Plasma-Activated Water (PAW) Decontamination of Foodborne Bacteria in Shucked Oyster Meats Using a Compact Flow-Through Generator
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. PAW Characterizations
2.2. In Vitro Assessment of the Antibacterial Activity of PAW
2.3. Assessment of PAW’s Effectiveness in Decontaminating Freshly Shucked Oysters
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
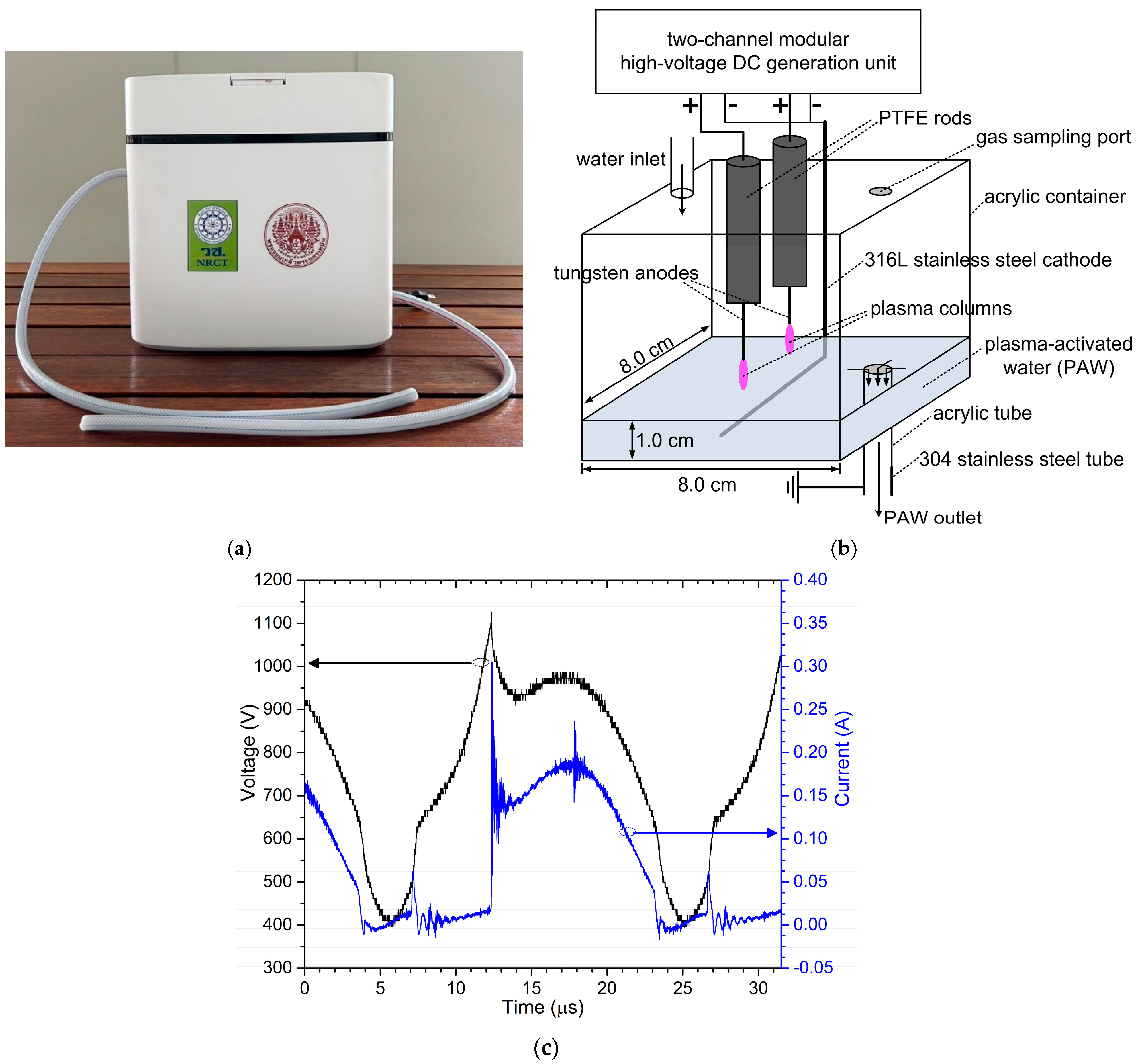
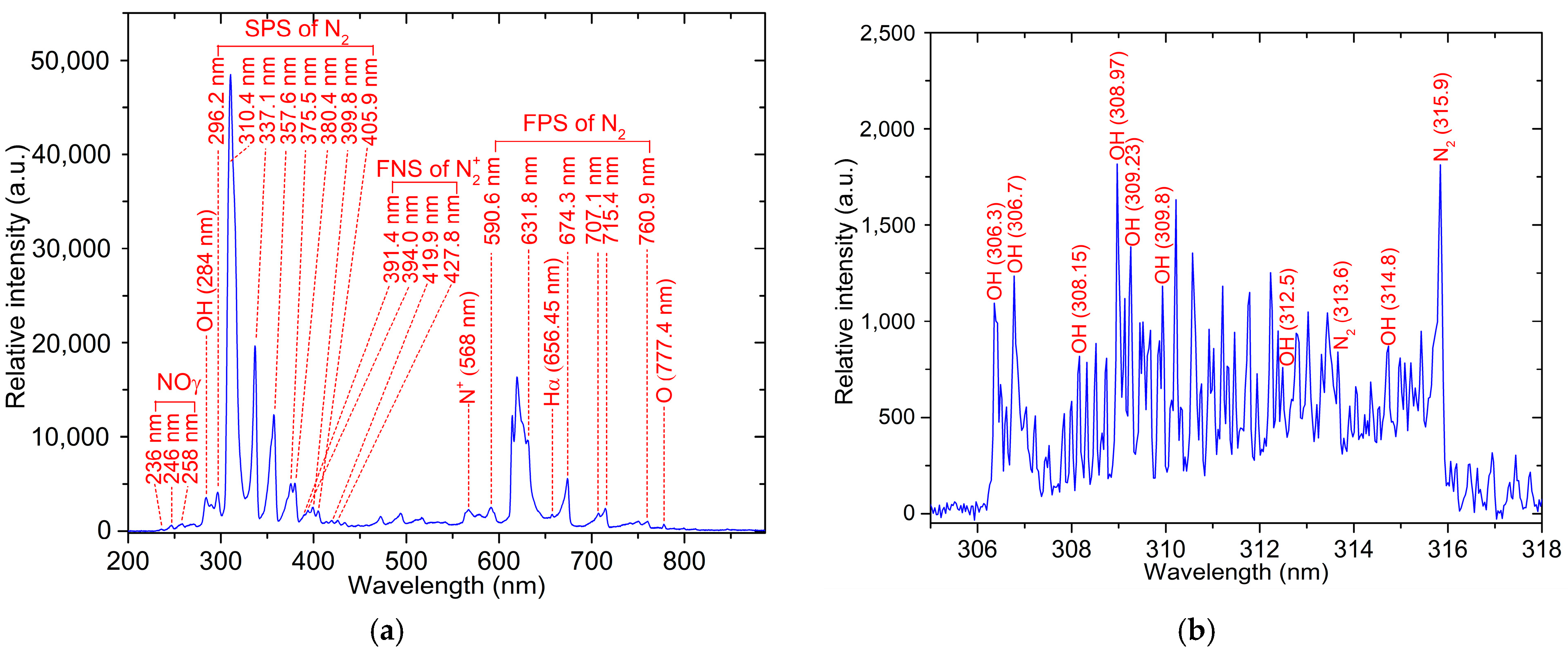
3.1. Plasma Diagnostics
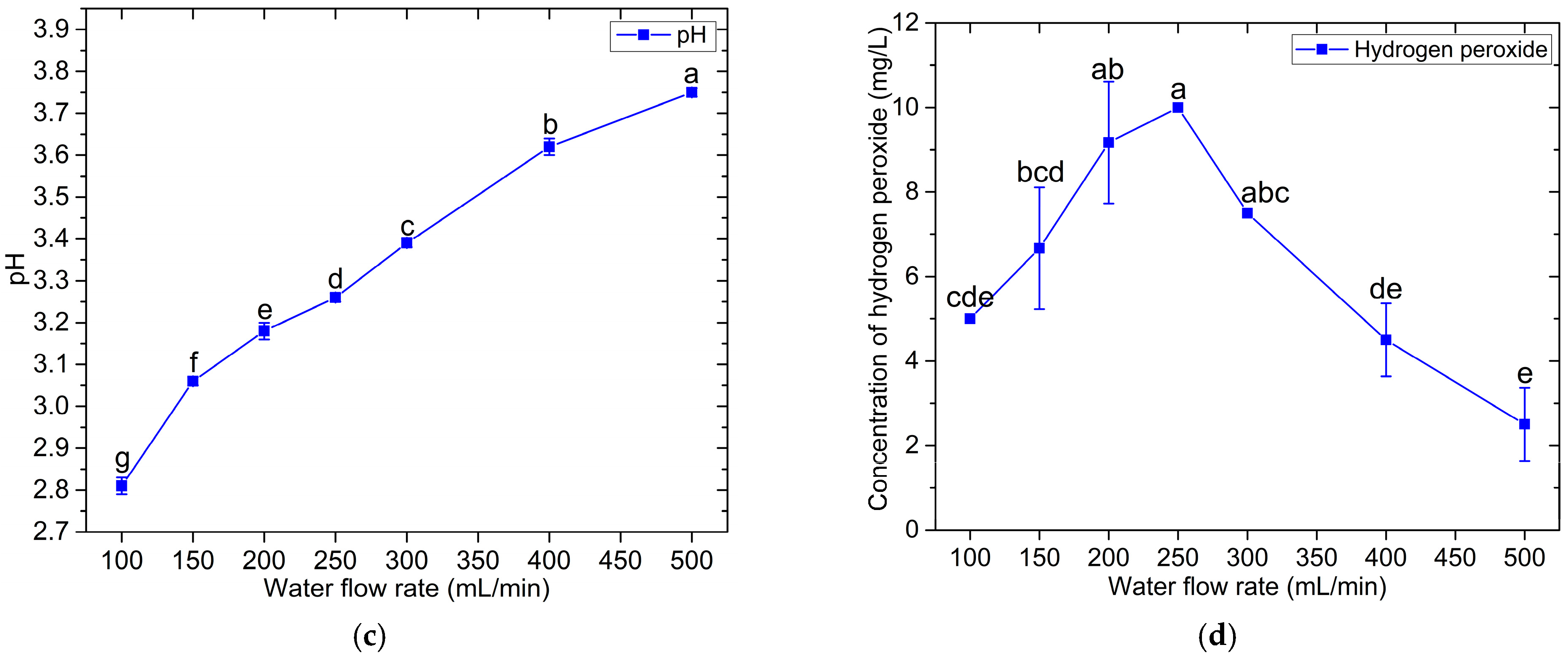
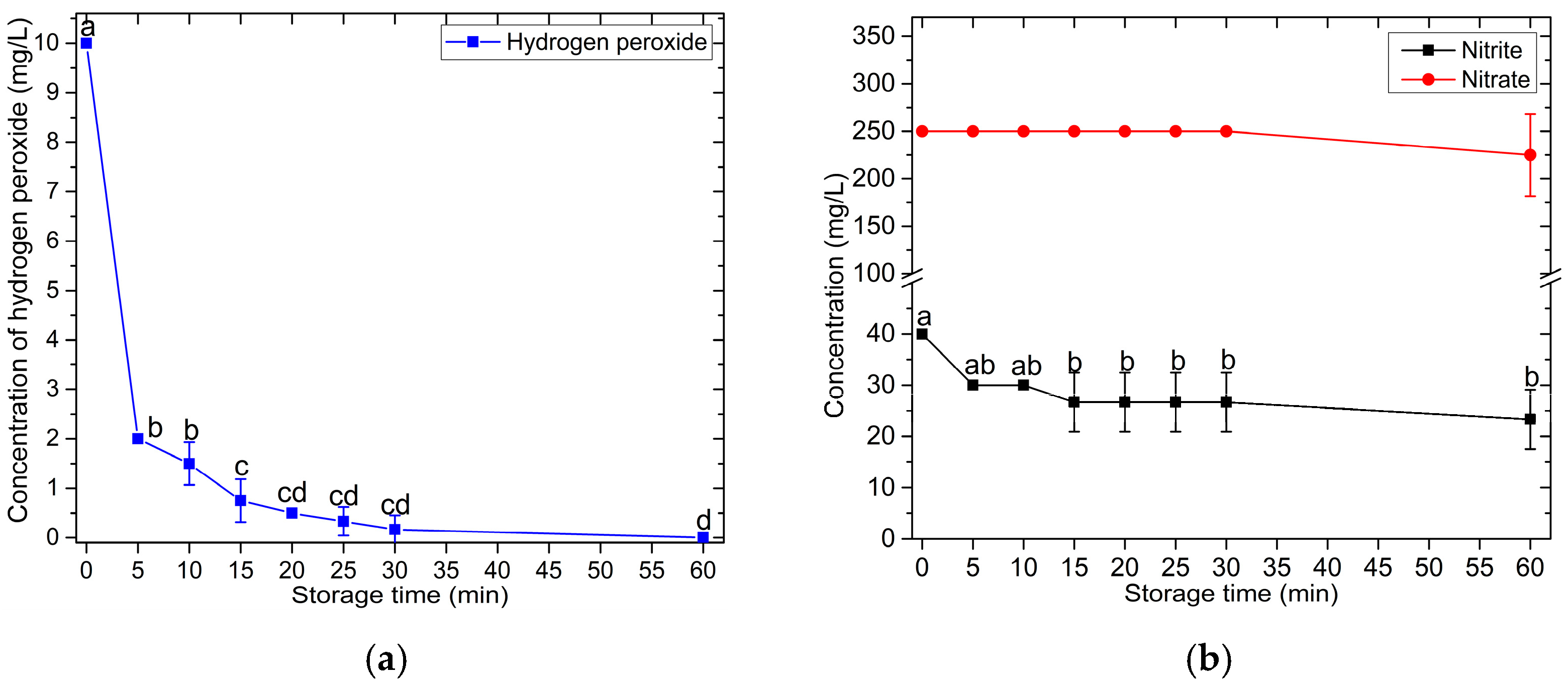
3.2. PAW Characteristics
3.3. In Vitro Evaluation of Bactericidal Activity of PAW
3.4. Decontamination Efficacy of PAW on Freshly Shucked Oysters
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Asha, K.K.; Anandan, R.; Mathew, S.; Lakshmanan, P.T. Biochemical profile of oyster Crassostrea madrasensis and its nutritional attributes. Egypt. J. Aquat. Res. 2014, 40, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, J.L.; Lüdeke, C.H.M.; Bowers, J.C.; DeRosia-Banick, K.; Carey, D.H.; Hastback, W. Abundance of Vibrio cholerae, V. vulnificus, and V. parahaemolyticus in Oysters (Crassostrea virginica) and Clams (Mercenaria mercenaria) from Long Island Sound. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 80, 7667–7672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Froelich, B.A.; Noble, R.T. Vibrio bacteria in raw oysters: Managing risks to human health. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2016, 371, 20150209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampaio, A.; Silva, V.; Poeta, P.; Aonofriesei, F. Vibrio spp.: Life Strategies, Ecology, and Risks in a Changing Environment. Diversity 2022, 14, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, V.M.; Chouljenko, A.; Hall, S.G. Depuration of live oysters to reduce Vibrio parahaemolyticus and Vibrio vulnificus: A review of ecology and processing parameters. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2022, 21, 3480–3506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diner, R.E.; Zimmer-Faust, A.; Cooksey, E.; Allard, S.; Kodera, S.M.; Kunselman, E.; Garodia, Y.; Verhougstraete, M.P.; Allen, A.E.; Griffith, J.; et al. Host and Water Microbiota Are Differentially Linked to Potential Human Pathogen Accumulation in Oysters. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2023, 89, e00318-23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Audemard, C.; Ben-Horin, T.; Kator, H.I.; Reece, K.S. Vibrio vulnificus and Vibrio parahaemolyticus in Oysters under Low Tidal Range Conditions: Is Seawater Analysis Useful for Risk Assessment? Foods 2022, 11, 4065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nuñal, S.N.; Monaya, K.J.M.; Mueda, C.R.T.; Santander-De Leon, S.M. Microbiological Quality of Oysters and Mussels Along Its Market Supply Chain. J. Food Prot. 2023, 86, 100063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanih, N.F.; Sekwadi, E.; Ndip, R.N.; Bessong, P.O. Detection of pathogenic Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus from cattle and pigs slaughtered in abattoirs in Vhembe District, South Africa. Sci. World J. 2015, 2015, 195972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rortana, C.; Nguyen-Viet, H.; Tum, S.; Unger, F.; Boqvist, S.; Dang-Xuan, S.; Koam, S.; Grace, D.; Osbjer, K.; Heng, T.; et al. Prevalence of Salmonella spp. and Staphylococcus aureus in Chicken Meat and Pork from Cambodian Markets. Pathogens 2021, 10, 556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cullen, P.J.; Lalor, J.; Scally, L.; Boehm, D.; Milosavljević, V.; Bourke, P.; Keener, K. Translation of plasma technology from the lab to the food industry. Plasma Process. Polym. 