 14.77 ± 0.13 fg | 10.03 ± 0.22 ef | 10.67 ± 0.1 e | 23.89 ± 0.08 g | 37.3 ± 0.91 d | 24.86 ± 0.01 e | 6.16 ± 0.12 e | 28.3 ± 0.72 ef | 18.28 ± 0.37 c | 19.75 ± 0.36 de | 3.13 ± 0 d | 16.74 ± 0 d | 26.28 ± 0.6 d |
| 3.6/6 | 2.55 ± 0.03 bc | 20.22 ± 0.06 de | 9.12 ± 0.09 bc | 1.88 ± 0.13 c | 13.59 ± 0.01 d | 9.94 ± 0.09 ef | 10.03 ± 0.03 d | 23 ± 0.1 efg | 38.53 ± 0.64 de | 25 ± 0.05 ef | 5.68 ± 0.05 d | 27.66 ± 0.11 e | 18.19 ± 0.19 c | 21.04 ± 0.07 f | 3.19 ± 0.08 d | 16.07 ± 0.14 c | 26.27 ± 0 d |
| 3.6/7 | 2.79 ± 0.2 cd | 21.61 ± 0.2 f | 9.99 ± 0.45 d | 2.2 ± 0.07 g | 14.07 ± 0.1 ef | 9.33 ± 0.28 cd | 9.84 ± 0.18 d | 21.58 ± 0.07 c | 35.88 ± 0.88 c | 22.57 ± 0.65 d | 5.44 ± 0.05 c | 26.73 ± 0.19 d | 18.25 ± 0.09 c | 18.92 ± 0.16 c | 3.55 ± 0.03 e | 15.69 ± 0.02 c | 25.41 ± 0.15 c |
| 3.8/5 | 2.18 ± 0 a | 17.05 ± 0.24 b | 8.38 ± 0.04 db | 1.97 ± 0.05 cd | 12.41 ± 0.13 b | 8.43 ± 0.01 b | 8.83 ± 0.01 bc | 19.55 ± 0.18 b | 32.66 ± 0.34 b | 21.8 ± 0.39 c | 4.29 ± 0.02 a | 24.04 ± 0.09 b | 15.9 ± 0.07 a | 16.68 ± 0.24 b | 2.66 ± 0.02 b | 13.66 ± 0.04 b | 23.52 ± 0.73 b |
| 3.8/6 | 3.16 ± 0.3 e | 23.05 ± 0.5 g | 9.66 ± 0.03 cd | 2.07 ± 0.08 ef | 13.97 ± 0.2 de | 10.19 ± 0.12 f | 10.68 ± 0.16 e | 23.84 ± 0.26 def | 38.34 ± 0.31 d | 26.32 ± 0.26 g | 6.13 ± 0.07 e | 28.41 ± 0.7 fg | 19.43 ± 0.16 d | 20.85 ± 0.73 f | 3.55 ± 0.1 e | 16.75 ± 0.31 d | 28.41 ± 0.01 e |
| 3.8/7 | 3.6 ± 0.04 f | 23.37 ± 0.21 h | 10.85 ± 0.1 e | 2.34 ± 0.05 h | 14.44 ± 0.2 fg | 9.81 ± 0.24 ef | 10.52 ± 0.13 e | 22.38 ± 0.14 cde | 39.7 ± 0.97 e | 25.43 ± 0.16 f | 5.8 ± 0.05 d | 29.09 ± 0.42 g | 17.66 ± 0.31 c | 19.31 ± 0.48 cd | 3.62 ± 0.08 e | 16.71 ± 0.42 d | 26.7 ± 0.49 d |
| 4.0/5 | 2.96 ± 0 de | 20.2 ± 0.93 dc | 8.96 ± 0.38 b | 2.17 ± 0.06 fg | 13.05 ± 0.41 c | 9.7 ± 0.13 de | 9.23 ± 0.42 c | 22.11 ± 0.29 cd | 36.39 ± 1.13 c | 22.71 ± 0.76 d | 4.63 ± 0.05 b | 26.04 ± 0.73 c | 18.15 ± 0.7 c | 20.6 ± 0.99 e | 3 ± 0.04 c | 16.28 ± 0.52 c | 25.74 ± 1.2 c |
| 4.0/6 | 2.76 ± 0.19 cd | 18.84 ± 0.31 c | 9.54 ± 0.94 cd | 1.72 ± 0.02 b | 13.79 ± 0.28 de | 9.18 ± 0.43 c | 8.66 ± 0.14 b | 19.22 ± 0.06 b | 33.09 ± 0.43 b | 20.53 ± 0.15 b | 4.34 ± 0.13 a | 24.54 ± 0.06 b | 16.59 ± 0.7 b | 16.87 ± 0.15 b | 3.17 ± 0.13 d | 13.6 ± 0.22 b | 22.69 ± 0.04 b |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kamanova, S.; Shaimenova, B.; Murat, L.; Saduakhasova, S.; Khamitova, D.; Muratkhan, M.; Tarabayev, B.; Ospankulova, G. The Impact of the Desugarization Process on the Physiochemical Properties of Duck Egg Mélange Powders. Foods 2025, 14, 1469. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14091469
Kamanova S, Shaimenova B, Murat L, Saduakhasova S, Khamitova D, Muratkhan M, Tarabayev B, Ospankulova G. The Impact of the Desugarization Process on the Physiochemical Properties of Duck Egg Mélange Powders. Foods. 2025; 14(9):1469. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14091469
Chicago/Turabian StyleKamanova, Svetlana, Bakhyt Shaimenova, Linara Murat, Saule Saduakhasova, Dina Khamitova, Marat Muratkhan, Baltash Tarabayev, and Gulnazym Ospankulova. 2025. "The Impact of the Desugarization Process on the Physiochemical Properties of Duck Egg Mélange Powders" Foods 14, no. 9: 1469. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14091469
APA StyleKamanova, S., Shaimenova, B., Murat, L., Saduakhasova, S., Khamitova, D., Muratkhan, M., Tarabayev, B., & Ospankulova, G. (2025). The Impact of the Desugarization Process on the Physiochemical Properties of Duck Egg Mélange Powders. Foods, 14(9), 1469. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14091469