2018, 15, 1700085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Salvi, D. Recent progress in the application of plasma-activated water (PAW) for food decontamination. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2021, 42, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mentheour, R.; Machala, Z. Coupled Antibacterial Effects of Plasma-Activated Water and Pulsed Electric Field. Front. Phys. 2022, 10, 895813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakiyama, Y.; Graves, D.B.; Chang, H.-W.; Shimizu, T.; Morfill, G.E. Plasma chemistry model of surface microdischarge in humid air and dynamics of reactive neutral species. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2012, 45, 425201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, F.; Vanraes, P.; Nikiforov, A.; Morent, R.; De Geyter, N. Applications of Plasma-Liquid Systems: A Review. Materials 2019, 12, 2751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palee, N.; Thana, P.; Wijaikham, A.; Pussadee, N.; Boonyawan, D. Modeling simulation of nitric oxide and ozone generated by the Compact Air Plasma Jet: Nightingale®. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2023, 2653, 12067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasiru, M.M.; Frimpong, E.B.; Muhammad, U.; Qian, J.; Mustapha, A.T.; Yan, W.; Zhuang, H.; Zhang, J. Dielectric barrier discharge cold atmospheric plasma: Influence of processing parameters on microbial inactivation in meat and meat products. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2021, 20, 2626–2659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Misra, N.N.; Pankaj, S.K.; Walsh, T.; O’Regan, F.; Bourke, P.; Cullen, P.J. In-package nonthermal plasma degradation of pesticides on fresh produce. J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 271, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, M.-S.; Jeon, E.B.; Kim, J.Y.; Choi, E.H.; Lim, J.S.; Choi, J.; Ha, K.S.; Kwon, J.Y.; Jeong, S.H.; Park, S.Y. Virucidal Effects of Dielectric Barrier Discharge Plasma on Human Norovirus Infectivity in Fresh Oysters (Crassostrea gigas). Foods 2020, 9, 1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambrico, P.F.; Šimek, M.; Rotolo, C.; Morano, M.; Minafra, A.; Ambrico, M.; Pollastro, S.; Gerin, D.; Faretra, F.; De Miccolis Angelini, R.M. Surface Dielectric Barrier Discharge plasma: A suitable measure against fungal plant pathogens. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 3673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Cheng, J.; Sun, D. Cold Plasma-Mediated Treatments for Shelf Life Extension of Fresh Produce: A Review of Recent Research Developments. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2019, 18, 1312–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulsen, P.; Csadek, I.; Bauer, A.; Bak, K.H.; Weidinger, P.; Schwaiger, K.; Nowotny, N.; Walsh, J.; Martines, E.; Smulders, F.J.M. Treatment of Fresh Meat, Fish and Products Thereof with Cold Atmospheric Plasma to Inactivate Microbial Pathogens and Extend Shelf Life. Foods 2022, 11, 3865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, M.-S.; Jeon, E.B.; Kim, J.Y.; Choi, E.H.; Lim, J.S.; Choi, J.; Park, S.Y. Application of dielectric barrier discharge plasma for the reduction of non-pathogenic Escherichia coli and E. coli O157:H7 and the quality stability of fresh oysters (Crassostrea gigas). LWT 2022, 154, 112698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boonyawan, D.; Lamasai, K.; Umongno, C.; Rattanatabtimtong, S.; Yu, L.D.; Kuensaen, C.; Maitip, J.; Thana, P. Surface dielectric barrier discharge plasma–treated pork cut parts: Bactericidal efficacy and physiochemical characteristics. Heliyon 2022, 8, e10915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poramapijitwat, P.; Thana, P.; Boonyawan, D.; Janpong, K.; Kuensaen, C.; Charerntantanakul, W.; Yu, L.D.; Sarapirom, S. Effect of dielectric barrier discharge plasma jet on bactericidal and human dermal fibroblasts adult cells: In vitro contaminated wound healing model. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2020, 402, 126482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thana, P.; Kuensaen, C.; Poramapijitwat, P.; Sarapirom, S.; Yu, L.; Boonyawan, D. A compact pulse-modulation air plasma jet for the inactivation of chronic wound bacteria: Bactericidal effects & host safety. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2020, 400, 126229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuea-uan, S.; Boonyawan, D.; Sawangrat, C.; Thanapornpoonpong, S. Using Plasma-Activated Water Generated by an Air Gliding Arc as a Nitrogen Source for Rice Seed Germination. Agronomy 2023, 14, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosumsupamala, K.; Thana, P.; Palee, N.; Lamasai, K.; Kuensaen, C.; Ngamjarurojana, A.; Yangkhamman, P.; Boonyawan, D. Air to H2-N2 Pulse Plasma Jet for In-Vitro Plant Tissue Culture Process: Source Characteristics. Plasma Chem. Plasma Process. 2022, 42, 535–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poramapijitwat, P.; Thana, P.; Sukum, P.; Liangdeng, Y.; Kuensaen, C.; Boonyawan, D. Selective Cytotoxicity of Lung Cancer Cells—A549 and H1299—Induced by Ringer’s Lactate Solution Activated by a Non-thermal Air Plasma Jet Device, Nightingale®. Plasma Chem. Plasma Process. 2023, 43, 805–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soni, A.; Choi, J.; Brightwell, G. Plasma-Activated Water (PAW) as a Disinfection Technology for Bacterial Inactivation with a Focus on Fruit and Vegetables. Foods 2021, 10, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, D.; Liu, H.; Zhou, L.; Xie, J.; He, C. Plasma-activated water production and its application in agriculture. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2021, 101, 4891–4899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Xue, X.; Jin, X.; Niu, B.; Chen, Z.; Ji, X.; Shi, M.; He, Y. Effect of annealing using plasma-activated water on the structure and properties of wheat flour. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 951588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mai-Prochnow, A.; Zhou, R.; Zhang, T.; Ostrikov, K.; Mugunthan, S.; Rice, S.A.; Cullen, P.J. Interactions of plasma-activated water with biofilms: Inactivation, dispersal effects and mechanisms of action. NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes 2021, 7, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, R.; Zhou, R.; Prasad, K.; Fang, Z.; Speight, R.; Bazaka, K.; Ostrikov, K. Cold atmospheric plasma activated water as a prospective disinfectant: The crucial role of peroxynitrite. Green Chem. 2018, 20, 5276–5284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruno, G.; Wenske, S.; Lackmann, J.-W.; Lalk, M.; von Woedtke, T.; Wende, K. On the Liquid Chemistry of the Reactive Nitrogen Species Peroxynitrite and Nitrogen Dioxide Generated by Physical Plasmas. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, K.S.; Chew, N.S.L.; Low, M.; Tan, M.K. Plasma-Activated Water: Physicochemical Properties, Generation Techniques, and Applications. Processes 2023, 11, 2213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, R.P.; Hogg, N.; Kim-Shapiro, D.B. The potential role of the red blood cell in nitrite-dependent regulation of blood flow. Cardiovasc. Res. 2011, 89, 507–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samouilov, A.; Woldman, Y.Y.; Zweier, J.L.; Khramtsov, V.V. Magnetic resonance study of the transmembrane nitrite diffusion. Nitric Oxide 2007, 16, 362–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milton-Laskibar, I.; Martínez, J.A.; Portillo, M.P. Current Knowledge on Beetroot Bioactive Compounds: Role of Nitrate and Betalains in Health and Disease. Foods 2021, 10, 1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Wang, Z.; Chen, J.; Liu, L.; Xi, W.; Zhang, F.; Guo, L.; Liu, D.; Rong, M. Gliding arc discharge used for water activation: The production mechanism of aqueous NO and its role in sterilization. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2023, 56, 035202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakhatov, V.A.; Lebedev, Y.A. Radiation spectroscopy in the study of the influence of a helium-nitrogen mixture composition on parameters of DC glow discharge and microwave discharge. High Temperature 2012, 50, 658–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machala, Z.; Tarabová, B.; Sersenová, D.; Janda, M.; Hensel, K. Chemical and antibacterial effects of plasma activated water: Correlation with gaseous and aqueous reactive oxygen and nitrogen species, plasma sources and air flow conditions. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2019, 52, 034002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaushik, N.K.; Ghimire, B.; Li, Y.; Adhikari, M.; Veerana, M.; Kaushik, N.; Jha, N.; Adhikari, B.; Lee, S.-J.; Masur, K.; et al. Biological and medical applications of plasma-activated media, water and solutions. Biol. Chem. 2018, 400, 39–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcinauskas, L.; Uscila, R.; Aikas, M. The Influence of Air Flow Rates and Voltage on the Plasma Emission Spectra and the Concentrations of Nitrogen Oxides Produced by Gliding Arc Discharge Plasma. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, R.P.; Thagard, S.M. Streamer-Like Electrical Discharges in Water: Part II. Environmental Applications. Plasma Chem. Plasma Process. 2013, 33, 17–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theepharaksapan, S.; Matra, K.; Thana, P.; Traiporm, T.; Aryuwong, W.; Tanakaran, Y.; Lerkmahalikhit, Y.; Malun, L.; Ittisupornrat, S. The Potential of Plasma-Activated Water as a Liquid Nitrogen Fertilizer for Microalgae Cultivation. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 2024, 52, 2392–2402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tewari, S.V.; Kshirsagar, R.J.; Roy, A.; Sarathi, R.; Sharma, A.; Mittal, K.C. Optical emission spectroscopy study on flashover along insulator surface due to particle contamination. Laser Part. Beams 2014, 32, 681–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotfy, K.; Al-Harbi, N.A.; Abd El-Raheem, H. Cold Atmospheric Pressure Nitrogen Plasma Jet for Enhancement Germination of Wheat Seeds. Plasma Chem. Plasma Process. 2019, 39, 897–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabani, H.; Dezhpour, A.; Jafari, S.; Moghaddam, M.J.M.; Nilkar, M. Antimicrobial activity of cold atmospheric-pressure argon plasma combined with chicory (Cichorium intybus L.) extract against P. aeruginosa and E. coli biofilms. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 9441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, F.; Abbasi-Firouzjah, M.; Shokri, B. Investigation of antibacterial and wettability behaviours of plasma-modified PMMA films for application in ophthalmology. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2014, 47, 085401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dave, P.; Balasubramanian, C.; Hans, S.; Patil, C.; Nema, S.K. Oxygen Plasma for Prevention of Biofilm Formation on Silicone Catheter Surfaces: Influence of Plasma Exposure Time. Plasma Chem. Plasma Process. 2022, 42, 815–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voráč, J.; Kusýn, L.; Synek, P. Deducing rotational quantum-state distributions from overlapping molecular spectra. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2019, 90, 123102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Q.; Nikiforov, A.Y.; Li, L.; Vanraes, P.; Britun, N.; Snyders, R.; Lu, X.P.; Leys, C. Absolute OH density determination by laser induced fluorescence spectroscopy in an atmospheric pressure RF plasma jet. Eur. Phys. J. D 2012, 66, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Punith, N.; Avaneesh, A.V.; Prasad, B.; Ravikrishna, R.V.; Rao, L. Unveiling the Impact of Operating Current on Active Species Generation in Pin-To-Water Plasma Activated Water System. Plasma Process. Polym. 2025, 22, 2400190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolouki, N.; Kuan, W.-H.; Huang, Y.-Y.; Hsieh, J.-H. Characterizations of a Plasma-Water System Generated by Repetitive Microsecond Pulsed Discharge with Air, Nitrogen, Oxygen, and Argon Gases Species. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 6158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoon Park, J.; Kumar, N.; Hoon Park, D.; Yusupov, M.; Neyts, E.C.; Verlackt, C.C.W.; Bogaerts, A.; Ho Kang, M.; Sup Uhm, H.; Ha Choi, E.; et al. A comparative study for the inactivation of multidrug resistance bacteria using dielectric barrier discharge and nano-second pulsed plasma. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 13849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, P.; Boehm, D.; Bourke, P.; Cullen, P.J. Achieving reactive species specificity within plasma-activated water through selective generation using air spark and glow discharges. Plasma Process. Polym. 2017, 14, 1600207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; He, B.; Chen, Q.; Li, J.; Xiong, Q.; Yue, G.; Zhang, X.; Yang, S.; Liu, H.; Liu, Q.H. Direct synthesis of hydrogen peroxide from plasma-water interactions. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 38454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruggeman, P.; Leys, C. Non-thermal plasmas in and in contact with liquids. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2009, 42, 053001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tochikubo, F.; Shimokawa, Y.; Shirai, N.; Uchida, S. Chemical reactions in liquid induced by atmospheric-pressure dc glow discharge in contact with liquid. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2014, 53, 126201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauvet, L.; Nenbangkaeo, C.; Grosse, K.; von Keudell, A. Chemistry in nanosecond plasmas in water. Plasma Process. Polym. 2020, 17, e1900192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.L.; Nikiforov, A.Y.; Vanraes, P.; Leys, C. Direct current plasma jet at atmospheric pressure operating in nitrogen and air. J. Appl. Phys. 2013, 113, 023305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruggeman, P.J.; Kushner, M.J.; Locke, B.R.; Gardeniers, J.G.E.; Graham, W.G.; Graves, D.B.; Hofman-Caris, R.C.H.M.; Maric, D.; Reid, J.P.; Ceriani, E.; et al. Plasma–liquid interactions: A review and roadmap. Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 2016, 25, 053002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, R.; Zhou, R.; Wang, P.; Xian, Y.; Mai-Prochnow, A.; Lu, X.; Cullen, P.J.; Ostrikov, K.; Bazaka, K. Plasma-activated water: Generation, origin of reactive species and biological applications. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2020, 53, 303001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jablonowski, H.; Schmidt-Bleker, A.; Weltmann, K.-D.; von Woedtke, T.; Wende, K. Non-touching plasma–liquid interaction—Where is aqueous nitric oxide generated? Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2018, 20, 25387–25398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, P.; Chen, P.; Addy, M.; Cheng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Anderson, E.; Zhou, N.; Schiappacasse, C.; Hatzenbeller, R.; Fan, L.; et al. In situ plasma-assisted atmospheric nitrogen fixation using water and spray-type jet plasma. Chem. Commun. 2018, 54, 2886–2889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heirman, P.; Van Boxem, W.; Bogaerts, A. Reactivity and stability of plasma-generated oxygen and nitrogen species in buffered water solution: A computational study. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2019, 21, 12881–12894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laroussi, M. Cold Plasma in Medicine and Healthcare: The New Frontier in Low Temperature Plasma Applications. Front. Phys. 2020, 8, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Zimmerman, A.; Stein, H.; Hannah, J. Pretreatment of Nitric Acid with Hydrogen Peroxide Reduces Total Procedural Os Blank to Femtogram Levels. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 7017–7021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.; Zhang, Y.; Lv, Y.; Sun, F. The key reactive species in the bactericidal process of plasma activated water. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2020, 53, 185207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukes, P.; Dolezalova, E.; Sisrova, I.; Clupek, M. Aqueous-phase chemistry and bactericidal effects from an air discharge plasma in contact with water: Evidence for the formation of peroxynitrite through a pseudo-second-order post-discharge reaction of H2O2 and HNO2. Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 2014, 23, 015019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizoi, K.; Rodríguez-González, V.; Sasaki, M.; Suzuki, S.; Honda, K.; Ishida, N.; Suzuki, N.; Kuchitsu, K.; Kondo, T.; Yuasa, M.; et al. Interactions between pH, reactive species, and cells in plasma-activated water can remove algae. RSC Adv. 2022, 12, 7626–7634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, B.; Ma, Y.; Gong, X.; Long, Z.; Li, J.; Xiong, Q.; Liu, H.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, X.; Yang, S.; et al. Simultaneous quantification of aqueous peroxide, nitrate, and nitrite during the plasma–liquid interactions by derivative absorption spectrophotometry. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2017, 50, 445207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutasi, K.; Popović, D.; Krstulović, N.; Milošević, S. Tuning the composition of plasma-activated water by a surface-wave microwave discharge and a kHz plasma jet. Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 2019, 28, 095010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thirumdas, R.; Kothakota, A.; Annapure, U.; Siliveru, K.; Blundell, R.; Gatt, R.; Valdramidis, V.P. Plasma activated water (PAW): Chemistry, physico-chemical properties, applications in food and agriculture. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 77, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mack, J.; Bolton, J.R. Photochemistry of nitrite and nitrate in aqueous solution: A review. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 1999, 128, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gen, M.; Liang, Z.; Zhang, R.; Go, B.R.; Chan, C.K. Particulate nitrate photolysis in the atmosphere. Environ. Sci. Atmos. 2022, 2, 111–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Q.; Tao, Y.; Krechmer, J.E.; Heald, C.L.; Murphy, J.G.; Kroll, J.H.; Ye, Q. Laboratory Investigation of Renoxification from the Photolysis of Inorganic Particulate Nitrate. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 854–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradu, C.; Kutasi, K.; Magureanu, M.; Puač, N.; Živković, S. Reactive nitrogen species in plasma-activated water: Generation, chemistry and application in agriculture. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2020, 53, 223001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.-M.; Ojha, S.; Burgess, C.M.; Sun, D.-W.; Tiwari, B.K. Inactivation efficacy and mechanisms of plasma activated water on bacteria in planktonic state. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2020, 129, 1248–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsoukou, E.; Delit, M.; Treint, L.; Bourke, P.; Boehm, D. Distinct Chemistries Define the Diverse Biological Effects of Plasma Activated Water Generated with Spark and Glow Plasma Discharges. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Jin, T.; Bai, Y.; Zhou, X.; Lv, H.; Dai, C.; Wu, Z.; Xu, Q. Plasma-activated water: Candidate hand disinfectant for SARS-CoV-2 transmission disruption. Heliyon 2024, 10, e34337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoeben, W.F.L.M.; van Ooij, P.P.; Schram, D.C.; Huiskamp, T.; Pemen, A.J.M.; Lukeš, P. On the Possibilities of Straightforward Characterization of Plasma Activated Water. Plasma Chem. Plasma Process. 2019, 39, 597–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.-H.; Fan, L.; Yuan, Z.; Bond, P.L. The concentration-determined and population-specific antimicrobial effects of free nitrous acid on Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 99, 2305–2312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinze, H.; Holzer, H. Analysis of the energy metabolism after incubation of Saccharomyces cerevisiae with sulfite or nitrite. Arch. Microbiol. 1986, 145, 27–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagy, Z.S.; Solymossy, M.; Antoni, F. Lethal effect of nitrous acid on Escherichia coli. Mutat. Res. Fundam. Mol. Mech. Mutagen. 1977, 42, 191–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbew, A.-W.; Amadu, A.A.; Qiu, S.; Champagne, P.; Adebayo, I.; Anifowose, P.O.; Ge, S. Understanding the influence of free nitrous acid on microalgal-bacterial consortium in wastewater treatment: A critical review. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 363, 127916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.-H.; Fan, L.; Peng, L.; Guo, J.; Agulló-Barceló, M.; Yuan, Z.; Bond, P.L. Determining Multiple Responses of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 to an Antimicrobial Agent, Free Nitrous Acid. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 5305–5312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tachibana, K.; Nakamura, T. Examination of UV-absorption spectroscopy for analysis of O3, NO2−, and HNO2 compositions and kinetics in plasma-activated water. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2020, 59, 056004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Francis, K.; Zhang, X. Review on formation of cold plasma activated water (PAW) and the applications in food and agriculture. Food Res. Int. 2022, 157, 111246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paiva, J.; Torres, S.; Viana, O.; Maggioni, R.; Teles, F.; Ramos Queiroga, F.; da Silva, P. Oyster (Crassostrea gasar) gastrointestinal tract microbiota and immunological responses after antibiotic administration. Lat. Am. J. Aquat. Res. 2019, 47, 78–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabello, A.E.; Espejo, R.T.; Romero, J. Tracing Vibrio parahaemolyticus in oysters (Tiostrea chilensis) using a Green Fluorescent Protein tag. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2005, 327, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, V.M.; Hall, S.; Salvi, D. Antimicrobial Effects of Plasma-Activated Simulated Seawater (PASW) on Total Coliform and Escherichia coli in Live Oysters during Static Depuration. Fishes 2023, 8, 396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Bacteria | Treatment Time (min) | Number of Viable Bacterial Cells (CFU/mL) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 min of Storage Time | 30 min of Storage Time | 60 min of Storage Time | ||
| E. coli | 0 | (4.93 ± 0.75) × 105 A | ||
| 5 | 0 B | 0 B | 0 B | |
| 10 | 0 B | 0 B | 0 B | |
| 20 | 0 B | 0 B | 0 B | |
| S. aureus | 0 | (2.10 ± 0.20) × 105 A | ||
| 5 | 0 B, b | (4.73 ± 0.50) × 103 B, a | (5.27 ± 0.47) × 103 B, a | |
| 10 | 0 B, c | (1.60 ± 0.30) × 103 B, b | (3.83 ± 0.21) × 103 B, a | |
| 20 | 0 B, b | 0 B, b | (5.00 ± 2.00) × 102 B, a | |
| Microorganism | Number of Viable Bacterial Cells | Percentage Reduction (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Untreated | PAW-Treated | ||
| Total bacterial count (CFU/g) | (4.14 ± 0.26) × 105 a | (2.03 ± 0.38) × 105 b | 51.0 |
| E. coli (MPN/g) | <3 | <3 | - |
| S. aureus (CFU/g) | 5.65 ± 0.82 a | 2.00 ± 1.74 b | 64.6 |
| Salmonella spp. (CFU/g) | 0.32 ± 0.04 a | 0.11 ± 0.06 b | 65.6 |
| V. cholerae (CFU/g) | 2.17 ± 0.30 a | 0.29 ± 0.13 b | 86.6 |
| V. parahaemolyticus (CFU/g) | 1.07 ± 0.23 a | 0.13 ± 0.23 b | 87.9 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Thana, P.; Boonyawan, D.; Jaikua, M.; Promsart, W.; Rueangwong, A.; Ungwiwatkul, S.; Prasertboonyai, K.; Maitip, J. Plasma-Activated Water (PAW) Decontamination of Foodborne Bacteria in Shucked Oyster Meats Using a Compact Flow-Through Generator. Foods 2025, 14, 1502. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14091502
Thana P, Boonyawan D, Jaikua M, Promsart W, Rueangwong A, Ungwiwatkul S, Prasertboonyai K, Maitip J. Plasma-Activated Water (PAW) Decontamination of Foodborne Bacteria in Shucked Oyster Meats Using a Compact Flow-Through Generator. Foods. 2025; 14(9):1502. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14091502
Chicago/Turabian StyleThana, Phuthidhorn, Dheerawan Boonyawan, Mathin Jaikua, Woranika Promsart, Athitta Rueangwong, Sunisa Ungwiwatkul, Kanyarak Prasertboonyai, and Jakkrawut Maitip. 2025. "Plasma-Activated Water (PAW) Decontamination of Foodborne Bacteria in Shucked Oyster Meats Using a Compact Flow-Through Generator" Foods 14, no. 9: 1502. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14091502
APA StyleThana, P., Boonyawan, D., Jaikua, M., Promsart, W., Rueangwong, A., Ungwiwatkul, S., Prasertboonyai, K., & Maitip, J. (2025). Plasma-Activated Water (PAW) Decontamination of Foodborne Bacteria in Shucked Oyster Meats Using a Compact Flow-Through Generator. Foods, 14(9), 1502. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14091502






